Evolution of Fish Let-7 MicroRNAs and Their Expression Correlated to Growth Development in Blunt Snout Bream
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
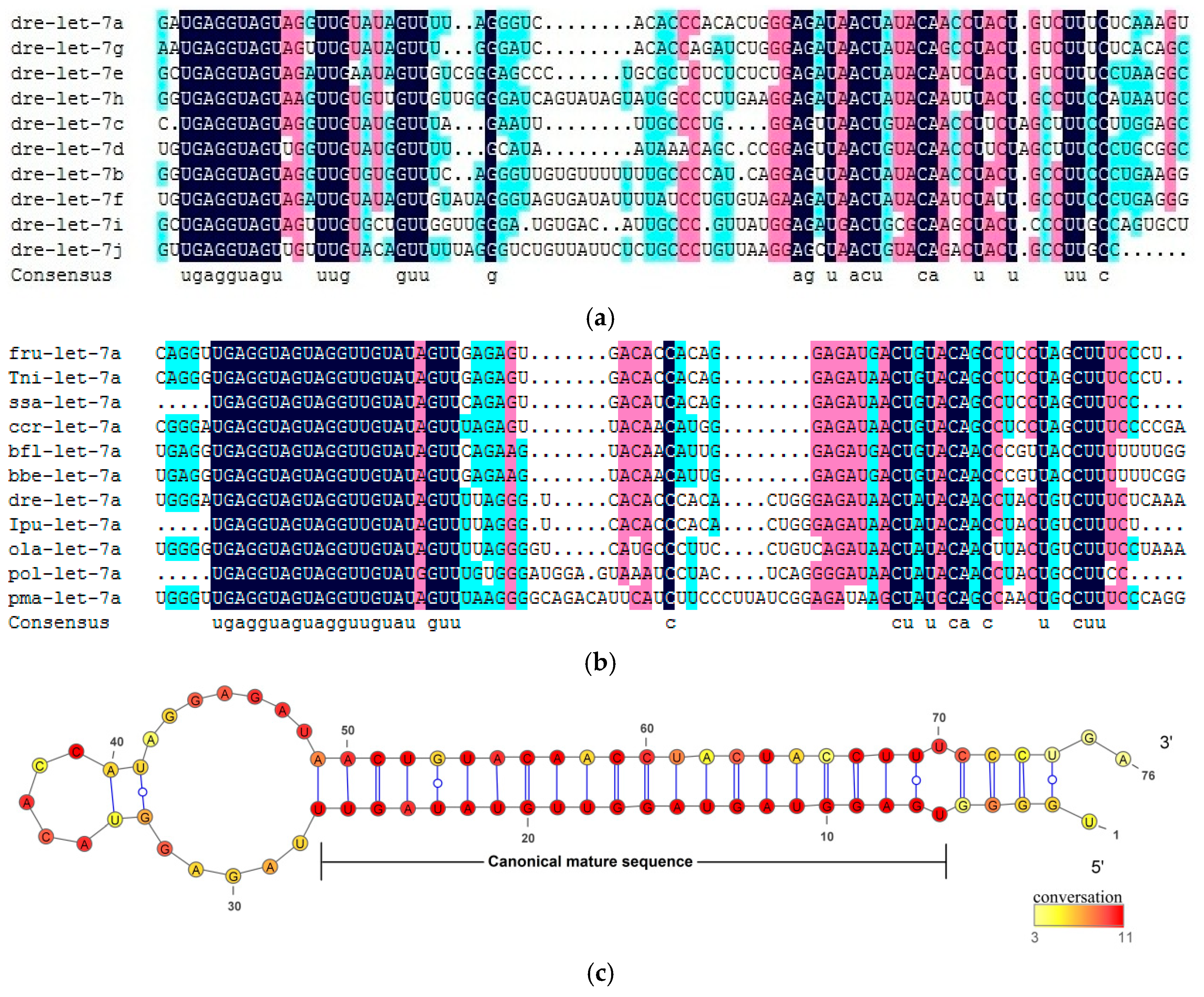
2.1. Conserved Characteristics of Let-7 miRNAs in Fish
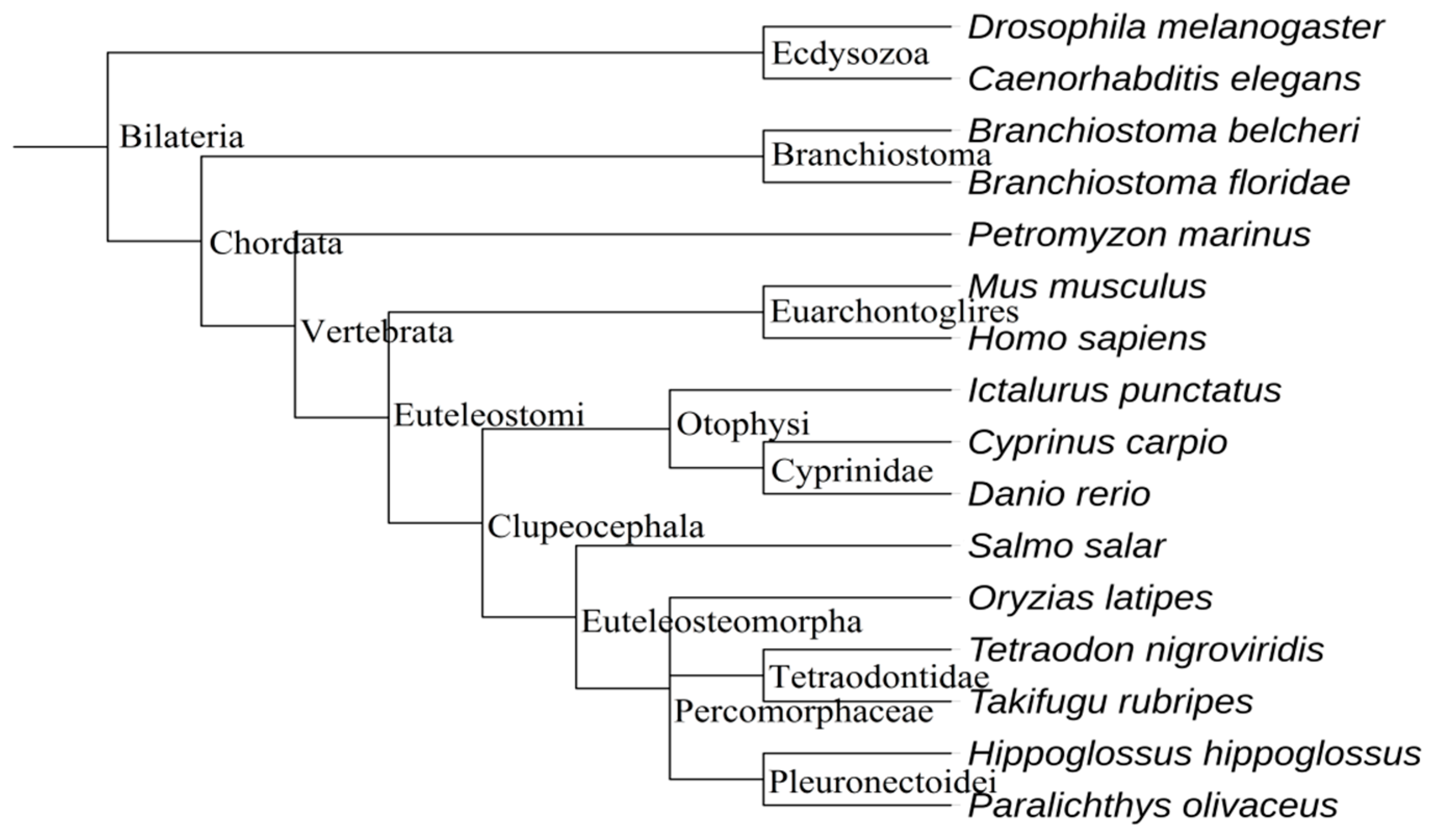
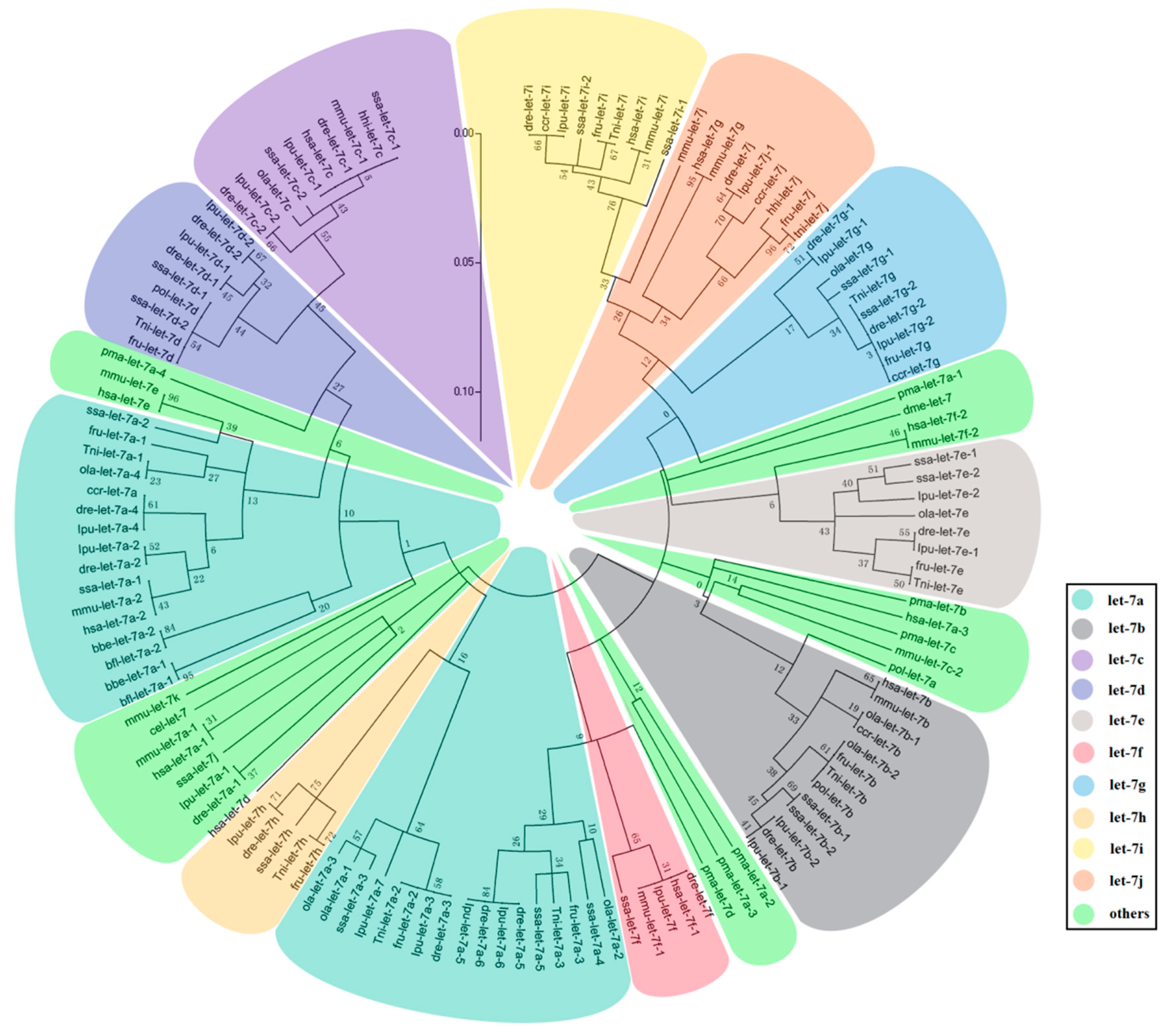
2.2. The Evolution of Let-7 miRNAs in Fish
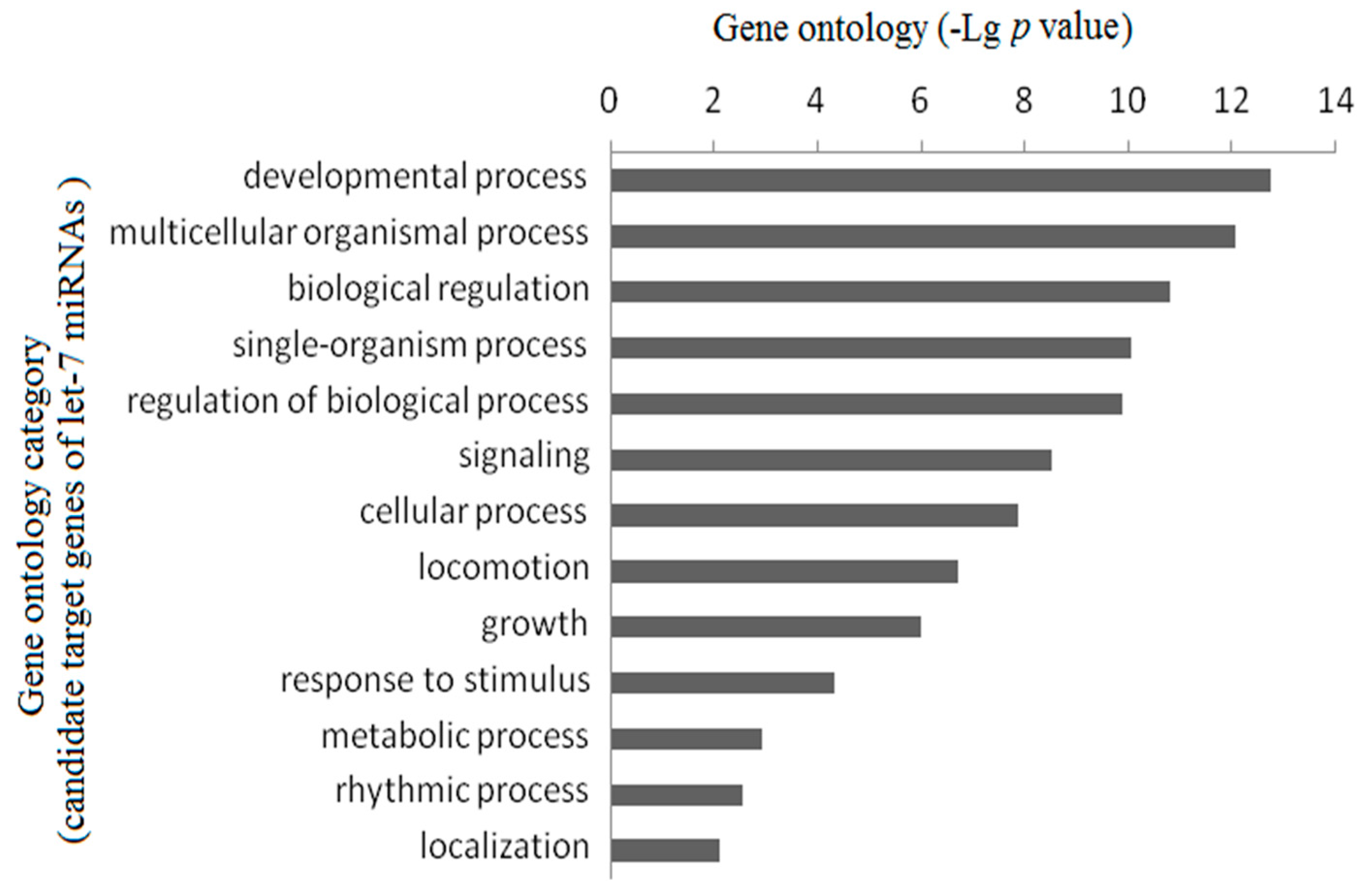
2.3. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
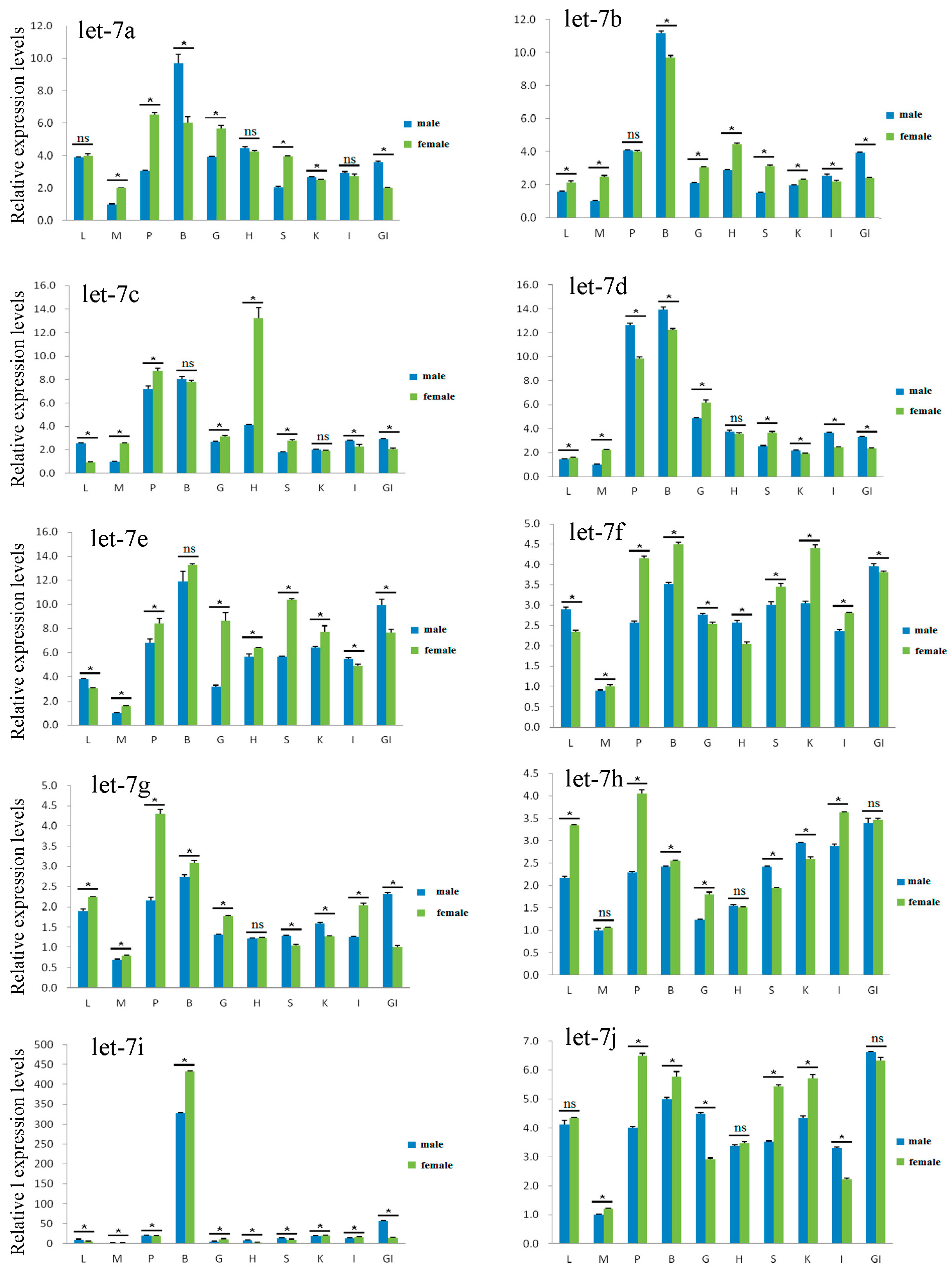
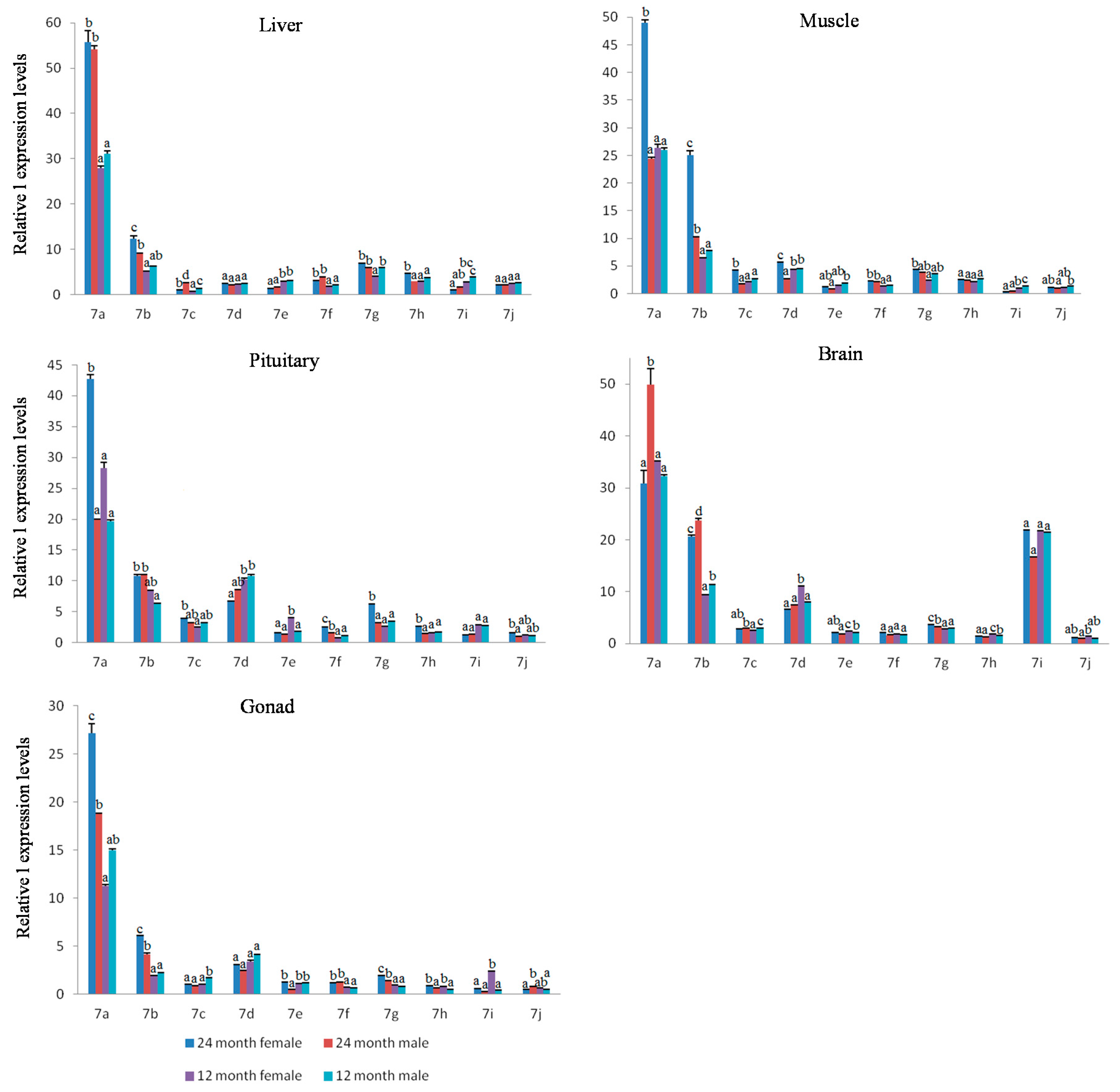
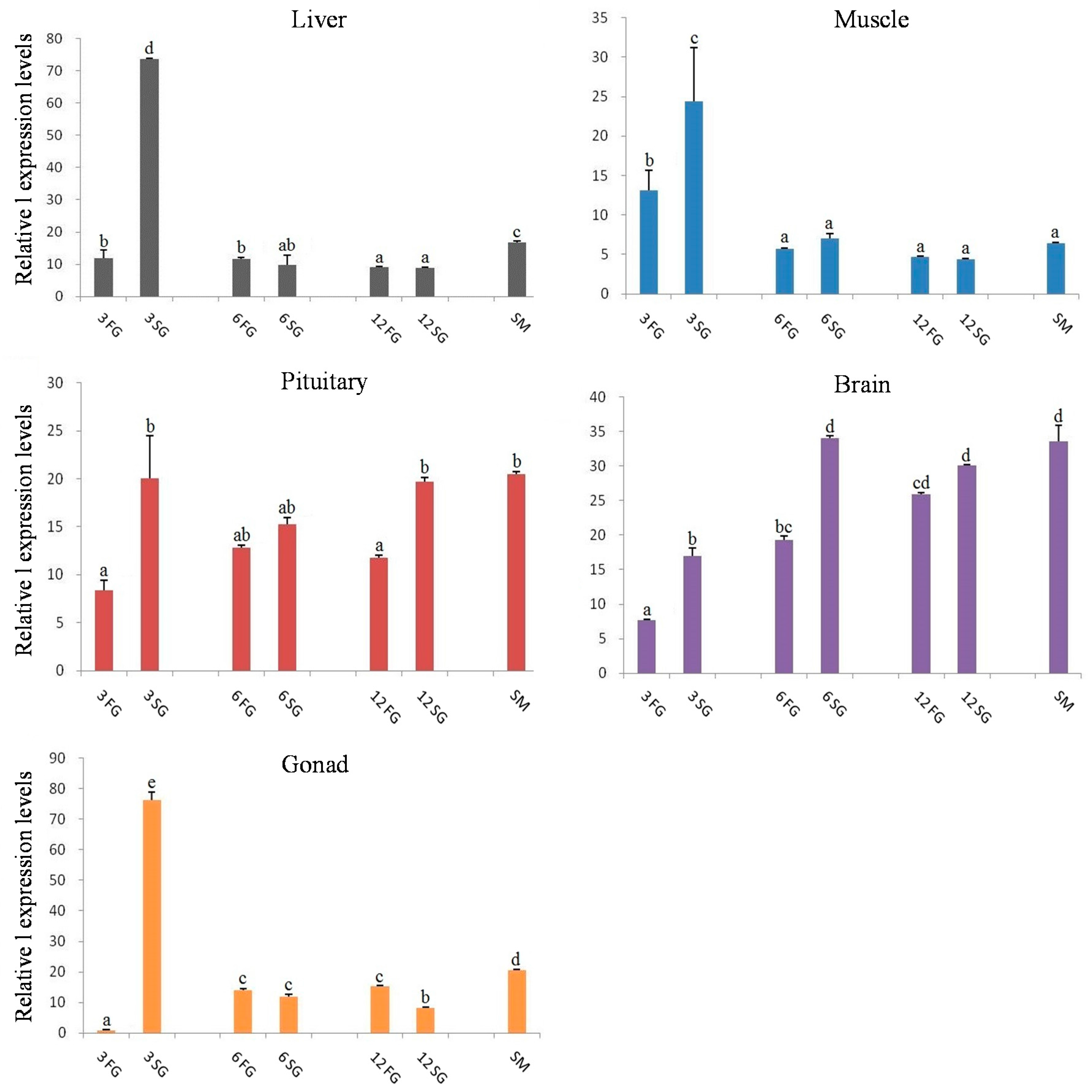
2.4. Expression Analysis of Let-7 miRNAs in Blunt Snout Bream
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Evolutionary Analysis of Let-7 miRNA
4.2. Prediction and Gene Ontology(GO) Analysis of Let-7 miRNAs Target Genes
4.3. Expression Analysis of Let-7 miRNA
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, M.S.; Erkeland, S.J.; Pester, R.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Ebert, M.S.; Sharp, P.A.; Jacks, T. Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3903–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecsedi, M.; Grosshans, H. LIN-41/TRIM71: Emancipation of a miRNA target. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 27581–27589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wit, E.; Linsen, S.E.; Cuppen, E.; Berezikov, E. Repertoire and evolution of miRNA genes in four divergent nematode species. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, A.; Hooks, K.; Griffiths-Jones, S. Evolution and function of the extended miR-2 microRNA family. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigall, P.G.; Dias, M.C.; Pinhal, D. Evolution and genomic organization of muscle microRNAs in fish genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Aksoy, M.; Shi, J.; Houbaviy, H.B. Evolution of the miR-290-295/miR-371-373 cluster family seed repertoire. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertel, J.; Lindemeyer, M.; Missal, K.; Fried, C.; Tanzer, A.; Flamm, C.; Hofacker, I.L.; Stadler, P.F. Students of Bioinformatics Computer Labs 2004 and 2005. The expansion of the metazoan microRNA repertoire. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimberg, A.M.; Sempere, L.F.; Moy, V.N.; Donoghue, P.C.J.; Peterson, K.J. MicroRNAs and the advent of vertebrate morphological complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, B.M.; Heimberg, A.M.; Moy, V.N.; Sperling, E.A.; Holstein, T.W.; Heber, S.; Peterson, K.J. The deep evolution of metazoan microRNAs. Evol. Dev. 2009, 11, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertel, J.; Bartschat, S.; Wintsche, A.; Otto, C.; Students of the Bioinformatics Computer Lab; Stadler, P.F. Evolution of the let-7 microRNA Family. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, S.S.; Kinoshita, S.; Wongwarangkana, C.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Asakawa, S.; Watabe, S. Evolution of the myosin heavy chain gene MYH14 and its intronic microRNA miR-499: Muscle-specific miR-499 expression persists in the absence of the ancestral host gene. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvignes, T.; Contreras, A.; Postlethwait, J.H. Evolution of the miR199-214 cluster and vertebrate skeletal development. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quah, S.; Holland, P.W. The Hox cluster microRNA miR-615: A case study of intronic microRNA evolution. EvoDevo 2015, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambms, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.J.; Basson, M.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Bettinger, J.C.; Rougvie, A.E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Ruvkun, G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2000, 403, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pasquinelli, A.E.; Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.; Martindale, M.Q.; Kuroda, M.I.; Maller, B.; Hayward, D.C.; Ball, E.E.; Degnan, B.; Müller, P.; et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000, 408, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Hsieh, L.C.; Kuo, M.W.; Yu, J.; Kuo, H.H.; Lo, W.L.; Lin, R.J.; Yu, A.L.; Li, W.H. Human TRIM71 and its nematode homologue are targets of let-7 microRNA and its zebrafish orthologue is essential for development. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roush, S.F.; Slack, F.J. Transcription of the C. eleganslet-7 microRNA is temporally regulated by one of its targets, hbl-1. Dev. Biol. 2009, 334, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, A.; Fuchs, H.; Hadian, K.; Smirnova, L.; Wulczyn, E.A.; Michel, G.; Nitsch, R.; Krappmann, D.; Wulczyn, F.G. The let-7 target gene mouse lin-41 is a stem cell specific E3 ubiquitin ligase for the miRNA pathway protein Ago2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Maki, N.; Trinh, A.; Trask, H.W.; Gui, J.; Tomlinson, C.R.; Tsonis, P.A. miRNAs in newt lens regeneration: Specific control of proliferation and evidence for miRNA networking. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Deng, C.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Gatalica, Z.; Recker, R.R.; Xiao, G.G. Let-7 family miRNAs regulate estrogen receptor α signaling in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 127, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagegaltier, D.; König, A.; Gordon, A.; Lai, E.C.; Gingeras, T.R.; Hannon, G.J.; Shcherbata, H.R. A genome-wide survey of sexually dimorphic expression of Drosophila miRNAs identifies the steroid hormone-induced miRNA let-7 as a regulator of sexual identity. Genetics 2014, 198, 647–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, Y.; Yamamoto, J.; Iwamoto, T. The heterochronic genes lin-28a and lin-28b play an essential and evolutionarily conserved role in early zebrafish development. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizuayehu, T.T.; Babiak, I. MicroRNA in Teleost Fish. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 1911–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L.; Chen, X. Identification and differential expression of microRNAs during metamorphosis of the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Xue, W.; Wang, J.T.; Wan, Y.M.; Wang, S.L.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.T.; Sun, X.W. Identification of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) microRNAs and microRNA-related SNPs. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Ge, J.; Pan, J.; Xu, X. Identification and characterization of microRNAs in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) by using Solexa sequencing technology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Guo, E.; Gan, X.; et al. Identification and characterization of microRNAs in ovary and testis of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by using Solexa sequencing technology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, I.A.; Lee, H.T.; Macqueen, D.J.; Paranthaman, K.; Kawashima, C.; Anwar, A.; Kinghorn, J.R.; Dalmay, T. Embryonic temperature affects muscle fibre recruitment in adult zebrafish: Genome-wide changes in gene and microRNA expression associated with the transition from hyperplastic to hypertrophic growth phenotypes. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 1781–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizuayehu, T.T.; Lanes, C.F.; Furmanek, T.; Karlsen, B.O.; Fernandes, J.M.; Johansen, S.D.; Babiak, I. Differential expression patterns of conserved miRNAs and isomiRs during Atlantic halibut development. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Jia, L. Expression of let-7 microRNAs that are involved in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) metamorphosis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 165, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Gao, Z.X.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, C.; Luo, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.M. Identification and characterization of microRNAs involved in growth of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) by Solexa sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Sun, X.; Jiang, D.; Ding, Y.; Lu, Z.; Gong, L.; Liu, H.; Xie, J. Origin and evolution of a placental-specific microRNA family in the human genome. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozawa, M.; Miura, S.; Nei, M. Origins and evolution of microRNA genes in Drosophila species. Genome Biol. Evol. 2010, 2, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D.; Zhang, Z. Evolution of an X-linked primate-specific micro RNA cluster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittbrodt, J.; Meyer, A.; Schartl, M. More genes in fish? Bioessays 1998, 20, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.; Lee, S.-C. Phosphoglucose isomerases of hagfish, zebrafish, gray mullet, toad, and snake, with reference to the evolution of the genes in vertebrates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Zou, M.; Wagner, A. Pervasive indels and their evolutionary dynamics after the fish-specific genome duplication. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 3005–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Lu, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, R. Fish specific duplication of Dmrt2: Characterization of zebrafish Dmrt2b. Biochimie 2008, 90, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; van de Peer, Y. From 2R to 3R: Evidence for a fish-specific genome duplication (FSGD). Bioessays 2005, 27, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisoulis, D.G.; Kai, Z.S.; Chang, R.K.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Autoregulation of microRNA biogenesis by let-7 and Argonaute. Nature 2012, 486, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.B.; Liu, W.J.; Pan, Z.J.; Cheng, T.Y.; Luo, C. Evolution of the mir-155 family and possible targets in cancers and the immune system. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 7547–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, P.; Cheng, T.; Hong, K.; Xiang, Z. Characterization and expression patterns of let-7 microRNA in the silkworm (Bombyx mori). BMC Dev. Biol. 2007, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Li, H.; Mu, H.; Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, S.; Jia, X.; Nie, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Let-7b regulates the expression of the growth hormone receptor gene in deletion-type dwarf chickens. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Ye, S.; Yu, K.; Huang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Mo, D. Integrative analysis of porcine microRNAome during skeletal muscle development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darty, K.; Denise, A.; Ponty, Y. VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1974–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lweis, B.P.; Shih, I.H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Huang, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Huang, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; de Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; van Roy, N.; de Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, RESEARCH0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Wen, J.F.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.M.; Gao, Z.X. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of major histocompatibility complex class I, IIA and IIB genes of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Danio rerio | Oryzias latipes | Fugu rubripes | Petromyzon marinus | Tetraodon nigroviridis | Branchiostoma floridae |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dre-let-7a-1/dre-let-7f | ola-let-7a-1/ola-let-7b-1 | ||||
| dre-mir-100-1/dre-let-7a-2/dre-mir-125b-1 | fru-mir-100/fru-let-7a-1/fru-mir-125b | tni-mir-100/tni-let-7a-1/tni-mir-125b | |||
| dre-let-7a-3/dre-let-7b | ola-let-7a-3/ola-let-7b-2 | pma-let-7a-3/pma-let-7d | |||
| dre-mir-100-2/dre-let-7a-4/dre-mir-125b-2 | ola-mir-100-2/ola-let-7a-4/ola-mir-125b-1 | ||||
| dre-let-7e/dre-let-7a-5 | ola-let-7e/ola-let-7a-2 | fru-let-7e/fru-let-7a-3 | |||
| dre-mir-99-1/dre-let-7c-1/dre-mir-125c | ola-mir-99/ola-let-7c/ola-mir-125b-2 | ||||
| dre-mir-99-2/dre-let-7c-2 | |||||
| dre-let-7g-2/dre-let-7h | fru-let-7g/fru-let-7h | tni-let-7g/tni-let-7h | |||
| pma-mir-100c/pma-mir-100a/pma-mir-125 | |||||
| bfl-mir-100/bfl-let-7a-1/bfl-let-7b/bfl-mir-125a/bfl-mir-125b/bfl-let-7a-2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, B.-W.; Zhou, L.-F.; Liu, Y.-L.; Wan, S.-M.; Gao, Z.-X. Evolution of Fish Let-7 MicroRNAs and Their Expression Correlated to Growth Development in Blunt Snout Bream. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030646
Zhao B-W, Zhou L-F, Liu Y-L, Wan S-M, Gao Z-X. Evolution of Fish Let-7 MicroRNAs and Their Expression Correlated to Growth Development in Blunt Snout Bream. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030646
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Bo-Wen, Lai-Fang Zhou, Yu-Long Liu, Shi-Ming Wan, and Ze-Xia Gao. 2017. "Evolution of Fish Let-7 MicroRNAs and Their Expression Correlated to Growth Development in Blunt Snout Bream" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030646
APA StyleZhao, B. -W., Zhou, L. -F., Liu, Y. -L., Wan, S. -M., & Gao, Z. -X. (2017). Evolution of Fish Let-7 MicroRNAs and Their Expression Correlated to Growth Development in Blunt Snout Bream. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030646





