Genetic and Environmental Effects on the Development of White Matter Hyperintensities in a Middle Age Twin Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. Image Processing
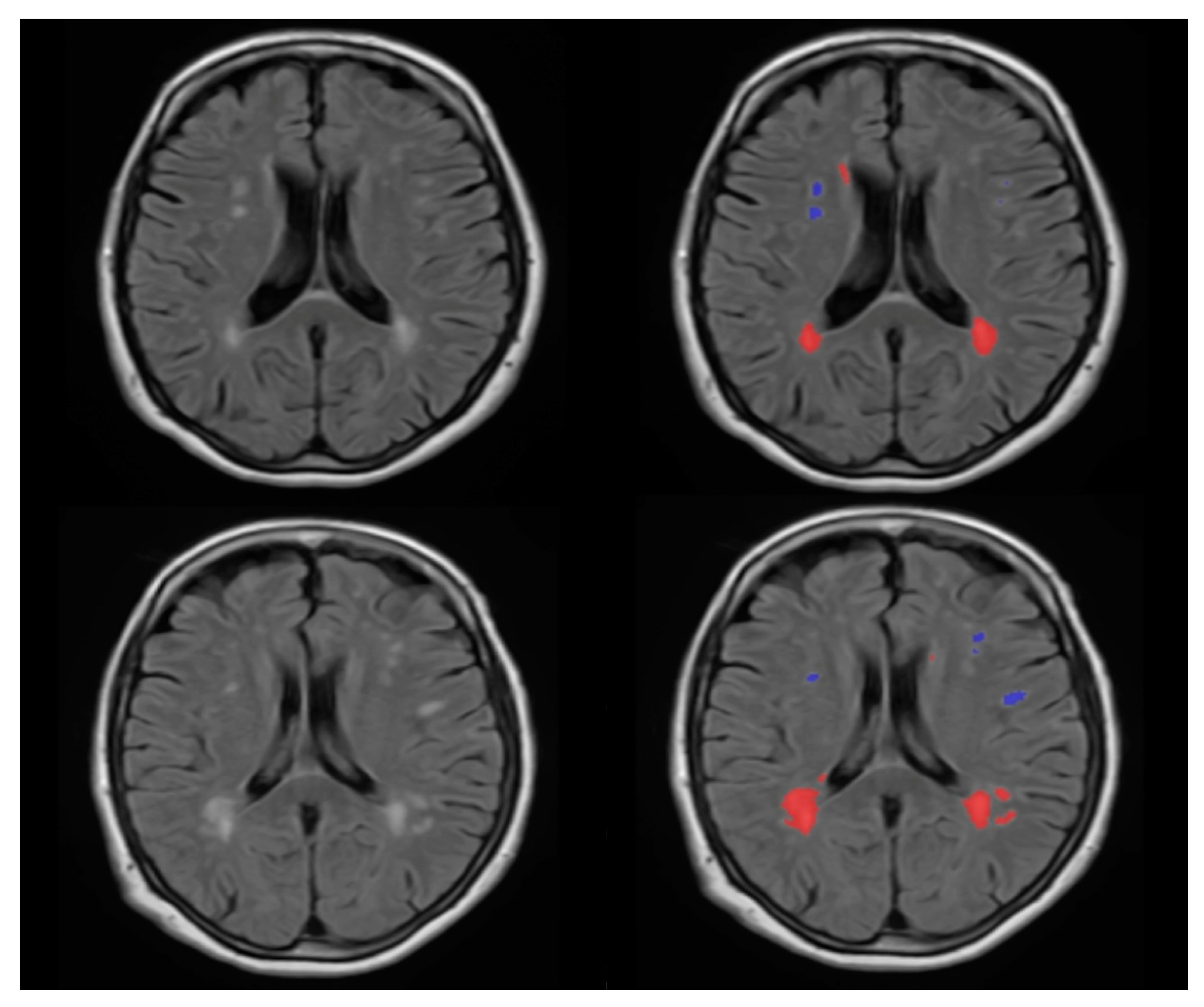
2.4. WMH Segmentation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Descriptive Statistics
2.5.2. Heritability Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
3.2. Results for WMH Count Measurement
3.3. Univariate Model Analysis for the WMH Count in Different Brain Regions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.-L.; Zhang, X.-X.; Yu, M.-M.; Li, W.-B.; Li, Y.-H. Prevalence of White Matter Hyperintensity in Young Clinical Patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Sachdev, P.; Li, J.J.; Chen, X.; Anstey, K. White matter hyperintensities in the forties: Their prevalence and topography in an epidemiological sample aged 44–48. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Sachdev, P. The topography of white matter hyperintensities on brain MRI in healthy 60- to 64-year-old individuals. NeuroImage 2004, 22, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; Biessels, G.J.; Cordonnier, C.; Fazekas, F.; Frayne, R.; Lindley, R.I.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barkhof, F.; Benavente, O.R.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prins, N.D.; Scheltens, P. White matter hyperintensities, cognitive impairment and dementia: An update. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, R.; Hernández, M.D.C.V.; Farrall, A.J. Automatic segmentation of white matter hyperintensities from brain magnetic resonance images in the era of deep learning and big data—A systematic review. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 88, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier-Crussard, A.; Desestret, V.; Cotton, F.; Chetelat, G.; Krolak-Salmon, P. White matter hyperintensities in ageing: Pathophysiology, associated cognitive disorders and prevention. La Rev. Med. Interne 2020, 41, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojdak-Łukasiewicz, J.; Dziadkowiak, E.; Zimny, A.; Paradowski, B. Cerebral small vessel disease: A review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habes, M.; Erus, G.; Toledo, J.; Zhang, T.; Bryan, N.; Launer, L.J.; Rosseel, Y.; Janowitz, D.; Doshi, J.; Van Der Auwera, S.; et al. White matter hyperintensities and imaging patterns of brain ageing in the general population. Brain 2016, 139 Pt 4, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.; Sekhon, S.; Cascella, M. White Matter Lesions. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kate, M.T.; Sudre, C.; Braber, A.D.; Konijnenberg, E.; Nivard, M.G.; Cardoso, M.J.; Scheltens, P.; Ourselin, S.; Boomsma, D.I.; Barkhof, F.; et al. White matter hyperintensities and vascular risk factors in monozygotic twins. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 66, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, Y.; Araki, A. Diabetes mellitus and white matter hyperintensity. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2015, 15 (Suppl. S1), 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grosu, S.; Lorbeer, R.; Hartmann, F.; Rospleszcz, S.; Bamberg, F.; Schlett, C.L.; Galie, F.; Selder, S.; Auweter, S.; Heier, M.; et al. White matter hyperintensity volume in pre-diabetes, diabetes and normoglycemia. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.C.; Deal, J.A.; Sharrett, A.R.; Jack, C.R.; Knopman, D.; Mosley, T.H.; Gottesman, R.F. Smoking and white matter hyperintensity progression: The ARIC-MRI Study. Neurology 2015, 84, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lampe, L.; Zhang, R.; Beyer, F.; Huhn, S.; Masouleh, S.K.; Preusser, S.; Bazin, P.; Schroeter, M.L.; Villringer, A.; Witte, A.V. Visceral obesity relates to deep white matter hyperintensities via inflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alosco, M.L.; Tripodis, Y.; Baucom, Z.H.; Adler, C.H.; Balcer, L.J.; Bernick, C.; Mariani, M.L.; Au, R.; Banks, S.J.; Barr, W.B.; et al. White matter hyperintensities in former American football players. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnoki, D.L.; Tarnoki, A.D. Twin Research and Imaging. Medicina 2022, 58, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomsma, D.I.; Busjahn, A.; Peltonen, L. Classical twin studies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Forgo, B.; Szabo, H.; Melicher, D.; Metneki, J.; Littvay, L. The Hungarian Twin Registry Update: Turning From a Voluntary to a Population-Based Registry. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2019, 22, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.C.; Nyholt, D.R.; Neuman, R.; Madden, P.A.; Bucholz, K.K.; Todd, R.D.; Nelson, E.C.; Montgomery, G.W.; Martin, N.G. Zygosity diagnosis in the absence of genotypic data: An approach using latent class analysis. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2003, 6, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorden, C.; Karnath, H.-O.; Bonilha, L. Improving lesion-symptom mapping. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjón, J.V.; Coupé, P. volBrain: An Online MRI Brain Volumetry System. Front. Neuroinform. 2016, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramírez, V.M.; Forbes, F.; Coupé, P.; Dojat, M. No Structural Differences Are Revealed by VBM in ‘De Novo’ Parkinsonian Patients. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2019, 264, 268–272. [Google Scholar]
- Fasola, S.; Montalbano, L.; Cilluffo, G.; Cuer, B.; Malizia, V.; Ferrante, G.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; La Grutta, S. A Critical Review of Statistical Methods for Twin Studies Relating Exposure to Early Life Health Conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, M.C.; Hunter, M.D.; Pritikin, J.N.; Zahery, M.; Brick, T.R.; Kirkpatrick, R.M.; Estabrook, R.; Bates, T.C.; Maes, H.H.; Boker, S.M. OpenMx 2.0: Extended Structural Equation and Statistical Modeling. Psychometrika 2016, 81, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.K.C. Data Analysis Using R Programming. Biostat. Hum. Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 1082, 47–122. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnoki, D.L.; Tarnoki, A.D.; Lazar, Z.; Medda, E.; Littvay, L.; Cotichini, R.; Fagnani, C.; Stazi, M.A.; Nisticó, L.; Lucatelli, P.; et al. Genetic and environmental factors on the relation of lung function and arterial stiffness. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neale, M.C.C.L.; Cardon, L.R. Methodology for Genetic Studies of Twins and Families; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 67. [Google Scholar]
- Sachdev, P.S.; Thalamuthu, A.; Mather, K.A.; Ames, D.; Wright, M.J.; Wen, W.; Bowden, J.; Lee, T.; Brodaty, H.; Crawford, J.; et al. White matter hyperintensities are under strong genetic influence. Stroke 2016, 47, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, N.J.; Mather, K.A.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Knol, M.J.; Malik, R.; Satizabal, C.L.; Yanek, L.R.; Wen, W.; Gudnason, V.G.; Dueker, N.D.; et al. Common genetic variation indicates separate causes for periventricular and deep white matter hyperintensities. Stroke 2020, 51, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, L.D.; Wolf, P.A.; Heard-Costa, N.; Massaro, J.; Beiser, A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; DeCarli, C. Genetic variation in white matter hyperintensity volume in the Framingham Study. Stroke 2004, 35, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, S.T.; Jack, C.; Fornage, M.; Mosley, T.H.; Boerwinkle, E.; de Andrade, M. Heritability of leukoaraiosis in hypertensive sibships. Hypertension 2004, 43, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochunov, P.; Glahn, D.; Winkler, A.; Duggirala, R.; Olvera, R.L.; Cole, S.; Dyer, T.D.; Almasy, L.; Fox, P.; Blangero, J. Analysis of genetic variability and whole genome linkage of whole-brain, subcortical, and ependymal hyperintense white matter volume. Stroke 2009, 40, 3685–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornage, M.; Debette, S.; Bis, J.C.; Schmidt, H.; Ikram, M.A.; Dufouil, C.; Sigurdsson, S.; Lumley, T.; DeStefano, A.L.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of cerebral white matter lesion burden: The CHARGE consortium. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmelli, D.; DeCarli, C.; Swan, G.E.; Jack, L.M.; Reed, T.; Wolf, P.A.; Miller, B.L. Evidence for genetic variance in white matter hyperintensity volume in normal elderly male twins. Stroke 1998, 29, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhaaren, B.F.; Debette, S.; Bis, J.C.; Smith, J.A.; Ikram, M.K.; Adams, H.H.; Beecham, A.H.; Rajan, K.B.; Lopez, L.M.; Barral, S.; et al. Multiethnic genome-wide association study of cerebral white matter hyperintensities on MRI. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assareh, A.; Mather, K.A.; Schofield, P.; Kwok, J.; Sachdev, P.S. The genetics of white matter lesions. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, P.; Wen, W.; Chen, X.; Brodaty, H. Progression of white matter hyperintensities in elderly individuals over 3 years. Neurology 2007, 68, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moroni, F.; Ammirati, E.; Hainsworth, A.H.; Camici, P.G. Association of white matter hyperintensities and cardiovascular disease: The importance of microcirculatory disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e010460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunstad, J.; Cohen, R.A.; Tate, D.F.; Paul, R.H.; Poppas, A.; Hoth, K.; MacGregor, K.L.; Jefferson, A.L. Blood pressure variability and white matter hyperintensities in older adults with cardiovascular disease. Blood Press. 2005, 14, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherbuin, N.; Wen, W.; Sachdev, P.; Anstey, K. Fasting blood glucose levels are associated with white matter hyperintensities’ burden in older individuals with and without type 2 diabetes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 357, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Launer, L.J.; Nilsson, L.G.; Pajak, A.; Sans, S.; Berger, K.; Breteler, M.M.; de Ridder, M.; Dufouil, C.; Fuhrer, R.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in diabetes: The Cardiovascular Determinants of Dementia (CASCADE) Study. Diabetes 2004, 53, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.-Q.; Wang, L.; Wei, M.-M.; Xia, X.-S.; Tian, X.-L.; Cui, X.-H.; Li, X. Relationship between type 2 diabetes and white matter hyperintensity: A systematic review. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 595962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-García, I.; Michaud, A.; Jurado, M.; Dagher, A.; Morys, F. Mechanisms linking obesity and its metabolic comorbidities with cerebral grey and white matter changes. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.W.; Seo, H.; Kwak, M.-S.; Kim, D. Visceral obesity is associated with white matter hyperintensity and lacunar infarct. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Yun, C.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, M.B.; Park, H.-K. Age-dependent association between cigarette smoking on white matter hyperintensities. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Total (n = 120) | MZ (n = 86) | DZ (n = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zygosity (nMZ:nDZ) | 86:34 | - | - | - |
| Sex (male:female) | 33:87 | 22:64 | 11:23 | 0.45 |
| Age (years) | 50 ± 26.5 | 46 ± 23 | 64 ± 29 | 0.03 †* |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.4 ± 4.3 | 24.3 ± 4.6 | 24.7 ± 3.4 | 0.68 |
| Smoking n(%) | 12(14.0) | 9(15.3) | 3(11.1) | 0.75 |
| Diabetes n(%) | 7(8.1) | 4(6.8) | 3(11.1) | 0.67 |
| Hypertension n(%) | 24(27.9) | 15(25.4) | 9(33.3) | 0.45 |
| Hyperlipidemia n(%) | 22(25.6) | 16(27.1) | 6(22.2) | 0.79 |
| COPD n(%) | 9(7.5) | 7(8.14) | 2(5.9) | 0.67 |
| Thyroid disorders n(%) | 24(20) | 16(18.6) | 8(23.5) | 0.54 |
| Variable | rMZ | rDZ |
|---|---|---|
| Total WMH count | 0.466 (0.195 0.671) | −0.025 (−0.451 0.421) |
| Deep white matter WMH count | 0.482 (0.038 1) | 0.093 (−0.631 1) |
| Infratentorial WMH count | 0.739 (0.371 1) | 0.390 (−0.32 0.686) |
| Cerebellar WMH count | 0.537 (0.041 0.84) | 0.372 (−0.348 0.522) |
| Periventricular WMH count | 0.473 (−1 1) | 0.190 (−1 1) |
| Variable | A | C | E | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total lesion count | 0.403 (0.156, 0.6) | 0 | 0.597 (0.4, 0.844) | 1 |
| Deep white matter lesion count | 0.450 (0, 0.766) | 0 | 0.550 (0.234, 1) | 1 |
| Infratentorial lesion count | 0.727 (0.371, 0.919) | 0 | 0.273 (0.081, 0.629) | 1 |
| Cerebellar lesion count | 0.555 (0.201, 1) | 0 | 0.445 (0, 0.799) | 0.776 |
| Periventricular lesion count | 0.472 (0.145, 0.712) | 0 | 0.528 (0.288, 0.855) | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alijanpourotaghsara, A.; Strelnikov, D.; Piroska, M.; Szalontai, L.; Forgo, B.; Jokkel, Z.; Persely, A.; Hernyes, A.; Kozak, L.R.; Szabo, A.; et al. Genetic and Environmental Effects on the Development of White Matter Hyperintensities in a Middle Age Twin Population. Medicina 2022, 58, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101425
Alijanpourotaghsara A, Strelnikov D, Piroska M, Szalontai L, Forgo B, Jokkel Z, Persely A, Hernyes A, Kozak LR, Szabo A, et al. Genetic and Environmental Effects on the Development of White Matter Hyperintensities in a Middle Age Twin Population. Medicina. 2022; 58(10):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101425
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlijanpourotaghsara, Amirreza, David Strelnikov, Marton Piroska, Laszlo Szalontai, Bianka Forgo, Zsofia Jokkel, Alíz Persely, Anita Hernyes, Lajos Rudolf Kozak, Adam Szabo, and et al. 2022. "Genetic and Environmental Effects on the Development of White Matter Hyperintensities in a Middle Age Twin Population" Medicina 58, no. 10: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101425
APA StyleAlijanpourotaghsara, A., Strelnikov, D., Piroska, M., Szalontai, L., Forgo, B., Jokkel, Z., Persely, A., Hernyes, A., Kozak, L. R., Szabo, A., Maurovich-Horvat, P., Tarnoki, A. D., & Tarnoki, D. L. (2022). Genetic and Environmental Effects on the Development of White Matter Hyperintensities in a Middle Age Twin Population. Medicina, 58(10), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101425











