RNase L Suppresses Androgen Receptor Signaling, Cell Migration and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
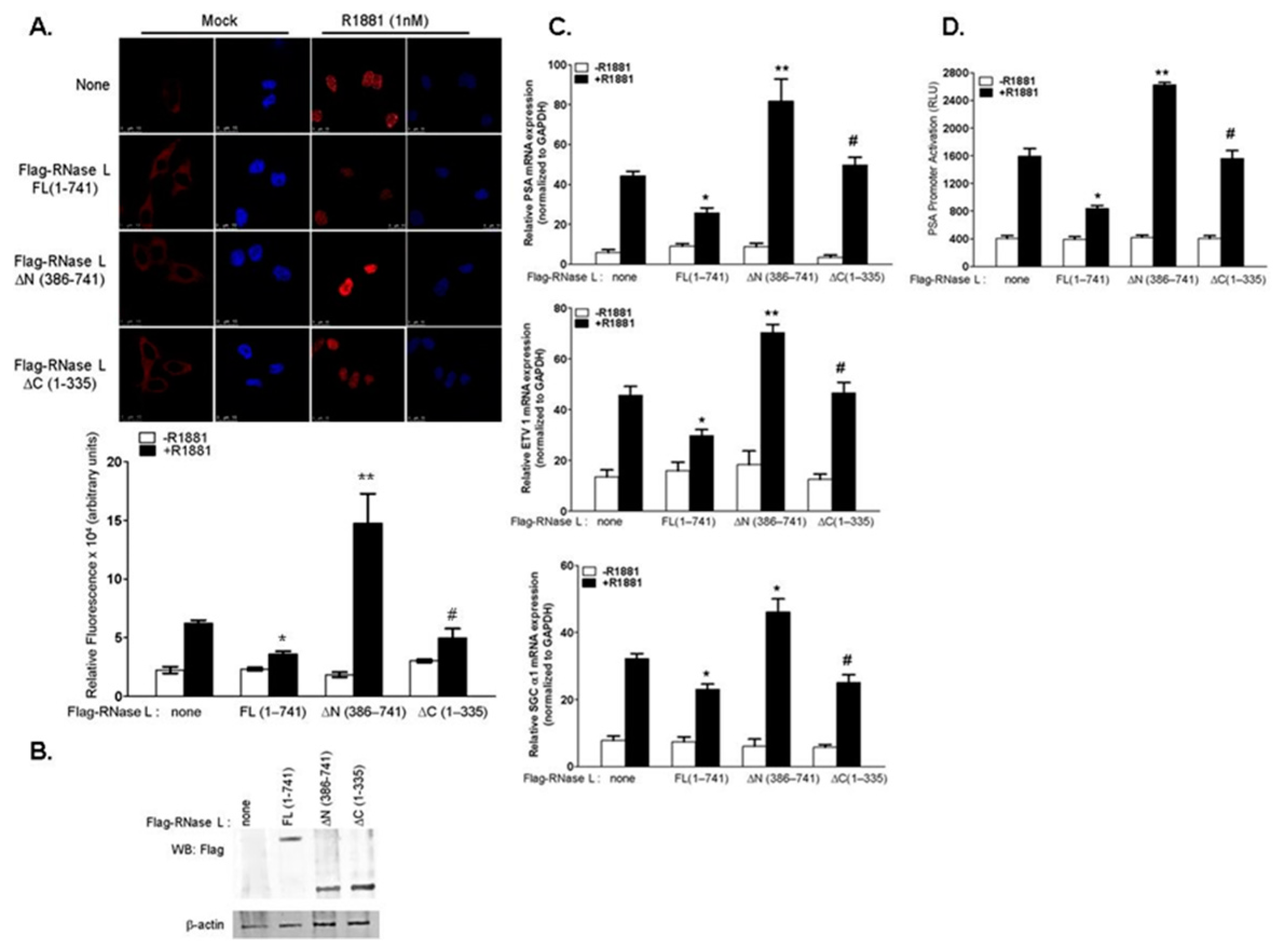
2.1. RNase L Negatively Regulates Androgen Signaling
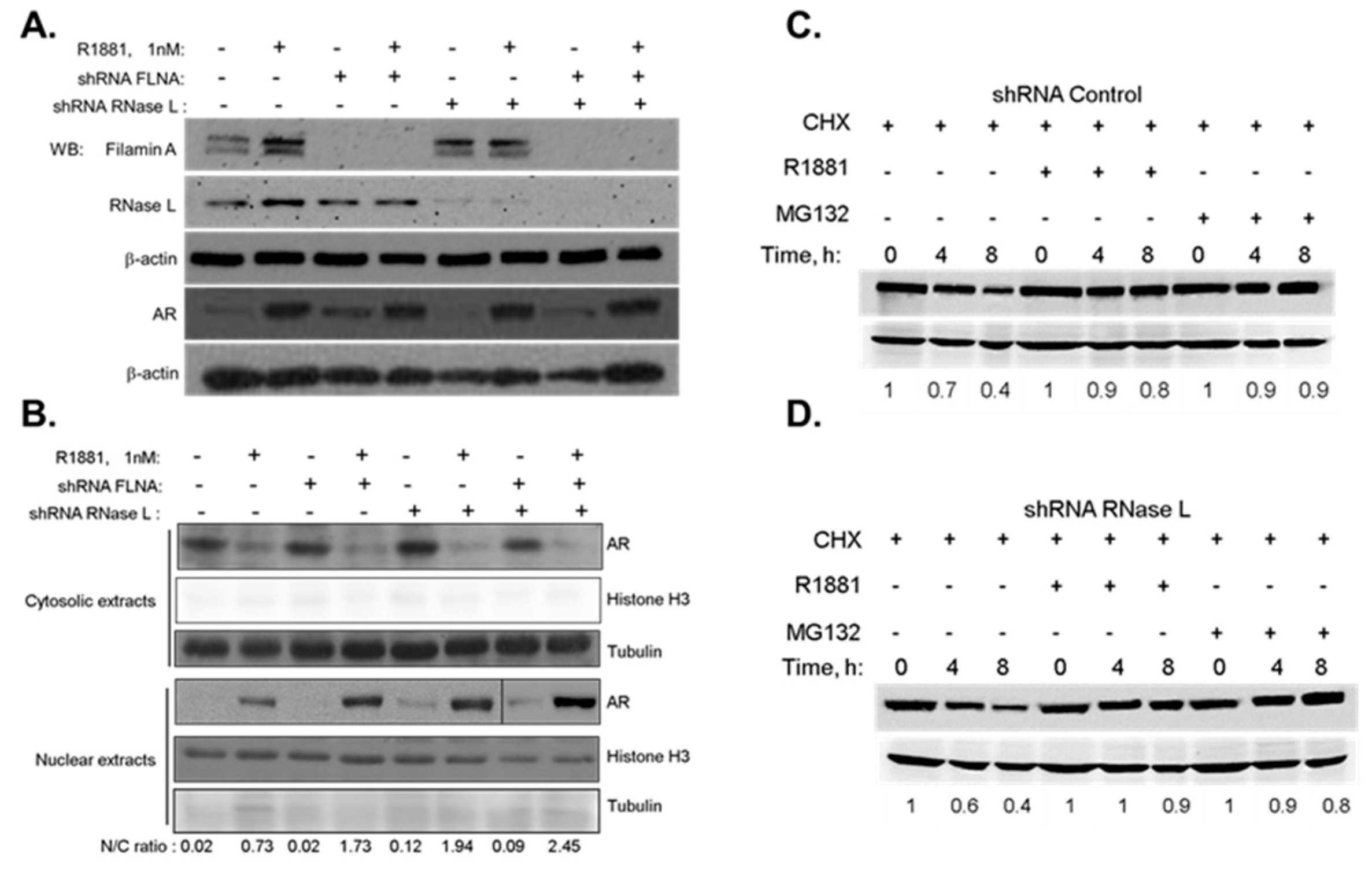
2.2. The Effect of RNase L on AR Signaling Is Not Due to Altered AR Stability
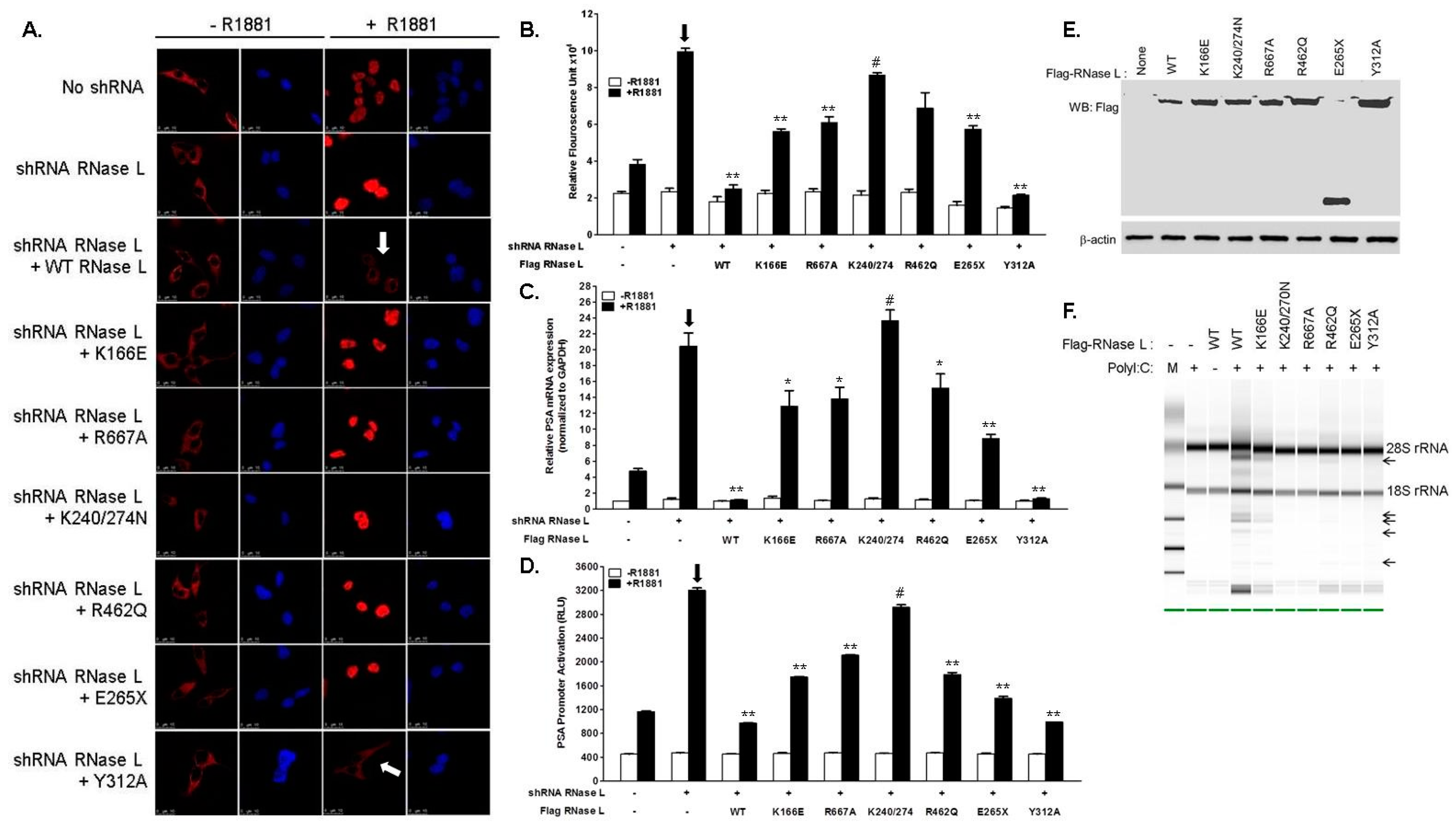
2.3. Hereditary Prostate Cancer 1 (HPC1)-Associated Mutants of RNase L Enhance AR Transcriptional Activity
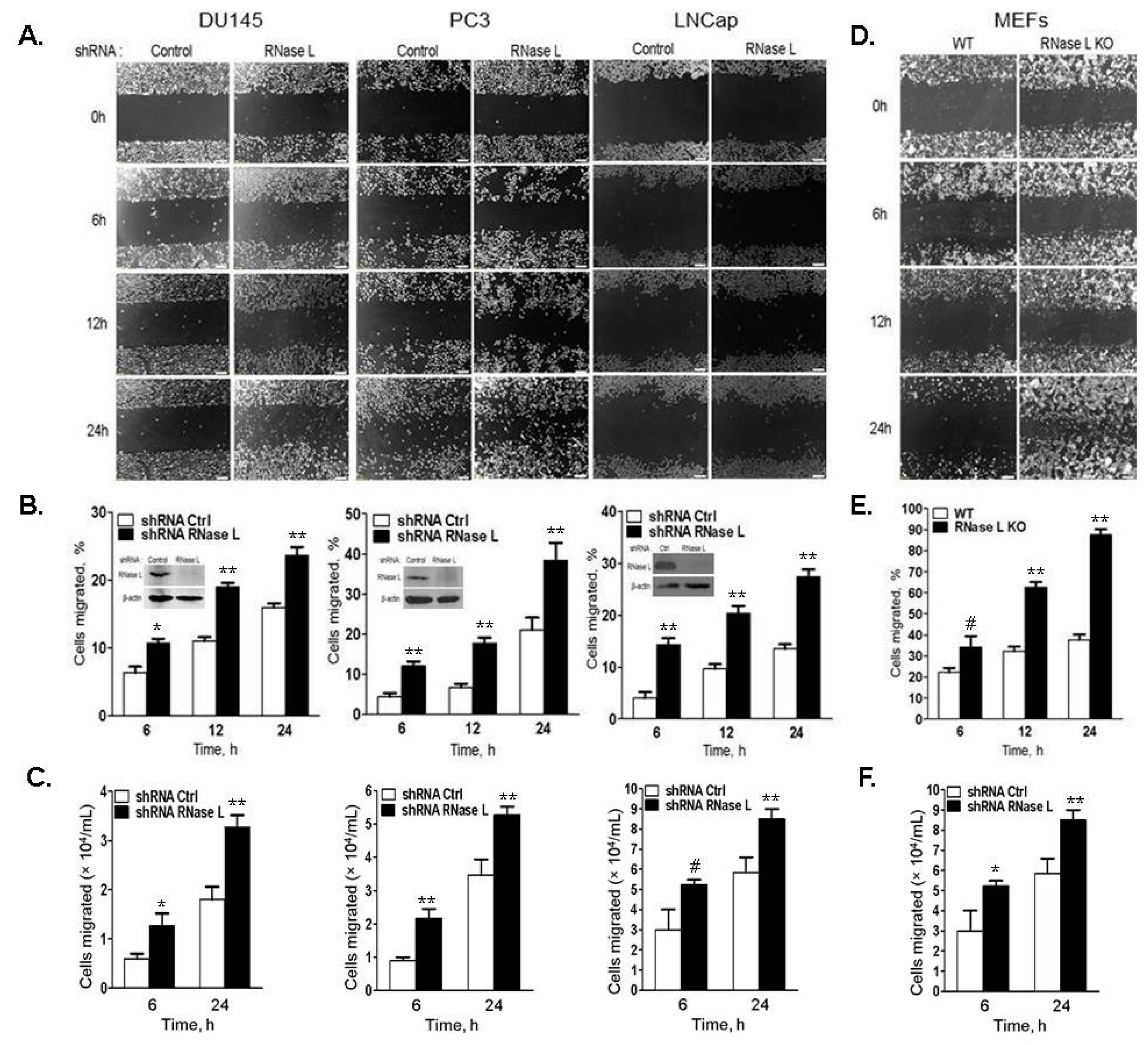
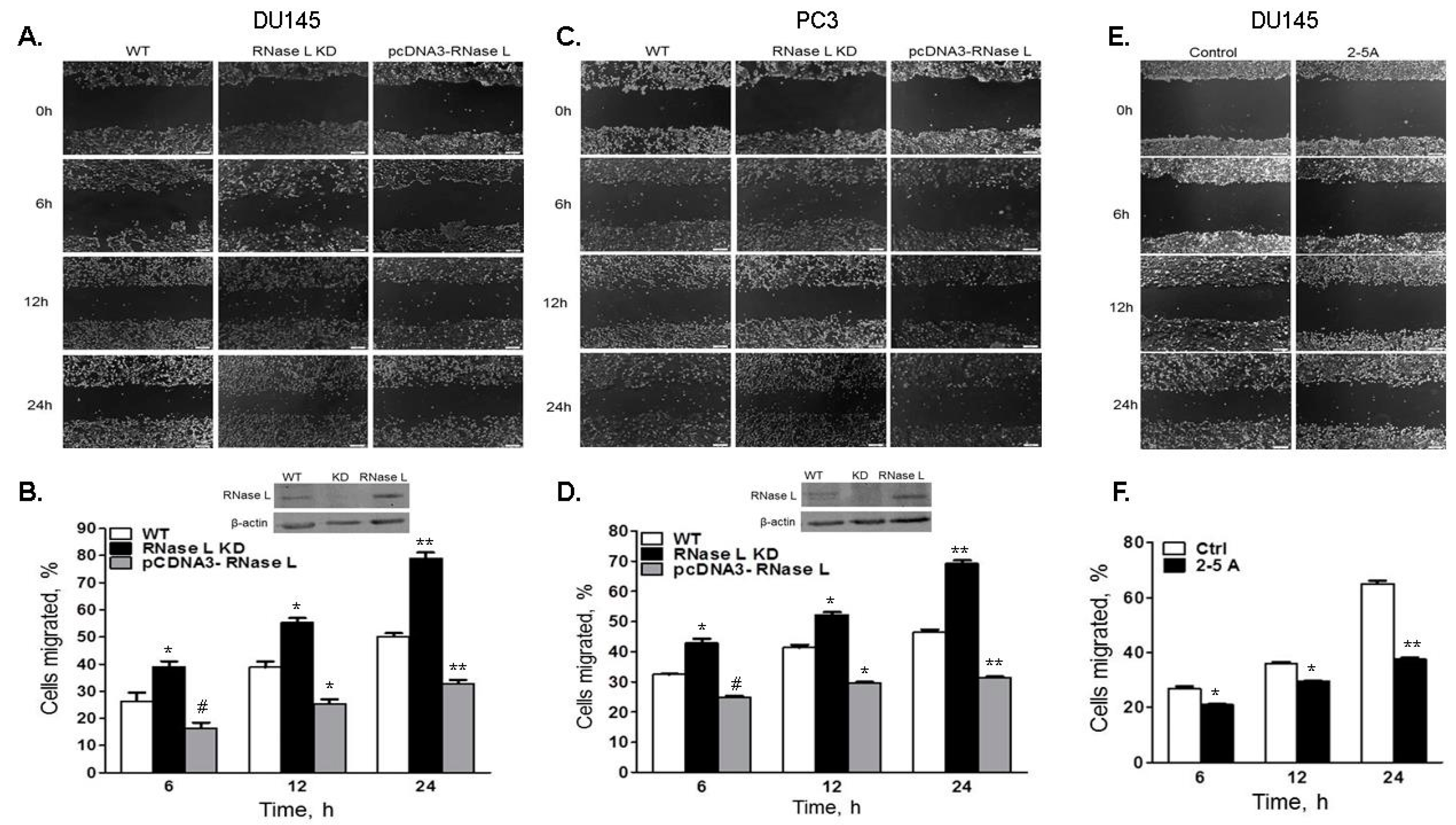
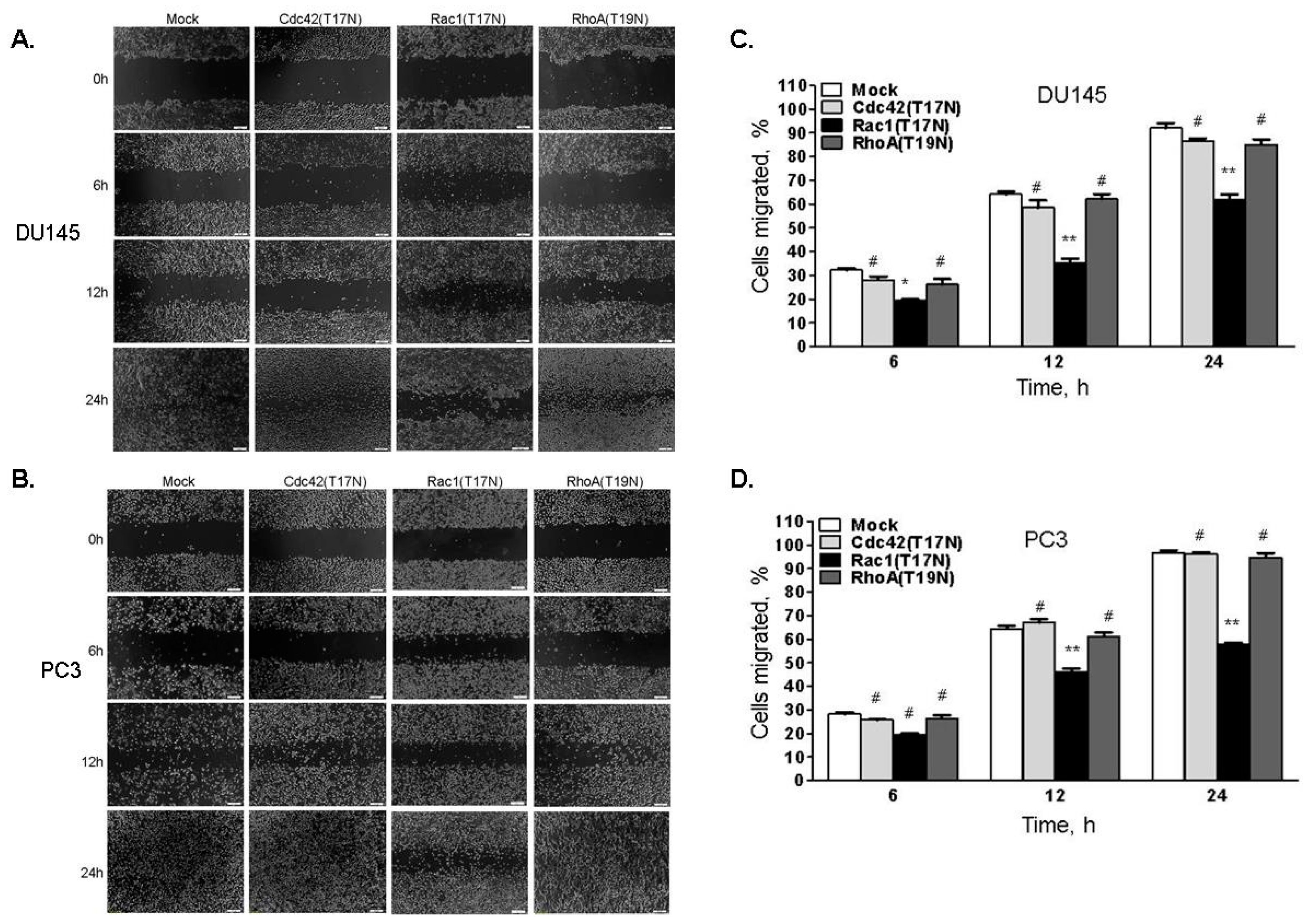
2.4. Cell Migration Is Increased in Cells with Reduced Levels of RNase L
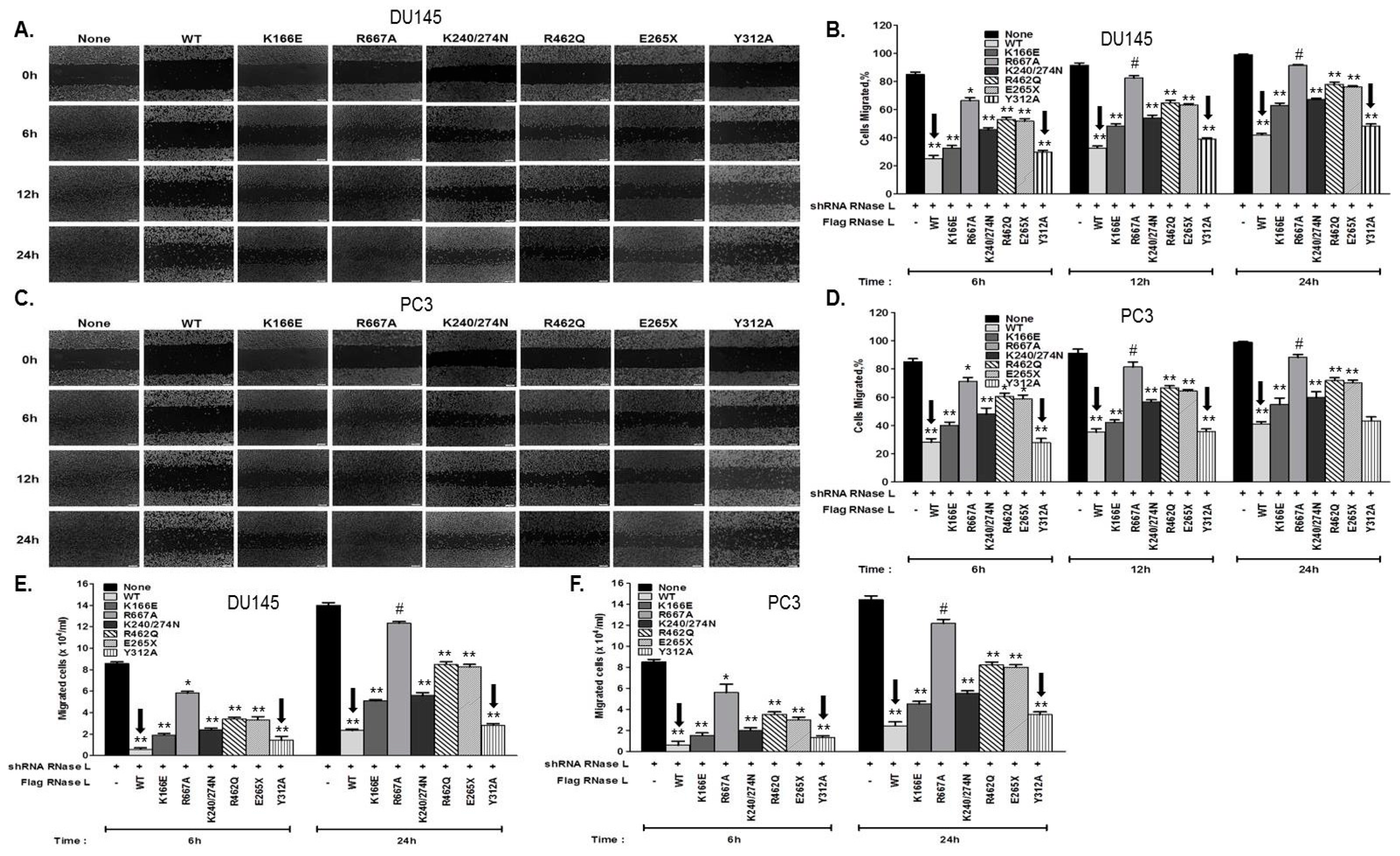
2.5. Hereditary Prostate Cancer-Associated Mutants of RNase L Promote Cell Migration
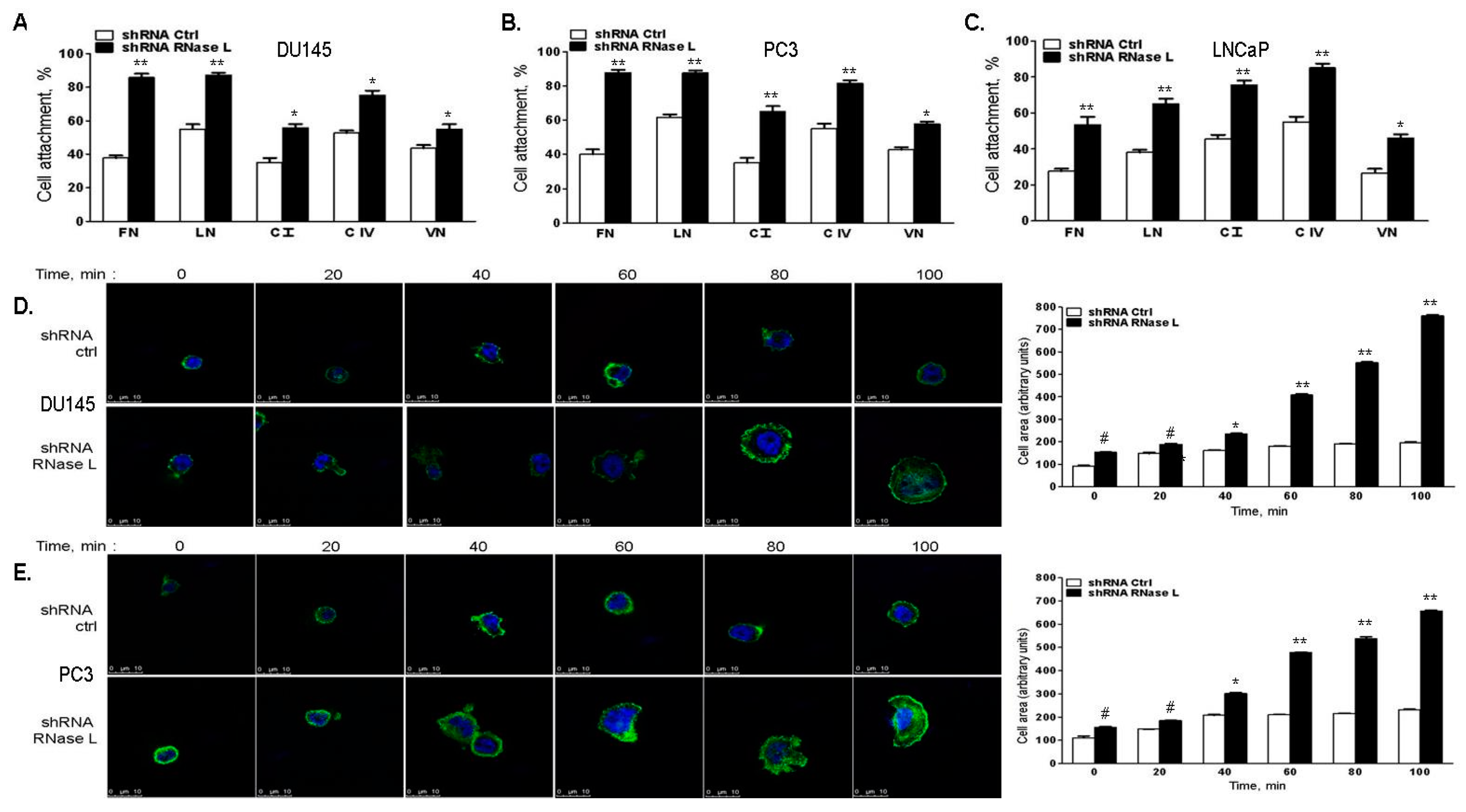
2.6. RNase L-Depletion Increases Cell Attachment and Cell Spreading
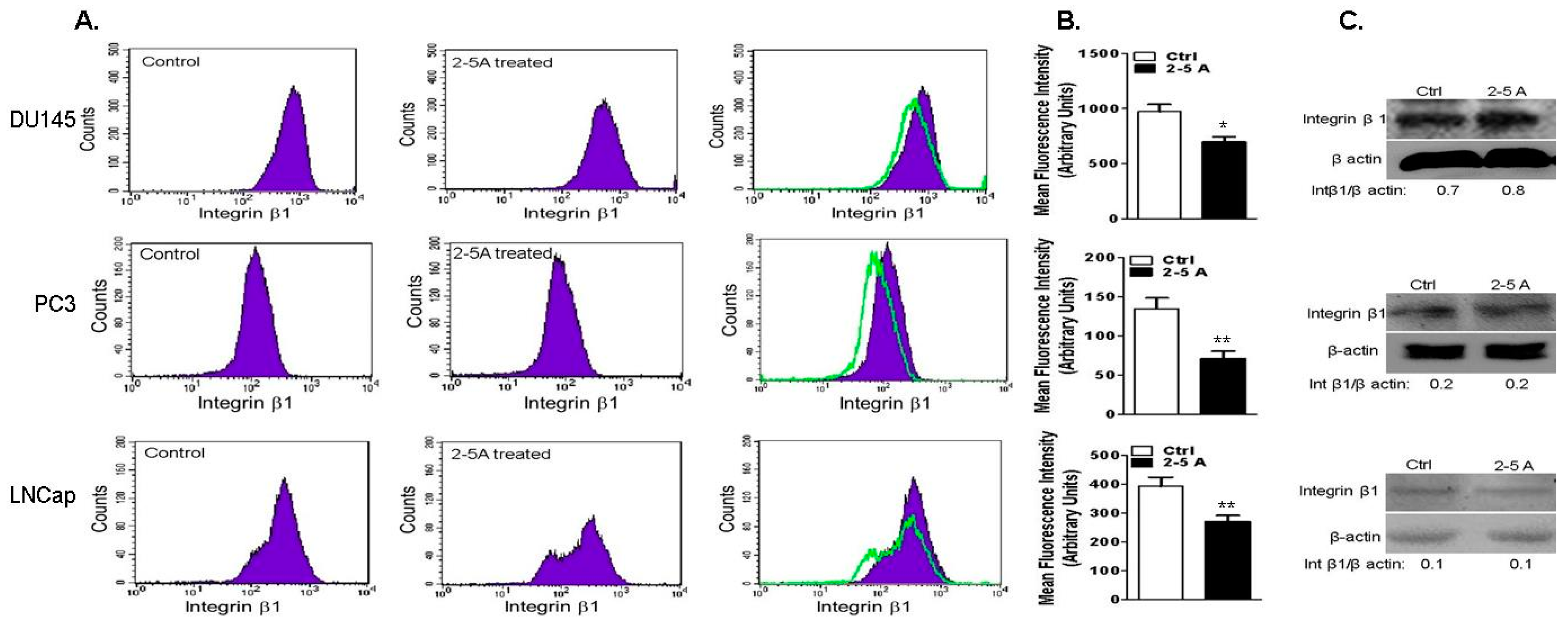
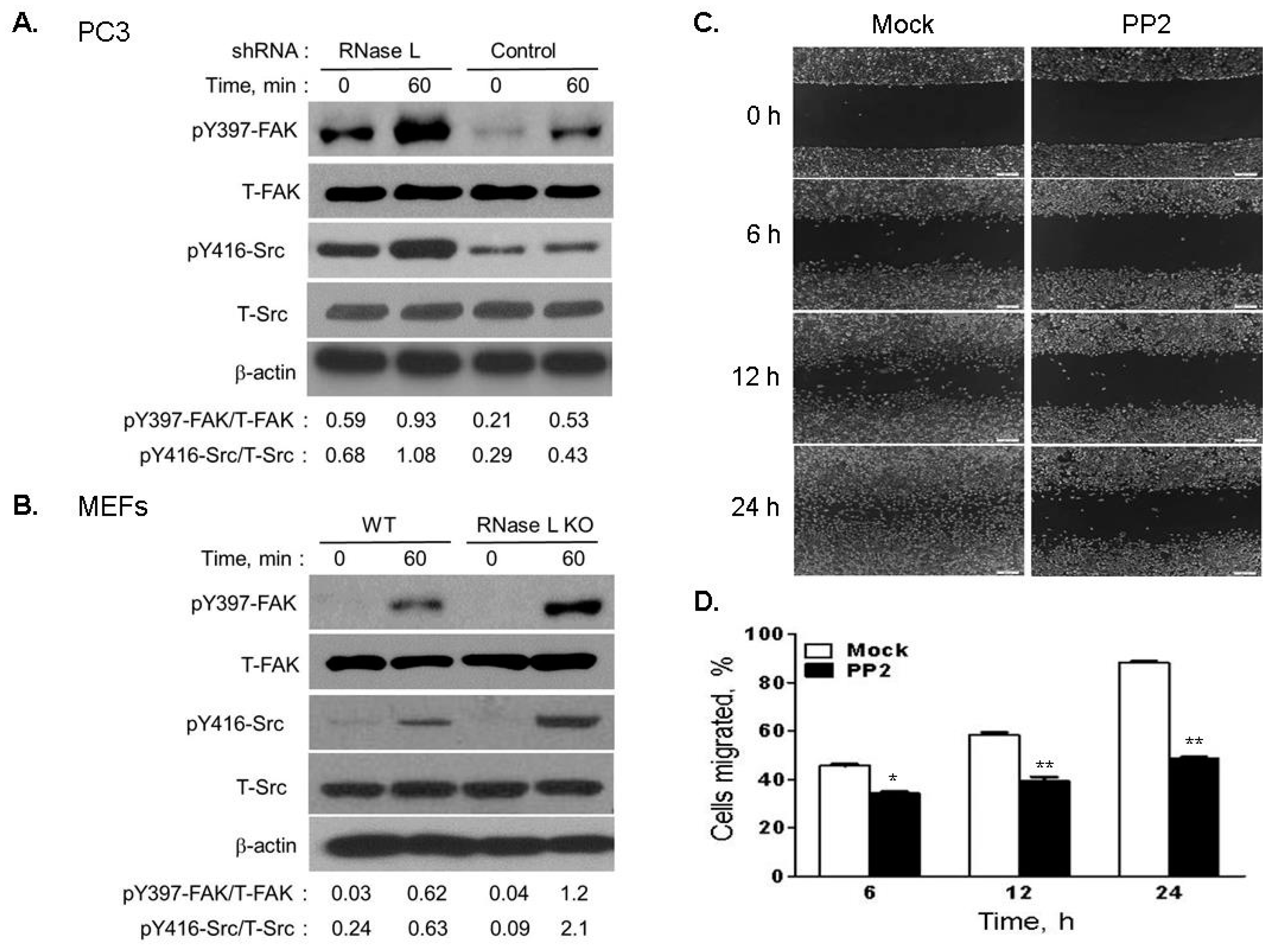
2.7. Depletion of RNase L Promotes Integrin Activation and FAK-Src Signaling in Response to Fibronection
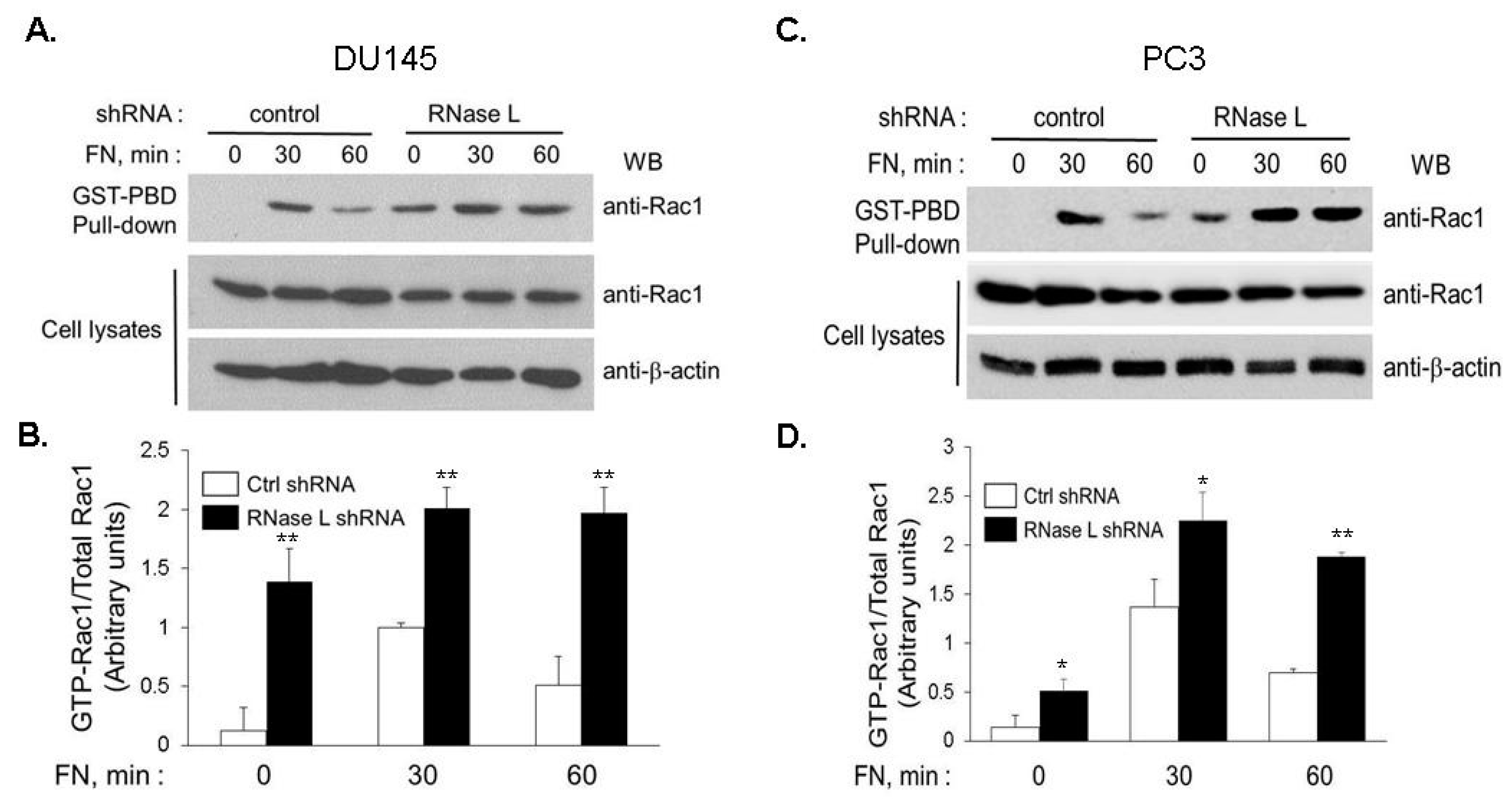
2.8. Increased Rac1 Activity Mediates Enhanced Cell Migration in RNase L-Depleted Cells
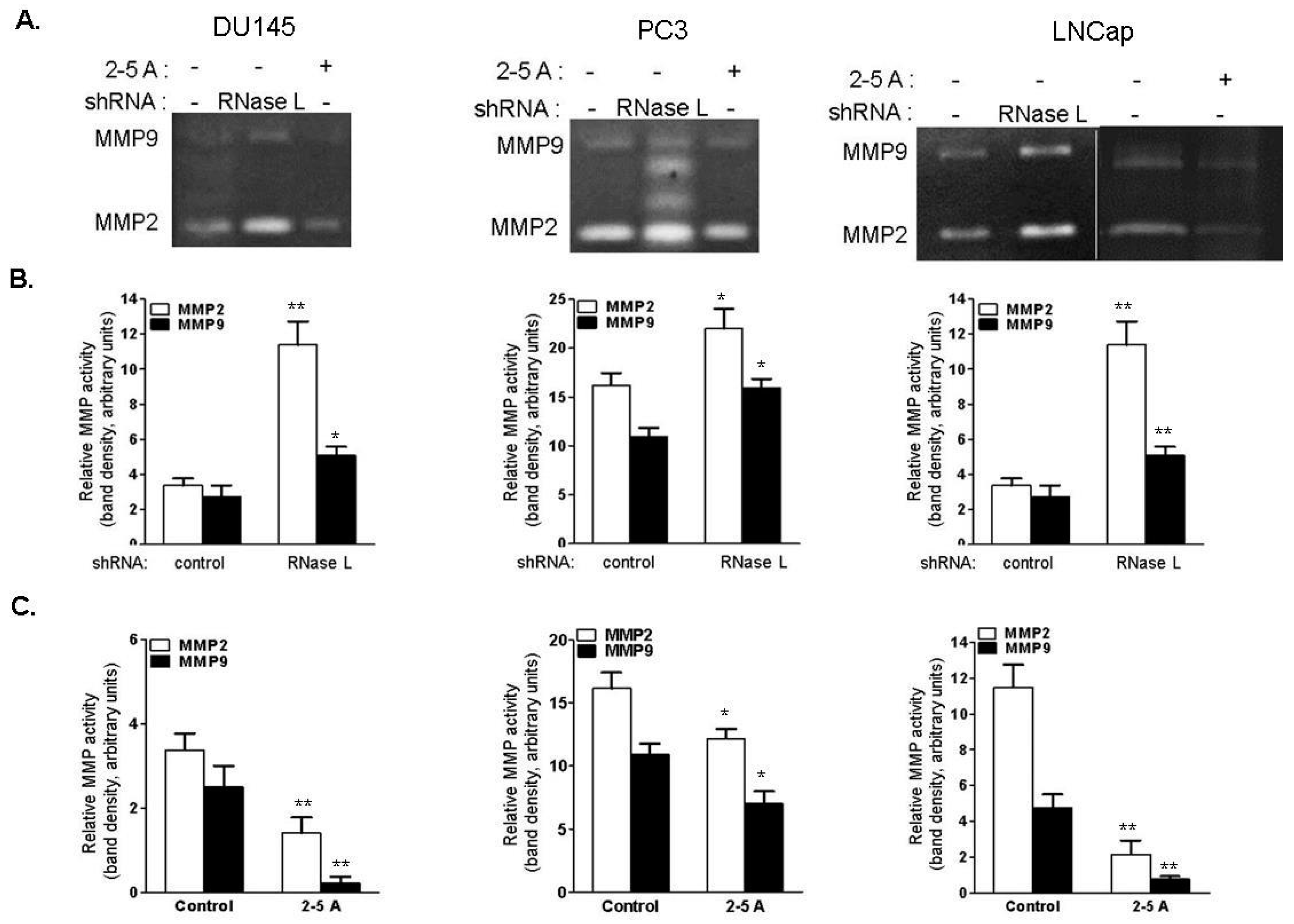
2.9. RNase L Regulates MMP-2 and MMP-9 Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture and Transfections
4.3. Plasmids
4.4. Co-Immunoprecipitation and Immunoblotting
4.5. Immunofluorescence Assays
4.6. Luciferase Reporter Gene Assays
4.7. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.8. Cell Fractionation
4.9. Wound Healing Assay
4.10. Cell Migration Assay
4.11. Cell Spreading Assay
4.12. Cell Attachment Assay
4.13. Flow Cytometry and Analysis
4.14. Rac Activity Assays
4.15. Gelatin Zymography
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borden, E.C.; Sen, G.C.; Uze, G.; Silverman, R.H.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Foster, G.R.; Stark, G.R. Interferons at age 50: Past, current and future impact on biomedicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, R.H. Viral encounters with 2′,5′-oligoadenylate synthetase and RNase L during the interferon antiviral response. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12720–12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malathi, K.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Dayal, S.; Naji, M.; Ezelle, H.J.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, A.; Hassel, B.A. RNase L interacts with filamin a to regulate actin dynamics and barrier function for viral entry. mBio 2014, 5, e02012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahmadi, W.; Al-Haj, L.; Al-Mohanna, F.A.; Silverman, R.H.; Khabar, K.S. RNase L downmodulation of the rna-binding protein, hur, and cellular growth. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Yi, X.; Zipris, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Malathi, K.; Jin, G.; Zhou, A. RNase L contributes to experimentally induced type 1 diabetes onset in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, O.; Salehzada, T.; Lambert, K.; Boo Seok, Y.; Zhou, A.; Mercier, J.; Bisbal, C. RNase L controls terminal adipocyte differentiation, lipids storage and insulin sensitivity via Chop10 mRNA regulation. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, D.D.; Stohlman, S.A.; Hinton, D.R.; Kapil, P.; Silverman, R.H.; Atkinson, R.A.; Bergmann, C.C. RNase L mediated protection from virus induced demyelination. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpten, J.; Nupponen, N.; Isaacs, S.; Sood, R.; Robbins, C.; Xu, J.; Faruque, M.; Moses, T.; Ewing, C.; Gillanders, E.; et al. Germline mutations in the ribonuclease l gene in families showing linkage with Hpc1. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, G.; Neville, P.J.; Plummer, S.J.; Xiang, Y.; Krumroy, L.M.; Klein, E.A.; Catalona, W.J.; Nupponen, N.; Carpten, J.D.; Trent, J.M.; et al. RNase L arg462gln variant is implicated in up to 13% of prostate cancer cases. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennert, H.; Bercovich, D.; Hubert, A.; Abeliovich, D.; Rozovsky, U.; Bar-Shira, A.; Soloviov, S.; Schreiber, L.; Matzkin, H.; Rennert, G.; et al. A novel founder mutation in the RNASEL gene, 471delaaag, is associated with prostate cancer in Ashkenazi jews. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokman, A.; Ikonen, T.; Seppala, E.H.; Nupponen, N.; Autio, V.; Mononen, N.; Bailey-Wilson, J.; Trent, J.; Carpten, J.; Matikainen, M.P.; et al. Germline alterations of the RNASEL gene, a candidate Hpc1 gene at 1q25, in patients and families with prostate cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Murakami, J.; Plummer, S.; Klein, E.A.; Carpten, J.D.; Trent, J.M.; Isaacs, W.B.; Casey, G.; Silverman, R.H. Effects of RNASEL mutations associated with prostate cancer on apoptosis induced by 2′,5′-oligoadenylates. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6795–6801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maier, C.; Haeusler, J.; Herkommer, K.; Vesovic, Z.; Hoegel, J.; Vogel, W.; Paiss, T. Mutation screening and association study of RNASEL as a prostate cancer susceptibility gene. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr-Urtreger, A.; Bar-Shira, A.; Bercovich, D.; Matarasso, N.; Rozovsky, U.; Rosner, S.; Soloviov, S.; Rennert, G.; Kadouri, L.; Hubert, A.; et al. RNASEL mutation screening and association study in Ashkenazi and non-Ashkenazi prostate cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklund, F.; Jonsson, B.A.; Brookes, A.J.; Stromqvist, L.; Adolfsson, J.; Emanuelsson, M.; Adami, H.O.; Augustsson-Balter, K.; Gronberg, H. Genetic analysis of the RNASEL gene in hereditary, familial, and sporadic prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7150–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malathi, K.; Paranjape, J.M.; Ganapathi, R.; Silverman, R.H. Hpc1/RNASEL mediates apoptosis of prostate cancer cells treated with 2′,5′-oligoadenylates, topoisomerase i inhibitors, and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 9144–9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, R.H. A scientific journey through the 2–5A/RNase L system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malathi, K.; Dong, B.; Gale, M., Jr.; Silverman, R.H. Small self-RNA generated by RNase L amplifies antiviral innate immunity. Nature 2007, 448, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Banerjee, S.; Franchi, L.; Loo, Y.M.; Gale, M., Jr.; Nunez, G.; Silverman, R.H. RNase L activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during viral infections. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Manivannan, P.; Malathi, K. RNase L cleavage products promote switch from autophagy to apoptosis by caspase-mediated cleavage of Beclin-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17611–17636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Gaughan, C.; Baskar, D.; Parker, Y.; Lindner, D.J.; Weiss, S.R.; Silverman, R.H. RNase L is a negative regulator of cell migration. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44360–44372. [Google Scholar]
- Rath, S.; Donovan, J.; Whitney, G.; Chitrakar, A.; Wang, W.; Korennykh, A. Human RNase L tunes gene expression by selectively destabilizing the microrna-regulated transcriptome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15916–15921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Naito, T.; Hiramoto, A.; Goda, K.; Omi, T.; Kitade, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Matsuda, A.; Fukushima, M.; Wataya, Y.; et al. Association of RNase L with a ras gtpase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 in mediating the apoptosis of a human cancer cell-line. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 4464–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezelle, H.J.; Malathi, K.; Hassel, B.A. The roles of RNase L in antimicrobial immunity and the cytoskeleton-associated innate response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, E74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettoun, D.J.; Scafonas, A.; Rutledge, S.J.; Hodor, P.; Chen, O.; Gambone, C.; Vogel, R.; McElwee-Witmer, S.; Bai, C.; Freedman, L.; et al. Interaction between the androgen receptor and RNase L mediates a cross-talk between the interferon and androgen signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38898–38901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Rath, P.C. Expression of mrna and protein-protein interaction of the antiviral endoribonuclease RNase L in mouse spleen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loy, C.J.; Sim, K.S.; Yong, E.L. Filamin-a fragment localizes to the nucleus to regulate androgen receptor and coactivator functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4562–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooso, B.A.; Vinall, R.L.; Tepper, C.G.; Savoy, R.M.; Cheung, J.P.; Singh, S.; Siddiqui, S.; Wang, Y.; Bedolla, R.G.; Martinez, A.; et al. Enhancing the effectiveness of androgen deprivation in prostate cancer by inducing Filamin A nuclear localization. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoy, R.M.; Ghosh, P.M. The dual role of filamin a in cancer: Can′t live with (too much of) it, can’t live without it. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.L.; Horbinski, C.M.; Garzotto, M.; Qian, D.Z.; Beer, T.M.; Kyprianou, N. Tubulin-targeting chemotherapy impairs androgen receptor activity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7992–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darshan, M.S.; Loftus, M.S.; Thadani-Mulero, M.; Levy, B.P.; Escuin, D.; Zhou, X.K.; Gjyrezi, A.; Chanel-Vos, C.; Shen, R.; Tagawa, S.T.; et al. Taxane-induced blockade to nuclear accumulation of the androgen receptor predicts clinical responses in metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6019–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, H.J.; Chang, C. Actin associated proteins function as androgen receptor coregulators: An implication of androgen receptor’s roles in skeletal muscle. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 111, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taplin, M.E.; Balk, S.P. Androgen receptor: A key molecule in the progression of prostate cancer to hormone independence. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 91, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karantanos, T.; Evans, C.P.; Tombal, B.; Thompson, T.C.; Montironi, R.; Isaacs, W.B. Understanding the mechanisms of androgen deprivation resistance in prostate cancer at the molecular level. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Chang, C. Endocrine mechanisms of disease: Expression and degradation of androgen receptor: Mechanism and clinical implication. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4043–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malathi, K.; Paranjape, J.M.; Bulanova, E.; Shim, M.; Guenther-Johnson, J.M.; Faber, P.W.; Eling, T.E.; Williams, B.R.; Silverman, R.H. A transcriptional signaling pathway in the IFN system mediated by 2′-5′-oligoadenylate activation of RNase L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14533–14538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zeqiraj, E.; Dong, B.; Jha, B.K.; Duffy, N.M.; Orlicky, S.; Thevakumaran, N.; Talukdar, M.; Pillon, M.C.; Ceccarelli, D.F.; et al. Dimeric structure of pseudokinase RNase L bound to 2–5A reveals a basis for interferon-induced antiviral activity. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliano, R.L.; Haskill, S. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 120, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Giancotti, F.G. Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, N.J.; Jones, P.L. Extracellular matrix and integrin signalling: The shape of things to come. Biochem. J. 1999, 339, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hunter, T. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix–a role for the focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase fak. Cell Struct. Funct. 1996, 21, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.K.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadi, A.; Bouali, M.; Dontenwill, M.; Stoeckel, H.; Takeda, K.; Ronde, P. Regulation of focal adhesion dynamics and disassembly by phosphorylation of FAK at tyrosine 397. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4415–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Mitra, S.K.; Ilic, D. Control of motile and invasive cell phenotypes by focal adhesion kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1692, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Salgado, E.G.; Lizano, S.; Sarkar, S.; Brugge, J.S.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Shattil, S.J. Src kinase activation by direct interaction with the integrin beta cytoplasmic domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13298–13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, A.F.; Eng, C.H.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Marcantonio, E.E.; Gundersen, G.G. Localized stabilization of microtubules by integrin- and FAK-facilitated rho signaling. Science 2004, 303, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.D.; Burridge, K. The on-off relationship of Rho and Rac during integrin-mediated adhesion and cell migration. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e27958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobes, C.D.; Hawkins, P.; Stephens, L.; Hall, A. Activation of the small GTP-binding proteins Rho and Rac by growth factor receptors. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hall, A. Small GTP-binding proteins and the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1994, 10, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulter, E.; Garcia-Mata, R.; Guilluy, C.; Dubash, A.; Rossi, G.; Brennwald, P.J.; Burridge, K. Regulation of Rho GTPase crosstalk, degradation and activity by Rhogdi1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgia, G.; Falsaperla, M.; Malaponte, G.; Madonia, M.; Indelicato, M.; Travali, S.; Mazzarino, M.C. Matrix metalloproteinases as diagnostic (MMP-13) and prognostic (MMP-2, MMP-9) markers of prostate cancer. Urol. Res. 2005, 33, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incorvaia, L.; Badalamenti, G.; Rini, G.; Arcara, C.; Fricano, S.; Sferrazza, C.; Di Trapani, D.; Gebbia, N.; Leto, G. MMP-2, MMP-9 and Activin A blood levels in patients with breast cancer or prostate cancer metastatic to the bone. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Fliss, A.E.; Robins, D.M.; Caplan, A.J. Hsp90 regulates androgen receptor hormone binding affinity in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 28697–28702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; Sepp-Lorenzino, L.; Nimmesgern, E.; Ouerfelli, O.; Danishefsky, S.; Rosen, N.; Hartl, F.U. Pharmacologic shifting of a balance between protein refolding and degradation mediated by hsp90. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14536–14541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Bai, S.; Hnat, A.T.; Kalman, R.I.; Minges, J.T.; Patterson, C.; Wilson, E.M. An androgen receptor NH2-terminal conserved motif interacts with the cooh terminus of the hsp70-interacting protein (chip). J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30643–30653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, S.J.; Oh, W.K. New paradigms in microtubule-mediated endocrine signaling in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Cai, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Yu, Z.; Balk, S.P. Androgen receptor functions in castration-resistant prostate cancer and mechanisms of resistance to new agents targeting the androgen axis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2815–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehm, S.M.; Schmidt, L.J.; Heemers, H.V.; Vessella, R.L.; Tindall, D.J. Splicing of a novel androgen receptor exon generates a constitutively active androgen receptor that mediates prostate cancer therapy resistance. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5469–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Jiang, R.; Linn, D.E.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Kong, X.; Melamed, J.; Tepper, C.G.; et al. A novel androgen receptor splice variant is up-regulated during prostate cancer progression and promotes androgen depletion-resistant growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Dunn, T.A.; Wei, S.; Isharwal, S.; Veltri, R.W.; Humphreys, E.; Han, M.; Partin, A.W.; Vessella, R.L.; Isaacs, W.B.; et al. Ligand-independent androgen receptor variants derived from splicing of cryptic exons signify hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Lu, C.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Gurel, M.; Tannahill, C.; Edwards, J.; Isaacs, W.B.; Nelson, P.S.; Bluemn, E.; et al. Distinct transcriptional programs mediated by the ligand-dependent full-length androgen receptor and its splice variants in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Ledet, E.; Alvarez, X.; Qi, Y.; Fu, X.; Sartor, O.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H. Androgen receptor Splice variants circumvent ar blockade by microtubule-targeting agents. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23358–23371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioeli, D.; Paschal, B.M. Post-translational modification of the androgen receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 352, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.K.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.C.; Altuwaijri, S.; Chang, C. Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitylation and degradation of androgen receptor by Akt require MDM2 E3 ligase. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4037–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Tripathi, M.; Mishra, R.; Sahgal, N.; Fazli, L.; Ettinger, S.; Placzek, W.J.; Claps, G.; Chung, L.W.; Bowtell, D.; et al. The e3 ubiquitin ligase siah2 contributes to castration-resistant prostate cancer by regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Shimelis, H.; Linn, D.E.; Jiang, R.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Guo, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; et al. Regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity and specificity by Rnf6-induced ubiquitination. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Donovan, J.; Rath, S.; Whitney, G.; Chitrakar, A.; Korennykh, A. Structure of human RNase L reveals the basis for regulated RNA decay in the IFN response. Science 2014, 343, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Hassel, B.A.; Silverman, R.H. Expression cloning of 2–5a-dependent RNaase: A uniquely regulated mediator of interferon action. Cell 1993, 72, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tnani, M.; Aliau, S.; Bayard, B. Localization of a molecular form of interferon-regulated RNase l in the cytoskeleton. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998, 18, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timpson, P.; Jones, G.E.; Frame, M.C.; Brunton, V.G. Coordination of cell polarization and migration by the rho family GTPases requires src tyrosine kinase activity. Curr. Biol. CB 2001, 11, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engers, R.; Ziegler, S.; Mueller, M.; Walter, A.; Willers, R.; Gabbert, H.E. Prognostic relevance of increased Rac GTPase expression in prostate carcinomas. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquemet, G.; Morgan, M.R.; Byron, A.; Humphries, J.D.; Choi, C.K.; Chen, C.S.; Caswell, P.T.; Humphries, M.J. Rac1 is deactivated at integrin activation sites through an Iqgap1-Filamin-A-Racgap1 pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4121–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Chippada-Venkata, U.D.; Oh, W.K. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their natural inhibitors in prostate cancer progression. Cancers 2014, 6, 1298–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Malathi, K. Rnase L induces autophagy via c-Jun N-terminal kinase and double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43651–43664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Hsieh, C.L.; Omwancha, J.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, S.Y.; Baert, J.L.; Shemshedini, L. Etv1 is a novel androgen receptor-regulated gene that mediates prostate cancer cell invasion. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilluy, C.; Dubash, A.D.; Garcia-Mata, R. Analysis of RhoA and Rho gef activity in whole cells and the cell nucleus. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 2050–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Dayal, S.; Ayoub, Y.Z.; Malathi, K. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines induced by toll-like receptor 9 agonists in prostate cancer cells. J. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 7, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Primer Name | Sequence of Primer |
|---|---|
| K274N R | 5′-CAAGCAGCAGTGCTGTATTGCCATCACTGTCTGTG-3′ |
| K274N F | 5′-CACAGACAGTGATGGCAATACAGCACTGCTGCTTG-3′ |
| K240N R | 5′-GGATCAGGGGAGTATTCCCTCTTTCTCCCC-3′ |
| K240N F | 5′-GGGGAGAAAGAGGGAATACTCCCCTGATCC-3′ |
| R667A R | 5′-CAATGTGTTCTCCCAAATTCGCGATGAACTTTAGCAGATCAC-3′ |
| R667A F | 5′-GTGATCTGCTAAAGTTCATCGCGAATTTGGGAGAACACATTG-3′ |
| R462Q R | 5′-TAAATATAGATGACAGGACATTTTGGGCAAATTCATCTTCCTCATTT-3′ |
| R462Q F | 5′-AAATGAGGAAGATGAATTTGCCCAAAATGTCCTGTCATCTATATTTA-3′ |
| E265X R | 5′-CTGTGTCATTAATCTATATGTGCTCTTGCTCCAGAAGC-3′ |
| E265X F | 5′-GCTTCTGGAGCAAGAGCACATATAGATTAATGACACAG-3′ |
| K166E F | 5′-AGAGCGGCTGAGGGAGGGAGGGGCCACAG-3′ |
| K166E R | 5′-CTGTGGCCCCTCCCTCCCTCAGCCGCTCT-3′ |
| Y312A R | 5′-CAAGGGAATGGTCAGCATTCCGCCTCGCTGTCATAACAAGAT-3′ |
| Y312A F | 5′-ATCTTGTTATGACAGCGAGGCGGAATGCTGACCATTCCCTTG-3′ |
| Primer Name | Sequence of Primer |
|---|---|
| PSA F | 5′-GCAGCATTGAACCAGAGGAG-3′ |
| PSA R | 5′-CCCATGACGTGATACCCTGA-3′ |
| sGCα1 F | 5′-CTGCCTCATTTGCTTCATCA-3′ |
| sGCα1 R | 5′-TTGCCATGCTGAGCTGTTTA-3′ |
| ETV1 F | 5′-CACTGGGTCGTGGTACTCCT-3′ |
| ETV1 R | 5′-TACCCCATGGACCACAGATT-3′ |
| MMP9 F | 5′-GCCATTCACGTCGTCCTTAT-3′ |
| MMP9 R | 5′-TTGACAGCGACAAGAAGTGG-3′ |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dayal, S.; Zhou, J.; Manivannan, P.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Ahmad, O.F.; Clark, M.; Awadia, S.; Garcia-Mata, R.; Shemshedini, L.; Malathi, K. RNase L Suppresses Androgen Receptor Signaling, Cell Migration and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030529
Dayal S, Zhou J, Manivannan P, Siddiqui MA, Ahmad OF, Clark M, Awadia S, Garcia-Mata R, Shemshedini L, Malathi K. RNase L Suppresses Androgen Receptor Signaling, Cell Migration and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030529
Chicago/Turabian StyleDayal, Shubham, Jun Zhou, Praveen Manivannan, Mohammad Adnan Siddiqui, Omaima Farid Ahmad, Matthew Clark, Sahezeel Awadia, Rafael Garcia-Mata, Lirim Shemshedini, and Krishnamurthy Malathi. 2017. "RNase L Suppresses Androgen Receptor Signaling, Cell Migration and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030529
APA StyleDayal, S., Zhou, J., Manivannan, P., Siddiqui, M. A., Ahmad, O. F., Clark, M., Awadia, S., Garcia-Mata, R., Shemshedini, L., & Malathi, K. (2017). RNase L Suppresses Androgen Receptor Signaling, Cell Migration and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030529







