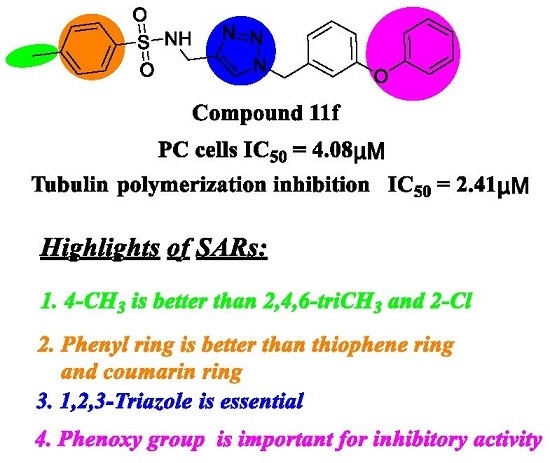
Design and Antiproliferative Evaluation of Novel Sulfanilamide Derivatives as Potential Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors
Abstract
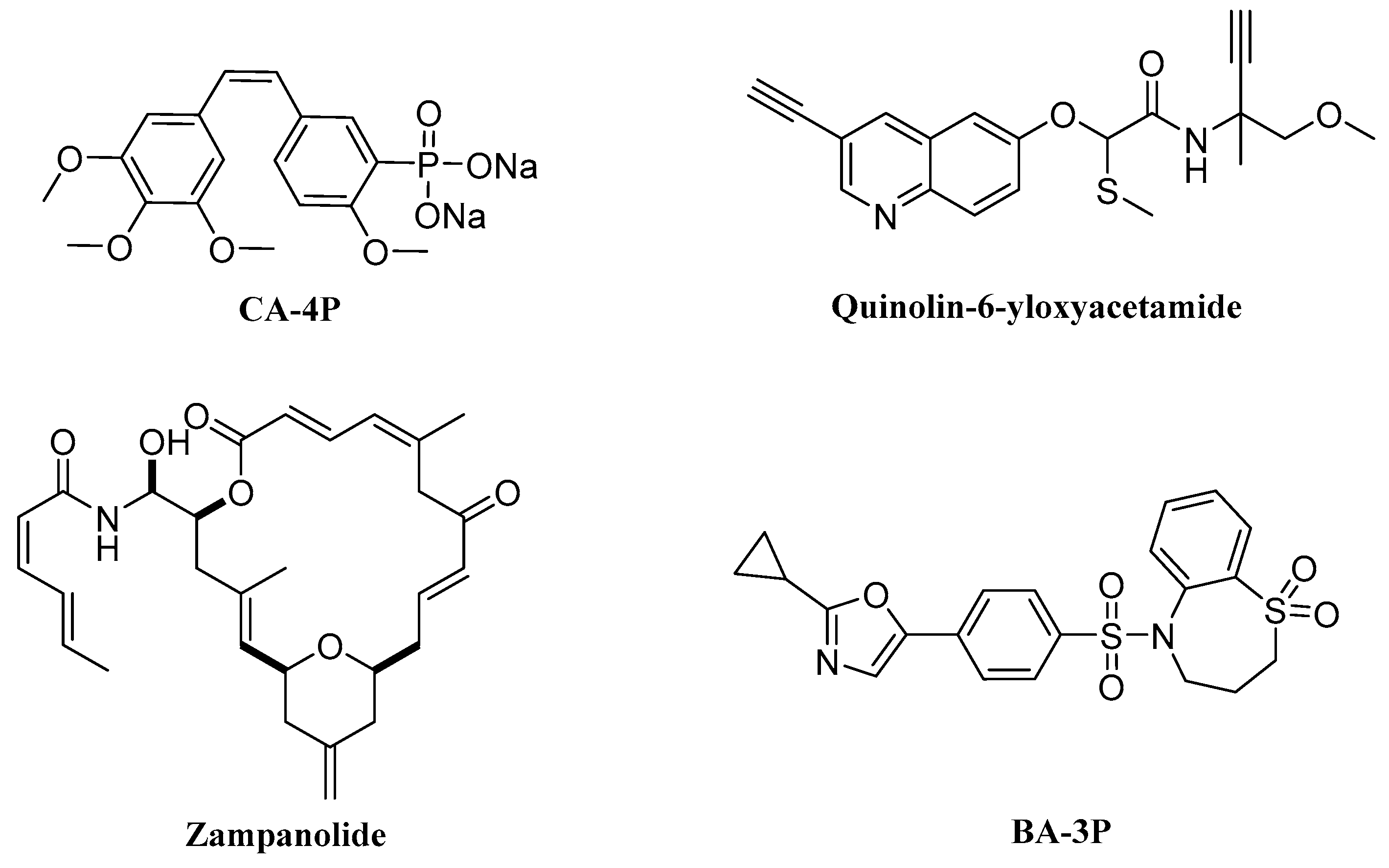
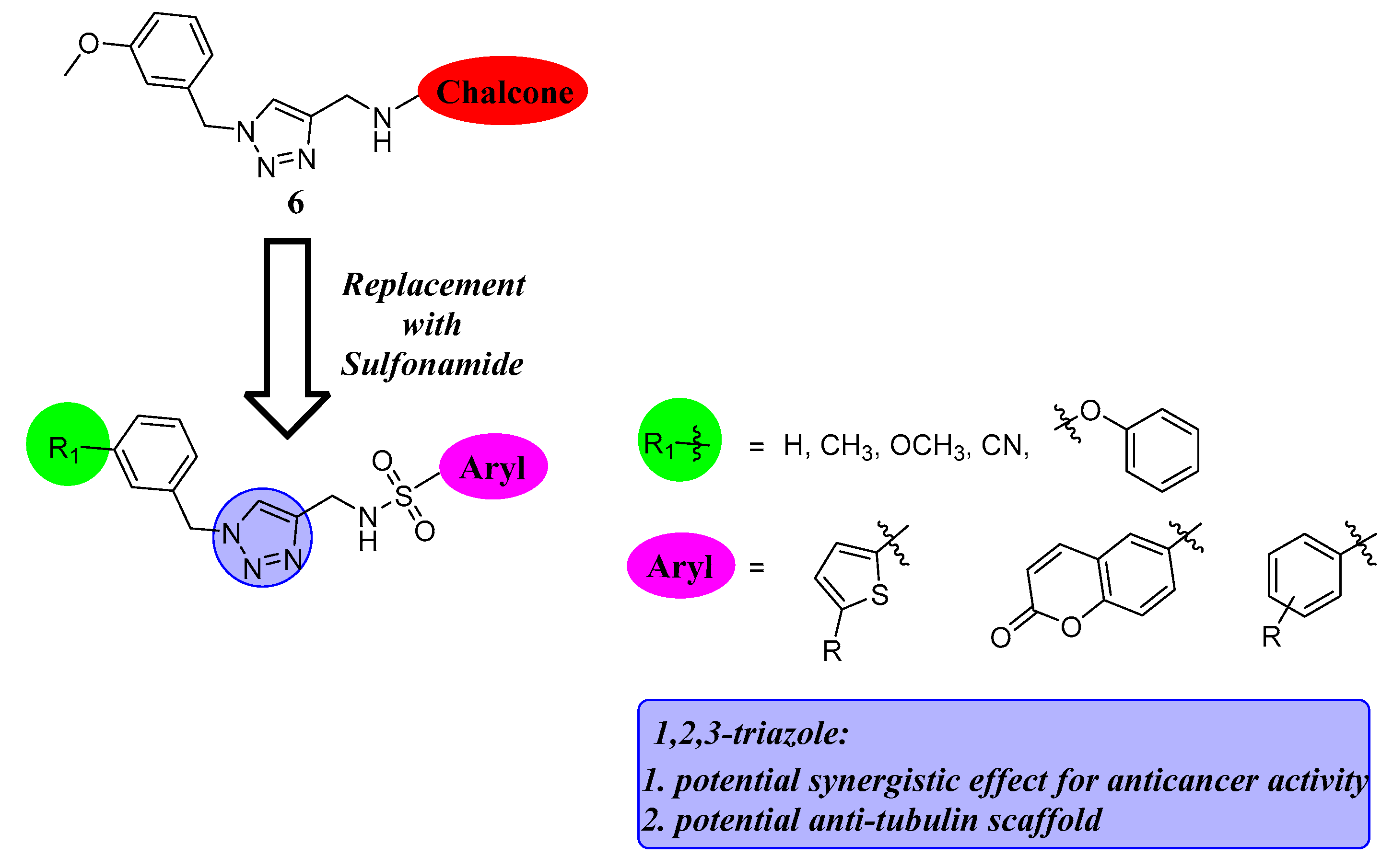
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
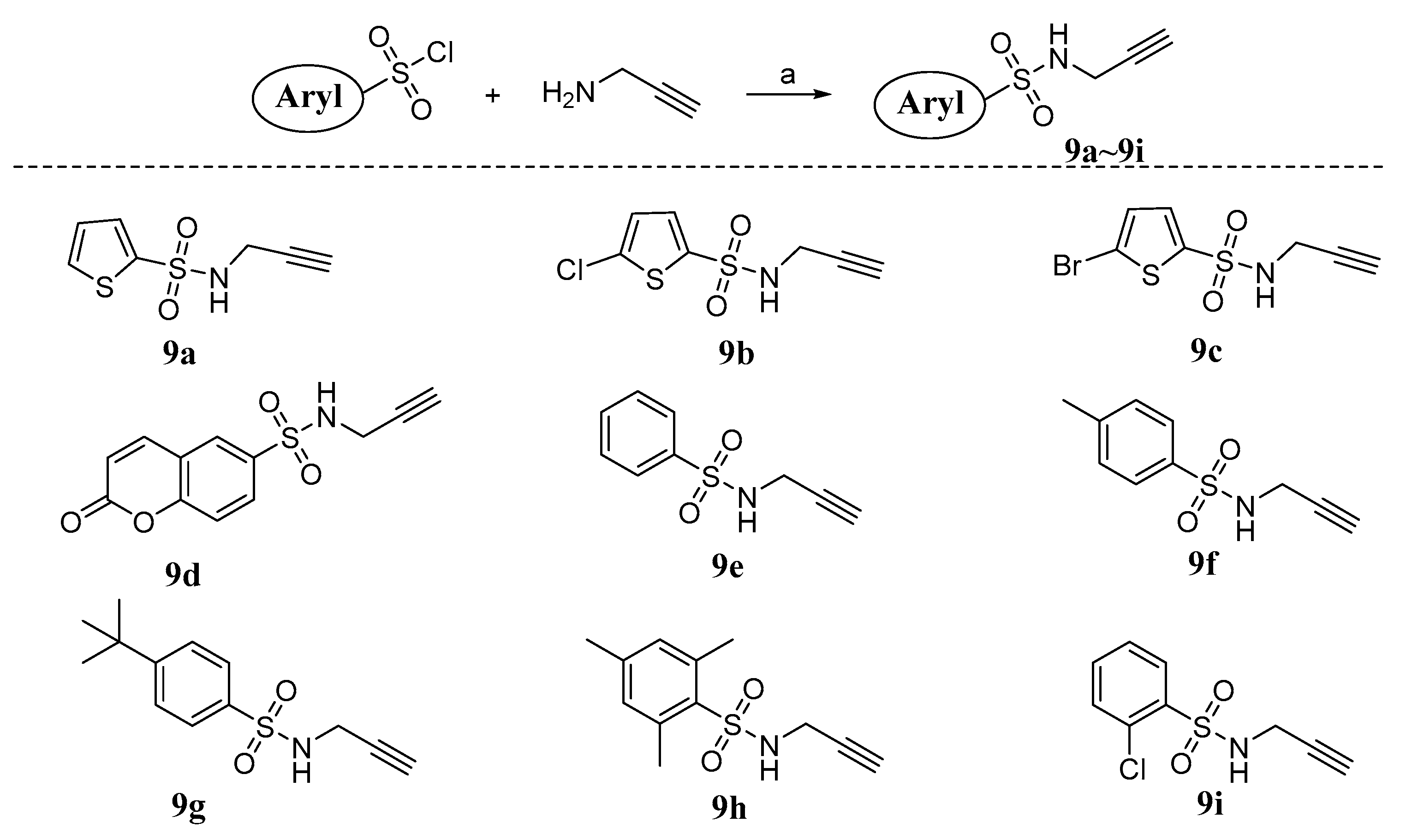
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Antiproliferative Activity and SARs Analysis
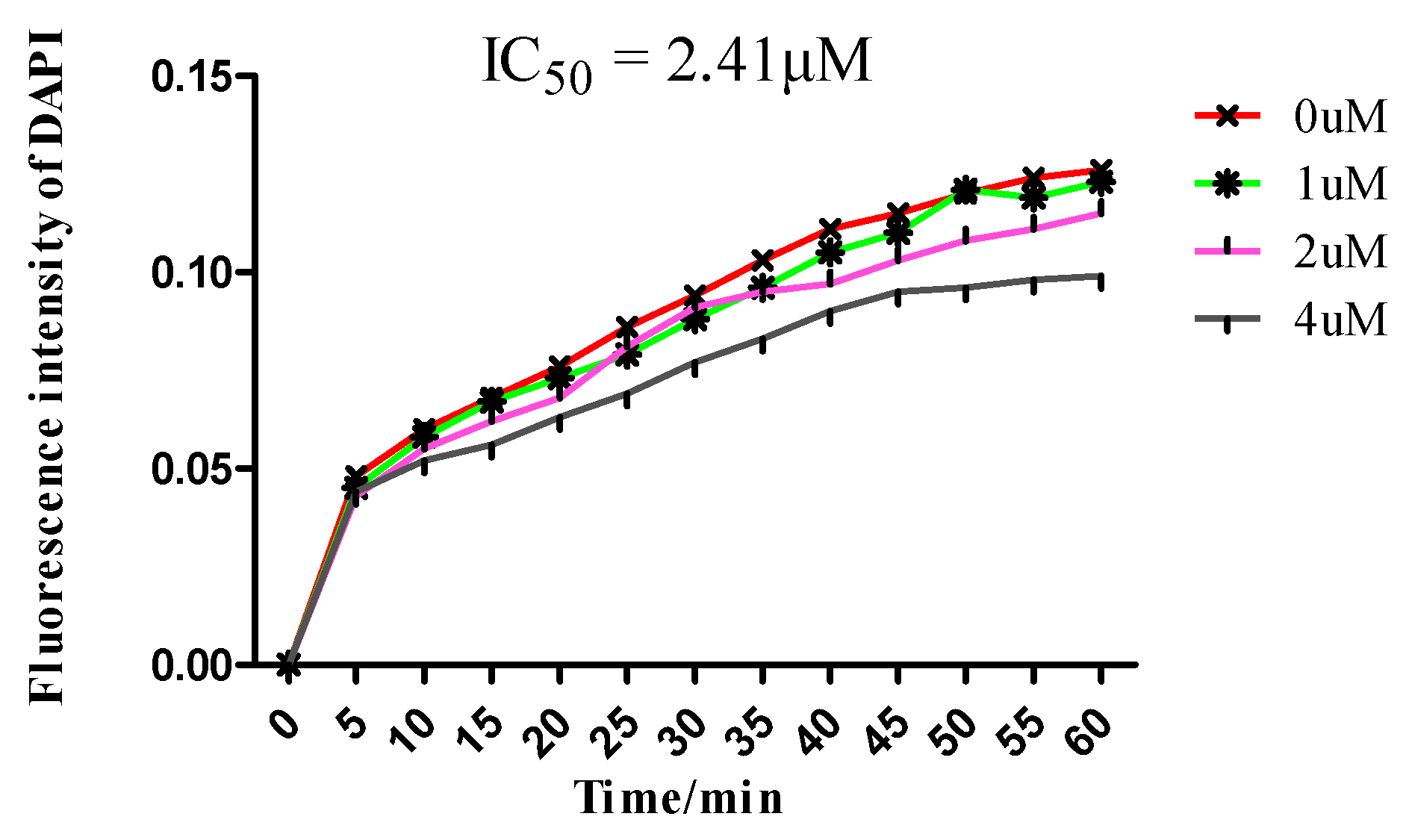
2.3. In Vitro Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitory Activity Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Chemical Experimental Procedures
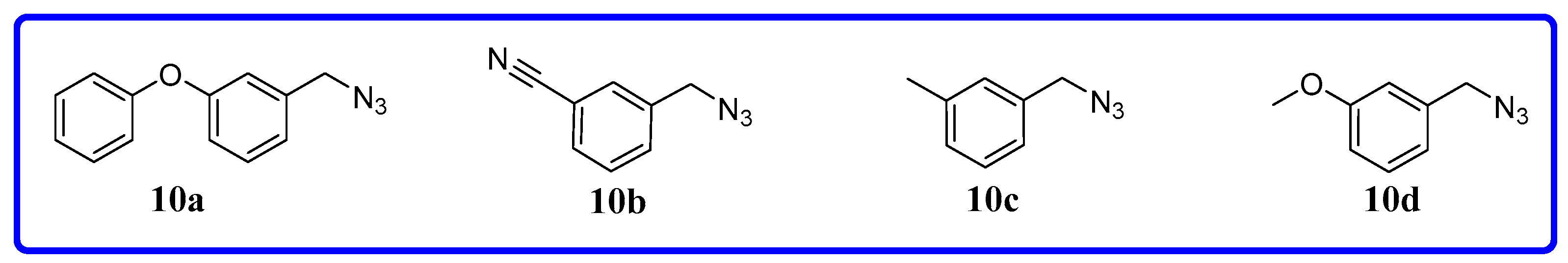
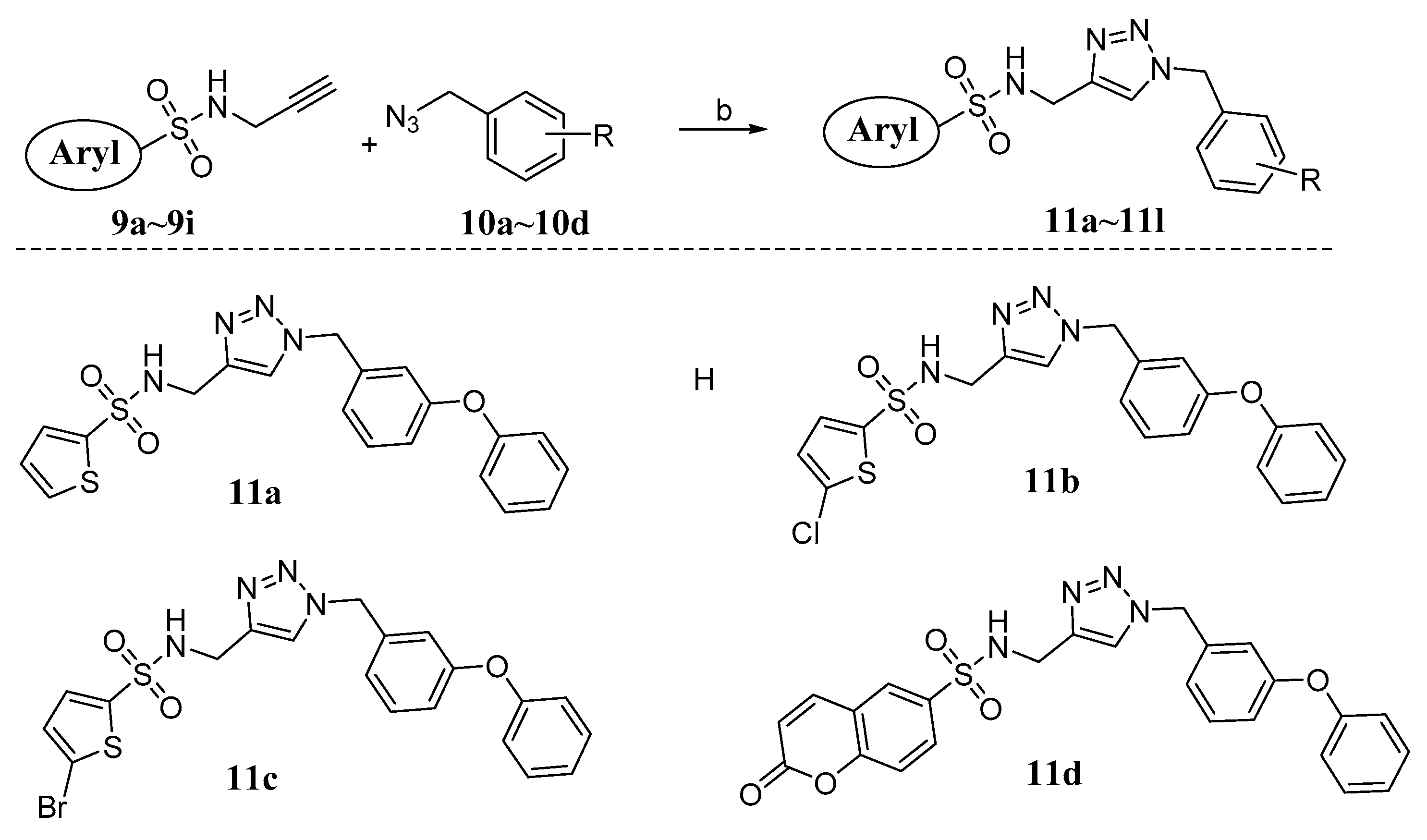
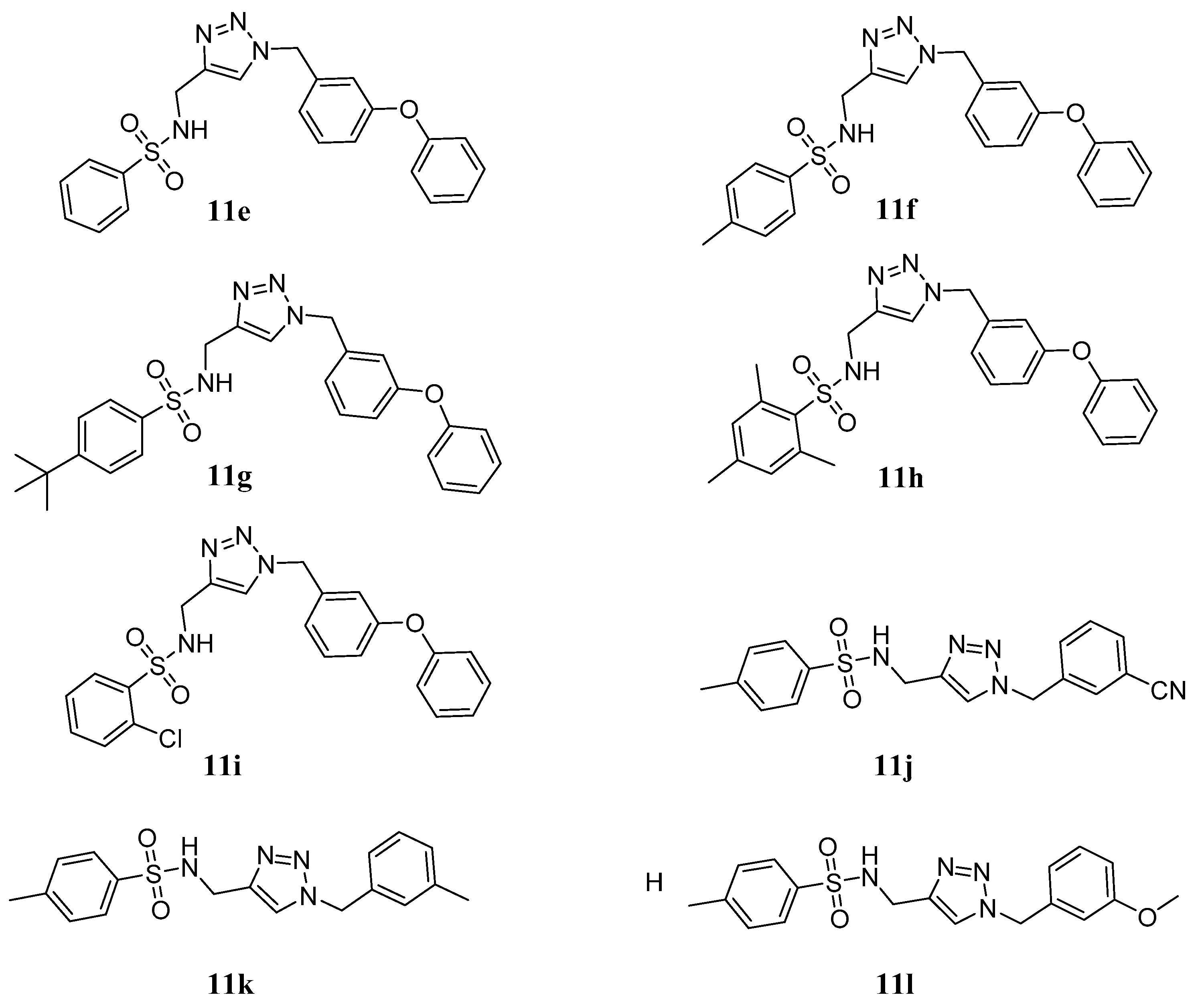
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 9a~i
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 11a~l
3.2. MTT Assay
3.3. In Vitro Tubulin Polymerization Inhibition Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA-4P | Combretastatin A-4P |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| 5-Fu | 5-Fluorouracil |
| CLog P | Lipo-hydro partition coefficient |
| SAR | Structure-activity relationship |
References
- Dong, M.; Liu, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhai, S.; Yan, B. Novel natural product- and privileged scaffold-based tubulin inhibitors targeting the colchicine binding site. Molecules 2016, 21, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.-T.; Liu, W.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Chen, B.-H.; Chuang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Lu, M.-J.; Chiou, S.-J.; Chou, C.-K.; et al. A 4-phenoxyphenol derivative exerts inhibitory effects on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through regulating autophagy and apoptosis accompanied by downregulating α-tubulin expression. Molecules 2017, 22, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohena, C.; Risinger, A.; Devambatla, R.; Dybdal-Hargreaves, N.; Kaul, R.; Choudhary, S.; Gangjee, A.; Mooberry, S. Janus compounds, 5-chloro-N4-methyl-N4-aryl-9H-pyrimido[4,5-b]indole-2,4-diamines, cause both microtubule depolymerizing and stabilizing effects. Molecules 2016, 21, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandić, B.; Simić, M.; Vučković, I.; Vujisić, L.; Novaković, M.; Trifunović, S.; Nikolić-Mandić, S.; Tešević, V.; Vajs, V.; Milosavljević, S. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids and fatty acids from the endemic plant species rindera umbellata and the effect of lindelofine-N-oxide on tubulin polymerization. Molecules 2013, 18, 10694–10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.L.; Teo, W.S.; McCarroll, J.A.; Kavallaris, M. An emerging role for tubulin isotypes in modulating cancer biology and chemotherapy resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sáez-Calvo, G.; Olieric, N.; de Asís Balaguer, F.; Barasoain, I.; Lamberth, C.; Díaz, J.; Steinmetz, M. Quinolin-6-yloxyacetamides are microtubule destabilizing agents that bind to the colchicine site of tubulin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, J.; Northcote, P.; Paterson, I.; Altmann, K.-H.; Díaz, J.; Miller, J. Zampanolide, a microtubule-stabilizing agent, is active in resistant cancer cells and inhibits cell migration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Zhou, S.; Lu, D.; Ji, L.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Meng, X. Synthesis, anti-cancer evaluation of benzenesulfonamide derivatives as potent tubulin-targeting agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 122, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacchiano, F.; Carta, F.; McDonald, P.C.; Lou, Y.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Dedhar, S.; Supuran, C.T. Ureido-substituted benzenesulfonamides potently inhibit carbonic anhydrase IX and show antimetastatic activity in a model of breast cancer metastasis. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilies, M.A.; Vullo, D.; Pastorek, J.; Scozzafava, A.; Ilies, M.; Caproiu, M.T.; Pastorekova, S.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Inhibition of Tumor-Associated Isozyme IX by Halogenosulfanilamide and Halogenophenylaminobenzolamide Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coxon, C.R.; Anscombe, E.; Harnor, S.J.; Martin, M.P.; Carbain, B.; Golding, B.T.; Hardcastle, I.R.; Harlow, L.K.; Korolchuk, S.; Matheson, C.J.; et al. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) inhibitors: Structure-activity relationships and insights into the CDK-2 selectivity of 6-substituted 2-arylaminopurines. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1746–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owa, T.; Yoshino, H.; Okauchi, T.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Sugi, N.H.; Nagasu, T.; Koyanagi, N.; Kitoh, K. Discovery of novel antitumor sulfonamides targeting G1 phase of the cell cycle. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 3789–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głowacka, I.; Andrei, G.; Schols, D.; Snoeck, R.; Piotrowska, D. Phosphonylated acyclic guanosine analogues with the 1,2,3-triazole linker. Molecules 2015, 20, 18789–18807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Yue, X.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Song, J.; Zhao, R.-H.; Li, F.; Sun, H.-H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; et al. Design, synthesis and antiproliferative activity studies of 1,2,3-triazole-chalcones. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solum, E.J.; Vik, A.; Hansen, T.V. Synthesis, cytotoxic effects and tubulin polymerization inhibition of 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole analogs of 2-methoxyestradiol. Steroids 2014, 87, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, P.; Murthy, T.R.; Rajkumar, K.; Srikanth, D.; Dayakar, C.; Kishor, C.; Addlagatta, A.; Kalivendi, S.V.; Raju, B.C. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of pyridinyl-1H-1,2,3-triazolyldihydroisoxazoles as potent inhibitors of tubulin polymerization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, H.C.; Sharpless, K.B. The growing impact of click chemistry on drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Fu, D.J.; Yue, X.X.; Liu, Y.C.; Song, J.; Sun, H.H.; Liu, H.M.; Zhang, Y.B. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel chalcone-1,2,3-triazole-azole derivates as antiproliferative agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasdev, R.; Preston, D.; Scottwell, S.; Brooks, H.; Crowley, J.; Schramm, M. Oxidatively locked [Co2L3]6+ cylinders derived from bis(bidentate) 2-pyridyl-1,2,3-triazole “click” ligands: Synthesis, stability, and antimicrobial studies. Molecules 2016, 21, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelriheem, N.; Mohamed, A.; Abdelhamid, A. Synthesis of some new 1,3,4-thiadiazole, thiazole and pyridine derivatives containing 1,2,3-triazole moiety. Molecules 2017, 22, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.J.; Li, Z.; Jian, S.; Mao, R.W.; Zhao, R.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Hou, Y.H.; Li, J.H.; Yang, J.J.; Jin, C.Y. Design and synthesis of formononetin-dithiocarbamate hybrids that inhibit growth and migration of PC-3cells via MAPK/Wnt signaling pathways. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 127, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Song, J.; Zhao, R.-H.; Mao, R.-W.; Liu, H.-M.; Zhang, Y.-B. Design, synthesis and antiproliferative evaluation of 3-aminopropyloxy derivatives of chalcone. J. Chem. Res. 2016, 40, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.-J.; Song, J.; Zhao, R.-H.; Li, F.; Sun, H.-H.; Liu, H.-M.; et al. Design, synthesis and antiproliferative activity studies of novel dithiocarbamate-chalcone derivates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3918–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.-J.; Song, J.; Zhao, R.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Liu, H.-M. Synthesis of novel antiproliferative 1,2,3-triazole hybrids using the molecular hybridisation approach. J. Chem. Res. 2016, 40, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonne, D.; Heuséle, C.; Simon, C.; Pantaloni, D. 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole, a fluorescent probe for tubulin and microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 2819–2825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelley, J.L.; Soroko, F.E. 9-(2-Fluorobenzyl)-6-(methylamino)-9H-purine hydrochloride. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity. J. Med. Chem. 1986, 29, 1133–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-H.; Yang, D.-X.; Geng, P.-F.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H.-M.; Hu, B.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.-H.; Guo, W.-G.; Zhao, B.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives possessing a hydrazone moiety as antiproliferative agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Geng, P.-F.; Ma, J.-L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, T.-Q.; Zhao, B.; Wei, H.-M.; Wang, C.; et al. Identification of thiazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives as potent antiproliferative agents through the drug repurposing strategy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 135, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosios, K.; Holwell, S.E.; McGown, A.T.; Pettit, G.R.; Bibby, M.C. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of combretastatin A-4 and its sodium phosphate prodrug. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, T.F.; Wang, S.; Greene, L.M.; Nathwani, S.M.; Pollock, J.K.; Malebari, A.M.; McCabe, T.; Twamley, B.; O’Boyle, N.M.; Zisterer, D.M.; et al. Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of 3-phenoxy-1,4-diarylazetidin-2-ones as tubulin-targeting antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 90–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustin, G.J.; Galbraith, S.M.; Anderson, H.; Stratford, M.; Folkes, L.K.; Sena, L.; Gumbrell, L.; Price, P.M. Phase I clinical trial of weekly combretastatin A4 phosphate: Clinical and pharmacokinetic results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2815–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |



| Compound | IC50 (μM) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MGC-803 | MCF-7 | PC-3 | |
| 9a | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9d | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9f | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 11a | 17.0 ± 1.8 | 78.5 ± 2.2 | 24.6 ± 0.9 |
| 11b | 15.3 ± 0.8 | 49.9 ± 1.2 | 19.8 ± 0.6 |
| 11c | 31.0 ± 2.2 | 34.7 ± 2.6 | 49.4 ± 1.0 |
| 11d | 88.8 ± 0.5 | 36.4 ± 2.0 | 34.1 ± 0.3 |
| 11e | 21.7 ± 0.1 | 39.6 ± 5.0 | 6.4 ± 1.2 |
| 11f | 13.7 ± 2.9 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 4.1 ± 1.4 |
| 11g | >100 | 54.9 ± 1.7 | 7.1 ± 0.5 |
| 11h | 18.4 ± 0.7 | 24.6 ± 1.6 | 24.7 ± 3.0 |
| 11i | 15.3 ± 0.5 | 77.5 ± 0.7 | 22.7 ± 0.5 |
| 11j | 41.3 ± 2.3 | >100 | >100 |
| 11k | 75.8 ± 0.6 | >100 | >100 |
| 11l | 77.2 ± 7.8 | >100 | >100 |
| 5-Fu | 15.6 ± 0.4 | 21.2 ± 3.6 | 13.9 ± 1.5 |
| CA-4P | 0.027 ± 0.003 | 0.039 ± 0.005 | nd b |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, D.-J.; Liu, J.-F.; Zhao, R.-H.; Li, J.-H.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-B. Design and Antiproliferative Evaluation of Novel Sulfanilamide Derivatives as Potential Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors. Molecules 2017, 22, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091470
Fu D-J, Liu J-F, Zhao R-H, Li J-H, Zhang S-Y, Zhang Y-B. Design and Antiproliferative Evaluation of Novel Sulfanilamide Derivatives as Potential Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors. Molecules. 2017; 22(9):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091470
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Dong-Jun, Ji-Feng Liu, Ruo-Han Zhao, Jia-Huan Li, Sai-Yang Zhang, and Yan-Bing Zhang. 2017. "Design and Antiproliferative Evaluation of Novel Sulfanilamide Derivatives as Potential Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors" Molecules 22, no. 9: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091470
APA StyleFu, D.-J., Liu, J.-F., Zhao, R.-H., Li, J.-H., Zhang, S.-Y., & Zhang, Y.-B. (2017). Design and Antiproliferative Evaluation of Novel Sulfanilamide Derivatives as Potential Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors. Molecules, 22(9), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091470