Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Marine Current Energy Converter for Profiling Floats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Blade Design and Analysis
2.1. Blade Design
2.2. Movement and Stress Analysis
3. Hydrodynamic Performance Analysis
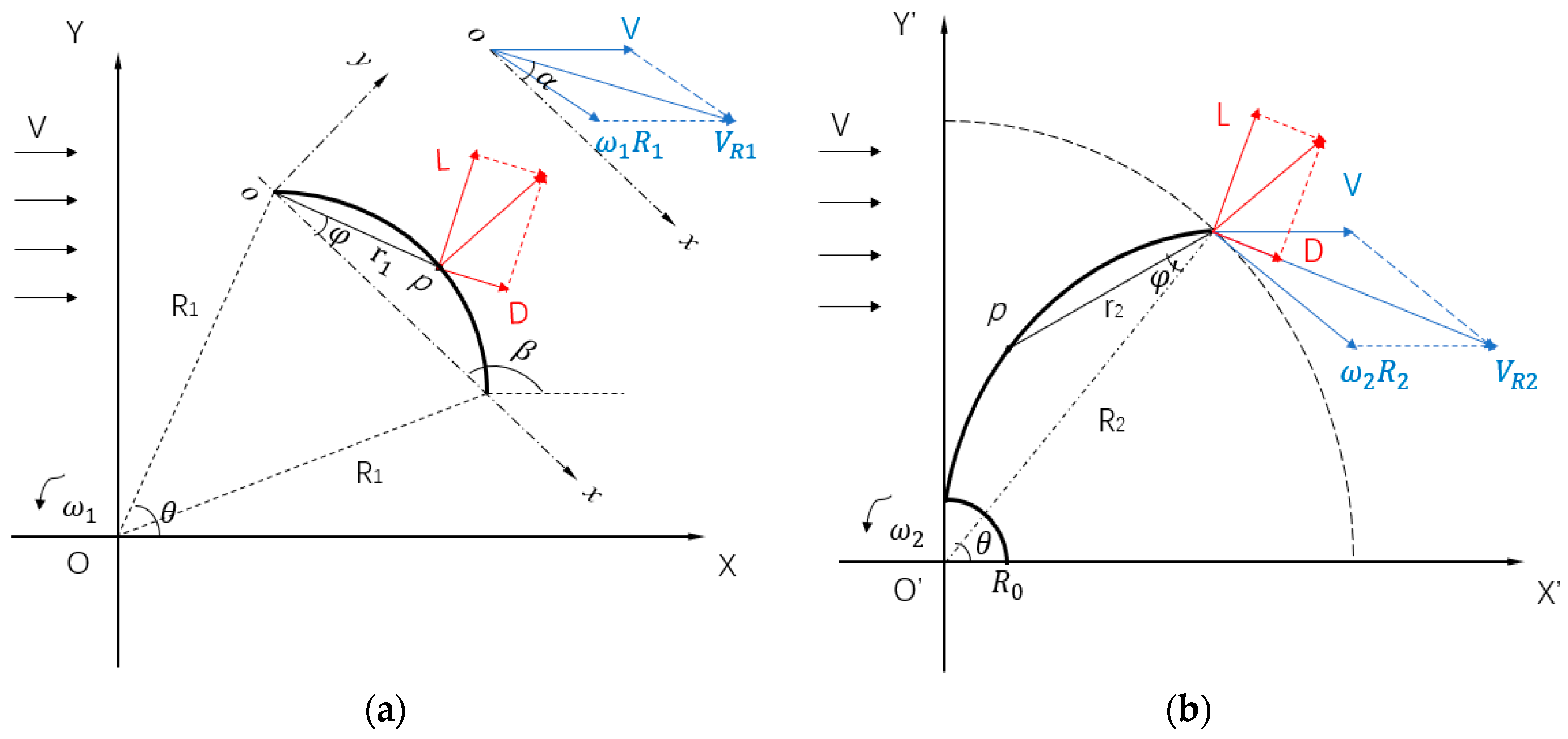
3.1. Hydrodynamic Equation
3.2. Numerical Models Establisment
3.3. Method Validation
4. Numerical Simulation Results Analysis
4.1. Self-Starting Analysis
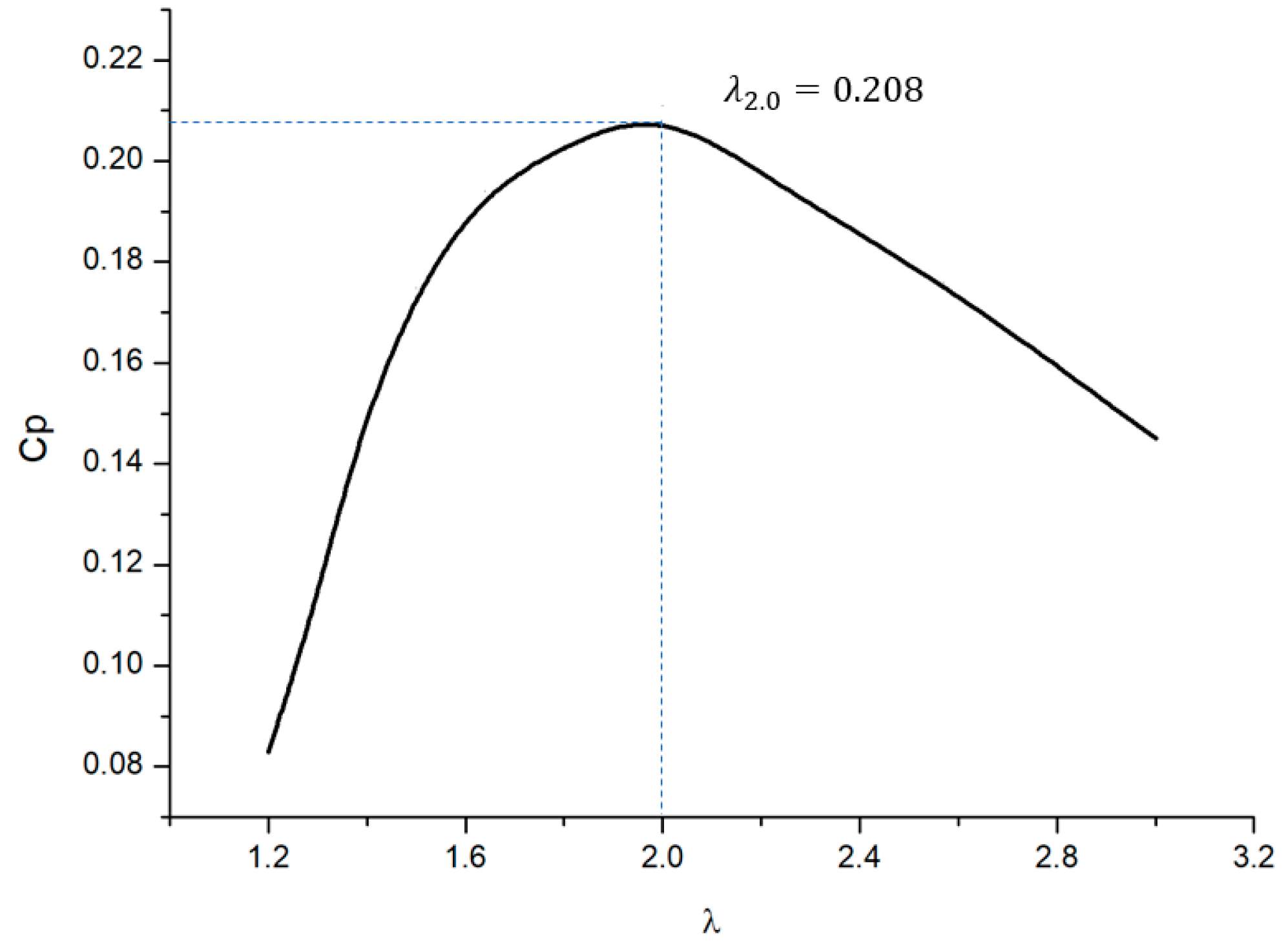
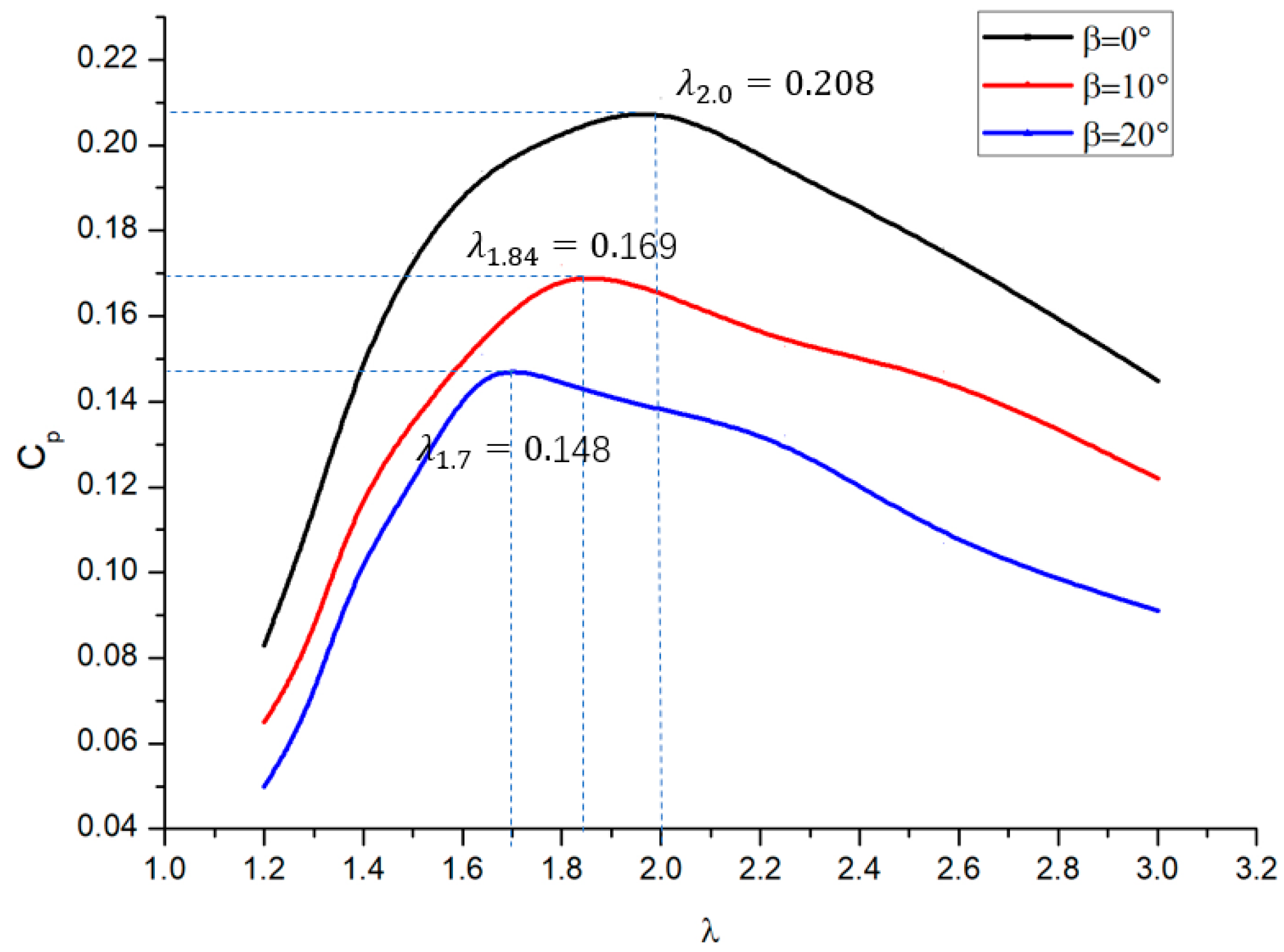
4.2. Energy Utilization Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Parameter | Symbol |
| Turbine diameter (mm) | D1 |
| Rotor shaft diameter (mm) | D2 |
| Involute base circle radius (mm) | r0 |
| Rotational speed (rad/s) | ωi (i = 1, 2) |
| Rotational radius (mm) | Ri (i = 1, 2) |
| Position angle (°) | θ, θ’ |
| Elevation angle (°) | φ, β, φ’ |
| Combined velocity (m/s) | VRi (i = 1, 2) |
| Flow velocity (m/s) | V |
| Attack angle (°) | α |
| Drag/lift force (N) | D, L |
| Drag/lift coefficient (N) | CD, CL |
| Fluid density (kg/m3) | |
| Inflow area (m2) | |
| Hydrodynamic torque (N·m) | |
| Load moment (N·m) | |
| Resistance moment (N·m) | Mf |
| Rotational inertia (kg·m2) | J |
| Load factor (N·ms2/rad2) | b |
| Output power (W) | P |
| Energy utilization rate | Cp |
| Reynolds stress tensor | Rij |
Appendix A
References
- State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University. Seafloor Observation System: An International Review; MGLab: Shanghai, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- IOOS U.S. Integrated Ocean Observing System: A Blueprint for Full Capability; Version 1.0.; IOOS Office: Maryland, MD, USA, 2010.
- Available online: https://www.marineinsight.com/shipping-news/leadership-2020 (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Available online: https://www.westernchannelobservatory.org.uk/ (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- Available online: http://theory.people.com.cn/n1/2017/1129/c40531-29674382.html (accessed on 29 November 2017).
- Shaolei, L. The position of the Beidou profile buoy in the global Argo real-time ocean observing network is at stake. Argo Newslett. 2016, 42, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Renqing, L.; Jianping, X. Argo: A successful decade. Basic Sci. China 2009, 4, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Teledyne Webb Research. Variable Bouyancy Profiling Float. U.S. Patent 8,875,645 B1, 4 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Petzrick, E.; Truman, J.; Fargher, H. Profiling From 6000 m with the APEX-Deep Float. Sea Technol. 2014, 55, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, S.; Waki, M.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R. Innovative Power Generators for Energy Harvesting Using Electroactive Polymer Artificial Muscles. SPIE Proc. 2008, 6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saupe, F.; Gilloteaux, J.C.; Bozonnet, P.; Creff, Y.; Tona, P. Latching Control Strategies for a Heaving Buoy Wave Energy Generator in a Random Sea. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 7710–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastien, S.P.; Sepe, R.B.; Grilli, A.R.; Grilli, S.T.; Spaulding, M.L. Ocean wave energy harvesting buoy for sensors. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–24 September 2009; pp. 3718–3725. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Du, M.; Zhou, Q.; Jie, M.; He, W. Proceeding of Tidal Current Energy Conversion System. Ocean Dev. Manag. 2016, 33, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Park, J.; Lee, K.; Park, W.; Yi, J. Evaluation of vertical axis turbine characteristics for tidal current power plant based on in situ experiment. Ocean Eng. 2013, 65, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, S.; Li, W.; Gu, H.; Lin, Y.; Sun, X. A review on the development of tidal current energy in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoji, M.A.; Kedare, S.B.; Prabhu, S.V. Performance tests on helical Savonius rotors. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorban, A.N.; Asme, A.M.; Gorlov, A.M.; Silantyev, V.M. Limits of the turbine efficiency for free fluid flow. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2001, 123, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlov, A.M. Helical turbines for the Gulf Stream: Conceptual approach to design of a large-scale floating power farm. Mar. Technol. 1998, 35, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Ocean Renewable Power Company [EB/OL]. 2014. Available online: http://orpc.co/default.aspx (accessed on 1 January 2018).
- Zangiabadi, E.; Edmunds, M.; Fairley, I.; Togneri, M.; Williams, A.; Masters, I.; Croft, N. Computational Fluid Dynamics and Visualisation of Coastal Flows in Tidal Channels Supporting Ocean Energy Development. Energies 2015, 8, 5997–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shih, T.; Liou, W.; Shabbir, A.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J. A new k-ε eddy viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows. Comput. Fluids 1995, 3, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xiao, Q.; Cheng, F. A bio-inspired study on tidal energy extraction with flexible flapping wings. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 036011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.Q.; Lee, K.S.; Park, J.S.; Ko, J.H. Flow-driven rotor simulation of vertical axis tidal turbines: A comparison of helical and straight blades. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2014, 6, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qu, H.; Shi, H. Numerical Study on Self-Starting Performance of Darrieus Vertical Axis Turbine for Tidal Stream Energy Conversion. Energies 2016, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shujie, W.; Xiaoli, Y.; Peng, Y.; Junzhe, T.; Xiancai, S. Numerical simulation and experimental research on performance of horizontal axis tidal turbine. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, P.W.; Myers, L.E.; Bahaj, A.S. Experimental and numerical results of rotor power and thrust of a tidal turbine perating at yaw and in waves. In Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress 2011, Linkoping, Sweden, 8–13 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, P.W.; Myers, L.E.; Bahaj, A.S. Quantifying wave and yaw effects on a scale tidal stream turbine. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.360doc.com/content/14/0107/17/12109864_343364720.shtml (accessed on 7 January 2014).
- Zhu, J.Y.; Huang, H.L.; Shen, H. Self-starting aerodynamics analysis of vertical axis wind turbine. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Numerical simulation of the tidal current in the East China Sea. Mar. Forecasts 2015, 32, 51–60. [Google Scholar]










| Description | Analysis Condition |
|---|---|
| Working fluid | Water (1025 kg/m3) |
| Left side velocity inlet | 0.1~2.0 m/s |
| Upper flow velocity inlet | 1.0 m/s |
| Pressure outlets | Relative pressure = 0 Pa |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; An, Q. Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Marine Current Energy Converter for Profiling Floats. Energies 2018, 11, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092218
Wu S, Liu Y, An Q. Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Marine Current Energy Converter for Profiling Floats. Energies. 2018; 11(9):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092218
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shuang, Yanjun Liu, and Qi An. 2018. "Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Marine Current Energy Converter for Profiling Floats" Energies 11, no. 9: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092218
APA StyleWu, S., Liu, Y., & An, Q. (2018). Hydrodynamic Analysis of a Marine Current Energy Converter for Profiling Floats. Energies, 11(9), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092218




