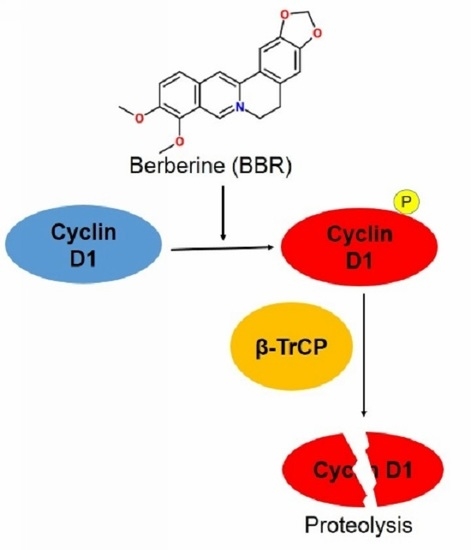
Berberine Suppresses Cyclin D1 Expression through Proteasomal Degradation in Human Hepatoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Berberine Suppresses In Vitro and In Vivo Cyclin D1 Expression in Hepatoma Cells
2.2. Berberine Triggers Post-Translational Suppression on Cyclin D1 Expression
2.3. Berberine Promotes Cyclin D1 Ubiquitination in HepG2 Cells and Facilitates β-TrCP Binding
2.4. Berberine Promotes Cyclin D1 Phosphorylation and Nuclear Export in HepG2 Cells
2.5. Berberine-Induced Cyclin D1 Degradation Is T286 Phosphorylation Dependent
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Plasmids
4.2. Cell Line and Cell Culture
4.3. Xenograft Model
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative Polymease Chain Reaction
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Immunofluoscence
4.7. Subcellular Fractionation
4.8. Immunoblotting
4.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.10. RNA Interference
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, D.C. Cyclin D1 in human neuroendocrine: Tumorigenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1014, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Sakamaki, T.; Pestell, R.G. Minireview: Cyclin D1: Normal and abnormal functions. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5439–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacey, D.W. Cyclin D1 serves as a cell cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003, 15, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, I.B. Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes—The achilles heal of cancer. Science 2002, 297, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, J.A. Cycling to cancer with cyclin D1. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2002, 1, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Fu, M.; Bouras, T.; Pestell, R.G. Signal transduction mediated by cyclin D1: From mitogens to cell proliferation: A molecular target with therapeutic potential. Cancer Treat. Res 2004, 119, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freemantle, S.J.; Liu, X.; Feng, Q.; Galimberti, F.; Blumen, S.; Sekula, D.; Kitareewan, S.; Dragnev, K.H.; Dmitrovsky, E. Cyclin degradation for cancer therapy and chemoprevention. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.I.; Barbash, O.; Kumar, K.G.; Weber, J.D.; Harper, J.W.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Rustgi, A.; Fuchs, S.Y.; Diehl, J.A. Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of cyclin D1 by the SCF (FBX4-αB crystallin) complex. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.S.; Yuk, D.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Han, S.B.; Moon, D.C.; Hong, J.T. Berberine inhibits human neuroblastoma cell growth through induction of p53-dependent apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3777–3784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantena, S.K.; Sharma, S.D.; Katiyar, S.K. Berberine inhibits growth, induces G1 arrest and apoptosis in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells by regulating Cdki-Cdk-cyclin cascade, disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and cleavage of caspase 3 and PARP. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Hao, Y.; Shi, T.P.; Deng, W.W.; Li, N. Berberine inhibits cyclin D1 expression via suppressed binding of AP-1 transcription factors to CCND1 AP-1 motif. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Feng, Y.; Tsao, S.; Wang, N.; Curtain, R.; Wang, Y. Berberine and coptidis rhizoma as novel antineoplastic agents: A review of traditional use and biomedical investigations. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsang, C.M.; Lau, E.P.; Di, K.; Cheung, P.Y.; Hau, P.M.; Ching, Y.P.; Wong, Y.C.; Cheung, A.L.; Wan, T.S.; Tong, Y.; et al. Berberine inhibits Rho GTPases and cell migration at low doses but induces G2 arrest and apoptosis at high doses in human cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 24, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.W.; Yin, S.C.; Ting, C.T.; Lin, S.J.; Hsueh, C.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, S.L. Berberine inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced growth and migration partly through an AMPK-dependent pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 590, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.W.; Ting, C.T.; Yin, S.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Lin, S.J.; Liao, J.K.; Hsu, S.L. Berberine suppresses MEK/ERK-dependent Egr-1 signaling pathway and inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell regrowth after in vitro mechanical injury. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantena, S.K.; Sharma, S.D.; Katiyar, S.K. Berberine, a natural product, induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Giessrigl, B.; Vonach, C.; Madlener, S.; Prinz, S.; Herbaceck, I.; Holzl, C.; Bauer, S.; Viola, K.; Mikulits, W.; et al. Berberine and a Berberis lycium extract inactivate Cdc25A and induce α-tubulin acetylation that correlate with HL-60 cell cycle inhibition and apoptosis. Mutat. Res. 2010, 683, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santra, M.K.; Wajapeyee, N.; Green, M.R. F-box protein FBXO31 mediates cyclin D1 degradation to induce G1 arrest after DNA damage. Nature 2009, 459, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, C.M.; Cheung, K.C.; Cheung, Y.C.; Man, K.; Lui, V.W.; Tsao, S.W.; Feng, Y. Berberine suppresses Id-1 expression and inhibits the growth and development of lung metastases in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Tan, H.Y.; Tsao, S.W.; Feng, Y. Berberine-induced tumor suppressor p53 upregulation gets involved in the regulatory network of MIR-23a in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, M.; Tsang, C.M.; Man, K.; Tong, Y.; Tsao, S.W. Berberine induces autophagic cell death and mitochondrial apoptosis in liver cancer cells: The cellular mechanism. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.; Yang, H.C.; Chuang, H.C.; Yang, J.; Kulp, S.K.; Lu, P.J.; Lai, M.D.; Chen, C.S. A novel mechanism by which thiazolidinediones facilitate the proteasomal degradation of cyclin D1 in cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26759–26770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, J.A.; Cheng, M.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcellular localization. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3499–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.K.; Gervais, J.L.; Zhang, H. Human CUL-1 associates with the SKP1/SKP2 complex and regulates p21(CIP1/WAF1) and cyclin d proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11324–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Li, J.Y.; Gosby, A.; To, S.W.; Cheng, Z.; Miyoshi, H.; Taketo, M.M.; Cooney, G.J.; Kraegen, E.W.; James, D.E.; et al. Berberine and its more biologically available derivative, dihydroberberine, inhibit mitochondrial respiratory complex I: A mechanism for the action of berberine to activate amp-activated protein kinase and improve insulin action. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Ge, B.; Zang, Y.Q. Berberine differentially modulates the activities of ERK, p38 MAPK, and JNK to suppress TH17 and TH1 T cell differentiation in type 1 diabetic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28420–28429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Terrada, D.; Cheung, S.W.; Finegold, M.J.; Knowles, B.B. Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 1512–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Sirota, M.; Fan-Minogue, H.; Hadley, D.; Butte, A.J. Relating hepatocellular carcinoma tumor samples and cell lines using gene expression data in translational research. BMC Med Genom. 2015, 8, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Z.; Zu, X.; Xie, Z.; Li, W.; Ning, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, W. Antitumor effect of F-PBF (β-TrCP)-induced targeted PTTG1 degradation in HeLa cells. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 425–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, C.M. Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frescas, D.; Pagano, M. Deregulated proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and β-TrCP: Tipping the scales of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, T. β-TrCP-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of PHLPP1 are negatively regulated by Akt. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 6192–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Tan, H.-Y.; Li, S.; Tsang, C.M.; Tsao, S.-W.; Feng, Y. Berberine Suppresses Cyclin D1 Expression through Proteasomal Degradation in Human Hepatoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111899
Wang N, Wang X, Tan H-Y, Li S, Tsang CM, Tsao S-W, Feng Y. Berberine Suppresses Cyclin D1 Expression through Proteasomal Degradation in Human Hepatoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111899
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ning, Xuanbin Wang, Hor-Yue Tan, Sha Li, Chi Man Tsang, Sai-Wah Tsao, and Yibin Feng. 2016. "Berberine Suppresses Cyclin D1 Expression through Proteasomal Degradation in Human Hepatoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111899
APA StyleWang, N., Wang, X., Tan, H.-Y., Li, S., Tsang, C. M., Tsao, S.-W., & Feng, Y. (2016). Berberine Suppresses Cyclin D1 Expression through Proteasomal Degradation in Human Hepatoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111899