A Microfluidic Chip Using Phenol Formaldehyde Resin for Uniform-Sized Polycaprolactone and Chitosan Microparticle Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion

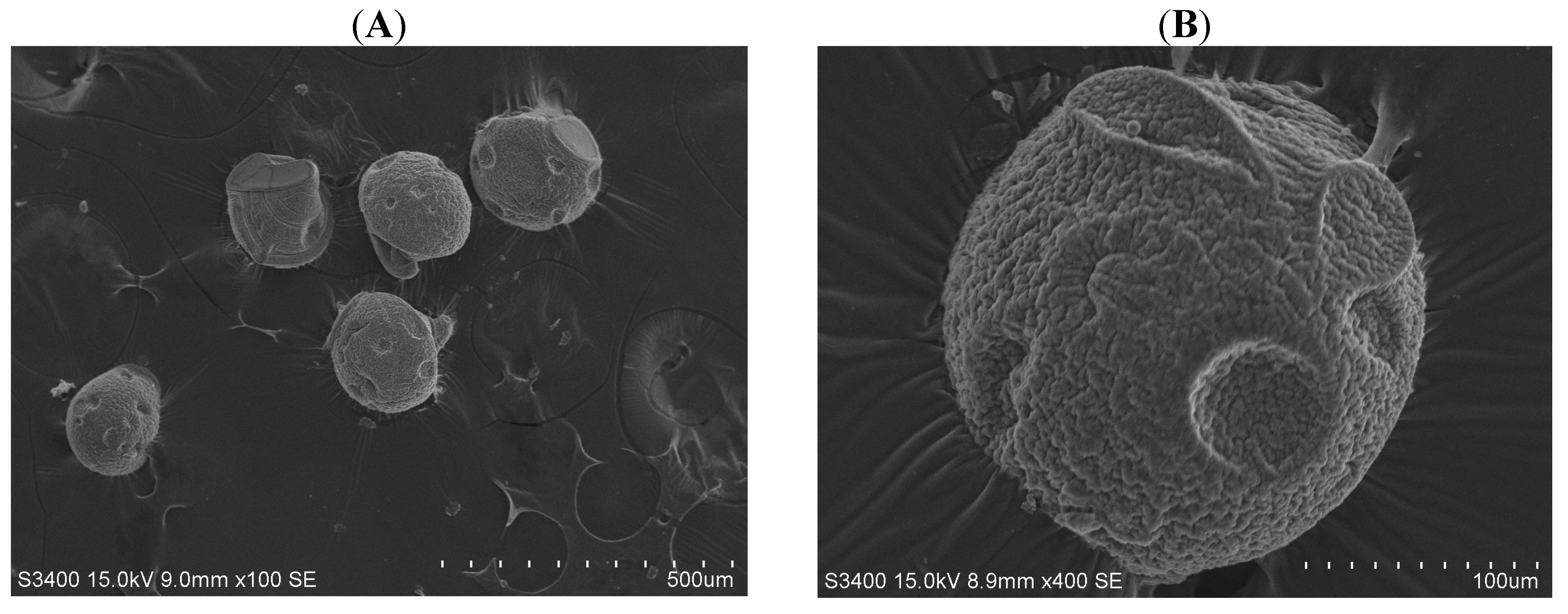
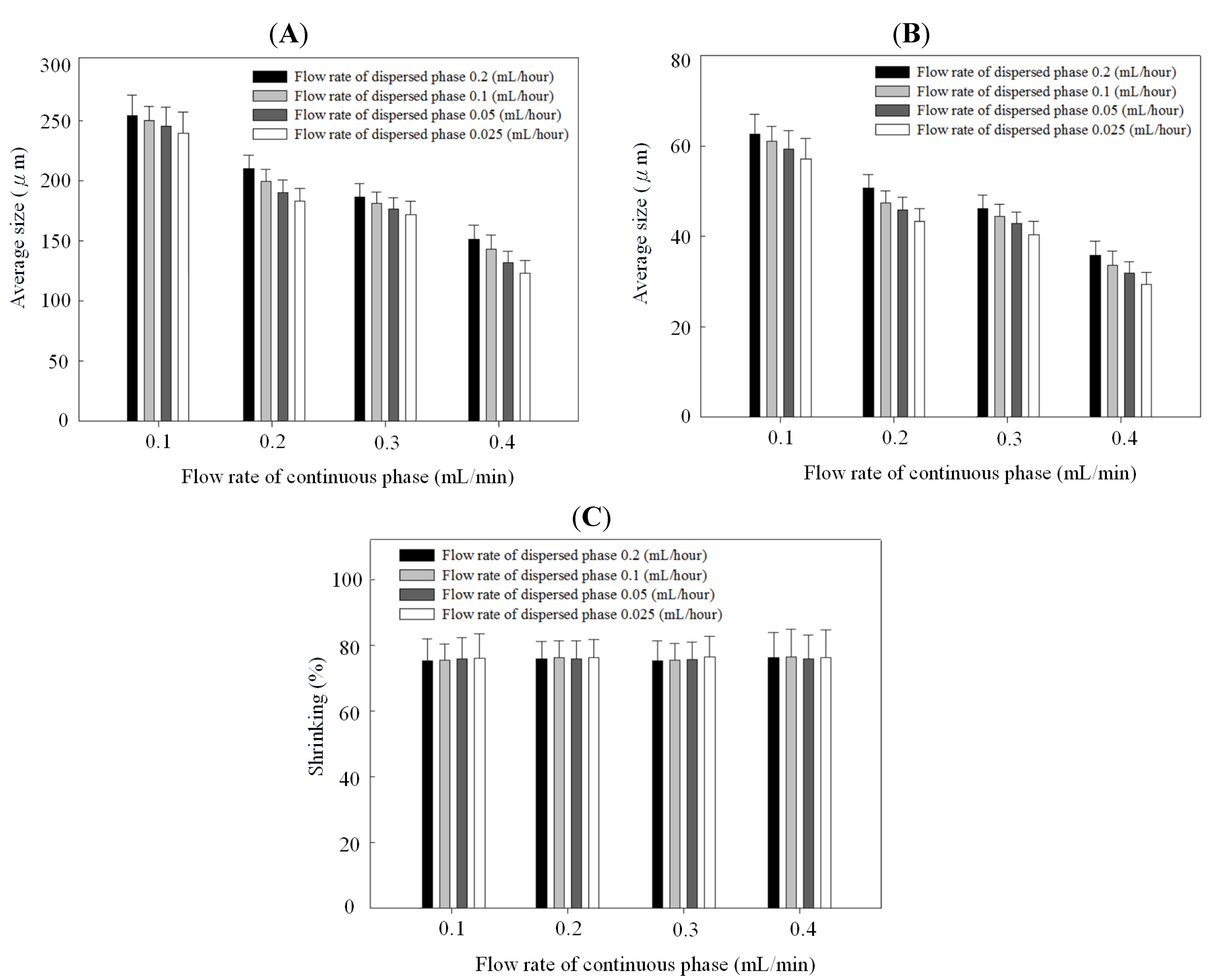
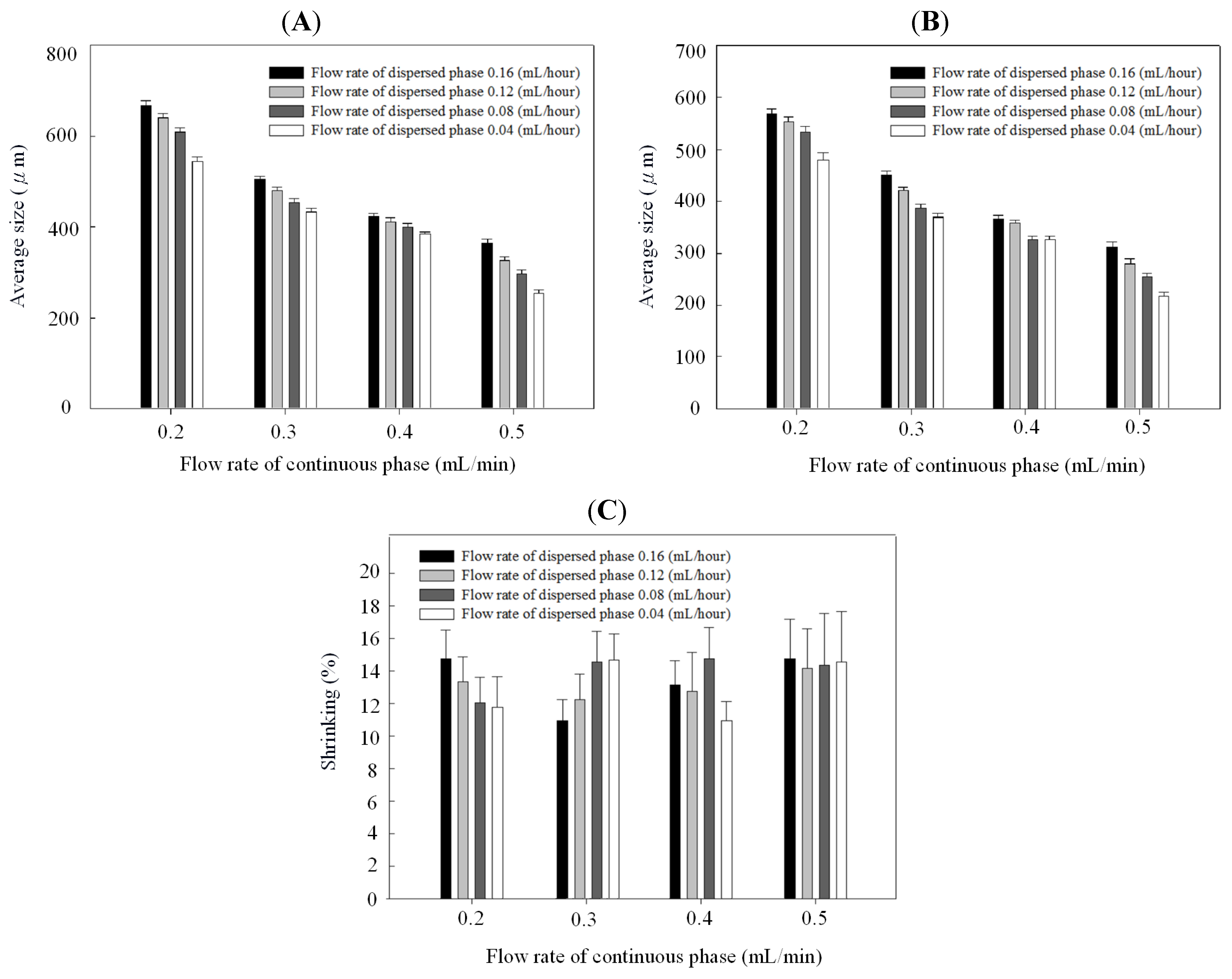
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
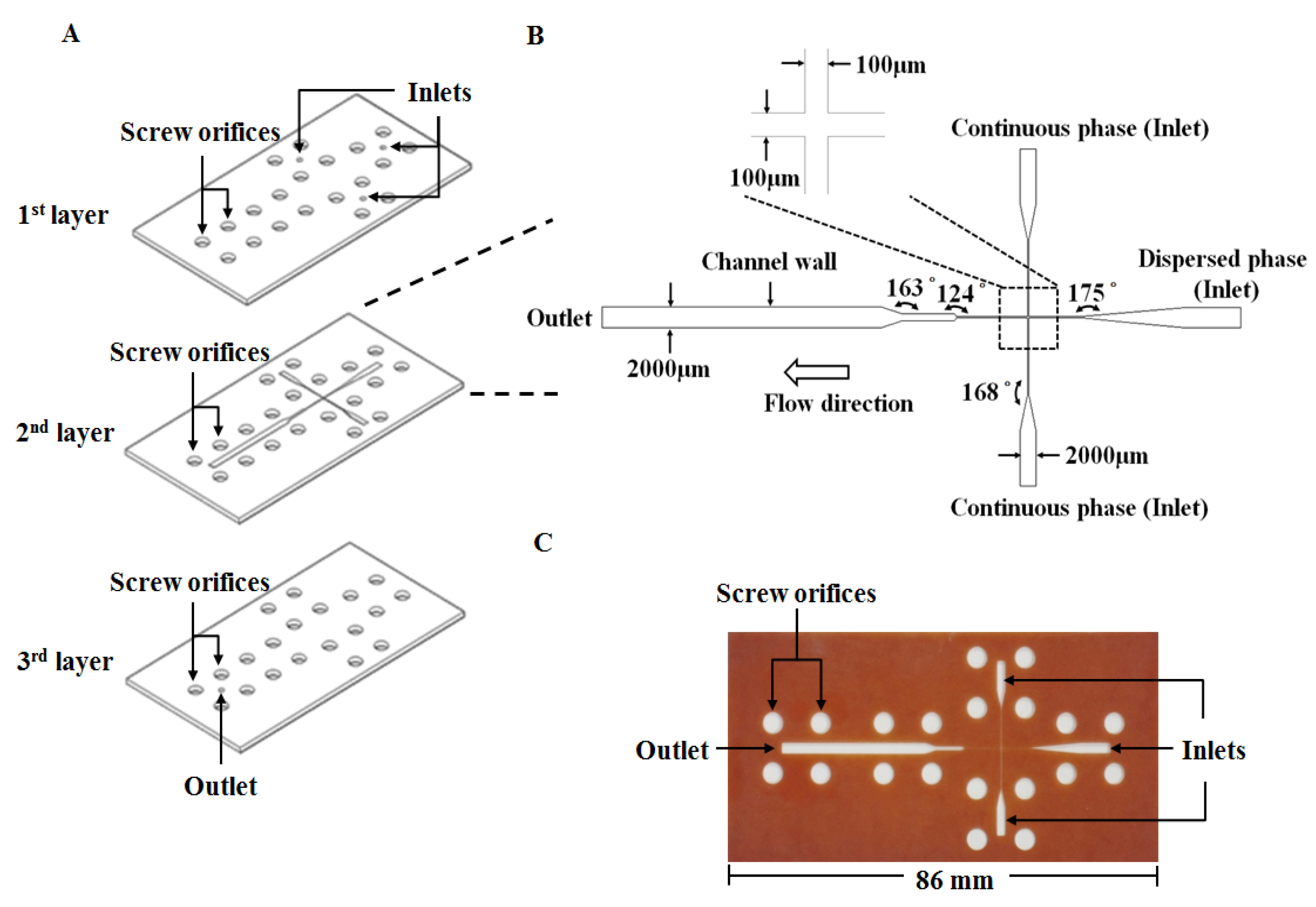
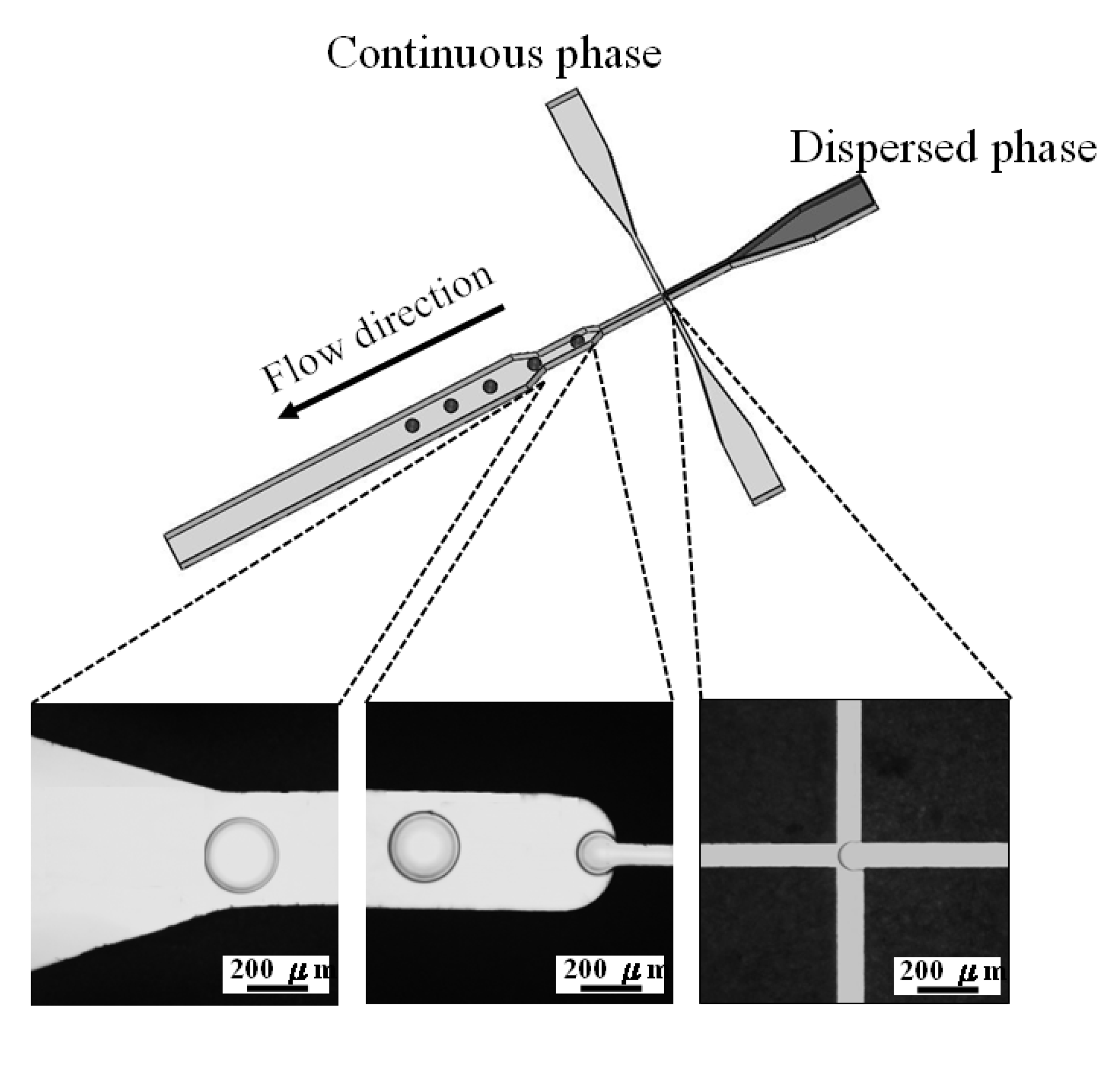
3.2. Construction of the Microfluidic Platform
3.3. Experimental Procedure
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellette, J. A new wave of microfluidic devices. Ind. Phys. 2003, 9, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Quake, S.R.; Scherer, A. From micro- to nanofabrication with soft materials. Science 2000, 290, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, C.; Shin, K.S.; Lee, J.W.; Ju, B.K.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kang, J.Y. Fabrication of round channels using the surface tension of PDMS and its application to a 3D serpentine mixer. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Yang, C.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Chang, F.R.; Huang, K.S.; Hsieh, W.C. An aluminum microfluidic chip fabrication using a convenient micromilling process for fluorescent poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microparticle generation. Sensors 2012, 12, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, H.; Locascio, L.E. Review: Polymer microfluidic devices. Talanta 2002, 56, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent compatibility of poly(dimethylsiloxane)- based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, J.P.; Van Dam, R.M.; Schorzman, D.A.; Quake, S.R.; DeSimone, J.M. Solvent-resistant photocurable liquid fluoropolymers for microfluidic device fabrication. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2322–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, C.; Girardo, S.; Mele, E.; Cingolani, R.; Pisignano, D. Ultraviolet-based bonding for perfluoropolyether low aspect-ratio microchannels and hybrid devices. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renckens, T.J.; Janeliunas, D.; van Vliet, H.; van Esch, J.H.; Mul, G.; Kreutzer, M.T. Micromolding of solvent resistant microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, P.K.; Pasirayi, G.; Auger, V.; Ali, Z. Development of a simple and low cost microbioreactor for high-throughput bioprocessing. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Castell, O.K.; Allender, C.J.; Barrow, D.A. Liquid-liquid phase separation: Characterisation of a novel device capable of separating particle carrying multiphase flows. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, D.J.; Porch, A.; Barrow, D.A.; Allender, C.J. Microfluidic device for compositional analysis of solvent systems at microwave frequencies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raqueza, J.M.; Deléglisea, M.; Lacrampea, M.F.; Krawczaka, P. Thermosetting (bio)materials derived from renewable resources: A critical review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 487–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Q.Z.; Xu, X.W.; Dong, L.; Yu, S.H. Phenol formaldehyde resin nanoparticles loaded with CdTe quantum dots: A fluorescence resonance energy transfer probe for optical visual detection of copper(II) ions. ACS Nano. 2011, 5, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The return of a forgotten polymer–polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estelle, J.M.; Vidaurre, A.; Duenas, J.M.M.; Cortazar, I.C. Physical characterization of polycaprolactone scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Sudheesh Kumar, P.T.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, K. Using drug-excipient interactions for siRNA delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1210–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, O. M.; Zheng, M.; Debus, H.; Kissel, T. Pulmonary gene delivery using polymeric nonviral vectors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cooke, M.J.; Shoichet, M.S. Creating permissive microenvironments for stem cell transplantation into the central nervous system. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Huang, K.S.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, E.C.; Jhong, J.Y.; Kuo, C.Y. Microfluidic emulsification and sorting assisted preparation of monodisperse chitosan microparticles. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Huang, K.S.; Lin, Y.S.; Lu, K.; Tzeng, C.C.; Wang, E.C.; Lin, C.H.; Hsu, W.Y.; Chang, J.Y. Microfluidic assisted synthesis of multi-functional polycaprolactone microspheres: Incorporation of CdTe quantum Dots, Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticles, and tamoxifen. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.S.; Lu, K.; Yeh, C.S.; Chung, S.R.; Lin, C.H.; Yang, C.H.; Dong, Y.S. Microfluidic controlling monodisperse microdroplet for 5-fluorouracil loaded genipin-gelatin microcapsules. J. Contr. Release 2009, 127, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.S.; Yang, C.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Lu, K.; Chang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.L. Electrostatic droplets assisted synthesis of alginate microcapsules. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.S.; Lin, Y.S.; Yang, C.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Hsu, M.Y. In situ synthesis of twin monodispersed alginate microparticles. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 6713–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Yang, C.H.; Lu, K.; Huang, K.S.; Zheng, Y.Z. Synthesis of agar microparticles using temperature-controlled microfluidic devices for Cordyceps Militaris cultivation. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 3157–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Huang, K.S.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Tzeng, S.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, Y.S. Synthesis of uniform PLA and PLGA microspheres using a microfluidic chip for comparison. Electrophoresis 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Huang, K.S.; Yeh, C.S.; Wang, A.H.; Wang, W.T.; Lin, M.Y. Facile synthesis of radial-like macroporous superparamagnetic chitosan spheres with in-situ co-precipitation and gelation of ferro-gels. PLoS One 2012, 7, e49329. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.H.; Huang, K.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Chang, F.R.; Lin, Y.S. Microfluidic-assisted synthesis of hemispherical and discoidal chitosan microparticles at an oil/water interface. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 3173–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Yang, C.H.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Hsieh, C.L. Microfluidic synthesis of tail-shaped alginate microparticles using slow sedimentation. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Lee, J.; Rhee, H.; Choo, J.; Chai, Y.G.; Lee, E.K. Applicability of laser-induced Raman microscopy for in situ monitoring of imine formation in a glass microfluidic chip. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.J.; Fang, Q.; Fang, Z.L. Bonding of glass microfluidic chips at room temperatures. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5597–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.Y.; Wu, Z.Y.; Fang, F.; Bai, Z.M.; Yang, D.Z.; Xu, S.K. A glass microfluidic chip for continuous blood cell sorting by a magnetic gradient without labeling. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltro, W.K.; de Jesus, D.P.; da Silva, J.A.; do Lago, C.L.; Carrilho, E. Toner and paper-based fabrication techniques for microfluidic applications. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, G.F.; Meister, B.J. Drop formation at low velocities in liquid-liquid systems: Part I. Prediction of drop volume. AIChE J. 1968, 14, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izard, J.A. Prediction of drop volumes in liquid-liduid systems. AIChE J. 1972, 18, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, S.Z.; Kovalev, N.; Zakharychev, A.P. Drop size with drop-type flow conditions out of nozzles in liquid/liquid systems. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 1973, 7, 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.R.; Weber, M.E. Formation and breakup of fluid particles. In Bubbles, Drops, and Particles; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 321–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Hartland, S. Correlation for drop size in liquid/liquid spray columns. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1984, 31, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Dynamics of drop formation in viscous flows. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 1759–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-S.; Yang, C.-H.; Wu, C.-T.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Huang, K.-S. A Microfluidic Chip Using Phenol Formaldehyde Resin for Uniform-Sized Polycaprolactone and Chitosan Microparticle Generation. Molecules 2013, 18, 6521-6531. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066521
Lin Y-S, Yang C-H, Wu C-T, Grumezescu AM, Wang C-Y, Hsieh W-C, Chen S-Y, Huang K-S. A Microfluidic Chip Using Phenol Formaldehyde Resin for Uniform-Sized Polycaprolactone and Chitosan Microparticle Generation. Molecules. 2013; 18(6):6521-6531. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066521
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yung-Sheng, Chih-Hui Yang, Chin-Tung Wu, Alexandru Mihai Grumezescu, Chih-Yu Wang, Wan-Chen Hsieh, Szu-Yu Chen, and Keng-Shiang Huang. 2013. "A Microfluidic Chip Using Phenol Formaldehyde Resin for Uniform-Sized Polycaprolactone and Chitosan Microparticle Generation" Molecules 18, no. 6: 6521-6531. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066521
APA StyleLin, Y.-S., Yang, C.-H., Wu, C.-T., Grumezescu, A. M., Wang, C.-Y., Hsieh, W.-C., Chen, S.-Y., & Huang, K.-S. (2013). A Microfluidic Chip Using Phenol Formaldehyde Resin for Uniform-Sized Polycaprolactone and Chitosan Microparticle Generation. Molecules, 18(6), 6521-6531. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066521






