A Case Study of Land-Surface-Temperature Impact from Large-Scale Deployment of Wind Farms in China from Guazhou
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. MODIS Data
2.3. Meteorological Data
2.4. Data Processing and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Climatic Features of Wind in Guazhou
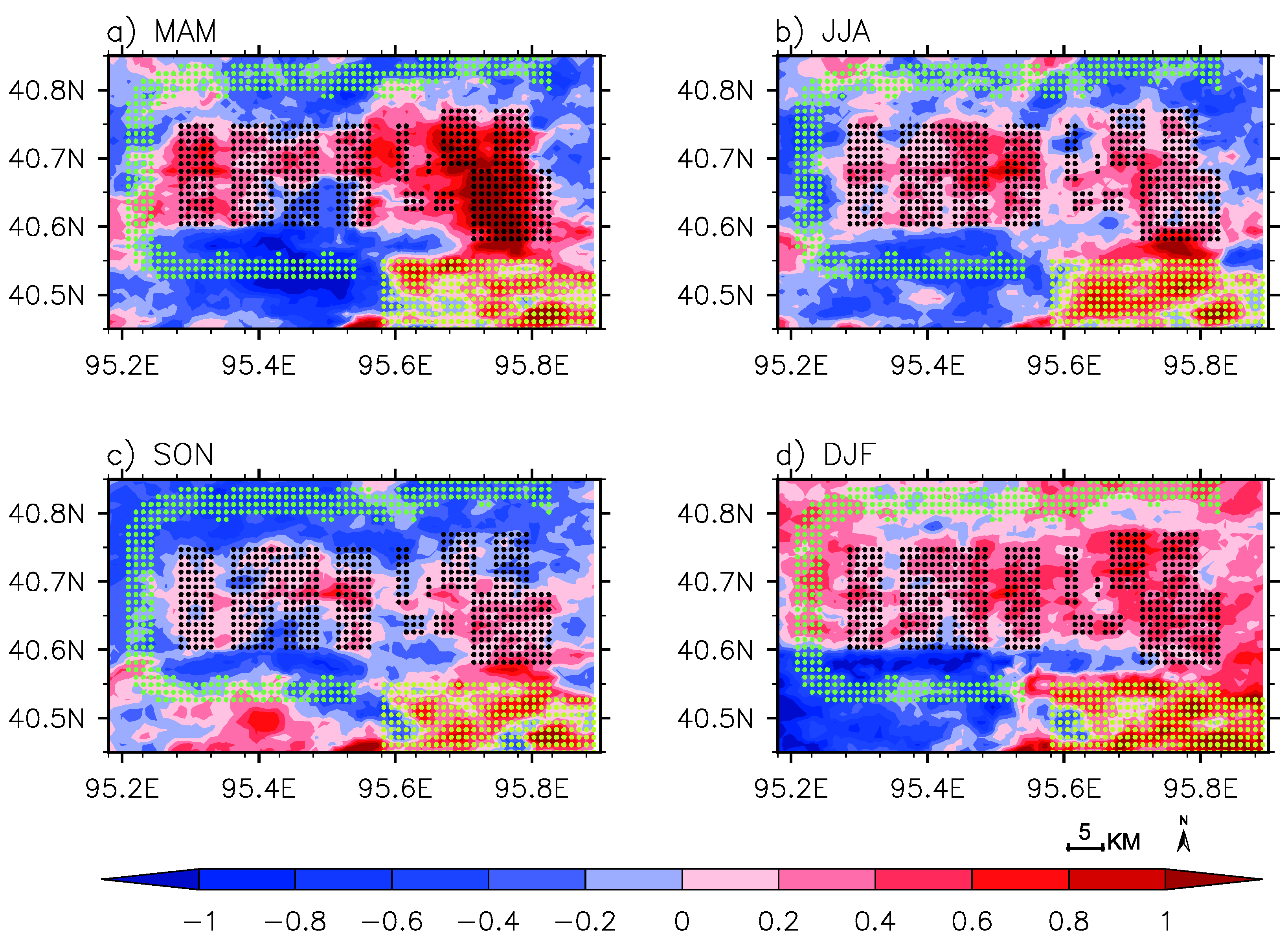
3.2. Spatial Coupling Analysis of LST Changes
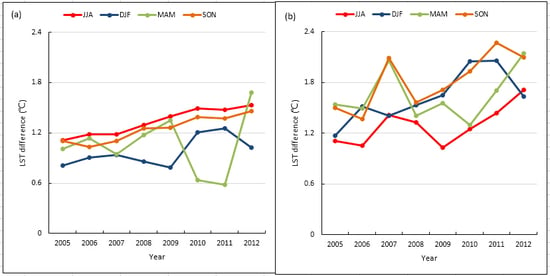
3.3. Temporal Variability of LST Impacts from Wind Farm Versus Guazhou County
4. Discussion
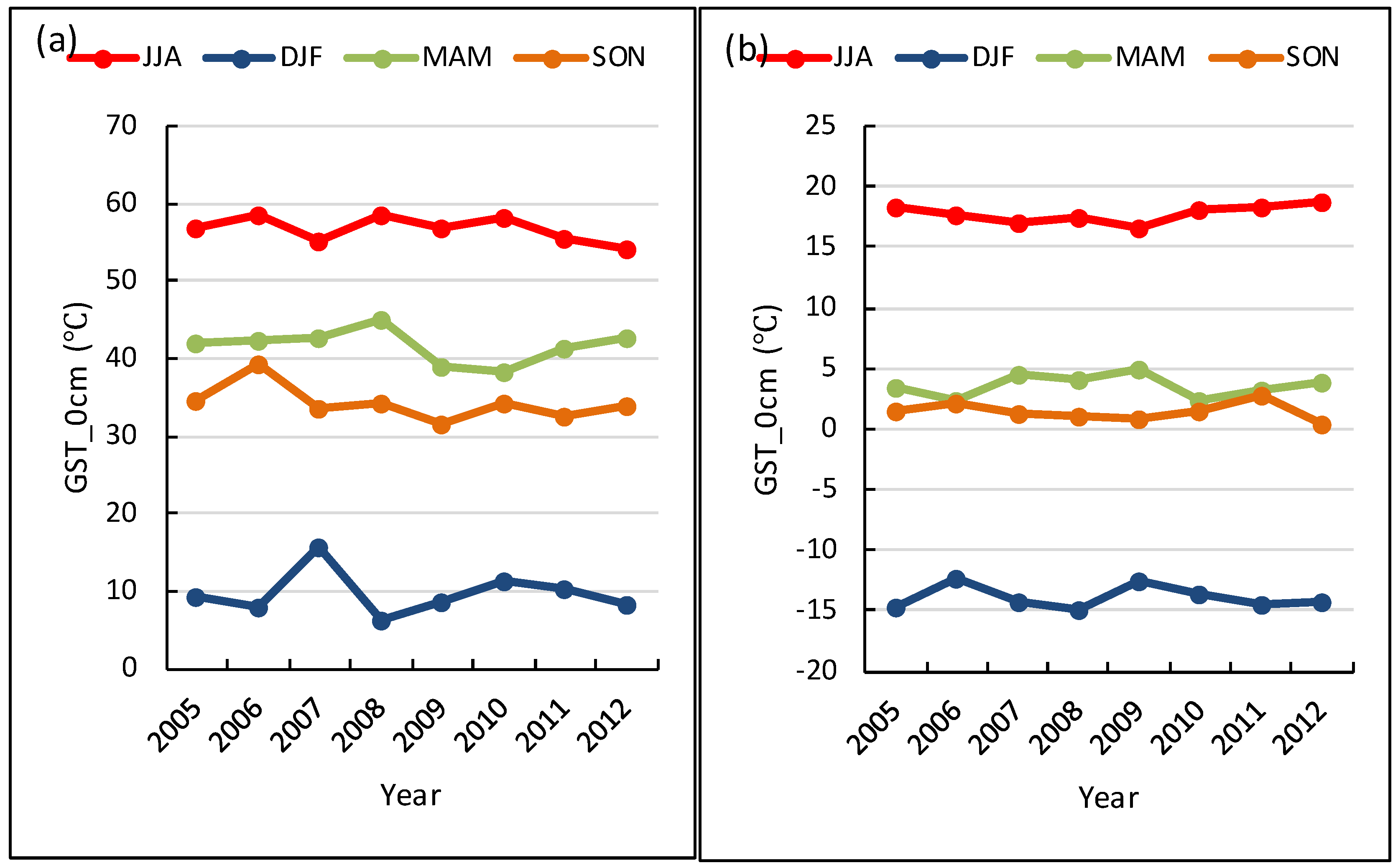
4.1. Inter-Annual Variations of GST Observed in Guazhou
4.2. Possible Impacts of Temporal Changes in Land Cover on LST Variability
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, C.; Sha, Y.; Gu, W.; Yin, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Trend in China’s wind power. Electricity 2009, 1, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.Z. High on Wind Power. In China Today-Explaining China to the World (Special Report on Website). Available online: http://www.chinatoday.com.cn/ctenglish/se/txt/2009-11/26/content_231445.htm (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Li, Z.; Yang, S. “Three Gorges on Land” emerges at Qiuquan: Song of the wind sang in Gobi and renewable energy turned out by rotors. RENMI RIBAO, 8 August 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Exploration of large-scale wind power base in Qiuquan. China News, 24 August 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Liu, X. Guazhou’s wind power generating capacity totaled at 15.36 billion degrees. Chinese Wind Energy Industry, 9 June 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Guazhou’s wind power installed capacity ranks the first in China. Gansu Daily, 23 February 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Guazhou’s wind power installed capacity has ranked the first in China. Gansu Daily, 9 July 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barrie, D.B.; Kirk-Davidoff, D.B. Weather response to a large wind turbine array. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Prinn, R.G. Potential climatic impacts and reliability of very large-scale wind farms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk-Davidoff, D.B.; David, W.K. On the climate impact of surface roughness anomalies. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 2215–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawsky, L.; Zhou, L.; Baidya, R.S.; Xia, G.; Vuille, M.; Harris, R.A. Observed thermal impacts of wind farms over northern illinois. Sensors 2015, 15, 14981–15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baidya, R.S.; Pacala, S.W.; Walko, R.L. Can large wind farms affect local meteorology? J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya, R.S.; Traiteur, J.J. Impacts of wind farms on surface air temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17899–17904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaganagar, K.; Mithu, D. Implications of stratified atmospheric boundary layer turbulence on the near-wake structure of wind turbines. Energies 2014, 7, 5740–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.W.; DeCarolis, J.F.; Denkenberger, D.C.; Donald, H.L.; Sergey, L.M.; Stephen, P.; Philip, J.R. The influence of large-scale wind-power on global climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16115–16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Baidya, R.S.; Thorncroft, C.; Bosart, L.F.; Hu, Y. Impacts of wind farms on land surface temperature. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Barthelmie, R.J.; Pryor, S.C. In situ observations of the influence of a large onshore wind farm on near-surface temperature, turbulence and wind speed profiles. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, B.H.; Bukovsky, M.S. The effect of a giant wind farm on precipitation in a regional climate model. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 045101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Cristina, L.A.; Willett, K. Taming hurricanes with arrays of offshore wind turbines. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajewski, D.A.; Takle, E.S.; Lundquist, J.K.; Oncley, S.; Prueger, J.H.; Horst, T.W.; Rhodes, M.E.; Pfeiffer, R.; Hatfield, J.L.; Spoth, K.K.; et al. Crop wind energy experiment: Observations of surface-layer, boundary layer, and meso-scale interactions with a wind farm. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, S.T.; Jorgensen, H.E.; Barthelmie, R.; Rathmann, O.; Badger, J.; Hansen, K.; Ott, S.; Rethore, P.E.; Larsen, S.E.; Jensen, L.E. The making of a second generation wind farm efficiency model complex. Wind Energy 2009, 12, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.; DeCarolis, J.; Denkenberger, D.; Lenschow, D.; Malyshev, S.; Pacala, S.; Rasch, P.J. The influence of large-scale wind power on global climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16115–16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, A.; Olson, J.; Lundquist, J.; Dudhia, J.; Gupta, A.; Michalakes, J.; Barstad, I. Local and mesoscale impacts of wind farms as parameterized in a mesoscale NWP model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 3017–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Baidya, S.R.; Dai, Y.; Chen, H. Diurnal and seasonal variations of wind farm impacts on land surface temperature over western Texas. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, A.C.; Olson, J.B.; Lundquist, J.K. Parameterization of wind farms in climate models. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 6439–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Fernando, P.A. Large-eddy simulation of a very large wind farm in a stable atmospheric boundary layer. Phys. Fluid. 2011, 23, 065101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Chen, H.; Dai, Y.; Harris, R.A. Effects of topography on assessing wind farm impacts using MODIS data. Earth Interact. 2013, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Zhou, L.; Xia, G. Satellite observations of wind farm impacts on nocturnal land surface temperature in Iowa. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12234–12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Zhou, L.; Freedman, J.M.; Baidya, S.R.; Harris, R.A.; Cervarich, M.C. A case study of effects of atmospheric boundary layer turbulence, wind speed, and stability on wind farm induced temperature changes using observations from a field campaign. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The CGIAR Consortium for Spatial Information. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/SELECTION/inputCoord.asp (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Land Processes Active Archive Center (LP DAAC). Available online: https://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov/data/search.html (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Wan, Z. Land Surface Temperature Measurements from EOS MODIS Data, Semi-Annual Report Submitted to the NASA; 2003. Available online: http://www.docin.com/p-1247583966.html (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the MODIS land surface temperature/ emissivity products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulatory Report about Situation of the Renewable Energy Power Generation and Network in Gansu. Available online: http://www.bipvcn.org/news/market/domestic/27605.html (accessed on 13 April 2016). (In Chinese)
- Barthelmie, R.J. Quantifying the impact of wind turbine wakes on power output at offshore wind farms. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2010, 27, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. China’s first 10 GW-plus wind project on verge of the completion. Wind Power Monthly, 16 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, K.W. “world wind library” turned to “land of Three Gorges”. Gansu Moring Paper, 12 January 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Y. Development of renewable energy—Wind power industry in Guazhou County. Jiuquan Daily, 10 November 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.X. The comprehensive economy of Guazhou has been increased markedly during the “Eleventh Five year”. Guazhou Development and Reform Commission, 8 December 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.Z. The Development and Variation of the Population in Guazhou County. Available online: http://www.gstj.gov.cn/www/HdClsContentDisp.asp?Id=23044 (accessed on 13 Arpil 2016). (In Chinese)
- Wei, F.Y. Modern Climatic Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Technology; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Min, W. MODIS/LST product validation for mixed pixels at Linzhi of Tibet. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2014, 25, 722–730. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Qin, Z. The validation of Chinese land surface temperature products retrieved from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2006, 69, 15–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]






| LSTWFM-NNWF Trend | LSTGZ-NNWF Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nighttime | MAM | 0.12 °C/8 years (R = 0.098) | 0.30 °C/8 years (R = 0.302) |
| JJA | 0.51 °C/8 years (R = 0.975) | 0.51 °C/8 years (R = 0.670) | |
| SON | 0.48 °C/8 years (R = 0.953) | 0.80 °C/8 years (R = 0.748) | |
| DJF | 0.38 °C/8 years (R = 0.665) | 0.76 °C/8 years (R = 0.767) | |
| Daytime | MAM | 0.13 °C/8 years (R = 0.197) | −0.03 °C/8 years (R = 0.014) |
| JJA | 0.08 °C/8 years (R = 0.112) | −0.46 °C/8 years (R = 0.532) | |
| SON | −0.25 °C/8 years (R = 0.324) | 0.03 °C/8 years (R = 0.026) | |
| DJF | −0.67 °C/8 years (R = 0.323) | −0.35 °C/8 years (R = 0.161) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, R.; Zhu, R.; Guo, P. A Case Study of Land-Surface-Temperature Impact from Large-Scale Deployment of Wind Farms in China from Guazhou. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100790
Chang R, Zhu R, Guo P. A Case Study of Land-Surface-Temperature Impact from Large-Scale Deployment of Wind Farms in China from Guazhou. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(10):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100790
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Rui, Rong Zhu, and Peng Guo. 2016. "A Case Study of Land-Surface-Temperature Impact from Large-Scale Deployment of Wind Farms in China from Guazhou" Remote Sensing 8, no. 10: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100790
APA StyleChang, R., Zhu, R., & Guo, P. (2016). A Case Study of Land-Surface-Temperature Impact from Large-Scale Deployment of Wind Farms in China from Guazhou. Remote Sensing, 8(10), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8100790