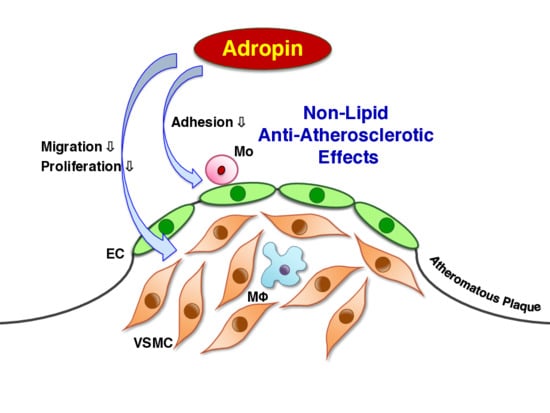
Adropin Contributes to Anti-Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation
Abstract
Share and Cite
Sato, K.; Yamashita, T.; Shirai, R.; Shibata, K.; Okano, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, Y.; Hirano, T.; Watanabe, T. Adropin Contributes to Anti-Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051293
Sato K, Yamashita T, Shirai R, Shibata K, Okano T, Yamaguchi M, Mori Y, Hirano T, Watanabe T. Adropin Contributes to Anti-Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051293
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Kengo, Tomoyuki Yamashita, Remina Shirai, Koichiro Shibata, Taisuke Okano, Maho Yamaguchi, Yusaku Mori, Tsutomu Hirano, and Takuya Watanabe. 2018. "Adropin Contributes to Anti-Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051293
APA StyleSato, K., Yamashita, T., Shirai, R., Shibata, K., Okano, T., Yamaguchi, M., Mori, Y., Hirano, T., & Watanabe, T. (2018). Adropin Contributes to Anti-Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051293