Deletion of afpab1 Causes Increased Sensitivity to Oxidative Stress and Hypovirulence in Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
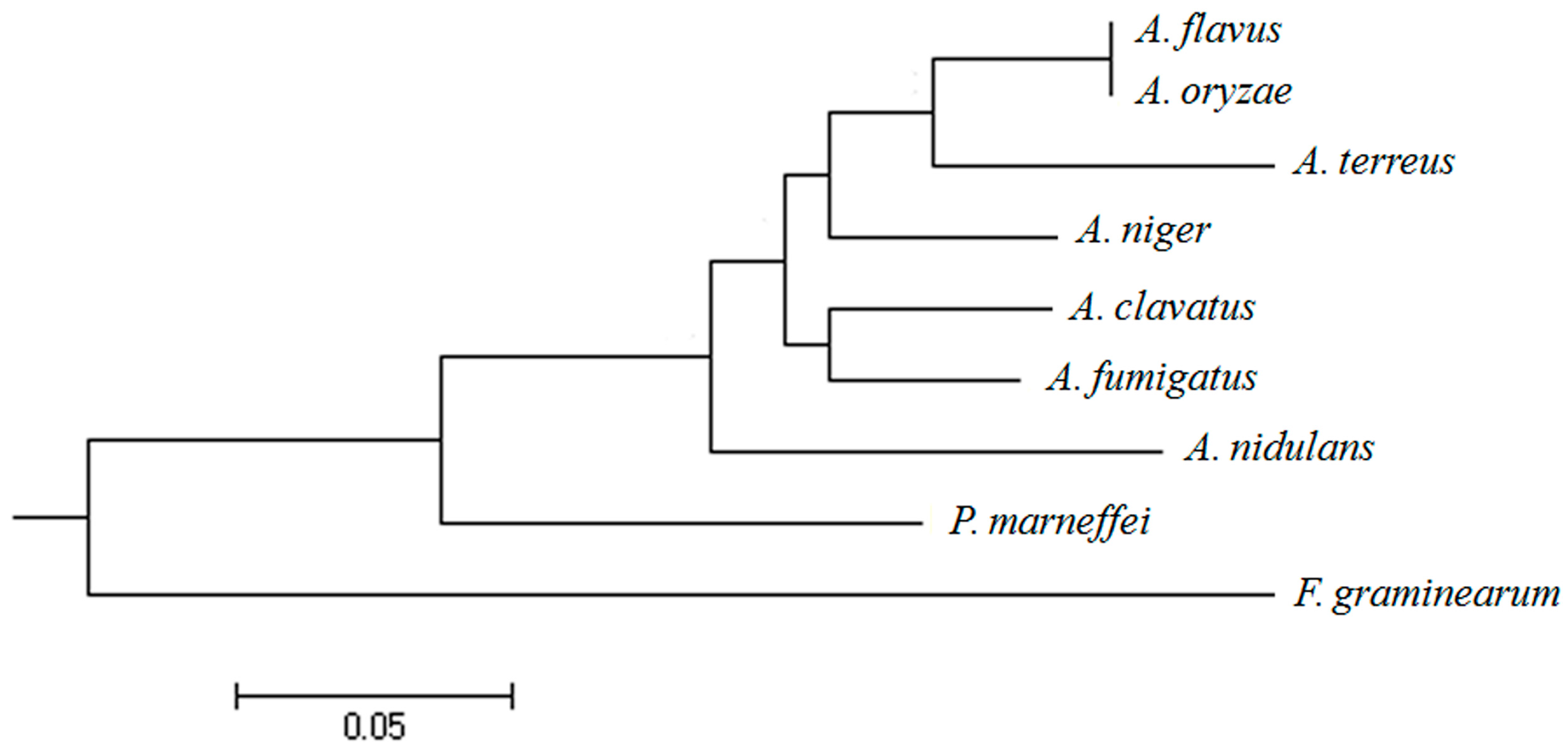
2.1. Isolation and Sequence Analysis of afpab1 Homolog from A. fumigatus
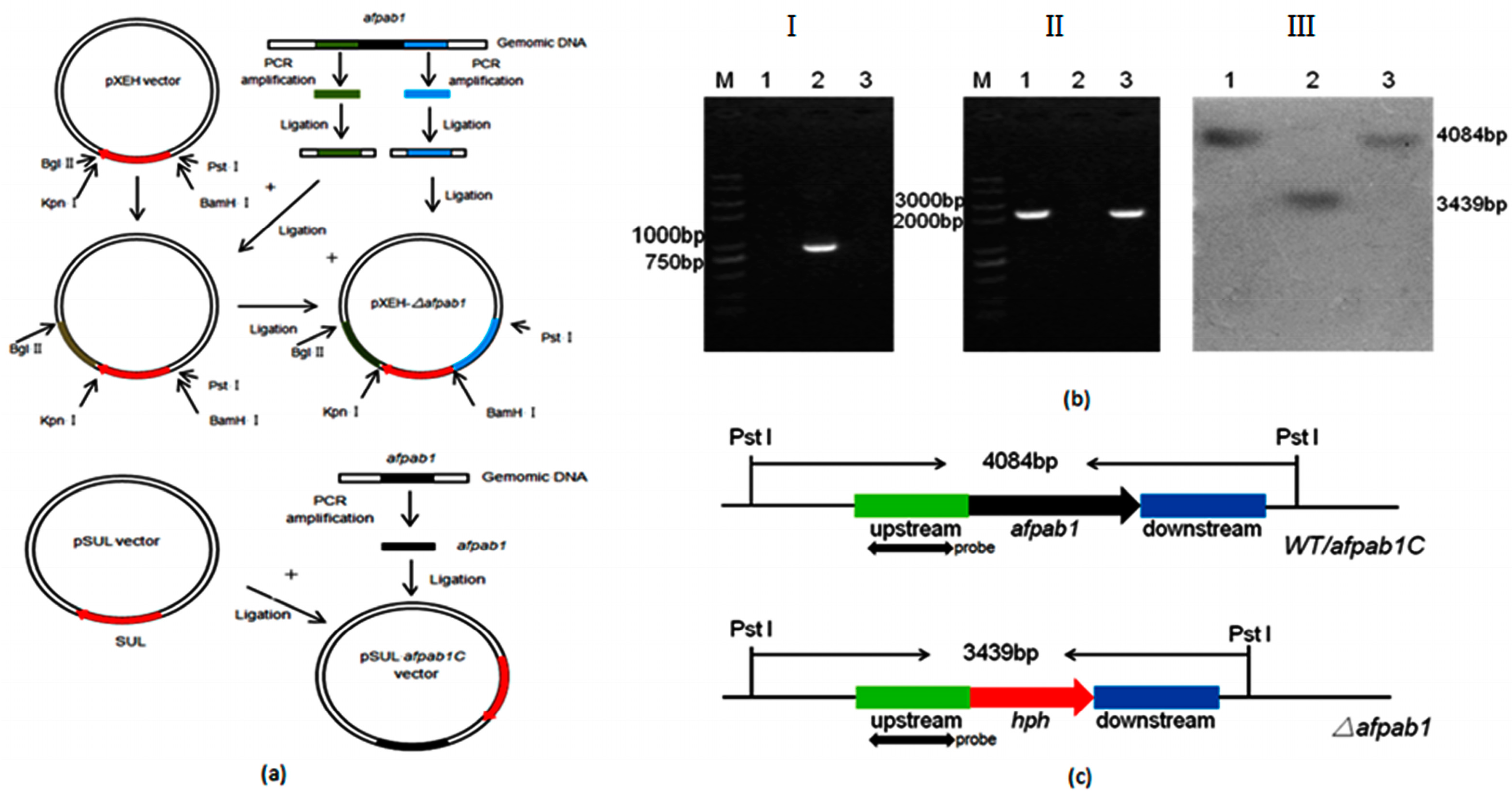
2.2. Deletion and Complementation of afpab1 in A. fumigatus
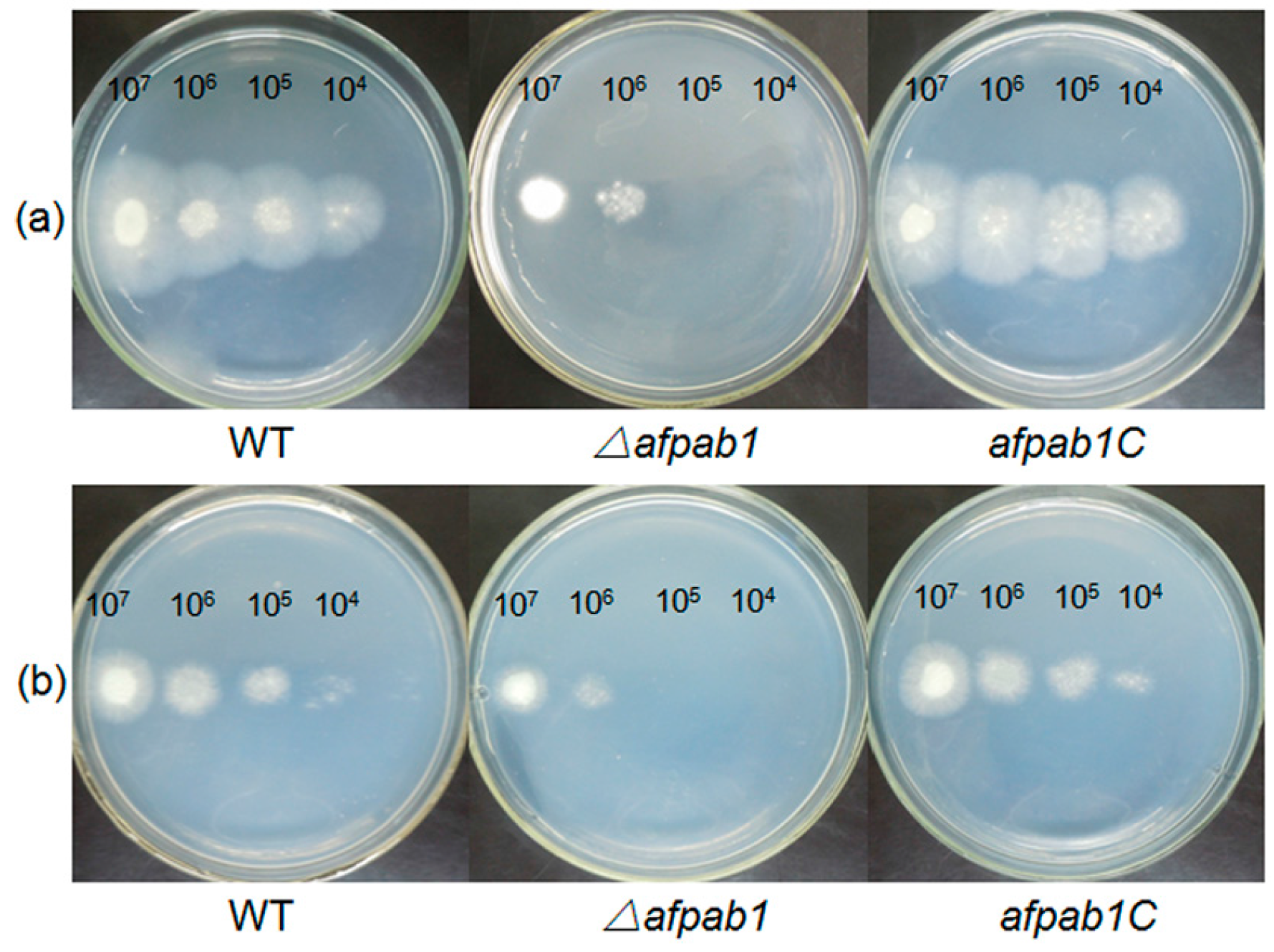
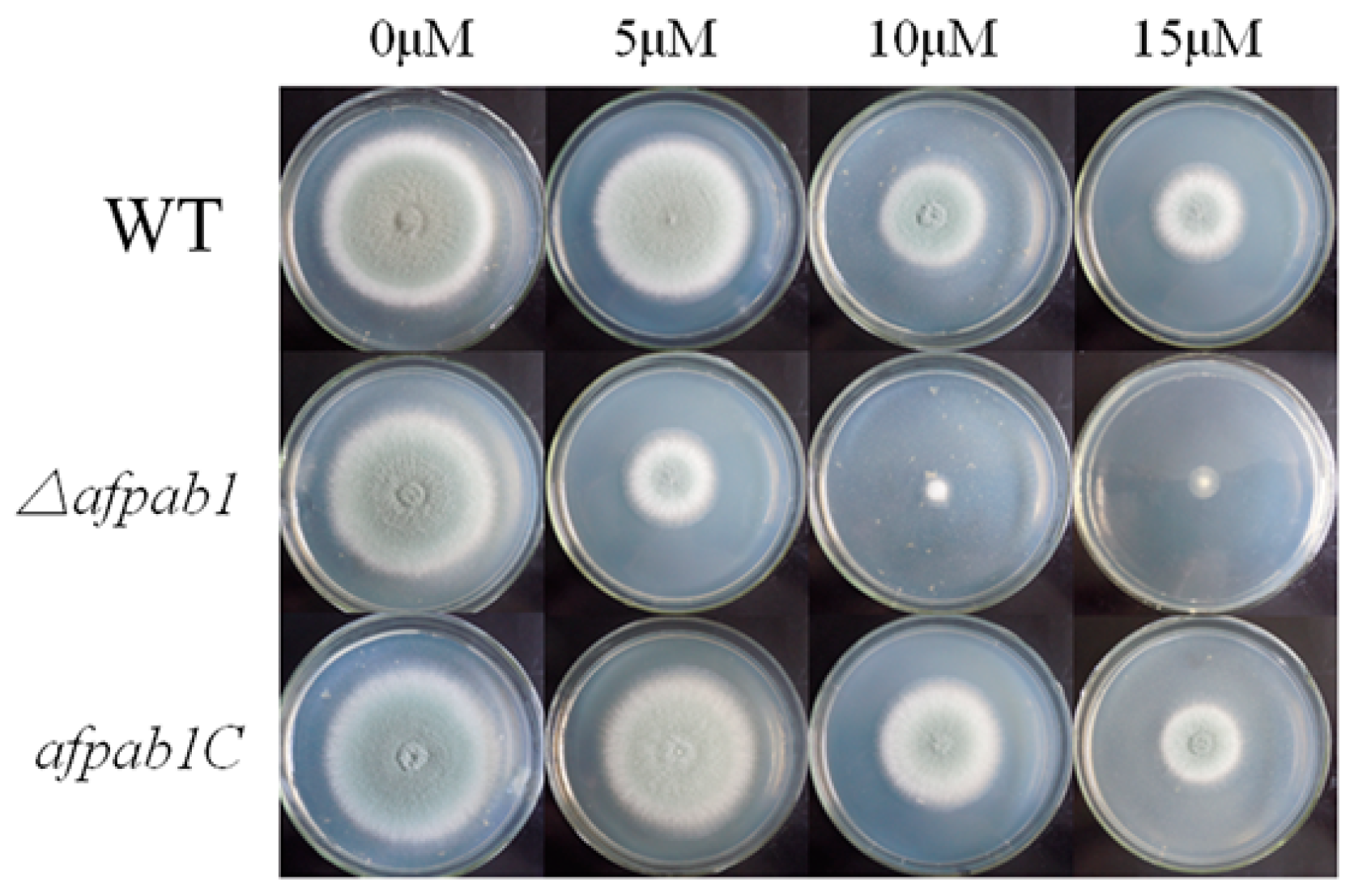
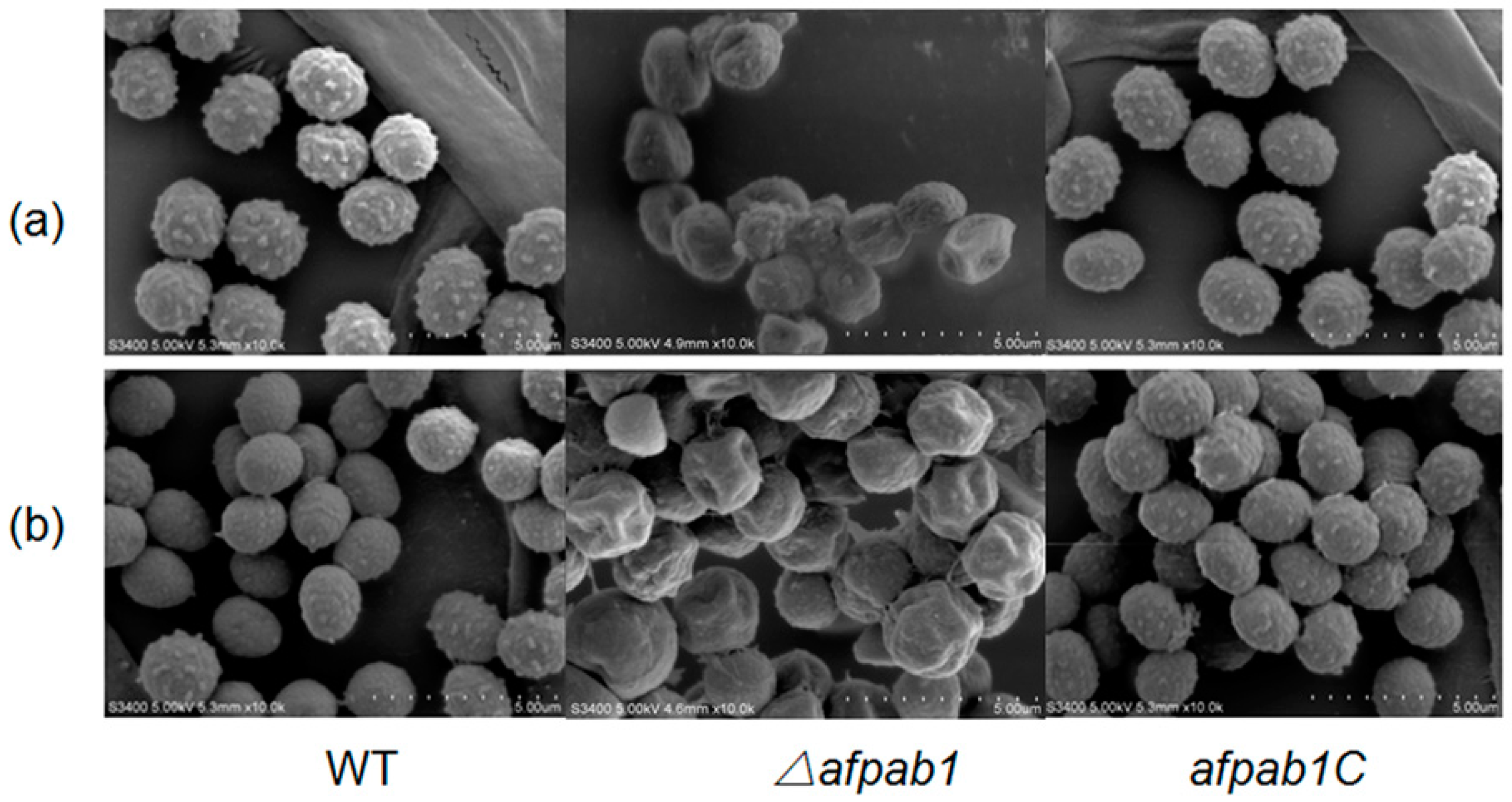
2.3. Growth and Phenotype of the Δafpab1 Strain
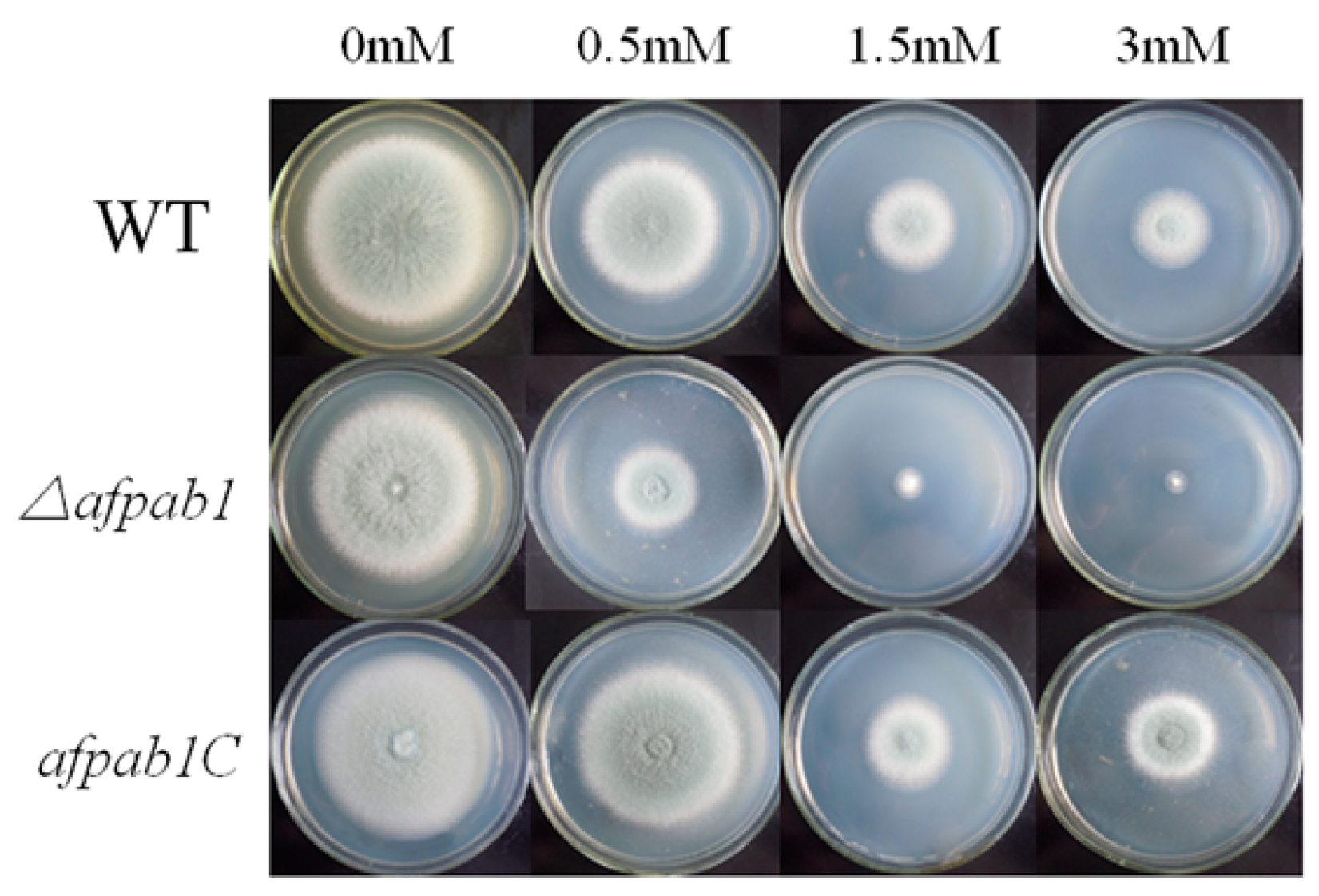
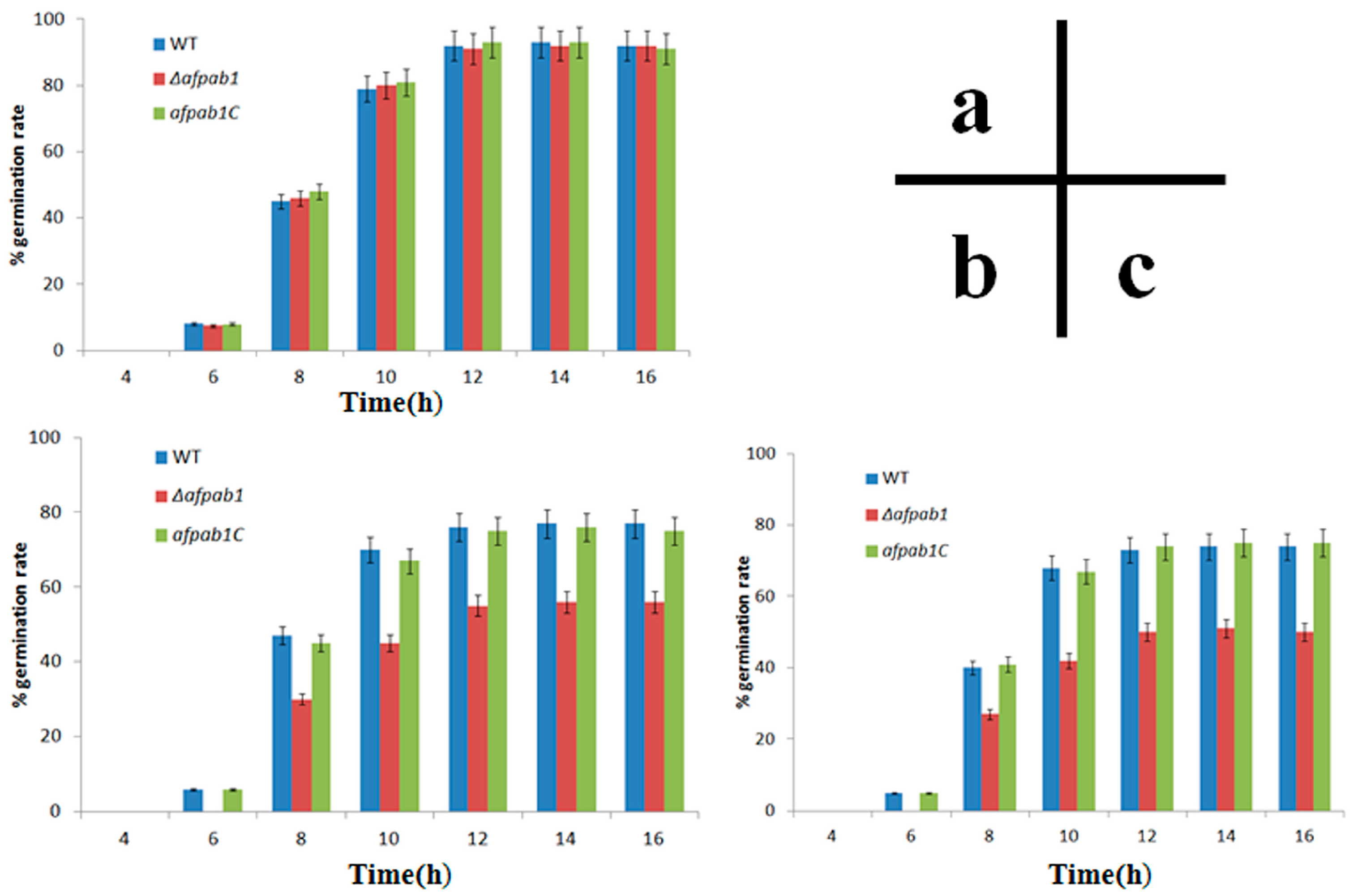
2.4. Δafpab1 Shows Increased Sensitivity to Oxidative Stress
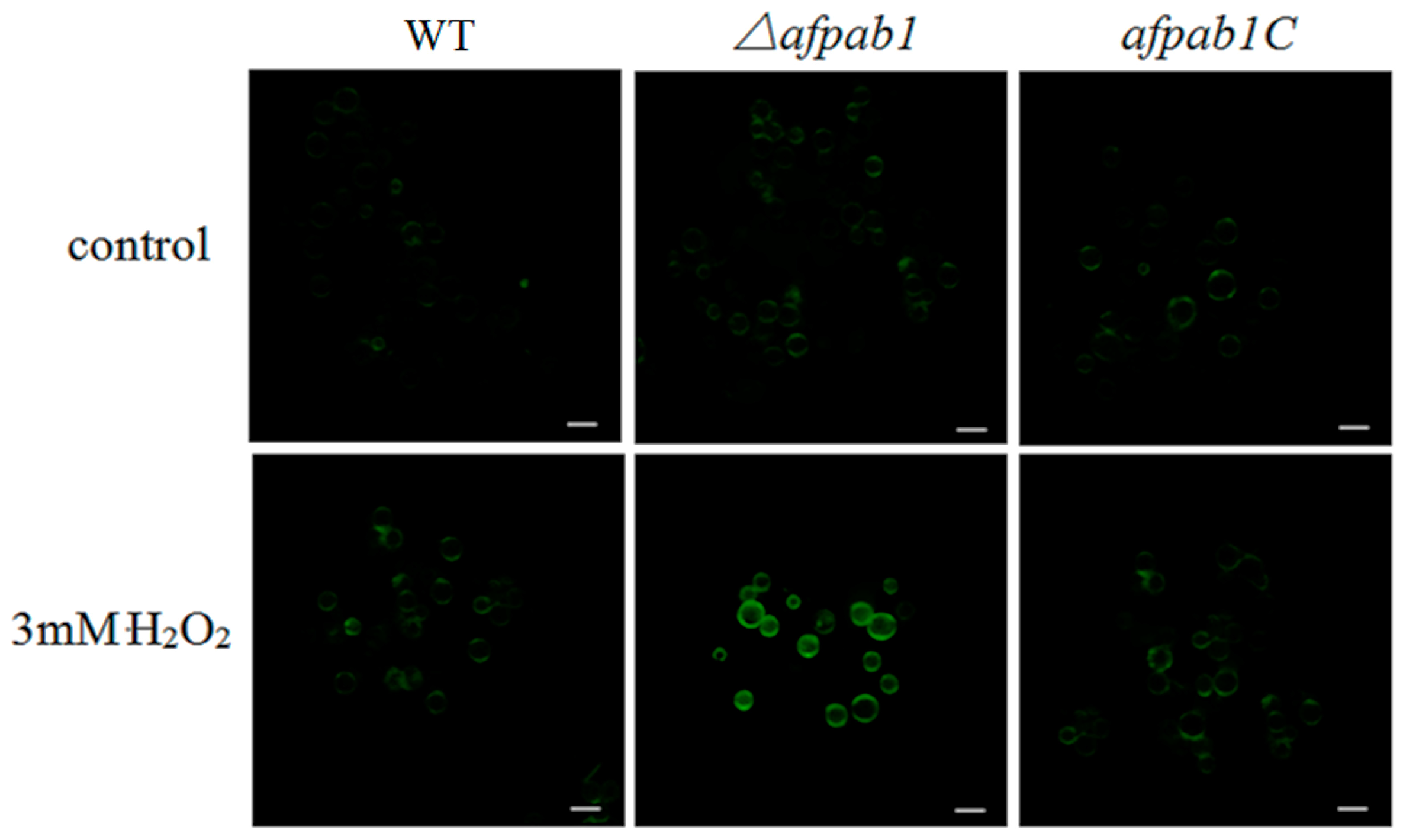
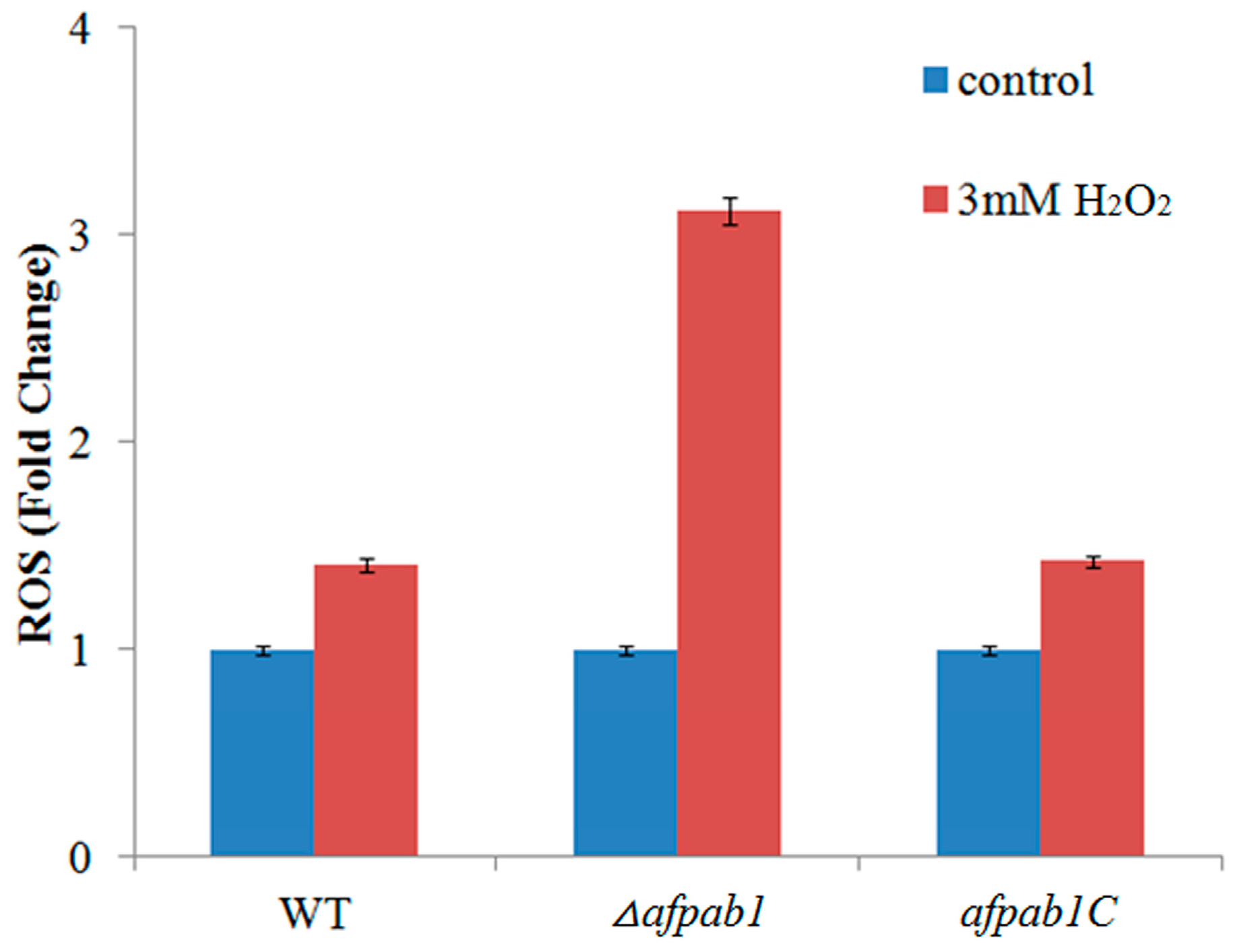
2.5. ROS Production of Δafpab1 Is Increased When Exposed to H2O2
2.6. Killing Rate for Δafpab1 Is Increased in RAW264.7 Cells
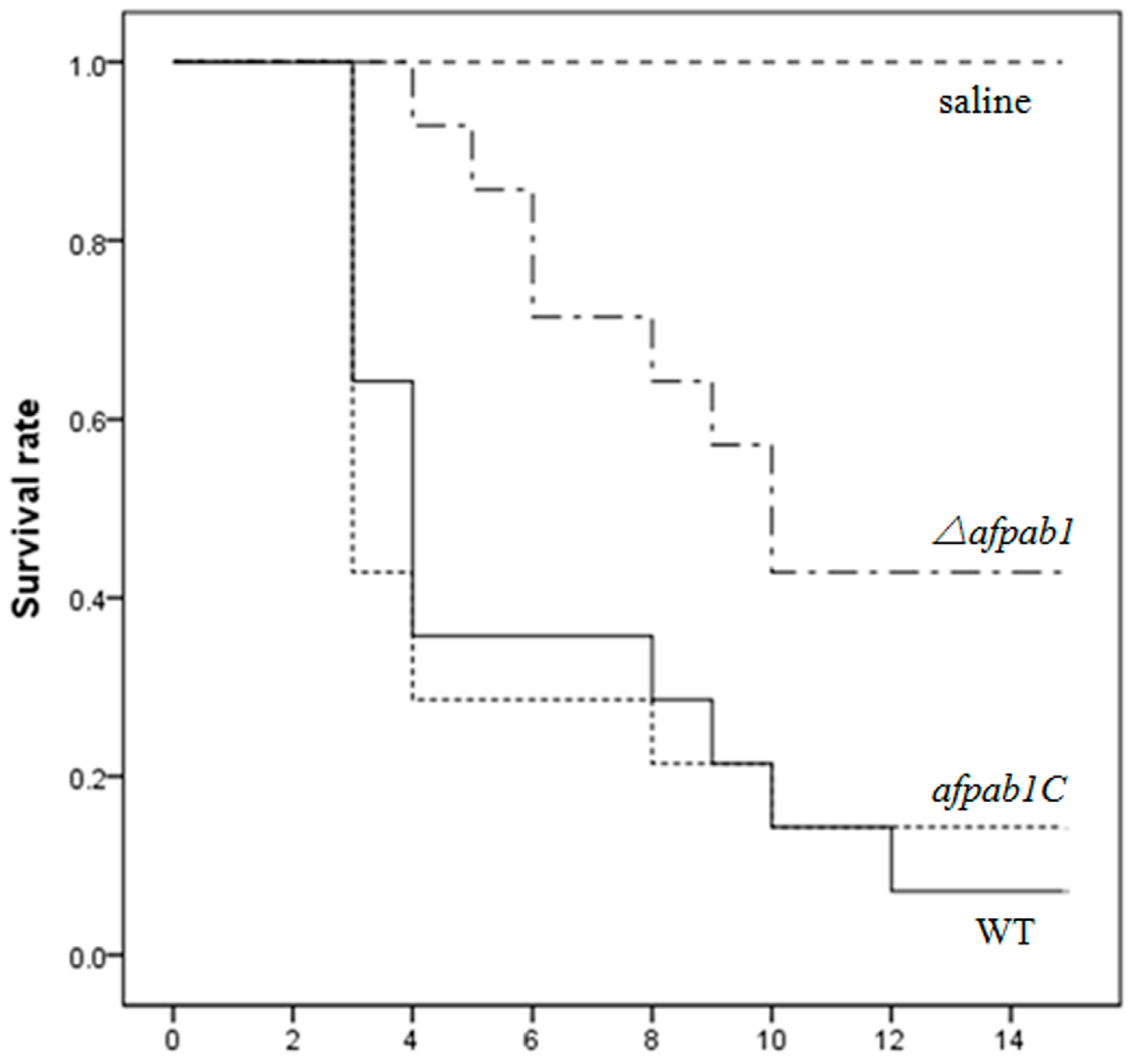
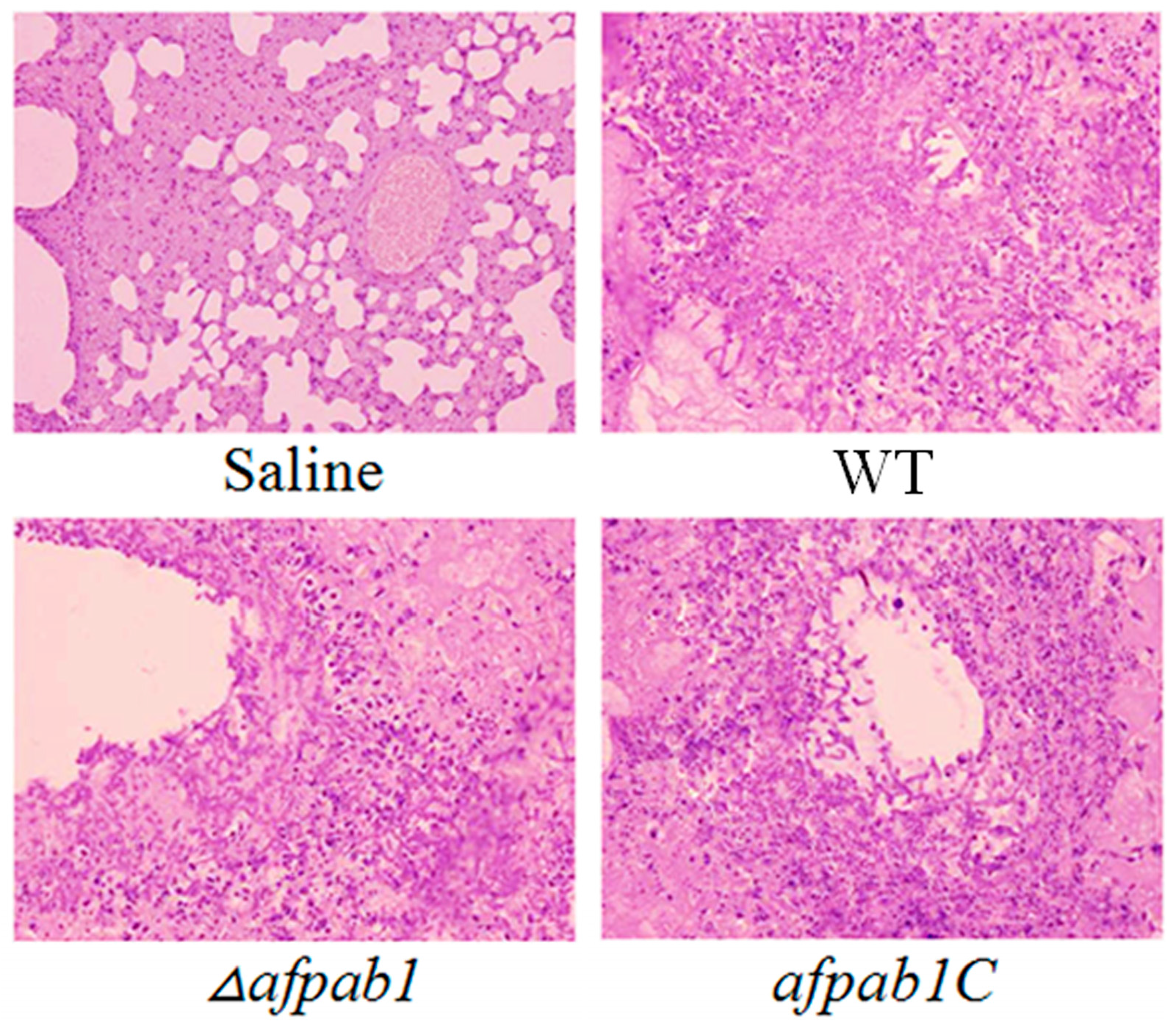
2.7. Murine Model of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Strains, Media, and Growth Conditions
4.2. Molecular Cloning of A. fumigatus afpab1
4.3. Construction of the Δafpab1 Deletion Strain and Complementation Strain
4.4. Growth Analysis and Morphological Observation
4.5. Plate Assay
4.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.7. Rates of Germination under Oxidative Stress
4.8. Protoplast Preparation
4.9. 2,7-Dichlorofluorescin Diacetate Staining
4.10. Macrophage Assay for Fungal Spores
4.11. Pathogenicity Assay
4.12. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCormick, A.; Loeffler, J.; Ebel, F. Aspergillus fumigatus: Contours of an opportunistic human pathogen. Cell Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balloy, V.; Chignard, M. The innate immune response to Aspergillus fumigatus. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, A.; Fernández-Molina, J.V.; Bikandi, J.; Ramírez, A.; Margareto, J.; Sendino, J.; Hernando, F.L.; Ponton, J.; Garaizar, J.; Rementeria, A. What makes Aspergillus fumigatus a successful pathogen? Genes and molecules involved in invasive aspergillosis. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2010, 27, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurla, C.; Lifland, A.W.; Santangelo, P.J. Characterizing mRNA interactions with RNA granules during translation initiation inhibition. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.T.; Maruyama, J.; Kitamoto, K. Aspergillus oryzae AoSO is a novel component of stress granules upon heat stress in filamentous fungi. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Kedersha, N. RNA granules. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, J.R.; Parker, R. Eukaryotic stress granules: The ins and outs of translation. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedersha, N.; Anderson, P. Stress granules: Site of mRNA triage that regulate mRNA stability and translatability. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Kedersha, N. RNA granules: Post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grousl, T.; Ivanov, P.; Malcova, I.; Pompach, P.; Frydlova, I.; Slaba, R.; Senohrabkova, L.; Novakova, L.; Hasek, J. Heat shock-induced accumulation of translation elongation and termination factors precedes assembly of stress granules in S. cerevisiae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.; Ren, Z.; Losada, L.; Nierman, W.C.; Lu, L.J.; Askew, D.S. Polysome profiling reveals broad translatome remodeling during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Dickman, M.B. Proline suppresses apoptosis in the fungal pathogen, Colletotrichum trifolii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3459–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, W.J.; Benjamin, D.K.; Trasi, S.A.; Miller, J.L.; Schell, W.A.; Zaas, A.K.; Foster, W.M.; Perfect, J.R. Value of an inhalational model of invasive aspergillosis. Med. Mycol. 2004, 42, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latgé, J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabrielli, E.; Fothergill, A.W.; Brescini, L.; Sutton, D.A.; Marchionni, E.; Orsetti, E.; Staffolani, S.; Castelli, P.; Gesuita, R.; Barchiesi, F. Osteomyelitis caused by Aspergillus species: A review of 310 reported cases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, B.; Xing, L.; et al. The Ccz1 mediates the autophagic clearance of damaged mitochondria in response to oxidative stress in Candida albicans. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 69, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambou, K.; Lamarre, C.; Beau, R.; Dufour, N.; Latge, J.P. Functional analysis of the superoxide dismutase family in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessing, F.; Kniemeyer, O.; Wozniok, I.; Loeffler, J.; Kurzai, O.; Haertl, A.; Brakhage, A.A. The Aspergillus fumigatus transcriptional regulator AfYap1 represents the major regulator for defense against reactive oxygen inter mediates but is dispensable for pathogenity in an intranasal mouse infection model. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 2290–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, M.V.; Oliveira, A.C.; Shida, C.S.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Nunes, L.R. Gene expression modulation by paraquat-induced oxidative stress conditions in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 60, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.J.; Haynes, K.; Quinn, J. Nitrosative and oxidative stress responses in fungal pathogenicity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Latge, J.P.; Calderone, R. Signalling and oxidant adaptation in Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippe, B.; Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Prévost, M.C.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; Sanchez Perez, M.; van der meeren, A.; Latgé, J.P. Killing of Aspergillus fumigatus by alveolar macrophages is mediated by reactive oxidant intermediates. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque, S.; Cerciat, M.; Gaugué, I.; Mora, L.; Floch, A.G.; de Zamaroczy, M.; Heurgué-Hamard, V.; Kervestin, S. Interaction between the poly(A)-binding protein Pab1 and the eukaryotic release factor eRF3 regulates translation termination but not mRNA decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA 2015, 21, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, E.P.; Reiber, K.; Neville, C.; Scheibner, O.; Kavanagh, K.; Doyle, S. A nonribosomal peptide synthetase (Pes1) confers protection against oxidative stress in Aspergillus fumigatus. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 3038–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.A.; Kaiser, B.N.; Franks, T.; Collins, G.; Sedgley, M. Improved methods in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of almond using positive (mannose/pmi) or negative (kanamycin resistance) selection-based protocols. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; He, D.; Li, G.; Gao, S.; Lv, H.; Shan, Q.; Wang, L. An efficient tool for random insertional mutagenesis: Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus terreus. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 98, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; He, D.; Yu, B.; Yokoyama, K.; Wang, L. Efficient insertional mutagenesis system for the dimorphic pathogenic fungus Sporothrix schenckii using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 84, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, R.A.; Perfect, B.Z.; Pinchai, N.; Park, S.; Perlin, D.S.; Asfaw, Y.G.; Heitman, J.; Perfect, J.R.; Steinbach, W.J. Calcineurin target CrzA regulates conidial germination, hyphal growth, and pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukup, A.A.; Farnoodian, M.; Berthier, E.; Keller, N.P. NosA, a transcription factor important in Aspergillus fumigatus stress and developmental response, rescues the germination defect of a laeA deletion. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2012, 49, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, H. O-Mannosyltransferase 1 in Aspergillus fumigatus (AfPmt1p) is crucial for cell wall integrity and conidium morphology, especially at an elevated temperature. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalhorst, P.S.; Krappmann, S.; Vervecken, W.; Rohde, M.; Müller, M.; Braus, G.H.; Contreras, R.; Braun, A.; Bakker, H.; Routier, F.H. Contribution of galactofuranose to the virulence of the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Name | Nucleotide Sequence(5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| PabIf | 5′-ATGTCTGCCGAAGTCTCTAC-3′ |
| PabIr | 5′-CGACTTGTTCTCTTCCGTAG-3′ |
| PabDfi | 5′-CTGCAGCCAGTGAAGACCAGGATC-3′ |
| PabDri | 5′-GGATCCGACGGACGAGGTGAAGTG-3′ |
| PabUf | 5′-GGTACCTCTTCCTATCCCGATTACAT-3′ |
| PabUr | 5′-AGATCTATCAACCGTCCCTCACTC-3′ |
| Pabf | 5′-GGACCACGAATACCCTGAC-3′ |
| Pabr | 5′-CTGCTTCCCTCTATGTCGG-3′ |
| Hphf | 5′-CGCCCAAGCTGCATCATCGAA-3′ |
| Hphr | 5′-CGACAGCGTCTCCGACCTGA-3′ |
| PabCF | 5′-ACTAGTGCGGCGAGGATAGATTAC-3′ |
| PabCB | 5′-TCTACAGCGGCGAGGATAGATTAC-3′ |
| PabSr | 5′-TCTTCCTATCCCGATTACAT-3′ |
| PabSf | 5′-ATCAACCGTCCCTCACTC-3′ |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Wang, S.; He, D.; Gao, S.; Xue, B.; Wang, L. Deletion of afpab1 Causes Increased Sensitivity to Oxidative Stress and Hypovirulence in Aspergillus fumigatus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111811
Wang D, Wang S, He D, Gao S, Xue B, Wang L. Deletion of afpab1 Causes Increased Sensitivity to Oxidative Stress and Hypovirulence in Aspergillus fumigatus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111811
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dongyang, Shunan Wang, Dan He, Song Gao, Baiji Xue, and Li Wang. 2016. "Deletion of afpab1 Causes Increased Sensitivity to Oxidative Stress and Hypovirulence in Aspergillus fumigatus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111811





