3D-QSAR Studies on Thiazolidin-4-one S1P1 Receptor Agonists by CoMFA and CoMSIA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. CoMFA Analysis
2.2. CoMSIA Analysis
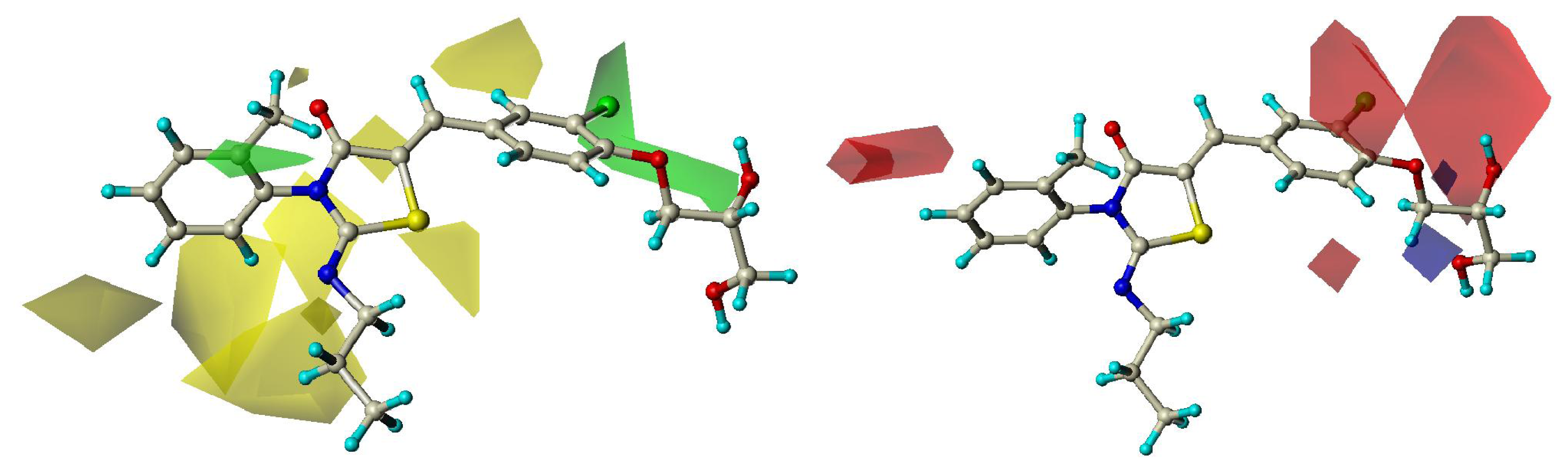
2.3. CoMFA Contour Maps
2.4. CoMSIA Contour Maps
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Set
3.2. Molecular Alignment
3.3. Partial Least Squares (PLS) Analysis
3.4. CoMFA Studies
3.5. CoMSIA Studies
3.6. Sensitivity of a PLS Model
3.7. Predictive Correlation Coefficient
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Gardell, SE; Dubi, AE; Chun, J. Emerging medicinal roles for lysophospholipid signaling. Trends Mol. Med 2006, 12, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, I; Fukushima, N; Ye, X; Chun, J. Lysophospholipid receptors: Signaling and biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2004, 73, 321–354. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J; Goetzl, EJ; Hla, T; Igarashi, Y; Lynch, KR; Moolenaar, W; Pyne, S; Tigyi, G. International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIV. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol. Rev 2002, 54, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, H; Gonzalez-Cabrera, PJ; Sanna, MG; Brown, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor Signaling. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2009, 78, 743–768. [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel, S; Milstien, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: An Enigmatic signalling lipid. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2003, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Kihara, A; Mitsutake, S; Mizutani, Y; Igarashi, Y. Metabolism and biological functions of two phosphorylated sphingolipids, sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide 1-phosphate. Prog. Lipid Res 2007, 46, 126–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hait, NC; Oskeritzian, CA; Paugh, SW; Milstien, S; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinases, sphingosine 1-phosphate, apoptosis and diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 2016–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Boli, MH; Abele, S; Binkert, C; Bravo, R; Buchmann, S; Bur, D; Gatfield, J; Hess, P; Kohl, C; Mangold, C; et al. 2-Imino-thiazolidin-4-one Derivatives as Potent, Orally Active S1P1 Receptor Agonists. J. Med. Chem 2010, 53, 4198–4211. [Google Scholar]
- Matloubian, M; Lo, CG; Cinamon, G; Lesneski, MJ; Xu, Y; Brinkmann, V; Allende, ML; Prola, RL; Cyster, JG. Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature 2004, 427, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, JJ; Neway, W; Mills, SG; Hajdu, R; Keohane, CA; Rosenbach, M; Milligan, J; Shei, GJ; Chrebet, G; Bergstrom, J; et al. Potent S1P receptor agonists replicate the pharmacologic actions of the novel immune modulator FTY720. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2004, 14, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar]
- Allende, ML; Dreier, JL; Mandala, S; Proia, RL. Expression of the sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor, S1P1, on T-cells controls thymic emigration. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 15396–15401. [Google Scholar]
- Forrest, M; Sun, SY; Hajdu, R; Bergstrom, J; Card, D; Doherty, G; Hale, J; Keohane, C; Meyers, C; Milligan, J; et al. Immune cell regulation and cardiovascular effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists in rodents are mediated via distinct receptor subtypes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 2004, 309, 758–768. [Google Scholar]
- Himmel, HM; Heringdorf, DMZ; Graf, E; Dobrev, D; Kortner, A; Schüler, S; Jakobs, KH; Ravens, U. Evidence for Edg-3 receptor-mediated activation of IK.ACh by sphingosine-1-phosphate in human atrial cardiomyocytes. Mol. Pharmacol 2000, 58, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Koyrakh, L; Roman, MI; Brinkmann, V; Wickman, K. The heart rate decrease caused by acute FTY720 administration is mediated by the G protein-gated potassium channel IKACh. Am. J. Transplant 2005, 5, 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Sanna, MG; Liao, J; Jo, E; Alfonso, C; Ahn, MY; Peterson, MS; Webb, B; Lefebvre, S; Chun, J; Gray, N; Rosen, H. Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor subtypes S1P1 and S1P3, respectively, regulate lymphocyte recircuculation and heart rate. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 13839–13848. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, C; Smith, N; Engle, R; Wood, H. Quantitative structure-activity relationships of antineoplastic drugs: nitrosoureas and triazenoimidazoles. Cancer Chemother. Rep 1972, 56, 443–456. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z; Sun, P. 3D-QSAR study of potent inhibitors of phosphodiesterase-4 using a CoMFA Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2007, 8, 714–722. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, V; Prabhakar, YS; Katti, SB. CoMFA and CoMSIA studies on thiazolidin-4-one as anti-HIV agents. J. Mol. Graph. Model 2009, 27, 735–743. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, V; Mourya, VK; Agrawal, RK. Prediction of anti-HIV activity of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones: QSAR approach. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct 2008, 3, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, RD, III; Patterson, DE; Bunce, JD. Comparative Molecular Field Analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of Shape on Binding of Steroids to Carrier Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1988, 110, 5959–5967. [Google Scholar]
- Klebe, G; Abraham, U; Mietzner, T. Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J. Med. Chem 1994, 37, 4130–4146. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, RD, III; Patterson, DE; Bunce, JD. Recent advances in comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). Prog. Clin. Biol. Res 1989, 291, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, F; Geladi, P; Rännar, S; Wold, S. Interactive variable selection (IVS) for PLS. Part 1: Theory and algorithms. J. Chemom 1994, 8, 349–363. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, SJ; Tropsha, A. Cross-validated R2-guided region selection for comparative molecular field analysis: a simple method to achieve consistent results. J. Med. Chem 1995, 38, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, MC; Cramer, RD, III; Van Opdenbosch, N. Validation of general purpose Tripos 5.2 force fields. J. Comput. Chem 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, RD, III; Clark, M; Simeroth, P; Patterson, DE. Recent developments in comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). Pharmacochem. Libr 1991, 16, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, BL; Nachbar, RBJ. Sample-distance partial least squares: PLS optimized for many variables, with application to CoMFA. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 1993, 7, 587–619. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M; Cramer, RD, III; Jones, DM; Patterson, DE; Simeroth, PE. Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 2. Toward its use with 3D-structural databases. Tetrahed. Comput. Methodol 1990, 3, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Klebe, G; Abraham, U. Comparative molecular similarity index analysis (CoMSIA) to study hydrogen bonding properties and to score combinatorial libraries. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 1999, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M; Cramer, RD, III. The probability of chance correlation using partial least squares (PLS). Quant. Struct. Act. Relat 1993, 12, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, V; Gupta, SP; Siddiqi, MI; Mishra, BN. 3D-QSAR studies on quinazoline antifolate thymidylate synthase inhibitors by CoMFA and CoMSIA models. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2010, 45, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Woodard, B; Saleh, MA. Three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationships of quorum-sensing and biofilm inhibitors in gram-negative bacteria. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2008, 43, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J; Wu, Z; Dai, M; Xu, Z; Li, X; Zhu, S; Lin, C; Hu, P; Zhang, L; Huang, H; et al. Quantitative structure activity relationship studies on a novel indolediones as long chain fatty acid elongase (ELOVL6) inhibitors. Lett. Drug Des. Discov 2011, 8, 422–429. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, RD; Sprous, DG; Leonard, JM. Validating Models Based on Large Data Sets. In Rational Approaches to Drug Design; Höltje, HD, Sippl, W, Eds.; Prous Science: Barcelona, Spain, 2001; pp. 475–485. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, RD; Fox, PC. Statistical variation in scrambling. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 2004, 18, 563–576. [Google Scholar]
- Luco, JM; Ferretti, FH. QSAR based on multiple linear regression and PLS methods for the anti-HIV activity of a large group of HEPT derivatives. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci 1997, 37, 392–401. [Google Scholar]
- Hevener, KE; Ball, DM; Buolamwini, JK; Lee, RE. Quantitative structure-activity relationship studie on nitrofuranyl anti-tubercular agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2008, 16, 8042–8053. [Google Scholar]
- Golbraikh, A; Tropsha, A. Beware of q2. J. Mol. Graph. Model 2002, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar]





| CoMFA | CoMSIA (Model 6) | |
|---|---|---|
| PLS statistics | ||
| LOO cross q2/SEP | 0.751/0.320 | 0.739/0.328 |
| Group cross q2/SEP | 0.744/0.325 | 0.740/0.332 |
| Non-validated r2/SEE | 0.973/0.106 | 0.923/0.178 |
| F | 250.674 | 84.398 |
| r2bootstrap | 0.985 ± 0.006 | 0.973 ± 0.007 |
| Sbootstrap | 0.074 ± 0.041 | 0.115 ± 0.064 |
| Optimal components | 5 | 5 |
| Field distribution% | ||
| Steric | 54.5 | 12.5 |
| Electrostatic | 45.5 | 29.0 |
| Hydrophobic | 30.3 | |
| H-bond donate | 28.2 | |
| r2 pred | 0.904 | 0.730 |
| Components | Q2 | cSDEP | dq2/dr2 yy′ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.403 | 0.531 | 1.391 |
| 4 | 0.350 | 0.585 | 1.230 |
| 5 | 0.540 | 0.542 | 1.021 |
| 6 | 0.393 | 0.517 | 1.427 |
| 7 | 0.433 | 0.583 | 1.391 |
| Model | Descriptors | LOO cross q2/SEP | Group cross q2/SEP | Bootstrap r2 | Bootstrapped SEE | Non-validated r2/SEE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S and E | 0.630/0.396 | 0.608/0.408 | 0.953 ± 0.011 | 0.129 ± 0.070 | 0.945/0.153 |
| 2 | S, E and H | 0.735/0.310 | 0.723/0.324 | 0.873 ± 0.036 | 0.213 ± 0.127 | 0.871/0.221 |
| 3 | S, E and A | 0.637/0.386 | 0.654/0.377 | 0.942 ± 0.017 | 0.152 ± 0.084 | 0.921/0.181 |
| 4 | S, E and D | 0.695/0.359 | 0.692/0.361 | 0.952 ± 0.020 | 0.143 ± 0.090 | 0.929/0.173 |
| 5 | S, E, D and A | 0.657/0.381 | 0.658/0.381 | 0.930 ± 0.021 | 0.175 ± 0.088 | 0.918/0.187 |
| 6 | S, E, D and H | 0.739/0.328 | 0.740/0.332 | 0.973 ± 0.007 | 0.115 ± 0.064 | 0.923/0.178 |
| 7 | S, E, A and H | 0.726/0.334 | 0.731/0.334 | 0.960 ± 0.011 | 0.139 ± 0.070 | 0.920/0.185 |
| 8 | S, E, D, A and H | 0.719/0.340 | 0.709/0.351 | 0.953 ± 0.018 | 0.142 ± 0.077 | 0.910/0.192 |
| No | O | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | Exp. | CoMFA | CoMSIA | |||
| Pred. | Res. | Pred. | Res. | |||||||
| 1 | dimethyl-mino | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.208 | 7.188 | 0.020 | 7.129 | 0.079 |
| 2 * | methyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.005 | 6.260 | −0.255 | 6.280 | −0.275 |
| 3 | ethyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.730 | 6.884 | −0.154 | 6.921 | −0.191 |
| 4 | n-propyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.174 | 7.149 | 0.025 | 7.107 | 0.067 |
| 5 | n-butyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.951 | 7.097 | −0.146 | 7.143 | −0.192 |
| 6 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.328 | 7.078 | 0.250 | 7.267 | 0.061 |
| 7 | sec-butyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.992 | 6.900 | 0.092 | 6.951 | 0.041 |
| 8 | tert-butyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.833 | 6.887 | −0.054 | 6.939 | −0.106 |
| 9 | cyclopropyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.987 | 6.921 | 0.066 | 6.998 | −0.011 |
| 10 | cyclobutyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.695 | 6.558 | 0.137 | 6.601 | 0.094 |
| 11 | cyclopentyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.460 | 6.548 | −0.088 | 6.564 | −0.104 |
| 12 * | cyclohexyl | phenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.234 | 6.265 | −0.031 | 6.260 | −0.026 |
| 13 * | isopropyl | isopropyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.237 | 6.865 | 0.372 | 6.890 | 0.347 |
| 14 | isopropyl | n-hexyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.550 | 6.555 | −0.005 | 6.495 | 0.010 |
| 15 * | isopropyl | cyclohexyl | H | Cl | OH | 8.000 | 7.624 | 0.376 | 7.610 | 0.390 |
| 16 * | isopropyl | ethoxycarbonylethyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.320 | 6.405 | −0.085 | 6.346 | −0.026 |
| 17 * | isopropyl | allyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.259 | 7.185 | 0.074 | 7.177 | 0.082 |
| 18 | isopropyl | 2-methylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.468 | 7.232 | 0.236 | 7.089 | 0.379 |
| 19 | isopropyl | 3-methylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.959 | 6.947 | 0.012 | 6.997 | −0.038 |
| 20 | isopropyl | 4-methylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.108 | 7.021 | 0.087 | 7.025 | 0.083 |
| 21 | isopropyl | 2,6-dimethylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.813 | 6.929 | −0.116 | 6.987 | −0.174 |
| 22 | isopropyl | 2,3-dimethylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.143 | 7.321 | −0.178 | 7.163 | −0.020 |
| 23 * | isopropyl | 2,4-dimethylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.747 | 7.394 | −0.647 | 7.202 | −0.455 |
| 24 | isopropyl | 2-ethylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.907 | 7.045 | −0.138 | 7.226 | −0.319 |
| 25 | isopropyl | 2-chlorophenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.268 | 7.178 | 0.090 | 7.218 | 0.050 |
| 26 | isopropyl | 3-chlorophenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.456 | 7.377 | 0.079 | 7.376 | 0.080 |
| 27 | isopropyl | 3-chloro-2-methylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.509 | 7.399 | 0.110 | 7.472 | 0.037 |
| 28 | isopropyl | 3-chloro-4-methylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.328 | 7.448 | −0.120 | 7.481 | −0.153 |
| 29 | isopropyl | 2-methoxylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.975 | 6.933 | 0.042 | 7.019 | −0.044 |
| 30* | isopropyl | 3-methoxylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.587 | 7.015 | −0.428 | 6.839 | −0.252 |
| 31 | isopropyl | 4-methoxylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.600 | 6.574 | 0.026 | 6.707 | −0.107 |
| 32 * | isopropyl | 2,4-dimethoxyphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.058 | 6.182 | −0.124 | 6.321 | −0.263 |
| 33 * | isopropyl | 3-pyridyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.449 | 6.613 | −0.164 | 6.623 | −0.174 |
| 34 | isopropyl | benzyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.201 | 6.268 | −0.067 | 6.195 | 0.006 |
| 35 | isopropyl | phenethyl | H | Cl | OH | 6.034 | 6.077 | −0.043 | 6.013 | 0.021 |
| 36 * | isopropyl | 4-phenylbutyl | H | Cl | OH | 5.741 | 5.952 | −0.211 | 6.053 | −0.312 |
| 37 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | H | 5.908 | 5.726 | 0.182 | 5.753 | 0.155 |
| 38 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | OH | 6.914 | 6.653 | 0.261 | 6.794 | 0.120 |
| 39 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | F | OH | 6.648 | 6.719 | −0.071 | 6.726 | −0.078 |
| 40 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | CH3 | OH | 7.432 | 7.674 | −0.242 | 6.928 | −0.496 |
| 41 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | OCH3 | OH | 6.699 | 6.654 | 0.045 | 6.597 | 0.102 |
| 42 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | OCH3 | 6.697 | 6.696 | 0.001 | 6.731 | −0.034 |
| 43 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | 6.650 | 6.739 | −0.089 | 6.695 | −0.045 |
| 44 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | NH(CH3)2 | 6.830 | 6.914 | −0.084 | 6.669 | 0.161 |
| 45 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | Br | 5.984 | 6.112 | −0.128 | 5.829 | 0.155 |
| 46 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | OCH3 | H | 6.733 | 6.521 | 0.212 | 6.299 | 0.434 |
| 47 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | OH | H | 6.124 | 6.008 | 0.116 | 6.087 | 0.037 |
| 48 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | OH | OCH3 | 6.353 | 6.283 | 0.070 | 6.471 | −0.118 |
| 49 | isopropyl | phenyl | CH3 | H | H | 5.190 | 5.196 | −0.006 | 5.609 | −0.419 |
| 50 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | CH2OH | 6.389 | 6.433 | −0.044 | 6.233 | 0.156 |
| 51 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | (CH2)2OH | 6.991 | 6.572 | 0.419 | 6.431 | 0.560 |
| 52 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | (CH2)3OH | 7.009 | 6.848 | 0.162 | 6.975 | 0.034 |
| 53 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | O(CH2)2OH | 7.022 | 7.031 | −0.009 | 6.905 | 0.117 |
| 54 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | O(CH2)3 OH | 7.237 | 6.979 | 0.258 | 6.859 | 0.378 |
| 55 * | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | OCH (CH2OH)2 | 5.064 | 5.607 | −0.543 | 5.438 | −0.374 |
| 56 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | O(CH2)2OH | H | 5.850 | 5.762 | 0.088 | 5.815 | 0.035 |
| 57 | isopropyl | phenyl | H | H | O(CH2)3N (CH3)2 | 6.465 | 6.512 | −0.047 | 6.535 | −0.070 |
| 58 | n-propyl | 2-methylphenyl | H | Cl | OH | 7.721 | 7.538 | 0.183 | 7.279 | 0.442 |
| 59 | n-propyl | 2-methylphenyl | H | Cl | O(CH2)2 OH | 7.959 | 7.933 | 0.026 | 8.154 | −0.195 |
| 60 | isopropyl | 2-methylphenyl | H | Cl | (R)-OCH2 CH(CH3) CH2OH | 8.041 | 8.026 | 0.015 | 8.031 | 0.010 |
| 61 | isopropyl | 2-methylphenyl | H | Cl | (S)-OCH2 CH(CH3) CH2OH | 8.013 | 8.061 | −0.048 | 7.907 | 0.106 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, C.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, G.; Guo, J.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Chao, W.; Rao, L.; Sun, P. 3D-QSAR Studies on Thiazolidin-4-one S1P1 Receptor Agonists by CoMFA and CoMSIA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6502-6516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106502
Qian C, Zheng J, Xiao G, Guo J, Yang Z, Huang L, Chao W, Rao L, Sun P. 3D-QSAR Studies on Thiazolidin-4-one S1P1 Receptor Agonists by CoMFA and CoMSIA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(10):6502-6516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106502
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Chuiwen, Junxia Zheng, Gaokeng Xiao, Jialiang Guo, Zhaoqi Yang, Li Huang, Wei Chao, Longyi Rao, and Pinghua Sun. 2011. "3D-QSAR Studies on Thiazolidin-4-one S1P1 Receptor Agonists by CoMFA and CoMSIA" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 10: 6502-6516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106502
APA StyleQian, C., Zheng, J., Xiao, G., Guo, J., Yang, Z., Huang, L., Chao, W., Rao, L., & Sun, P. (2011). 3D-QSAR Studies on Thiazolidin-4-one S1P1 Receptor Agonists by CoMFA and CoMSIA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(10), 6502-6516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106502




