Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
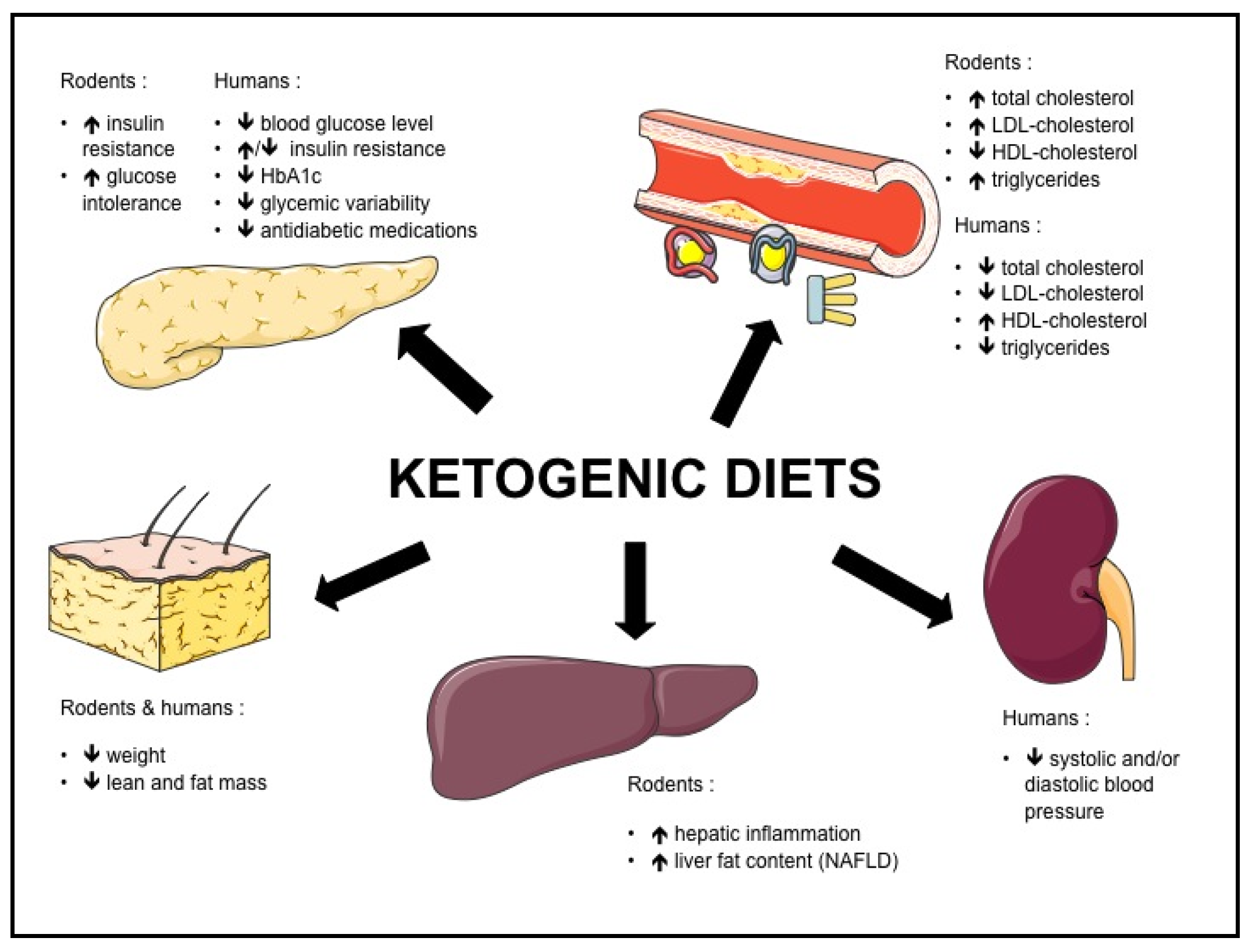
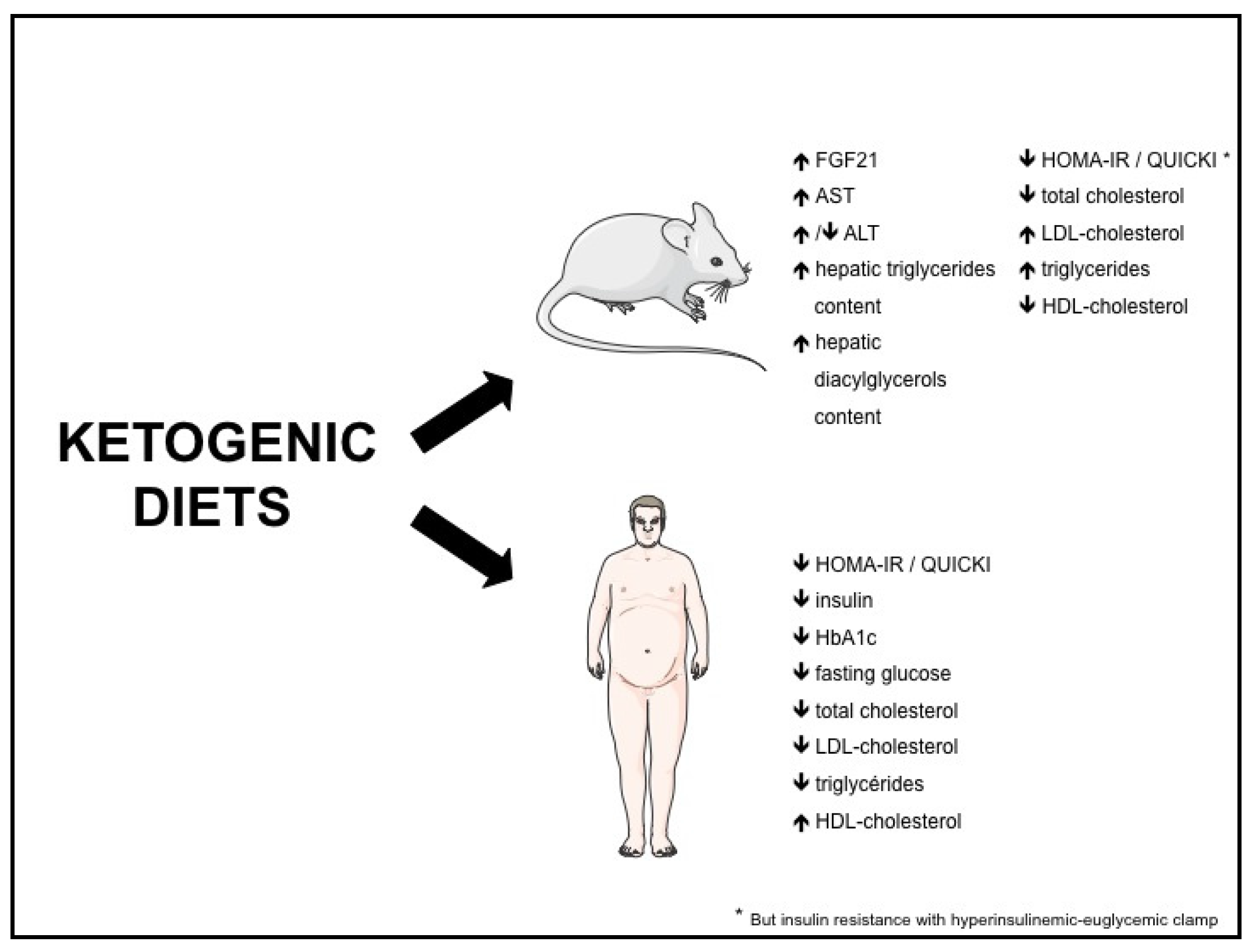
3. Results
3.1. KD and Obesity
3.2. KD and NAFLD
3.3. KD and Insulin Resistance / Type 2 Diabetes
3.4. KD and Dyslipidemia
3.5. KD and Blood Pressure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh-Banerjee, P.; Wang, Y.; Hu, F.B.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B. Changes in body weight and body fat distribution as risk factors for clinical diabetes in US men. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 159, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Magkos, F.; Mohammed, B.S.; Pietka, T.; Abumrad, N.A.; Patterson, B.W.; Okunade, A.; Klein, S. Intrahepatic fat, not visceral fat, is linked with metabolic complications of obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15430–15435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Sullivan, S.; Klein, S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology 2010, 51, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1592–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariani, K.; Philippe, J.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance: From bench to bedside. Diabetes Metab. 2013, 39, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Cortez-Pinto, H. Hepatic histology in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, N.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Liu, S.; Saltzman, E.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Jacques, P.F. Carbohydrate nutrition, insulin resistance, and the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrih, M.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Diets and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The good and the bad. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Fernandez, M.L.; Feinman, R.D.; Phinney, S.D. Dietary carbohydrate restriction induces a unique metabolic state positively affecting atherogenic dyslipidemia, fatty acid partitioning, and metabolic syndrome. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008, 47, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Phinney, S.D.; Forsythe, C.E.; Quann, E.E.; Wood, R.J.; Puglisi, M.J.; Kraemer, W.J.; Bibus, D.M.; Fernandez, M.L.; Feinman, R.D. Carbohydrate restriction has a more favorable impact on the metabolic syndrome than a low fat diet. Lipids 2009, 44, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Feinman, R.D. Carbohydrate restriction improves the features of Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome may be defined by the response to carbohydrate restriction. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, R.C. Dr Atkins’ Diet Revolution: The High Calorie Way to Stay Thin Forever; D. McKay Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Veech, R.L. The therapeutic implications of ketone bodies: The effects of ketone bodies in pathological conditions: Ketosis, ketogenic diet, redox states, insulin resistance, and mitochondrial metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2004, 70, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossoff, E.H.; Cervenka, M.C.; Henry, B.J.; Haney, C.A.; Turner, Z. A decade of the modified Atkins diet (2003–2013): Results, insights, and future directions. Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 29, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinman, R.D.; Pogozelski, W.K.; Astrup, A.; Bernstein, R.K.; Fine, E.J.; Westman, E.C.; Westman, E.C.; Accurso, A.; Frassetto, L.; Gower, B.A.; et al. Dietary carbohydrate restriction as the first approach in diabetes management: Critical review and evidence base. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accurso, A.; Bernstein, R.K.; Dahlqvist, A.; Draznin, B.; Feinman, R.D.; Fine, E.J.; Gleed, A.; Jacobs, D.B.; Larson, G.; Lustig, R.H.; et al. Dietary carbohydrate restriction in type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome: Time for a critical appraisal. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, O.E.; Morgan, A.P.; Kemp, H.G.; Sullivan, J.M.; Herrera, M.G.; Cahill, G.F. Brain metabolism during fasting. J. Clin. Invest. 1967, 46, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, S.K.; Neal, E.G.; Camfield, C.S.; Kossoff, E.H. Dietary therapies for epilepsy: Future research. Epilepsy Behav. 2011, 22, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.R.; Pissios, P.; Otu, H.; Roberson, R.; Xue, B.; Asakura, K.; Furukawa, N.; Marino, F.E.; Liu, F.F.; Kahn, B.B.; et al. A high-fat, ketogenic diet induces a unique metabolic state in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1724–E1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badman, M.K.; Kennedy, A.R.; Adams, A.C.; Pissios, P.; Maratos-Flier, E. A very low carbohydrate ketogenic diet improves glucose tolerance in ob/ob mice independently of weight loss. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E1197–E1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbow, J.R.; Doherty, J.M.; Schugar, R.C.; Travers, S.; Weber, M.L.; Wentz, A.E.; Ezenwajiaku, N.; Cotter, D.G.; Brunt, E.M.; Crawford, P.A. Hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and ER stress in mice maintained long term on a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G956–G967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielohuby, M.; Sisley, S.; Sandoval, D.; Herbach, N.; Zengin, A.; Fischereder, M.; Menhofer, D.; Stoehr, B.J.M.; Stemmer, K.; Wanke, R.; et al. Impaired glucose tolerance in rats fed low-carbohydrate, high-fat diets. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E1059–E1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornayvaz, F.R.; Jurczak, M.J.; Lee, H.-Y.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Frederick, D.W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.M.; Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. A high-fat, ketogenic diet causes hepatic insulin resistance in mice, despite increasing energy expenditure and preventing weight gain. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E808–E815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenbroek, J.H.; van Dijck, L.; Tons, H.A.; Rabelink, T.J.; Carlotti, F.; Ballieux, B.E.; de Koning, E.J.P. Long-term ketogenic diet causes glucose intolerance and reduced B- and a-cell mass but no weight loss in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E552–E558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douris, N.; Melman, T.; Pecherer, J.M.; Pissios, P.; Flier, J.S.; Cantley, L.C.; Locasale, J.W.; Maratos-Flier, E. Adaptive changes in amino acid metabolism permit normal longevity in mice consuming a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrih, M.; Altirriba, J.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Ketogenic Diet Impairs FGF21 Signaling and Promotes Differential Inflammatory Responses in the Liver and White Adipose Tissue. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frommelt, L.; Bielohuby, M.; Menhofer, D.; Stoehr, B.J.M.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Kienzle, E. Effects of low carbohydrate diets on energy and nitrogen balance and body composition in rats depend on dietary protein-to-energy ratio. Nutrition 2014, 30, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, A.M.; Kephart, W.C.; Mumford, P.W.; Mobley, C.B.; Lowery, R.P.; Shake, J.J.; Patel, R.K.; Healy, J.C.; McCullough, D.J.; Kluess, H.A.; et al. Effects of a ketogenic diet on adipose tissue, liver, and serum biomarkers in sedentary rats and rats that exercised via resisted voluntary wheel running. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R337–R351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partsalaki, I.; Karvela, A.; Spiliotis, B.E. Metabolic impact of a ketogenic diet compared to a hypocaloric diet in obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisho, Y.; Butler, A.E.; Manesso, E.; Elashoff, D.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. β-cell mass and turnover in humans: Effects of obesity and aging. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaha, F.F.; Iqbal, N.; Seshadri, P.; Chicano, K.L.; Daily, D.A.; McGrory, J.; Williams, T.; Williams, M.; Gracely, E.J.; Stem, L. A Low-Carbohydrate as Compared with a Low-Fat Diet in Severe Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Hill, J.O.; McGuckin, B.G.; Brill, C.; Mohammed, B.S.; Szapary, P.O.; Rader, D.J.; Edman, J.S.; Klein, S. A Randomized Trial of a Low-Carbohydrate Diet for Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Nieuwenhuizen, A.; Tomé, D.; Soenen, S.; Westerterp, K.R. Dietary protein, weight loss, and weight maintenance. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, E.J.; Feinman, R.D. Thermodynamics of weight loss diets. Nutr. Metab. 2004, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinman, R.D.; Fine, E.J. Nonequilibrium thermodynamics and energy efficiency in weight loss diets. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2007, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halton, T.L.; Hu, F.B. The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: A critical review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhorst, M.A.B.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Westerterp, K.R. Gluconeogenesis and energy expenditure after a high-protein, carbohydrate-free diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumithran, P.; Prendergast, L.A.; Delbridge, E.; Purcell, K.; Shulkes, A.; Kriketos, A.; Proietto, J. Ketosis and appetite-mediating nutrients and hormones after weight loss. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, A.M.; Horgan, G.W.; Murison, S.D.; Bremner, D.M.; Lobley, G.E. Effects of a high-protein ketogenic diet on hunger, appetite, and weight loss in obese men feeding ad libitum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Benelli, M.; Brancaleoni, M.; Dainelli, G.; Merlini, D.; Negri, R. Middle and Long-Term Impact of a Very Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet on Cardiometabolic Factors: A Multi-Center, Cross-Sectional, Clinical Study. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2015, 22, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, A.; Bianco, A.; Grimaldi, K.A.; Lodi, A.; Bosco, G. Long term successful weight loss with a combination biphasic ketogenic Mediterranean diet and Mediterranean diet maintenance protocol. Nutrients 2013, 5, 5205–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, J.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Thompson, C.H.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D.; Wittert, G.A.; Yancy, W.S.; Brinkworth, G.D. Comparison of low- and high-carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes management: A randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabekk, P.T.; Moe, I.A.; Meen, H.D.; Tomten, S.E.; Høstmark, A.T. Resistance training in overweight women on a ketogenic diet conserved lean body mass while reducing body fat. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris-Stiff, G.; Feldstein, A.E. Fibroblast growth factor 21 as a biomarker for NAFLD: Integrating pathobiology into clinical practice. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 795–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dushay, J.; Chui, P.C.; Gopalakrishnan, G.S.; Varela-Rey, M.; Crawley, M.; Fisher, F.M.; Badman, M.K.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Maratos-Flier, E. Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Fang, Q.; Gao, F.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Pan, X.; Bao, Y.; Xiang, K.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 levels are increased in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients and are correlated with hepatic triglyceride. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, Y.; Nishio, K.; Mochiyama, T.; Konishi, M.; Shimada, M.; Ohta, H.; Itoh, N. Fgf21 Impairs Adipocyte Insulin Sensitivity in Mice Fed a Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Ketogenic Diet. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badman, M.K.; Pissios, P.; Kennedy, A.R.; Koukos, G.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornayvaz, F.R.; Shulman, G.I. Diacylglycerol activation of protein kinase Cε and hepatic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporez, J.P.G.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Petersen, M.C.; Pesta, D.; Guigni, B.A.; Serr, J.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Cellular mechanisms by which FGF21 improves insulin sensitivity in male mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lloyd, D.J.; Hale, C.; Stanislaus, S.; Chen, M.; Sivits, G.; Vonderfecht, S.; Hecht, R.; Li, Y.S.; Lindberg, R.A.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases energy expenditure, and improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badman, M.K.; Koester, A.; Flier, J.S.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Maratos-Flier, E. Fibroblast growth factor 21-deficient mice demonstrate impaired adaptation to ketosis. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4931–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporez, J.P.G.; Asrih, M.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Jurczak, M.J.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Hepatic insulin resistance and increased hepatic glucose production in mice lacking Fgf21. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laeger, T.; Henagan, T.M.; Albarado, D.C.; Redman, L.M.; Bray, G.A.; Noland, R.C.; Münzberg, H.; Hutson, S.M.; Gettys, T.W.; Schwartz, M.W.; et al. FGF21 is an endocrine signal of protein restriction. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3913–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerbacka, J.; Lammi, K.; Häkkinen, A.-M.; Rissanen, A.; Salminen, I.; Aro, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Dietary fat content modifies liver fat in overweight nondiabetic subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2804–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, E.; Reeds, D.N.; Finck, B.N.; Mayurranjan, S.M.; Mayurranjan, M.S.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Dietary fat and carbohydrates differentially alter insulin sensitivity during caloric restriction. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, J.D.; Baker, J.A.; Rogers, T.; Davis, J.; Satapati, S.; Burgess, S.C. Short-term weight loss and hepatic triglyceride reduction: Evidence of a metabolic advantage with dietary carbohydrate restriction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, H.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, N.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Effects of dietary interventions on liver volume in humans. Obesity 2014, 22, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevastianova, K.; Kotronen, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Perttilä, J.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, J.; Orho-Melander, M.; Lundbom, N.; Ferrannini, E.; Rissanen, A.; et al. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 (adiponutrin) confers sensitivity to weight loss-induced decrease in liver fat in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Chan, R.S.-M.; Chan, H.-Y.; Chu, W.C.-W.; Cheung, B.H.-K.; Yeung, D.K.-W.; Li, L.S.; Sea, M.M.-M.; et al. PNPLA3 gene polymorphism and response to lifestyle modification in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornayvaz, F.R. Fibroblast growth factor 21, ketogenic diets, and insulin resistance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinzig, K.P.; Honors, M.A.; Hargrave, S.L. Insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance are altered by maintenance on a ketogenic diet. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3105–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisschop, P.H.; de Metz, J.; Ackermans, M.T.; Endert, E.; Pijl, H.; Kuipers, F.; Meijer, A.J.; Sauerwein, H.P.; Romijn, J.A. Dietary fat content alters insulin-mediated glucose metabolism in healthy men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Westman, E.C.; Feinman, R.D.; Mavropoulos, J.C.; Vernon, M.C.; Volek, J.S.; Wortman, J.A.; Yancy, W.S.; Phinney, S.D. Low-carbohydrate nutrition and metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.A.; Mathew, T.C.; Dashti, A.A.; Asfar, S.; Al-Zaid, N.; Dashti, H.M. Effect of low-calorie versus low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet in type 2 diabetes. Nutrition 2012, 28, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q. Control of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes without weight loss by modification of diet composition. Nutr. Metab. 2006, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G.; Sargrad, K.; Homko, C.; Mozzoli, M.; Stein, T.P. Effect of a low-carbohydrate diet on appetite, blood glucose levels, and insulin resistance in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.B.; Jeffreys, A.S.; Olsen, M.K.; McDuffie, J.R.; Feinglos, M.N.; Yancy, W.S. Two diets with different haemoglobin A1c and antiglycaemic medication effects despite similar weight loss in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, J.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Thompson, C.H.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D.; Wittert, G.A.; Yancy, W.S.; Brinkworth, G.D. A Very Low-Carbohydrate, Low–Saturated Fat Diet for Type 2 Diabetes Management: A Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q. Effect of a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet on blood glucose control in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halton, T.L.; Liu, S.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Low-carbohydrate-diet score and risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yancy, W.S.; Foy, M.; Chalecki, A.M.; Vernon, M.C.; Westman, E.C. A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to treat type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saslow, L.R.; Kim, S.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Moskowitz, J.T.; Phinney, S.D.; Goldman, V.; Murphy, E.J.; Cox, R.M.; Moran, P.; Hecht, F.M. A randomized pilot trial of a moderate carbohydrate diet compared to a very low carbohydrate diet in overweight or obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, H.M.; Al-Zaid, N.S.; Mathew, T.C.; Al-Mousawi, M.; Talib, H.; Asfar, S.K.; Behbahani, A.I. Long term effects of ketogenic diet in obese subjects with high cholesterol level. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 286, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, N.; Vetter, M.L.; Moore, R.H.; Chittams, J.L.; Dalton-Bakes, C.V.; Dowd, M.; Williams-Smith, C.; Cardillo, S.; Wadden, T.A. Effects of a low-intensity intervention that prescribed a low-carbohydrate vs. a low-fat diet in obese, diabetic participants. Obesity 2010, 18, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koning, L.; Fung, T.T.; Liao, X.; Chiuve, S.E.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Spiegelman, D.; Hu, F.B. Low-carbohydrate diet scores and risk of type 2 diabetes in men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbiner, B.; Wendel, J.A.; McDermott, M.P. Effects of diet composition and ketosis on glycemia during very-low-energy-diet therapy in obese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farrés, J.; Pujol, A.; Coma, M.; Ruiz, J.; Naval, J.; Mas, J.; Molins, A.; Fondevila, J.; Aloy, P. Revealing the molecular relationship between type 2 diabetes and the metabolic changes induced by a very-low-carbohydrate low-fat ketogenic diet. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, M.J.; Kraemer, W.J.; Love, D.M.; Avery, N.G.; Gómez, A.L.; Scheett, T.P.; Volek, J.S. A ketogenic diet favorably affects serum biomarkers for cardiovascular disease in normal-weight men. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Sharman, M.J.; Forsythe, C.E. Modification of lipoproteins by very low-carbohydrate diets. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Hill, J.O.; Makris, A.P.; Rosenbaum, D.L.; Brill, C.; Stein, R.I.; Mohammed, B.S.; Miller, B.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Weight and metabolic outcomes after 2 years on a low-carbohydrate versus low-fat diet: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkworth, G.D.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M. Long-term effects of a very-low-carbohydrate weight loss diet compared with an isocaloric low-fat diet after 12 mo. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, P.A.; de Brito Sampaio, L.P.; Damasceno, N.R.T. Ketogenic diet in epileptic children: Impact on lipoproteins and oxidative stress. Nutr. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westman, E.C.; Yancy, W.S.; Mavropoulos, J.C.; Marquart, M.; McDuffie, J.R. The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, L.; Iqbal, N.; Seshadri, P.; Chicano, K.L.; Daily, D.A.; McGrory, J.; Williams, M.; Gracely, E.J.; Samaha, F.F. The effects of low-carbohydrate versus conventional weight loss diets in severely obese adults: One-year follow-up of a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.J.; Mente, A.; Maroleanu, A.; Cozma, A.I.; Ha, V.; Kishibe, T.; Uleryk, E.; Budylowski, P.; Schünemann, H.; Beyene, J.; et al. Intake of saturated and trans unsaturated fatty acids and risk of all cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, T.T.; van Dam, R.M.; Hankinson, S.E.; Stampfer, M.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Low-carbohydrate diets and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Two cohort studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Li, X.-J.; Jiang, W.-L.; Sun, H.-B.; Liu, J. Efficacy of and Patient Compliance with a Ketogenic Diet in Adults with Intractable Epilepsy: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.L.; Esteves, S.S.; da Costa Pereira, A.; Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Nunes, J.P. Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of the effects of low carbohydrate diets on cardiovascular risk factors: Low carbohydrate diets and cardiovascular risk factors. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 1048–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, N.B.; de Melo, I.S.; de Oliveira, S.L.; da Rocha Ataide, T. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naude, C.E.; Schoonees, A.; Senekal, M.; Young, T.; Garner, P.; Volmink, J. Low carbohydrate versus isoenergetic balanced diets for reducing weight and cardiovascular risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergqvist, A.G.C. Long-term monitoring of the ketogenic diet: Do’s and Don’ts. Epilepsy Res. 2012, 100, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossoff, E.; Wang, H.-S. Dietary Therapies for Epilepsy. Biomed. J. 2013, 36, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagiou, P.; Sandin, S.; Weiderpass, E.; Lagiou, A.; Mucci, L.; Trichopoulos, D.; Adami, H.-O. Low carbohydrate-high protein diet and mortality in a cohort of Swedish women. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Orfanos, P.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Trichopoulos, D. Low-carbohydrate-high-protein diet and long-term survival in a general population cohort. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classical KD | Defined as <130 g carbohydrate per day or <26% of caloric intake by the American Diabetes Association |
|---|---|
| Modified Atkins Diet | 65% caloric intake from fat, 30% protein, 6% carbohydrates |
| Very low-carbohydrate KD | Carbohydrates < 30 g/day |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosinski, C.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050517
Kosinski C, Jornayvaz FR. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients. 2017; 9(5):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050517
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosinski, Christophe, and François R. Jornayvaz. 2017. "Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies" Nutrients 9, no. 5: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050517
APA StyleKosinski, C., & Jornayvaz, F. R. (2017). Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients, 9(5), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050517




