Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba Attenuate CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury: An Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) Based Metabolomic Approach for the Pharmacodynamic Study of Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hepatoprotective Effect of RPA and RPR against CCl4-Induced Injury
2.2. Multivariate Analysis
2.3. Identification of Potential Biomarkers
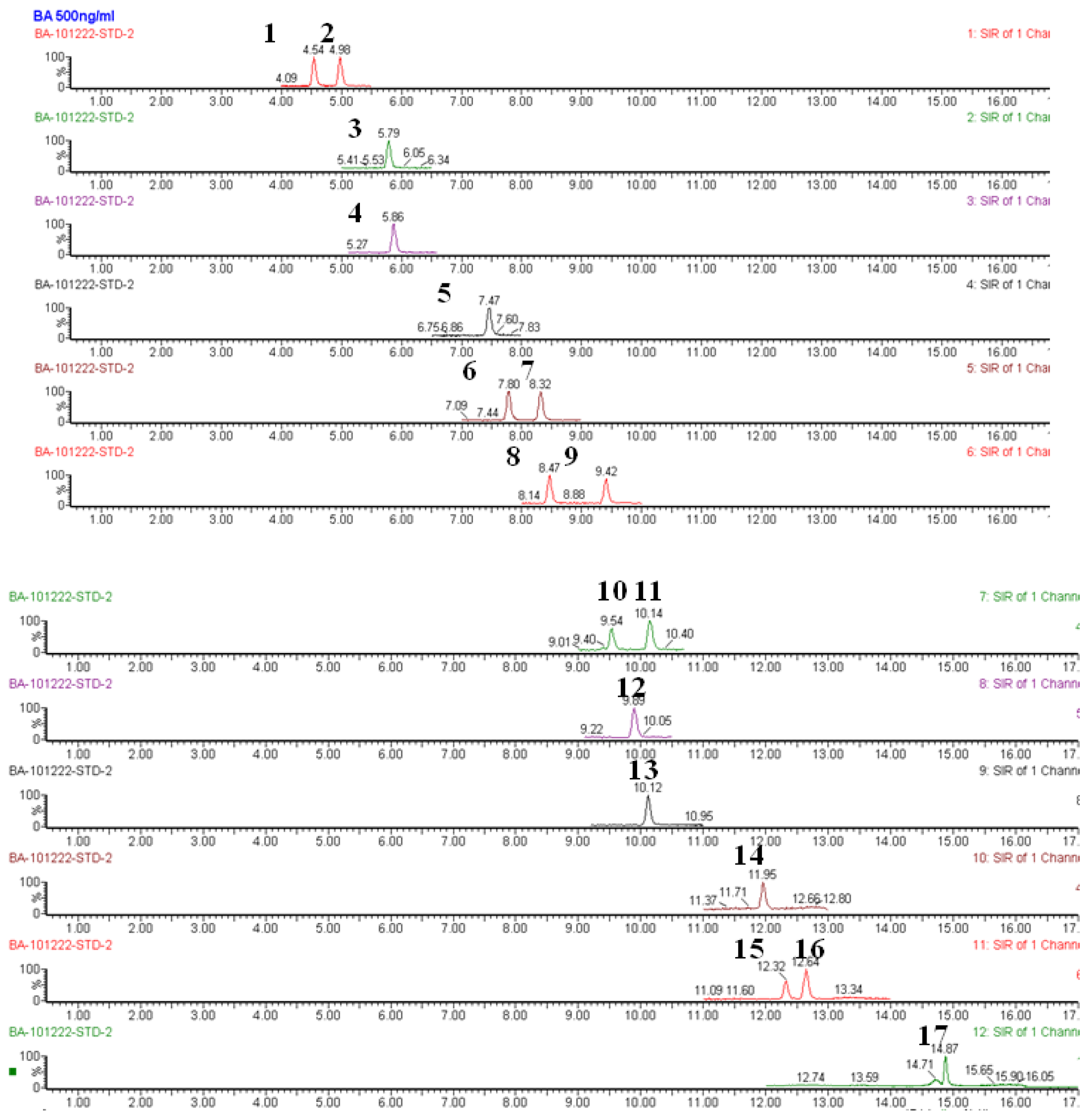
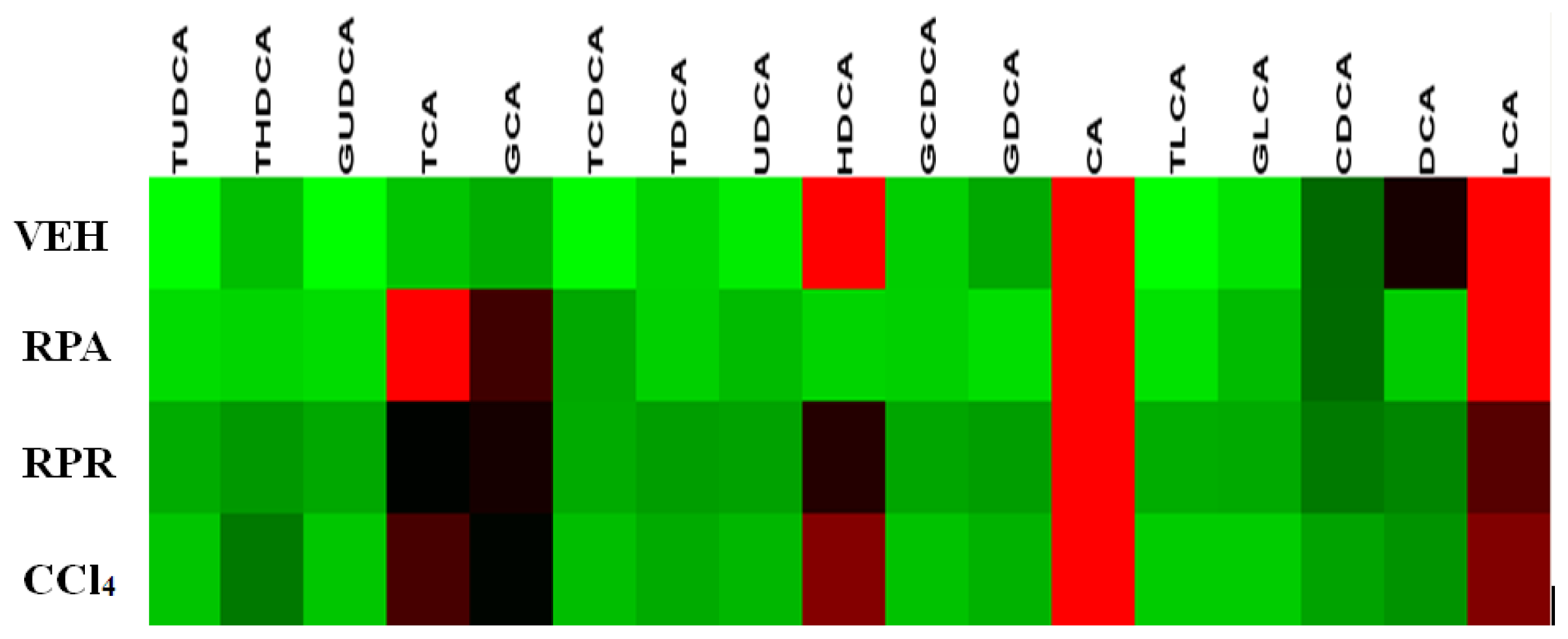
2.4. Bile Acid Profiling Analysis
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Animal Experiments
3.3. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
3.4. Assay of Serum Aminotransferase Activities
3.5. Metabolomic Fingerprinting Analysis
3.6. Metabolomic Profiling Analysis of Bile Acids
3.7. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Appendix
| Bile acid | ALT | AST | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | |
| CA | 0.385 * | 0.029 | 0.395 * | 0.025 |
| DCA | 0.095 | 0.605 | 0.093 | 0.614 |
| CDCA | 0.032 | 0.862 | −0.042 | 0.820 |
| UDCA | 0.408 * | 0.021 | 0.414 * | 0.019 |
| HDCA | 0.408 * | 0.020 | 0.393 * | 0.026 |
| LCA | 0.271 | 0.134 | 0.255 | 0.160 |
| GCA | 0.300 | 0.095 | 0.333 | 0.062 |
| GDCA | 0.145 | 0.428 | 0.108 | 0.558 |
| GCDCA | 0.129 | 0.480 | 0.149 | 0.416 |
| GUDCA | 0.218 | 0.230 | 0.242 | 0.182 |
| GLCA | −0.095 | 0.604 | −0.099 | 0.591 |
| TCA | 0.542 ** | 0.001 | 0.578 ** | 0.001 |
| TDCA | 0.393 * | 0.026 | 0.419 * | 0.017 |
| TCDCA | 0.456 ** | 0.009 | 0.514 ** | 0.003 |
| TUDCA | 0.654 ** | 0.000 | 0.643 ** | 0.000 |
| THDCA | 0.588 ** | 0.000 | 0.611 ** | 0.000 |
| TLCA | −0.156 | 0.395 | −0.169 | 0.356 |
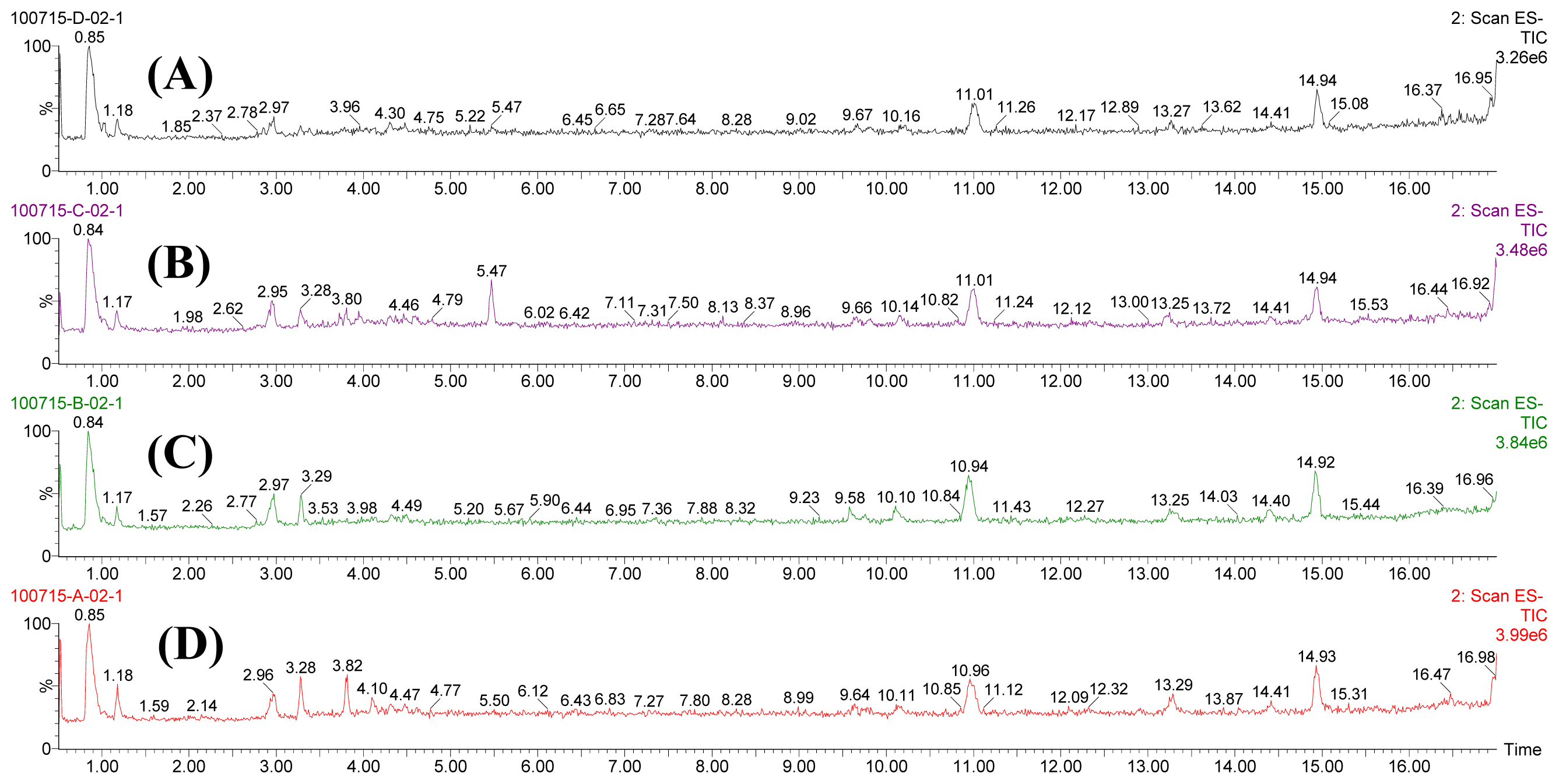
References
- Feng, C.; Liu, M.; Shi, X.W. Pharmacokinetic properties of paeoniflorin, albiflorin and oxypaeoniflorin after oral gavage of extracts of Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol 2010, 130, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.H.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.G. Metabolomics: Towards understanding traditional Chinese medicine. Planta Med 2010, 76, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Wilson, I.D. Understanding ‘global’ systems biology: Metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nat. Rev 2003, 2, 668–676. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K. Global systems biology, personalized medicine and molecular epidemiology. Mol. Syst. Biol 2006, 2, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lao, Y.M.; Jiang, J.G.; Yan, L. Application of metabonomic analytical techniques in the modernization and toxicology research of traditional Chinese medicine. Brit. J. Pharmacol 2009, 157, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabonomics techniques and applications to pharmaceutical research & development. Pharm. Res 2006, 23, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeckx, K.; Bijlsmac, S.; Jespersend, S. Characterization of anti-inflammatory compounds using transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics in combination with multivariate data analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol 2004, 4, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.M.; Liu, F.; Dong, P.L.; Cheng, C.P.; Liu, C.F. Study the relationship between drug property of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs and property-effect based on metabonomics of the ouerall characterization. J. Yunnan Univ. TCM 2009, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Committee of the Pharmacopoeia of China, Pharmacopoeia of PR China, Part I; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- Jiang, Y.P.; Liu, Y.G.; Chen, H.C. Effect of aqueous extract of Radix Paeoniae Rubra against Carbon Tetrachloride induced liver fibrosis in rat. Herald Med 2004, 23, 527–529. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xiong, A.Z.; He, Y.Q. Bile acids metabonomic study on the CCl4− and α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced animal models: Quantitative analysis of 22 bile acids by ultraperformance liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol 2008, 21, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, L.W.; Boll, M.; Stampfl, A. Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: Carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit. Rev. Toxicol 2003, 33, 105–136. [Google Scholar]
- Recknagel, R.O.; Glende, E.A., Jr; Dolak, J.A. Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol. Ther. 1989, 43, 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, T.L. An optimized procedure for metabonomic analysis of rat liver tissue using gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed 2010, 52, 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Shao, L.; Gong, Y. A metabonomic characterization of CCl4-induced acute liver failure using partial least square regression based on the GC/MS metabolic profiles of plasma in mice. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 870, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Si, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C. An integrated metabonomic method for profiling of metabolic changes in carbon tetrachloride induced rat urine. Toxicology 2009, 256, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Sjostrom, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometr. Intel. Lab 2010, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, F.; Motsinger-Rrif, A.A.; Hoskins, J.M. Methylentetrahydrofolate reductase genetic polymorphisms and toxicity to 5-FU-based chemoradiation in rectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Goppelt-Struebe, M.; Hahn, A.; Stroebel, M. Independent regulation of cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression by p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinases and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase. Biochem. J 1999, 339, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Houten, S.M.; Watanabe, M.; Auwerx, J. Endocrine functions of bile acids. EMBO J 2006, 25, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Christiane, P.M.; Meier, P.J. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. J. Clin. Gastroenterol 2005, 39, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA; p. 1996.
 CCl4 group).
CCl4 group).
 CCl4 group).
CCl4 group).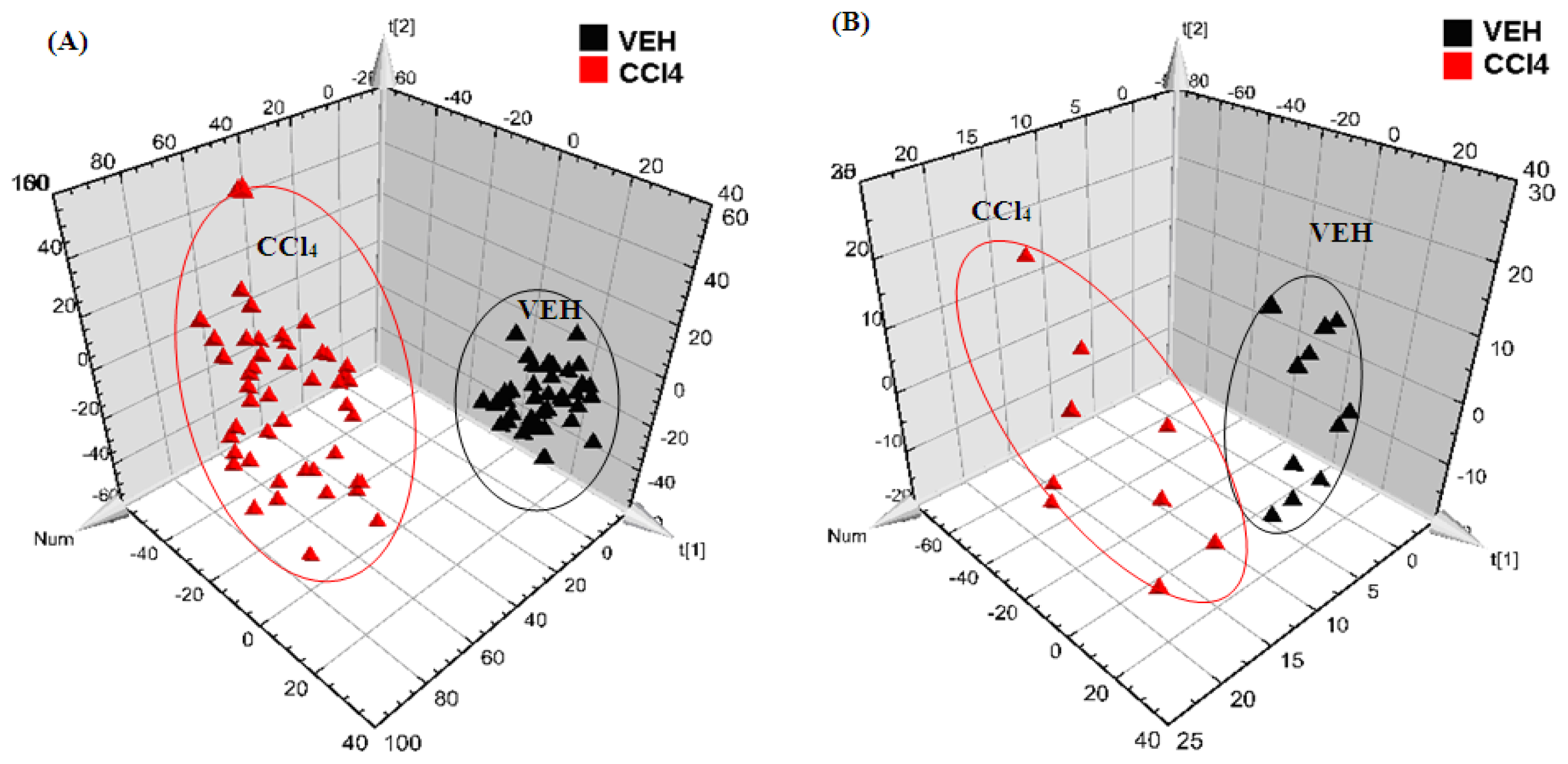
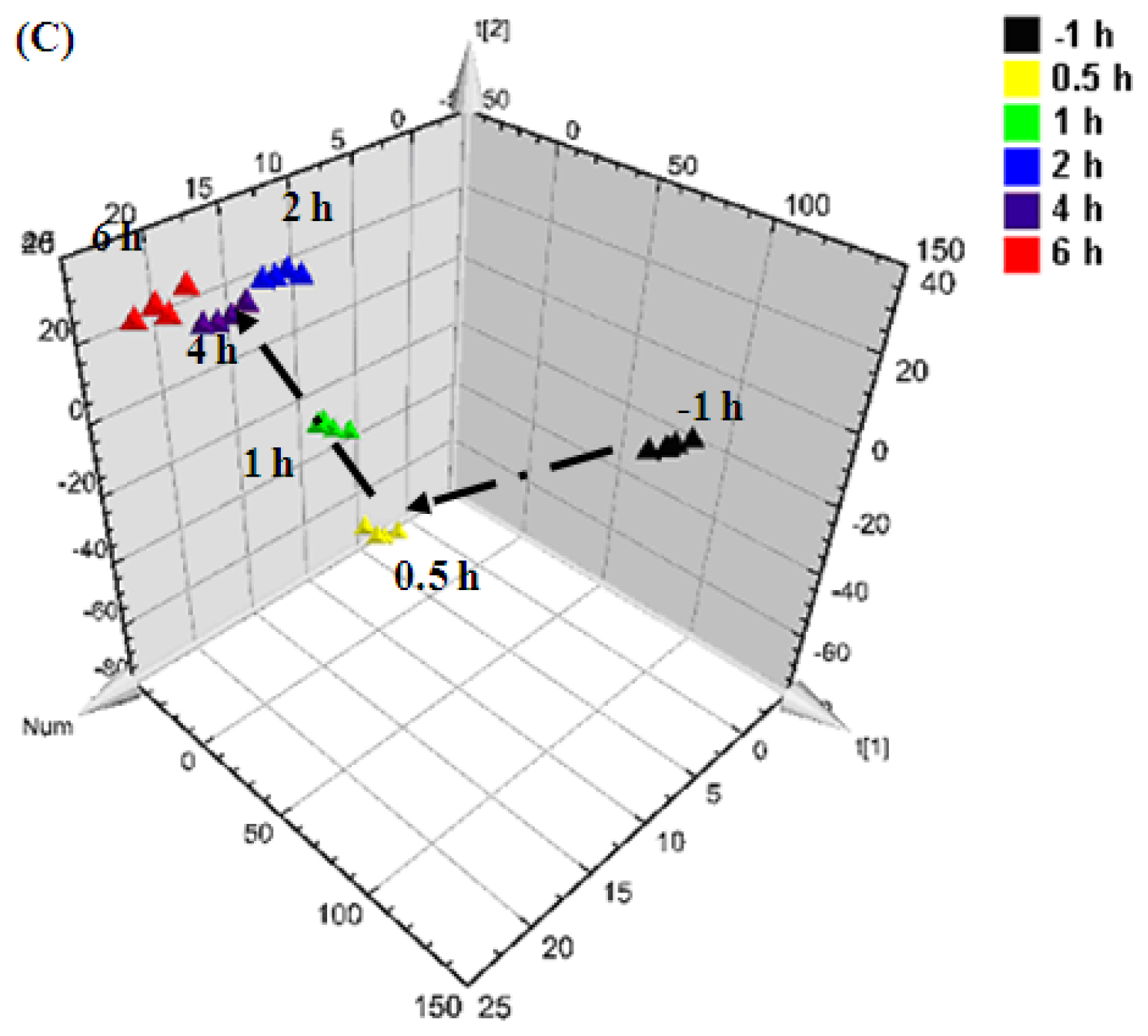
 0.5 h after injection,
0.5 h after injection,
 1 h after injection,
1 h after injection,
 2 h after injection,
2 h after injection,
 4 h after injection, and
4 h after injection, and
 6 h after injection).
6 h after injection).
 0.5 h after injection,
0.5 h after injection,
 1 h after injection,
1 h after injection,
 2 h after injection,
2 h after injection,
 4 h after injection, and
4 h after injection, and
 6 h after injection).
6 h after injection).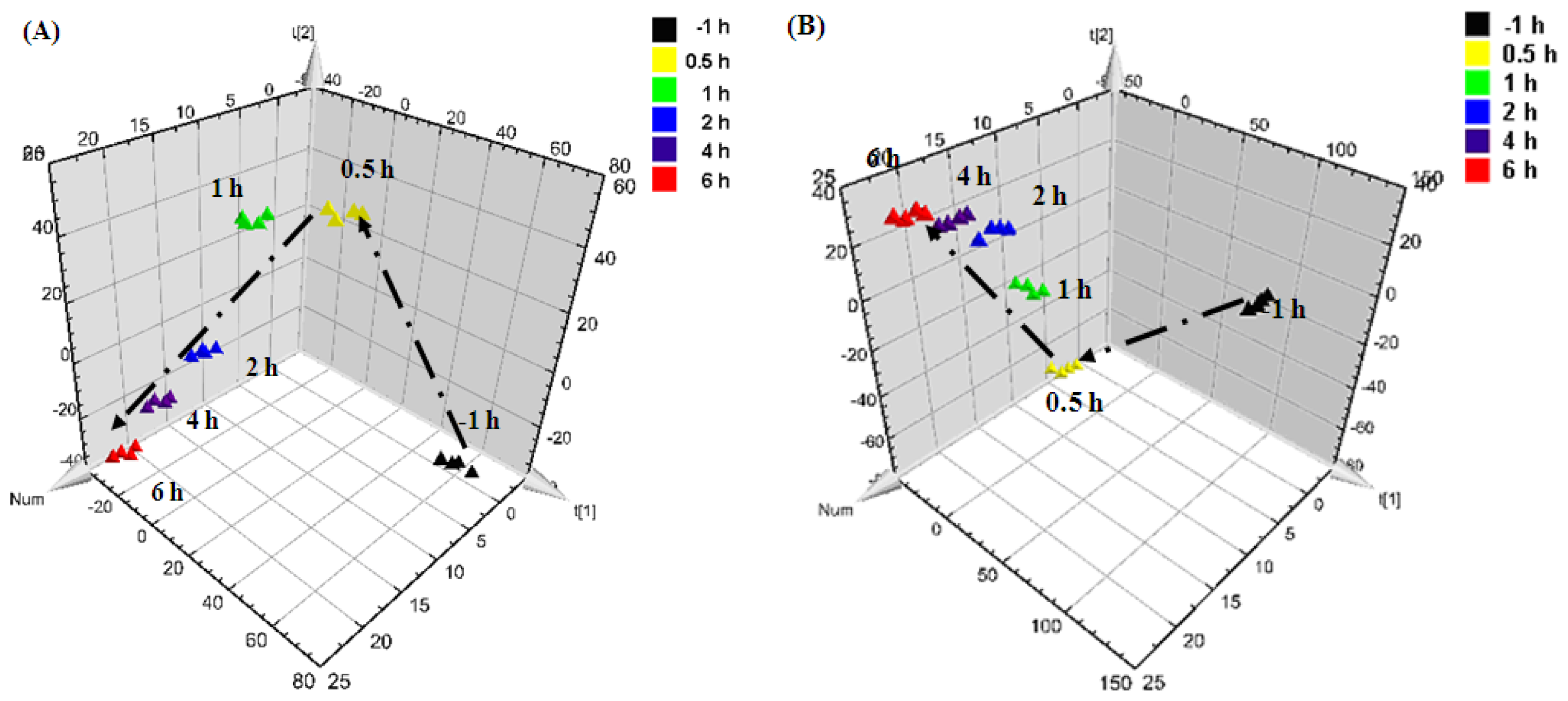
 RPA group,
RPA group,
 RPR group,
RPR group,
 CCl4 group).
CCl4 group).
 RPA group,
RPA group,
 RPR group,
RPR group,
 CCl4 group).
CCl4 group).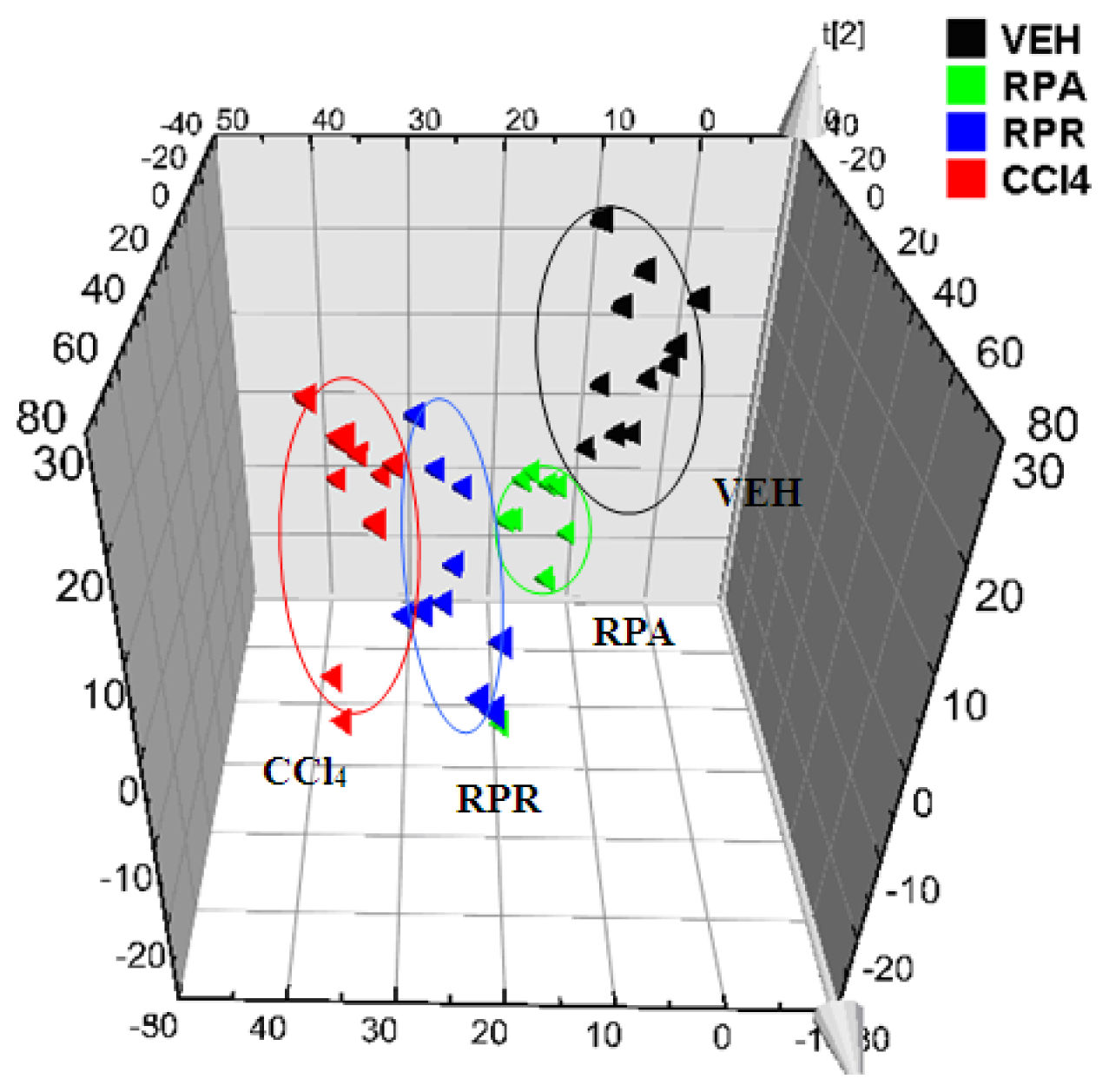
| Group No. | Dosage | ALT (IU/L) | AST (IU/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VEH | distilled water for 6 days and olive oil (1 mL/kg) | 85.0 ± 4.9 | 195.1 ± 62.3 |
| CCl4 | distilled water for 6 days and CCl4 (1 mL/kg) | 1200.0 ± 386.2 △△ | 2790.1 ± 936.9 △△ |
| RPR | RPR (12 g/kg) for 6 days and CCl4 (1 mL/kg) | 420.4 ± 93.1 ▲▲ | 1026.8 ± 182.5 ▲▲ |
| RPA | RPA (12 g/kg) for 6 days and CCl4 (1 mL/kg) | 316.4 ± 89.2 ▲▲ | 734.3 ± 206.1 ▲▲ |
| m/z ([M-H]−) | tR (min) | Compounds | Change in the RPR group | Change in the RPA group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 269.5 | 4.63 | Inosine | ↑ | ↑ |
| 318.6 | 5.44 | Phytosphingosine | ↓ | — |
| 498.6 | 3.93 | Tauroursodeoxycholic acid * | ↑ | ↑ |
| 464.6 | 4.38 | Glycocholic acid * | ↑ | ↑ |
| 407.5 | 5.48 | Cholic acid * | ↑ | ↑ |
| 391.6 | 5.72 | Deoxycholic acid * | ↑ | ↑ |
| 228.5 | 4.11 | 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate | ↓ | ↓ |
| 103.4 | 1.18 | Choline | ↓ | ↓ |
| Bile acids | VEH group | CCl4 group | RPR group | RPA group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 72.9 ± 60.9 | 474.4 ± 299.3 *** | 621.7 ± 355.5 *** | 141.8 ± 183.8 |
| DCA | 20.1 ± 10.5 | 15.6 ± 10.9 | 13.8 ± 9.5 | 2.2 ± 4.0 *** |
| CDCA | 10.4 ± 11.0 | 11.2 ± 9.6 | 17.9 ± 10.6 | 11.1 ± 20.5 |
| UDCA | 1.3 ± 2.7 | 5.8 ± 8.7 | 3.8 ± 3.8 | 3.7 ± 6.0 |
| HDCA | 86.2 ± 51.8 | 112.3 ± 82.5 | 80.9 ± 33.9 | 1.3 ± 2.7 * |
| LCA | 73.4 ± 25.9 | 111.2 ± 27.2 ** | 108.5 ± 34.0 | 81.4 ± 20.1 |
| GCA | 5.7 ± 7.4 | 54.1 ± 52.9 ** | 72.7 ± 40.1 *** | 30.0 ± 22.0 ** |
| GDCA | 6.0 ±4.4 | 7.1 ± 8.9 | 5.4 ± 6.0 | 0.5 ± 1.4 * |
| GCDCA | 3.4 ±5.1 | 2.8 ± 5.2 | 2.3 ± 3.4 | 1.8 ± 3.3 |
| GUDCA | - | 1.7 ± 2.8 | 1.6 ± 2.3 * | 0.6 ± 1.1 |
| GLCA | 2.0 ± 4.6 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 1.0 ± 1.6 | 3.7 ± 8.2 |
| TCA | 4.1 ± 5.2 | 85.9 ± 56.4 *** | 60.0 ± 38.3 *** | 59.3 ± 52.7 ** |
| TDCA | 0.3 ± 0.7 | 3.9 ± 4.6 * | 0.8 ± 1.7 | 5.4 ± 5.5 ** |
| TCDCA | 3.1 ± 2.6 | 9.1 ± 7.5 * | 5.2 ± 4.3 | 1.8 ± 3.3 |
| TUDCA | 0.2 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 2.0 * | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.9 |
| THDCA | 4.5 ± 8.1 | 22.6 ± 20.5 * | 7.5 ± 5.6 | 1.2 ± 2.1 |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Xiong, A.-Z.; Teng, Z.-Q.; Yang, Q.-W.; Shi, Y.-H.; Yang, L. Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba Attenuate CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury: An Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) Based Metabolomic Approach for the Pharmacodynamic Study of Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14634-14647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114634
Wang R, Xiong A-Z, Teng Z-Q, Yang Q-W, Shi Y-H, Yang L. Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba Attenuate CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury: An Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) Based Metabolomic Approach for the Pharmacodynamic Study of Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(11):14634-14647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114634
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rui, Ai-Zhen Xiong, Zhong-Qiu Teng, Qi-Wei Yang, Yan-Hong Shi, and Li Yang. 2012. "Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba Attenuate CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury: An Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) Based Metabolomic Approach for the Pharmacodynamic Study of Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 11: 14634-14647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114634
APA StyleWang, R., Xiong, A.-Z., Teng, Z.-Q., Yang, Q.-W., Shi, Y.-H., & Yang, L. (2012). Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba Attenuate CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury: An Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) Based Metabolomic Approach for the Pharmacodynamic Study of Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(11), 14634-14647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114634




