Role of Titanium Surface Topography and Surface Wettability on Focal Adhesion Kinase Mediated Signaling in Fibroblasts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ti Surfaces
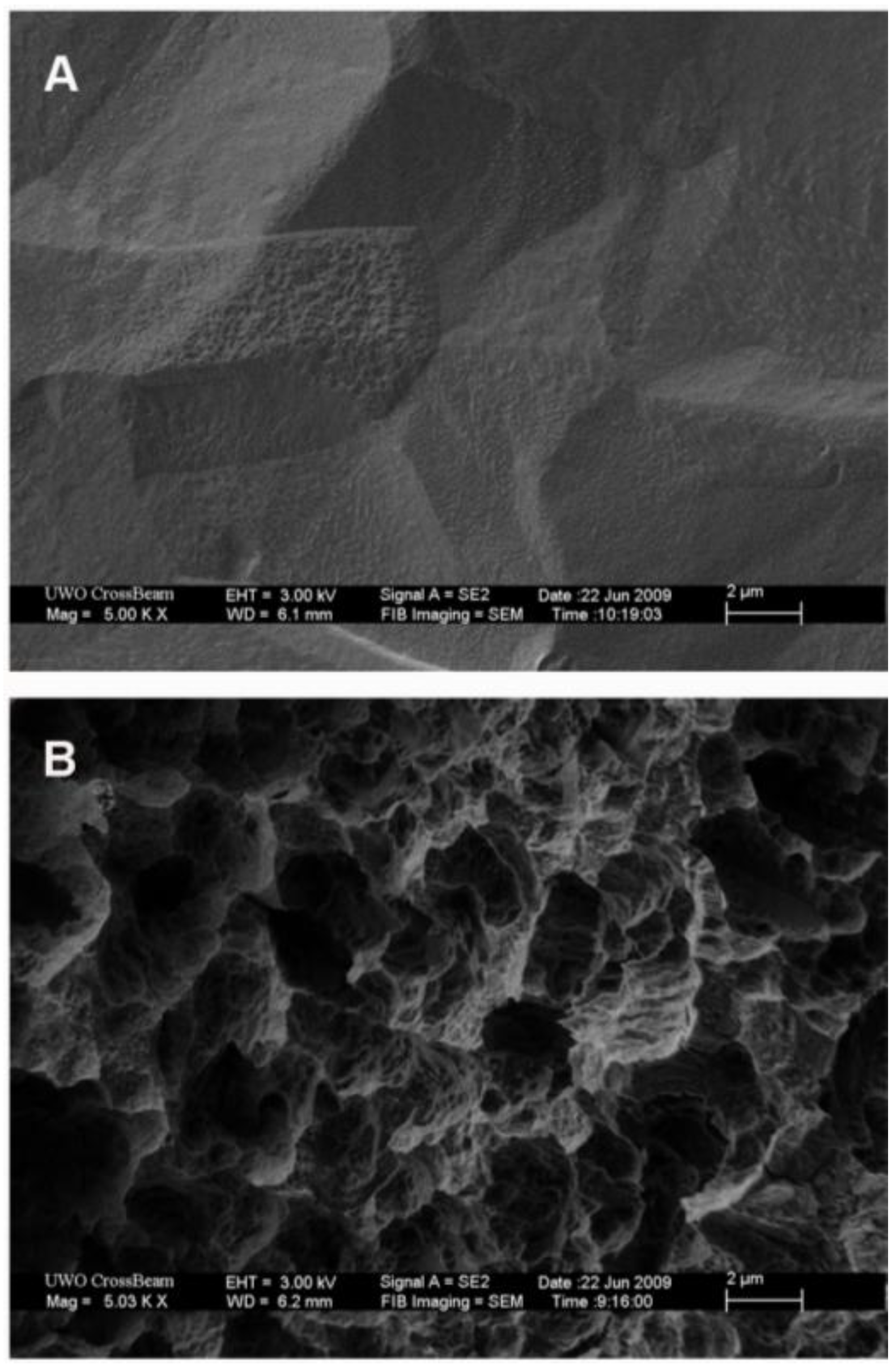
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Adhesion, and Spreading and Proliferation Assays
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Taq Man Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fibroblast Attachment
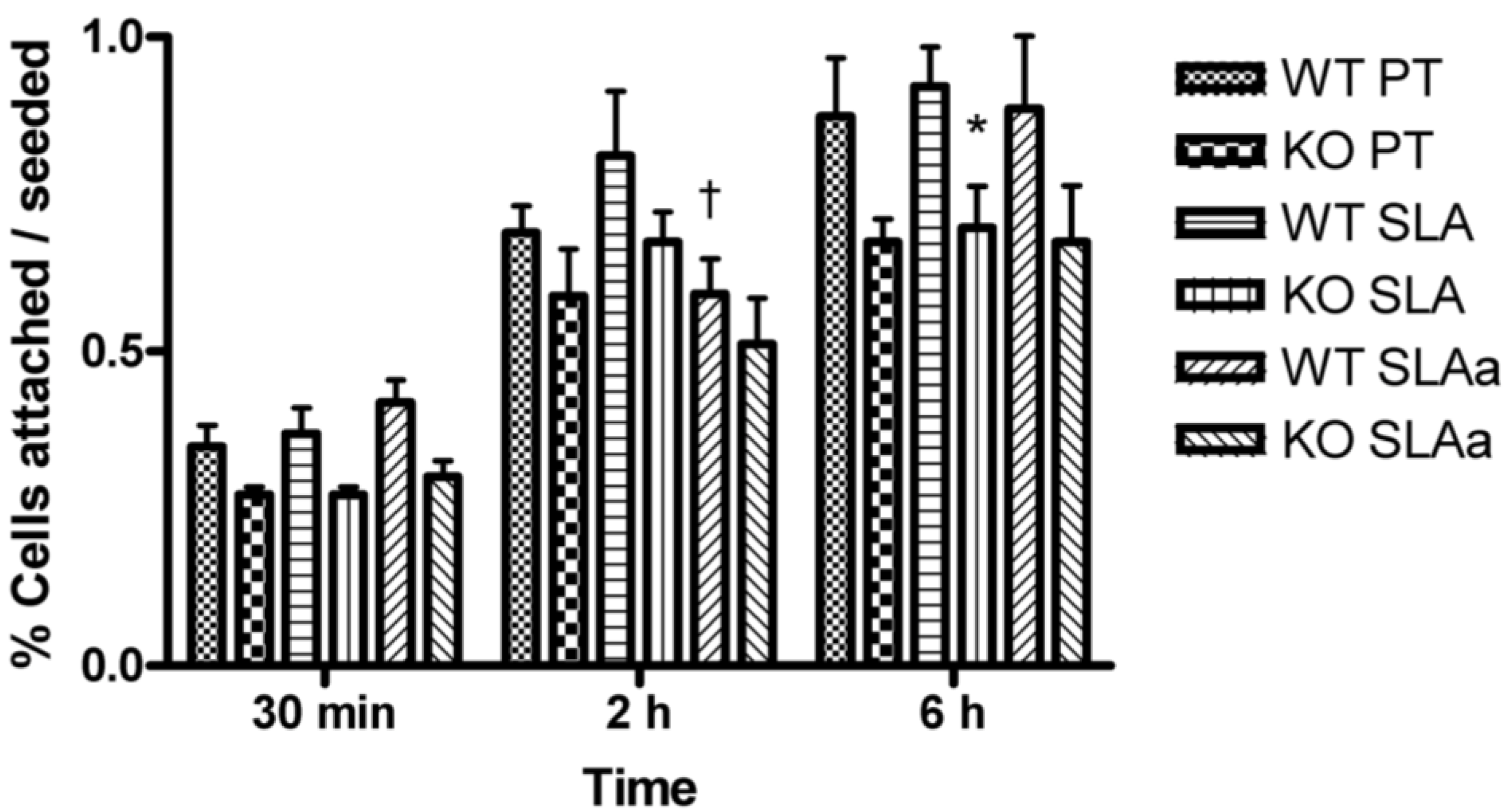
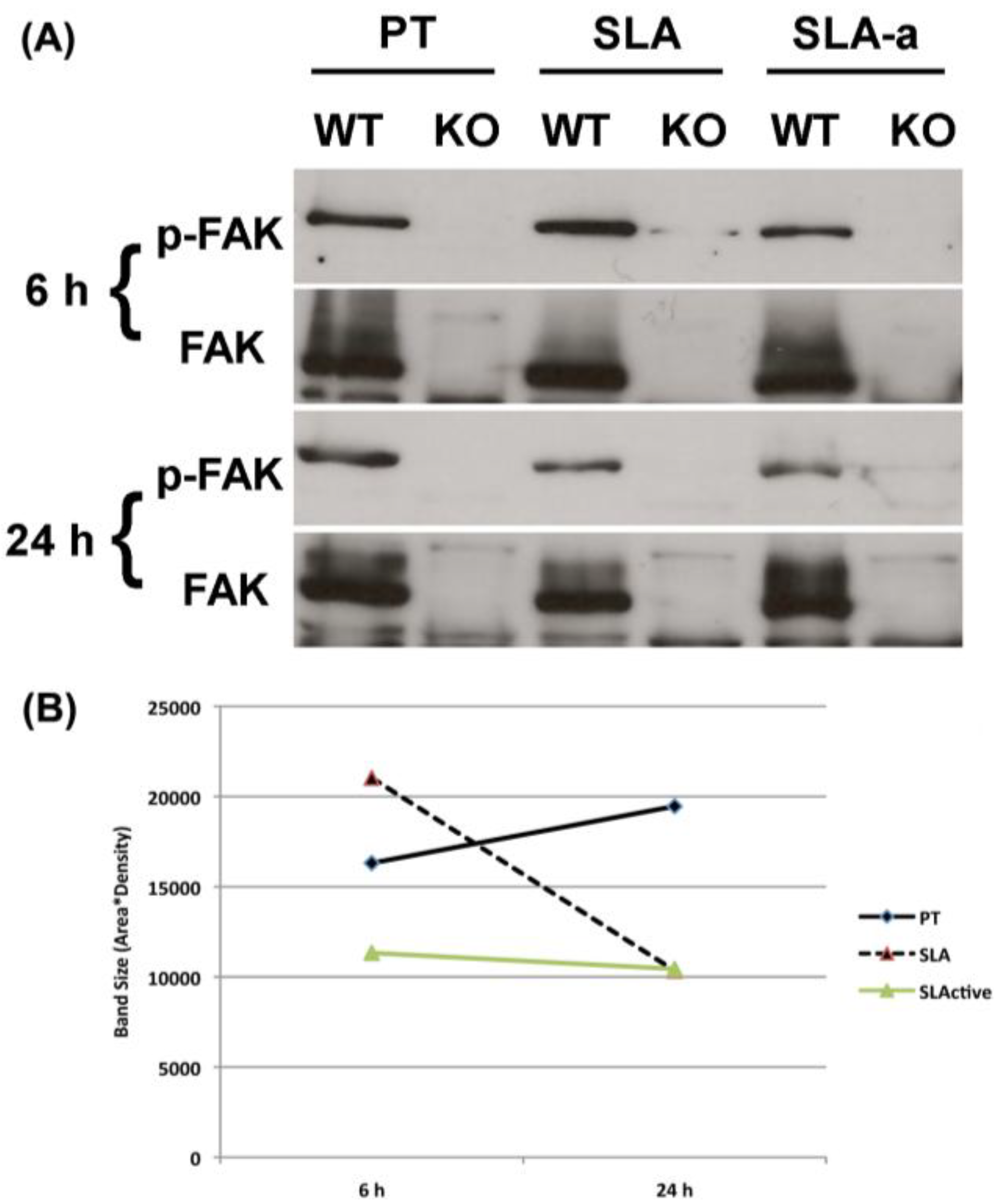
3.2. Focal Adhesion Formation, Spreading and FAK Phosphorylation
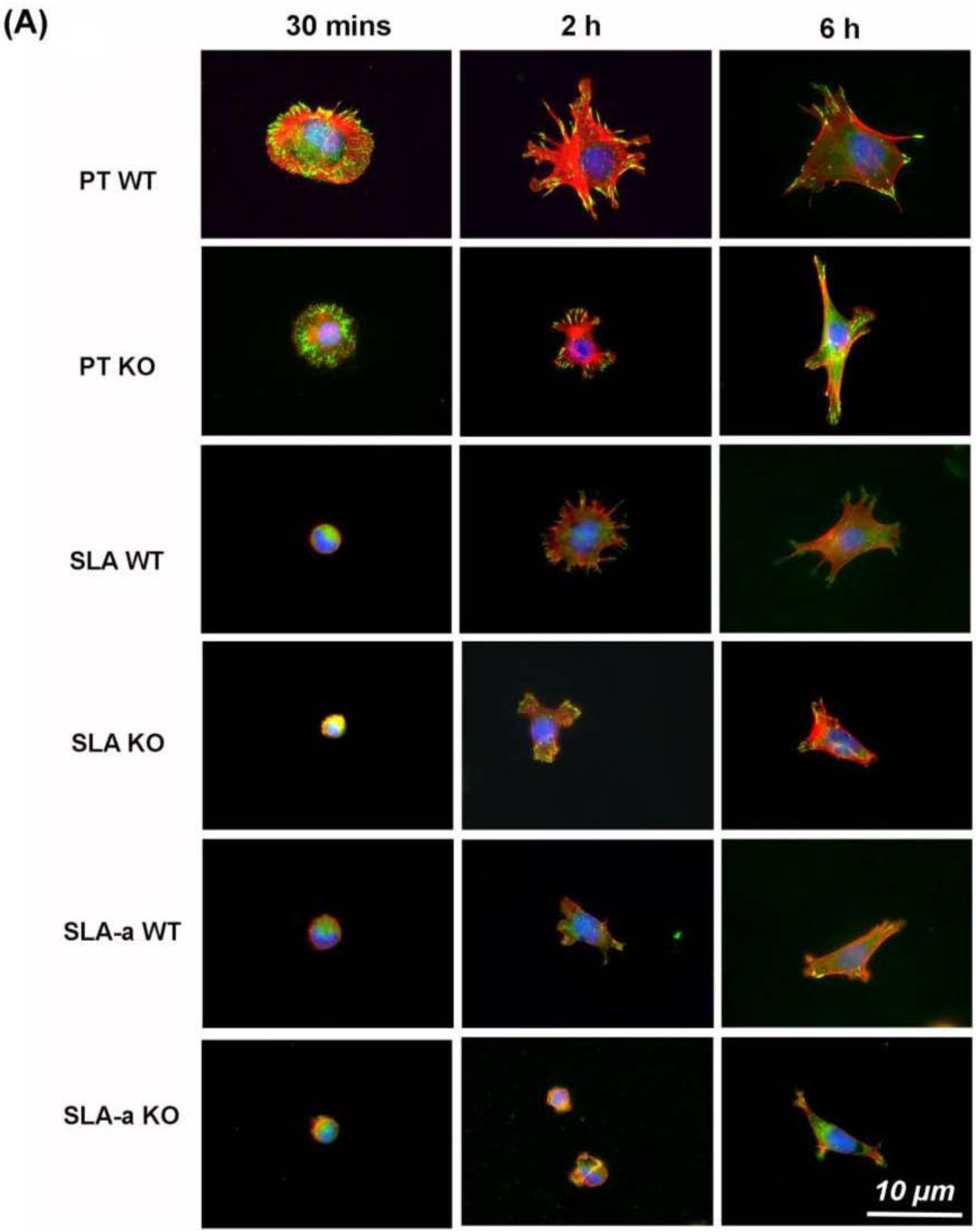

3.3. F-actin Arrangement and Cortactin Localization

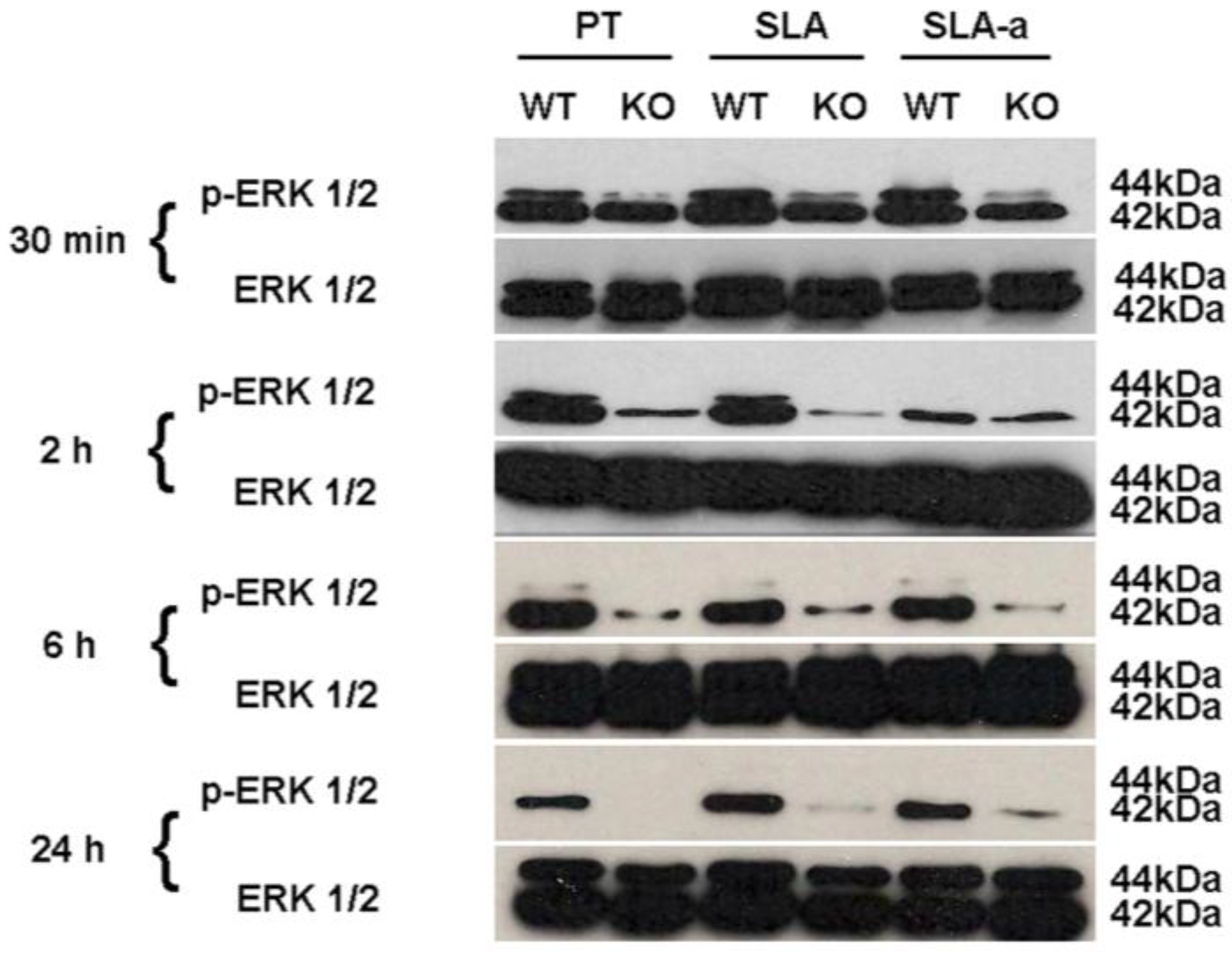
3.4. Activation of ERK 1/2
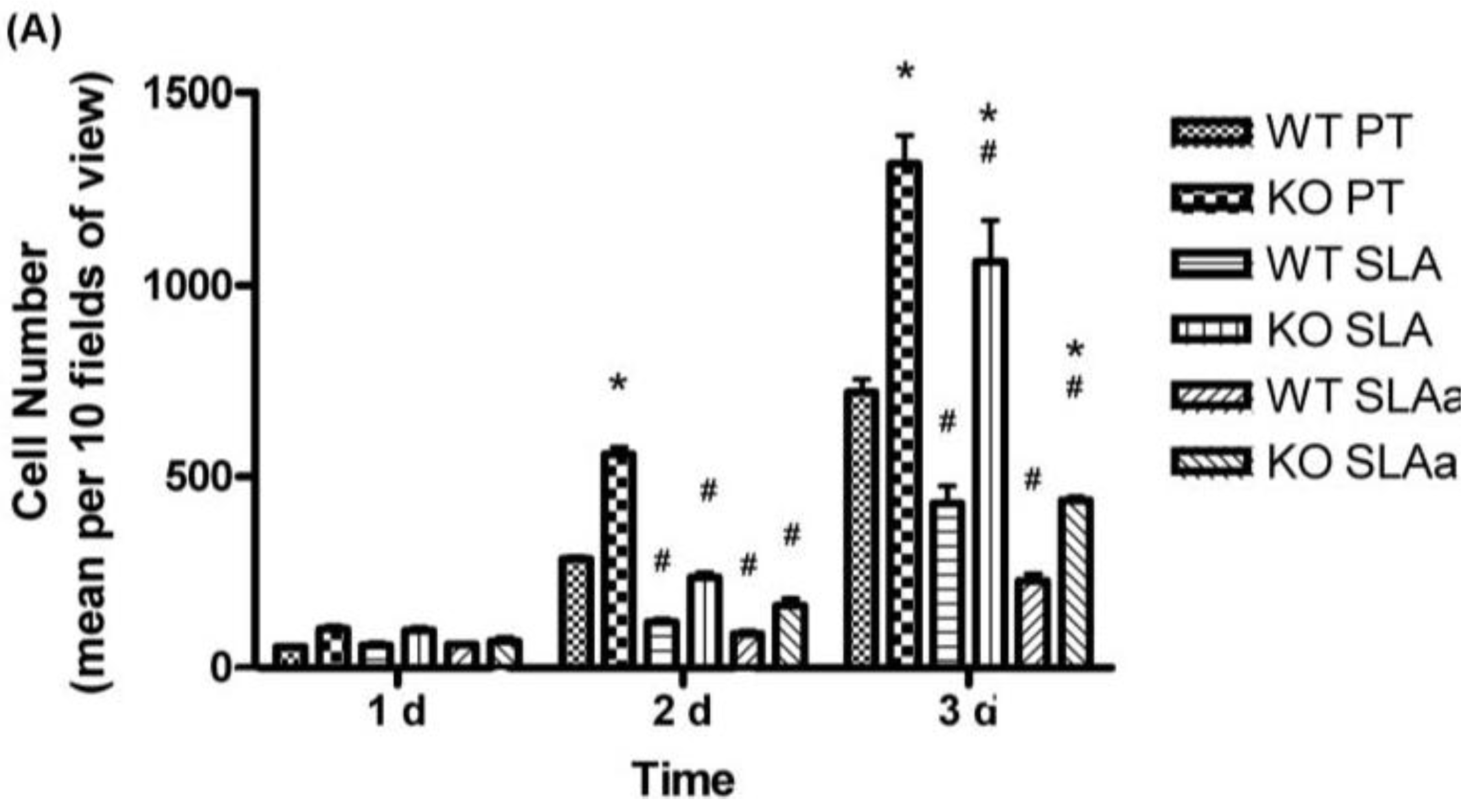
3.5. Proliferation
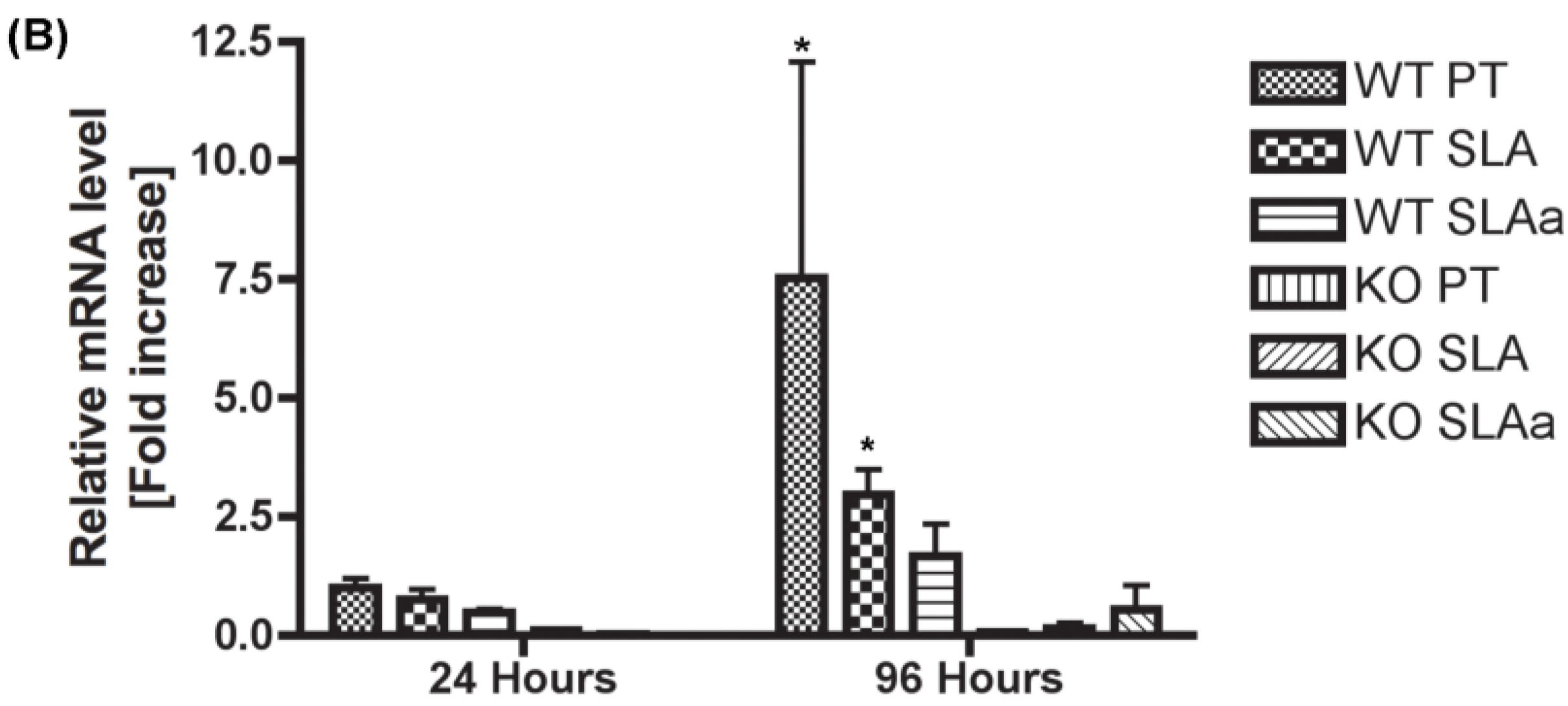
3.6. Fibroblast Differentiation—Collagen I Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Kim, T.I.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Knowles, J.C.; Ku, Y. Biomimetic approach to dental implants. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guehennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taborelli, M.; Jobin, M.; Francois, P.; Vaudaux, P.; Tonetti, M.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Simpson, J.P.; Descouts, P. Influence of surface treatments developed for oral implants on the physical and biological properties of titanium. (I) Surface characterization. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1997, 8, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.C. Dental implants: Materials and design considerations. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1993, 6, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeung, S.C. Biological basis for soft tissue management in implant dentistry. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53, S39–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Murakami, H.; Chehroudi, B.; Textor, M.; Brunette, D.M. Effects of surface topography on the connective tissue attachment to subcutaneous implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac Implant. 2006, 21, 354–365. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Olshanska, N.; de Wild, M.; Wieland, M.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Enhancing surface free energy and hydrophilicity through chemical modification of microstructured titanium implant surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 76, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Rehbein, D.; Axmann, D.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Roughness induced dynamic changes of wettability of acid etched titanium implant modifications. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scacchi, M.; Merz, B.R.; Schar, A.R. The development of the ITI DENTAL IMPLANT SYSTEM. Part 2: 1998–2000: Steps into the next millennium. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2000, 11, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.K.; Denzer, A.J.; Cochran, D.L; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S.G. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.J.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; de Wild, M.; Rupp, F.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Cochran, D.L.; Buser, D. Biomechanical evaluation of the interfacial strength of a chemically modified sandblasted and acid-etched titanium surface. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 78, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Herten, M.; Sager, M.; Wieland, M.; Dard, M.; Becker, J. Histological and immunohistochemical analysis of initial and early subepithelial connective tissue attachment at chemically modified and conventional SLA titanium implants. A pilot study in dogs. Clin. Oral Investig. 2007, 11, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Herten, M.; Sager, M.; Wieland, M.; Dard, M.; Becker, J. Histological and immunohistochemical analysis of initial and early subepithelial connective tissue attachment at chemically modified and conventional SLA(R)titanium implants. A pilot study in dogs. Clin. Oral Investig. 2007, 11, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubu, E.; Hamilton, D.W.; Inoue, T.; Brunette, D.M. Modulation of human gingival fibroblast adhesion, morphology, tyrosine phosphorylation, and ERK 1/2 localization on polished, grooved and SLA substratum topographies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 91, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Rausch-Fan, X.; Wieland, M.; Matejka, M.; Schedle, A. The initial attachment and subsequent behavior regulation of osteoblasts by dental implant surface modification. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 82, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Raines, A.L.; Wieland, M.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. Requirement for both micron- and submicron scale structure for synergistic responses of osteoblasts to substrate surface energy and topography. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Raz, P.; Zhao, G.; Chen, J.; Wieland, M.; Cochran, D.L.; Chaudhri, R.A.; Ornoy, A.; Boyan, B.D.; Schwartz, Z. Integrin alpha2beta1 plays a critical role in osteoblast response to micron-scale surface structure and surface energy of titanium substrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15767–15772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.O.; Bijelic, A.; Toyoshima, T.; Gotz, H.; von Koppenfels, R.L.; Al-Nawas, B.; Duschner, H. Long-term response of osteogenic cells on micron and submicron-scale-structured hydrophilic titanium surfaces: sequence of cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.C.; Zhuang, L.F.; Liu, X.; Wieland, M.; Zhang, Z.Y. The influence of surface energy on early adherent events of osteoblast on titanium substrates. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Andrukhov, O.; Berner, S.; Matejka, M.; Wieland, M.; Rausch-Fan, X.; Schedle, A. Osteogenic properties of hydrophilic and hydrophobic titanium surfaces evaluated with osteoblast-like cells (MG63) in coculture with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlacic-Zischke, J.; Hamlet, S.M.; Friis, T.; Tonetti, M.S.; Ivanovski, S. The influence of surface microroughness and hydrophilicity of titanium on the up-regulation of TGFbeta/BMP signalling in osteoblasts. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cary, L.A.; Guan, J.L. Focal adhesion kinase in integrin-mediated signaling. Front. Biosci. 1999, 4, D102–D113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hauck, C.R.; Sieg, D.J. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1999, 71, 435–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbi, S.; Guan, J.L. Focal adhesion kinase: Protein interactions and cellular functions. Histol. Histopathol. 2002, 17, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanks, S.K.; Polte, T.R. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Bioessays 1997, 19, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xu, S.W.; Kennedy, L.; Pala, D.; Chen, Y.; Eastwood, M.; Carter, D.E.; Black, C.M.; Abraham, D.J.; Leask, A. FAK is required for TGFbeta-induced JNK phosphorylation in fibroblasts: implications for acquisition of a matrix-remodeling phenotype. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, L.; Shi-Wen, X.; Carter, D.E.; Abraham, D.J.; Leask, A. Fibroblast adhesion results in the induction of a matrix remodeling gene expression program. Matrix Biology 2008, 27, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, R.J.; Oates, C.J.; Molenberg, A.; Dard, M.; Hamilton, D.W. The effect of enamel matrix proteins on the spreading, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts cultured on titanium surfaces. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.W.; Wong, K.S.; Brunette, D.M. Microfabricated discontinuous-edge surface topographies influence osteoblast adhesion, migration, cytoskeletal organization, and proliferation and enhance matrix and mineral deposition in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006, 78, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.W.; Brunette, D.M. The effect of substratum topography on osteoblast adhesion mediated signal transduction and phosphorylation. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1806–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.W.; Chehroudi, B.; Brunette, D.M. Comparative response of epithelial cells and osteoblasts to microfabricated tapered pit topographies in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, D.; Furuta, Y.; Kanazawa, S.; Takeda, N.; Sobue, K.; Nakatsuji, N.; Nomura, S.; Fujimoto, J.; Okada, M.; Yamamoto, T. Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature 1995, 377, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howerton, K.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Ilic, D. Establishment of cell lines from mouse embryos with early embryonic lethality. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2008, 15, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J.D.; Ruest, P.J.; Fry, D.W.; Hanks, S.K. Induced focal adhesion kinase (FAK) expression in FAK-null cells enhances cell spreading and migration requiring both auto- and activation loop phosphorylation sites and inhibits adhesion-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Pyk2. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 4806–4818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tilghman, R.W.; Slack-Davis, J.K.; Sergina, N.; Martin, K.H.; Iwanicki, M.; Hershey, E.D.; Beggs, H.E.; Reichardt, L.F.; Parsons, J.T. Focal adhesion kinase is required for the spatial organization of the leading edge in migrating cells. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruchten, A.E.; Krueger, E.W.; Wang, Y.; McNiven, M.A. Distinct phospho-forms of cortactin differentially regulate actin polymerization and focal adhesions. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C1113–C1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voisin, L.; Saba-El-Leil, M.K.; Julien, C.; Fremin, C.; Meloche, S. Genetic demonstration of a redundant role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinases in promoting fibroblast proliferation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 2918–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponticos, M.; Holmes, A.M.; Shi-Wen, X.; Leoni, P.; Khan, K.; Rajkumar, V.S.; Hoyles, R.K.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Black, C.M.; Denton, C.P.; et al. Pivotal role of connective tissue growth factor in lung fibrosis: MAPK-dependent transcriptional activation of type I collagen. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2142–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zeng, B.; Chai, Y.; Cai, P.; Fan, C.; Cheng, T. The linker region of Smad2 mediates TGF-beta-dependent ERK2-induced collagen synthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Oates, C.J.; Wen, W.; Hamilton, D.W. Role of Titanium Surface Topography and Surface Wettability on Focal Adhesion Kinase Mediated Signaling in Fibroblasts. Materials 2011, 4, 893-907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050893
Oates CJ, Wen W, Hamilton DW. Role of Titanium Surface Topography and Surface Wettability on Focal Adhesion Kinase Mediated Signaling in Fibroblasts. Materials. 2011; 4(5):893-907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050893
Chicago/Turabian StyleOates, Christine J., Weiyan Wen, and Douglas W. Hamilton. 2011. "Role of Titanium Surface Topography and Surface Wettability on Focal Adhesion Kinase Mediated Signaling in Fibroblasts" Materials 4, no. 5: 893-907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050893
APA StyleOates, C. J., Wen, W., & Hamilton, D. W. (2011). Role of Titanium Surface Topography and Surface Wettability on Focal Adhesion Kinase Mediated Signaling in Fibroblasts. Materials, 4(5), 893-907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4050893



