Butterbur Leaves Attenuate Memory Impairment and Neuronal Cell Damage in Amyloid Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Models
Abstract
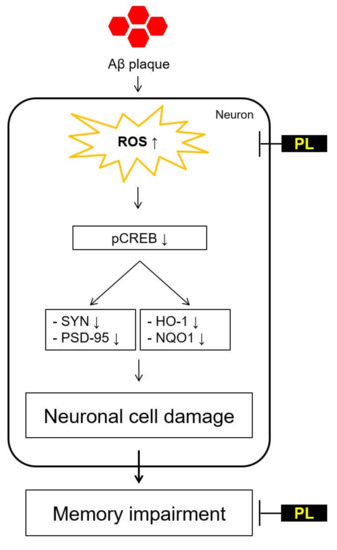
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Standardization of PL
2.2. PL Protects Neuronal Cells against Aβ25–35 Plaque Toxicity
2.3. PL Reduces the Accumulation of ROS Induced by Aβ25–35 Plaque via Antioxidant Responses
2.4. PL Increases Phosphorylation of CREB in Aβ25–35 Plaque-Stimulated HT22 Cells and Mice
2.5. PL Protects Hippocampal Cells against Aβ25–35 Plaque Toxicity in Mice
2.6. PL Inhibits Aβ25–35 Plaque-Induced Synaptotoxicity in Mice
2.7. PL Ameliorates Memory Impairment Induced by Aβ25–35 Plaque
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Standardization of PL
4.3. Preparation of Aβ25–35 Plaque
4.4. Free Radical Scavenging Assay
4.4.1. ABTS Radical Cation Assay
4.4.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
4.5. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.6. Measurement of Cell Viability
4.7. Measurement of Intracellular ROS
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. qRT-PCR Analysis
4.10. Animals
4.11. Surgery Procedure
4.12. Behavior Test
4.12.1. Novel Object Recognition Test
4.12.2. Passive Avoidance Test
4.13. Brain Tissue Preparation
4.14. Immunohistochemistry
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ewbank, D.C. Deaths attributable to Alzheimer’s disease in the United States. Am. J. Public Health 1999, 89, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, M.S.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Neurodegenerative diseases: A decade of discoveries paves the way for therapeutic breakthroughs. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, C.A.; Mann, D.M.; Sumpter, P.Q.; Yates, P.O. A quantitative morphometric analysis of the neuronal and synaptic content of the frontal and temporal cortex in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 1987, 78, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliah, E.; Mallory, M.; Alford, M.; DeTeresa, R.; Hansen, L.A.; McKeel, D.W., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Altered expression of synaptic proteins occurs early during progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 2001, 56, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheff, S.W.; Price, D.A.; Schmitt, F.A.; DeKosky, S.T.; Mufson, E.J. Synaptic alterations in CA1 in mild Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2007, 68, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, H.; Nishitoh, H.; Urano, F.; Sadamitsu, C.; Matsuzawa, A.; Takeda, K.; Masutani, H.; Yodoi, J.; Urano, Y.; Nagano, T.; Ichijo, H. Amyloid β induces neuronal cell death through ROS-mediated ASK1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamat, P.K.; Kalani, A.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Tota, S.; Nath, C.; Tyagi, N. Mechanism of Oxidative Stress and Synapse Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Understanding the Therapeutics Strategies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Sok, D.E.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.R. Butterbur (Petasites japonicus Max.) extract improves lipid profiles and antioxidant activities in monosodium l-glutamate-challenged mice. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.P.; Kang, S.; Park, S.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, Y.G.; Im, D.S. Anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects of bakkenolide B isolated from Petasites japonicus leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.W.; Lee, K.P.; Kim, J.M.; Kang, S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.M.; Moon, H.R.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, Y.G.; Im, D.S. Petatewalide B, a novel compound from Petasites japonicus with anti-allergic activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 178, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.S.; Kim, M.R.; Sok, D.E. Protection by petaslignolide A, a major neuroprotective compound in the butanol extract of Petasites japonicus leaves, against oxidative damage in the brains of mice challenged with kainic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8526–8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.H.; Sok, D.E.; Kim, M.R. Neuroprotective effects of butterbur and rough aster against kainic Acid-induced oxidative stress in mice. J. Med. Food 2005, 8, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.J.; Kim, G.S.; Jun, M.; Song, K.S. Kaempferol attenuates the glutamate-induced oxidative stress in mouse-derived hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, M.H.; Li, M.; Li, K.; Park, G.; Choi, Y.W. AMPK/Nrf2 signaling is involved in the anti-neuroinflammatory action of Petatewalide B from Petasites japonicus against lipopolysaccharides in microglia. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2018, 40, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, M.H.; Park, G.; Choi, Y.W. Petasites japonicus bakkenolide B inhibits lipopolysaccharideinduced proinflammatory cytokines via AMPK/Nrf2 induction in microglia. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okada, M.; Okada, Y. Potential Properties of Plant Sprout Extracts on Amyloid β. Biochem. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9347468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.F.; Kim, S.M.; Song, D.G.; Pan, C.H.; Lee, W.J.; Um, B.H. Isolation and identification of antioxidant compounds from Ligularia fischeri. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C530-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Hwang, B.Y.; Kim, S.; Yoo, J.K.; Seong, Y.H. Neuroprotection of Ilex latifolia and caffeoylquinic acid derivatives against excitotoxic and hypoxic damage of cultured rat cortical neurons. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Park, R.Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Kwon, Y.S.; Chun, W. Neuroprotective effects of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid on hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mates, J.M. Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology 2000, 153, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzelino, R.; Jeney, V.; Soares, M.P. Mechanisms of cell protection by heme oxygenase-1. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Talalay, P. NAD(P)H:quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), a multifunctional antioxidant enzyme and exceptionally versatile cytoprotector. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walton, M.R.; Dragunow, I. Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithianantharajah, J.; Levis, H.; Murphy, M. Environmental enrichment results in cortical and subcortical changes in levels of synaptophysin and PSD-95 proteins. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2004, 81, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.; Mishra, S.K.; Pant, H.C. Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 2011, 572634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, R.J.; Buck, C.R.; Smith, A.M. NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 1992, 116, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glantz, L.A.; Gilmore, J.H.; Hamer, R.M.; Lieberman, J.A.; Jarskog, L.F. Synaptophysin and postsynaptic density protein 95 in the human prefrontal cortex from mid-gestation into early adulthood. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer-Luehmann, M.; Spires-Jones, T.L.; Prada, C.; Garcia-Alloza, M.; de Calignon, A.; Rozkalne, A.; Koenigsknecht-Talboo, J.; Holtzman, D.M.; Bacskai, B.J.; Hyman, B.T. Rapid appearance and local toxicity of amyloid-β plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2008, 451, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gella, A.; Durany, N. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2009, 3, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pugazhenthi, S.; Wang, M.; Pham, S.; Sze, C.I.; Eckman, C.B. Downregulation of CREB expression in Alzheimer’s brain and in Aβ-treated rat hippocampal neurons. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Jung, W.J.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, C.M.; Park, G.; Choi, Y.W. Neuroprotective effects of α-iso-cubebene against glutamate-induced damage in the HT22 hippocampal neuronal cell line. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisman, J.; Cooper, K.; Sehgal, M.; Silva, A.J. Memory formation depends on both synapse-specific modifications of synaptic strength and cell-specific increases in excitability. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, P.; Federoff, H.; Kurlan, R. A focus on the synapse for neuroprotection in Alzheimer disease and other dementias. Neurology 2004, 63, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spires-Jones, T.L.; Hyman, B.T. The intersection of amyloid beta and tau at synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2014, 82, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Miyamae, Y.; Shigemori, H.; Isoda, H. Neuroprotective effect of 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid on SH-SY5Y cells and senescence-accelerated-prone mice 8 through the up-regulation of phosphoglycerate kinase-1. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.G.; Ju, M.S.; Park, H.; Seo, Y.; Jang, Y.P.; Hong, J.; Oh, M.S. Evaluation of Samjunghwan, a traditional medicine, for neuroprotection against damage by amyloid-beta in rat cortical neurons. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, O.; Park, B.K.; Bang, M.; Cho, K.S.; Lee, S.H.; Gonzales, E.L.T.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, S.; Eun, P.H.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Effects of Several Cosmetic Preservatives on ROS-Dependent Apoptosis of Rat Neural Progenitor Cells. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Oh, M.S. Memory-enhancing effect of Mori Fructus via induction of nerve growth factor. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K. Paxinos and Franklin’s the Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 360. [Google Scholar]
- Weon, J.B.; Jung, Y.S.; Ma, C.J. Cognitive-Enhancing Effect of Dianthus superbus var. Longicalycinus on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2016, 24, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.; Choi, J.G.; Park, S.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, M.S. Butterbur Leaves Attenuate Memory Impairment and Neuronal Cell Damage in Amyloid Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061644
Kim N, Choi JG, Park S, Lee JK, Oh MS. Butterbur Leaves Attenuate Memory Impairment and Neuronal Cell Damage in Amyloid Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061644
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Namkwon, Jin Gyu Choi, Sangsu Park, Jong Kil Lee, and Myung Sook Oh. 2018. "Butterbur Leaves Attenuate Memory Impairment and Neuronal Cell Damage in Amyloid Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061644
APA StyleKim, N., Choi, J. G., Park, S., Lee, J. K., & Oh, M. S. (2018). Butterbur Leaves Attenuate Memory Impairment and Neuronal Cell Damage in Amyloid Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061644