Changes in Brain Monoamines Underlie Behavioural Disruptions after Zebrafish Diet Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Environmental Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
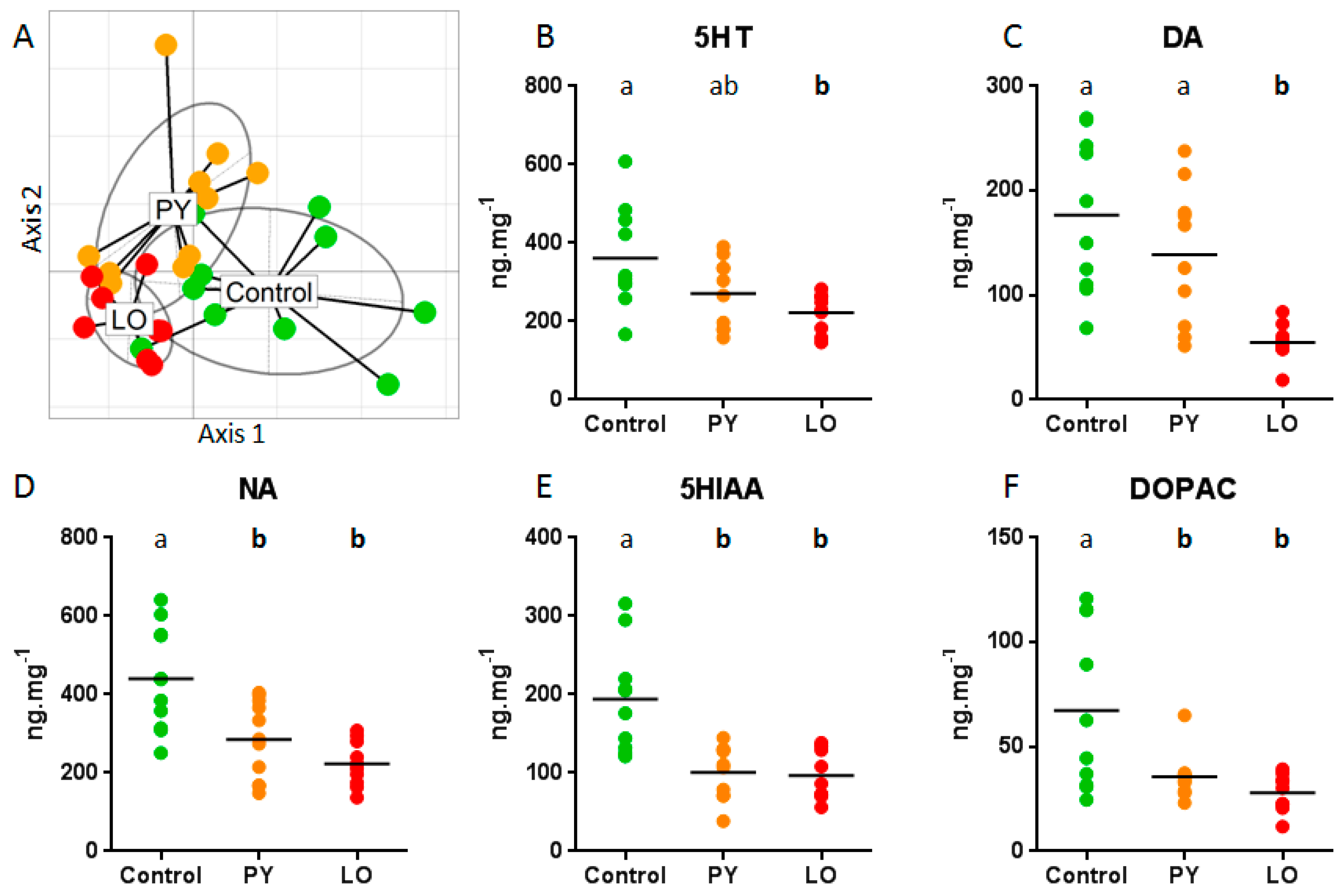
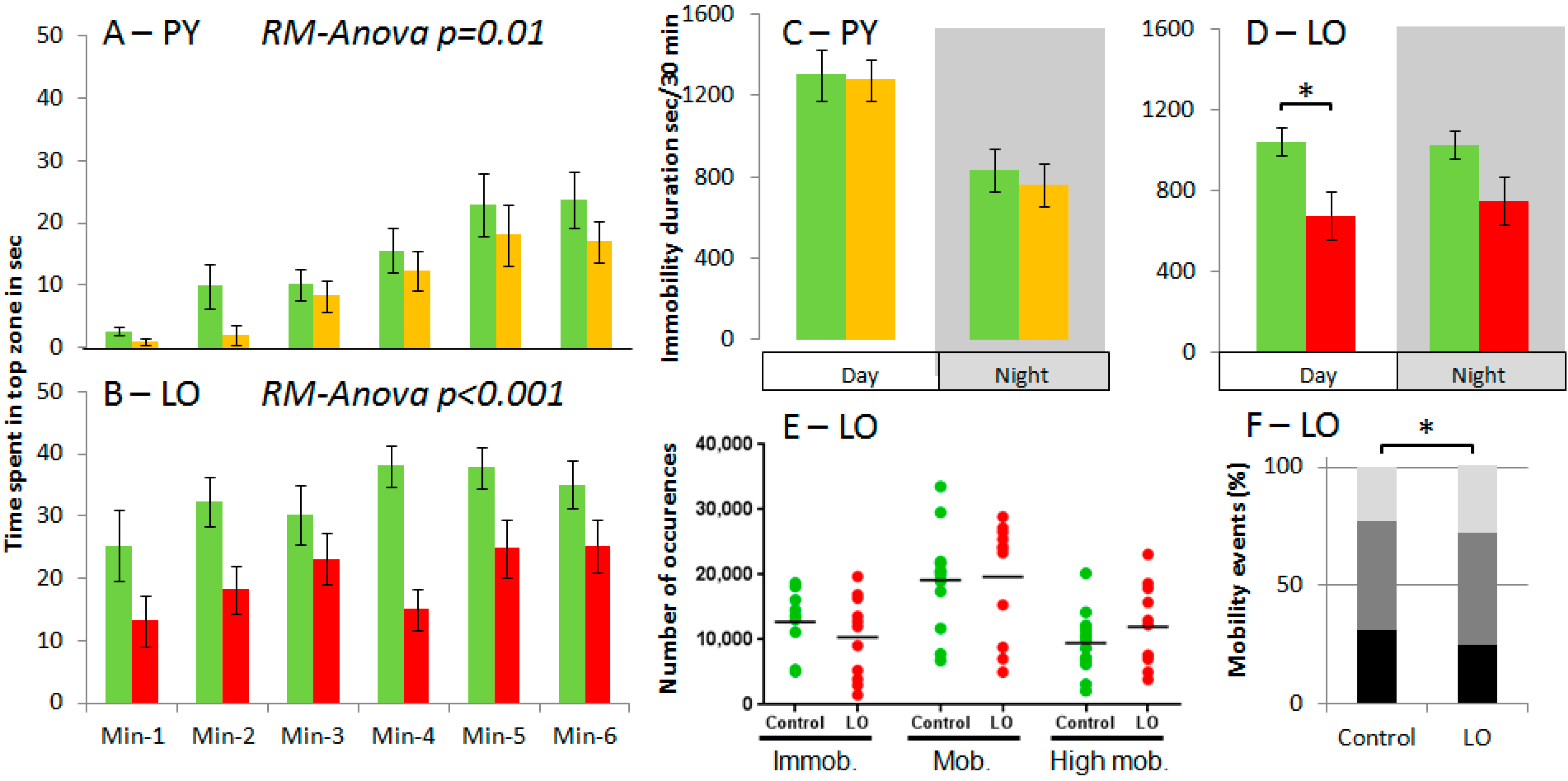
2. Results and Discussion
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Diet Preparation
3.2. Fish Exposure
3.3. Behaviour Analysis
3.4. HPLC Analysis of Whole Brain
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, D.S.; Eisenhofer, G.; McCarty, R. Catecholamines: Bridging Basic Science with Clinical Medicine; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; Volume 42, p. 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, E.D.; Kalueff, A.V.; Gerlai, R.T. Perspectives on zebrafish neurobehavioral pharmacology. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 139, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; da Silva Batista, A.W.; Herculano, A.M.; Morato, S.; Gouveia, A., Jr. Measuring anxiety in zebrafish: A critical review. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, W.; Bally-Cuif, L. Adult zebrafish as a model organism for behavioural genetics. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillesaar, C. The serotonergic system in fish. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Vernier, P. The evolution of dopamine systems in chordates. Front. Neuroanat. 2011, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winberg, S.; Nilsson, G.E. Roles of brain monoamine neurotransmitters in agonistic behaviour and stress reactions, with particular reference to fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1993, 106, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignet, C.; Le Menach, K.; Lyphout, L.; Guionnet, T.; Frere, L.; Leguay, D.; Budzinski, H.; Cousin, X.; Begout, M.L. Chronic dietary exposure to pyrolytic and petrogenic mixtures of PAHs causes physiological disruption in zebrafish--part II: Behavior. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 13818–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pean, S.; Daouk, T.; Vignet, C.; Lyphout, L.; Leguay, D.; Loizeau, V.; Begout, M.L.; Cousin, X. Long-term dietary-exposure to non-coplanar PCBs induces behavioral disruptions in adult zebrafish and their offspring. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2013, 39, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotto, J.W.; Cognato, G.P.; Christoff, R.R.; Roesler, L.N.; Leite, C.E.; Kist, L.W.; Bogo, M.R.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Long-term exposure to paraquat alters behavioral parameters and dopamine levels in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Zebrafish 2014, 11, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazer, L.; Hahn, M.E.; Aluru, N. Delayed effects of developmental exposure to low levels of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist 3,3',4,4',5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126) on adult zebrafish behavior. Neurotoxicology 2016, 52, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, S.T.; Remick, D.; Creton, R.; Colwill, R.M. Effects of embryonic exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) on anxiety-related behaviors in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, L.; Mandrell, D.; Mandrell, R.; Simonich, M.; Tanguay, R.L. A rapid throughput approach identifies cognitive deficits in adult zebrafish from developmental exposure to polybrominated flame retardants. Neurotoxicology 2014, 43, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravato, C.; Guilhermino, L. Effects of benzo(a)pyrene on seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.): Biomarkers, growth and behavior. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess.: Int. J. 2009, 15, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Gravato, C.; Guilhermino, L. Acute toxic effects of pyrene on Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei, Gobiidae): Mortality, biomarkers and swimming performance. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 19, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R.; Bailey, J.M.; Oliveri, A.N.; Levin, E.D.; di Giulio, R.T. Developmental exposure to a complex pah mixture causes persistent behavioral effects in naive Fundulus heteroclitus (killifish) but not in a population of PAH-adapted killifish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knecht, A.L.; Truong, L.; Simonich, M.T.; Tanguay, R.L. Developmental benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) exposure impacts larval behavior and impairs adult learning in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 59, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, Q.; Han, J.; Guo, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhou, B. The developmental neurotoxicity of polybrominated diphenyl ethers: Effect of DE-71 on dopamine in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesto, M.; Soengas, J.L.; Miguez, J.M. Acute and prolonged stress responses of brain monoaminergic activity and plasma cortisol levels in rainbow trout are modified by PAHs (naphthalene, beta-naphthoflavone and benzo(a)pyrene) treatment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 86, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesto, M.; Tintos, A.; Soengas, J.L.; Miguez, J.M. β-naphthoflavone and benzo(a)pyrene alter dopaminergic, noradrenergic, and serotonergic systems in brain and pituitary of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesto, M.; Tintos, A.; Alvarez, R.; Soengas, J.L.; Miguez, J.M. Alterations in the brain monoaminergic neurotransmitters of rainbow trout related to naphthalene exposure at the beginning of vitellogenesis. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesto, M.; Tintos, A.; Soengas, J.L.; Miguez, J.M. Effects of acute and prolonged naphthalene exposure on brain monoaminergic neurotransmitters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 144, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledge, D.; Yen, J.; Morton, T.; Dishaw, L.; Petro, A.; Donerly, S.; Linney, E.; Levin, E.D. Critical duration of exposure for developmental chlorpyrifos-induced neurobehavioral toxicity. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddins, D.; Cerutti, D.; Williams, P.; Linney, E.; Levin, E.D. Zebrafish provide a sensitive model of persisting neurobehavioral effects of developmental chlorpyrifos exposure: Comparison with nicotine and pilocarpine effects and relationship to dopamine deficits. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Wang, X.; Zuo, Z.; Cai, J.; Wang, C. Tributyltin exposure influences predatory behavior, neurotransmitter content and receptor expression in Sebastiscus marmoratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 128–129, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hylland, K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) ecotoxicology in marine ecosystems. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, D.; Li, W.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Global atmospheric emissions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from 1960 to 2008 and future predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Metre, P.C.; Mahler, B.J. Trends in hydrophobic organic contaminants in urban and reference lake sediments across the uUnited States, 1970–2001. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5567–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, L.H. The source of U.S. EPA's sixteen PAH priority pollutants. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.T.; Achten, C. Time to say goodbye to the 16 EPA PAHs? Toward an up-to-date use of pacs for environmental purposes. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 330–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Z. Chronic exposure to low benzo[a]pyrene level causes neurodegenerative disease-like syndromes in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 167, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignet, C.; Le Menach, K.; Mazurais, D.; Lucas, J.; Perrichon, P.; Le Bihanic, F.; Devier, M.H.; Lyphout, L.; Frere, L.; Begout, M.L.; et al. Chronic dietary exposure to pyrolytic and petrogenic mixtures of PAHs causes physiological disruption in zebrafish—Part I: Survival and growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 13804–13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, J.R.; Driskell, W.B.; Short, J.W.; Larsen, M.L. Long term monitoring for oil in the Exxon valdez spill region. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 2067–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachot, J.; Geffard, O.; Augagneur, S.; Lacroix, S.; Le Menach, K.; Peluhet, L.; Couteau, J.; Denier, X.; Devier, M.H.; Pottier, D.; et al. Evidence of genotoxicity related to high PAH content of sediments in the upper part of the Seine estuary (Normandy, France). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 79, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephanou, P.; Konstandi, M.; Pappas, P.; Marselos, M. Alterations in central monoaminergic neurotransmission induced by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rats. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 23, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstandi, M.; Harkitis, P.; Thermos, K.; Ogren, S.O.; Johnson, E.O.; Tzimas, P.; Marselos, M. Modification of inherent and drug-induced dopaminergic activity after exposure to benzo(α)pyrene. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.; Bonnieux, A.; Lyphout, L.; Cousin, X.; Miramand, P.; Lefrancois, C. Trophic contamination by pyrolytic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons does not affect aerobic metabolic scope in zebrafish Danio rerio. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.; Percelay, I.; Larcher, T.; Lefrancois, C. Effects of pyrolytic and petrogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on swimming and metabolic performance of zebrafish contaminated by ingestion. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 132, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackerman, J.; Donegan, J.J.; Cunningham, C.S.; Nguyen, N.N.; Lawless, K.; Long, A.; Benno, R.H.; Gould, G.G. Zebrafish behavior in novel environments: Effects of acute exposure to anxiolytic compounds and choice of Danio rerio line. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2010, 23, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Wu, N.; Cachat, J.; Hart, P.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K.; Utterback, E.; Gilder, T.; Kyzar, E.; Newman, A.; et al. Pharmacological modulation of anxiety-like phenotypes in adult zebrafish behavioral models. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesto, M.; Tintos, A.; Rodriguez-Illamola, A.; Soengas, J.L.; Miguez, J.M. Effects of naphthalene, β -naphthoflavone and benzo(a)pyrene on the diurnal and nocturnal indoleamine metabolism and melatonin content in the pineal organ of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, I.D.; Zhu, L.; Moquin, L.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Gratton, A.; Giros, B.; Storch, K.F. A highly tunable dopaminergic oscillator generates ultradian rhythms of behavioral arousal. eLife 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crépeaux, G.; Bouillaud-Kremarik, P.; Sikhayeva, N.; Rychen, G.; Soulimani, R.; Schroeder, H. Late effects of a perinatal exposure to a 16 PAH mixture: Increase of anxiety-related behaviours and decrease of regional brain metabolism in adult male rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crépeaux, G.; Bouillaud-Kremarik, P.; Sikhayeva, N.; Rychen, G.; Soulimani, R.; Schroeder, H. Exclusive prenatal exposure to a 16 PAH mixture does not impact anxiety-related behaviours and regional brain metabolism in adult male rats: A role for the period of exposure in the modulation of pah neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 221, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedrychowski, W.; Whyatt, R.M.; Camann, D.E.; Bawle, U.V.; Peki, K.; Spengler, J.D.; Dumyahn, T.S.; Penar, A.; Perera, F.F. Effect of prenatal PAH exposure on birth outcomes and neurocognitive development in a cohort of newborns in Poland. Study design and preliminary ambient data. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2003, 16, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perera, F.P.; Tang, D.; Wang, S.; Vishnevetsky, J.; Zhang, B.; Diaz, D.; Camann, D.; Rauh, V. Prenatal polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) exposure and child behavior at age 6–7 years. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignet, C.; Devier, M.H.; Le Menach, K.; Lyphout, L.; Potier, J.; Cachot, J.; Budzinski, H.; Begout, M.L.; Cousin, X. Long-term disruption of growth, reproduction, and behavior after embryonic exposure of zebrafish to PAH-spiked sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 13877–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Cheng, S.; He, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, H.; He, L.; Lu, T.; Tu, B.; Wang, Y. Effects of subchronic exposure to benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) on learning and memory, and neurotransmitters in male Sprague-Dawley rat. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazeas, L.; Budzinski, H. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon 13C/12C ratio measurement in petroleum and marine sediments application to standard reference materials and a sediment suspected of contamination from the Erika oil spill. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 923, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeas, L.; Budzinski, H. Improved accuracy of GC-MS quantification of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediments and petroleums. Validation on reference matrices and application to the Erika oil spill. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2002, 82, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Gerlai, R. High precision liquid chromatography analysis of dopaminergic and serotoninergic responses to acute alcohol exposure in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 200, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolédec, S.; Chessel, D. Rythmes Saisonniers et Composantes Stationnelles en Milieu Aquatique. I: Description d'un Plan D'observation Complet par Projection de Variables; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1987; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.-B. The ade4 package: Implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Siber-Chicot, A. An s4 Lattice-Based Package for the Representation of Multivariate Data, R package version 1.0-5; The Comprehensive R Archive Network: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bathke, A.C.; Harrar, S.W.; Madden, L.V. How to compare small multivariate samples using nonparametric tests. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 4951–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.V. Least-squares means: The R package lsmeans. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 69, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vignet, C.; Trenkel, V.M.; Vouillarmet, A.; Bricca, G.; Bégout, M.-L.; Cousin, X. Changes in Brain Monoamines Underlie Behavioural Disruptions after Zebrafish Diet Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Environmental Mixtures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030560
Vignet C, Trenkel VM, Vouillarmet A, Bricca G, Bégout M-L, Cousin X. Changes in Brain Monoamines Underlie Behavioural Disruptions after Zebrafish Diet Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Environmental Mixtures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030560
Chicago/Turabian StyleVignet, Caroline, Verena M. Trenkel, Annick Vouillarmet, Giampiero Bricca, Marie-Laure Bégout, and Xavier Cousin. 2017. "Changes in Brain Monoamines Underlie Behavioural Disruptions after Zebrafish Diet Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Environmental Mixtures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030560
APA StyleVignet, C., Trenkel, V. M., Vouillarmet, A., Bricca, G., Bégout, M.-L., & Cousin, X. (2017). Changes in Brain Monoamines Underlie Behavioural Disruptions after Zebrafish Diet Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Environmental Mixtures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030560






