Integrated Time and Phase Synchronization Strategy for a Multichannel Spaceborne-Stationary Bistatic SAR System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The phase error can be eliminated by compressing the echo signal in the range direction using the direct signal as the matched filter [24]. This strategy requires a delicate system design, which will be introduced in Section 2.1.
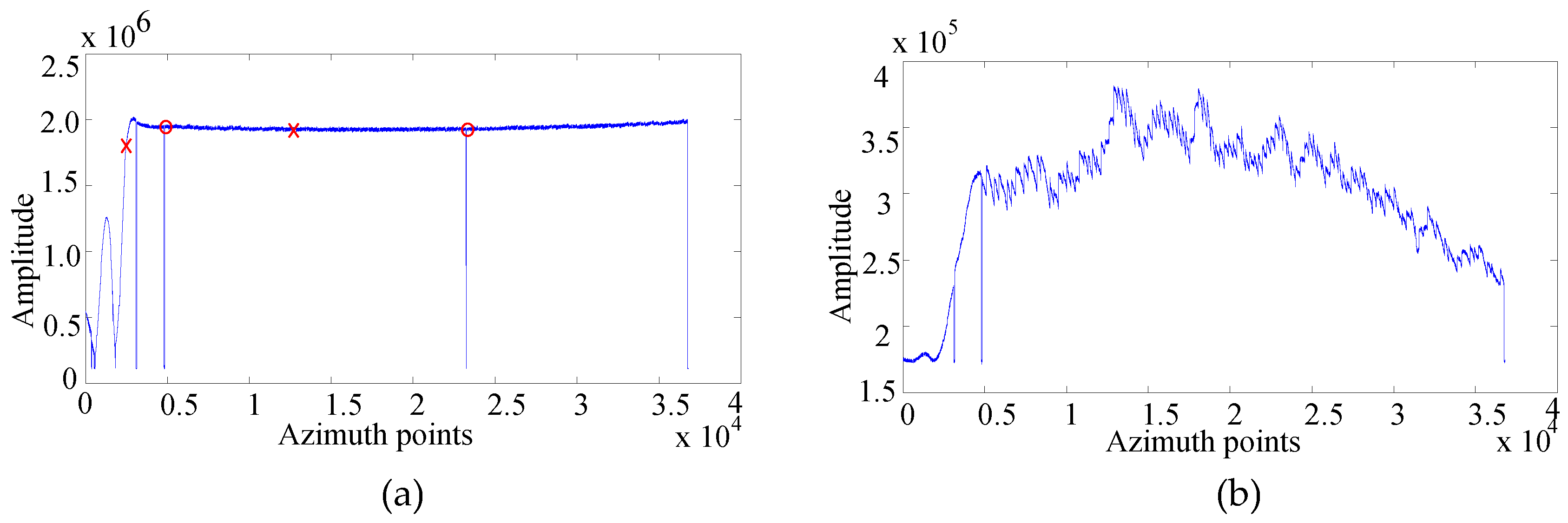
- The SNR of the direct signal varies and cannot be guaranteed for each PRF time, since the energy received by the direct channel is variant within the whole Synthetic Aperture Time (SAT). For example, the direct signal power is too small to achieve high SNR at the start time, while a high gain is directly achieved during the illuminated main lobe time in view of the long SAT for spotlight mode.
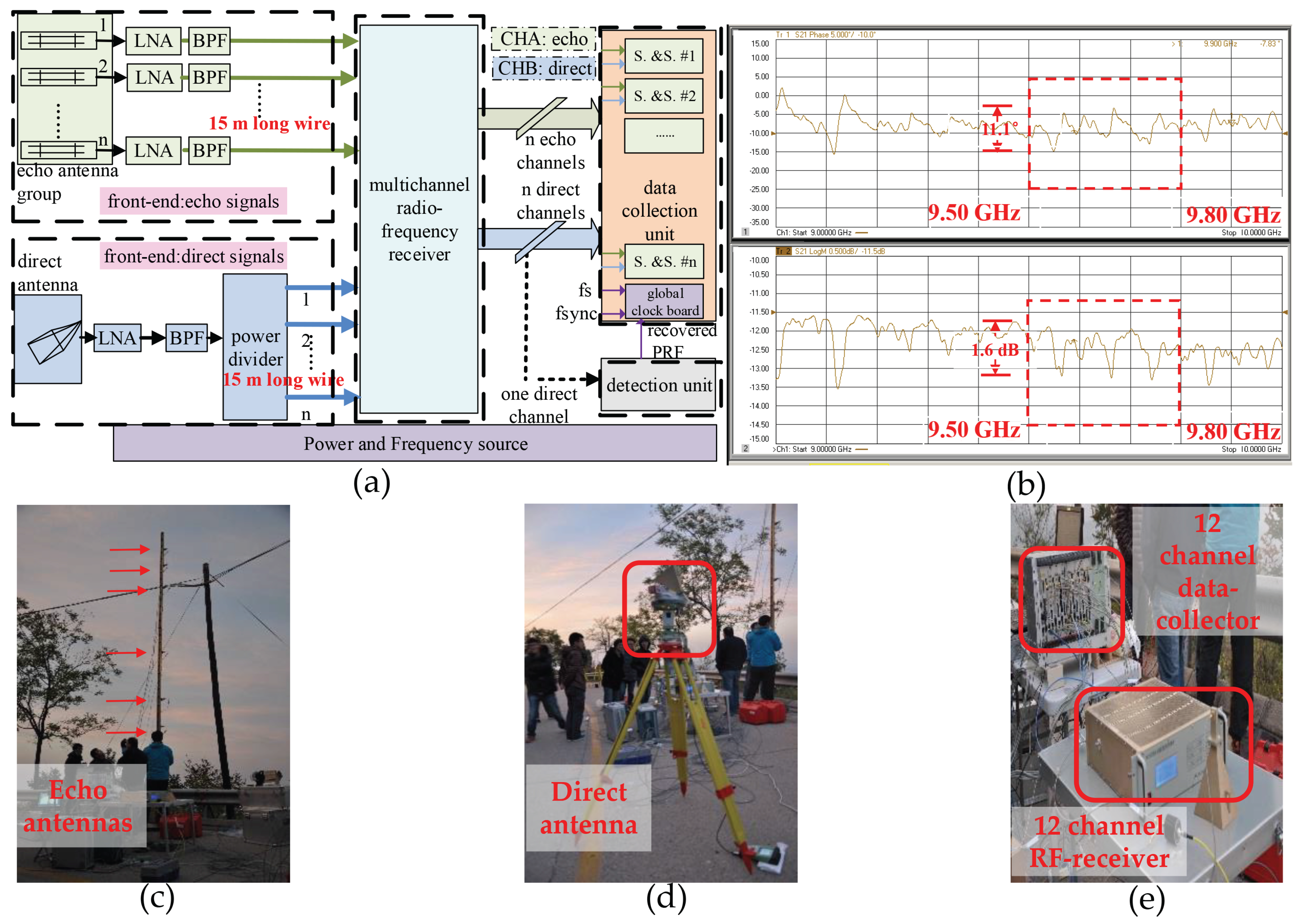
- The direct-path and scattered path measurements and the thermal sensitivity of the system hardware can impact the phase errors and relative gains of the signal paths. In a multichannel system, the perturbations on each channel, such as the different thermal noise and electromagnetic properties, can seriously affect the signal quality. For example, the twelve long cables (i.e., 15 m, X-band) in our experiment can differentially lead to the appearance of phase errors and amplitude inequality.
2. Experimental System Description and Signal Model
2.1. Experimental System Description
2.2. Signal Model
2.2.1. Phase Error
2.2.2. Signal Model
3. Integrated Synchronization Strategy
3.1. Time Synchronization
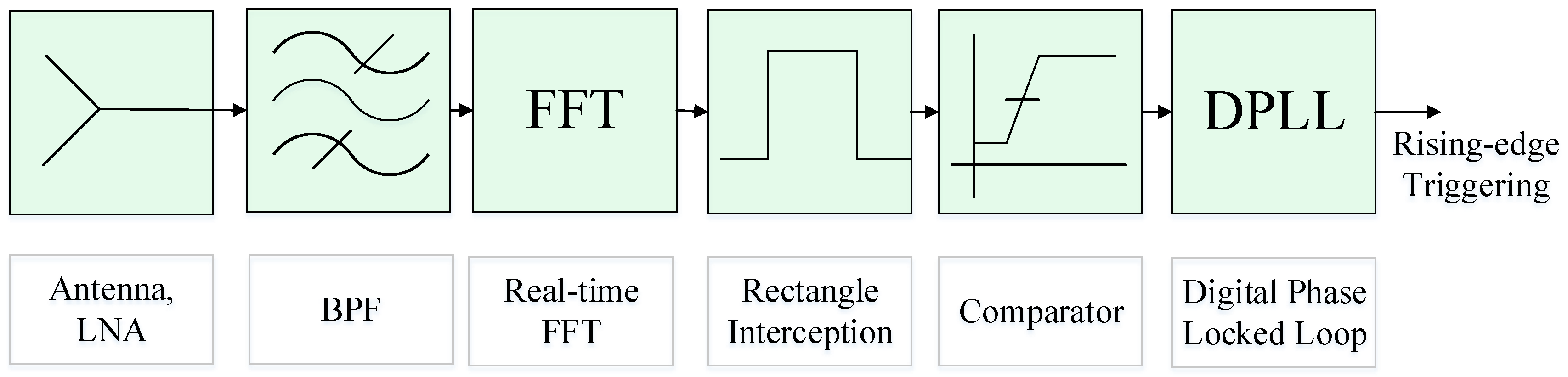
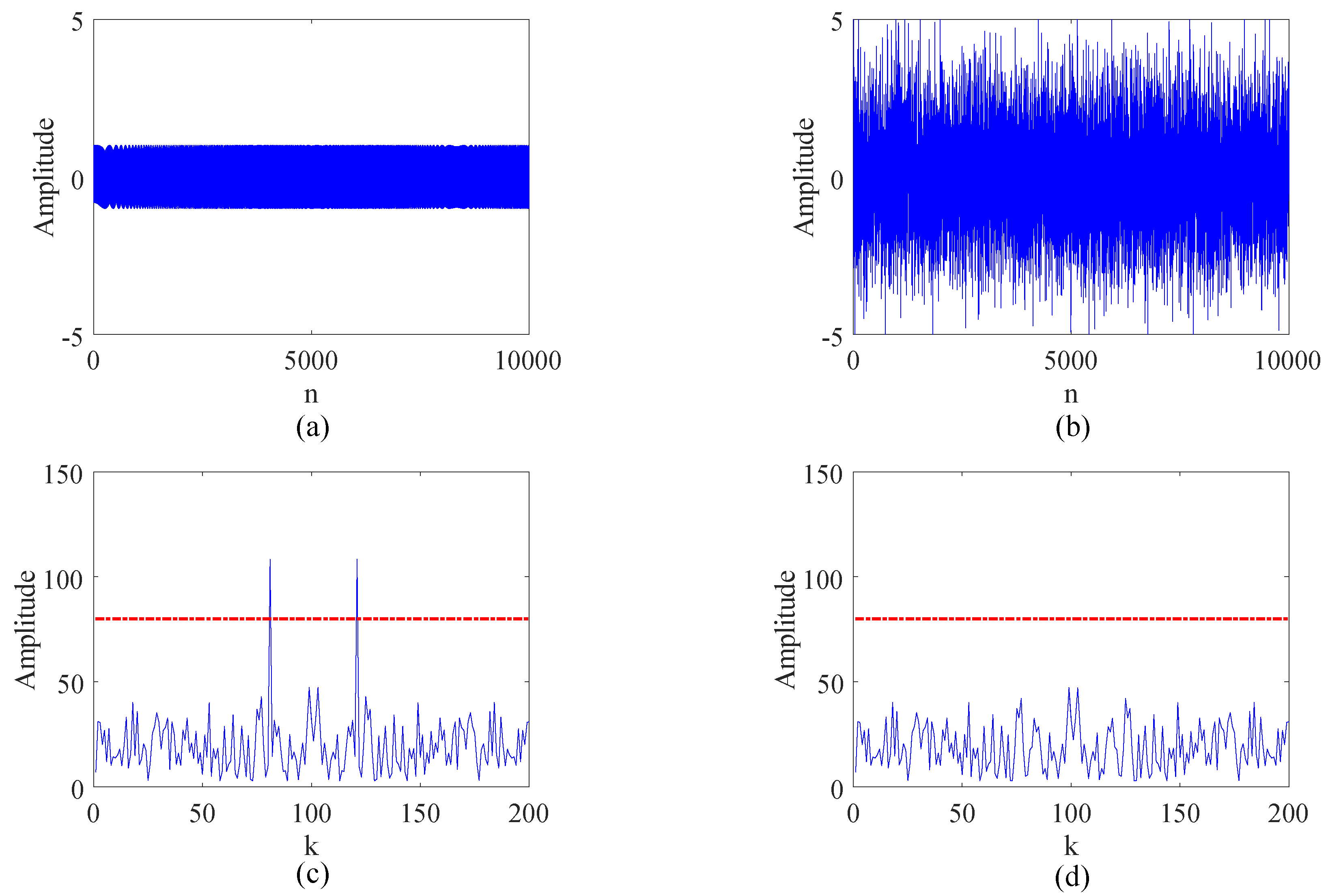
3.1.1. PRF Generation under Noisy Conditions
3.1.2. Multichannel Calibration
3.1.3. Alignment of the Recorded Data with the Orbital Data
3.2. Phase Synchronization
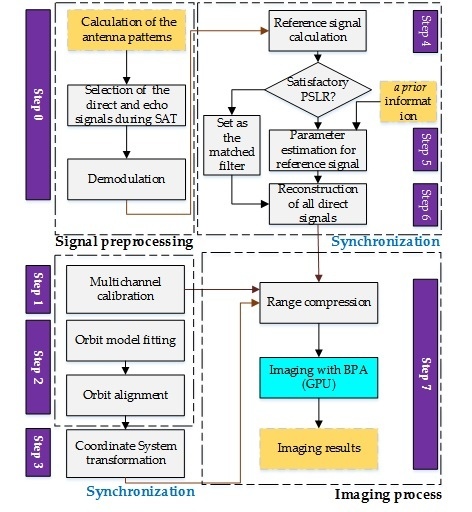
3.3. Integrated Process Flow
- Step 0:
- Signal preprocessing. Calculate the direct and echo antenna patterns; select the direct and echo signals during SAT; and perform demodulation operations.
- Step 1:
- Multichannel calibration. Correlate the signals of all other boards (2∼n) with the signals of Board 1 on each PRF time, and compensate the delay and jitter errors for signals of all other boards.
- Step 2:
- Orbit model fitting and aligning the recorded data with the orbital data (orbit alignment).
- Step 3:
- Coordinate system transformation. The location of the orbit and the synchronization and echo receivers are transformed into the BiSAR coordinate system [38].
- Step 4:
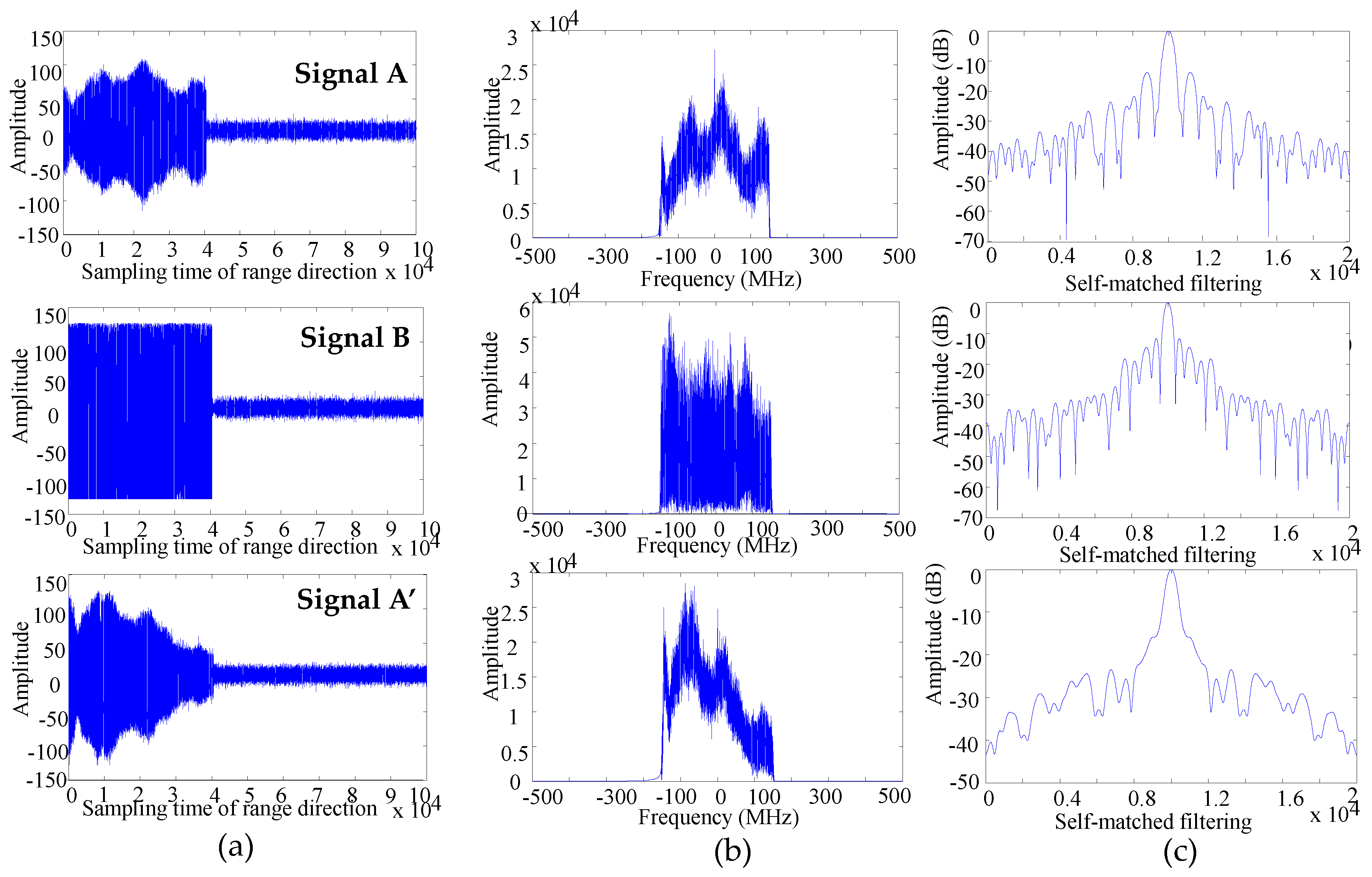
- Selecting the reference signal from the signals through calculation. If the Peak Side Lobe Ratio (PSLR) of the reference signal meets the requirements of dB, go to Step 6; else, go to Step 5.
- Step 5:
- Estimating parameters for the reference signal. The parameters are linear frequency modulation rate, delay time and linear phase offset, respectively.
- Step 6:
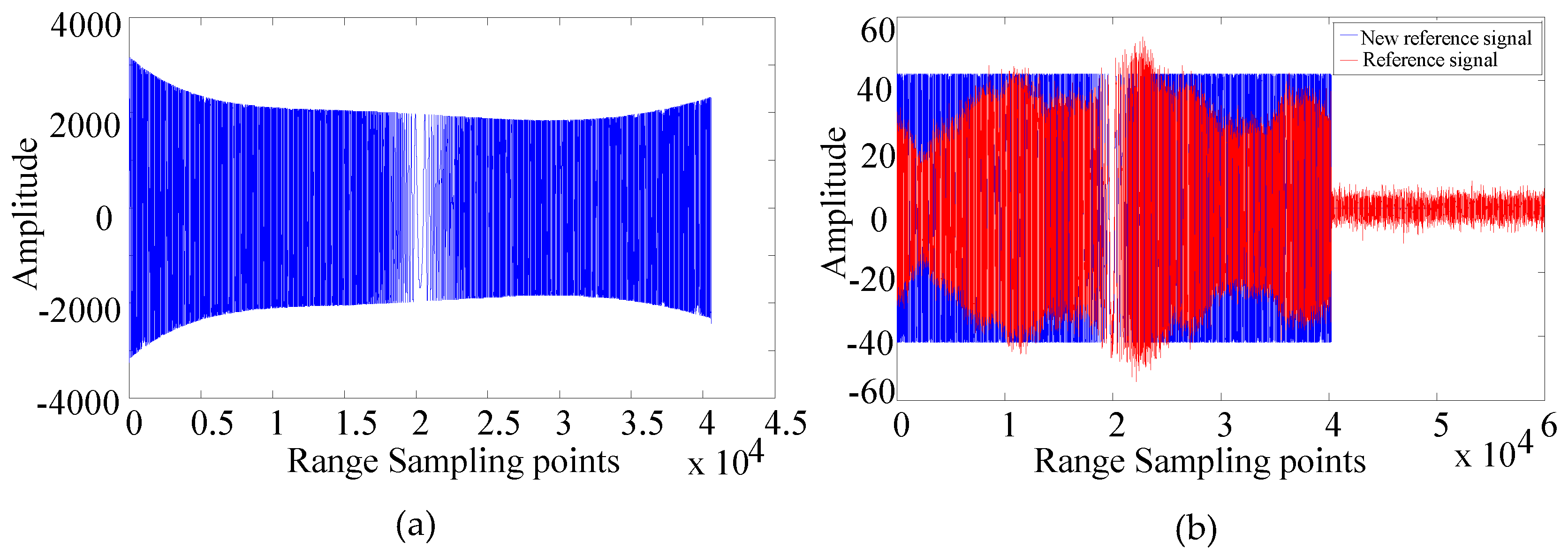
- Reconstruction of all direct signals. Employ the reference signal or new reference signal to reconstruct all signals during SAT with a shift and phase compensation operation.
- Step 7:
- Imaging process. After range compression, the imaging algorithm can be accelerated by the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
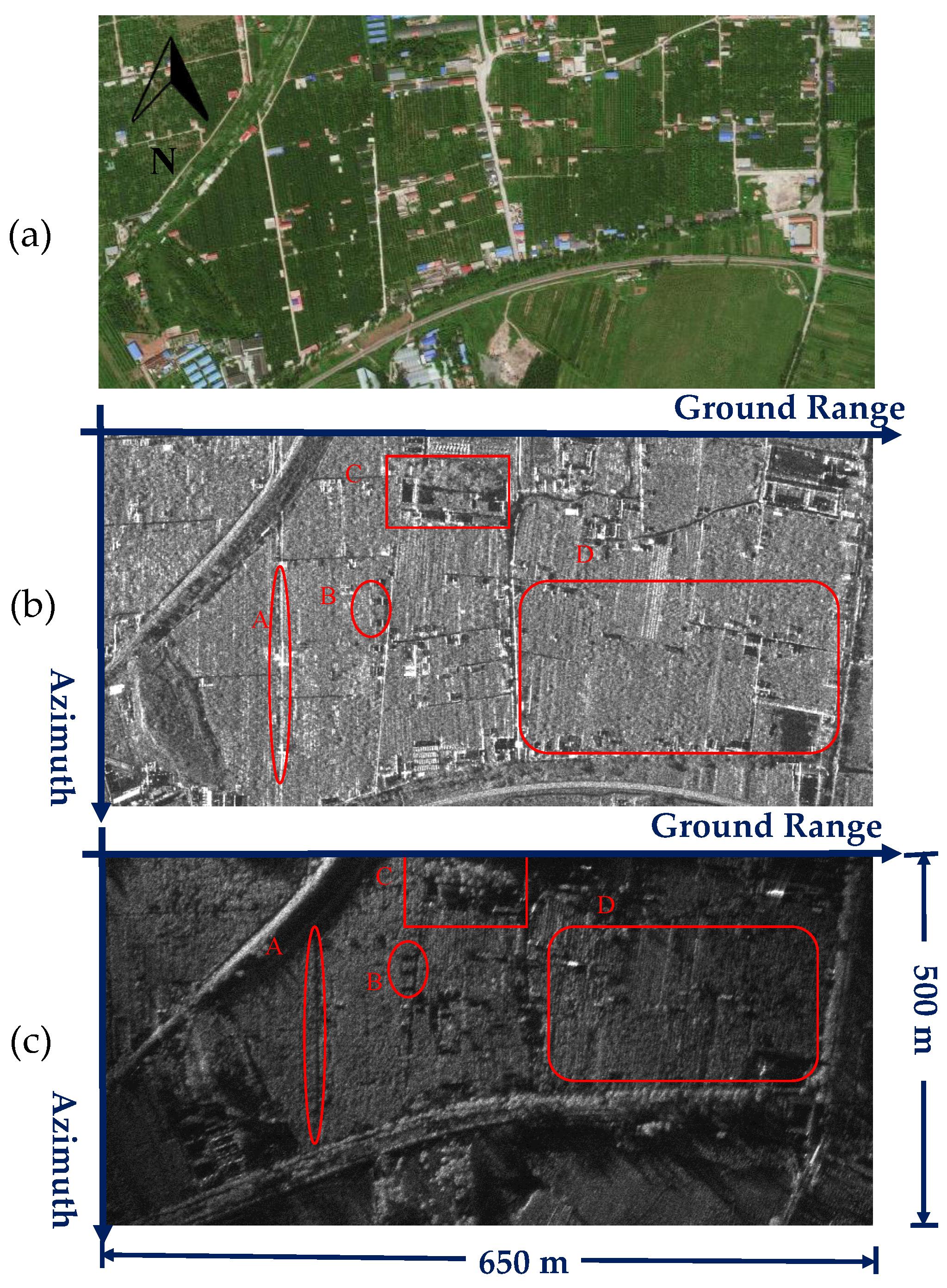
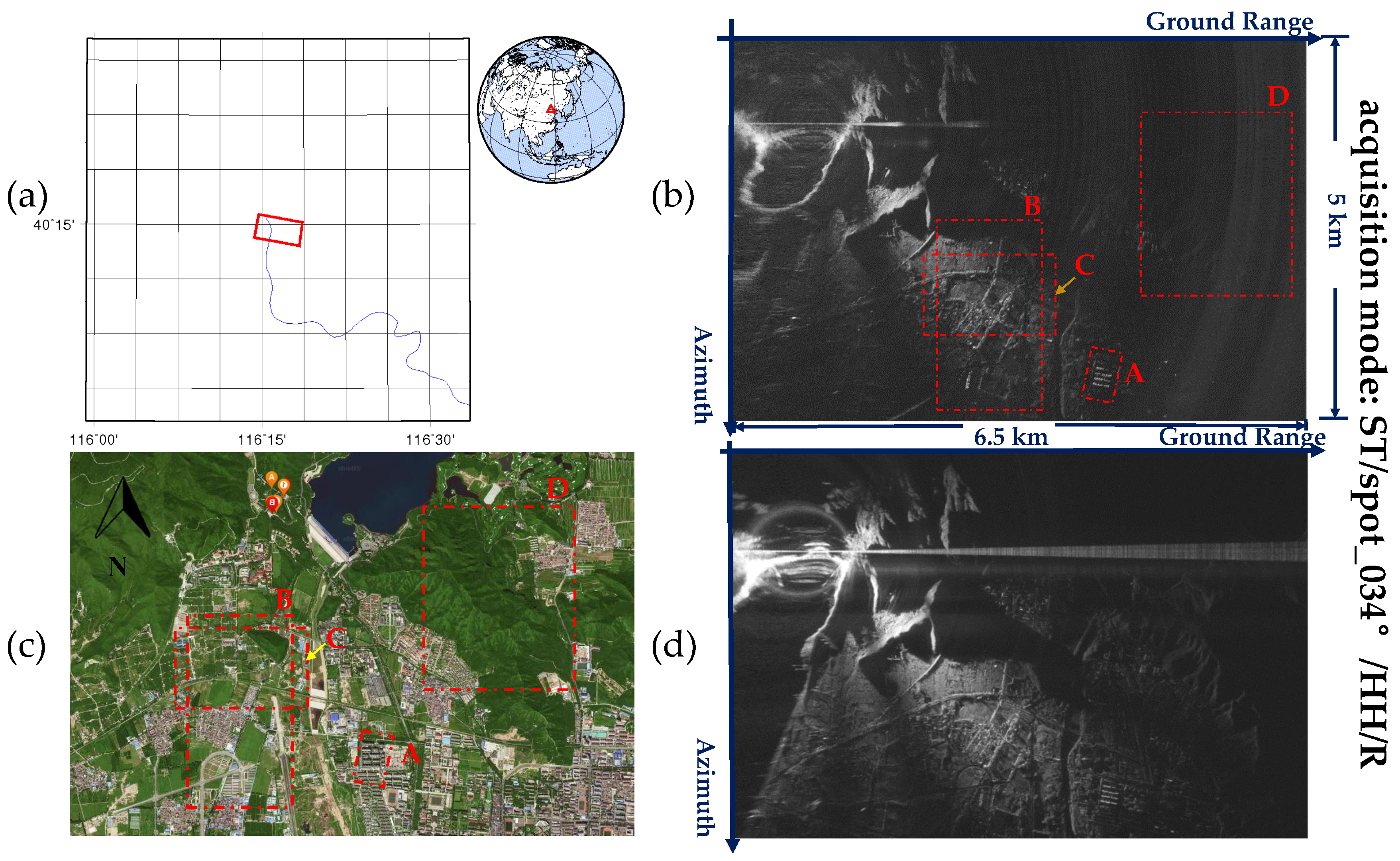
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BiSAR | Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio |
| BPA | Back-Projection Algorithm |
| SAT | Synthetic Aperture Time |
| PRI | Pulse Repetition Interval |
| PRF | Pulse Repetition Frequency |
| FPGA | Field Programmable Gate Array |
| LNA | Low Noise Amplifier |
| S.&S. | Sampling and Storage |
| CHA | Channel A |
| BiSAR | Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| CHB | Channel B |
| A/D | Analog/Digital |
| VNA | Vector Network Analyzer |
| IF | Intermediate-Frequency |
| BPF | Band-Pass Filter |
| DPLL | Digital Phase Locked Loop |
| PSLR | Peak Side Lobe Ratio |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
References
- Walterscheid, I.; Espeter, T.; Brenner, A.R.; Klare, J.; Ender, J.H.G.; Nies, H.; Wang, R.; Loffeld, O. Bistatic SAR experiments with PAMIR and TerraSAR-X-setup, processing, and image results. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3268–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Spaceborne bi- and multistatic SAR: Potential and challenges. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2006, 153, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walterscheid, I.; Klare, J.; Brenner, A.R.; Ender, J.H.G.; Otmar, L. Challenges of a bistatic spaceborne/airborne SAR experiment. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Dresden, Germany, 16–18 May 2006.
- Loffeld, O.; Nies, H.; Peters, V.; Knedlik, S. Models and useful relations for bistatic SAR processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, G.; Younis, M. Impact of oscillator noise in bistatic and multistatic SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auterman, J.L. Phase stability requirements for a bistatic SAR. In Proceedings of the 1984 IEEE National Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 29 February–3 March 1984; pp. 48–52.
- Weiß, M. Time and frequency synchronization aspects for bistatic SAR systems. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Ulm, Germany, 25–27 May 2004; pp. 395–398.
- Weiß, M. Synchronisation of bistatic radar systems. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; pp. 1750–1753.
- López-Dekker, P.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Serra-Morales, P.; Sanz-Marcos, J. Phase synchronization and doppler centroid estimation in fixed receiver bistatic SAR systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar]
- Behner, F.; Reuter, S. HITCHHIKER, Hybrid bistatic high resolution SAR experiment using a stationary receiver and TerraSAR-X transmitter. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010.
- Behner, F.; Reuter, S.; Nies, H.; Loffeld, O. Synchronization and Processing in the HITCHHIKER Bistatic SAR Experiment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Hounam, D.; Werner, M.; Riegger, S.; Settelmeyer, E. TanDEM-X: A TerraSAR-X add-on satellite for single-pass SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; pp. 1000–1003.
- Breit, H.; Younis, M.; Balss, U.; Niedermeier, A.; Grigorov, C.; Hueso-Gonzalez, J.; Fritz, T. Bistatic synchronization and processing of Tandem-X data. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011.
- Eineder, M. Ocillator clock drift compensation in bistatic interferometric SAR. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003.
- Younis, M.; Metzig, R.; Krieger, G. Performance prediction of a phase synchronization link for bistatic SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.; Metzig, R.; Krieger, G.; Klein, R. Performance prediction and verification for bistatic SAR synchronization link. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Dresden, Germany, 16–18 May 2006.
- Gierull, C.; Pike, C.; Paquet, F. Mitigation of phase noise in bistatic SAR systems with extremely large synthetic apertures. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Dresden, Germany, 16–18 May 2006.
- Krieger, G.; Moreira, A.; Fiedler, H.; Hajnsek, I.; Werner, M.; Younis, M.; Zink, M. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3317–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; He, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Dong, Z.; Liang, D. Echo domain phase synchronization algorithm for bistatic SAR in alternating bistatic/ping-pong mode. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 604–608. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, S.V.; Rodriguez-Cassola, M.; Nottensteiner, A.; Horn, R.; Scheiber, R.; Schwerdt, M.; Krieger, G. Bistatic experiment using TerraSAR-X and DLR’s new F-SAR system. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2–5 June 2008; pp. 57–60.
- Rodriguez-Cassola, M.; Baumgartner, S.V.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Bistatic TerraSAR-X/F-SAR Spaceborne-Airborne SAR experiment: Description, data processing, and results. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Dekker, P.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Serra-Morales, P.; Sanz-Marcos, J. Phase and temporal synchronization in bistatic SAR systems using sources of opportunity. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Barcelona, Spain, 23–27 July 2007; pp. 97–100.
- Wang, W.; Ding, C.; Liang, X. Time and phase synchronization via direct-path signal for bistatic synthetic aperture radar systems. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2008, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Hou, J.; Liu, G.; Wu, X. Double-channel bistatic SAR system with spaceborne illuminator for 2-D and 3-D SAR remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4496–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broquetas, A.; Fortes, M.; Siddique, M.A.; Duque, S.; Merlano, J.C.; Lopez-Dekker, P.; MallorquÍ, J.J.; Aguasca, A. Bistatic SAR based on Terrasar-X and ground based receivers. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 114–117.
- Zeng, T.; Hu, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Tian, W.; Zhu, M.; Long, T. Extended NLCS algorithm of BiSAR systems with a squinted transmitter and a fixed receiver: Theory and experimental confirmation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5019–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walterscheid, I.; Espeter, T.; Gierull, C.; Klare, J.; Brenner, A.R.; Ender, J.H. Results and analysis of hybrid bistatic SAR experiments with spaceborne, airborne and stationary sensors. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009.
- Nies, H.; Behner, F.; Reuter, S.; Loffeld, O.; Wang, R. SAR Experiments in a bistatic hybrid configuration for generating PolInSAR data with TerraSAR-X illumination. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010.
- Sanz-Marcos, J.; López-Dekker, P.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Aguasca, A.; Prats, P. SABRINA: A SAR bistatic receiver for interferometric applications. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhu, M.; Hu, C.; Tian, W.; Long, T. Experimental results and algorithm analysis of DEM generation using bistatic SAR interferometry with stationary receiver. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5835–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, H.; Behner, F.; Reuter, S.; Loffeld, O.; Wang, R. Polarimetric and interferometric applications in a bistatic hybrid SAR mode using Terrasar-X. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 110–113.
- Duque, S.; López-Dekker, P.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Merlano, J.C. Repeat-pass interferometry using a fixed-receiver and ERS-2/ENVISAT as transmitters of opportunity. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009.
- Duque, S.; López-Dekker, P.; Merlano, J.C.; Mallorqui, J.J. Bistatic SAR along track interferometry with multiple fixed receivers. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 4099–4102.
- Duque, S.; López-Dekker, P.; Mallorqui, J.J. Single-pass bistatic SAR interferometry using fixed-receiver configurations: Theory and experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.; Zeng, Z.; Feifeng, L.; Cherniakov, M. Experimental demonstration of passive BSAR imaging using navigation satellites and a fixed receiver. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Shao, Y. First bistatic demonstration of digital beamforming in elevation with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 54, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Tang, J.; Lu, P. Multichannel DEM reconstruction method based on Markov random fields for bistatic SAR. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2015, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y. Error analysis of bistatic SAR imaging and stereoscopy bistatic SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4518–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, N.; Zhao, S.; Hong, F.; Wu, L.; Loffeld, O. Spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR imaging with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator in staring-spotlight mode. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espeter, T.; Walterscheid, I.; Gierull, C.; Brenner, A.; Ender, J.; Loffeld, O. Progress of hybrid bistatic SAR: Synchronization experiments and first imaging results. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2–5 June 2008.




| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 9.65 GHz | |
| Signal bandwidth | 300 MHz | |
| Sampling rate | 1 GHz | |
| Sampling window length | 100 s | |
| PRF | 4.85 KHz | |
| SAT | 6.58 s | |
| Total recorded pulse number | 36,580 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, F.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, P.; Balz, T. Integrated Time and Phase Synchronization Strategy for a Multichannel Spaceborne-Stationary Bistatic SAR System. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080628
Hong F, Wang R, Zhang Z, Lu P, Balz T. Integrated Time and Phase Synchronization Strategy for a Multichannel Spaceborne-Stationary Bistatic SAR System. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(8):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080628
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Feng, Robert Wang, Zhimin Zhang, Pingping Lu, and Timo Balz. 2016. "Integrated Time and Phase Synchronization Strategy for a Multichannel Spaceborne-Stationary Bistatic SAR System" Remote Sensing 8, no. 8: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080628
APA StyleHong, F., Wang, R., Zhang, Z., Lu, P., & Balz, T. (2016). Integrated Time and Phase Synchronization Strategy for a Multichannel Spaceborne-Stationary Bistatic SAR System. Remote Sensing, 8(8), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080628