Incidence and Determinants of Spontaneous Cardioversion of Early Onset Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
3. Results
3.1. Main Determinants of AF Spontaneous Cardioversion
3.2. Heart Failure
3.3. Left Atrial Size
3.4. Duration of AF
3.5. Atrial Fibrillatory Rate
3.6. The Relationship between Heart Rate, Blood Pressure and the Number of Past Episodes of AF
3.7. Biological Clockwork and Hormonal Factors
3.8. Recent Findings
3.9. Different Percentage of SCV among Different Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boriani, G.; Diemberger, I.; Ziacchi, M.; Valzania, C.; Gardini, B.; Cimaglia, P.; Martignani, C.; Biffi, M. AF burden is important-fact or fiction? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2014, 68, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Johnsen, S.P.; Guo, Y.; Lip, G.Y.H. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation: Geographic/Ecological Risk Factors, Age, Sex, Genetics. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornej, J.; Börschel, C.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Schnabel, R.B. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation in the 21st Century: Novel Methods and New Insights. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerk, L.; Sherer, J.A.; Ko, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Helm, R.H. Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Outcomes. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1501–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerman, S.; Wenger, N. Gender Differences in Atrial Fibrillation: A Review of Epidemiology, Management, and Outcomes. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 15, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitolo, M.; Proietti, M.; Harrison, S.; Lane, D.A.; Potpara, T.S.; Boriani, G.; Lip, G.Y.H. The Euro Heart Survey and EURObservational Research Programme (EORP) in atrial fibrillation registries: Contribution to epidemiology, clinical management and therapy of atrial fibrillation patients over the last 20 years. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020, 15, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas, R.; Thune, J.J.; Pehrson, S.; Køber, L.; Nielsen, J.C.; Videbæk, L.; Haarbo, J.; Korup, E.; Bruun, N.E.; Brandes, A.; et al. Atrial fibrillation is a marker of increased mortality risk in nonischemic heart failure-Results from the DANISH trial. Am. Heart J. 2021, 232, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddox, V.; Sandven, I.; Munkhaugen, J.; Skattebu, J.; Edvardsen, T.; Otterstad, J.E. Atrial fibrillation and the risk for myocardial infarction, all-cause mortality and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, M.; Laroche, C.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Crijns, H.J.; Maggioni, A.P.; Lane, D.A.; Boriani, G.; Lip, G.Y. Increased burden of comorbidities and risk of cardiovascular death in atrial fibrillation patients in Europe over ten years: A comparison between EORP-AF pilot and EHS-AF registries. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 55, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzinis, G.; Schiöler, L.; Kahan, T.; Boström, K.B.; Hjerpe, P.; Hasselström, J.; Manhem, K. Antihypertensive control and new-onset atrial fibrillation: Results from the Swedish Primary Care Cardiovascular Database (SPCCD). Eur J Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larstorp, A.C.K.; Stokke, I.M.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Olsen, M.H.; Okin, P.M.; Devereux, R.B.; Wachtell, K. Antihypertensive therapy prevents new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with isolated systolic hypertension: The LIFE study. Blood Press. 2019, 28, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, L.L.; Siliste, C.; Vinereanu, D. Modifiable Risk Factors and Atrial Fibrillation: The Quest for a Personalized Approach. Maedica 2021, 16, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seccia, T.M.; Caroccia, B.; Maiolino, G.; Cesari, M.; Rossi, G.P. Arterial Hypertension, Aldosterone, and Atrial Fibrillation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2019, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.H.; Shenasa, H.A.; Shenasa, M. Hypertension, Prehypertension, Hypertensive Heart Disease, and Atrial Fibrillation. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, P.; Angeli, F.; Reboldi, G. Hypertension and Atrial Fibrillation: Doubts and Certainties from Basic and Clinical Studies. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michniewicz, E.; Mlodawska, E.; Lopatowska, P.; Tomaszuk-Kazberuk, A.; Malyszko, J. Patients with atrial fibrillation and coronary artery disease-Double trouble. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladding, P.A.; Legget, M.; Fatkin, D.; Larsen, P.; Doughty, R. Polygenic Risk Scores in Coronary Artery Disease and Atrial Fibrillation. Heart Lung Circ. 2020, 29, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, H.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial fibrillation and vascular disease: Coronary artery disease and/or peripheral artery disease? Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 114, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakis, G. Coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2017, 58, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, M.A.; Fudim, M.; DeVore, A.D.; Piccini, J.P. Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation, Like Fire and Fury. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugumar, H.; Nanayakkara, S.; Prabhu, S.; Voskoboinik, A.; Kaye, D.M.; Ling, L.-H.; Kistler, P.M. Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: Dangerous Interactions. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Voskoboinik, A.; Kaye, D.M.; Kistler, P.M. Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure-Cause or Effect? Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachmann, J.; Sohns, C.; Andresen, D.; Siebels, J.; Sehner, S.; Boersma, L.; Merkely, B.; Pokushalov, E.; Sanders, P.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Burden and Clinical Outcomes in Heart Failure: The CASTLE-AF Trial. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, Y.N.V.; Obokata, M.; Verbrugge, F.H.; Lin, G.; Borlaug, B.A. Atrial Dysfunction in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.C. Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Two Chronic Troublemakers. Heart Fail Clin. 2021, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartipy, U.; Dahlström, U.; Fu, M.; Lund, L.H. Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure with Preserved, Mid-Range, and Reduced Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, M. Atrial Fibrillation and Chronic Kidney Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2824–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotalczyk, A.; Ding, W.Y.; Wong, C.F.; Rao, A.; Gupta, D.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Cardiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.Y.; Gupta, D.; Wong, C.F.; Lip, G.Y.H. Pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franczyk, B.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Cia|kowska-Rysz, A.; Banach, M.; Rysz, J. The Problem of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 14, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Wu, P.J.; Fang, C.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, M.C. Impact of chronic kidney disease on atrial fibrillation recurrence following radiofrequency and cryoballoon ablation: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.Y.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Pastori, D.; Shantsila, A. Effects of Atrial Fibrillation and Chronic Kidney Disease on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 132, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, C.J.; Pandey, A.; Lau, D.H.; Alpert, M.A.; Sanders, P. Obesity and Atrial Fibrillation Prevalence, Pathogenesis, and Prognosis: Effects of Weight Loss and Exercise. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2022–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, B.S.; Chavez-Moreno, A.; Koh, W.; Akar, J.G.; Akar, F.G. Oxidative stress and inflammation as central mediators of atrial fibrillation in obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, H.; Scherlag, B.J.; Sun, L.; Xing, S.; Xu, J.; Luo, M.; Guo, Y.; Cao, G.; Jiang, H. Atrial fibrillation in obstructive sleep apnea: Neural mechanisms and emerging therapies. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 31, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Mariani, M.V.; Maraone, A.; Piro, A.; Ceccacci, A.; Tarsitani, L.; Maestrini, V.; Mancone, M.; LaValle, C.; Pasquini, M.; et al. Triggers for Atrial Fibrillation: The Role of Anxiety. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 1208505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, C.A.; Banerjee, A.; Perel, P.; Wood, D.; Jouven, X. Atrial fibrillation: The current epidemic. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccarelli, G.V.; Johnston, S.S.; Lin, J.; Patel, P.P.; Schulman, K.L. Cost burden of cardiovascular hospitalization and mortality in ATHENA-like patients with atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter in the United States. Clin. Cardiol. 2010, 33, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodchis, W.P.; Bhatia, R.S.; Leblanc, K.; Meshkat, N.; Morra, D. A review of the cost of atrial fibrillation. Value Health 2012, 15, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Kamal, K.M. Impact of atrial fibrillation on inpatient cost for ischemic stroke in the USA. Int. J. Stroke 2019, 14, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, A.; Patel, N.J.; Nalluri, N.; Agnihotri, K.; Spagnola, J.; Patel, A.; Asti, D.; Kanotra, R.; Khan, H.; Savani, C.; et al. Trends in hospitalization for atrial fibrillation: Epidemiology, cost, and implications for the future. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguli, I.; Thakore, N. Cost Conversations about Atrial Fibrillation Care—Who Is Talking the Talk? JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2116670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migdady, I.; Russman, A.; Buletko, A.B. Atrial Fibrillation and Ischemic Stroke: A Clinical Review. Semin. Neurol. 2021, 41, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, A.M.; Strout, T.D.; Perron, A.D. Electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation in the emergency department: A large single-center experience. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 42, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, V.; Knoery, C.; Rushworth, G.; Rudd, I.; Ortner, A.; Begley, D.; Leslie, S.J. A review of factors associated with maintenance of sinus rhythm after elective electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation. Clin. Cardiol. 2018, 41, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, K.A.; Hogarth, A.J.; MacDonald, W.; Lewis, N.T.; Tan, L.B.; Tayebjee, M.H. Restoration of sinus rhythm results in early and late improvements in the functional reserve of the heart following direct current cardioversion of persistent AF: FRESH-AF. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 199, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Singh, S.N.; Reda, D.J.; Tang, X.C.; Lopez, B.; Harris, C.L.; Fletcher, R.D.; Sharma, S.C.; Atwood, J.E.; Jacobson, A.K.; et al. Amiodarone versus sotalol for atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, T.; Yoshioka, K.; Watanabe, E.; Omori, H.; Yagi, M.; Okumura, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Kusano, K.; Oshiro, C.; Ikeda, T.; et al. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation recurrences and quality of life in symptomatic patients: A crossover study of flecainide and pilsicainide. J. Arrhythm. 2017, 33, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, A.; Piangerelli, L.; Ricciotti, J.; Gabrielli, D.; Guerra, F. Flecainide-metoprolol combination reduces atrial fibrillation clinical recurrences and improves tolerability at 1-year follow-up in persistent symptomatic atrial fibrillation. EP Eur. 2016, 18, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuermeyer, F.X.; Atzema, C.L. Converting emergency physician management of patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter. Can. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 23, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiell, I.G.; Sivilotti, M.L.A.; Taljaard, M.; Birnie, D.; Vadeboncoeur, A.; Hohl, C.M.; McRae, A.D.; Rowe, B.H.; Brison, R.J.; Thiruganasambandamoorthy, V.; et al. Electrical versus pharmacological cardioversion for emergency department patients with acute atrial fibrillation (RAFF2): A partial factorial randomised trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, W.; Ptaszek, L.M. Management of Atrial Fibrillation in the Emergency Department. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weant, K.A.; Matuskowitz, A.J.; Gregory, H.; Caporossi, J.; Hall, G.A. Emergency Department Management of Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation. Adv. Emerg. Nurs. J. 2020, 42, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzema, C.L.; Singh, S.M. Acute Management of Atrial Fibrillation: From Emergency Department to Cardiac Care Unit. Cardiol. Clin. 2018, 36, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, D.A.; Levy, A.R.; Vidaillet, H.; Fenwick, E.; Slee, A.; Blackhouse, G.; Greene, H.L.; Wyse, D.G.; Nichol, G.; O’Brien, B.J.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of rhythm versus rate control in atrial fibrillation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Orfano, J.T.; Kramer, R.K.; Naccarelli, G.V. Cost-effective strategies in the acute management of atrial fibrillation. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2000, 15, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuermeyer, F.X.; Grafstein, E.; Stenstrom, R.; Innes, G.; Poureslami, I.; Sighary, M. Thirty-day outcomes of emergency department patients undergoing electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation or flutter. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2010, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Thom, H.H.Z.; Higgins, J.; Hingorani, A.; Okoli, G.N.; Davies, P.A.; Bodalia, P.N.; A Bryden, P.; Welton, N.; et al. Oral anticoagulants for prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation: Systematic review, network meta-analysis, and cost effectiveness analysis. BMJ 2017, 359, j5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicelli, A.P.; Hong, H.; Connolly, S.J.; Eikelboom, J.; Giugliano, R.P.; Morrow, D.A.; Patel, M.R.; Wallentin, L.; Alexander, J.H.; Bahit, M.C.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Patient-Level Network Meta-Analyses of Randomized Clinical Trials With Interaction Testing by Age and Sex. Circulation 2022, 145, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjuan, J. Prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation. Neurologia 2012, 27 (Suppl. 1), 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.V.; Magnocavallo, M.; Straito, M.; Piro, A.; Severino, P.; Iannucci, G.; Chimenti, C.; Mancone, M.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Forleo, G.B.; et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists in patients with atrial fibrillation and cancer a meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnocavallo, M.; Bellasi, A.; Mariani, M.V.; Fusaro, M.; Ravera, M.; Paoletti, E.; Di Iorio, B.; Barbera, V.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Palumbo, R.; et al. Thromboembolic and Bleeding Risk in Atrial Fibrillation Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Anticoagulation Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, M.V.; di Lullo, L.; Lavalle, C. Direct oral anticoagulants and chronic kidney disease: It is time to be brave. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1419–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnocavallo, M.; Vetta, G.; Trivigno, S.; Mariani, M.V.; DI Lullo, L.; Bellasi, A.; DELLA Rocca, D.G.; Severino, P.; Piro, A.; Giunta, G.; et al. The connubium among diabetes, chronic kidney disease and atrial fibrillation. Minerva Cardiol. Angiol. 2022, 70, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lullo, L.; Mariani, M.V.; Ronco, C.; Bellasi, A.; Lavalle, C.; Chimenti, C.; Paoletti, E.; Ravera, M.; Zanella, M. Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulant Treatment in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Where Do We Stand. Cardiorenal Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre-Vallverdu, M.; Ligero, C.; Vidal-Perez, R.; Martinez-Rubio, A.; Vinolas, X.; Alegret, J.M. Improvement in Atrial Fibrillation-Related Symptoms after Cardioversion: Role of NYHA Functional Class and Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, N.J.; Feinberg, J.; Nielsen, E.E.; Safi, S.; Gluud, C.; Jakobsen, J.C. The effects of rhythm control strategies versus rate control strategies for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter: A systematic review with meta-analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.C.; Breithardt, G.; Camm, A.J.; Crijns, H.J.; Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Kowey, P.R.; Le Heuzey, J.-Y.; Naditch-Brûlé, L.; Prystowsky, E.N.; Schwartz, P.J.; et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation treated with rhythm control versus rate control: Insights from a prospective international registry (Registry on Cardiac Rhythm Disorders Assessing the Control of Atrial Fibrillation: RECORD-AF). Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2014, 7, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.C.; Stewart, J.; Klein, G.; Roy, D.; Connolly, S.; Koren, A.; Dorian, P. Impact of electrical cardioversion on quality of life for patients with symptomatic persistent atrial fibrillation: Is there a treatment expectation effect? Am. Heart J. 2020, 226, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, R.K.; Smigorowsky, M.; Lockwood, E.; Savu, A.; Kaul, P.; McAlister, F.A. Impact of Electrical Cardioversion on Quality of Life for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorian, P.; Ha, A.C.T. Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Improves Quality of Life: It’s Obvious (or Isn’t It?). Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koniari, I.; Artopoulou, E.; Velissaris, D.; Kounis, N.; Tsigkas, G. Atrial fibrillation in patients with systolic heart failure: Pathophysiology mechanisms and management. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 376–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slee, A.; Saad, M.; Saksena, S. Heart failure progression and mortality in atrial fibrillation patients with preserved or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2019, 55, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohendanner, F.; Heinzel, F.R.; Blaschke, F.; Pieske, B.M.; Haverkamp, W.; Boldt, H.L.; Parwani, A.S. Pathophysiological and therapeutic implications in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2018, 23, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalife, J.; Kaur, K. Atrial remodeling, fibrosis, and atrial fibrillation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 25, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Khunger, M.; Seicean, S.; Chung, M.K.; Tchou, P.J. Incidence of Thromboembolic Complications Within 30 Days of Electrical Cardioversion Performed Within 48 Hours of Atrial Fibrillation Onset. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.M.; Perry, J.J.; Cheng, W.; Zheng, B.; Guo, K.; Taljaard, M.; Skanes, A.C.; Stiell, I.G. Thromboembolic events following cardioversion of acute atrial fibrillation and flutter: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 23, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borre, E.D.; Goode, A.; Raitz, G.; Shah, B.; Lowenstern, A.; Chatterjee, R.; Sharan, L.; LaPointe, N.M.A.; Yapa, R.; Davis, J.K.; et al. Predicting Thromboembolic and Bleeding Event Risk in Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 2171–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killu, A.M.; Granger, C.B.; Gersh, B.J. Risk stratification for stroke in atrial fibrillation: A critique. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; Roldán, V.; Esteve-Pastor, M.A.; Valdés, M.; Vicente, V.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Marín, F. Long-Term Stroke Risk Prediction in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Comparison of the ABC-Stroke and CHA2DS2-VASc Scores. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.B.; Overvad, T.F. Female Sex as a Risk Modifier for Stroke Risk in Atrial Fibrillation: Using CHA2DS2-VASc versus CHA2DS2-VA for Stroke Risk Stratification in Atrial Fibrillation: A Note of Caution. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cove, C.L.; Albert, C.M.; Andreotti, F.; Badimon, L.; van Gelder, I.C.; Hylek, E.M. Female sex as an independent risk factor for stroke in atrial fibrillation: Possible mechanisms. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altiok, E.; Marx, N. Oral Anticoagulation. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2018, 115, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iung, B.; Rodes-Cabau, J. The optimal management of anti-thrombotic therapy after valve replacement: Certainties and uncertainties. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2942–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Sciammarella, J.C.; Chhabra, L.; Singhal, M. Synchronized Electrical Cardioversion; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29489237/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Galve, E.; Rius, T.; Ballester, R.; Artaza, M.A.; Arnau, J.M.; García-Dorado, D.; Soler-Soler, J. Intravenous amiodarone in treatment of recent-onset atrial fibrillation: Results of a randomized, controlled study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 27, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Biffi, M.; Capucci, A.; Botto, G.L.; Broffoni, T.; Rubino, I.; Casa, S.D.; Sanguinetti, M.; Magnani, B. Oral Propafenone To Convert Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with and without Underlying Heart Disease A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 126, 621–625. Available online: http://annals.org/ (accessed on 10 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Cotter, G.; Blatt, A.; Kaluski, E.; Metzkor-Cotter, E.; Koren, M.; Litinski, I.; Simantov, R.; Moshkovitz, Y.; Zaidenstein, R.; Peleg, E.; et al. Article No. Euhj. 1999. Volume 20. Available online: http://www.idealibrary.comon (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Lindberg, S.; Hansen, S.; Nielsen, T. Spontaneous conversion of first onset atrial fibrillation. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleris, P.; Stavrati, A.; Afthonidis, D.; Kirpizidis, H.; Boudoulas, H. Spontaneous conversion to sinus rhythm of recent (within 24 hours) atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 103–107. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11255692/ (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Danias, P.G.; Caulfield, T.A.; Weigner, M.J.; Silverman, D.I.; Manning, W.J. Likelihood of Spontaneous Conversion of Atrial Fibrillation to Sinus Rhythm. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’orfano, J.T.; Patel, H.; Wolbrette, D.L.; Luck, J.C.; Naccarelli, G.V. Acute Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation: Spontaneous Conversion Rates and Cost of Care. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.B.; Holmqvist, F.; Carlson, J.; Nilsson, H.J.; Roijer, A.; Platonov, P.G. Low atrial fibrillatory rate is associated with spontaneous conversion of recent-onset atrial fibrillation. EP Eur. 2013, 15, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svennberg, E.; Stridh, M.; Engdahl, J.; Al-Khalili, F.; Friberg, L.; Frykman, V.; Rosenqvist, M. Safe automatic one-lead electrocardiogram analysis in screening for atrial fibrillation. EP Eur. 2017, 19, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrea, D.N.; Ekmektzoglou, K.A.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tsitsilonis, S.; Koudouna, E.; Stroumpoulis, K.; Xanthos, T. A formula for the stratified selection of patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in the emergency setting: A retrospective pilot study. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 40, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stridh, M.; Sörnmo, L.; Meurling, C.J.; Olsson, S.B. Sequential characterization of atrial tachyarrhythmias based on ECG time-frequency analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, A.V.; Vivoli, D.; Borella, P.; Mattioli, G. Clinical, echocardiographic, and hormonal factors influencing spontaneous conversion of recent-onset atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 86, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, M.P.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; van Gelder, I.C.; de Kam, P.J.; Lie, K.I. Atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with heart failure and chronic atrial fibrillation: Role of duration of atrial fibrillation. Am. Heart J. 1998, 135 Pt 2, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluymaekers, N.A.H.A.; Dudink, E.A.M.P.; Weijs, B.; Vernooy, K.; Hartgerink, D.E.J.; Jacobs, J.S.; Erküner, Ö.; Marcks, N.G.H.M.; van Cauteren, Y.J.M.; Dinh, T.; et al. Clinical determinants of early spontaneous conversion to sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation. Neth. Heart J. 2021, 29, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederdöckl, J.; Simon, A.; Cacioppo, F.; Buchtele, N.; Merrelaar, A.; Schütz, N.; Schnaubelt, S.; Spiel, A.O.; Roth, D.; Schörgenhofer, C.; et al. Predicting spontaneous conversion to sinus rhythm in symptomatic atrial fibrillation: The ReSinus score. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 83, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
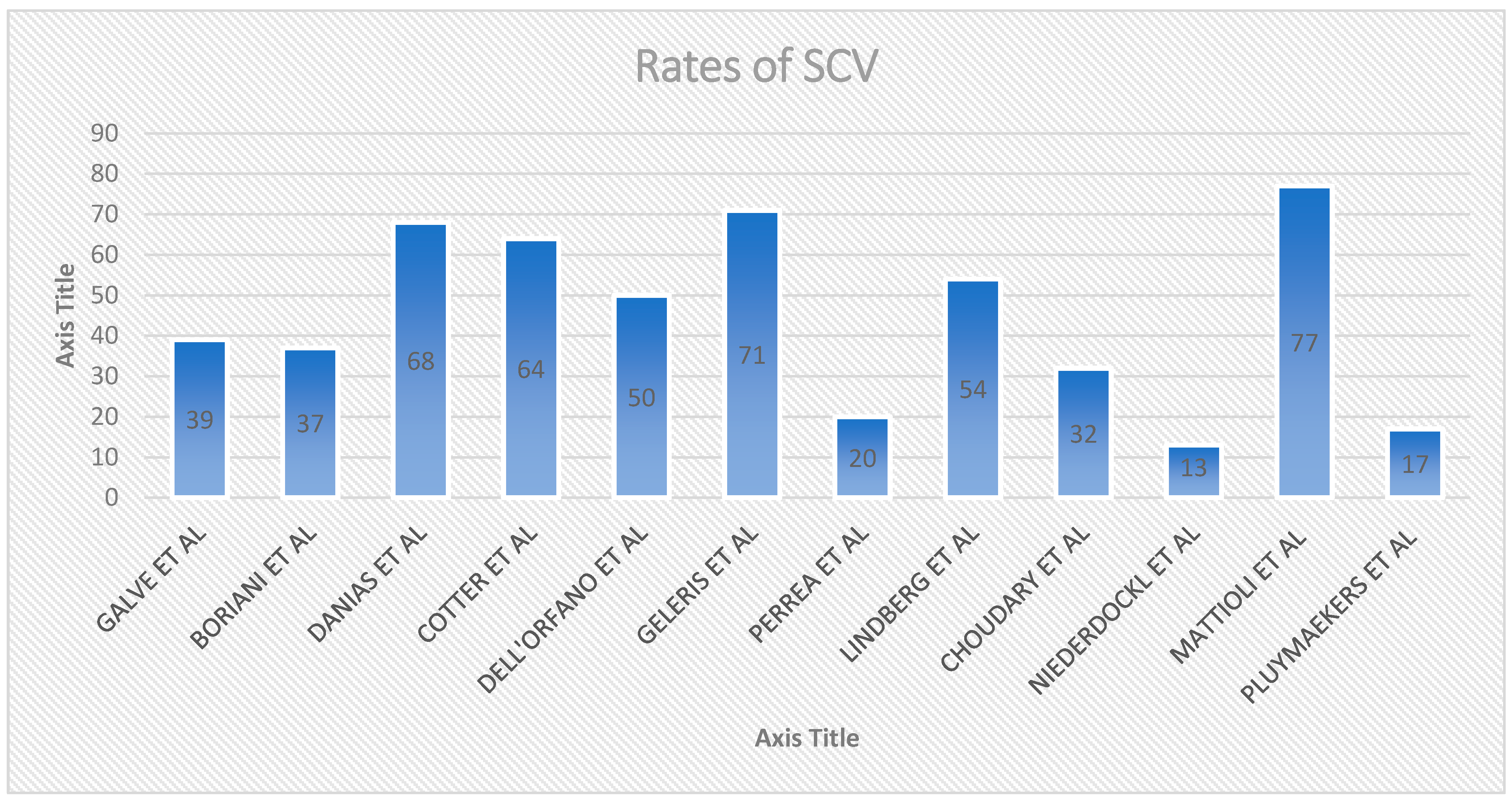
| Study, Year | Study Design, Intervention | Setting, Observation Time | Patient Included | SCV Rate % | Main Determinant(s) of SCV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galve et al., 1996 [88] | IV Amiodaron VS Placabeo | ED/hospitalized, 24 h observation | Recent onset AF (<7 days) | 24/62 (39%) | HF, Left atrial size |
| Boriani et al., 1997 [89] | Oral propafenone Vs Placebo | ED/Hospitalized, 8 h observation | Recent onset AF (<7 days) | 45/121 (37%) | HF |
| Danias et al., 1998 [93] | Prospective | ED/hospitalized, observation 4.6 days | Recent onset AF < 72 h | 242/356 (68%) | atrial fibrillation of 24 h duration at presentation |
| Cotter et al., 1999 [90] | IV Amiodaron VS Placabeo | ED/hospitalized, 24 h observation | Paroxysmal AF < 48 h and at least one previous episode of paroxysmal AF | 32/50 (64%) | HF, left atrial size |
| Dell’orfano et al., 1999 [94] | Retrospective | ED < 48 h observation | Primary diagnosis of AF by 12 lead ECG or single channel | 57/114 (50%) | Duration of AF |
| Mattioli et al. (2000) [99] | Prospective | ED 48 h observation | Consecutive with recent onset AF (<6 h) | 108/140 (77%) | AF developed during sleep, ANP |
| Geleris et al., 2001 [92] | Prospective | ED 24 h observation | Consecutive patients with recents onset AF (<24 h) | 109/153 (71%) | Left Atrial Size |
| Perrea et al., 2011 [97] | Retrospective study, SCV, Amiodaron | ED no observation time | AF at the time of presentation (<48 h) | 28/141 (20%) | Heart rate, Blood Pressure, number of past episodes of AF |
| Lindberg et al., 2012 [91] | Retrospective | ED < 48 h observation | Consecutive patients admitted to hospital with first onset AF | 203/374 (54%) | HF, Duration of AF |
| Choudary et al., 2013 [95] | Retrospective | ED SCV < 18 h after | Patients with Paroxysmal AF < 48 h | 48/148 (32%) | Atrial Fibrillatory rate |
| Niederdöckl et al., 2020 [102] | Retrospective | ED atrial fibrillation confirmed by 12-lead electrocardiography. | First detected or recurrent hemodynamically stable non-permanent symptomatic atrial fibrillation | 186/2426 (13%) | Resinus score (duration of af symptoms < 24 h, no previous electrical cv, heart rate > 125 bpm, potassium replacement at k+ level < 3.9 mmol/L, nt-probnp < 1300 pg/mL, ldh < 200 u/i |
| Pluymaekers et al., 2021 [101] | prospective | ED, 3 h | first detected hemodynamically stable non-permanent symptomatic AF | 158/943 (16.8%) | duration of AF < 24 h, left atrial volume index (lavi) < 42 mL, symptoms of near-collapse at presentation, a lower BMI, a longer qtc time during AF, and first-detected AF |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mariani, M.V.; Pierucci, N.; Piro, A.; Trivigno, S.; Chimenti, C.; Galardo, G.; Miraldi, F.; Vizza, C.D. Incidence and Determinants of Spontaneous Cardioversion of Early Onset Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation. Medicina 2022, 58, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111513
Mariani MV, Pierucci N, Piro A, Trivigno S, Chimenti C, Galardo G, Miraldi F, Vizza CD. Incidence and Determinants of Spontaneous Cardioversion of Early Onset Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation. Medicina. 2022; 58(11):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111513
Chicago/Turabian StyleMariani, Marco Valerio, Nicola Pierucci, Agostino Piro, Sara Trivigno, Cristina Chimenti, Gioacchino Galardo, Fabio Miraldi, and Carmine Dario Vizza. 2022. "Incidence and Determinants of Spontaneous Cardioversion of Early Onset Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation" Medicina 58, no. 11: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111513
APA StyleMariani, M. V., Pierucci, N., Piro, A., Trivigno, S., Chimenti, C., Galardo, G., Miraldi, F., & Vizza, C. D. (2022). Incidence and Determinants of Spontaneous Cardioversion of Early Onset Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation. Medicina, 58(11), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111513






