The Application of Rice Straw with Reduced N Fertilizer Improves the Rice Yield While Decreasing Environmental N Losses in Southern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.3. Collection and Measurement of Grain and Soil Samples
2.4. Gas Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Soil NH3 Sampling and Analysis
2.6. PFPN and NECB
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
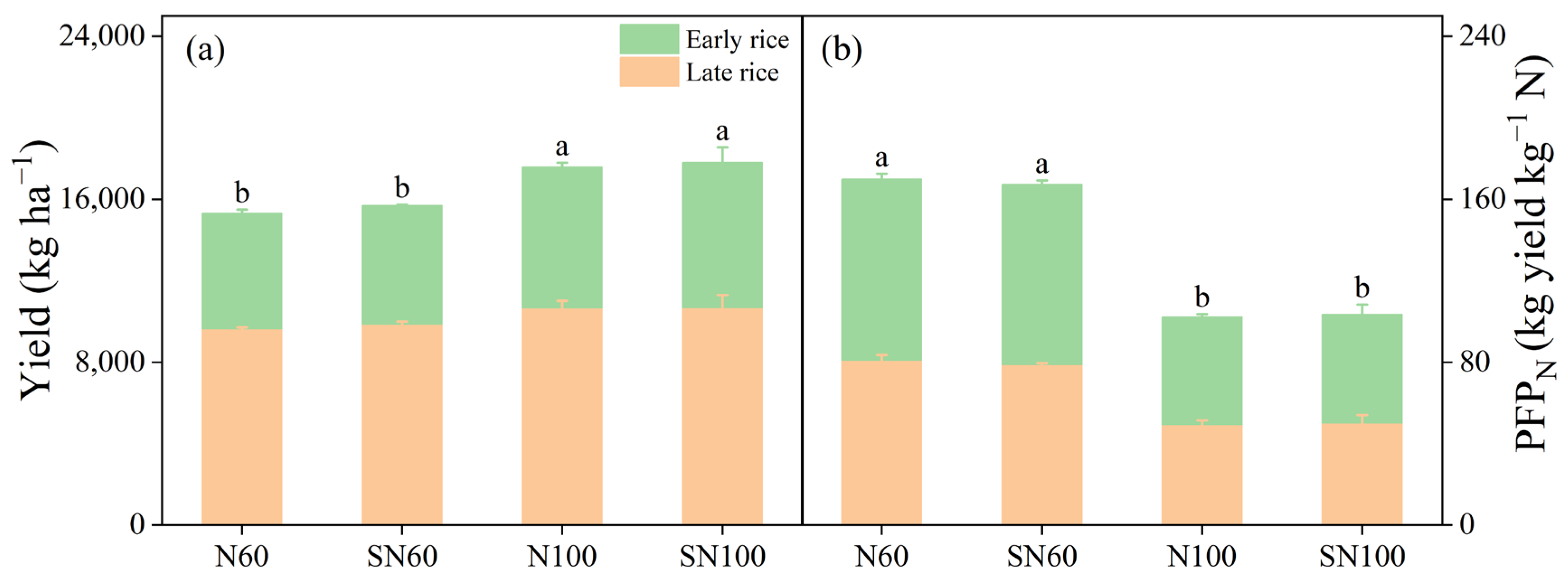
3.1. Rice Yield and PFPN
3.2. Soil Physicochemical Parameters
3.3. CH4, CO2, and N2O Emissions
3.4. GWP, GHGI, and NECB
3.5. Soil NH3 Volatilization
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Straw Residues with Reduced N Fertilizer on Soil Fertility and Rice Yield
4.2. Effect of Straw Residues with Reduced N Fertilizer on GHG, GWP, GHGI, and NECB
4.3. Effect of Straw Residues with Reduced N Fertilizer on NH3 Volatilization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO FAOSTAT. Production Data. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Xia, L.; Li, X.; Ma, Q.; Lam, S.K.; Wolf, B.; Kiese, R.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Yan, X. Simultaneous quantification of N2, NH3 and N2O emissions from a flooded paddy field under different N fertilization regimes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2292–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Xie, K.; Yin, C.; Hou, H.; Xie, X. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer combined with straw retention on greenhouse gas budget and crop production in double rice fields. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; He, P.; Zhou, W. Nitrogen balance acts an indicator for estimating thresholds of nitrogen input in rice paddies of China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Elrys, A.S.; Zhao, C.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C. Global patterns and controls of yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Hou, P.; Xue, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, L. Treated domestic sewage irrigation significantly decreased the CH4, N2O and NH3 emissions from paddy fields with straw incorporation. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Muhammad, A.; Zhong, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, P.; Yang, B.; Huang, G. Rice Yield and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Affected by Chinese Milk Vetch and Rice Straw Retention with Reduced Nitrogen Fertilization. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 3028–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yao, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Dijkstra, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, B. Replacing urea-N with Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) mitigates CH4 and N2O emissions in rice paddy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 336, 108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Effects of controlled-release fertilizer on rice grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency, and greenhouse gas emissions in a paddy field with straw incorporation. Field Crops Res. 2020, 253, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Jiang, S.; Cao, C.; Li, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, J. Combined Effects of Straw Returning and Chemical N Fertilization on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Yield from Paddy Fields in Northwest Hubei Province, China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.Y.; Kim, G.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Haque, M.M.; Khan, M.I.; Kim, P.J. Effect of cover cropping on the net global warming potential of rice paddy soil. Geoderma 2017, 292, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, N.K.; Lal, R. Soil aggregation and greenhouse gas flux after 15 years of wheat straw and fertilizer management in a no-till system. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Cao, H.; Qi, C.; Hu, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, Z. Straw management in paddy fields can reduce greenhouse gas emissions: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2024, 306, 109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Hu, F.; Shi, W. Soil nitrous oxide emissions following crop residue addition: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2956–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.D.; Ros, G.H.; De Vries, W. Impacts of agronomic measures on crop, soil, and environmental indicators: A review and synthesis of meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xi, Y.; Wu, X.; Pei, X.; Liang, G.; Bai, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; et al. Partial substitution of manure reduces nitrous oxide emission with maintained yield in a winter wheat crop. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W. Reducing ammonia volatilization from paddy field with rice straw derived biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, J.; Ding, W.; Bol, R.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Bolan, N. Stage-specific response of litter decomposition to N and S amendments in a subtropical forest soil. Biol. Fertil Soils 2016, 52, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C. Effect of wheat straw application on ammonia volatilization from urea applied to a paddy field. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 94, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Adeli, A.; Yan, H. Effects of application methods and urea rates on ammonia volatilization, yields and fine root biomass of alfalfa. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, S.; Yuan, W. Effects of returning double-season rice straw to the field and reducing N-fertilizer on yield and quality of rice. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2021, 43, 711–720. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, G. Effects of returning straw and milk vetch on rice growth and greenhouse gas emissions. Res. Ecol. 2021, 3, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Pi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Mai, K.; He, G. Improved utilization of soybean meal through fermentation with commensal Shewanella sp. MR-7 in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Hui, R.; Sui, T.; Yang, L.; Du, W.; Dong, Z. A 4-year field measurement of N2O emissions from a maize-wheat rotation system as influenced by partial organic substitution for synthetic fertilizer. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, M.C.T.; Sumner, E. Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 551–574. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Gao, S.; Xu, C.; Zeng, N.; Rees, R.M.; Cao, W. Co-incorporation of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.) straw minimizes CH4 emissions by changing the methanogenic and methanotrophic communities in a paddy soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.B.; Tigno, M.; Miller, H.L. (Eds.) International panel on climate change—The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, F.; Jia, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Li, X.; et al. Cover crops and N fertilization affect soil ammonia volatilization and N2O emission by regulating the soil labile carbon and nitrogen fractions. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, L.; Hu, J.; Xue, T.; Lv, H.; Yao, Z.; Meng, F.; Li, G.; Lin, S.; et al. Assessing the environmental sustainability of different soil disinfestation methods used in solar greenhouse vegetable production systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Chen, D.; Yan, X. Optimizing nitrogen fertilization rate to enhance soil carbon storage and decrease nitrogen pollution in paddy ecosystems with simultaneous straw incorporation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 298, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Wolf, B.; Kiese, R.; Chen, D.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5919–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pang, C.; Qin, J.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Li, H. Rice straw incorporation in winter with fertilizer-N application improves soil fertility and reduces global warming potential from a double rice paddy field. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Fan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, C.; Filimonenko, E.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, X.; et al. Nitrogen fertilizer builds soil organic carbon under straw return mainly via microbial necromass formation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 188, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Butterly, C.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. pH change, carbon and nitrogen mineralization in paddy soils as affected by Chinese milk vetch addition and soil water regime. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Huan, W.; Song, H.; Lu, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. Effects of straw incorporation and potassium fertilizer on crop yields, soil organic carbon, and active carbon in the rice–wheat system. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, S.; Linderman, M.; Mouazen, A.M.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; et al. Exploring the potential of airborne hyperspectral image for estimating topsoil organic carbon: Effects of fractional-order derivative and optimal band combination algorithm. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Shen, X.; Xu, H.; Jiao, J.; Li, H.; Hu, F. Crop yield-soil quality balance in double cropping in China’s upland by organic amendments: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Cotton, A.; Wei, Z.; Xia, Y.; Daniell, T.; Yan, X. How does partial substitution of chemical fertiliser with organic forms increase sustainability of agricultural production? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Song, F.; Yin, Z.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Wang, B.; Zheng, E. Organic fertilizer substitutions maintain maize yield and mitigate ammonia emissions but increase nitrous oxide emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 53115–53127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tian, H.; Zhang, M.; Fan, P.; Ashraf, U.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Duan, M.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer increases rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency with fewer greenhouse gas emissions in a mechanical direct-seeded cropping system. Crop. J. 2021, 9, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, M.; Khan, I.; Shaaban, M.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, R. Nitrogen fertilizer application in the rice-growing season can stimulate methane emissions during the subsequent flooded fallow period. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, D.L.; Schwenke, G.; Yang, B. The global warming potential of straw-return can be reduced by application of straw-decomposing microbial inoculants and biochar in rice-wheat production systems. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Sheng, F.; Cao, C.; Li, C. Effects of long-term no tillage and straw return on greenhouse gas emissions and crop yields from a rice-wheat system in central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, C.; Costa, F.D.S.; Pedroso, G.M.; Zschornack, T.; Camargo, E.S.; Lima, M.A.D.; Frigheto, R.T.S.; Gomes, J.; Marcolin, E.; Macedo, V.R.M. Yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions from flood irrigated rice under long-term conventional tillage and no-till systems in a Humid Subtropical climate. Field Crops Res. 2014, 162, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Wang, J.; Sainju, U.M.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.; Khan, A. Cover cropping enhances soil microbial biomass and affects microbial community structure: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2021, 381, 114696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, Y. Crop residue incorporation and nitrogen fertilizer effects on greenhouse gas emissions from a subtropical rice system in Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 1972–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, S.A.; Tian, X.H.; You, D.H.; Wang, X.D. Emission of carbon dioxide influenced by nitrogen and water levels from soil incubated straw. Plant Soil Environ. 2011, 57, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, R.; Sheng, K.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y. Blending loss-control and normal urea maximizes nitrogen utilization of summer maize by mitigating ammonia volatilization and nitrate leaching. Plant Soil 2023, 490, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Fu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Liang, C.; Lin, Z.; Hu, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Biochar decreases soil N2O emissions in Moso bamboo plantations through decreasing labile N concentrations, N-cycling enzyme activities and nitrification/denitrification rates. Geoderma 2019, 348, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Reichel, R.; Xu, Z.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. Return of crop residues to arable land stimulates N2O emission but mitigates NO3− leaching: A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Chae, H.G.; Kim, P.J.; Lee, J.G. Benefits of organic amendments on soil C stock may be offset by increased methane flux in rice paddy field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 359, 108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicklighter, D.W.; Melillo, J.M.; Monier, E.; Sokolov, A.P.; Zhuang, Q. Future nitrogen availability and its effect on carbon sequestration in Northern Eurasia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, S.; Guo, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Lei, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; et al. Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and ammonia volatilization from cotton fields by integrating cover crops with reduced use of nitrogen fertilizer. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 332, 107946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Min, J.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Lu, K.; Shi, W.; Yu, M.; Li, X. Biochar application mode influences nitrogen leaching and NH3 volatilization losses in a rice paddy soil irrigated with N-rich wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2090–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Basal Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Tiller Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Rice Straw (kg ha−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | N | ||
| Early rice | |||||
| N60 | 55 | 75 | 120 | 36 | 0 |
| SN60 | 55 | 75 | 120 | 36 | 6000 |
| N100 | 91 | 75 | 120 | 60 | 0 |
| SN100 | 91 | 75 | 120 | 60 | 6000 |
| Late rice | |||||
| N60 | 65 | 75 | 150 | 43 | 0 |
| SN60 | 65 | 75 | 150 | 43 | 6000 |
| N100 | 108 | 75 | 150 | 72 | 0 |
| SN100 | 108 | 75 | 150 | 72 | 6000 |
| Treatment | pH | SOC | TN | AN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g C kg−1) | (g N kg−1) | (mg N kg−1) | (mg P kg−1) | (mg K kg−1) | ||
| Early rice | ||||||
| N60 | 6.4 ± 0.12 a | 19.5 ± 0.4 b | 2.1 ± 0.20 a | 222 ± 14 a | 11.3 ± 0.2 a | 112 ± 8 b |
| SN60 | 6.4 ± 0.06 a | 20.8 ± 0.2 a | 2.0 ± 0.21 a | 230 ± 15 a | 11.6 ± 0.1 a | 131 ± 5 ab |
| N100 | 6.2 ± 0.09 b | 21.0 ± 0.3 a | 2.1 ± 0.03 a | 241 ± 2 a | 12.3 ± 0.8 a | 115 ± 12 ab |
| SN100 | 6.1 ± 0.03 b | 21.3 ± 0.9 a | 2.2 ± 0.01 a | 256 ± 34 a | 13.2 ± 2.7 a | 133 ± 7 a |
| Late rice | ||||||
| N60 | 6.0 ± 0.01 a | 21.4 ± 0.65 b | 2.2 ± 0.08 a | 158 ± 9 b | 8.3 ± 0.1 b | 130 ± 10 a |
| SN60 | 5.9 ± 0.10 a | 21.9 ± 1.0 ab | 2.2 ± 0.16 a | 167 ± 6 b | 9.3 ± 1.0 b | 151 ± 8 a |
| N100 | 5.7 ± 0.05 b | 23.2 ± 0.6 a | 2.3 ± 0.13 a | 205 ± 13 a | 8.7 ± 0.2 b | 131 ± 5 a |
| SN100 | 5.8 ± 0.18 ab | 23.4 ± 0.7 a | 2.4 ± 0.12 a | 207 ± 13 a | 11.5 ± 0.3 a | 151 ± 12 a |
| Treatment | CH4 | CO2 | N2O | GWP | GHGI | NECB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kg C ha−1) | (kg C ha−1) | (kg N ha−1) | (kg CO2-eq ha−1) | (kg CO2-eq kg−1) | (kg ha−1) | |
| N60 | 272 ± 16 d | 30,744 ± 1331 c | 3.6 ± 0.1 c | 39,307 ± 1607 c | 2.4 ± 0.1 c | 3085 ± 369 c |
| SN60 | 412 ± 13 b | 38,449 ± 2696 b | 3.3 ± 0.2 c | 50,868 ± 2912 b | 3.0 ± 0.2 a | 3648 ± 904 a |
| N100 | 335 ± 38 c | 36,218 ± 1130 b | 5.7 ± 0.3 a | 47,127 ± 2263 b | 2.7 ± 0.1 b | 2840 ± 585 b |
| SN100 | 465 ± 9 a | 43,922 ± 1539 a | 5.0 ± 0.2 b | 58,273 ± 1734 a | 3.2 ± 0.1 a | 3320 ± 104 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Ma, T.; Wan, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, A.; Chen, X.; Liu, J. The Application of Rice Straw with Reduced N Fertilizer Improves the Rice Yield While Decreasing Environmental N Losses in Southern China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072737
Liu H, Ma T, Wan L, Zhou G, Zhu A, Chen X, Liu J. The Application of Rice Straw with Reduced N Fertilizer Improves the Rice Yield While Decreasing Environmental N Losses in Southern China. Sustainability. 2024; 16(7):2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072737
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Han, Tingting Ma, Li Wan, Guopeng Zhou, Anfan Zhu, Xiaofen Chen, and Jia Liu. 2024. "The Application of Rice Straw with Reduced N Fertilizer Improves the Rice Yield While Decreasing Environmental N Losses in Southern China" Sustainability 16, no. 7: 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072737







