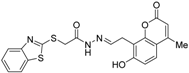
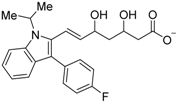
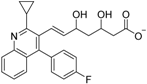
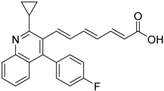
Abstract
Retinoid X receptor (RXR) antagonists are not only useful as chemical tools for biological research, but are also candidate drugs for the treatment of various diseases, including diabetes and allergies, although no RXR antagonist has yet been approved for clinical use. In this review, we present a brief overview of RXR structure, function, and target genes, and describe currently available RXR antagonists, their structural classification, and their evaluation, focusing on the latest research.
1. Introduction
Retinoid X receptors (RXRs; NR2B1–3) are nuclear receptors that function either as homodimers or as heterodimers with other receptors such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs; NR1C1–3), liver X receptors (LXRs; NR1H2–3), or farnesoid X receptor (FXR; NR1H4), and others [1,2,3]. RXR heterodimers that can be activated by RXR agonists alone are known as permissive heterodimers [4]. 9-cis-Retinoic acid (1, Figure 1) is a potent natural agonist toward RXRs, but also works as an activator of retinoic acid receptors (RARs) [5]. The RXR synthetic agonist bexarotene (LGD1069, Targretin®, 2, Figure 1) is used for the treatment of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) [6], but, on the other hand, no RXR antagonist has yet entered clinical use, even though anti-type 2 diabetes [7] and anti-allergy activities [8] have been found in animal models. At present, RXR antagonists are mainly employed as analytical tools in studies of RXR function. In this review, we will first present a brief overview of the RXR structure, function, and target genes, and then describe currently available RXR antagonists, their structural classification, and their evaluation, focusing on the latest research.
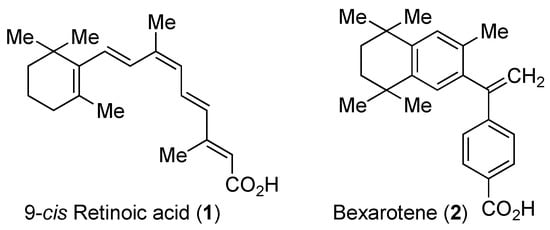
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of 9-cis-retinoic acid (1) and bexarotene (2).
2. The RXRs
Among the 48 members of the nuclear receptor superfamily that have identified by sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree construction [3,9], 24 are ligand-binding receptors. These include three different subtypes of RXR, i.e., RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ, which are encoded by distinct genes [3] (Table 1). Historically, these receptors have been named after their ligands. However, the Nuclear Receptor Nomenclature Committee has recommended a systematic nomenclature based on genome analysis [3]. Thus, RXRα is designated as NR2B1, RXRβ as NR2B2, and RXRγ as NR2B3; in this review, we retain the established nomenclature. Each RXR has two isoforms: RXRα1/α2, RXRβ1/β2, and RXRγ1/γ2 [10]. RXRα exists in liver, lung, muscle, kidney, epidermis (major subtype), and intestine, while RXRβ is distributed ubiquitously. On the other hand, RXRγ1 is expressed in the brain and muscle, while RXRγ2 is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscles [10]. Most research has so far been focused on RXRα; one reason for this may be that the functions of the RXR subtypes are the same, even though their distributions are different. RXRα was the first RXR subtype to have its structure determined by X-ray crystallography [11].

Table 1.
Definitions of terms and abbreviations concerning nuclear receptors (adapted and modified from [3]).
RXRs, like other nuclear receptors, consist of six domains A, B, C, D, E, and F (Figure 2) [3]. The N-terminal A/B region has a transcriptional activation function and is referred as AF-1 (Figure 2, Table 1). AF-1 can operate in a ligand-independent/dependent manner; i.e., it is controlled by ligand binding to the ligand-binding domain (LBD) (Figure 2, Table 1) in the full-length receptor, but when located outside of the receptor, it acts in a ligand-independent manner [3]. Next, the C domain acts as a DNA-binding domain (DBD) (Figure 2, Table 1), which contributes to the response element specificity for recognition of the target gene. Dimerization of RXR with itself or a heterodimer partner is caused by strong interactions between the LBDs of the interacting partners, as well as binding of the two DBDs. RXR homodimers bind to RXR response elements (RXREs) composed of a direct repeat of hexad half-sites (A/G)G(G/T)TCA separated by one nucleotide as a spacer (DR-1 element, direct repeat with 1 nucleotide) (Table 2). RXR heterodimers also bind preferentially to specific hormone response elements (HREs), which are composed of two hexad half-sites arranged as tandem repeats. The specificity of each dimer for the target DNA is based not only on the DNA sequences of the two half-sites, but also on the geometry, spacing, and relative orientation of the half-sites in the HRE [12,13,14,15]. Other response elements with different numbers of spacer nucleotides, DR2, DR3, DR4, DR5, and others, also exist. The RXR LBD can adopt multiple conformations, providing the dimerization domain with sufficient flexibility to occupy the partner receptor [14,15]. Interestingly, RXRs can form RXR tetramers with high affinity at protein concentrations higher than about 70 nM [16]. Noy and collaborators presented evidence that binding of the apo-RXR homotetramer to two RXREs, which were separated by 250 base-pairs in a 382 base-pair sequence, permitted transcriptional regulation by DNA-looping [17]. The reason why one RXR homotetramer can bind to two different RXREs is that their DBDs are exposed. Indeed, the inhibition of mammary carcinoma cell growth by RXR ligands stems from the ability of these compounds to regulate the oligomeric state of RXR, and is independent of the direct intrinsic transcriptional activity of the receptor [18]. Compounds that trigger dissociation of RXR tetramers may comprise a novel class of anti-carcinogenic agents.
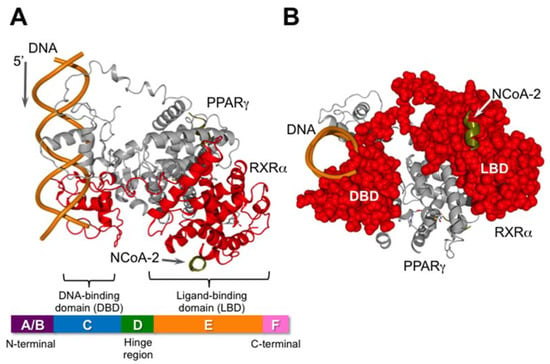
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the nuclear receptor heterodimer PPARγ/RXRα and its co-activator (NCoA-2: nuclear receptor co-activator 2) bound to DNA. This figure was created using PDB coordinates from [13] (pdb: 3DZY). RXR is shown in red. The X-ray data was obtained using only a part of N-CoA2, consisting of EKHKILHRLLQDSY. (A) View from the side. The bar at the bottom is a schematic illustration of the general domain structure of nuclear receptors; (B) View from the 3′-end of the DNA. RXR is shown as a CPK model in red.

Table 2.
Classification and nomenclature of nuclear receptors (adapted and modified from [32]).
Target genes of RXR heterodimers are dependent on the identity of the heterodimer partner. On the other hand, in the case of RXR homodimers, the DBDs bind to natural DR1 elements for the calcitonin receptor activity-modifying protein 2 (Ramp2), the NR subfamily 1, group D, member 1 (Nr1d1) and the glycerophospho-diester phosphodiesterase 1 (Gde1) genes, as well as the malic enzyme PPRE gene (MEp) [15,19,20]. Since both RXR and PPAR bind to DR1, RXR homodimers can bind not only RXRE, but also PPRE [20].
Domain D acts as the binder and cushion of domains C and E. Domains E/F are referred as the ligand-binding domain (LBD) (Table 1, Figure 2). The LBD contains four structurally distinct, but functionally linked surfaces: (1) a dimerization surface with a partner; (2) the ligand-binding pocket (LBP) for lipophilic small molecules; (3) a co-regulator binding surface; and (4) a ligand-dependent activation function helix 12 (termed AF-2) (Figure 2, Table 1) [3]. Activation of RXRs occurs when an agonist binds to the LBP and induces a conformational change in the LBD [21]. The resulting conformation allows recruitment of co-regulatory complexes, which contain chromatin-modifying enzymes required for transcription, RNA polymerase II, and general transcription factors [22,23]. RXR heterodimers with PPARs, LXRs, or FXR, which can be activated by RXR agonists alone, are known as permissive heterodimers [4]. In contrast, RXR heterodimers with RAR or TRs cannot be activated by RXR agonists alone, and are termed non-permissive. The difference between permissive and non-permissive heterodimers arises from the strong constitutive interaction between the unliganded non-permissive hetero partner and co-repressors [24]. Unliganded permissive heterodimer partners, such as PPAR or LXR, do not have a strong constitutive interaction with co-repressors [25], so their RXR heterodimers can be activated by an RXR agonist alone.
Small molecules or compounds that bind reversibly to nuclear receptors into the C-terminal ligand-binding pocket (LBP) are defined as “nuclear receptor ligands” [3]. Due to the ability to alter activity of the receptors, these are often termed “receptor modulators” [26]. However, since there are small molecules that bind to a different site from the LBP, the definition of “nuclear receptor modulators” should be broadened as compounds that bind to nuclear receptors (Table 1). Nuclear receptor ligands are classified into three categories; agonists, inverse agonists, and antagonists (Table 1). Agonists are defined as compounds that bind to the LBP and activate the receptor. Inverse agonists are compounds that bind to the LBP and result in a conformational change that reduces the basal level of activity (reduces basal co-activator binding). In contrast, Antagonists simply bind to the LBD and prevents the conformational change that an agonist would cause, thus preventing co-activator recruitment and subsequent stimulation of transcription. The definition of other terms is listed in Table 1.
RXR antagonists interfere with the binding of RXR agonists to RXRs. Although some subtype-preferential agonists and antagonists have been reported [27,28,29], their selectivities are not sufficient to allow their use as pharmacological tools [30]. The main reason for the difficulty in developing highly selective RXR ligands may be that the amino acid residues of helices (H) 3, 5, 7, and 11, and the β-turn, which form the ligand-binding pocket, are highly conserved in RXRα, β, and γ.
3. Representative RXR Antagonists
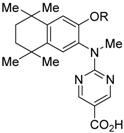
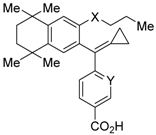
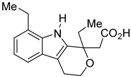
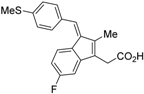
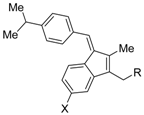
RXR antagonists are classified into three categories; (1) compounds having a long-chain alkoxy group introduced to an RXR agonist structure as a scaffold (Table 3); (2) compounds possessing another side-chain group instead of the alkoxy group introduced to an RXR agonist structure as a scaffold (Table 4); and (3) compounds discovered from among natural products or by docking simulation or high-throughput screening (Table 5). The common structure of RXR agonists is composed of three parts: a hydrophobic moiety composed of a tetramethyltetraline structure, an acidic moiety composed of trienoic acid, benzoic acid, nicotinic acid, or pyrimidinecarboxylic acid, and a linking moiety between the two.

Table 3.
Chemical structures, binding affinities, and RXR antagonistic activities of RXR antagonists having an alkoxy side chain on an RXR agonistic scaffold.

Table 4.
Chemical structures, binding affinities, and RXR antagonistic activities of RXR antagonists having a non-alkoxy side chain or another structure on an RXR agonistic scaffold.

Table 5.
Chemical structures, binding affinities, and RXR antagonistic activities of RXR antagonists from natural products or others.
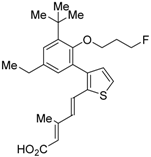
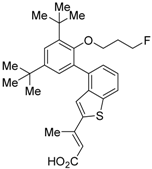
3.1. RXR Antagonists Having a Long-Chain Alkoxy Group
The chemical structures of RXR antagonists in this category are illustrated in Table 3. LG100754 (3) was reported as the first RXR antagonist in 1996 [42]. Prior to that, in 1994, Boehm et al. had noted that some compounds having RXR binding affinity, but not showing RXR agonist activity, might exhibit RXR antagonistic activity [73]. Compound 3 was designed by introducing an n-propoxy group into the 3′-position of the backbone of tetrahydrotetramethylnaphthyl octatrienoic acid, whose chemical structure is similar to that of 9-cis-retinoic acid (1) (Figure 3). A similar compound, AGN195393 (4) [43], was also reported. Compound 3 showed IC50 = 16 nM against 32 nM 2 (EC50 = 33 nM) [73] in reporter assay for RXRα in CV-1 cells. Although initially identified as an RXR homodimer antagonist, subsequent experiments revealed that 3 acts as an agonist toward RAR/RXR [74], PPARα/RXR [75], and PPARγ/RXR [76,77]. Although 3 has been reported to act as a ‘phantom ligand’ activating RAR via allosteric control through the binding to RXR [74], it is revealed that the activation of RAR/RXR by 3 is caused by a direct binding of 3 to RAR that stabilizes co-activator interactions [78].
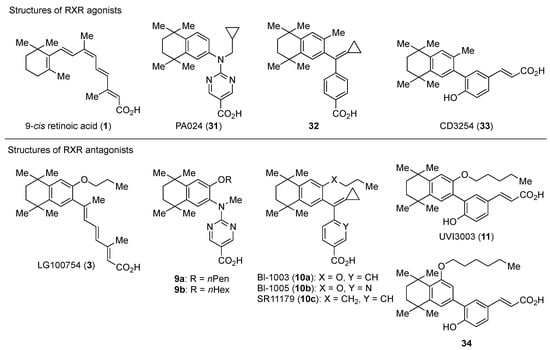
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of RXR agonists and RXR antagonists having a long-chain alkoxy group.
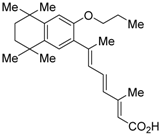
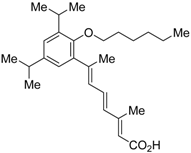
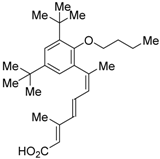
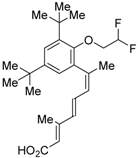
Ro26-5450 (5) [44] and LG101506 (6) [45] have a (2E,4E,6Z)-7-(2-alkoxy-3,5-di-alkylbenzene)-3-methylocta-2,4,6-trienoic acid scaffold. Compound 6 binds to RXRα at low concentrations and shows RXR antagonist activity, but a synergistic effect with an agonist of PPARγ was also found. Subsequently, 7, which has a ring structure at the 6 and 7 positions of the trienoic acid structure of 6, and 8, which has another ring structure at the 4 and 5 positions of 7, were created [47,48]. Compound 8 shows more potent RXR antagonist activity than 6 [47]. Their Ki values for RXRα in the presence of [3H]9-cis retinoic acid are 3 nM (6), 9.9 nM (7), and 3 nM (8). Although the IC50 values toward RXRα in reporter assay using CV-1 cells were also reported as 8 nM (6), 10.3 nM (7), and 8 nM (8), the RXR agonist and the concentration used were not mentioned [45,46,47]. Since these RXR ligands activate specific heterodimers, the authors refer to the compounds as “selective RXR modulators” [45].
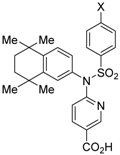
PA451 (9a) and PA452 (9b) are RXR antagonists having a pentoxy or a hexoxy group at the ortho position of the amino group on the benzene ring forming the tetramethyltetraline structure of an N-methyl derivative of RXR agonist PA024 (27). These compounds inhibit RXR/RAR heterodimers [48]. The pA2 value of 9b in the presence of RXR agonist NEt-TMN (36, EC50 = 5.28 nM) [49] was determined as 7.11 from a Shild plot [50].
Bl-1003 (10a) [51] is a propoxy derivative of RXR agonist 28 [79]. Compounds 10b and 10c were designed by replacing the benzoic acid of 10a with nicotinic acid and the propoxy group of 10a with a butyl group, respectively. Reporter assay toward RXRα using 0.1 μM 1 in CV-1 cells gave IC50 = 1100 nM (10a), >10,000 nM (10b), and 67 nM (10c), respectively [52]. Interestingly, although 10c showed a 10-times-greater Kd value than 10a in a competition test using tritium-labeled 1, the antagonism in the reporter assay was 20 times more potent.
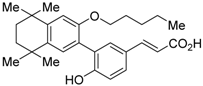
UVI3003 (11) is an RXR antagonist obtained by converting the 3′-methyl group of RXR agonist CD3254 (33) [54] to a pentoxy group. In this study, the authors synthesized analogs with an alkyl chain ranging from C1 to C6 in length, and evaluated RXR agonistic and antagonistic activities. Compounds having a short alkoxy side chain act as partial or weak RXR agonists, but when the number of carbons is more than 3, they show RXR antagonist activity. Among them, 11 shows potent RXR antagonistic activity. Since 34, the positional isomer of 11, shows only weak RXR antagonist activity, the position of the alkoxy group is important for the activity [80]. Compound 11 showed IC50 = 0.24 μM against 10 nM IRX4204 (formerly designated AGN194204 and NRX 194204, RXR agonist) [53] in a reporter assay for RXRα in COS-7 cells [55].
3.2. RXR Antagonists Possessing Another Side Group
RXR antagonists possessing another side group instead of the alkoxy chain are summarized in Figure 4 and Table 4.
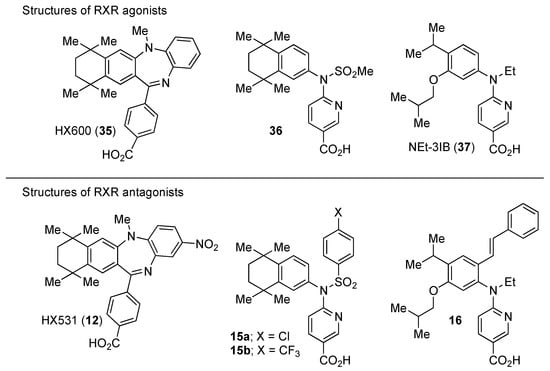
Figure 4.
Chemical structures of RXR agonists and RXR antagonists possessing another side group instead of the alkoxy group on an RXR agonist structure.
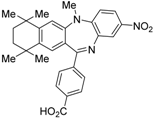
HX531 (12) was designed by introducing a nitro group into the structure of the diazepinylbenzoic acid derivative RXR agonist HX600 (35) [56]. Compound 12 showed IC50 = 1.0 μM against 10 nM IRX4204 in a reporter assay toward RXRα in COS-7 cells [55]. Compound 12 has been reported to show antagonism towards not only RXR, but also RAR [56]. It also shows antagonistic activity against RAR/RXR or PPARγ/RXR heterodimers [7]. Compound 12 shows a hypoglycemic effect in an animal model of type 2 diabetes, and is thought to improve insulin resistance through antagonism to the PPARγ/RXR heterodimer [7]. An improvement of leptin resistance was also reported [81]. However, the Cmax value at 100 mg/kg oral administration of 12 to mice was 4.1 μg/mL (8.5 μM). Two-week administration of diet containing 12 at 0.1% weight showed a hypoglycemic effect [7]. For the purpose of improving the oral availability of 12, 13a, and 13b were created [57]. When they were orally administered to rats at 1 mg/kg, the Cmax values were 468 nM and 519 nM, respectively. Further development of these structures yielded 13c, which was reported to show a hypoglycemic effect in KK-Ay mouse, a type 2 diabetes model [58].
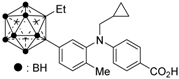
Compound 14 has a boron cluster (carborane) at the hydrophobic site instead of a tetramethyltetraline structure [59]. At 1 μM, 14 completely represses RXRα transcription induced by 10 nM RXR agonist PA024 (31).
Morishita and colleagues produced new RXR antagonists, 15a and 15b, having a sulfonamide on an amino linking group instead of the N-ethyl group of NEt-TMN (36) [29]. However, their RXR antagonist activity was weaker than that of HX531 (12).
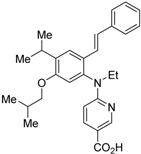
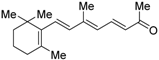
To reduce the lipid solubility of existing RXR agonists, the RXR full agonist NEt-3IB (37, EC50 = 19 nM), which has an isobutoxy group at a hydrophobic site, was designed [27,82]. The para position to the isobutoxy group on the benzene ring is electron-rich because this position is also at the ortho position relative to the nitrogen atom of the amino linking group. Therefore, it is easily halogenated. A new RXR antagonist 16, which has a stilbene structure, was created by transformation of an iodine precursor using a palladium catalyst [50]. The pA2 value of 16 toward RXRα agonist NEt-TMN (EC50 = 5.28 nM) [49] was 8.23 based on a Shild plot, while that of PA452 (9b) was 7.11; thus, 16 is one of the strongest RXR antagonists discovered thus far.
3.3. RXR Antagonists Discovered among Natural Products or by Docking Simulation or High-Throughput Screening
The chemical structures and assay data of RXR antagonists classified in this category are shown in Table 5.
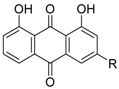
Danthron (17a), a component of rhubarb, used in Chinese medicine, showed RXR antagonist activity with IC50 = 0.11 μM for 1 μM 1 in a reporter assay for Gal4-RXRα-LBD in HEK293T cells [60]. The Kd value for RXRα is 6.2 μM. Compound 17a shows antagonist activity toward not only RXR homodimer, but also heterodimers such as PPARγ/RXRα and LXRα/RXRα. Compound 17a has also been evaluated in vivo and was found to improve insulin resistance in DIO mice. Rhein (17b), another compound derived from rhubarb, likewise shows RXR antagonist activity with IC50 = 0.75 μM for 1 in the same assay system [61].
β-Apo-13-carotenone (18), which is produced by β-carotene cleavage, antagonizes RXRα activation by 1 through receptor tetramerization, which stabilizes the inactive state [62]. Though competition assay against 1 in a reporter assay in COS-7 cells has been investigated, the IC50 value was not described.
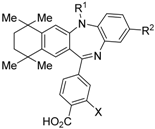
R-Etodolac (19), a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), induces apoptosis of tumor cells in a mouse model of prostate cancer [63]. Zhang et al., reported that 19 acts as an antagonist of RXRα and down-regulates RXR. A competition assay with 38.1 nM [3H]1 revealed that the IC50 value of 19 is about 200 μM. After this study, sulindac (20), another NSAID, was also found to bind to RXRα and induce apoptosis [64]. The IC50 value of 20 in competition assay for [3H]1 is 82.9 μM. K-80003 (21a) was created to improve the affinity for RXR (IC50 = 2.4 μM),, and to eliminate COX inhibition [65,66]. Though K-8008 (22b), which has a tetrazole instead of the carboxylic acid moiety of 21a, showed a slightly decreased affinity for RXRα (IC50 = 16.8 μM), crystal structure analysis showed that it binds at the RXRα interface and stabilizes the tetramer of RXR [65].
Zhang et al., also discovered triptolide (22a) [67], which has antagonistic activity against RXRα and induces apoptosis, as well as NSC-640358 (23) [69], by virtual screening. The Kd value of 23 for RXRα is 15.7 μM. Furthermore, they conducted a one hybrid assay using their in-house compound library and identified 24 and 25, which are nitrostyrene derivatives, as RXRα modulators [70]. They detected RXR agonistic activity in the mammalian one-hybrid assay using Gal4-DBD-RXRα-LBD, and antagonistic activity in reporter assay using the full-length RXR homodimer. Zhang et al., demonstrated that nitrostyrene derivatives 24 and 25 could inhibit the TNFα/NFκB signaling pathway by binding to N-terminally truncated RXRα (tRXRα), leading to TNFα and tRXRα-dependent apoptosis of cancer cells.
Moreover, Zhang et al., identified 26 and 27 as RXR antagonists by means of virtual screening using the structure of RXRα-LBD in the complex with CD3254 (33) and a coactivator peptide (PDB code, 3FUG) [71]. These compounds do not bind to the ligand-binding pockets, but bind at the surface of the co-regulator binding site and inhibit co-regulator binding there. Reporter assay using 0.1 μM 1 toward RXRα in MCF-7 cells yielded IC50 values of 2 μM for 26 and 2.45 μM for 27.
Zhang and colleagues also found that the statin drugs fluvastatin (28) and pitavastatin (29) are RXR antagonists by virtual screening of an FDA-approved drug database [72]. Further structure optimization of 28 afforded 30, whose Kd value for RXRα is 5.1 μM, which is lower than that of danthron (17a).
4. Evaluation of RXR Antagonistic Activity
Though various RXR antagonists have been reported so far, their antagonistic activity has been evaluated in various ways, i.e., in terms of the dissociation constant (Ki value) using a tritium-labeled ligand such as 9-cis-retinoic acid (1), the binding constant obtained by the SPR method, the Kd value, the IC50 value, and pA2 against an RXR agonist in reporter assays (Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5).
The dissociation constant has been measured by using radioisotopes. However, this technique is complicated and requires special laboratory equipment, as well as disposal arrangements for radioactive waste. So far, no method using a fluorescent ligand has been established. Additionally, even if the binding ability to the receptor is detected, poor membrane permeability of the compound may influence the actual activity, as in the cases of 10a and 10c [52].
Antagonistic activity of LG100754 (3), the first reported RXR antagonist, was evaluated in terms of the IC50 value on transcriptional activation by 2 in reporter gene assays using CV-1 cells [42]. Similarly, PA452 (9b) [48] and UVI3003 (11) [54] were evaluated using PA024 (31) and CD3254 (33) as agonists, respectively. Since the activity differs depending on the coexisting RXR agonist, it is difficult to compare the observed potencies. The most widely used RXR agonist for reporter gene assays is 1 at the concentration of 0.1 μM. Therefore, it may be better to use this method as one index of activity in screening for new RXR antagonists.
The pA2 value is used as an index of competitive antagonist activity. It is the negative logarithm of the molar concentration of the competitive antagonist required to shift the agonist’s EC50 to two-fold higher concentration. The pA2 value is also consistent with the affinity constant for the receptor [83]. Thus, it is desirable to include this method in a more rigorous evaluation of antagonist activity. However, in order to obtain these data, it is necessary to obtain a capacity activity curve of the agonist at three different antagonist concentrations at minimum. Compounds 9b and 16 have been evaluated using the pA2 value as an indicator of competitive antagonist activity [50].
RXR forms not only RXR homodimers, but also heterodimers with various nuclear receptors [2]. Therefore, it is interesting to know whether RXR antagonists act as homodimer antagonists and/or heterodimer antagonists. Though 3 was found as an RXR homodimer antagonist, subsequent experiments revealed that it also acts as an agonist toward RAR/RXR [74], PPARα/RXR [75], and PPARγ/RXR [76,77]. Compound 6 has been found to show a synergistic effect in the presence of an agonist of PPARγ [45]. Compound 9b selectively antagonizes RXR in RXR/RAR heterodimer [48]. One micromole of 12 suppressed the activity of 100 nM rosiglitazone (PPARγ agonist) toward PPARγ/RXR to about a half [7]. Compound 17a has antagonistic activity not only towards the RXR homodimer, but also towards heterodimers such as PPARγ/RXRα, FXR/RXRα, LXRα/RXRα, etc. [60]. However, there was no description of the concentration of each agonist for partner receptors. Among them, for LXR/RXR, T0901317 [84] with an EC50 of 20 nM for LXRα was used at 5 μM. Based on these facts, it seems necessary to standardize assay systems for heterodimers.
5. Latest Research on RXR Antagonists
Here, we will briefly summarize research on RXR antagonists reported in the last five years, and then consider the prospects for RXR antagonists.
LG100754 (3) was reported to have a protective effect against oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelial cells [85]. This effect is thought to be caused by activation of PPARγ/RXR.
PA452 (9b) was reported to decrease an infection marker concentration-dependently in an HBV infection model using human hepatic stem cells [86]. It is considered that 9b suppresses transcription of viral RNA in HBV-infected hepatocyte-like cells by antagonizing RXR.
Teratogenicity of UVI3003 (11) was studied using zebrafish and Xenopus [87,88]. A difference in gene expression in Xenopus eggs was found depending on the exposure time to 11 [89]. In 2017, 11 was found to activate PPARγ in a reporter assay using Xenopus embryos. Moreover, studies using Xenopus treated with RXR agonist bexarotene (2) or 11 revealed that T3-dependent gene expression was altered during transformation of tadpoles [90].
Ro26-5405 (5) is reported to block T helper 2 differentiation and to prevent allergic lung inflammation [8]. The mechanism was suggested to be inhibition of Th2 differentiation by antagonizing RXR. In addition, in an atopic dermatitis model mouse, 11 was used as a tool to investigate the expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), which is triggered in atopic dermatitis and is involved in suppression [91]. TSLP is an IL-7-like cytokine and was shown to be a master switch of allergic inflammation at the epithelial cell–dendritic cell interface, leading to allergic sensitization. It is reported that the expression of TSLP involves RARγ/RXR.
Huang et al. used 12 as a tool to show that activation of RXR has a protective effect against hypoxia-reoxygenation disorder in H9c2 cardiomyocytes [92]. Franklin and colleagues revealed that phagocytosis and remyelination of myelin debris accompanying aging progressed upon activation of RXR using 12 [93]. Kajta et al. reported that apoptotic neurotoxic activity of 4-para-nonylphenol occurs simultaneously with RXR activation and a decrease in classical estrogen receptor signaling. They found that the effect of 4-para-nonylphenol on mitochondrial membrane potential was canceled by 12, indicating that this neurotoxicity involves activation of RXR [94]. Compound 12 is also reported to decrease both mobility and growth of Trichuris muris (a parasite) in vitro, indicating its potential as an anthelmintic drug [95]. RXR is negatively regulated by 1 and 12 through a nongenomic effect on platelets and thrombus formation [96].
Compound 12 is also used as a tool to investigate the influence of environmental hormones on RXR. For example, the mechanism of neurotoxicity by dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) [97], the effect of tributyltin on osteogenesis [98], and the toxicity of organotin [99] were found to involve transcriptional activation of RXR.
Zhang and colleagues found that R-etodolac (19), a NSAID, induces an antitumor effect via antagonistic activity toward RXRα, and also induces degradation of RXRα via the ubiquitin-proteasome system [63]. Subsequently, they also found RXR antagonist activity of sulindac (20), another NSAID. They suggested that nongenomic action of an N-terminally truncated RXRα (tRXRα) could play a role in the crosstalk with TNFα signaling in cancer cells [64,100]. tRXRα, which is produced by proteolytic cleavage of full-length RXRα, is highly expressed in a variety of tumor cells and tissues [101,102]. Furthermore, 20 was structurally developed to afford compounds 21a and 21b [64,65]. Crystal structure analysis of 21b in RXRα revealed that it binds to the RXR interface rather than the ligand-binding pocket, stabilizing RXR tetramers [65].
Similarly, Zhang et al., discovered triptolide (22a) in a natural product library [67]. Compound 22a regulates the survival of tRXRα-dependent cancer cells by apoptosis induction. Furthermore, 22a was structurally converted to TRC4 (22b), and 22b showed tRXRα-selective antagonism without transcriptional activation of RXRα [68]. In addition, NSC-640358 (23), which was discovered by virtual screening (Kd = 15.7 μM), induces apoptosis of cancer cells [69]. Compound 23 has been reported to inhibit the transcriptional activation of RXR homodimer by 1, but the IC50 value was not given.
In addition, Zhang et al., carried out one-hybrid assay with a compound library and found nitrostyrene derivatives 24 and 25 as RXR modulators [70]. Although these compounds showed RXR activity in mammalian one-hybrid assay using Gal4-DBD-RXRα-LBD, they showed antagonist activity in reporter assays using full-length RXR homodimer. Interestingly, 24 and 25 stabilize the RXR homodimer, unlike 21b. Size-exclusion chromatography indicated that the structure of the homodimer differs from the activated structure. These compounds have no activity to down-regulate tRXRα. Compounds 26, 27 were also discovered by virtual screening [71].
6. Important Points in the Use of RXR Antagonists
Some RXR antagonists reported to date show agonistic activity on RXR heterodimers. For example, LG100754 (3), in addition to antagonism of the RXR homodimer [43], shows agonist activity toward RAR/RXR [74], PPARα/RXR [75], and PPARγ/RXR. [76,77] UVI3003 (11) also shows agonistic activity for PPARγ/RXR [55]. HX531 (12), the most widely used RXR antagonist in vivo, has also been reported to antagonize RAR. [7] Chen et al. reported that down-regulation of RXRα leads to cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production in aged macrophages [103]. These data were obtained by administering 12 to mice. However, 12 was administered at a high concentration of 10 mg/kg i.p., every 24 h for seven days. The Cmax of 12 in mice after 100 mg/kg oral administration was only 4.1 µg/mL (8.5 μM) [7]. In order to improve oral absorption, 13a, 13b and 13c were created [57,58]. However, although 13a and 13b give Cmax values of approximately 500 nM after oral administration to rats at 1 mg/kg, there is no report as yet on their activities toward RXR heterodimers.
7. Conclusions
RXR antagonists are of increasing interest because of their therapeutic effects, i.e., hypoglycemic effect in type 2 diabetes models and anti-tumor effect via tRXRα. However, currently available RXR antagonists require high dosages in vivo when orally administered because of their poor absorption, and some of them activate heterodimers. Thus, there is still a need to develop new RXR antagonists to overcome these problems, and such compounds would be promising drug candidates, as well as useful experimental tools for biological studies on the roles of nuclear receptors.
Funding
This paper was supported by Okayama University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| i.p. | Intraperitoneal injection |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| NR | Nuclear receptor |
| Th2 | T helper type 2 |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TR | Thyroid hormone receptor |
| VDR | Vitamin D receptor |
| PXR | Pregnane X receptor |
References
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Thummel, C.; Beato, M.; Herrlich, P.; Schütz, G.; Umesono, K.; Blumberg, B.; Kastner, P.; Mark, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 1995, 83, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Evans, R.M. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 1995, 83, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Staels, B.; Dacquet, C.; Spedding, M.; Laudet, V. Overview of nomenclature of nuclear receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, B.M.; Umesono, K.; Chen, J.; Evans, R.M. Unique response pathways are established by allosteric interactions among nuclear hormone receptors. Cell 1995, 81, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenby, G.; Bocquel, M.T.; Saunders, M.; Kazmer, S.; Speck, J.; Rosenberger, M.; Lovey, A.; Kastner, P.; Grippo, J.F.; Chambon, P. Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: Interactions with endogenous retinoic acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileri, A.; Delfino, C.; Grandi, V.; Pimpinelli, N. Role of bexarotene in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: The clinical and immunological sides. Immunotherapy 2013, 5, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Waki, H.; Kamon, J.; Murakami, K.; Motojima, K.; Komeda, K.; Miki, H.; Kubota, N.; Terauchi, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; et al. Inhibition of RXR and PPARγ ameliorates diet-induced obesity and type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenningloh, R.; Gho, A.; di Lucia, P.; Klaus, M.; Bollag, W.; Ho, I.C.; Sinigaglia, F.; Panina-Bordignon, P. Cutting Edge: Inhibition of the Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) Blocks T Helper 2 Differentiation and Prevents Allergic Lung Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5161–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuclear Receptor Nomenclature Committee. A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily. Cell 1999, 97, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Chambon, P.; Eichele, G.; Evans, R.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Leid, M.; De Lera, A.R.; Lotan, R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Gronemeyer, H. International Union of Pharmacology. LXIII. Retinoid X receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourguet, W.; Ruff, M.; Chambon, P.; Gronemeyer, H.; Moras, D. Crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the human nuclear receptor RXR-alpha. Nature 1995, 375, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, F.; Gewirth, D.T. DNA recognition by nuclear receptors. Essays Biochem. 2004, 40, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Hamuro, Y.; Raghuram, S.; Wang, Y.; Burris, T.P.; Rastinejad, F. Structure of the intact PPAR-gamma-RXR-nuclear receptor complex on DNA. Nature 2008, 456, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; Toresson, G.; Benod, C.; Suh, J.H.; Philips, K.J.; Webb, P.; Gustafsson, J.A. Structure of the retinoid X receptor α-liver X receptor β (RXRα-LXRβ) heterodimer on DNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osz, J.; McEwen, A.G.; Poussin-Courmontagne, P.; Moutier, E.; Birck, C.; Davidson, I.; Moras, D.; Rochel, N. Structural basis of natural promoter recognition by the retinoid X nuclear receptor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, S.; Kelleher, D.; Chambon, P.; Gronemeyer, H.; Noy, N. Retinoid X receptor α forms tetramers in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8645–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, R.; Yeung, K.T.; Chung, R.H.; Gaczynska, M.E.; Osmulski, P.A.; Noy, N. DNA-looping by RXR tetramers permits transcriptional regulation “at a distance”. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, R.; Kannan-Thulasiraman, P.; Kagechika, H.; Dawson, M.I.; Noy, N. Inhibition of mammary carcinoma cell growth by RXR is mediated by the receptor’s oligomeric switch. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delacroix, L.; Moutier, E.; Altobelli, G.; Legras, S.; Poch, O.; Choukrallah, M.A.; Bertin, I.; Jost, B.; Davidson, I. Cell-specific interaction of retinoic acid receptors with target genes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts and embryonic stem cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IJpenberg, A.; Tan, N.S.; Gelman, L.; Kersten, S.; Seydoux, J.; Xu, J.; Metzger, D.; Canaple, L.; Chambon, P.; Wahli, W.; et al. In vivo activation of PPAR target genes by RXR homodimers. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourguet, W.; Germain, P.; Gronemeyer, H. Nuclear receptor ligand-binding domains: Three-dimensional structures, molecular interactions and pharmacological implications. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, R.G. The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Hu, X.; DiRenzo, J.; Lazar, M.A.; Brown, M. Cofactor dynamics and sufficiency in estrogen receptor-regulated transcription. Cell 2000, 103, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lazar, M.A. The CoRNR motif controls the recruitment of corepressors by nuclear hormone receptors. Nature 1999, 402, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiRenzo, J.; Söderstrom, M.; Kurokawa, R.; Ogliastro, M.H.; Ricote, M.; Ingrey, S.; Hörlein, A.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Glass, C.K. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and retinoic acid receptors differentially control the interactions of retinoid X receptor heterodimers with ligands, coactivators, and corepressors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 2166–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burris, T.P.; Solt, L.A.; Wang, Y.; Crumbley, C.; Banerjee, S.; Griffett, K.; Lundasen, T.; Hughes, T.; Kojetin, D.J. Nuclear receptors and their selective pharmacologic modulators. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 710–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, K.; Takano, A.; Yakushiji, N.; Morohashi, K.; Morishita, K.; Matsuura, N.; Makishima, M.; Tai, A.; Sasaki, K.; Kakuta, H. The First Potent Subtype-Selective Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) Agonist Possessing a 3-Isopropoxy-4-isopropylphenylamino Moiety, NEt-3IP (RXRα/β-dual agonist). ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, K.; Takano, A.; Yakushiji, N.; Morishita, K.; Matsuura, N.; Makishima, M.; Ali, H.I.; Akaho, E.; Tai, A.; Sasaki, K.; et al. Reduction of lipophilicity at the lipophilic domain of RXR agonists enables production of subtype preference: RXRalpha-preferential agonist possessing a sulfonamide moiety. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, K.; Yakushiji, N.; Ohsawa, F.; Takamatsu, K.; Matsuura, N.; Makishima, M.; Kawahata, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tai, A.; Sasaki, K.; et al. Replacing alkyl sulfonamide with aromatic sulfonamide in sulfonamide-type RXR agonists favors switch towards antagonist activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, E.; Bourguet, W.; Gronemeyer, H.; de Lera, A.R. Modulation of RXR function through ligand design. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayaratne, A.L.; McDonnell, D.P. The human estrogen receptor-alpha is a ubiquitinated protein whose stability is affected differentially by agonists, antagonists, and selective estrogen receptor modulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35684–35692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rőszer, T.; Menéndez-Gutiérrez, M.P.; Cedenilla, M.; Ricote, M. Retinoid X receptors in macrophage biology. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valledor, A.F.; Ricote, M. Nuclear receptor signaling in macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Széles, L.; Póliska, S.; Nagy, G.; Szatmari, I.; Szanto, A.; Pap, A.; Lindstedt, M.; Santegoets, S.J.; Rühl, R.; Dezsö, B.; et al. Research resource: Transcriptome profiling of genes regulated by RXR and its permissive and nonpermissive partners in differentiating monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 2218–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, L.; Szanto, A.; Szatmari, I.; Széles, L. Nuclear hormone receptors enable macrophages and dendritic cells to sense their lipid environment and shape their immune response. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 739–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saijo, K.; Crotti, A.; Glass, C.K. Regulation of microglia activation and deactivation by nuclear receptors. Glia 2013, 61, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, K.; Cowie, D.E.; Konstantinou, D.K.; Hill, S.J.; Tjelle, T.E.; Axon, A.; Koruth, M.; White, S.A.; Carlsen, H.; Mann, D.A.; et al. The PXR is a drug target for chronic inflammatory liver disease. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 120, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavassori, P.; Mencarelli, A.; Renga, B.; Distrutti, E.; Fiorucci, S. The bile acid receptor FXR is a modulator of intestinal innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6251–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, P.; Chinetti, G.; Staels, B. Nur77turing macrophages in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, L.C.; Soto, E.; Hong, C.; Ito, A.; Pei, L.; Chawla, A.; Conneely, O.M.; Tangirala, R.K.; Evans, R.M.; Tontonoz, P. Bone marrow NR4A expression is not a dominant factor in the development of atherosclerosis or macrophage polarization in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, R.N.; Shaked, I.; Hubbeling, H.G.; Punt, J.A.; Wu, R.; Herrley, E.; Zaugg, C.; Pei, H.; Geissmann, F.; Ley, K.; et al. NR4A1 (Nur77) deletion polarizes macrophages toward an inflammatory phenotype and increases atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canan Koch, S.S.; Dardashti, L.J.; Hebert, J.J.; White, S.K.; Croston, G.E.; Flatten, K.S.; Heyman, R.A.; Nadzan, A.M. Identification of the First Retinoid X Receptor Homodimer Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 3229–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WO2001019770 RXR Modulators with Improved Pharmacologic Profile. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2001019770 (accessed on 24 May 2018).
- WO2000053562 Retinoid Antagonists and Use Thereof. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2000053562 (accessed on 24 May 2018).
- Michellys, P.Y.; Ardecky, R.J.; Chen, J.H.; Crombie, D.L.; Etgen, G.J.; Faul, M.M.; Falkner, A.L.; Grese, T.A.; Heyman, R.A.; Karanewsky, D.S.; et al. Novel (2E,4E,6Z)-7-(2-Alkoxy-3,5-dialkylbenzene)-3-methylocta-2,4,6-trienoic Acid Retinoid X Receptor Modulators Are Active in Models of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2683–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michellys, P.Y.; Ardecky, R.J.; Chen, J.H.; D’Arrigo, J.; Grese, T.A.; Karanewsky, D.S.; Leibowitz, M.D.; Liu, S.; Mais, D.A.; Mapes, C.M.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Novel 6,7-Locked-[7-(2-alkoxy-3,5-dialkylbenzene)-3-methylocta]-2,4,6-trienoic Acids. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4087–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michellys, P.Y.; D’Arrigo, J.; Grese, T.A.; Karanewsky, D.S.; Leibowitz, M.D.; Mais, D.A.; Mapes, C.M.; Reifel-Miller, A.; Rungta, D.; Boehm, M.F. Design, synthesis and structure–activity relationship of novel RXR-selective modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, B.; Ohta, K.; Kawachi, E.; Fukasawa, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kagechika, H. Novel Retinoid X Receptor Antagonists: Specific Inhibition of Retinoid Synergism in RXR-RAR Heterodimer Actions. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 3327–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Ohsawa, F.; Yamada, S.; Shinozaki, R.; Fukai, R.; Makishima, M.; Enomoto, S.; Tai, A.; Kakuta, H. Modification at the acidic domain of RXR agonists has little effect on permissive RXR-heterodimer activation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5139–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Yamada, S.; Ohsawa, F.; Ohta, Y.; Kawata, K.; Makishima, M.; Kakuta, H. Discovery of a Potent Retinoid X Receptor Antagonist Structurally Closely Related to RXR Agonist NEt-3IB. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavasotto, C.N.; Liu, G.; James, S.Y.; Hobbs, P.D.; Peterson, V.J.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Kolluri, S.K.; Zhang, X.K.; Leid, M.; Abagyan, R.; et al. Determinants of Retinoid X Receptor Transcriptional Antagonism. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 4360–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Dawson, M.I.; Hu, Q.Y.; Xia, Z.; Dambacher, J.D.; Ye, M.; Zhang, X.K.; Li, E. The effect of antagonists on the conformational exchange of the retinoid X receptor alpha ligand-binding domain. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuligonda, V.; Thacher, S.M.; Chandraratna, R.A. Enantioselective Syntheses of Potent Retinoid X Receptor Ligands: Differential Biological Activities of Individual Antipodes. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 2298–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahoum, V.; Pérez, E.; Germain, P.; Rodríguez-Barrios, F.; Manzo, F.; Kammerer, S.; Lemaire, G.; Hirsch, O.; Royer, C.A.; Gronemeyer, H.; et al. Modulators of the structural dynamics of the retinoid X receptor to reveal receptor function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17323–17328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Janesick, A.; Wu, L.; Hu, L.; Tang, W.; Blumberg, B.; Shi, H. The unexpected teratogenicity of RXR antagonist UVI3003 via activation of PPARγ in Xenopus tropicalis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 314, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebisawa, M.; Umemiya, H.; Ohta, K.; Fukasawa, H.; Kawachi, E.; Christoffel, G.; Gronemeyer, H.; Tsuji, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Shudo, K.; et al. Retinoid X receptor-antagonistic diazepinylbenzoic acids. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaki, J.; Konishi, K.; Kishida, M.; Gunji, H.; Kanazawa, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Fukaya, H.; Mitani, H.; Kimura, M. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of RXR antagonists based on the diazepinylbenzoic acid structure. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4808–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaki, J.; Kishida, M.; Konishi, K.; Gunji, H.; Toyao, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Fukaya, H.; Mitani, H.; et al. Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of novel RXR antagonists: Orally active anti-diabetic and anti-obesity agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4804–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, K.; Iijima, T.; Kawachi, E.; Kagechika, H.; Endo, Y. Novel retinoid X receptor (RXR) antagonists having a dicarba-closo-dodecaborane as a hydrophobic moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5913–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, R.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Ding, H.; Yu, L.; Hu, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Danthron Functions as a Retinoic X Receptor Antagonist by Stabilizing Tetramers of the Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X. Structural Basis for Retinoic X Receptor Repression on the Tetramer. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24593–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Narayanasamy, S.; Curley, R.W., Jr.; Harrison, E.H. β-Apo-13-carotenone regulates retinoid X receptor transcriptional activity through tetramerization of the receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 33118–33124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolluri, S.K.; Corr, M.; James, S.Y.; Bernasconi, M.; Lu, D.; Liu, W.; Cottam, H.B.; Leoni, L.M.; Carson, D.A.; Zhang, X.K. The R-enantiomer of the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug etodolac binds retinoid X receptor and induces tumor-selective apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2525–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.; Wei, Z.; Liu, J.; Kolluri, S.K.; Wu, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. NSAID Sulindac and Its Analogs Bind RXRα and Inhibit RXRα-dependent AKT Signaling. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.G.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J.F.; Gao, W.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.K.; Huang, P.Q.; Su, Y. Synthesis and SAR study of modulators inhibiting tRXRα-dependent AKT activation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 62, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Z.G.; Aleshin, A.E.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Jiang, F.; Alitongbieke, G.; Zeng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Huang, M.; et al. Sulindac-derived RXRα modulators inhibit cancer cell growth by binding to a novel site of RXRα. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, F.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Zeng, W.; Cao, X.; Yan, T.; et al. Antagonist effect of triptolide on AKT activation by truncated retinoid X receptor-alpha. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.Y.; Zeng, W.J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Pang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Yan, X.; Wong, A.S.T.; et al. TRC4, an improved triptolide derivative, specifically targets to truncated form of retinoid X receptor-alpha in cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 124, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Cheltsov, A.V.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, L.; Huang, M.; Hu, M.; et al. NSC-640358 acts as RXRα ligand to promote TNFα-mediated apoptosis of cancer cell. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Sun, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Huang, F.; et al. Nitrostyrene Derivatives Act as RXRα Ligands to Inhibit TNFα Activation of NF-κB. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Huang, M.; Hu, M.; Su, Y.; Zhang, X.K. Identification of a New RXRα Antagonist Targeting the Coregulator-Binding Site. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Cai, L.; Guo, S.; Xie, L.; Yin, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Su, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, X. Virtual screening and experimental validation identify novel modulators of nuclear receptor RXRα from Drugbank database. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, M.F.; Zhang, L.; Badea, B.A.; White, S.K.; Mais, D.E.; Berger, E.; Suto, C.M.; Goldman, M.E.; Heyman, R.A. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationships of Novel Retinoid XReceptor-Selective Retinoids. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 2930–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, I.G.; Li, C.; Schwabe, J.W.; Evans, R.M. The phantom ligand effect: Allosteric control of transcription by the retinoid X receptor. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, D.S.; Mukherjee, R.; Schulman, I.G.; Koch, S.S.; Dardashti, L.J.; Nadzan, A.M.; Croston, G.E.; Evans, R.M.; Heyman, R.A. Activation of specific RXR heterodimers by an antagonist of RXR homodimers. Nature 1996, 383, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, R.; Jow, L.; Croston, G.E.; Paterniti, J.R., Jr. Identification, characterization, and tissue distribution of human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) isoforms PPARgamma2 versus PPARgamma1 and activation with retinoid X receptor agonists and antagonists. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 8071–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesario, R.M.; Klausing, K.; Razzaghi, H.; Crombie, D.; Rungta, D.; Heyman, R.A.; Lala, D.S. The Rexinoid LG100754 Is a Novel RXR:PPARγ Agonist and Decreases Glucose Levels in Vivo. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Ramalanjaona, N.; Huet, T.; Potier, N.; Osz, J.; Antony, P.; Peluso-Iltis, C.; Poussin-Courmontagne, P.; Ennifar, E.; Mély, Y.; et al. The “Phantom Effect” of the Rexinoid LG100754: Structural and functional insights. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, M.I.; Hobbs, P.D.; Jong, L.; Xiao, D.; Chao, W.R.; Pan, C.; Zhang, X.K. sp2-Bridged Diaryl Retinoids: Efects of Bridge-Region Substitution on Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) Selectivity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 1307–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Santín, E.; Germain, P.; Quillard, F.; Khanwalkar, H.; Rodríguez-Barrios, F.; Gronemeyer, H.; de Lera, A.R.; Bourguet, W. Modulating Retinoid X Receptor with a Series of (E)-3-[4-Hydroxy-3-(3-alkoxy-5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)phenyl]acrylic Acids and Their 4-Alkoxy Isomers. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3150–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotsumoto, T.; Naitoh, T.; Kanaki, T.; Tsuruzoe, N. A retinoid X receptor antagonist, HX531, improves leptin resistance without increasing plasma leptin level in KK-Ay mice under normal dietary conditions. Metabolism 2005, 54, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, K.; Morishita, K.; Nakayama, M.; Yamada, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Furusawa, Y.; Arimoto-Kobayashi, S.; Oohashi, T.; Makishima, M.; Naitou, H.; et al. RXR Partial Agonist Produced by Side Chain Repositioning of Alkoxy RXR Full Agonist Retains Antitype 2 Diabetes Activity without the Adverse Effects. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazareno, S.; Birdsall, N.J. Estimation of competitive antagonist affinity from functional inhibition curves using the Gaddum, Schild and Cheng-Prusoff equations. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 109, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.R.; Tu, H.; Luk, A.; Repa, J.J.; Medina, J.C.; Li, L.; Schwendner, S.; Wang, S.; Thoolen, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala-Peña, V.B.; Pilotti, F.; Volonté, Y.; Rotstein, N.P.; Politi, L.E.; German, O.L. Protective effects of retinoid x receptors on retina pigment epithelium cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Carpentier, A.; Cheng, X.; Block, P.D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Protzer, U.; Liang, T.J. Human stem cell-derived hepatocytes as a model for hepatitis B virus infection, spreading and virus-host interactions. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Xu, T.; Li, D.; Zhou, J. A representative retinoid X receptor antagonist UVI3003 induced teratogenesis in zebrafish embryos. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Yu, J.; Shi, H.; Xia, L.; Xin, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Luo, J.; Jin, W.; Li, D.; Zhou, J. Quantitative toxicoproteomic analysis of zebrafish embryos exposed to a retinoid X receptor antagonist UVI3003. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, H.; Zhu, P.; Hu, L.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Rotchell, J.M. Effects of antagonist of retinoid X receptor (UVI3003) on morphology and gene profile of Xenopus tropicalis embryos. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengeling, B.J.; Goodson, M.L.; Furlow, J.D. RXR Ligands Modulate Thyroid Hormone Signaling Competence in Young Xenopus laevis Tadpoles. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2576–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihály, J.; Gericke, J.; Lucas, R.; de Lera, A.R.; Alvarez, S.; Törőcsik, D.; Rühl, R. TSLP expression in the skin is mediated via RARγ-RXR pathways. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, P.R.; Xu, W.W.; Huang, Z.Q.; Pu, J.; Huang, W.J. Protective role of retinoid X receptor in H9c2 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in rats. World J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 5, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natrajan, M.S.; de la Fuente, A.G.; Crawford, A.H.; Linehan, E.; Nuñez, V.; Johnson, K.R.; Wu, T.; Fitzgerald, D.C.; Ricote, M.; Bielekova, B.; et al. Retinoid X receptor activation reverses age-related deficiencies in myelin debris phagocytosis and remyelination. Brain 2015, 138, 3581–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwa, E.; Rzemieniec, J.; Wnuk, A.; Lason, W.; Krzeptowski, W.; Kajta, M. Apoptotic and neurotoxic actions of 4-para-nonylphenol are accompanied by activation of retinoid X receptor and impairment of classical estrogen receptor signaling. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, R.J.; Hopwood, T.; Gallagher, A.L.; Partridge, F.A.; Burgis, T.; Sattelle, D.B.; Else, K.J. An antagonist of the retinoid X receptor reduces the viability of Trichuris muris in vitro. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, A.J.; Flora, G.D.; Sasikumar, P.; Bye, A.P.; Sage, T.; Kriek, N.; Crescente, M.; Gibbins, J.M. RXR Ligands Negatively Regulate Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnuk, A.; Rzemieniec, J.; Litwa, E.; Lasoń, W.; Krzeptowski, W.; Wójtowicz, A.K.; Kajta, M. The Crucial Involvement of Retinoid X Receptors in DDE Neurotoxicity. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 29, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.H.; Watt, J.; Huang, C.K.; Gerstenfeld, L.C.; Schlezinger, J.J. Tributyltin engages multiple nuclear receptor pathways and suppresses osteogenesis in bone marrow multipotent stromal cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urushitani, H.; Katsu, Y.; Kagechika, H.; Sousa, A.C.A.; Barroso, C.M.; Ohta, Y.; Shiraishi, H.; Iguchi, T.; Horiguchi, T. Characterization and comparison of transcriptional activities of the retinoid X receptors by various organotin compounds in three prosobranch gastropods; Thais clavigera, Nucella lapillus and Babylonia japonica. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.H.; Jiang, F.Q.; Duan, Y.H.; Zeng, Z.P.; Chen, F.; Dai, Y.; Chen, J.B.; Liu, J.X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Targeting Truncated Retinoid X Receptor-α by CF31 Induces TNF-α-Dependent Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liu, J.; Hu, M.; Huang, M.; Cai, S.; Zeng, Z.; Lin, B.; Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Zeng, J.Z.; et al. Regulation of proteolytic cleavage of retinoid X receptor-α by GSK-3β. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.K.; Su, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H. Regulation of the nongenomic actions of retinoid X receptor-α by targeting the coregulator-binding sites. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ma, F.; Hu, X.; Jin, T.; Xiong, C.; Teng, X. Elevated COX2 expression and PGE2 production by downregulation of RXRα in senescent macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 440, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).