New Techniques in Hemorrhoidal Disease but the Same Old Problem: Anal Stenosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Surgical Techniques
- a.
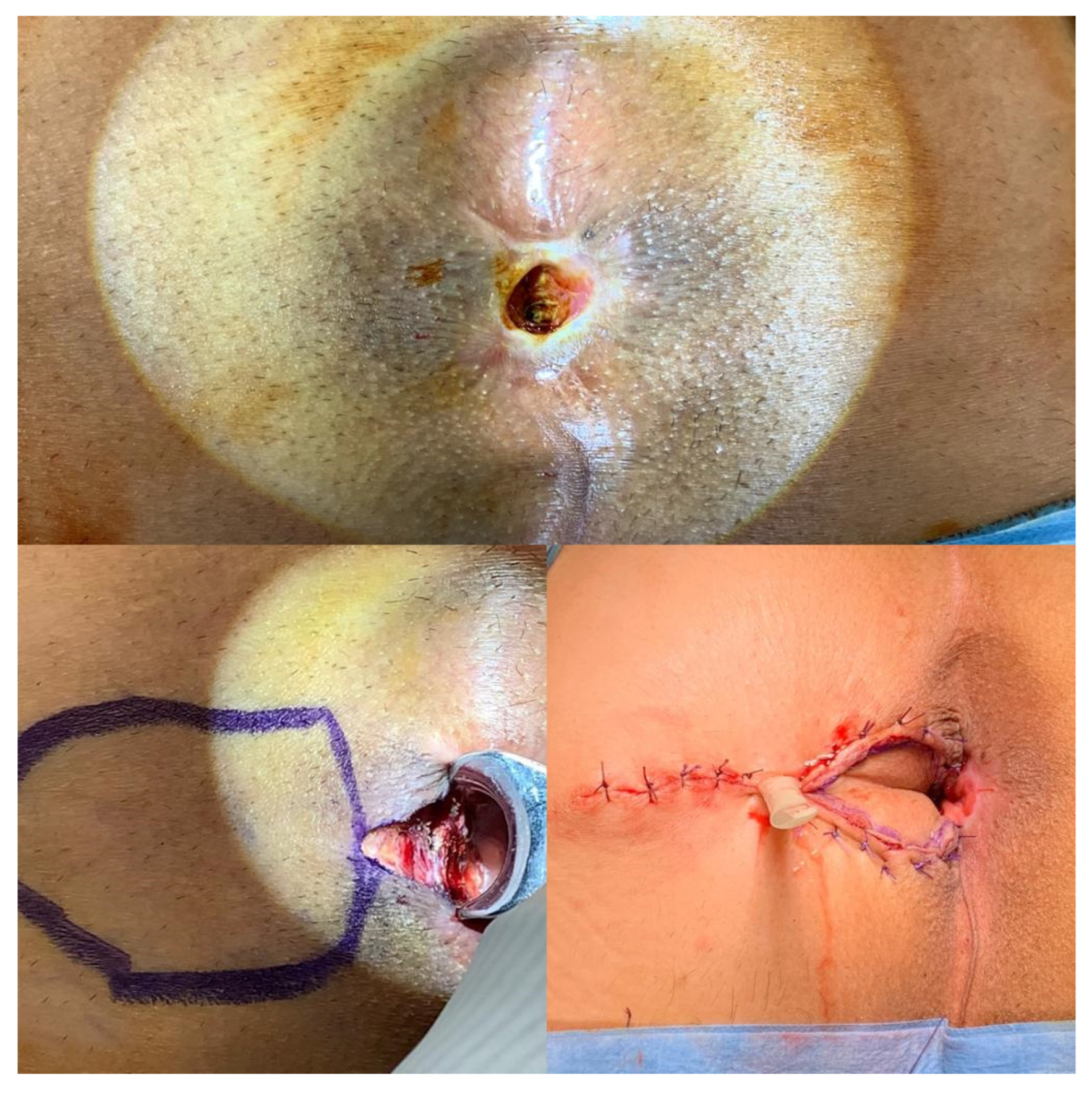
- Mucosal advancement flap
- b.
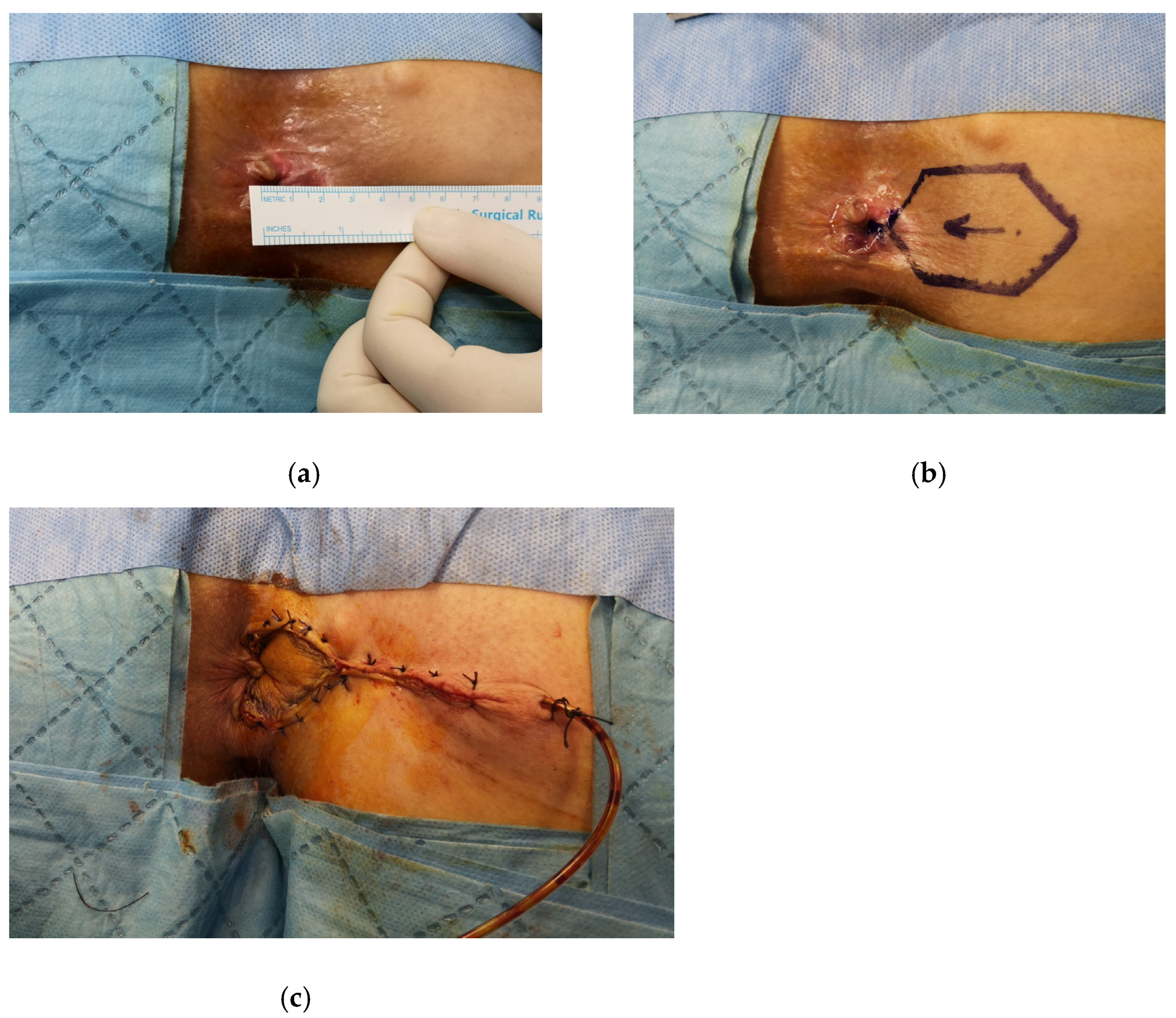
- House flap
- c.
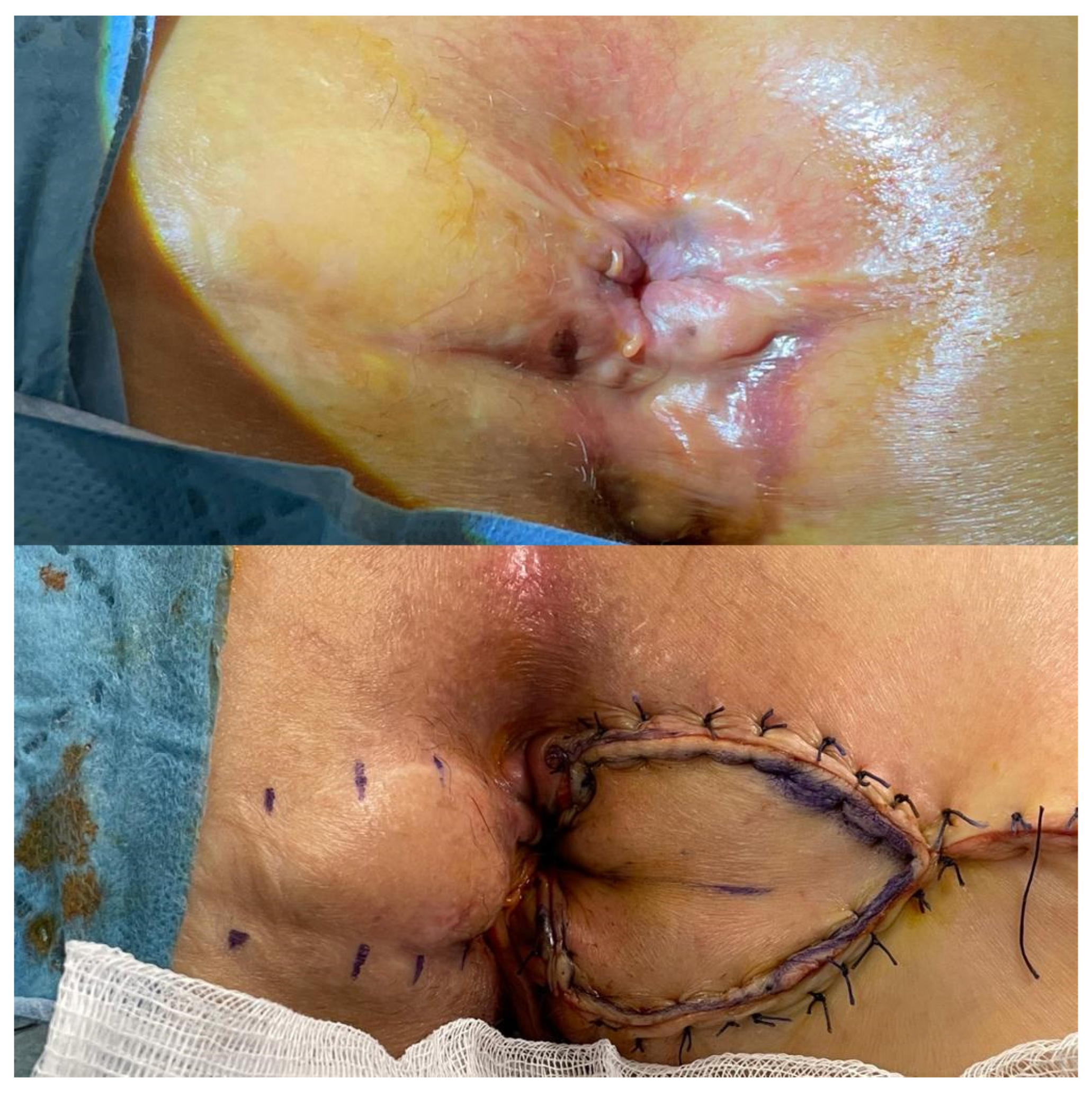
- Diamond flap
- d.
- Y-V flap/V-Y flap
- a.
- Rhomboid flap/Modified rhomboid flap
- a.
- U-flap
- b.
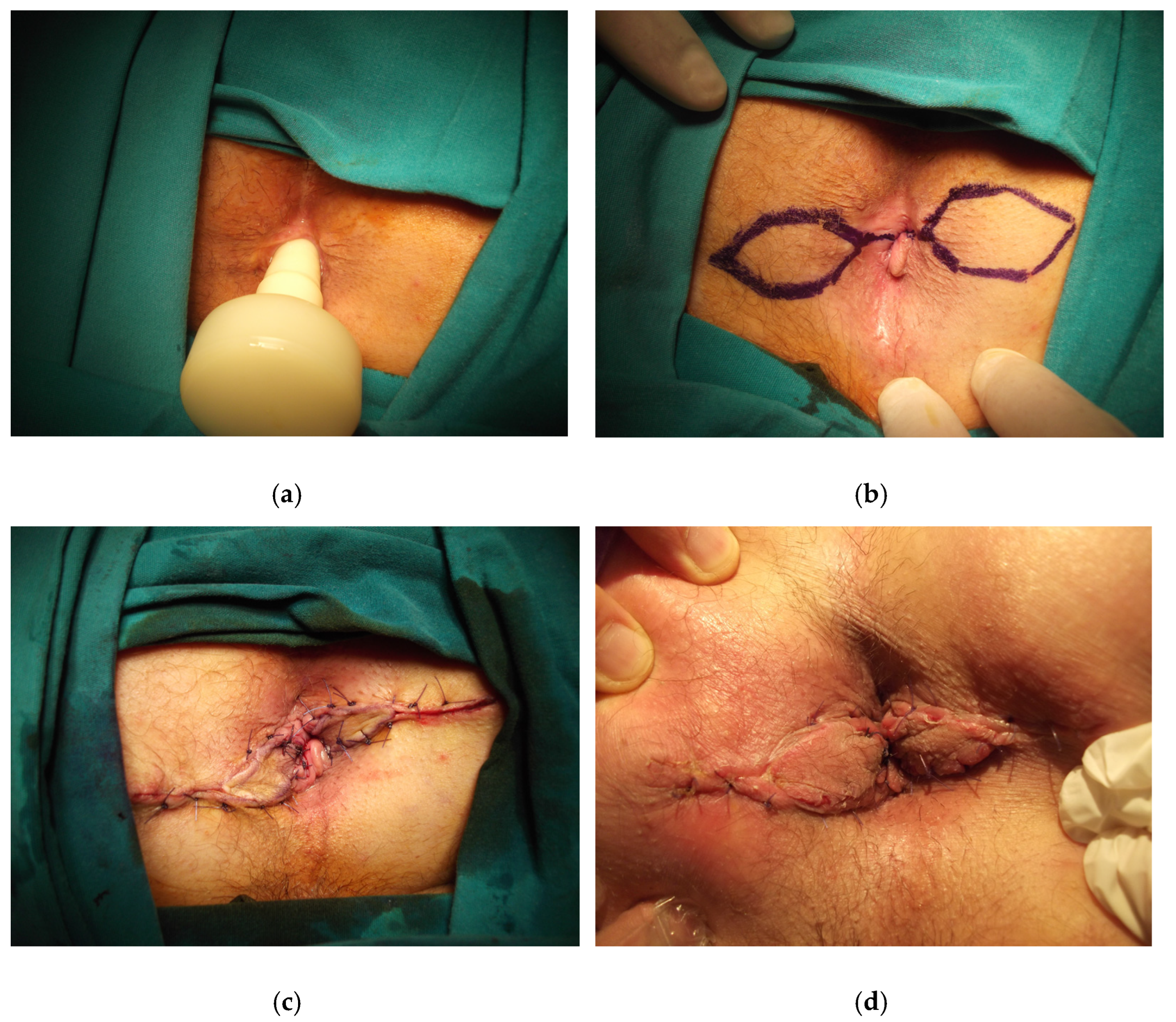
- Rotational S-plasty
3. Postoperative Care and Complications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brisinda, G.; Vanella, S.; Cadeddu, F.; Marniga, G.; Mazzeo, P.; Brandara, F.; Maria, G. Surgical treatment of anal stenosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadesus, D.; Villasana, L.E.; Diaz, H.; Chavez, M.; Sanchez, I.M.; Martinez, P.P.; Diaz, A. Treatment of anal stenosis: A 5-year review. ANZ J. Surg. 2007, 77, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eu, K.W.; Teoh, T.A.; Seow-Choen, F.; Goh, H.S. Anal stricture following haemorrhoidectomy: Early diagnosis and treat-ment. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1995, 65, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, D.F.; Picciariello, A.; Pecorella, G.; Milito, G.; Naldini, G.; Amato, A.; Ratto, C.; Perinotti, R. The Italian Haemorrhoid Survey group Surgical management of haemorrhoids: An Italian survey of over 32 000 patients over 17 years. Colorectal Dis. 2018, 20, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumetti, J. Anal stenosis. In Complications of Anorectal Surgery: Prevention and Management, 1st ed.; Abcarian, H., Cintron, J.R., Nelson, R.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Corman, M. Hemorrhoids. In Corman’s Colon and Rectal Surgery, 3rd ed.; Corman, M., Ed.; JB Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 54–115. [Google Scholar]
- Milsom, J.W.; Mazier, W.P. Classification and management of postsurgical anal stenosis. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1986, 163, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kmiot, W.A. Anal stenosis. In Surgery of the Colon, Rectum and Anus, 1st ed.; Mazier, W., Levien, D., Luchtefeld, M., Senagore, A., Eds.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, A.; Smith, A.; McNeill, A.D.; Finlay, I.G. Manual dilatation of the anus. Br. J. Surg. 1992, 79, 1381–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, H.; Thorson, A.G. How I do it. Anal stenosis. Am. J. Surg. 2000, 179, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, W.B.; Woodward, E.R. Advancement flaps for treatment of anal stricture. Arch. Surg. 1972, 104, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; Zinberg, J. Anoplasty for anal stricture. Dis. Colon Rectum 1982, 25, 809–810. [Google Scholar]
- Angelchik, P.D.; Harms, B.A.; Starling, J.R. Repair of anal stricture and mucosal ectropion with Y-V or pedicle flap anoplasty. Am. J. Surg. 1993, 166, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingold, B.S.; Arvanitis, M. Y-V anoplasty for treatment of anal stricture. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1986, 162, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pidala, M.J.; A Slezak, F.; A Porter, J. Island flap anoplasty for anal canal stenosis and mucosal ectropion. Am. Surg. 1994, 60, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habr-Gama, A.; Sobrado, C.W.; De Araújo, S.E.A.; Nahas, S.C.; Birbojm, I.; Nahas, C.S.R.; Kiss, D.R. Surgical treatment of anal stenosis: Assessment of 77 anoplasties. Clinics 2005, 60, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aitola, P.T.; Hiltunen, K.M.; Matikainen, M.J. Y-V anoplasty combined with internal sphincterotomy for stenosis of the anal canal. Eur. J. Surg. 1997, 163, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filingeri, V.; Gravante, G.; Cassisa, D. Radiofrequency Y-V anoplasty in the treatment of anal stenosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 10, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Carditello, A.; Milone, A.; Stilo, F.; Mollo, F.; Basile, M. Surgicaltreatment of anal stenosis following hemorrhoid sur-gery.Results of 150 combined mucosal advancement and internalsphincterotomy. Chir. Ital. 2002, 54, 841–844. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhmanine, M.; Rosen, L.; Khubchandani, I.; Stasik, J.; Riether, R.D. Lateral mucosal advancement anoplasty for anal stricture. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 1423–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, O.; Ersoy, Y.E.; Aydemir, I.; Erguney, S.; Teksoz, S.; Apaydin, B.; Ertem, M. Use of “House” Advancement Flap in Anorectal Diseases. World J. Surg. 2008, 32, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentovich, S.M.; Falk, P.M.; Christensen, M.A.; Thorson, A.G.; Blatchford, G.J.; Pitsch, R.M. Operative results of House advancement anoplasty. Br. J. Surg. 1996, 83, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, M.; Youssef, M.; El Nakeeb, A.; Fikry, A.; El Awady, S.; Morshed, M. Comparative Study of the House Advancement Flap, Rhomboid Flap, and Y-V Anoplasty in Treatment of Anal Stenosis: A Prospective Randomized Study. Dis. Colon Rectum 2010, 53, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplin, D.A.; Kodner, I.J. Repair of anal stricture and mucosal ectropion by simple flap procedures. Dis. Colon Rectum 1986, 29, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülen, M.; Leventoğlu, S.; Ege, B.; Menteş, B.B. Surgical Treatment of Anal Stenosis with Diamond Flap Anoplasty Performed in a Calibrated Fashion. Dis. Colon Rectum 2016, 59, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balci, B.; Yildiz, A.; Leventoglu, S.; Mentes, B.B. Diamond-shaped flap anoplasty for severe anal stenosis—A video vignette. Colorectal Dis. 2021, 23, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, G.; Brisinda, G.; Civello, I.M. Anoplasty for the treatment of anal stenosis. Am. J. Surg. 1998, 175, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, J.A.H.; Zahid, A.; Young, C.J. Rhomboid-shaped advancement flap anoplasty to treat anal stenosis. Tech. Coloproctol. 2016, 21, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, G.; Stratta, E.; Luc, A.R.; Clerico, G.; Trompetto, M. A tailored rhomboid mucocutaneous advancement flap to treat anal stenosis. Colorectal Dis. 2020, 22, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, R.K.; Hooks, V.H., 3rd; Abcarian, H.; Orsay, C.P.; Nelson, R.L. Island flap anoplasty for the treatment of anal stricture and mucosal ectropion. Dis. Colo Rectum 1990, 33, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Ferguson, J. Repair of Whitehead deformity of the anus. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1959, 108, 115–116. [Google Scholar]
- Corman, M.L.; Veidenheimer, M.C.; Coller, J.A. Anoplasty for Anal Stricture. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1976, 56, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.R.; De Oliveira, O.; Verzaro, R.; Nogueras, J.; Wexner, S.D. Anoplasty for stenosis and other anorectal defects. Am. Surg. 1995, 61, 526–529. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, C.; Albanese, C. S-plasty for various anal lesions. Am. J. Surg. 1992, 163, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisinda, G. How to treat haemorrhoids. Prevention is best; haemorrhoidectomy needs skilled operators. BMJ 2000, 321, 582–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, G.; Luc, A.R.; Tiesi, V.; Trompetto, M. Sign of the times: The Milligan–Morgan era. Tech. Coloproctol. 2021, 25, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Classification based on the severity |
| Mild: Tight anal canal can be examined by a well-lubricated index finger or a medium Hill-Ferguson retractor. |
| Moderate: Forceful dilatation is required to insert either the index finger or a medium Hill-Ferguson retractor. |
| Severe: Neither the little finger nor the small Hill-Ferguson retractor can be inserted unless a forceful dilatation is employed. |
| Classification based on the level of stenosis |
| Low: Distal anal canal at least 0.5 cm below the dentate line |
| Middle: 0.5 cm proximal to 0.5 cm distal to the dentate line |
| High: Proximal to 0.5 cm above the dentate line |
| Surgical Technique | Indications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mucosal advancement flap | Middle or high mild anal stenosis | - | The risk of ectropion unless the wound is left open |
| House flap | Moderate to severe anal stenosis | Provides adequate extension in the anal canal diameter | - |
| Diamond flap | Moderate to severe anal stenosis | Covers the defect in the anal canal while sparing the sphincter complex | - |
| Y-V flap/V-Y flap | Mild to moderate anal stenosis | - | Flap’s tip prone to ischemia and lacks sufficient extension of the anal canal diameter |
| Rhomboid flap/Modified rhomboid flap | Moderate to severe anal stenosis | Enables a tailored-anoplasty in different sizes | - |
| U-flap | Excising the mucosal ectropion | - | Leaving the wound open results in delay of recovery |
| Rotational S-plasty | Moderate to severe anal stenosis | Provides a large tissue rotation without compromising vascular supply | - |
| Authors | Study Method | Total N of Included Patients | Indications for Anoplasty (N of Patients) | Surgical Techniques | Functional Outcomes | Surgical Outcomes (N of Patients) | Mean Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rakhmanine et al. [20] | Retrospective | 95 | Hemorrhoidectomy (35) Chronic anal fissure (10) Perianal fistula (4) Anal carcinoma (1) Various (10) | Mucosal advancement flap | Reported as good in 74 patients and as poor in 8 patients | Abscess (1) Seepage of liquid stool (2) | 50 |
| Alver et al. [21] | Retrospective | 28 | Chronic anal fissure (14) Anal stenosis (8) Rectovaginal fistula (1) Perianal fistula (3) Anal carcinoma (1) Obstetric injury (1) | House flap | Reported as good in 8 patients with anal stenosis | Wound dehiscence (3) Recurrence of rectovaginal fistula (1) | 26 |
| Sentovich et al. [22] | Retrospective | 29 | Anal stenosis (21) Ectropion (4) Bowen’s disease (2) Key-hole deformity (2) Perianal fistula (1) | House flap | Reported as good in 26 patients and as poor in 3 patients | Donor-site separation (14) Urinary retention (8) Sepsis (4) | 28 |
| Farid et al. [23] | Prospective-randomized | 60 | Anal stenosis (60) | Rhomboid flap/Y-V flap/House flap | Better anal caliber increase and improvement in GI-QLI score with house-flap | 12 | |
| Gulen et al. [25] | Retrospective | 18 | Anal stenosis (18) | Diamond flap | Significant increase in anal caliber and improvement in ODS score | Wound dehiscence (4) | 35 |
| Maria et al. [27] | Comparative | 42 | Anal stenosis (42) | Diamond flap/Y-V flap | Reported as good in 89% of patients with Y-V flap, and 100% with diamond flap | Wound dehiscence (1) Ischemia in tip of the flap (1) | 24 |
| Sloane et al. [28] | Retrospective | 9 | Anal stenosis (9) | Rhomboid flap | Reported as significant improvements in 9 patients | Single quadrant stenosis (1) | 12 |
| Gallo et al. [29] | Retrospective | 50 | Anal stenosis (50) | Modified rhomboid flap | Significant increase in anal caliber and improvement in ODS and CCI score | Ischemia of donor site (1) Wound dehiscence (2) | 97 |
| Pearl et al. [30] | Retrospective | 25 | Anal stenosis (20) Ectropion (5) | Island flap (U-shaped and Diamond-shaped) | Reported as excellent in 64% of patients and good in 25% of patients | - | 19 |
| Gonzalez et al. [33] | Comparative | 17 | Anal stenosis (13) Perianal fistula (2) Key-hole deformity (1) Chronic anal fissure (1) | Rotational S-plasty/Advancement flap | Reported as good in 16 patients | Sepsis (1) | 18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leventoglu, S.; Mentes, B.; Balci, B.; Kebiz, H.C. New Techniques in Hemorrhoidal Disease but the Same Old Problem: Anal Stenosis. Medicina 2022, 58, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030362
Leventoglu S, Mentes B, Balci B, Kebiz HC. New Techniques in Hemorrhoidal Disease but the Same Old Problem: Anal Stenosis. Medicina. 2022; 58(3):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030362
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeventoglu, Sezai, Bulent Mentes, Bengi Balci, and Halil Can Kebiz. 2022. "New Techniques in Hemorrhoidal Disease but the Same Old Problem: Anal Stenosis" Medicina 58, no. 3: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030362
APA StyleLeventoglu, S., Mentes, B., Balci, B., & Kebiz, H. C. (2022). New Techniques in Hemorrhoidal Disease but the Same Old Problem: Anal Stenosis. Medicina, 58(3), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030362





