Dust Detection and Intensity Estimation Using Himawari-8/AHI Observation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Himawari-8 (H8) Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) Data
2.2. MODIS/Aqua and Terra
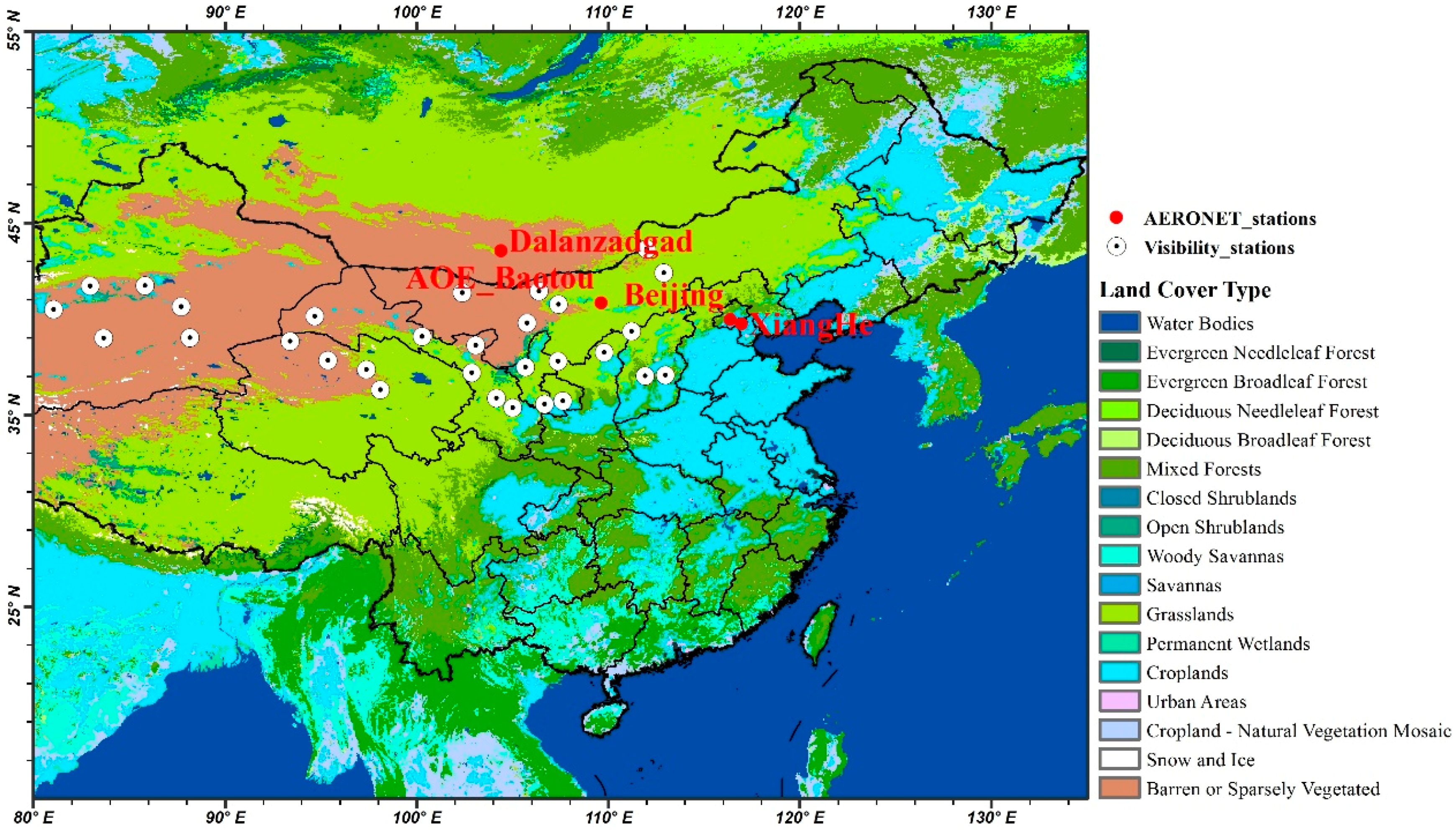
2.3. AERONET Data
2.4. Visibility Data
3. Methods
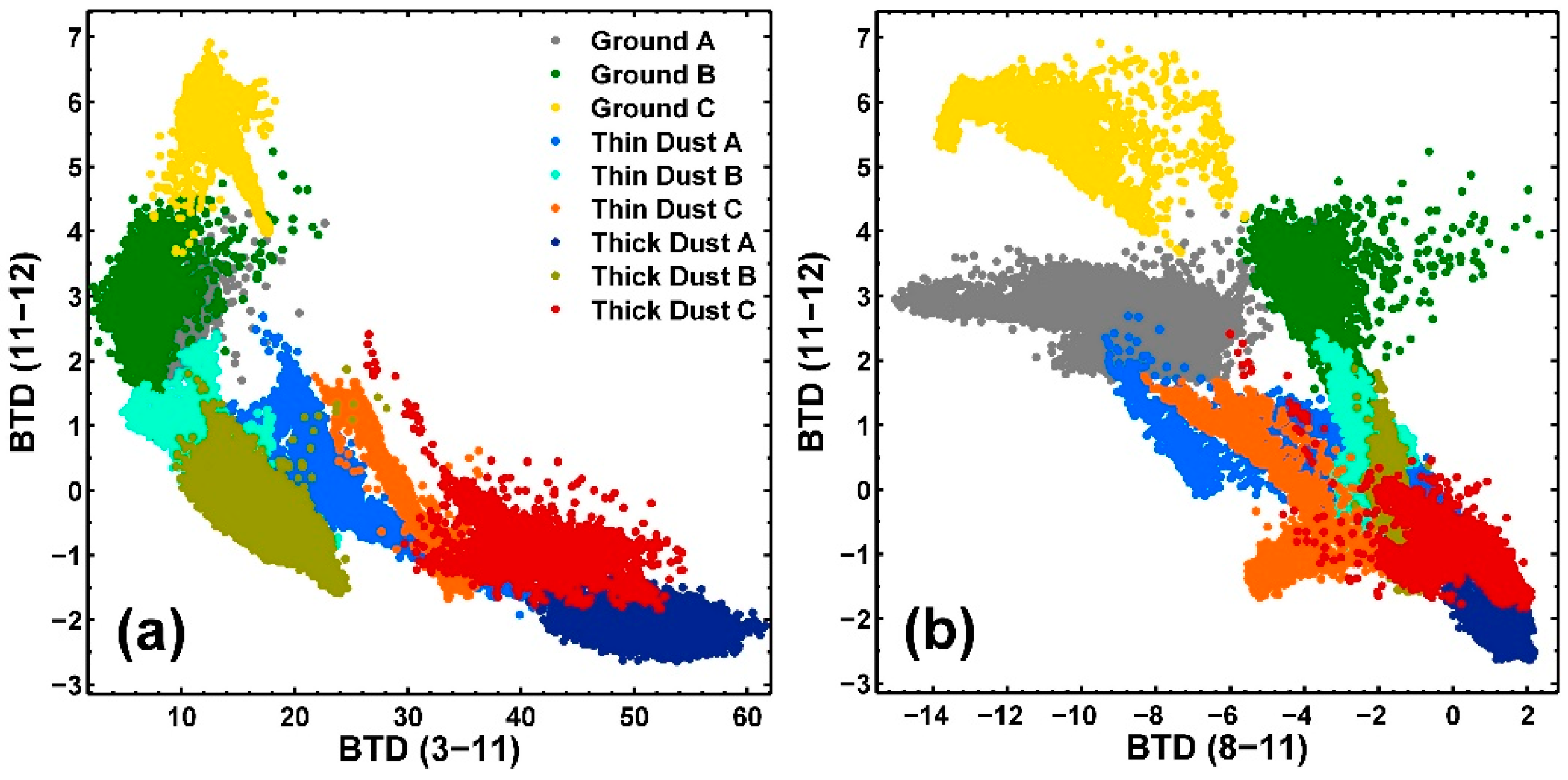
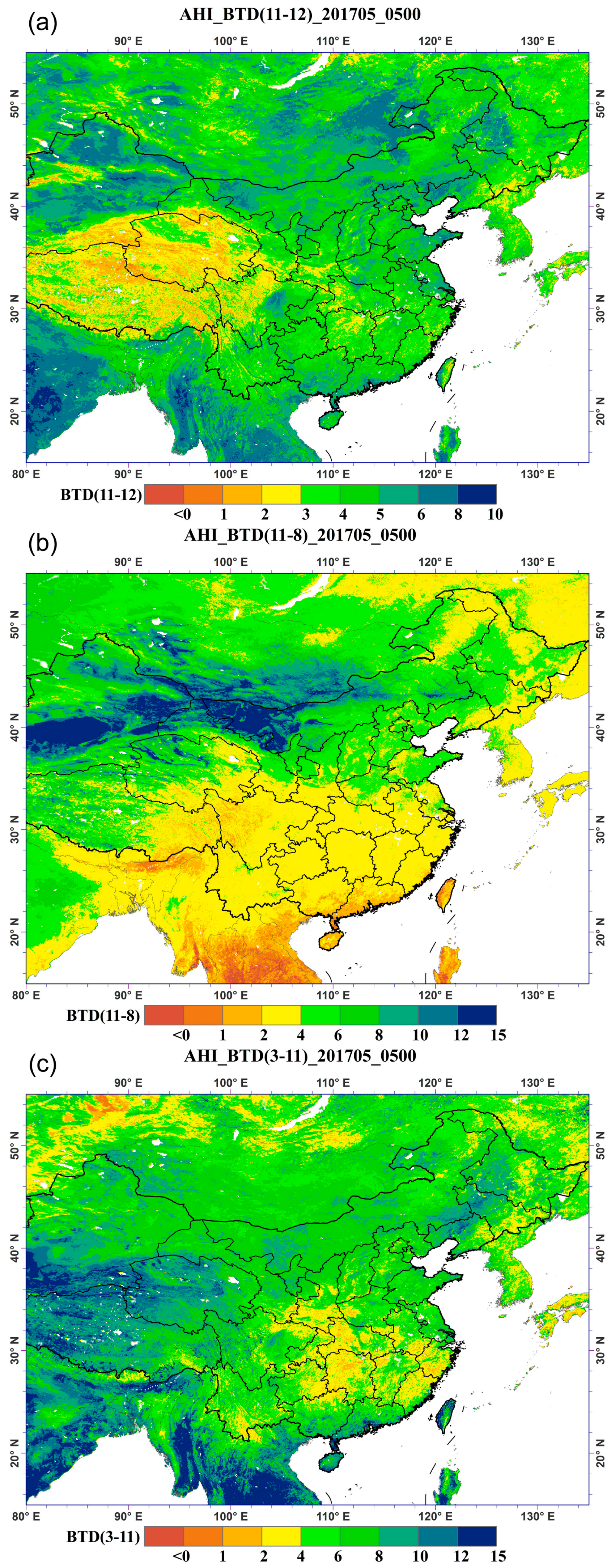
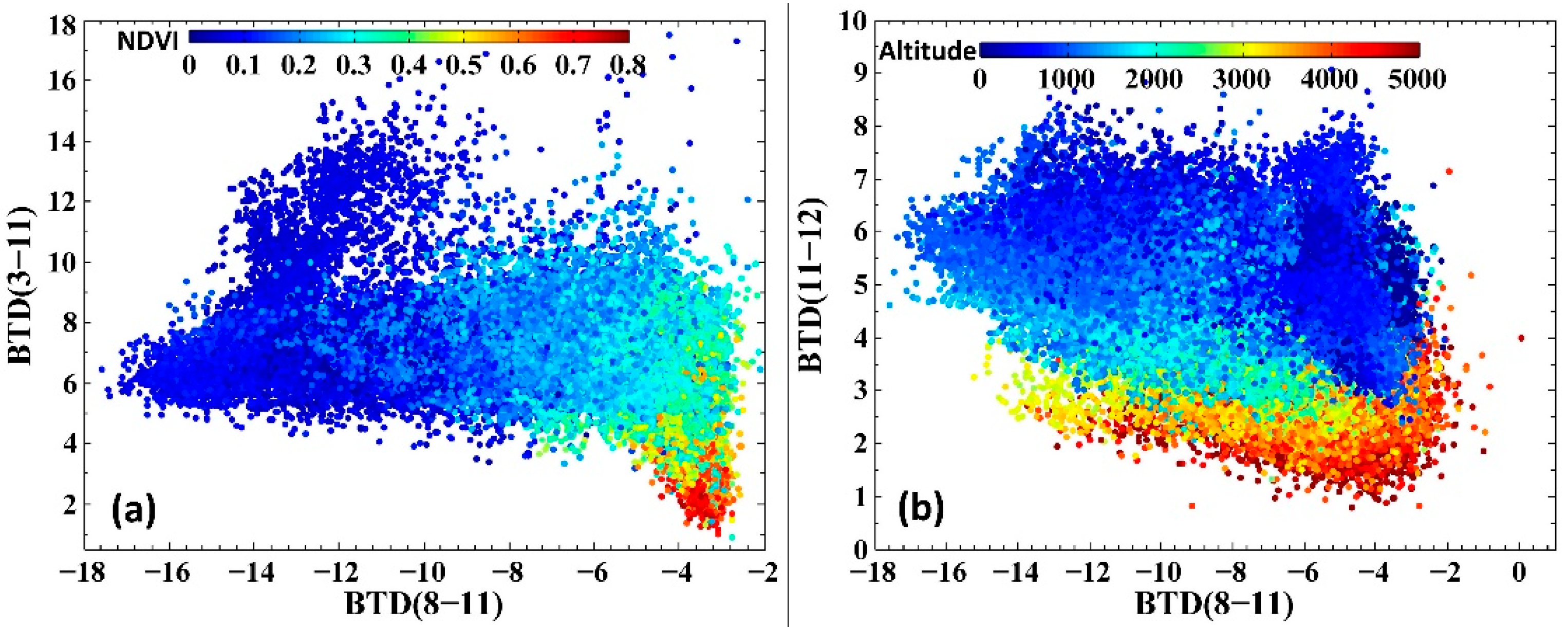
3.1. Therory Base of Dust Detection and Intensity Indication
3.2. Dust Detection
3.3. Dust Index
4. Results and Validation
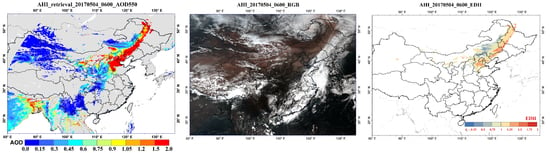
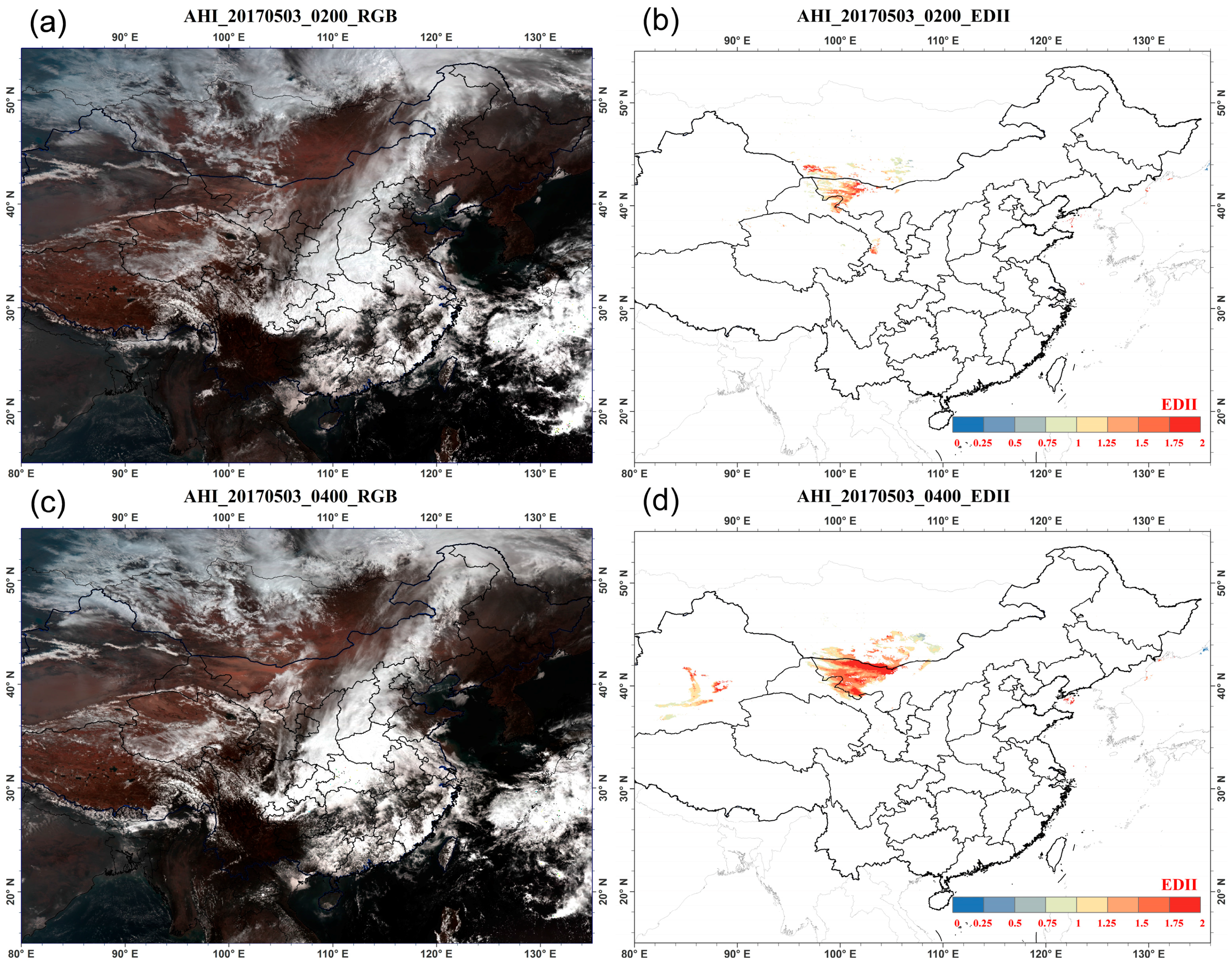
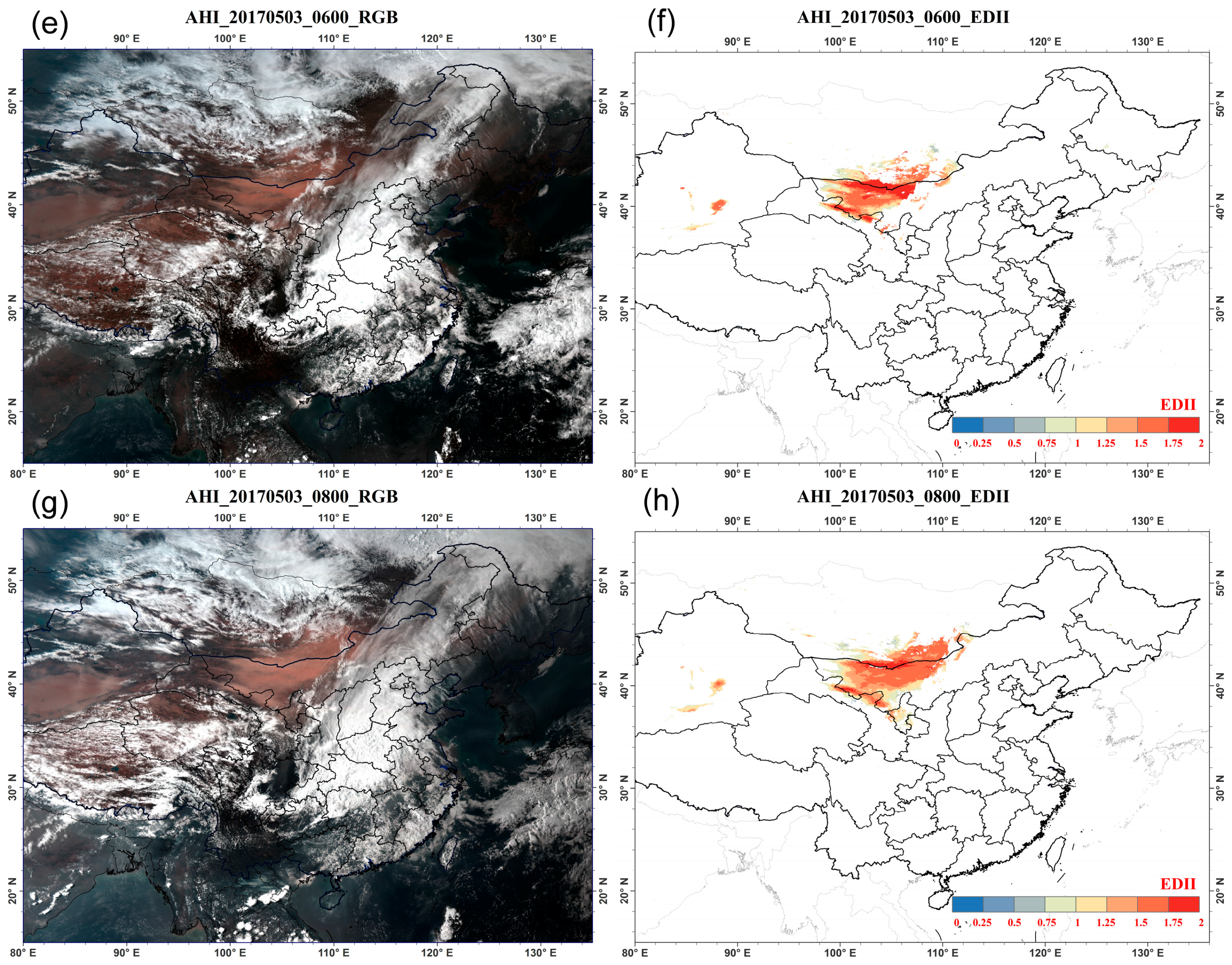
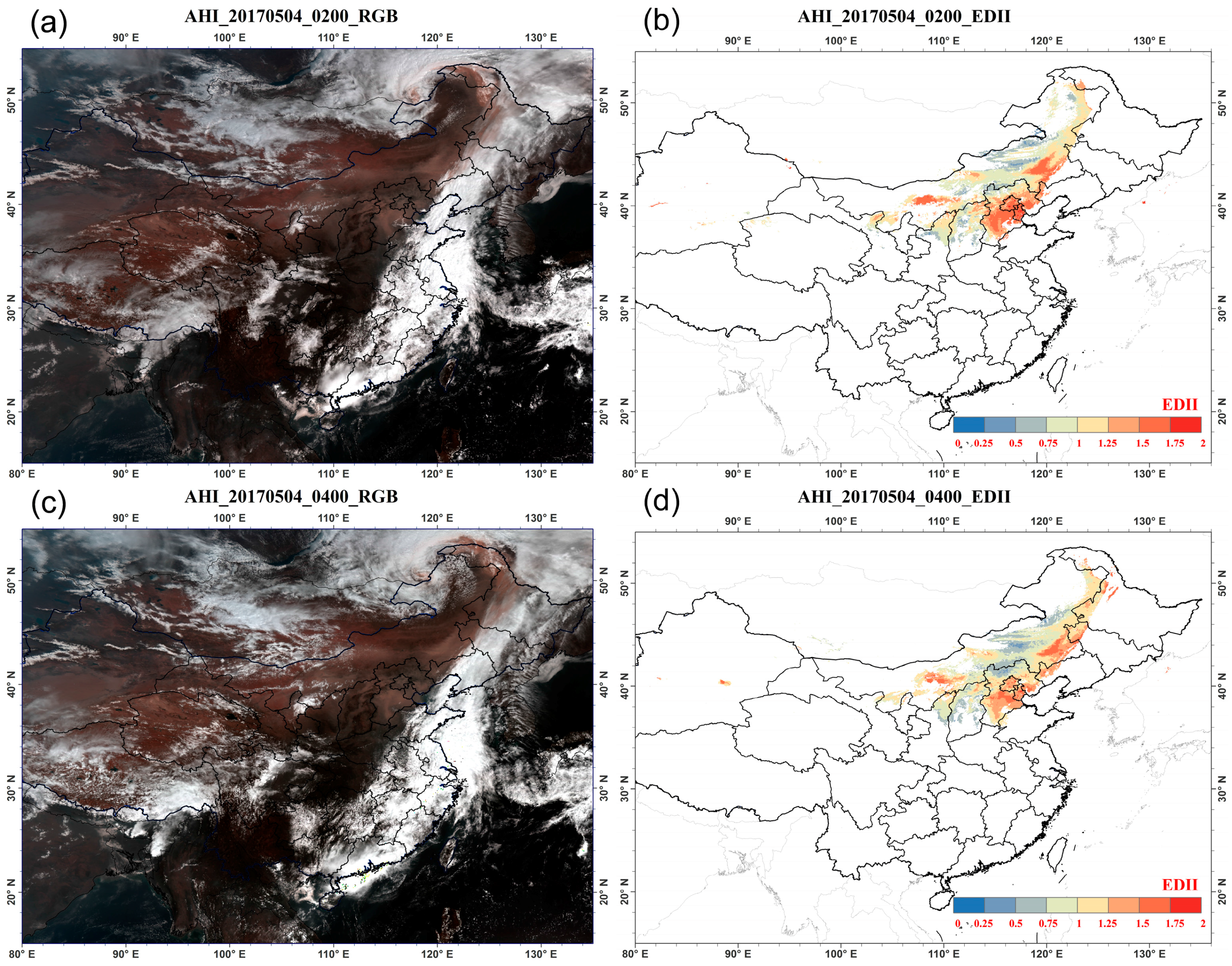
4.1. Results of Dust Detection and Dust Index
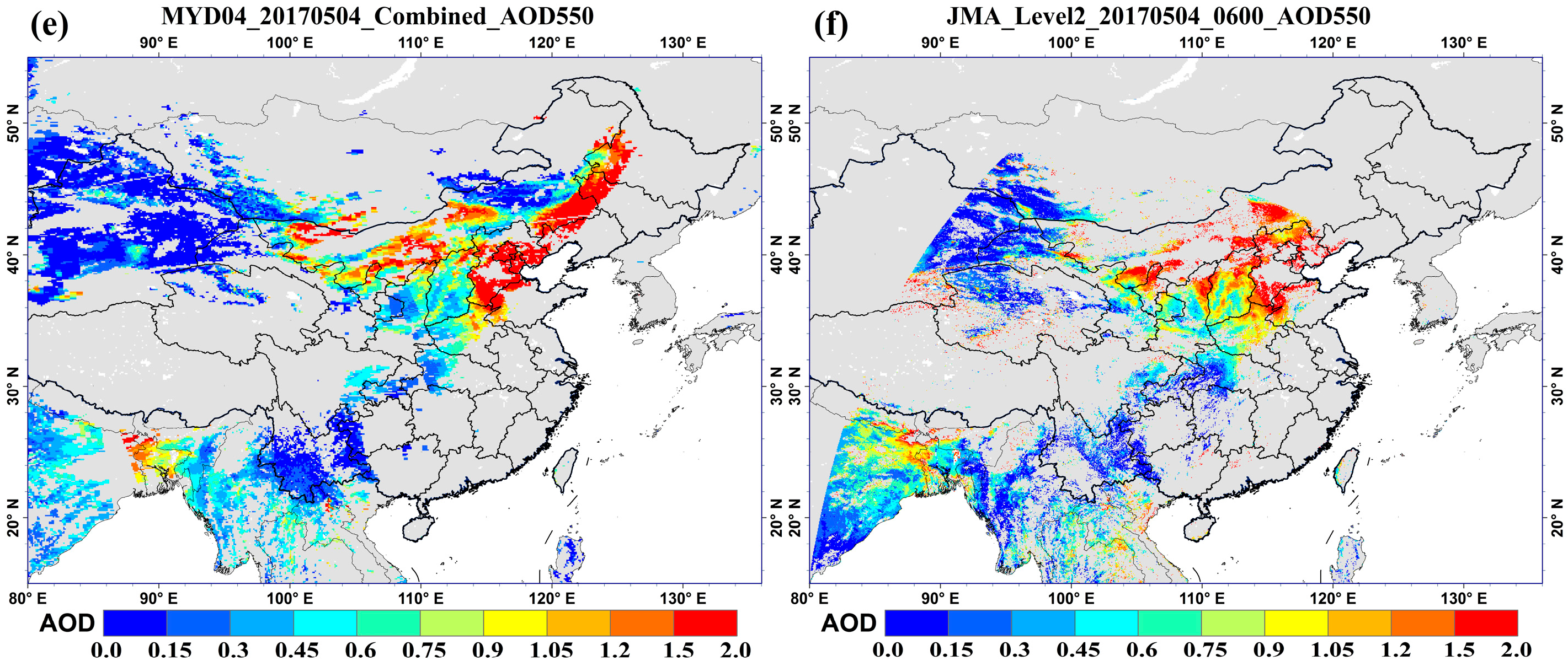
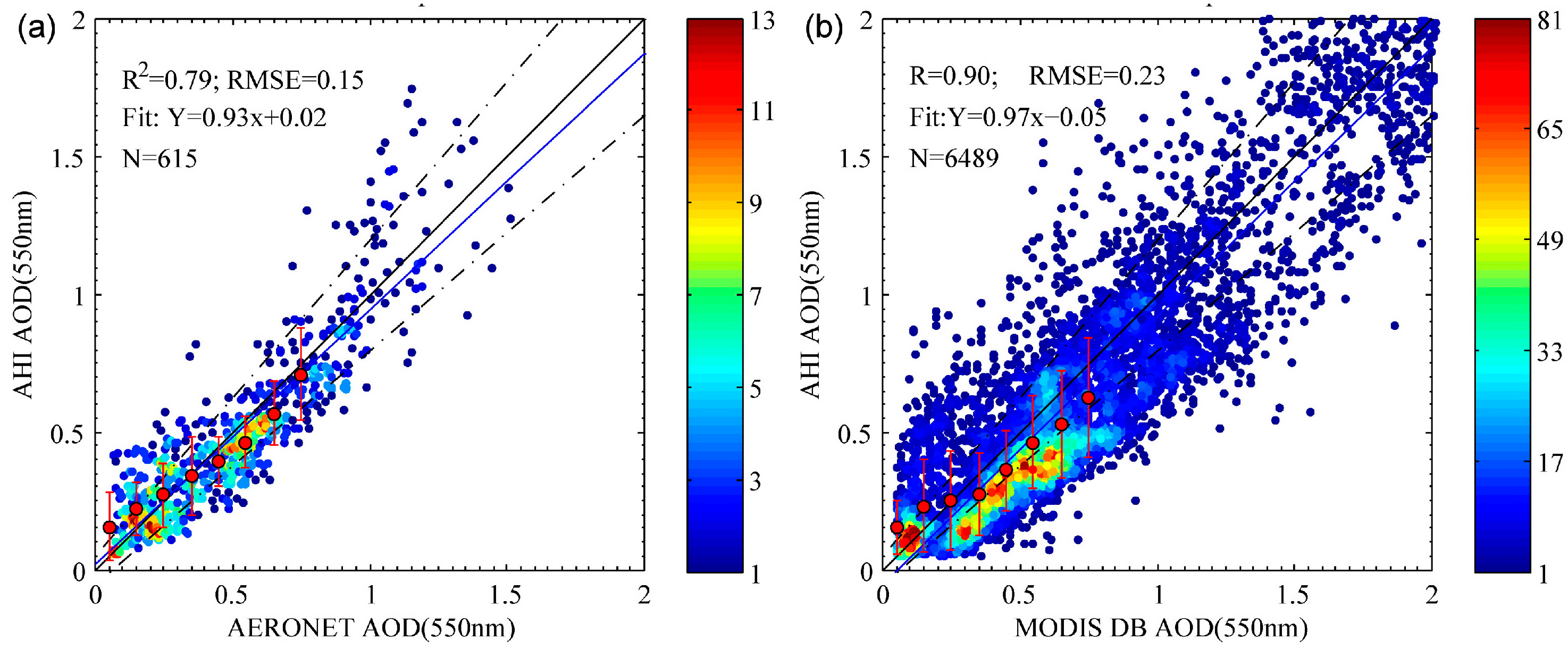
4.2. Results of Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kohfeld, K.E.; Tegen, I. Record of mineral aerosols and their role in the earth system. Treatise Geochem. 2007, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Choobari, O.A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The global distribution of mineral dust and its impacts on the climate system: A review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MüLler, D.; Heinold, B.; Tesche, M.; Tegen, I.; Althausen, D.; Alados Arboledas, L.; Amiridis, V.; Amodeo, A.; Ansmann, A.; Balis, D.; et al. Earlinet observations of the 14–22-may long-range dust transport event during SAMUM 2006: Validation of results from dust transport modelling. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegner, M.; Groß, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Schnell, F.; Gasteiger, J. The May/June 2008 Saharan dust event over Munich: Intensive aerosol parameters from lidar measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D23213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, C.; Wiegner, M.; Garhammer, M.; Seefeldner, M.; Gasteiger, J.; MüLler, D.; Koepke, P. Spectral aerosol optical depth characterization of desert dust during SAMUM 2006. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, G.; Újvári, G.; Kovács, J. Spatiotemporal patterns of saharan dust outbreaks in the Mediterranean Basin. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Rudich, Y.; Lahav, R. Desert dust suppressing precipitation: A possible desertification feedback loop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5975–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegen, I. Modeling the mineral dust aerosol cycle in the climate system. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2003, 22, 1821–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K. Indirect climate forcing over the western us from Asian dust storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 103-1–103-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangert, M.; Nenes, A.; Vogel, B.; Vogel, H.; Barahona, D.; Karydis, V.A.; Kumar, P.; Kottmeier, C.; Blahak, U. Saharan dust event impacts on cloud formation and radiation over Western Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4045–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, S.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. A review of methods for long term in situ characterization of aerosol dust. Aeolian Res. 2012, 6, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Dust storms: Recent developments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basha, G.; Phanikumar, D.V.; Kumar, K.N.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Marpu, P.R. Investigation of aerosol optical, physical, and radiative characteristics of a severe dust storm observed over UAE. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D. A consolidated technique for enhancing desert dust storms with MODIS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Schepanski, K.; Heinold, B. Comparing two years of saharan dust source activation obtained by regional modelling and satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, J. A-train satellite measurements of dust aerosol distributions over Northern China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 122, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, M.; Shi, G.Y.; Uno, I.; Yabuki, S.; Iwasaka, Y.; Yasui, M.; Aoki, T.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Kurosaki, Y.; Masuda, K.; et al. Aeolian dust experiment on climate impact: An overview of Japan–China joint project ADEC. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 142–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lou, M.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; He, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Min, M.; et al. Trans-Pacific transport of dust aerosols from East Asia: Insights gained from multiple observations and modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimoto, R. Chemical composition of atmospheric aerosols from Zhenbeitai, China, and Gosan, South Korea, during ACE-Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D19S04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rosa, J.D.D.L.; Zhang, X. Global sand and dust storms in 2008: Observation and HYSPLIT model verification. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6368–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Solomos, S.; Proestakis, E.; Konsta, D.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Tsekeri, A.; Vlastou, G.; et al. Three-dimensional evolution of saharan dust transport towards europe based on a 9-year earlinet-optimized calipso dataset. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5893–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, C.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols and surface UV products from ozone monitoring instrument observations: An overview. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D24S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Ahmad, Z.; Gleason, J. Derivation of aerosol properties from satellite measurements of backscattered ultraviolet radiation: Theoretical basis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 17099–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciren, P.; Kondragunta, S. Dust aerosol index (DAI) algorithm for MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4770–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.S.; Chang, L.S.; Ou, S. Combined dust detection algorithm by using MODIS infrared channels over East Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-M.; Nasiri, S.L.; Yang, P.; Laszlo, I.; Zhao, X.T. Detection of optically thin mineral dust aerosol layers over the ocean using MODIS. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 896–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Lu, N.M.; Niu, T.; Zhang, P. Operational retrieval of asian sand and dust storm from fy-2c geostationary meteorological satellite and its application to real time forecast in Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klüser, L.; Schepanski, K. Remote sensing of mineral dust over land with MSG infrared channels: A new bitemporal mineral dust index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Schmit, T.J.; Schmetz, J.; Menzel, W.P. Technical note: Quantitative monitoring of a Saharan dust event with SEVIRI on Meteosat-8. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanré, D.; Legrand, M. On the satellite retrieval of Saharan dust optical thickness over land: Two different approaches. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 5221–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.J.; Hao, X.; Kafatos, M.; Wang, L. Asian dust stormmonitoring combining terra and Aqua MODIS SRB measurements. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Asian dust detection from the satellite observations of moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.X.P.; Ackerman, S.; Guo, W. Dust and smoke detection for multi-channel imagers. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2347–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.A. Using the radiative temperature difference at 3.7 and 11 μm to tract dust outbreaks. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 27, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.A. Remote sensing aerosols using satellite infrared observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17069–17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, N.-M.; Hu, X.-Q.; Dong, C.-H. Identification and physical retrieval of dust storm using three MODIS thermal IR channels. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddock, M.C.; Bullard, J.E.; Bryant, R.G. Dust source identification using MODIS: A comparison of techniques applied to the Lake Eyre Basin, Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1511–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, X. Saharan dust storm detection using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer thermal infrared bands. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 013510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, R.A.; Ou, S.C.; Liou, K.N.; Roskovensky, J.K.; Tsay, S.C.; Hsu, C.; Ji, Q. Simultaneous detection/separation of mineral dust and cirrus clouds using MODIS thermal infrared window data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskovensky, J.K. Detection of thin cirrus from 1.38 μm/0.65 μm reflectance ratio combined with 8.6–11 μm brightness temperature difference. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskovensky, J.K.; Liou, K.N. Differentiating airborne dust from cirrus clouds using MODIS data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L12809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B.; Bergstrom, R.W. Modeling the radiative characteristics of airborne mineral aerosols at infrared wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 8813–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangelo, C.; Ch’edin, A.; Heilliette, S.; Jacquinet-Husson, N.; Armante, R. Dust altitude and infrared optical depth from airs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caquineau, S. Mineralogy of Saharan dust transported over northwestern tropical atlantic ocean in relation to source regions. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, D15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, C.J.; Embury, O.; Le Borgne, P.; Bellec, B. Saharan dust in nighttime thermal imagery: Detection and reduction of related biases in retrieved sea surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Malekian, M. Comparison and evaluation of dust detection algorithms using MODIS Aqua/Terra Level 1b data and MODIS/OMI dust products in the middle east. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Plana-Fattori, A.; N’Doumé, C. Satellite detection of dust using the IR imagery of meteosat: 1. Infrared difference dust index. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18251–18274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, A.; Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Leys, J.; Guang, J.; Mei, L.; Wang, J.; She, L.; Hu, Y.; He, X.; et al. Dust aerosol optical depth retrieval and dust storm detection for Xinjiang region using indian national satellite observations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; McIver, D.K.; Hodges, J.C.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Muchoney, D.; Strahler, A.H.; Woodcock, C.E.; Gopal, S.; Schneider, A.; Cooper, A.; et al. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xin, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. The variations and trends of MODIS c5 & c6 products’ errors in the recent decade over the background and urban areas of North China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Munchak, L.A.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Modis collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between Aqua’s e-deep blue, dark target, and “merged” data sets, and usage recommendations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 13965–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS collection 6 “deep blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. Aeronet—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, S.W.; Borbas, E.E.; Knuteson, R.O.; Stephenson, G.R.; Huang, H.-L. Development of a global infrared land surface emissivity database for application to clear sky sounding retrievals from multispectral satellite radiance measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmenov, A. Identifying the regional thermal-ir radiative signature of mineral dust with MODIS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L16803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Zhou, W. An enhanced dust index for asian dust detection with MODIS images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6484–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhu, J.; Wei, J.; Su, Q.; Sun, W.; Liu, F.; Shu, M. A simplified suomi NPP VIIRS dust detection algorithm. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2017, 164, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; He, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q. The brightness temperature adjusted dust index: An improved approach to detect dust storms using MODIS imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 57, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Xue, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Guang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; et al. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth over land based on a time series technique using msg/seviri data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9167–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xue, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; Hou, T.; Marir, F. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth and surface reflectance over land from NOAA AVHRR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K.N. An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wanner, W.; Li, X.; Strahler, A.H. On the derivation of kernels for kernel-driven models of bidirectional reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 21077–21089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Muller, J.P. First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, C.D. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, Y.; Wagner, S.; Lattanzio, A.; Watts, P. Application of the optimal estimation method to the joint retrieval of aerosol load and surface reflectance from MSG/SEVIRI observations. AIP Conf. Proc. 2009, 1100, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Liang, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J. Estimation of surface albedo and directional reflectance from moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Sinyuk, A.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Dickerson, R.R.; Thompson, A.M.; Schafer, J.S. An analysis of aeronet aerosol absorption properties and classifications representative of aerosol source regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddock, M.C.; Strong, C.L.; Leys, J.F.; Heidenreich, S.K.; Tews, E.K.; McTainsh, G.H. A visibility and total suspended dust relationship. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camino, C.; Cuevas, E.; Basart, S.; Alonso-Pérez, S.; Baldasano, J.M.; Terradellas, E.; Marticorena, B.; Rodríguez, S.; Berjón, A. An empirical equation to estimate mineral dust concentrations from visibility observations in Northern Africa. Aeolian Res. 2015, 16, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappalardo, G.; Amodeo, A.; Apituley, A.; Comeron, A.; Freudenthaler, V.; Linné, H.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; D’Amico, G.; Mattis, I.; et al. Earlinet: Towards an advanced sustainable european aerosol lidar network. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2389–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegner, M.; Madonna, F.; Binietoglou, I.; Forkel, R.; Gasteiger, J.; Geiß, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Schäfer, K.; Thomas, W. What is the benefit of ceilometers for aerosol remote sensing? An answer from earlinet. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1979–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Fine and coarse dust separation with polarization lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3717–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

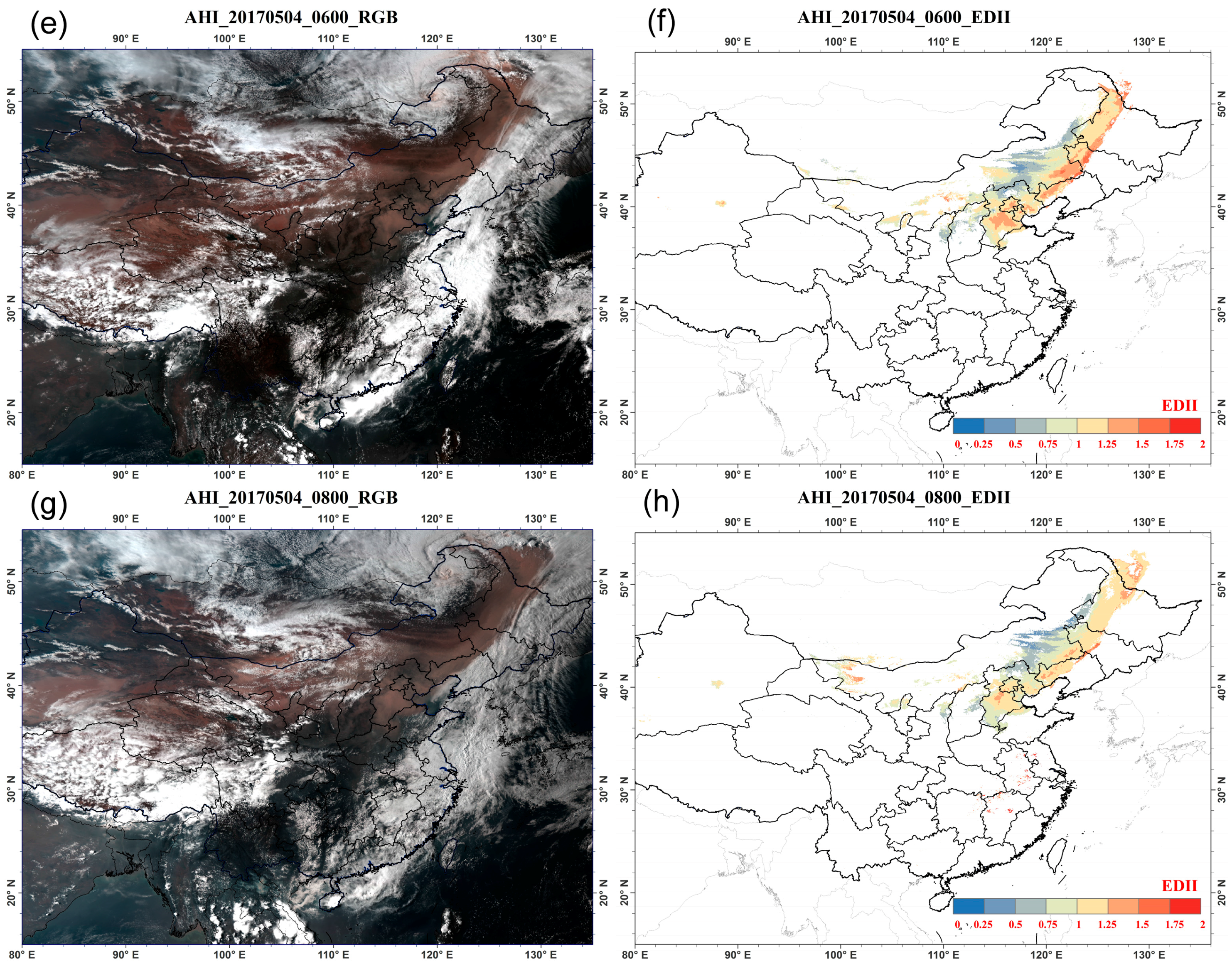
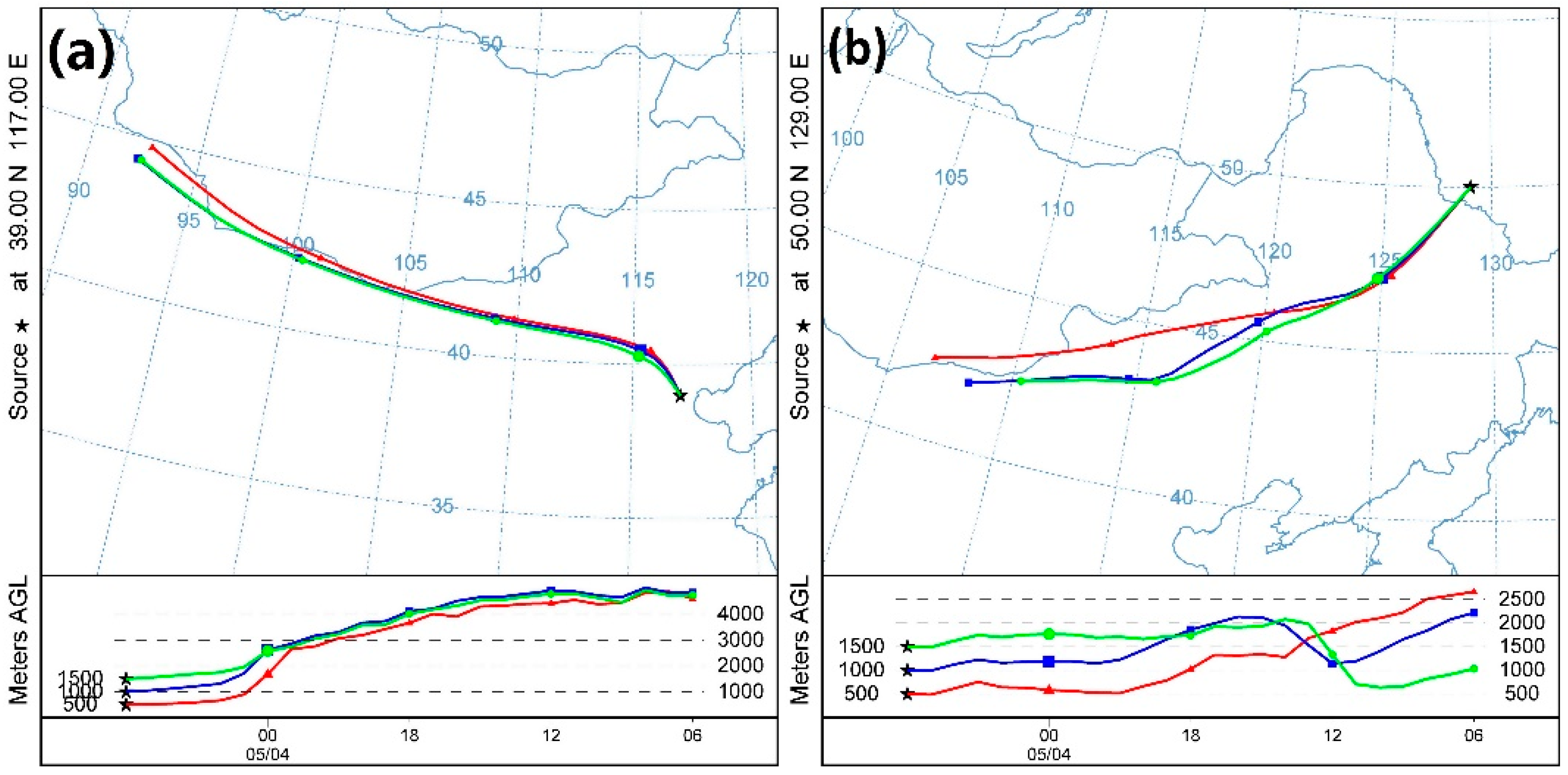
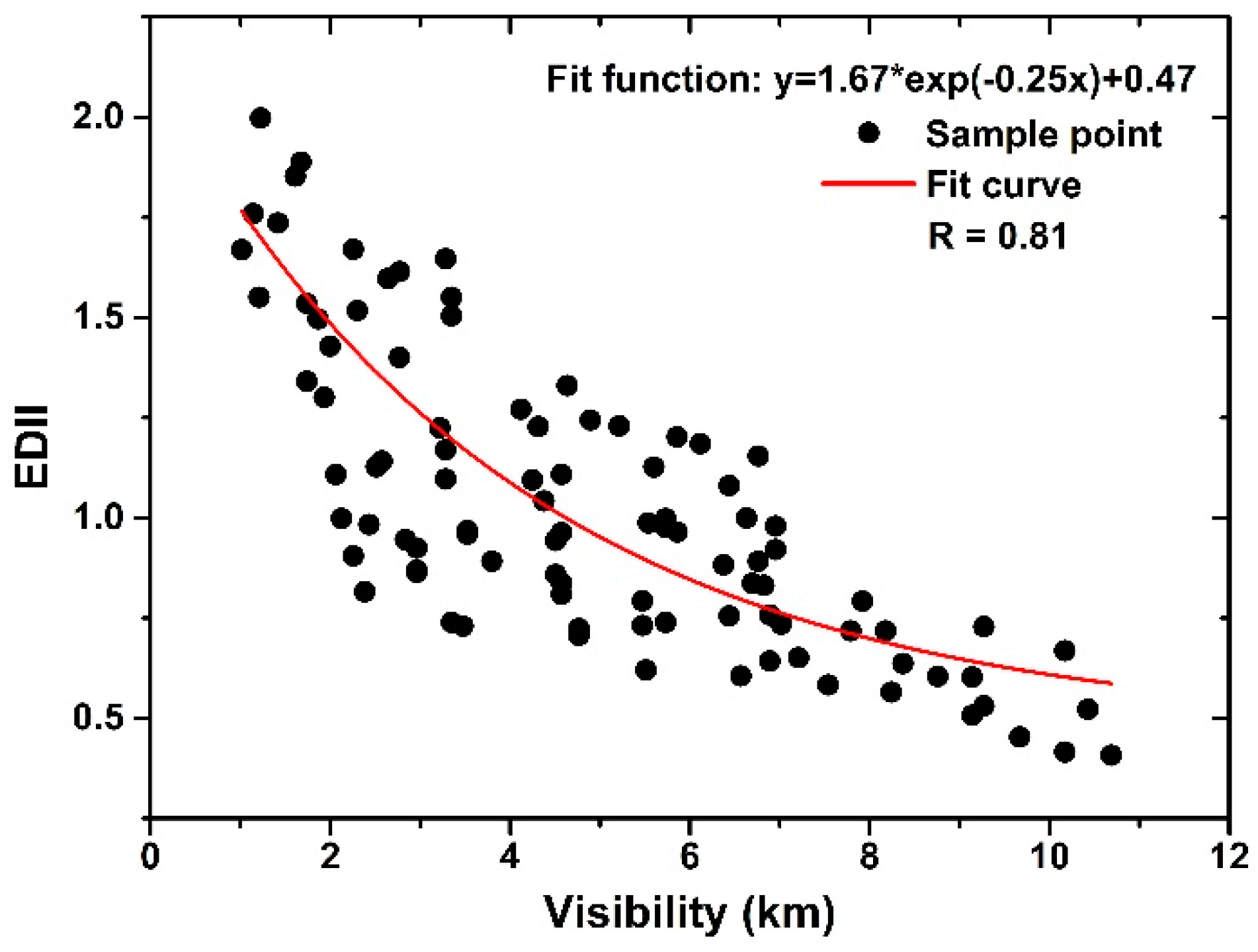
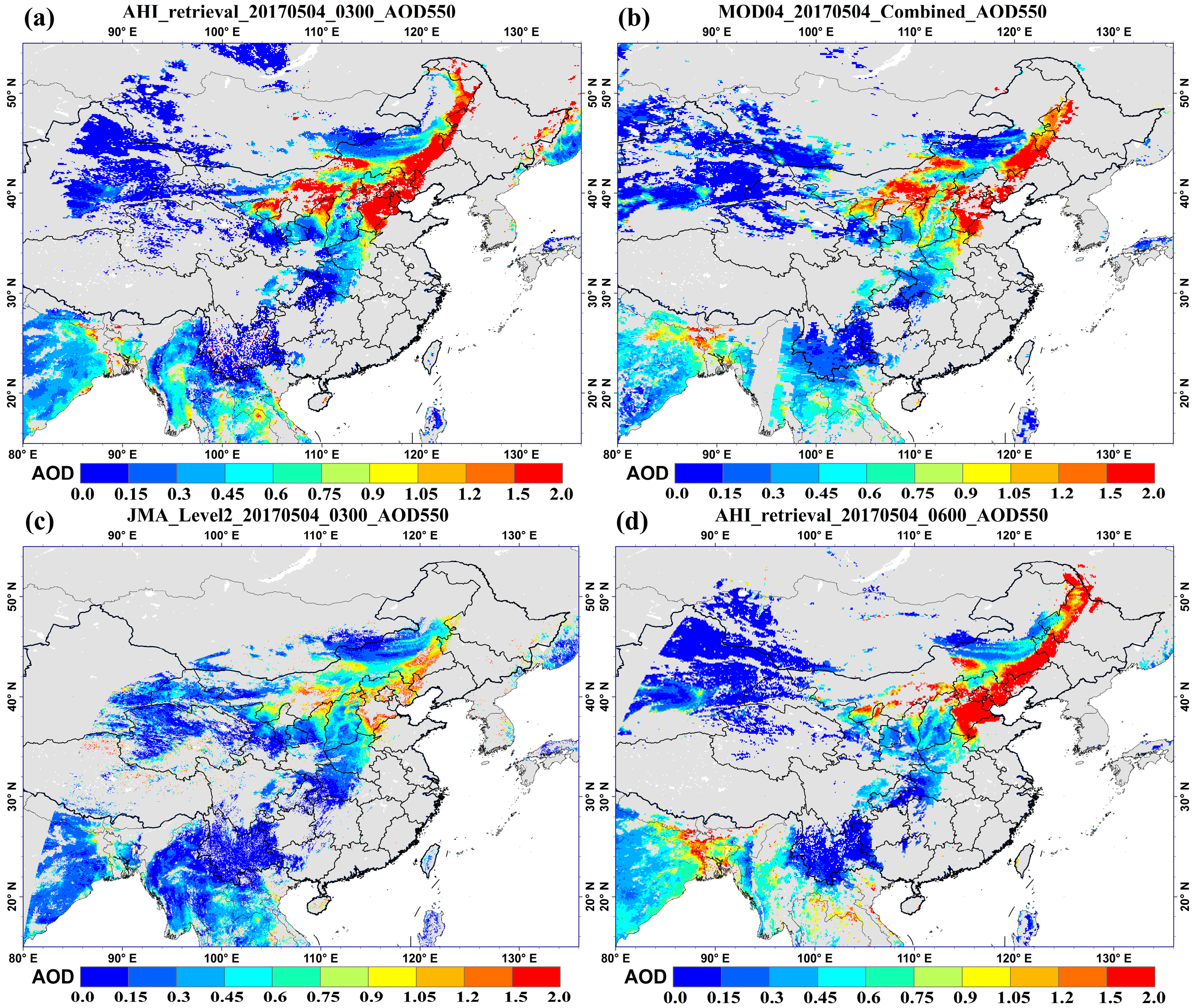
| Channel Number | Central Wavelength (µm) | Channel Number | Central Wavelength (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.47 | 9 | 6.94 |
| 2 | 0.51 | 10 | 7.35 |
| 3 | 0.64 | 11 | 8.60 |
| 4 | 0.86 | 12 | 9.64 |
| 5 | 1.61 | 13 | 10.41 |
| 6 | 2.25 | 14 | 11.24 |
| 7 | 3.89 | 15 | 12.38 |
| 8 | 6.24 | 16 | 13.28 |
| Dates (yyyy-mmdd) | Dates (yyyy-mmdd) | Dates (yyyy-mmdd) | Dates (yyyy-mmdd) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016-0303 | 2016-0406 | 2016-0505 | 2017-0504 |
| 2016-0308 | 2016-0411 | 2016-0506 | 2017-0508 |
| 2016-0311 | 2016-0416 | 2016-0510 | 2017-0529 |
| 2016-0316 | 2016-0421 | 2016-0517 | 2017-0614 |
| 2016-0317 | 2016-0424 | 2016-0530 | |
| 2016-0318 | 2016-0425 | 2016-0606 | |
| 2016-0331 | 2016-0430 | 2016-0625 |
| Station | DD | DN | ND | NN | Accuracy (%) | PCD (%) | PFD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOE_Baotou | 13 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 81 | 86 | 13 |
| Beijing | 22 | 10 | 1 | 45 | 86 | 69 | 4 |
| Dalanzadgad | 16 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 72 | 80 | 16 |
| Xianghe | 20 | 5 | 1 | 22 | 88 | 80 | 5 |
| Total | 71 | 21 | 7 | 73 | 84 | 77 | 9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
She, L.; Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Guang, J.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.; Fan, C.; Xie, Y. Dust Detection and Intensity Estimation Using Himawari-8/AHI Observation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040490
She L, Xue Y, Yang X, Guang J, Li Y, Che Y, Fan C, Xie Y. Dust Detection and Intensity Estimation Using Himawari-8/AHI Observation. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(4):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040490
Chicago/Turabian StyleShe, Lu, Yong Xue, Xihua Yang, Jie Guang, Ying Li, Yahui Che, Cheng Fan, and Yanqing Xie. 2018. "Dust Detection and Intensity Estimation Using Himawari-8/AHI Observation" Remote Sensing 10, no. 4: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040490
APA StyleShe, L., Xue, Y., Yang, X., Guang, J., Li, Y., Che, Y., Fan, C., & Xie, Y. (2018). Dust Detection and Intensity Estimation Using Himawari-8/AHI Observation. Remote Sensing, 10(4), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040490