Novel Biological Hydrogel: Swelling Behaviors Study in Salt Solutions with Different Ionic Valence Number
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of γ-PGA/ε-PL Hydrogels
2.3. Swelling Study
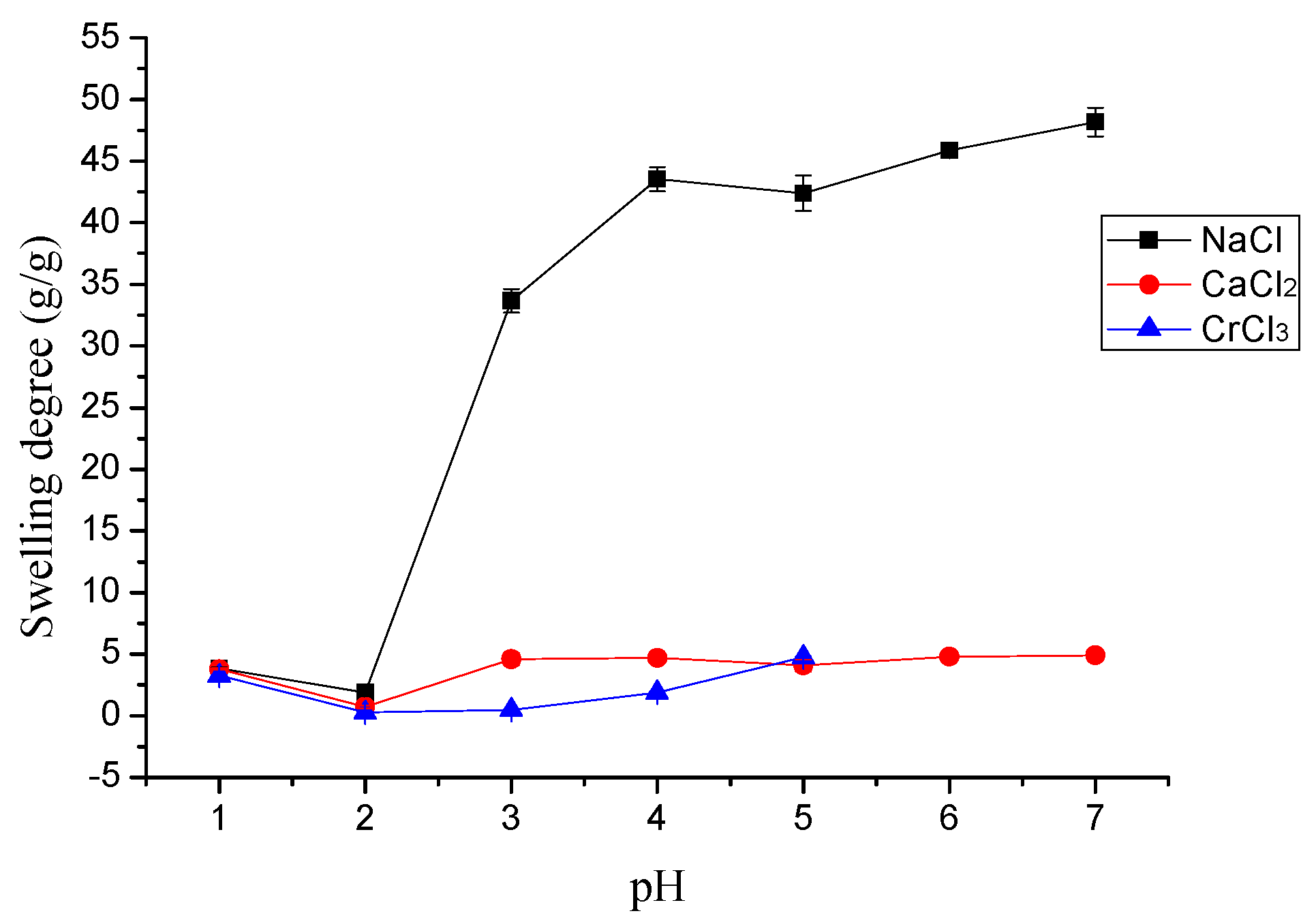
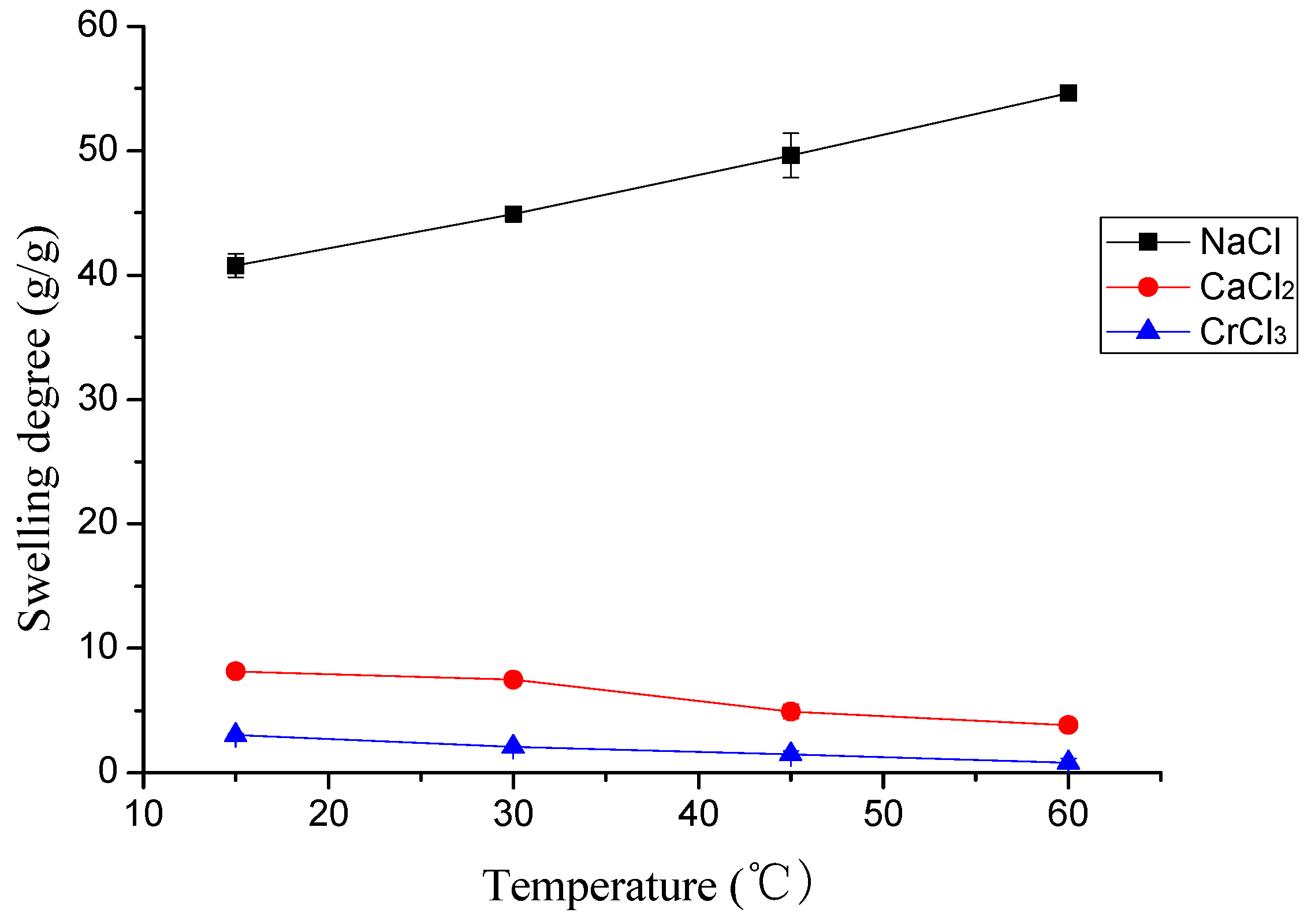
2.3.1. The Effects of pH and Temperature
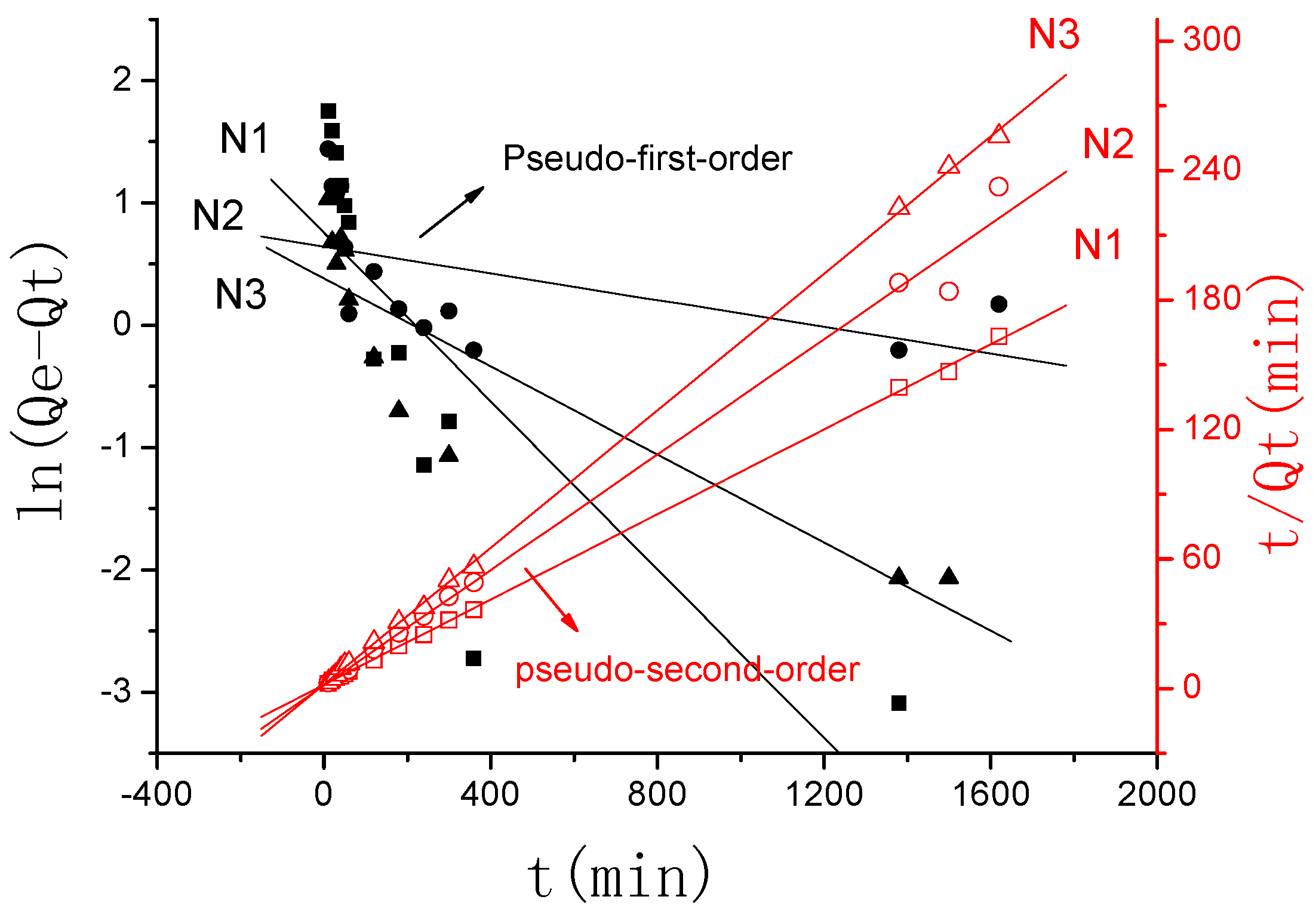
2.3.2. The Swelling Kinetic Study
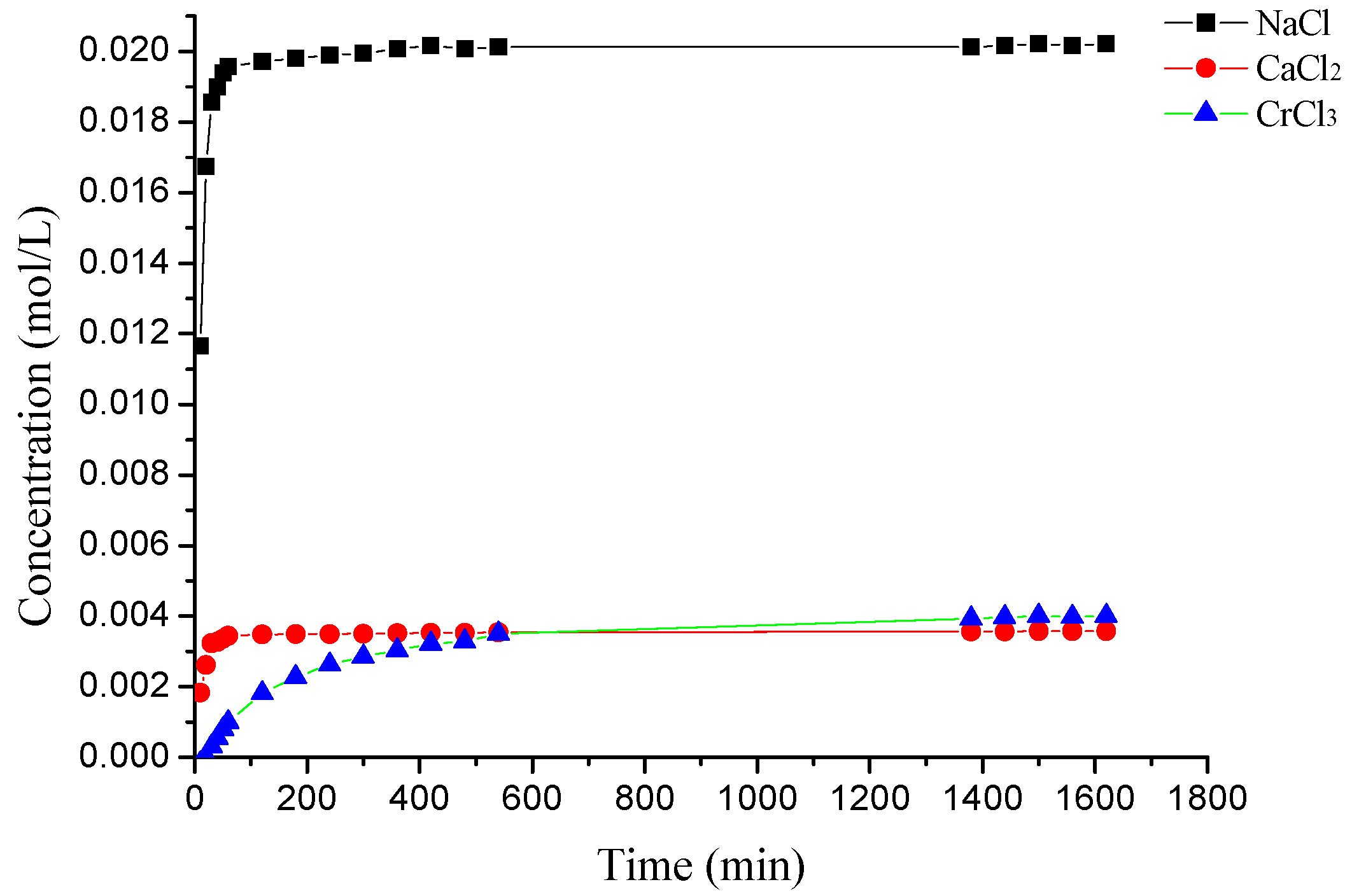
2.4. The Desorption Kinetic
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Hydrogels
3.2. Swelling Study
3.2.1. The Effects of pH and Temperature
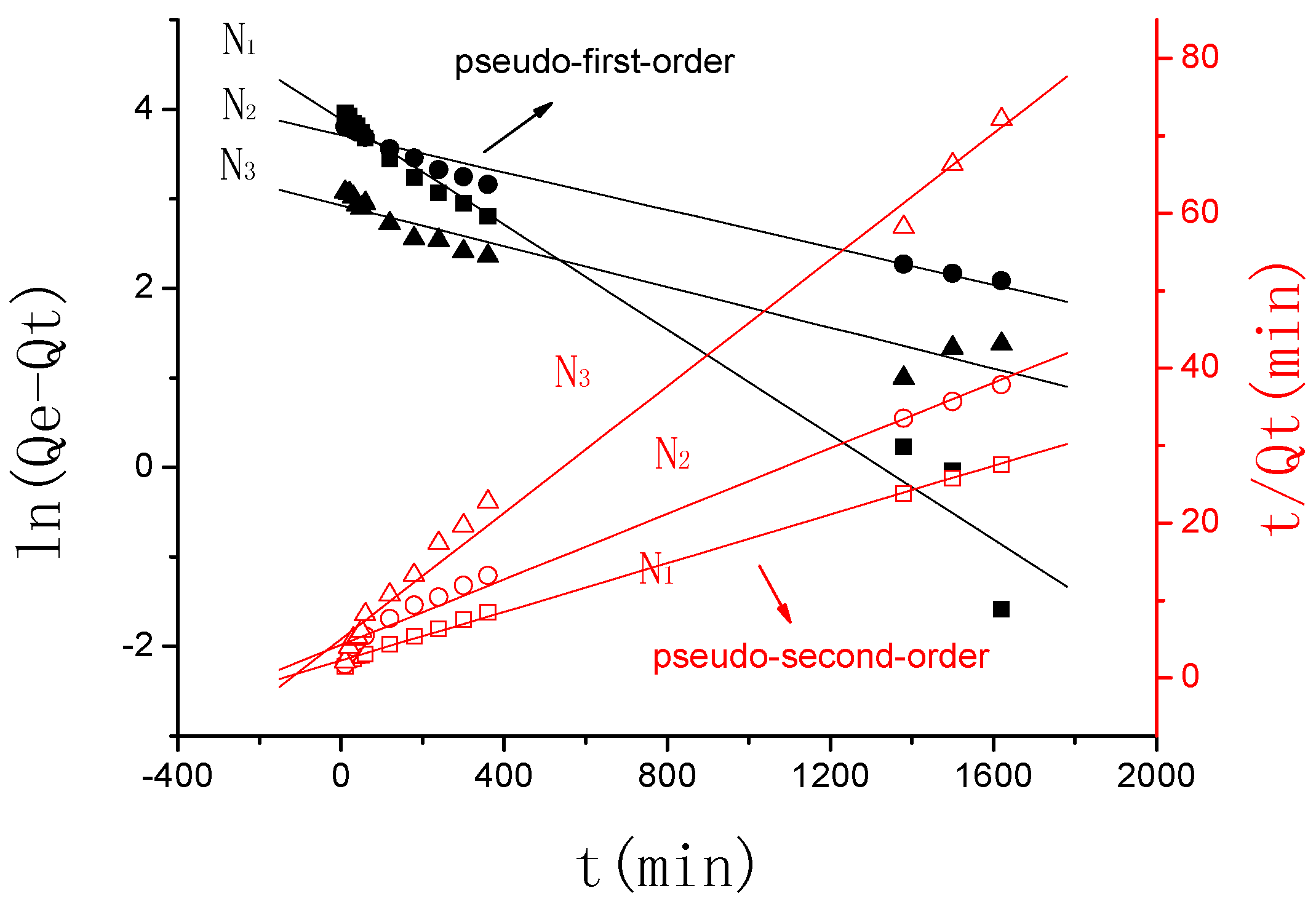
3.2.2. The Swelling Kinetic Study
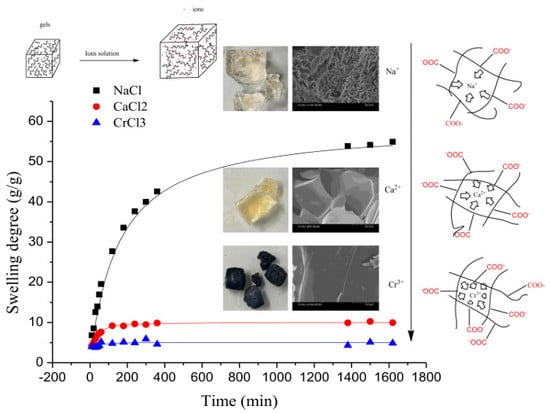
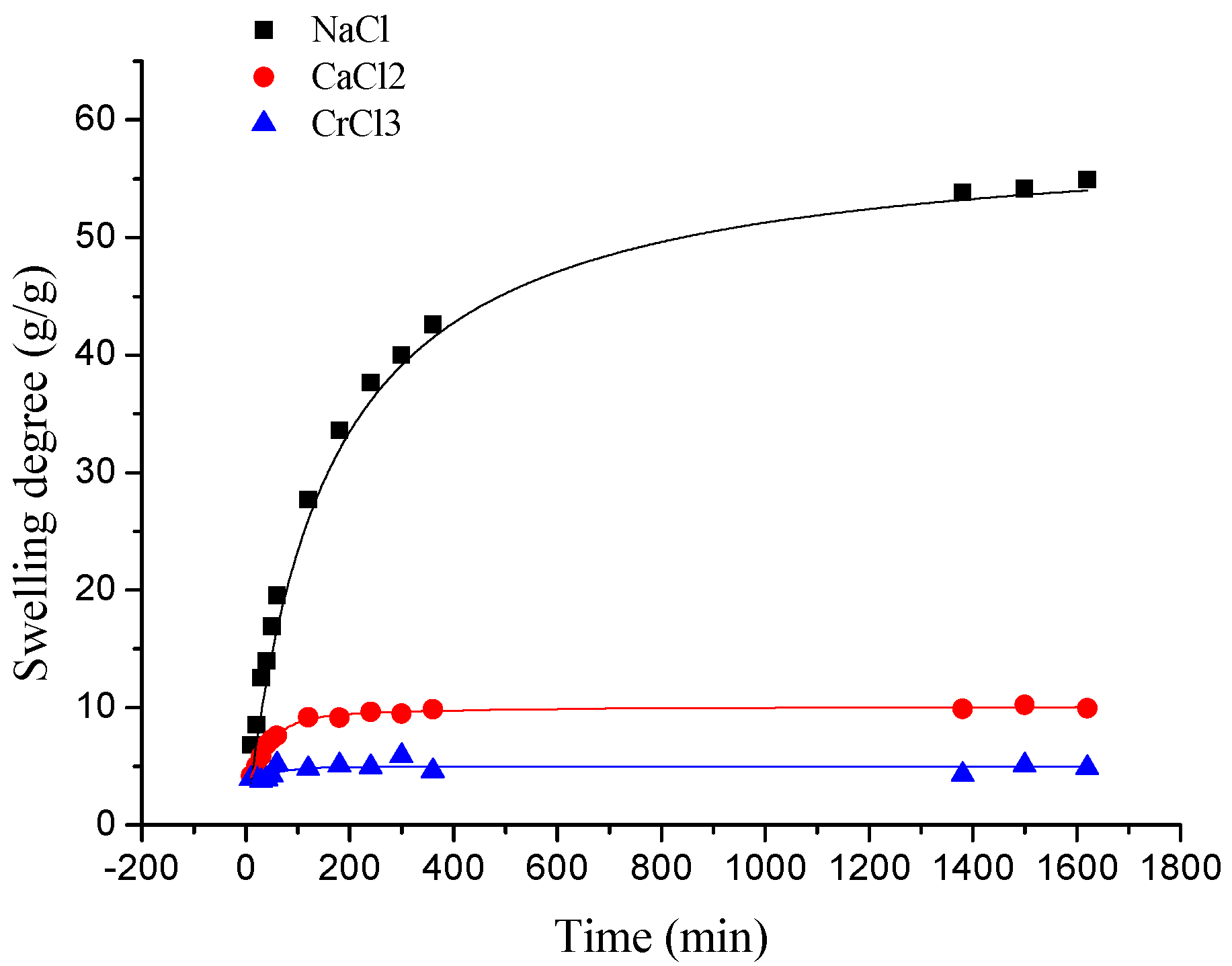
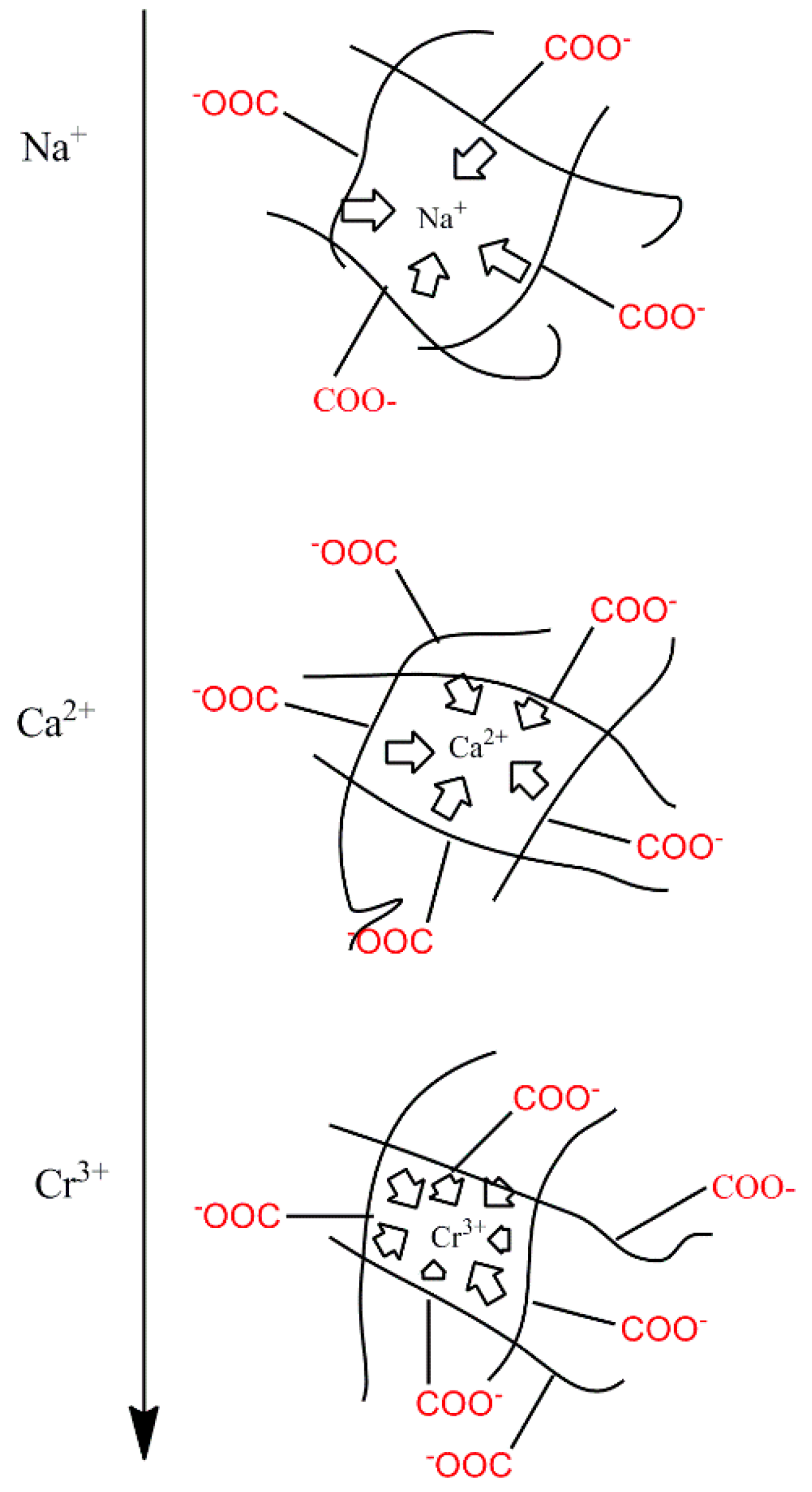
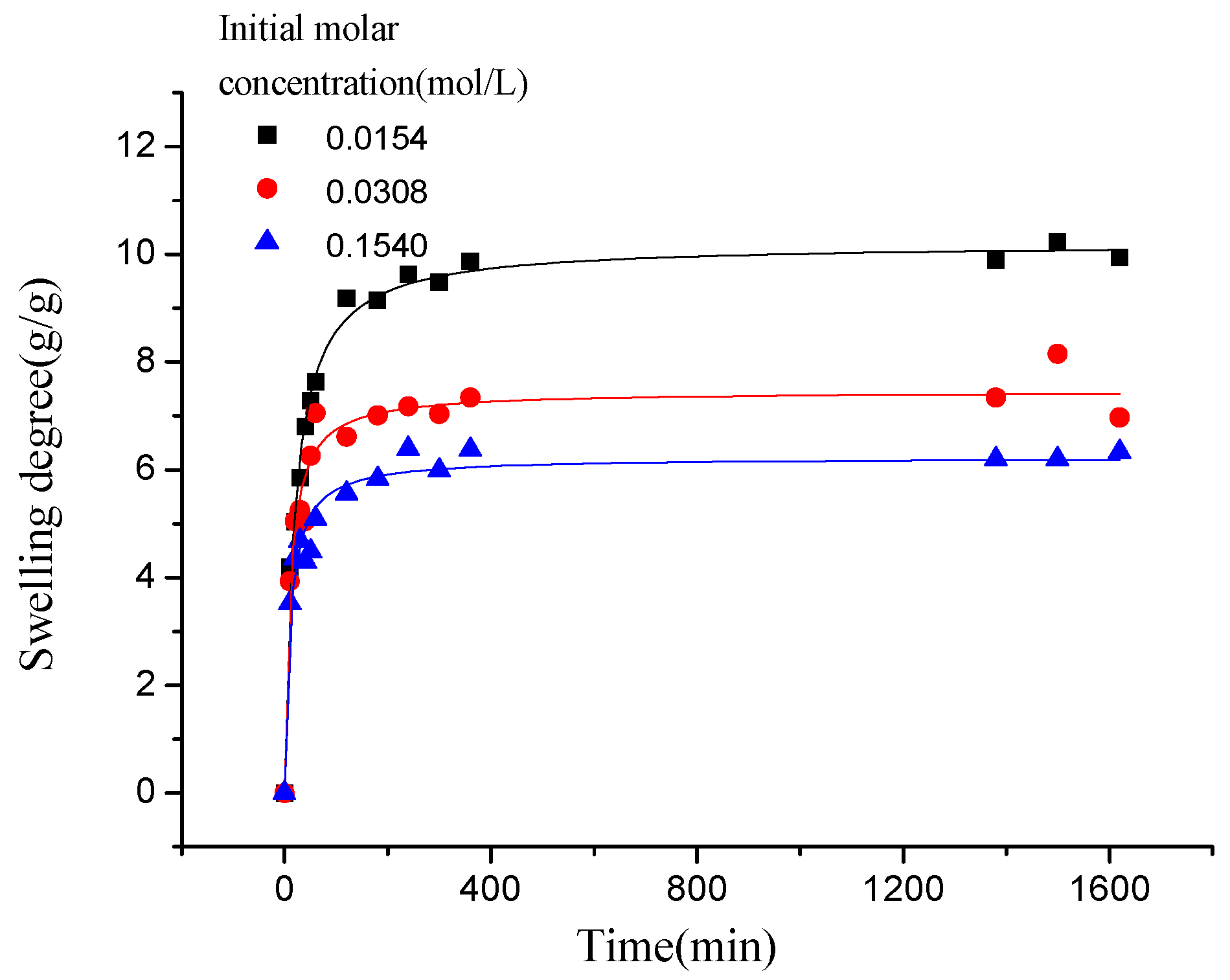
3.2.2.1. The Effect of Ion Valence Number
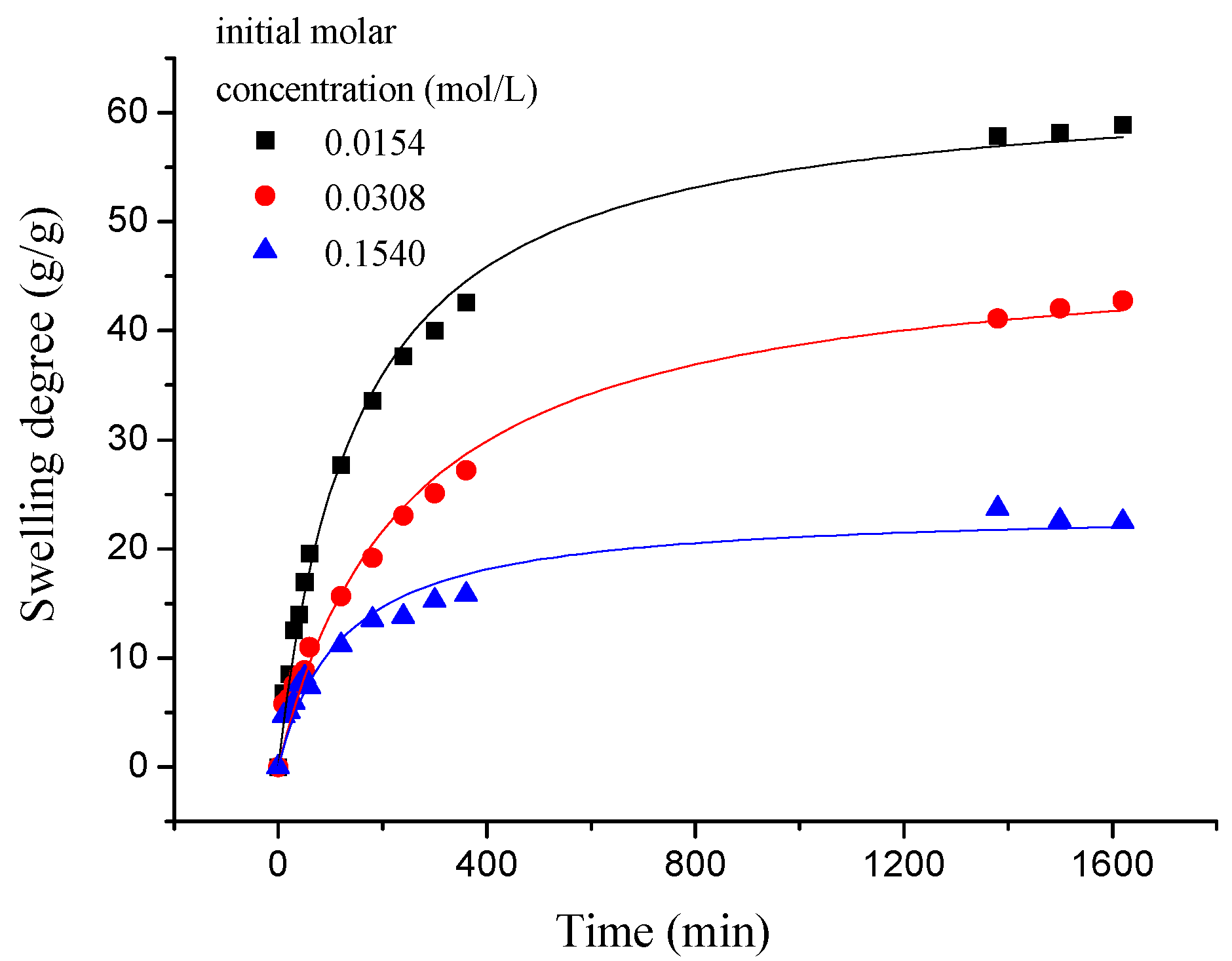
3.2.2.2. The Effect of NaCl Concentration
3.2.2.3. The Effect of CaCl2 Concentration
3.2.2.4. The Effect of CrCl3 Concentration
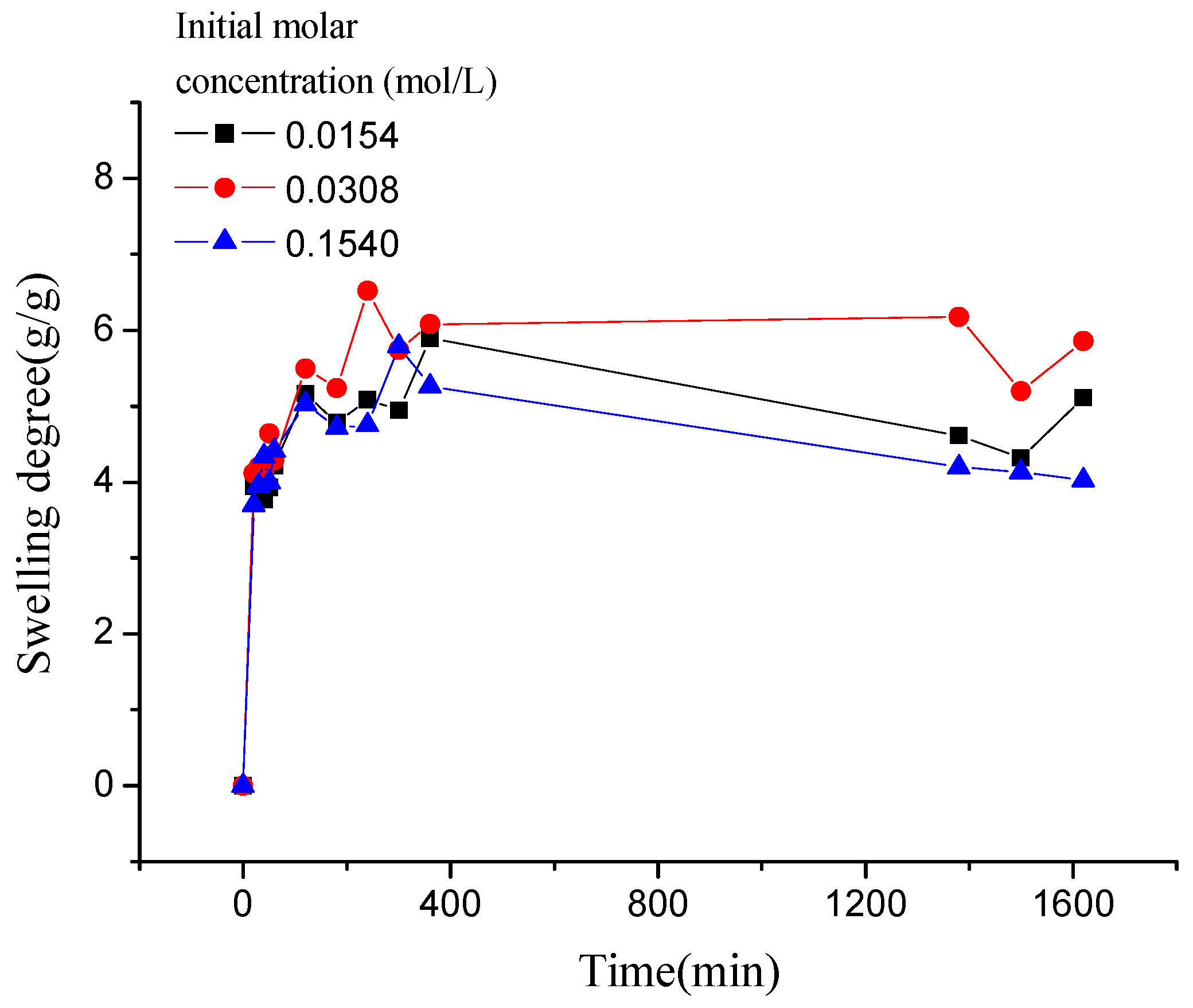
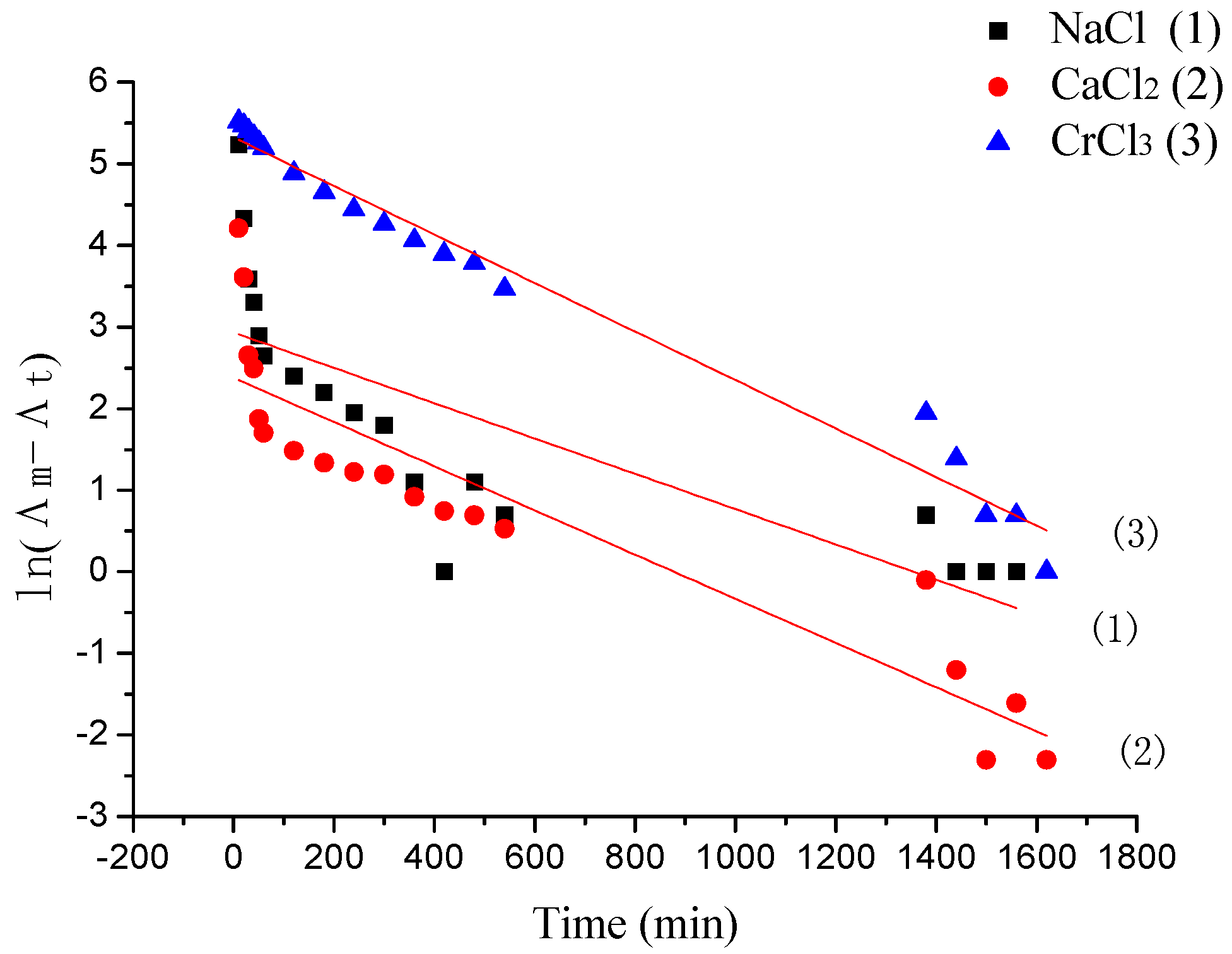
3.3. The Desorption Kinetic
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Slaughter, B.V.; Khurshid, S.S.; Fisher, O.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Peppas, N.A. Hydrogels in Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3307–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, T.K.; Thakur, A.; Alexander, A.; Ajazuddin; Badwaik, H.; Tripathi, D.K. Modified chitosan hydrogels as drug delivery and tissue engineering systems: Present status and applications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, K.M.; D’Souza, R.N.; Hartgerink, J.D.; Schmalz, G. Scaffolds for Dental Pulp Tissue Engineering. Adv. Dent. Res. 2011, 23, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhumathi, K.; Shalumon, K.T.; Rani, V.V.; Tamura, H.; Furuike, T.; Selvamurugan, N.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Wet chemical synthesis of chitosan hydrogel-hydroxyapatite composite membranes for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 45, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Chang, J.; Yang, M.; Chien, C.; Lai, W. Acceleration of wound healing in diabetic rats by layered hydrogel dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, M.D.M.; Cavalcante, D.R.R.; Araújo, F.E.N.; Barretto, S.R.; Aciole, G.T.S.; Pinheiro, A.L.B.; Ribeiro, M.A.G.; Lima-Verde, I.B.; Melo, C.M.; Cardoso, J.C.; et al. Improvement of dermal burn healing by combining sodium alginate/chitosan-based films and low level laser therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2011, 105, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jo Lewis, P.; Chu, C. Fabrication and characterization of a smart drug delivery system: microsphere in hydrogel. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3299–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, L.; Su, Z.; Ma, G. A thermosensitive hydrogel based on quaternized chitosan and poly(ethylene glycol) for nasal drug delivery system. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, A.T.; Guilherme, M.R.; Reis, A.V.; Campese, G.M.; Muniz, E.C.; Nozaki, J. Removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous media using superabsorbent hydrogel supported on modified polysaccharide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Ma, J.; B, N. L. Synthesis and swelling behaviors of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(AA-co-AM-co-AMPS)/MMT superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.P.D.; Hsieh, M.; Bonifacio Tobias Doma, J.; Peruelo, D.C.; Chen, I.; Lee, H. Synthesis of Gelatin-γ-Polyglutamic Acid- Based Hydrogel for the In Vitro Controlled Release of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) from Camellia sinensis. Polymers 2014, 6, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier Leach, J.; Bivens, K.A.; Patrick, C.W.J.; Schmidt, C.E. Photocrosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels: Natural, biodegradable tissue engineering scaffolds. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 82, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.Y.; Kuo, T.F.; Wu, H.D.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, S.Y. A novel injectable chitosan/polyglutamate polyelectrolyte complex hydrogel with hydroxyapatite for soft-tissue augmentation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Li, Z.; Xia, W.; Yang, N.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C. Preparation and properties of EDC/NHS mediated crosslinking poly(gamma-glutamic acid)/epsilon-polylysine hydrogels. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, W.; Song, L.; Zhang, T. Preparation of Uniform Magnetic Chitosan Microcapsules and Their Application in Adsorbing Copper Ion(II) and Chromium Ion(III). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 14099–14106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.F.; Nie, W.Y.; Song, L.Y. Preparation of Fe3O4 /chitosan/poly(acrylic acid) composite particles and its application in adsorbing copper ion(II). Cellulose 2012, 19, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3935–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, D.W.; Birkinshaw, C.; O’Dwyer, T.F. Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6709–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linghu, W.S.; Wang, C. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution by Chitosan. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 881–883, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, S.S.; Goyal, D. Removal of Heavy Metals by Waste Tea Leaves from Aqueous Solution. Eng. Life Sci. 2005, 5, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhong, L.; Ren, J.; Sun, R. Highly Effective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Macroporous Xylan-Rich Hemicelluloses-Based Hydrogel. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozay, O.; Ekici, S.; Baran, Y.; Aktas, N.; Sahiner, N. Removal of toxic metal ions with magnetic hydrogels. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4403–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.F.; Qiao, C.S. Preparation and Properties of Pullulan Composite Films. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 476–478, 2100–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliktar, D. Designing cell-compatible hydrogels for biomedical applications. Science 2012, 336, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooley, S.A.; Rivas, B.L.; Carcamo, A.L.; Del, C.; Pizarro, G. Hydrogels from N,N′-dimethylacrylamide-co-2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid with salt-, temperature- and pH-responsiveness properties. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2008, 53, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Yu, S.; Ho, Y.; Huang, B.; Tsai, G.; Hsieh, H.; Sung, H.; Mi, F. Characterization of tea catechins-loaded nanoparticles prepared from chitosan and an edible polypeptide. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, I.; Van, Y. The production of poly-(γ-glutamic acid) from microorganisms and its various applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 79, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Nagasawa, T. ε-Poly-l-lysine: Microbial production, biodegradation and application potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sersy, N.A.; Abdelwahab, A.E.; Abouelkhiir, S.S.; Abou-Zeid, D.M.; Sabry, S.A. Antibacterial and Anticancer activity of ε-poly-l-lysine (ε-PL) produced by a marine Bacillus subtilis sp. J. Basic Microbiol. 2012, 52, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Xu, H.; Wan, C.; Peng, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xiong, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Wei, H. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of ε-poly-l-lysine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitra, J.; Singh, N. Swelling behavior of starch chitosan polymeric blend. Adv. Polym. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2014, 4, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kunioka, M.; Choi, H.J. Preparation conditions and swelling equilibria of biodegradable hydrogels prepared from microbial poly(γ-glutamic acid) and poly(ε-lysine). J. Polym. Environ. 1996, 4, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Fast removal of copper ions from aqueous solution by chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, R.; Ul Abdeen, Z. Kinetics of desorption of KCL from polyvinyl alcohol-borate hydrogel in aqueous-alcoholic solvents at different temperatures. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 89, 2126–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.; Li, Z. Sulfhydryl functionalized hydrogel with magnetism: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 249, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Su, H.; Fang, L.; Tan, T. Superabsorbent hydrogels from poly(aspartic acid) with salt-, temperature- and pH-responsiveness properties. Polymer 2005, 46, 5368–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Maity, A.; Ray, S.S. Synthesis of co-polymer-grafted gum karaya and silica hybrid organic-inorganic hydrogel nanocomposite for the highly effective removal of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Shanmuga Sundaram, K.; Anantha Iyengar, G.; Lee, K. A novel chitosan functional gel included with multiwall carbon nanotube and substituted polyaniline as adsorbent for efficient removal of chromium ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Fan, T.; Zhang, D. Adsorption of copper ions from aqueous solution by citric acid modified soybean straw. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidian, H.; Hashemi, S.A.; Sammes, P.G.; Meldrum, I. A model for the swelling of superabsorbent polymers. Polymer 1998, 39, 6697–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Rastogi, A. Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by green algae Spirogyra species: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; He, G.; Hua, J.; Wu, M.; Guo, W.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C. Preparation of γ-PGA hydrogels and swelling behaviors in salt solutions with different ionic valence numbers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 11085–11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NaCl | CaCl2 | CrCl3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form | 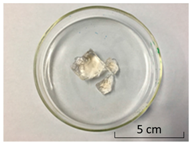 | 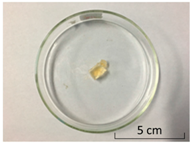 |  |
| Cross-section |  | 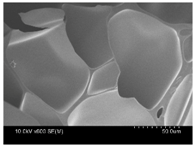 |  |
| Surface | 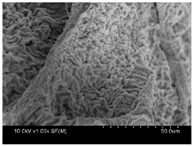 |  | 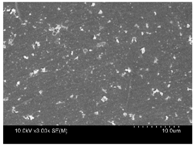 |
| Qe,e (g/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | Qe,c (g/g) | Radj2 | K2 (min−1) | Qe,c (g/g) | Radj2 | ||
| N1 | 59.12 | 0.00293 | 48.68 | 0.97646 | 0.000110385 | 63.61 | 0.9983 |
| N2 | 50.80 | 0.00105 | 41.01 | 0.97574 | 0.000105524 | 47.24 | 0.99106 |
| N3 | 26.42 | 0.00104 | 18.66 | 0.93623 | 0.000333858 | 24.49 | 0.9931 |
| Qe,e (g/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | Qe,c (g/g) | Radj2 | K2 (min−1) | Qe,c (g/g) | Radj2 | ||
| N1 | 9.94 | 0.00344 | 2.13 | 0.63707 | 0.005619146 | 10.14 | 0.99965 |
| N2 | 8.15 | 0.00091 | 1.99 | 0.34821 | 0.012211097 | 7.49 | 0.99345 |
| N3 | 6.33 | 0.0018 | 1.47 | 0.79817 | 0.013841741 | 6.30 | 0.99973 |
| Λm,m (μs) | Pseudo-First-Order | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | Λm,c (μs) | Radj2 | ||
| (1) | 2358.5 | 0.00216 | 2185.29 | 0.57959 |
| (2) | 832.3 | 0.00271 | 822.59 | 0.82502 |
| (3) | 1409.56 | 0.00297 | 1400.79 | 0.97701 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; He, G.; Li, Z.; Hua, J.; Wu, M.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Ban, L.-t.; Huang, L. Novel Biological Hydrogel: Swelling Behaviors Study in Salt Solutions with Different Ionic Valence Number. Polymers 2018, 10, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020112
Wang Y, He G, Li Z, Hua J, Wu M, Gong J, Zhang J, Ban L-t, Huang L. Novel Biological Hydrogel: Swelling Behaviors Study in Salt Solutions with Different Ionic Valence Number. Polymers. 2018; 10(2):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020112
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Guidong He, Zheng Li, Jiachuan Hua, Maoqi Wu, Jixian Gong, Jianfei Zhang, Li-tong Ban, and Liang Huang. 2018. "Novel Biological Hydrogel: Swelling Behaviors Study in Salt Solutions with Different Ionic Valence Number" Polymers 10, no. 2: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020112
APA StyleWang, Y., He, G., Li, Z., Hua, J., Wu, M., Gong, J., Zhang, J., Ban, L.-t., & Huang, L. (2018). Novel Biological Hydrogel: Swelling Behaviors Study in Salt Solutions with Different Ionic Valence Number. Polymers, 10(2), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020112