A Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback Converter with Resonant Operation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
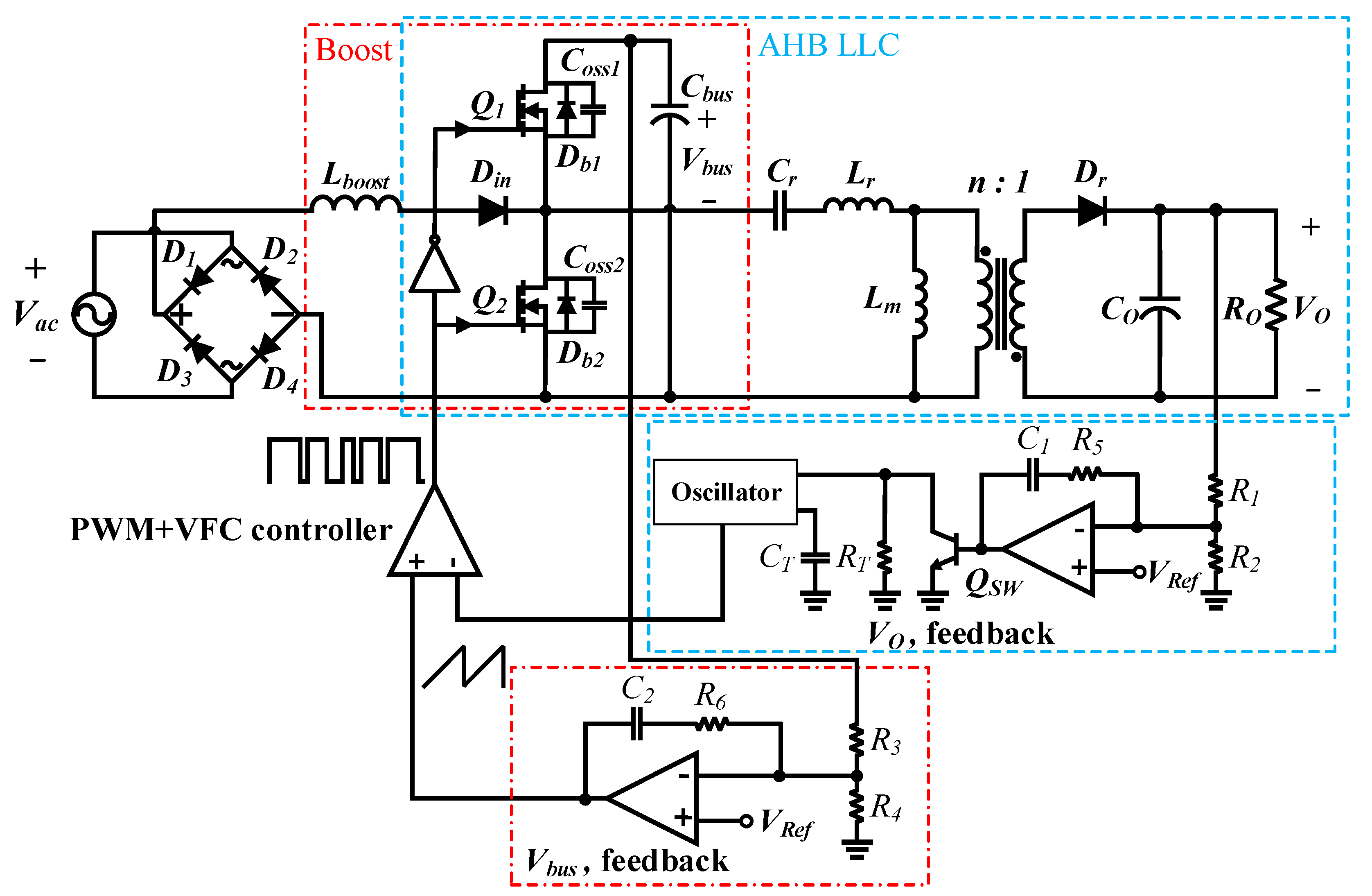
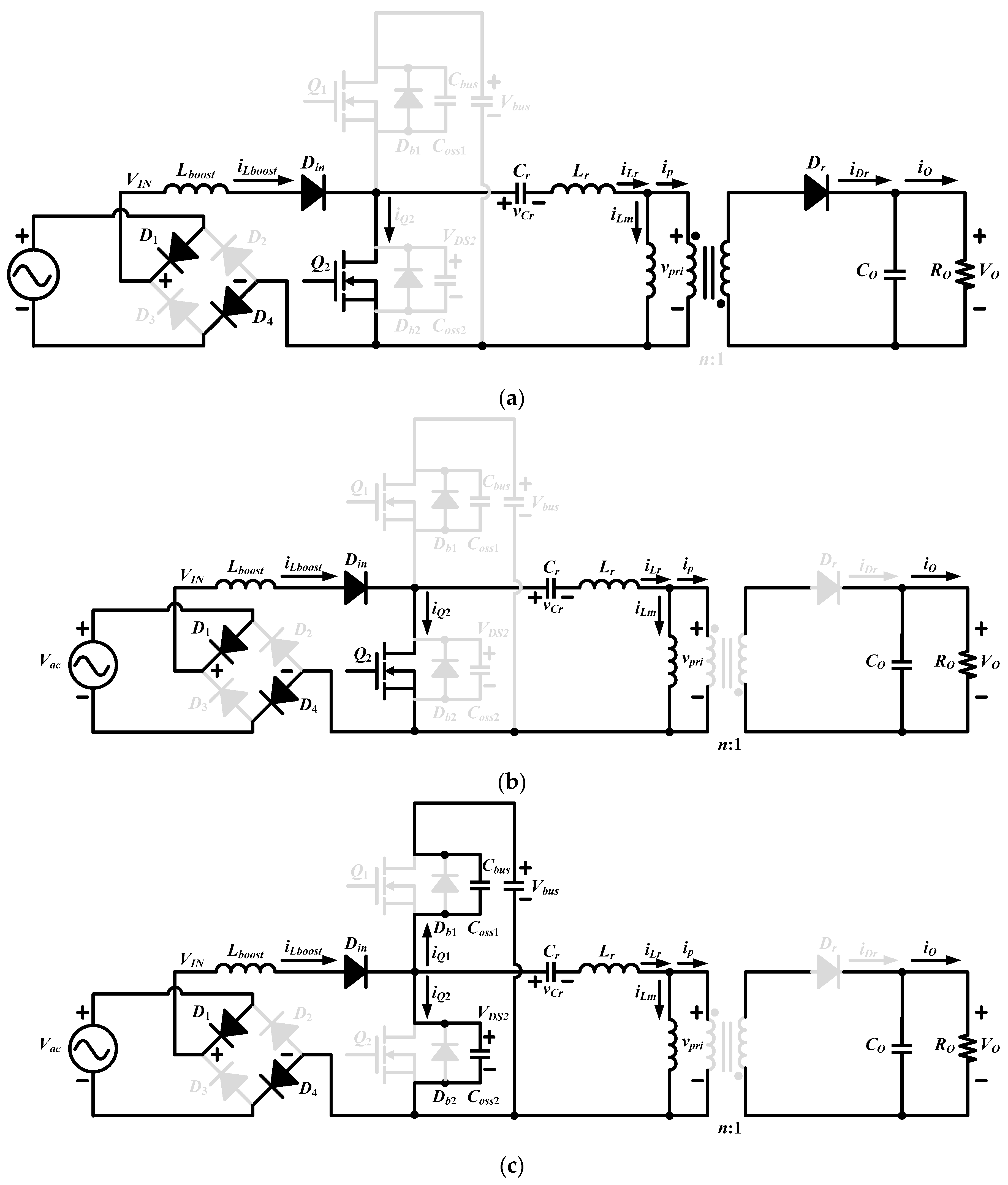
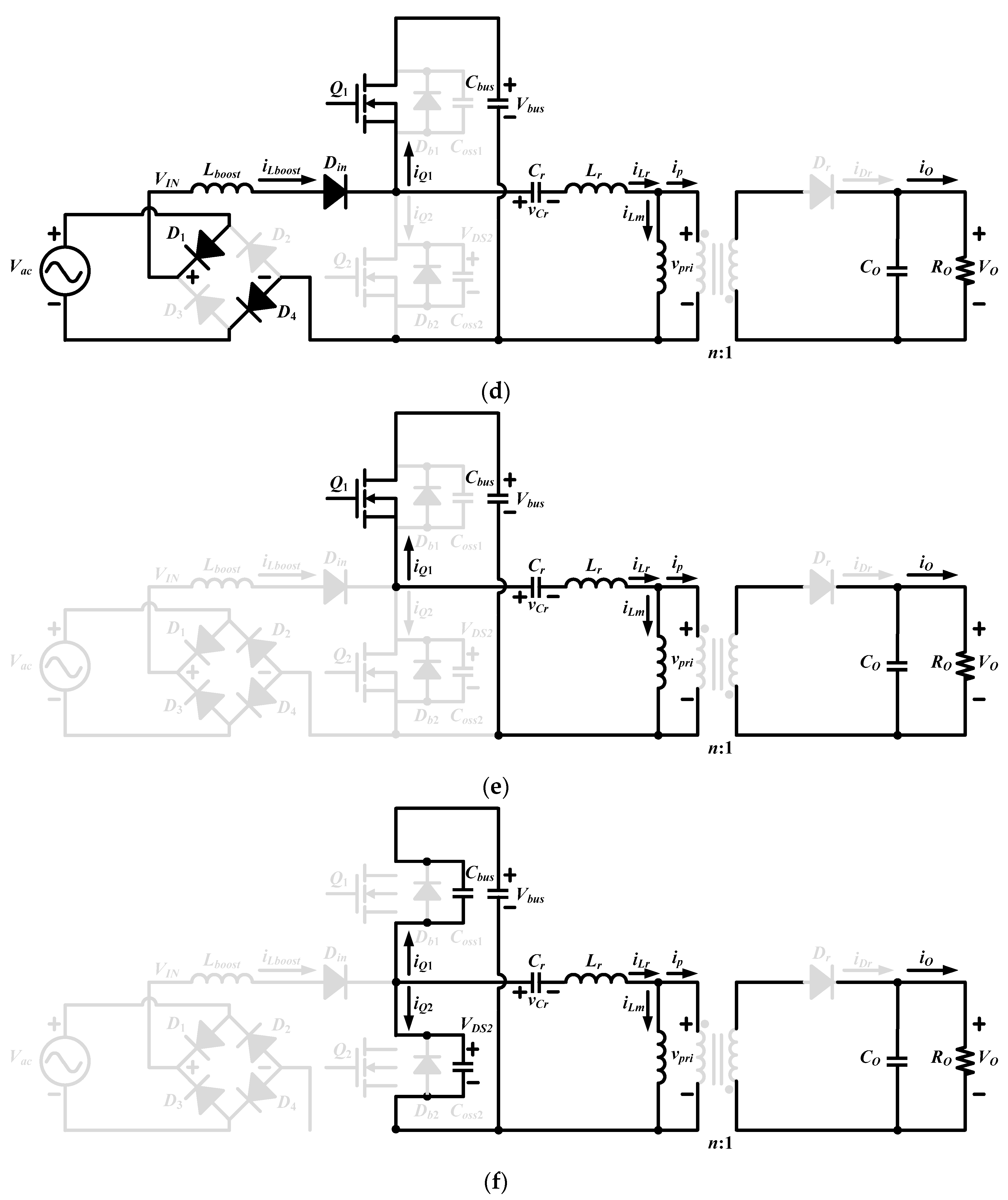
2. Circuit Description and Principle Operation of Proposed Converter
- -
- These conduction losses of all switches, diodes and layout traces, and the copper losses of the transformer are neglected.
- -
- The turn ratio of the transformer windings is n = N1/N2.
- -
- The resonant inductor Lr is composed of a leakage inductor and external inductor, where Lr = Leakage + Lex.
- -
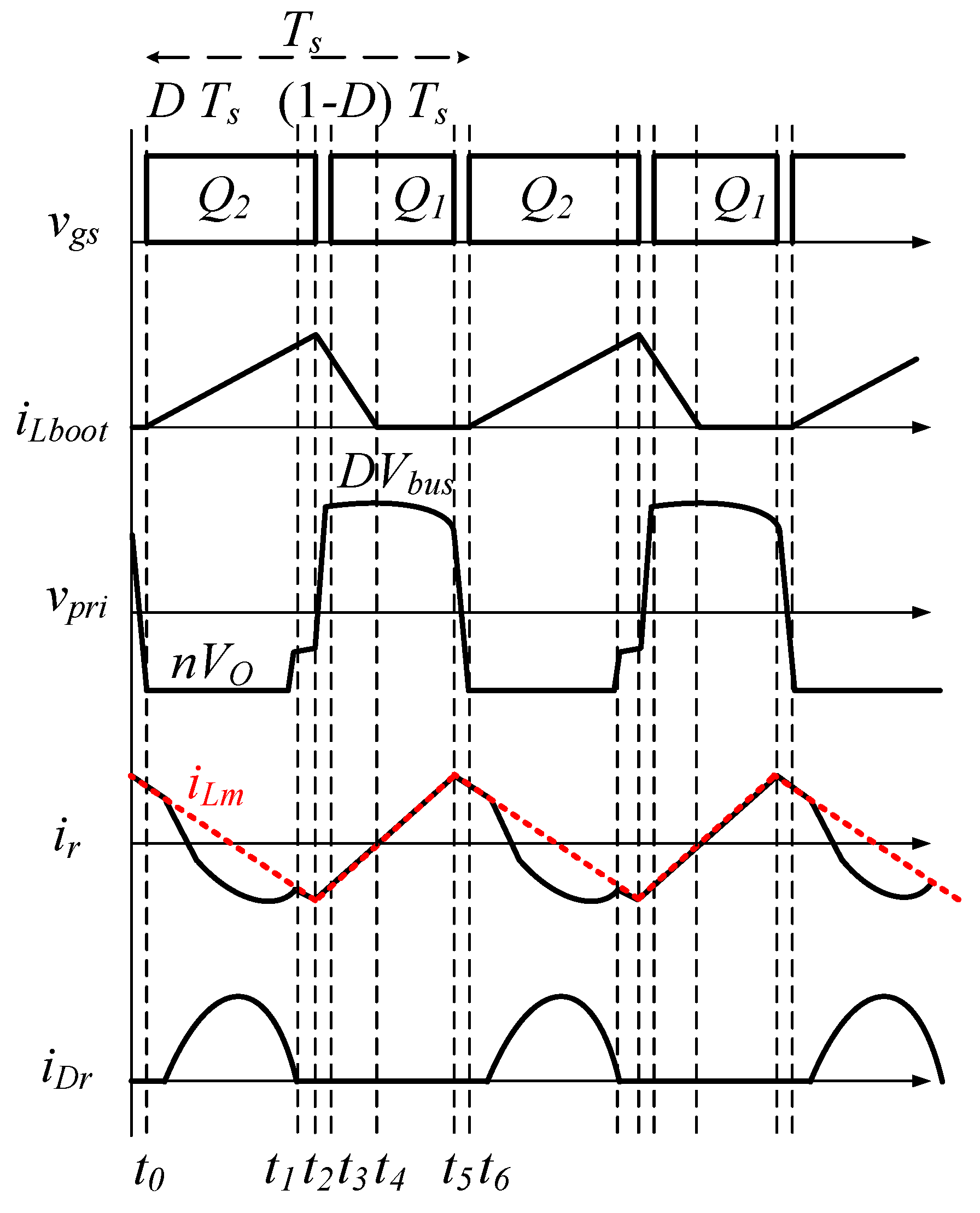
- The conduction times for Q1 are (1 − D)Ts and Q2 is DTs, respectively, where D is the duty cycle for Q2, and Ts denotes the switching period. In addition, the dead time is much smaller than that other of conduction times.
- -
- In the steady state the bus capacitance Cbus and output capacitance CO are large enough so that the bus voltage Vbus and output voltage VO are a constant value.
3. Circuit Design for the Proposed Converter
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, J.; Lee, F.C. A high-efficiency single-stage single-switch high-power-factor AC/DC converter with universal input. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1998, 13, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.S.; Park, S.J.; Kim, C.U. ZVZCS single-stage PFC AC-to-DC half-bridge converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lee, F.C.; Jovanovic, M.M. An improved CCM single-stage PFC converter with a low frequency auxiliary switch. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2003, 18, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, M.; Nishi, T. Graph-theoretical approach to 2-switch DC-DC converter. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2005, 33, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.L.; Egan, M.G.; Willers, M.J. A Family of Single-Stage Resonant AC/DC Converters with PFC. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willers, M.J.; Egan, M.G.; Daly, S.; Murphy, J.M.D. Analysis and design of a practical discontinuous-conduction-mode BIFRED converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1999, 46, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Lin, B.T. Add active clamping and soft switching to boost flyback single stage isolated power factor corrected power supplies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3144–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Li, Z.R.; Chen, C.L. Analysis and Design of single stage AC/DC LLC resonant converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wei, H.; Zhu, G.; Batarseh, I. Several Schemes of Alleviating Bus Voltage Stress in Single Stage Power Factor Correction Converters. In Proceedings of the Power Electronics and Drive Systems Conference, Hong Kong, China, 27–29 July 1999; pp. 921–926. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M. Design Considerations of Soft-Switched Buck PFC Converter with Constant On-Time (COT) Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3144–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ye, X.; Qian, Z. Analysis and Derivations for a Family ZVS Converter Based on a New Active Clamp ZVS Cell. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Lim, W.; Bang, S.; Choi, S. Small-signal analysis and control design of asymmetrical half-bridge DC-DC converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.; Hua, G.C.; Lee, F.C. Characterization of an active clamp flyback topology for power factor correction applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1996, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.M.; Choi, W.Y.; Do, H.L.; Kwon, B.H. Single-stage half-bridge converter using a coupled-inductor. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2005, 152, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H. Feed-Forward Compensator of operating Frequency for APWM HB Flyback Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Jung, J.H.; Baek, J.W.; Kim, H.J. Analysis and design of a multioutput converter using a symmetrical PWM half-bridge flyback converter employing a parallel-series transformer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.T.; Kwon, J.M.; Lee, H.M.; Kwon, B.H. Single-stage high-power factor half-bridge flyback converter with synchronous rectifier. IET Power Electron. 2014, 7, 1755–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buso, S.; Spiazzi, G.; Sichirollo, F. Study of the asymmetrical half-bridge flyback converter as an effective line fed solid state lamp driver. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6730–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. A Study of Z-Source Dual-Bridge Matrix Converter Immune to Abnormal Input Voltage Disturbance and with High Voltage Transfer Ratio. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2013, 9, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, S.; Yi, X. Analysis and Design of High Frequency Asymmetrical Half Bridge Flyback Converter. In Proceedings of the Electrical Machines and Systems International Conference, Wuhan, China, 17–20 October 2008; pp. 1902–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, C.K.; Chow, M.H.L. New Single-Stage Power-Factor-Corrected Regulators Operating in Discontinuous Capacitor Voltage Mode. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Saint Louis, MO, USA, 27–27 June 1997; pp. 371–377. [Google Scholar]



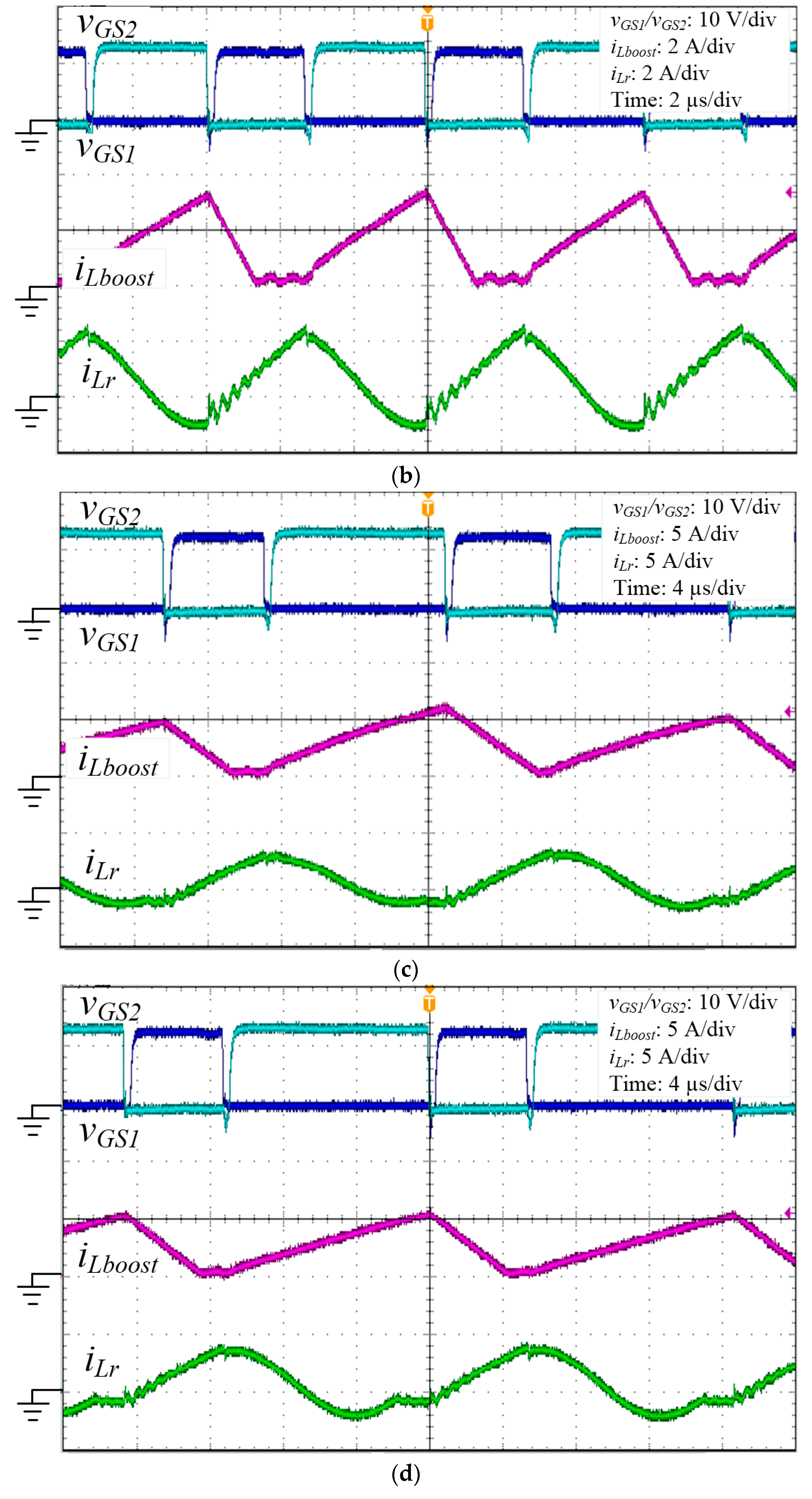
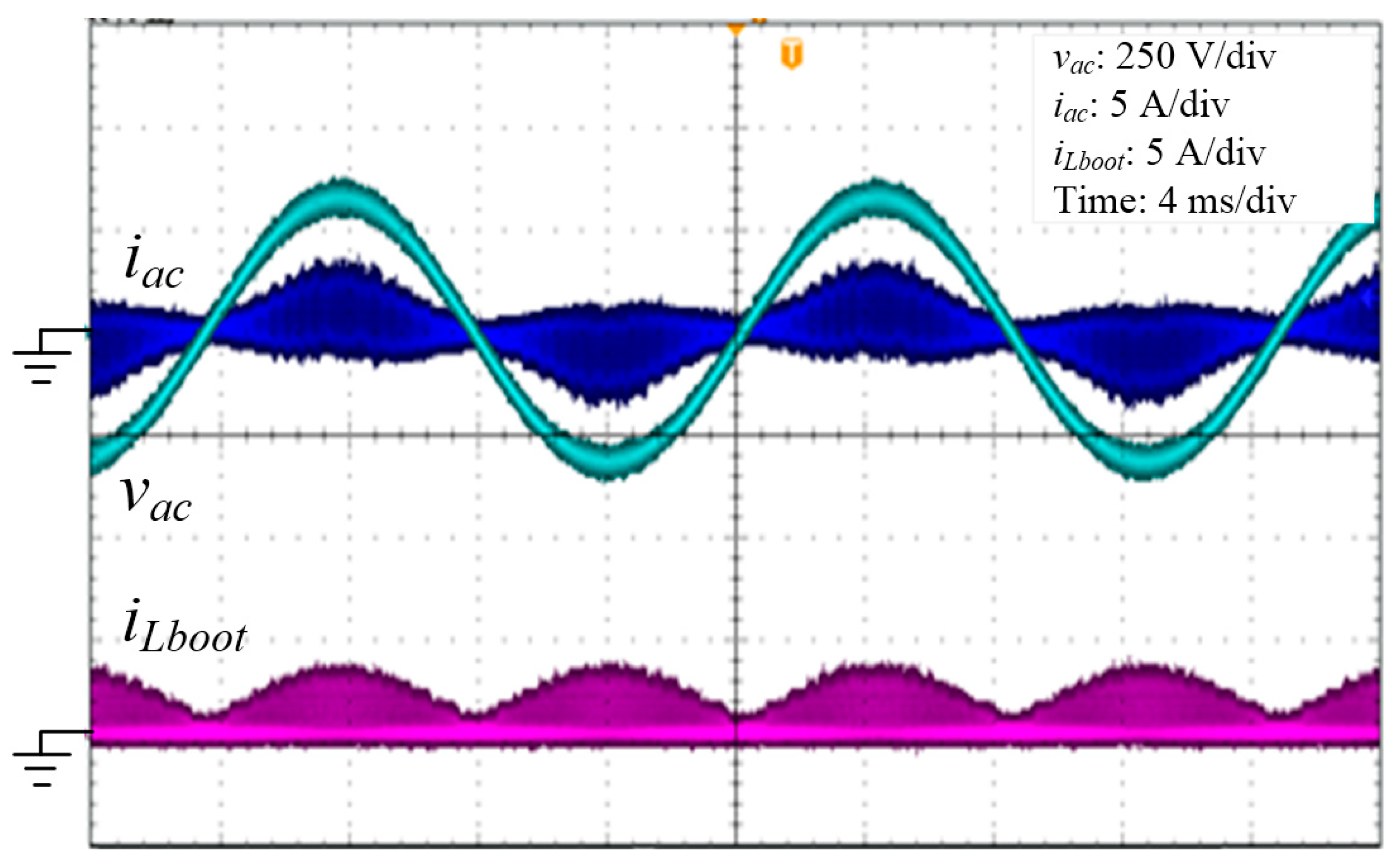
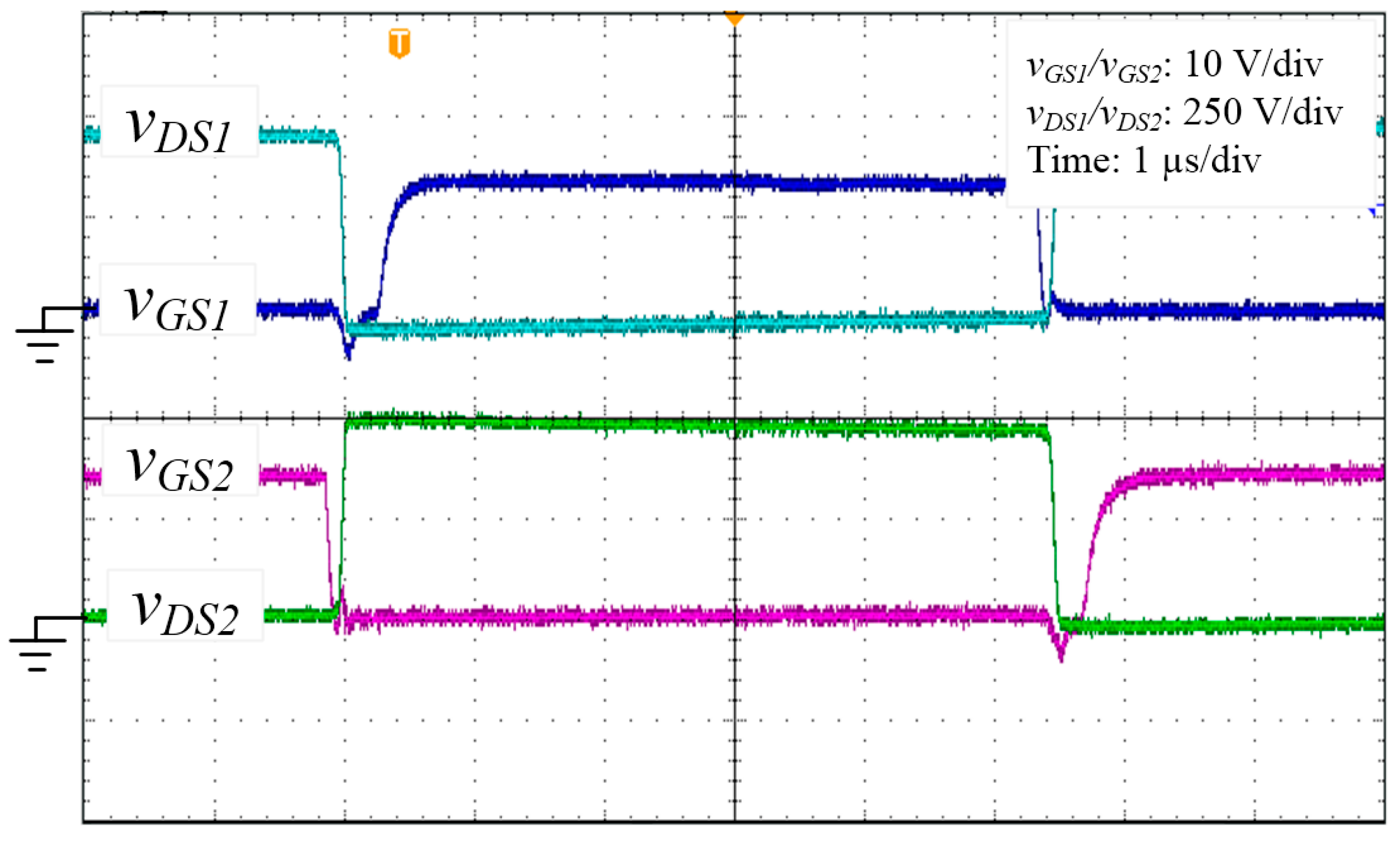
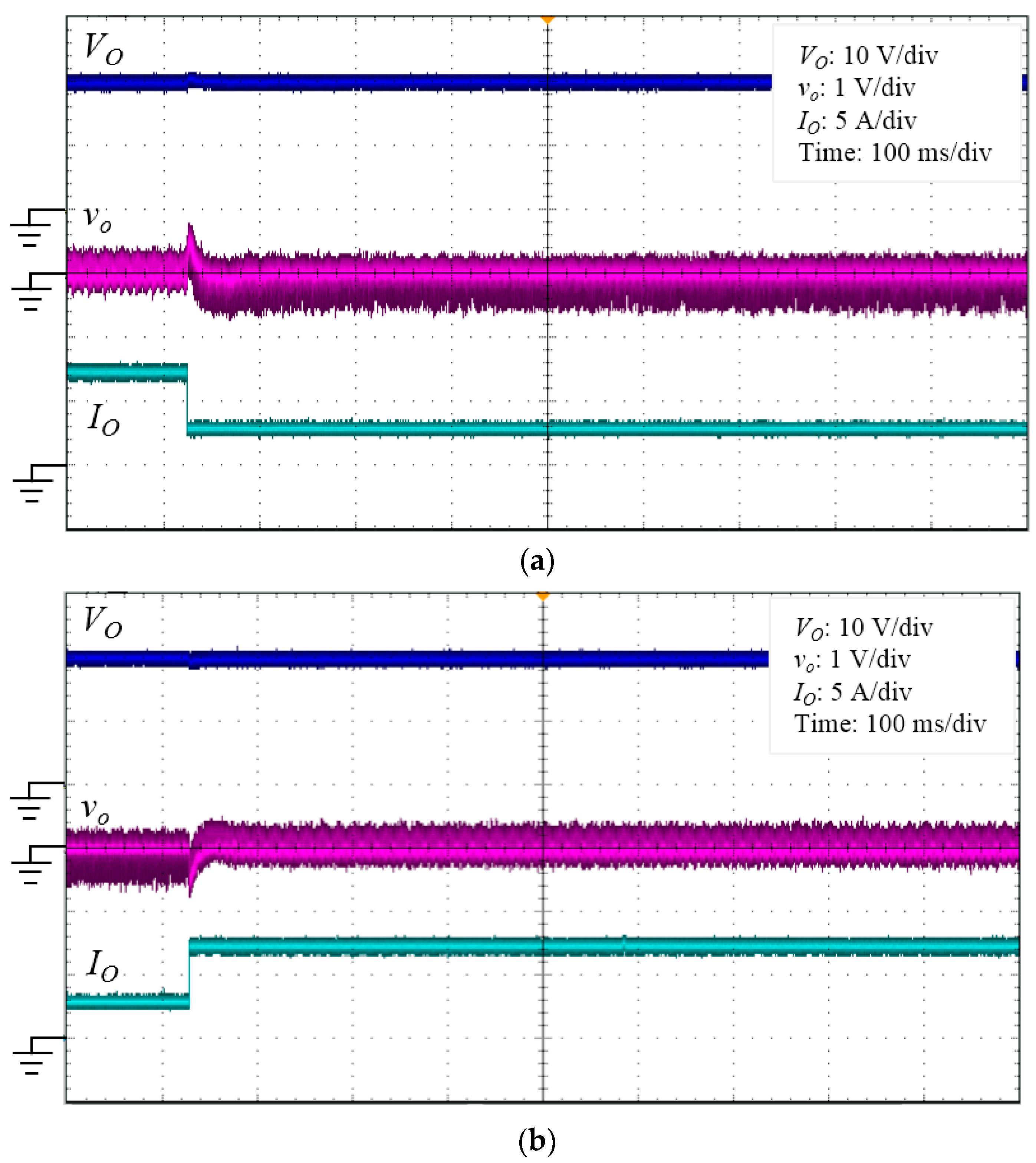

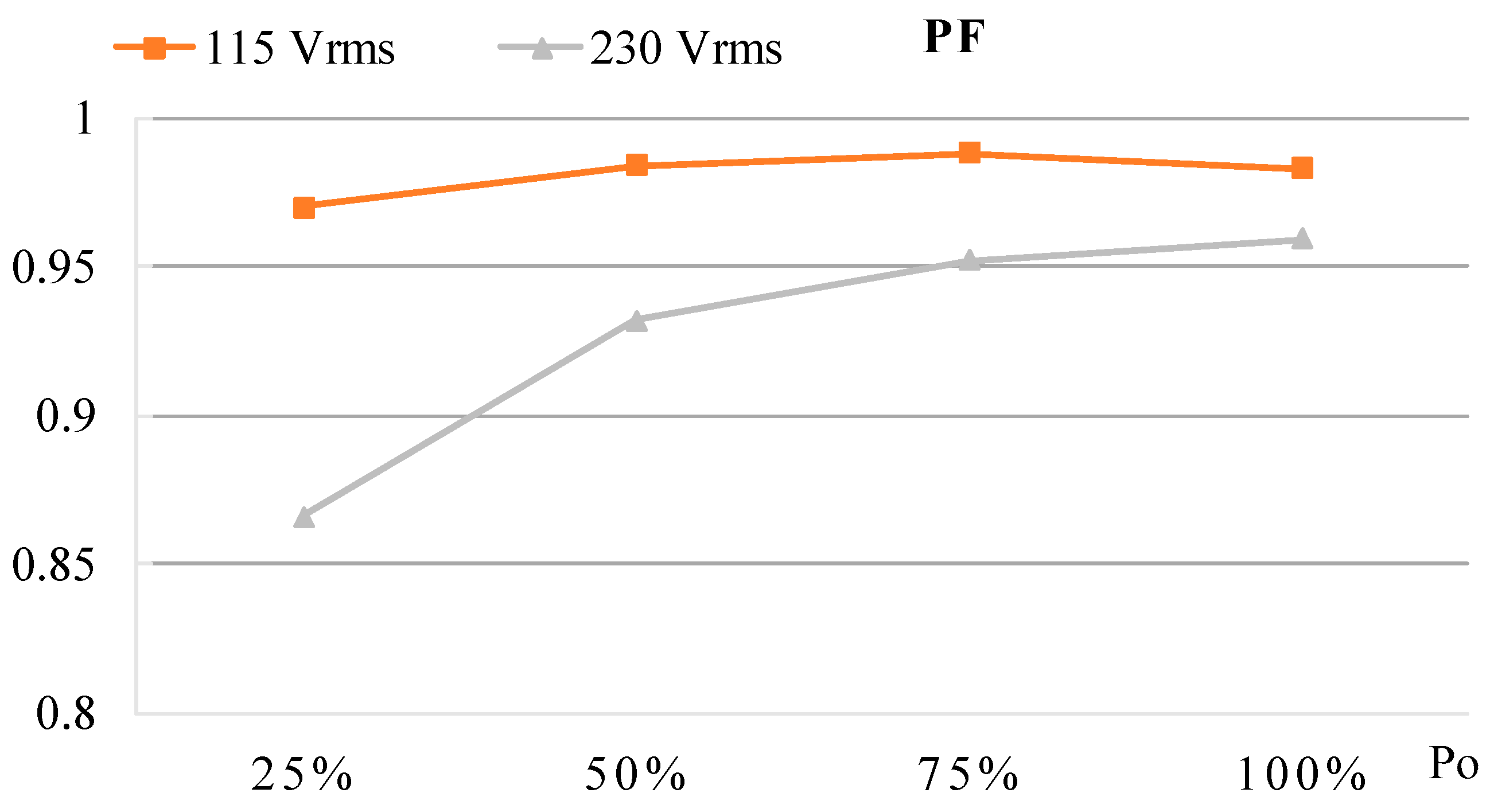

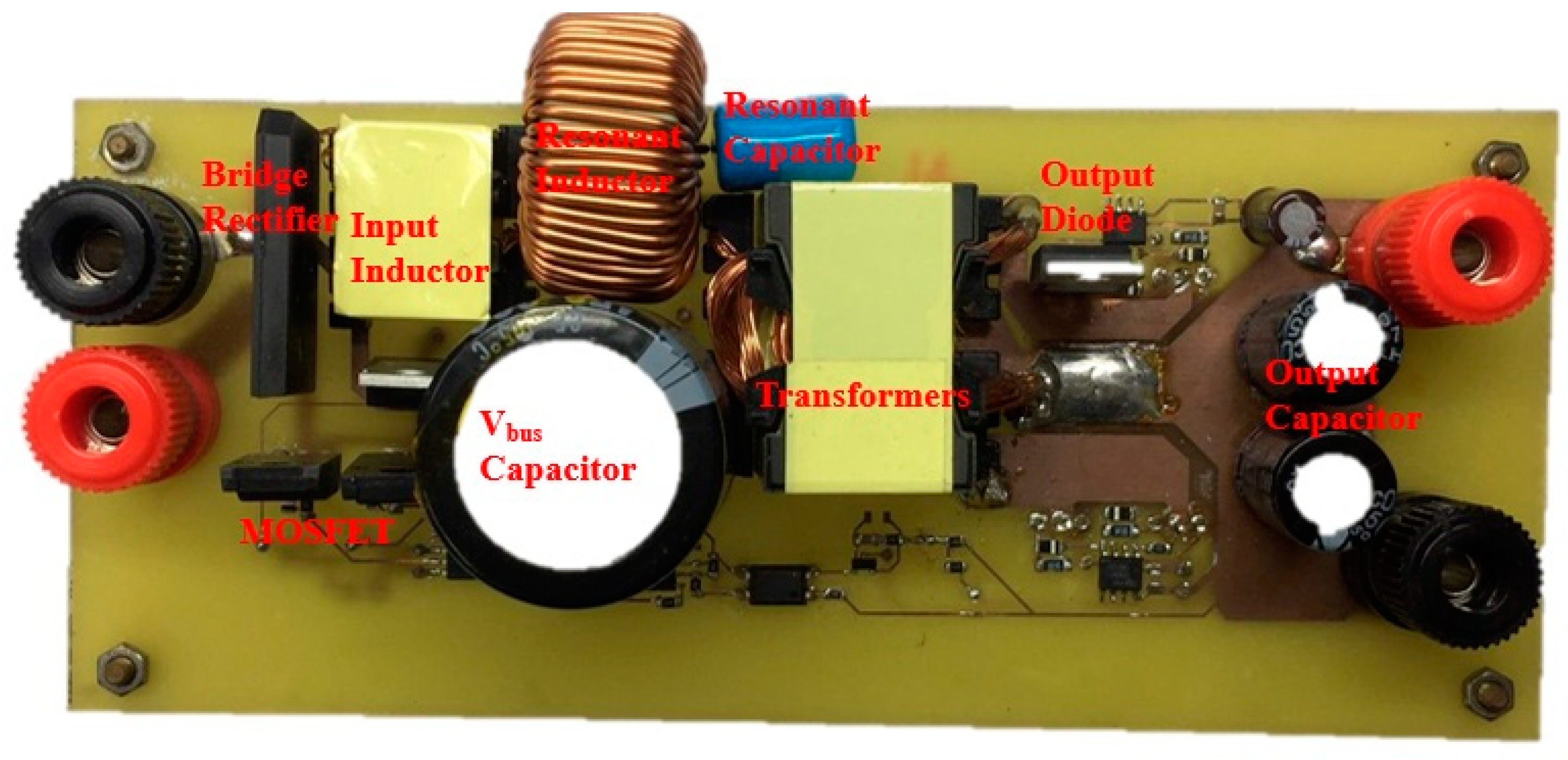
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Input ac voltage range: | 85–264 Vrms |
| Output voltage: | VO = 19 V |
| Output voltage ripple: | △VO = 0.95 V |
| Intermediate bus voltage: | Vbus = 420 V |
| Maximum output current: | IO = 6.32 A |
| Input inductor: | Lboost = 200 µH |
| Magnetizing inductance: | Lm = 450 µH |
| Turns ratio: | n = Np/Ns = 3T |
| Resonant inductor: | Lr = 100 µH |
| Maximum duty cycle: | Dmax = 0.75 |
| Resonant capacitors: | Cr = 40 nF |
| Switching frequency: | fs = 60–150 kHz |
| Output capacitor: | CO = 1200 µF |
| Proposed Converter | 2005 [14] | 2012 [15] | 2014 [17] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 90–264 Vrms | 180–265 Vrms | 180–270 Vrms | 180–265 Vrms |
| Output Voltage | 19 V | 24 V | 24 V | 24 V |
| Switching Frequency | 60–150 kHz | 100 kHz | 99–119 kHz | 100 kHz |
| Efficiency | 90% | 91% | 91.5% | 92% |
| Power Factor | 98% | 99% | None | 99% |
| ZVS/ZCS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Control Techniques for power factor | VCF and PWM | Coupled Inductor | Frequency Compensator | PWM |
| Cost | Low | High | Middle | High |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ting, C.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-P. A Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback Converter with Resonant Operation. Energies 2018, 11, 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071721
Ting C-Y, Hsu Y-C, Lin J-Y, Chen C-P. A Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback Converter with Resonant Operation. Energies. 2018; 11(7):1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071721
Chicago/Turabian StyleTing, Chung-Yi, Yi-Chieh Hsu, Jing-Yuan Lin, and Chung-Ping Chen. 2018. "A Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback Converter with Resonant Operation" Energies 11, no. 7: 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071721
APA StyleTing, C.-Y., Hsu, Y.-C., Lin, J.-Y., & Chen, C.-P. (2018). A Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback Converter with Resonant Operation. Energies, 11(7), 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071721




