Electrophysiological Characterization of the Antarease Metalloprotease from Tityus serrulatus Venom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
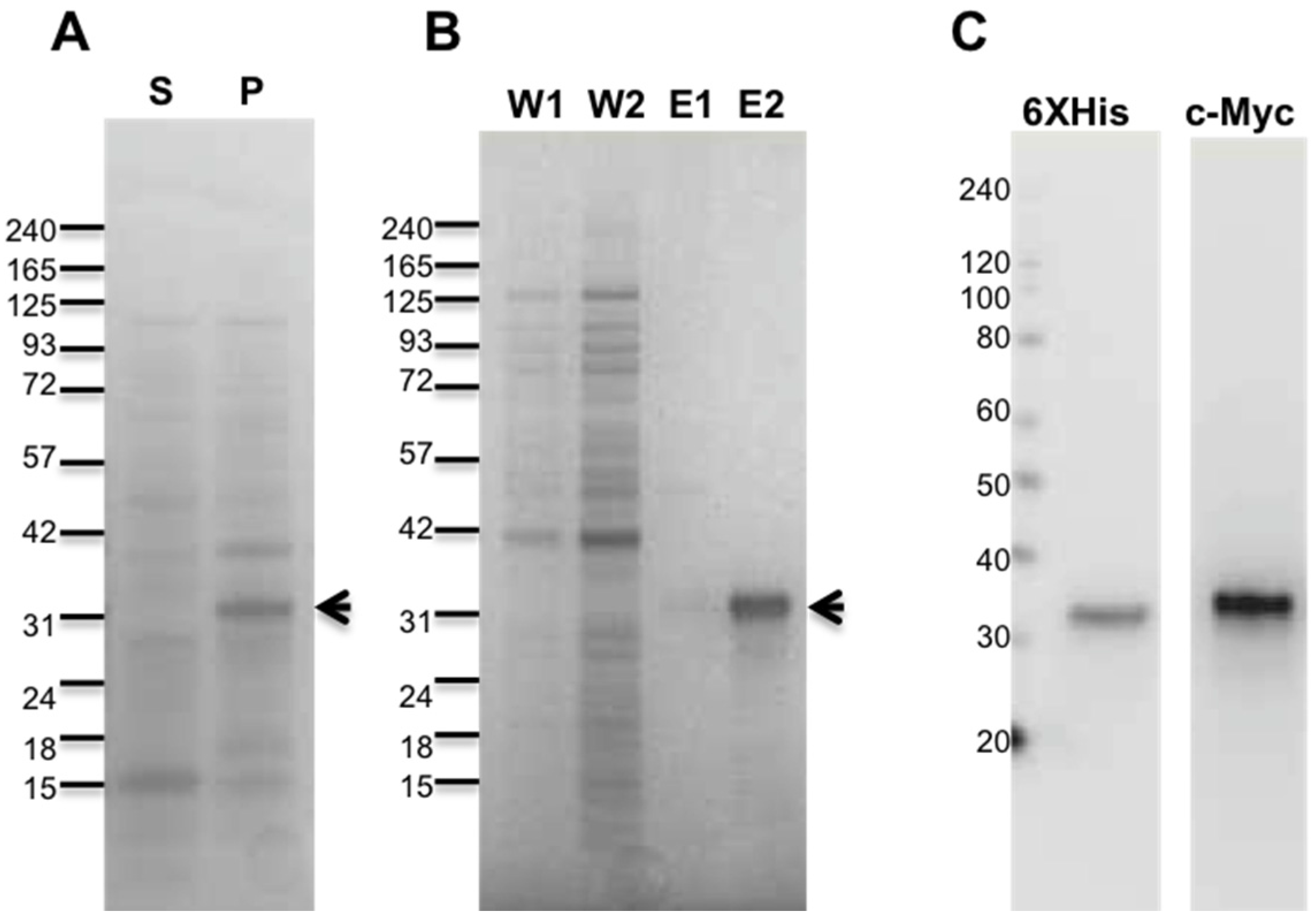
2.1. Purification of Recombinant Antarease and Its Mutant
2.2. Antarease, but Not Its Metalloprotease Active Site Mutant, Paralyzes the Drosophila melanogaster Neuromuscular Junction
2.3. Antarease, but Not Its Metalloprotease Active Site Mutant, Paralyzes Mouse Neuromuscular Junction
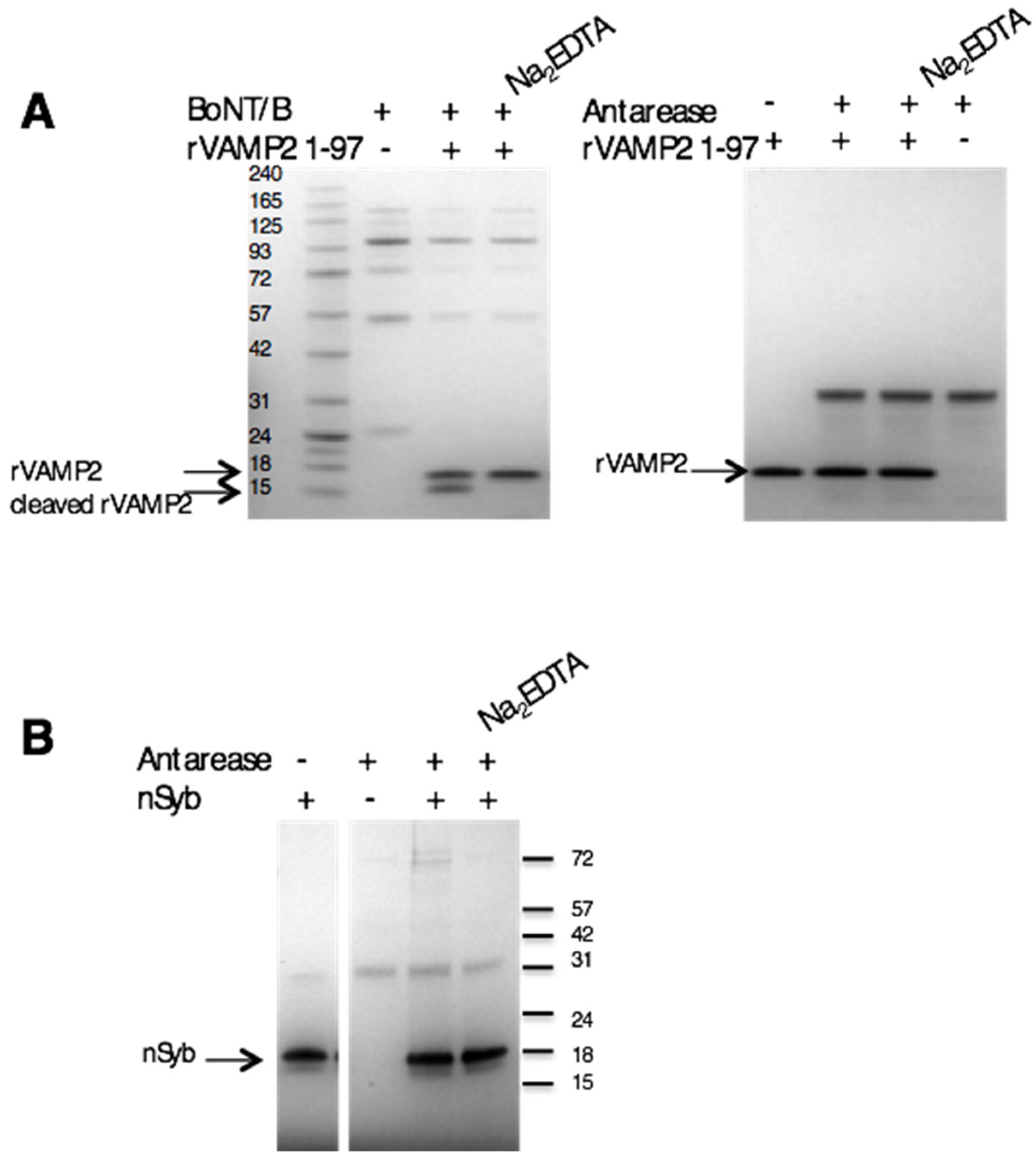
2.4. Antarease Does Not Cleave the SNARE Proteins Involved in Neuroexocytosis
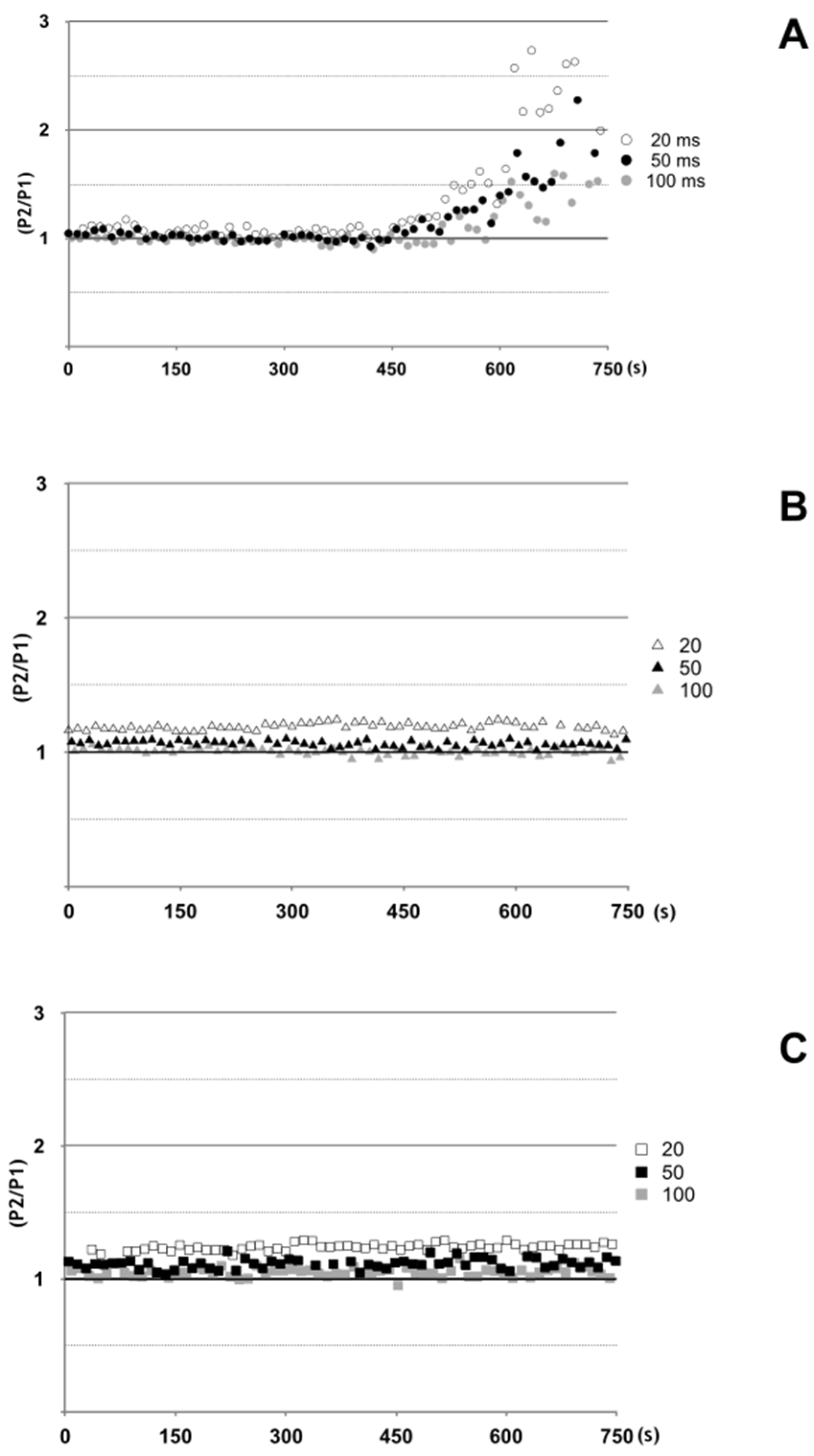
2.5. Antarease Alters the Pair-Pulse Stimulation of the Drosophila melanogaster NMJ
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Recombinant Antarease and Its Mutant E162A Cloning, Expression, and Purification
4.3. In Vitro VAMP2 Cleavage
4.4. Electrophysiology on NMJ of Third Instar Larva Preparation
4.5. Assay of the Mouse Hemidiaphragm Paralysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chippaux, J.P.; Goyffon, M. Epidemiology of scorpionism: A global appraisal. Acta Trop. 2008, 107, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, W. Scorpion Diversity and Distribution: Past and Present Patterns. In Scorpion Venoms; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Possani, L.D., Schwartz, E.F., Rodríguez de la Vega, R.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Rabies and Envenomings: A Neglected Public Health Issue; Report of a Consultative Meeting; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Peigneur, S.; Bordo, K.C.F.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Revealing the function and the structural model of Ts4: Insight into non-toxic toxin from Tytus serrulatus venom. Toxins 2015, 7, 2534–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P. Epidemiology of envenomations by terrestrial venomous animals in Brazil based on case reporting: From obvious facts to contingencies. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amitai, Y. Clinical manifesta tions and management of scorpion envenomation. Public Health Rev. 1998, 26, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Mining on scorpion venom biodiversity. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, D.D.; Scortecci, K.C.; Kobashi, L.S.; Agnez-Lima, L.F.; Medeiros, S.R.B.; Silva-Junior, A.A.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F. Profiling the resting venom gland of the scorpion Tityus stigmurus through a transcriptomic survey. BMC Genom. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venancio, E.J.; Portaro, F.C.; Kuniyoshi, A.K.; Carvalho, D.C.; Pidde-Queiroz, G.; Tambourgi, D.V. Enzymatic properties of venoms from Brazilian scorpions of Tityus genus and the neutralisation potential of therapeutical antivenoms. Toxicon 2013, 69, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, A.O.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.; Horta, C.C.; Magalhaes, B.F.; Dantas, A.E.; Chaves, L.M.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E. Molecular and functional characterization of metalloserrulases, new metalloproteases from the Tityus serrulatus venom gland. Toxicon 2014, 90, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verano-Braga, T.; Rocha-Resende, C.; Silva, D.M.; Ianzer, D.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Bougis, P.E.; de Lima, M.E.; Santos, R.A.S.; Pimenta, A.M.C. Tityus serrulatus Hypotensins: A new family of peptides from scorpion venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. Ion channel voltage sensors: Structure, function, and pathophysiology. Neuron 2010, 67, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima, M.E.; Figueiredo, S.G.; Pimenta, A.M.C.; Santos, D.M.; Borges, M.H.; Cordeiro, M.N.; Richardson, M.; Oliveira, L.C.; Stankiewicz, M.; Pelhate, M. Peptides of arachnid venoms with insecticidal activity targeting sodium channels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.J.; Herzig, V.; King, G.F.; Alewood, P.F. The insecticidal potential of venom peptides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3665–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Purification and N-terminal sequence of a serine proteinase-like protein (BMK-CBP) from the venom of the Chinese scorpion (Buthus martensii Karsch). Toxicon 2008, 52, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, P.L.; Fletcher, M.D.; Weninger, K.; Anderson, T.E.; Martin, B.M. Vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) cleavage by a new metalloprotease from the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7405–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, H.; Takahashi, N.; Tokumaru, H. Distinct Initial SNARE Configurations Underlying the Diversity of Exocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1915–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Martin, B.M.; Fletcher, M.D.; Fletcher, P.L. Discharge effect on pancreatic exocrine secretion produced by toxins purified from Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 3178–3185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, E.; Rendón-Anaya, M.; Rego, S.C.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Antarease-like Zn-metalloproteases are ubiquitous in the venom of different scorpion genera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Matteoli, M.; Montecucco, C. Neurotoxins affecting neuroexocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 717–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Binz, T. Clostridial neurotoxin light chains: Devices for SNARE cleavage mediated blockade of neurotransmission. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 364, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, A. The many forms and functions of cellular proteinases. Fed. Proc. 1980, 39, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brownell, P.; Polis, G.A. Scorpion Biology and Research; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bigalke, H.; Rummel, A. Botulinum neurotoxins: Qualitative and quantitative analysis using the mouse phrenic nerve hemidiaphragm assay (MPN). Toxins 2015, 7, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Jones, R.G.A.; Liu, Y.; Sesardic, D. Measurement of botulinum types A, B and E neurotoxicity using the phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm: Improved precision with in-bred mice. Toxicon 2009, 53, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhof, T. Neurotransmitter release: The last milisecond in the life of a synaptic vesicle. Neuron 2013, 80, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantano, S.; Montecucco, C. The blockade of the neurotransmitter release apparatus by botulinum neurotoxins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Rossetto, O.; Catsicas, S.; Delaureto, P.P.; Dasgupta, B.R.; Benfenati, F.; Montecucco, C. Identification of the Nerve-Terminal Targets of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype-A, Serotype-D, and Serotype-E. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23784–23787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Shone, C.C.; Rossetto, O.; Alexander, F.C.G.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype F is a zinc endopeptidase specific for VAMP/synaptobrevin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11516–11519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Malizio, C.; Trimble, W.S.; De Laureto, P.P.; Milan, G.; Sugiyama, H.; Johnson, E.A.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum G neurotoxin cleaves VAMP/synaptobrevin at a single Ala-Ala peptide bond. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20213–20216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, S.; Baumeister, A.; Binz, T.; Blasi, J.; Link, E.; Cornille, F.; Roques, B.; Fykse, E.M.; Südhof, T.C.; Jahn, R. Cleavage of members of the synaptobrevin/VAMP family by types D and F botulinal neurotoxins and tetanus toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 12764–12772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rigoni, M.; Caccin, P.; Johnson, E.A.; Montecucco, C.; Rossetto, O. Site-directed mutagenesis identifies active-site residues of the light chain of botulinum neurotoxin type A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Caccin, P.; Rigoni, M.; Tonello, F.; Bortoletto, N.; Stevens, R.C.; Montecucco, C. Active-site mutagenesis of tetanus neurotoxin implicates TYR-375 and GLU-271 in metalloproteolytic activity. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binz, T.; Bade, S.; Rummel, A.; Kollewe, A.; Alves, J. Arg362 and tyr365 of the botulinum neurotoxin type a light chain are involved in transition state stabilization. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binz, T.; Sikorra, S.; Mahrhold, S. Clostridial neurotoxins: Mechanism of SNARE cleavage and outlook on potential substrate specificity reengineering. Toxins 2010, 2, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zornetta, I.; Azarnia Tehran, D.; Arrigoni, G.; Anniballi, F.; Bano, L.; Leka, O.; Zanotti, G.; Binz, T.; Montecucco, C. The first non Clostridial botulinum-like toxin cleaves VAMP within the juxtamembrane domain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Schiavo, G.; Montecucco, C.; Poulain, B.; Deloy, F.; Lozzi, L.; Shone, C.C. SNARE motif and neurotoxins. Nature 1994, 372, 415–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Morbiato, L.; Caccin, P.; Rigoni, M.; Montecucco, C. Presynaptic enzymatic neurotoxins. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, L.S.; Fu, X.W. Factors affecting paired-pulse facilitation in hippocampal CA1 neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1994, 650, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, D.B.; Stevens, R.C. Recombinant expression and purification of the botulinum neurotoxin type A translocation domain. Protein Expr. Purif. 1997, 11, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccin, P.; Rossetto, O.; Rigoni, M.; Johnson, E.; Schiavo, G.; Montecucco, C. VAMP/synaptobrevin cleavage by tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins is strongly enhanced by acidic liposomes. FEBS Lett. 2003, 542, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulism neurotoxins: Isolation and assay. Methods Enzimol. 1995, 248, 643–652. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, B.A.; Atwood, H.L.; Renger, J.J.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.F. Improved stability of Drosophila larval neuromuscular preparations in haemolymph-like physiological solutions. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1994, 175, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolatto, C.; Chifflet, S.; Megighian, A.; Cantera, R. Synaptic activity modifies the levels of Dorsal and Cactus at the neuromuscular junction of Drosophila. J. Neurobiol. 2003, 54, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zornetta, I.; Scorzeto, M.; Mendes Dos Reis, P.V.; De Lima, M.E.; Montecucco, C.; Megighian, A.; Rossetto, O. Electrophysiological Characterization of the Antarease Metalloprotease from Tityus serrulatus Venom. Toxins 2017, 9, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9030081
Zornetta I, Scorzeto M, Mendes Dos Reis PV, De Lima ME, Montecucco C, Megighian A, Rossetto O. Electrophysiological Characterization of the Antarease Metalloprotease from Tityus serrulatus Venom. Toxins. 2017; 9(3):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9030081
Chicago/Turabian StyleZornetta, Irene, Michele Scorzeto, Pablo Victor Mendes Dos Reis, Maria E. De Lima, Cesare Montecucco, Aram Megighian, and Ornella Rossetto. 2017. "Electrophysiological Characterization of the Antarease Metalloprotease from Tityus serrulatus Venom" Toxins 9, no. 3: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9030081
APA StyleZornetta, I., Scorzeto, M., Mendes Dos Reis, P. V., De Lima, M. E., Montecucco, C., Megighian, A., & Rossetto, O. (2017). Electrophysiological Characterization of the Antarease Metalloprotease from Tityus serrulatus Venom. Toxins, 9(3), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9030081







