Anatomical Characterization of the Human Structural Connectivity between the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and Globus Pallidus via Multi-Shell Multi-Tissue Tractography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Data Acquisition
2.2. MRI Images Post-Processing
2.3. Tractography Analysis
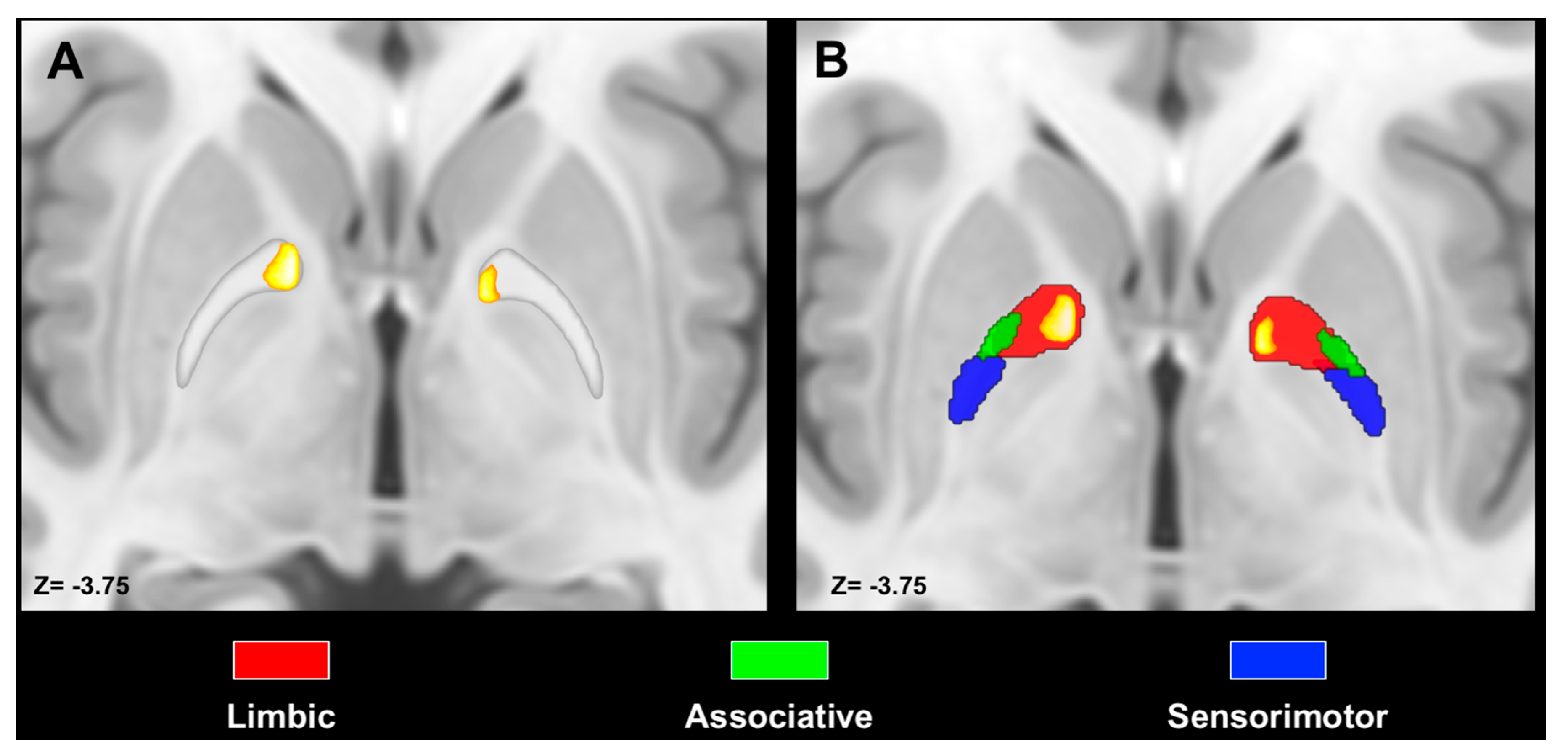
2.4. Maximum Probability Maps and Spatial Relations with Pallidal Functional Territories
- 1-
- Streamlines of the pallidotegmental tract were mapped to voxels, thus reconstructing track density-weighted maps [58], which were then multiplied for pallidal ROIs in order to obtain pallidal voxels connected to the PPN at the subject-level.
- 2-
- 3-
- Thresholded maps were registered in the ICBM template by means of direct transformations obtained by SyN.
- 4-
- Maps at the subject-level registered on the ICBM template were binarized and summed in order to obtain average maps representative of the whole sample. Furthermore, in this case, a threshold of 50% was applied to MPMs in order to retain only voxels overlapping by at least 50%.
3. Results
3.1. Anatomical Characterization of the Pallidotegmental Tract
3.2. Quantitative Analysis
3.3. Spatial Relation with Pallidal Territories
4. Discussion
4.1. Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Implications
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieuwenhuys, R. The Human Central Nervous System; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 53, ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Parent, A.; Hazrati, L.-N. Reviews Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. Brain Res. Rev. 1995, 20, 91–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, G. Parallel Organization of Functionally Segregated Circuits Linking Basal Ganglia and Cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1986, 9, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedreen, J.C.; Delong, M.R. Organization of striatopallidal, striatonigral, and nigrostriatal projections in the macaque. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 304, 569–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Y.; Hazrati, L.-N.; Parent, A. Efferent projections of the subthalamic nucleus in the squirrel monkey as studied by the PHA-L anterograde tracing method. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990, 294, 306–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draganski, B.; Kherif, F.; Klöppel, S.; Cook, P.A.; Alexander, D.C.; Parker, G.J.M.; Deichmann, R.; Ashburner, J.; Frackowiak, R.S.J. Evidence for segregated and integrative connectivity patterns in the human Basal Ganglia. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 7143–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patriat, R.; Cooper, S.E.; Duchin, Y.; Niederer, J.; Lenglet, C.; Aman, J.; Park, M.C.; Vitek, J.L.; Harel, N. Individualized tractography-based parcellation of the globus pallidus pars interna using 7T MRI in movement disorder patients prior to DBS surgery. Neuroimage 2018, 178, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantinga, B.R.; Temel, Y.; Duchin, Y.; Uludağ, K.; Patriat, R.; Roebroeck, A.; Kuijf, M.; Jahanshahi, A.; ter Haar Romenij, B.; Vitek, J.; et al. Individualized parcellation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with Parkinson’s disease with 7T MRI. Neuroimage 2018, 168, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cacciola, A.; Milardi, D.; Bertino, S.; Basile, G.A.; Calamuneri, A.; Chillemi, G.; Rizzo, G.; Anastasi, G.; Quartarone, A. Structural connectivity-based topography of the human globus pallidus: Implications for therapeutic targeting in movement disorders. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saga, Y.; Hoshi, E.; Tremblay, L. Roles of Multiple Globus Pallidus Territories of Monkeys and Humans in Motivation, Cognition and Action: An Anatomical, Physiological and Pathophysiological Review. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrem, J.L.; Starr, P.A. Treatment of Dystonia with Deep Brain Stimulation. Neurotherapeutics 2008, 5, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, F.M.; Follett, K.A.; Stern, M.; Luo, P.; Harris, C.L.; Hur, K.; Marks, W.J.; Rothlind, J.; Sagher, O.; Moy, C.; et al. Randomized trial of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: Thirty-six-month outcomes. Neurology 2012, 79, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldermann, J.C.; Schüller, T.; Huys, D.; Becker, I.; Timmermann, L.; Jessen, F.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Kuhn, J. Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette-Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, L.; Parent, M. Chemical anatomy of pallidal afferents in primates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 4291–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charara, A.; Parent, A. Brainstem dopaminergic, cholinergic and serotoninergic afferents to the pallidum in the squirrel monkey. Brain Res. 1994, 640, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, B.; Parent, A. Pedunculopontine nucleus in the squirrel monkey: Distribution of cholinergic and monoaminergic neurons in the mesopontine tegmentum with evidence for the presence of glutamate in cholinergic neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 344, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewegen, H.J.; Berendse, H.W.; Haber, S.N. Organization of the output of the ventral striatopallidal system in the rat: Ventral pallidal efferents. Neuroscience 1993, 57, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, K.; Fibiger, H.C. Afferent connections of the laterodorsal and the pedunculopontine tegmental nuclei in the rat: A retro- and antero-grade transport and immunohistochemical study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 323, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.B.S.; Hommer, D.W.; Pert, A.; Skirboll, L.R. Innervation of substantia nigra neurons by cholinergic afferents from pedunculopontine nucleus in the rat: Neuroanatomical and electrophysiological evidence. Neuroscience 1987, 23, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVito, J.L.; Anderson, M.E.; Walsh, K.E. A horseradish peroxidase study of afferent connections of the globus pallidus in Macaca mulatta. Exp. Brain Res. 1980, 38, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, L.N.; Parent, A. Contralateral pallidothalamic and pallidotegmental projections in primates: An anterograde and retrograde labeling study. Brain Res. 1991, 567, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rill, E.; Saper, C.B.; Rye, D.B.; Kofler, M.; Nonnekes, J.; Lozano, A.; Valls-Solé, J.; Hallett, M. Focus on the pedunculopontine nucleus. Consensus review from the May 2018 brainstem society meeting in Washington, DC, USA. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena-Segovia, J.; Bolam, J.P. Rethinking the Pedunculopontine Nucleus: From Cellular Organization to Function. Neuron 2017, 94, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- French, I.T.; Muthusamy, K.A. A review of the pedunculopontine nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thevathasan, W.; Debu, B.; Aziz, T.; Bloem, B.R.; Blahak, C.; Butson, C.; Czernecki, V.; Foltynie, T.; Fraix, V.; Grabli, D.; et al. Pedunculopontine nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: A clinical review. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesulam, M.-M.; Mash, D.; Hersh, L.; Bothwell, M.; Geula, C. Cholinergic innervation of the human striatum, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 323, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciola, A.; Bertino, S.; Basile, G.A.; Di Mauro, D.; Calamuneri, A.; Chillemi, G.; Duca, A.; Bruschetta, D.; Flace, P.; Favaloro, A.; et al. Mapping the structural connectivity between the periaqueductal gray and the cerebellum in humans. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milardi, D.; Quartarone, A.; Bramanti, A.; Anastasi, G.; Bertino, S.; Basile, G.A.; Buonasera, P.; Pilone, G.; Celeste, G.; Rizzo, G.; et al. The Cortico-Basal Ganglia-Cerebellar Network: Past, Present and Future Perspectives. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, A.; Milardi, D.; Livrea, P.; Flace, P.; Anastasi, G.; Quartarone, A. The Known and Missing Links Between the Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia, and Cerebral Cortex. Cerebellum 2017, 16, 753–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, A.; Calabrò, R.S.; Costa, A.; Naro, A.; Milardi, D.; Bruschetta, D. Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces in a young man: A constrained spherical deconvolution tractography study. Acta BioMed. 2017, 88, 337–351. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciola, A.; Milardi, D.; Anastasi, G.; Quartarone, A. Cortico-pallidal connectivity: Lessons from patients with dystonia. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, K.A.; Aravamuthan, B.R.; Kringelbach, M.L.; Jenkinson, N.; Voets, N.L.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z. Connectivity of the human pedunculopontine nucleus region and diffusion tensor imaging in surgical targeting. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravamuthan, B.R.; Muthusamy, K.A.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z.; Johansen-Berg, H. Topography of cortical and subcortical connections of the human pedunculopontine and subthalamic nuclei. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravamuthan, B.R.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z. The anatomy and localization of the pedunculopontine nucleus determined using probabilistic diffusion tractagrophy. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sébille, S.B.; Belaid, H.; Philippe, A.C.; André, A.; Lau, B.; François, C.; Karachi, C.; Bardinet, E. Anatomical evidence for functional diversity in the mesencephalic locomotor region of primates. Neuroimage 2017, 147, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasser, M.F.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Wilson, J.A.; Coalson, T.S.; Fischl, B.; Andersson, J.L.; Xu, J.; Jbabdi, S.; Webster, M.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Essen, D.C.; Smith, S.M.; Barch, D.M.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Yacoub, E.; Ugurbil, K. The WU-Minn Human Connectome Project: An overview. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Jbabdi, S.; Xu, J.; Andersson, J.L.; Moeller, S.; Auerbach, E.J.; Glasser, M.F.; Hernandez, M.; Sapiro, G.; Jenkinson, M.; et al. Advances in diffusion MRI acquisition and processing in the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uǧurbil, K.; Xu, J.; Auerbach, E.J.; Moeller, S.; Vu, A.T.; Duarte-Carvajalino, J.M.; Lenglet, C.; Wu, X.; Schmitter, S.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; et al. Pushing spatial and temporal resolution for functional and diffusion MRI in the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.M. Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patenaude, B.; Smith, S.M.; Kennedy, D.N.; Jenkinson, M. A Bayesian model of shape and appearance for subcortical brain segmentation. Neuroimage 2011, 56, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23, S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tournier, J.D.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. Robust determination of the fibre orientation distribution in diffusion MRI: Non-negativity constrained super-resolved spherical deconvolution. Neuroimage 2007, 35, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, J.D.; Yeh, C.H.; Calamante, F.; Cho, K.H.; Connelly, A.; Lin, C.P. Resolving crossing fibres using constrained spherical deconvolution: Validation using diffusion-weighted imaging phantom data. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurissen, B.; Tournier, J.D.; Dhollander, T.; Connelly, A.; Sijbers, J. Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 2014, 103, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, J.D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. Neuroimage 2019, 202, 116137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonov, V.; Evans, A.; McKinstry, R.; Almli, C.; Collins, D. Unbiased nonlinear average age-appropriate brain templates from birth to adulthood. Neuroimage 2009, 47, S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.; Tustison, N.; Song, G. Advanced Normalization Tools (ANTS). Insight J. 2009, 2, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, A.; Li, N.; Dembek, T.A.; Kappel, A.; Boulay, C.; Ewert, S.; Tietze, A.; Husch, A.; Perera, T.; Neumann, W.J.; et al. Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. Neuroimage 2019, 184, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, W.M.; Nili, A.N.; Michael Tyszka, J. Data Descriptor: A high-resolution probabilistic in vivo atlas of human subcortical brain nuclei. Sci. Data 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alho, A.T.D.L.; Hamani, C.; Alho, E.J.L.; da Silva, R.E.; Santos, G.A.B.; Neves, R.C.; Carreira, L.L.; Araújo, C.M.M.; Magalhães, G.; Coelho, D.B.; et al. Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging for the pedunculopontine nucleus: Proof of concept and histological correlation. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2547–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, J.-D.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. Improved probabilistic streamlines tractography by 2nd order integration over fibre orientation distributions. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 2010, 18, 1670. [Google Scholar]
- Maffei, C.; Sarubbo, S.; Jovicich, J. Diffusion-based tractography atlas of the human acoustic radiation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calamante, F.; Tournier, J.D.; Smith, R.E.; Connelly, A. A generalised framework for super-resolution track-weighted imaging. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2494–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domin, M.; Lotze, M. Parcellation of motor cortex-associated regions in the human corpus callosum on the basis of Human Connectome Project data. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, N.M.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Tafula, S.N.; Cunha, J.P.S.; Bötzel, K.; Vollmar, C.; Rozanski, V.E. A diffusion-based connectivity map of the GPi for optimised stereotactic targeting in DBS. Neuroimage 2017, 144, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamante, F.; Tournier, J.D.; Heidemann, R.M.; Anwander, A.; Jackson, G.D.; Connelly, A. Track density imaging (TDI): Validation of super resolution property. Neuroimage 2011, 56, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cacciola, A.; Milardi, D.; Basile, G.A.; Bertino, S.; Calamuneri, A.; Chillemi, G.; Paladina, G.; Impellizzeri, F.; Trimarchi, F.; Anastasi, G.; et al. The cortico-rubral and cerebello-rubral pathways are topographically organized within the human red nucleus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertino, S.; Basile, G.A.; Bramanti, A.; Anastasi, G.P.; Quartarone, A.; Milardi, D.; Cacciola, A. Spatially coherent and topographically organized pathways of the human globus pallidus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelnik, J. Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, S15–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachi, C.; Francois, C.; Parain, K.; Bardinet, E.; Tande, D.; Hirsch, E.; Yelnik, J. Three-dimensional cartography of functional territories in the human striatopallidal complex by using calbindin immunoreactivity. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 450, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehéricy, S.; Ducros, M.; Van De Moortele, P.F.; Francois, C.; Thivard, L.; Poupon, C.; Swindale, N.; Ugurbil, K.; Kim, D.S. Diffusion Tensor Fiber Tracking Shows Distinct Corticostriatal Circuits in Humans. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, D.S.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Clos, M.; Fox, P.T. Human pulvinar functional organization and connectivity. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 2417–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeVito, J.L.; Anderson, M.E. An autoradiographic study of efferent connections of the globus pallidus in Macaca mulatta. Exp. Brain Res. 1982, 46, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlebrooks, E.H.; Tuna, I.S.; Grewal, S.S.; Almeida, L.; Heckman, M.G.; Lesser, E.R.; Foote, K.D.; Okun, M.S.; Holanda, V.M. Segmentation of the globus pallidus internus using probabilistic diffusion tractography for deep brain stimulation targeting in Parkinson disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Schwabe, K.; Krauss, J.K. The pedunculopontine nucleus area: Critical evaluation of interspecies differences relevant for its use as a target for deep brain stimulation. Brain 2011, 134, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eid, L.; Parent, A.; Parent, M. Asynaptic feature and heterogeneous distribution of the cholinergic innervation of the globus pallidus in primates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haber, S. Anatomical relationship between the basal ganglia and the basal nucleus of Meynert in human and monkey forebrain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pahapill, P.A.; Lozano, A.M. The pedunculopontine nucleus and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2000, 123, 1767–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravamuthan, B.R.; McNab, J.A.; Miller, K.L.; Rushworth, M.; Jenkinson, N.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z. Cortical and subcortical connections within the pedunculopontine nucleus of the primate Macaca mulatta determined using probabilistic diffusion tractography. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 16, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, A.; Hazrati, L.N. Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. II. The place of subthalamic nucleus and external pallidium in basal ganglia circuitry. Brain Res. Rev. 1995, 20, 128–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, C.; Yelnik, J.; Percheron, G.; Fénelon, G. Topographic distribution of the axonal endings from the sensorimotor and associative striatum in the macaque pallidum and substantia nigra. Exp. Brain Res. 1994, 102, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rill, E.; Skinner, R.D. Modulation of rhythmic function in the posterior midbrain. Neuroscience 1988, 27, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rill, E.; Houser, C.R.; Skinner, R.D.; Smith, W.; Woodward, D.J. Locomotion-inducing sites in the vicinity of the pedunculopontine nucleus. Brain Res. Bull. 1987, 18, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rill, E.; Kinjo, N.; Atsuta, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Webber, M.; Skinner, R.D. Posterior midbrain-induced locomotion. Brain Res. Bull. 1990, 24, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, L.; Piallat, B.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Mathieu, H.; David, O.; Chabardès, S. On the role of the pedunculopontine nucleus and mesencephalic reticular formation in locomotion in nonhuman primates. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 4917–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, B.; Welter, M.L.; Belaid, H.; Fernandez Vidal, S.; Bardinet, E.; Grabli, D.; Karachi, C. The integrative role of the pedunculopontine nucleus in human gait. Brain 2015, 138, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tattersall, T.L.; Stratton, P.G.; Coyne, T.J.; Cook, R.; Silberstein, P.; Silburn, P.A.; Windels, F.; Sah, P. Imagined gait modulates neuronal network dynamics in the human pedunculopontine nucleus. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, B.; François, C.; Karachi, C. Structure and function of the mesencephalic locomotor region in normal and parkinsonian primates. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2019, 8, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubert, C.; Galtieri, D.; Surmeier, D.J. The pedunclopontine nucleus and Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 128, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnen, N.I.; Albin, R.L. The cholinergic system and Parkinson disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraņois, C.; Grabli, D.; McCairn, K.; Jan, C.; Karachi, C.; Hirsch, E.C.; Féger, J.; Tremblay, L. Behavioural disorders induced by external globus pallidus dysfunction in primates II. Anatomical study. Brain 2004, 127, 2055–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grabli, D.; McCairn, K.; Hirsch, E.C.; Agid, Y.; Féger, J.; Fraņois, C.; Tremblay, L. Behavioural disorders induced by external globus pallidus dysfunction in primates: I. Behavioural study. Brain 2004, 127, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tremblay, L.; Worbe, Y.; Thobois, S.; Sgambato-Faure, V.; Féger, J. Selective dysfunction of basal ganglia subterritories: From movement to behavioral disorders. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Martin, P.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Rojo-Abuin, J.M.; Rodriguez-Blazquez, C.; Alvarez-Sanchez, M.; Arakaki, T.; Bergareche-Yarza, A.; Chade, A.; Garretto, N.; Gershanik, O.; et al. Assessing the non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: MDS-UPDRS and NMS Scale. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutt, J.G.; Bloem, B.R.; Giladi, N.; Hallett, M.; Horak, F.B.; Nieuwboer, A. Freezing of gait: Moving forward on a mysterious clinical phenomenon. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, A.H.; Takakusaki, K.; Debu, B.; Lozano, A.M.; Krishna, V.; Fasano, A.; Aziz, T.Z.; Papa, S.M.; Factor, S.A.; Hallett, M. Physiology of freezing of gait. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 644–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P.; Lozano, A.; Stanzione, P.; Galati, S.; Scarnati, E.; Peppe, A.; Stefani, A. Implantation of human pedunculopontine nucleus: A safe and clinically relevant target in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaha, P.; Gill, S.S. Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the pedunculopontine nucleus for Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamani, C.; Lozano, A.M.; Mazzone, P.A.M.; Moro, E.; Hutchison, W.; Silburn, P.A.; Zrinzo, L.; Alam, M.; Goetz, L.; Pereira, E.; et al. Pedunculopontine nucleus region deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease: Surgical techniques, side effects, and postoperative imaging. Stereotact Funct. Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazky, I.; Kluge, C.; Schmitt, F.C.; Kopitzki, K.; Zaehle, T.; Voges, J.; Büntjen, L.; Kupsch, A.; Hinrichs, H. Pallidal stimulation modulates pedunculopontine nuclei in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irmen, F.; Horn, A.; Mosley, P.; Perry, A.; Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Dafsari, H.S.; Barbe, M.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Schneider, G.H.; Li, N.; et al. Left Prefrontal Connectivity Links Subthalamic Stimulation with Depressive Symptoms. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldermann, J.C.; Melzer, C.; Zapf, A.; Kohl, S.; Timmermann, L.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Huys, D.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Kühn, A.A.; Horn, A.; et al. Connectivity Profile Predictive of Effective Deep Brain Stimulation in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, D.; Algarni, M.; Wong, A.; Lozano, A.M.; Fasano, A. Stimulation-induced reversed plus-minus syndrome: Insights into eyelid physiology. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 951–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.W.; Chou, M.C.; Chen, C.Y. Principles and limitations of computational algorithms in clinical diffusion tensor MR tractography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossini, P.M.; Di Iorio, R.; Bentivoglio, M.; Bertini, G.; Ferreri, F.; Gerloff, C.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Miraglia, F.; Nitsche, M.A.; Pestilli, F.; et al. Methods for analysis of brain connectivity: An IFCN-sponsored review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1833–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, C.J.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Jbabdi, S.; Hernandez-Fernandez, M.; Behrens, T.E.; Dyrby, T.B.; Coalson, T.; Kennedy, H.; Knoblauch, K.; Van Essen, D.C.; et al. Using Diffusion Tractography to Predict Cortical Connection Strength and Distance: A Quantitative Comparison with Tracers in the Monkey. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6758–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jbabdi, S.; Johansen-Berg, H. Tractography: Where Do We Go from Here? Brain Connect 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen-Berg, H.; Behrens, T.E.J. Just pretty pictures? What diffusion tractography can add in clinical neuroscience. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier-Hein, K.H.; Neher, P.F.; Houde, J.C.; Côté, M.A.; Garyfallidis, E.; Zhong, J.; Chamberland, M.; Yeh, F.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Ji, Q.; et al. The challenge of mapping the human connectome based on diffusion tractography. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.K.; Knösche, T.R.; Turner, R. White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: The do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 2013, 73, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagmann, P.; Cammoun, L.; Gigandet, X.; Meuli, R.; Honey, C.J.; Van Wedeen, J.; Sporns, O. Mapping the structural core of human cerebral cortex. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.H.; Smith, R.E.; Liang, X.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. Correction for diffusion MRI fibre tracking biases: The consequences for structural connectomic metrics. Neuroimage 2016, 67, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.E.; Tournier, J.D.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. SIFT: Spherical-deconvolution informed filtering of tractograms. Neuroimage 2013, 119, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.E.; Tournier, J.D.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. SIFT2: Enabling dense quantitative assessment of brain white matter connectivity using streamlines tractography. Neuroimage 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Zalesky, A. Building connectomes using diffusion MRI: Why, how and but. NMR BioMed. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertino, S.; Basile, G.A.; Anastasi, G.; Bramanti, A.; Fonti, B.; Cavallaro, F.; Bruschetta, D.; Milardi, D.; Cacciola, A. Anatomical Characterization of the Human Structural Connectivity between the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and Globus Pallidus via Multi-Shell Multi-Tissue Tractography. Medicina 2020, 56, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090452
Bertino S, Basile GA, Anastasi G, Bramanti A, Fonti B, Cavallaro F, Bruschetta D, Milardi D, Cacciola A. Anatomical Characterization of the Human Structural Connectivity between the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and Globus Pallidus via Multi-Shell Multi-Tissue Tractography. Medicina. 2020; 56(9):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090452
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertino, Salvatore, Gianpaolo Antonio Basile, Giuseppe Anastasi, Alessia Bramanti, Bartolo Fonti, Filippo Cavallaro, Daniele Bruschetta, Demetrio Milardi, and Alberto Cacciola. 2020. "Anatomical Characterization of the Human Structural Connectivity between the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and Globus Pallidus via Multi-Shell Multi-Tissue Tractography" Medicina 56, no. 9: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090452





