A New Esterase from Thermobifida halotolerans Hydrolyses Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Culture Conditions
2.3. General Recombinant DNA Techniques
2.4. Cloning of Thh_est
2.5. DNA Sequencing, Alignments and Deposition of Sequence Data
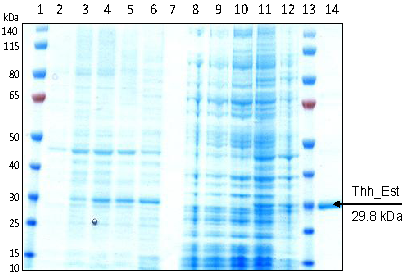
2.6. Expression and Purification
2.7. Esterase Activity Assay
2.8. PET and PLA Hydrolysis
2.9. Hydrolysis of PET Model Substrate bis(benzoyloxyethyl)terephthalate
2.10. Analysis of PET, 3PET and PLA Hydrolysis Released Products
2.11. PET and PLA Hydrophilicity Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
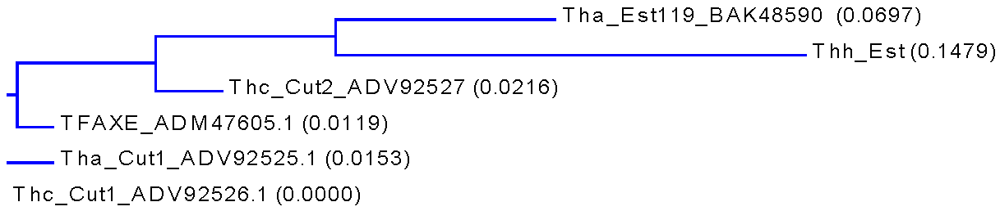
3.1. Cloning, Sequence Analysis and Heterologous Expression in E. coli of an Esterase from Thermobifida Halotolerans
| Thh_Est | Tha_Est119 | Thc_Cut2 | TFAXE | Tha_Cut1 | Thc_Cut1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thh_Est | 0 | 87% | 87% | 86% | 85% | 87% |
| Tha_Est119 | 0 | 93% | 89% | 88% | 89% | |
| Thc_Cut2 | 0 | 95% | 94% | 95% | ||
| TFAXE | 0 | 98% | 99% | |||
| Tha_Cut1 | 0 | 98% | ||||
| Thc_Cut1 | 0 |
3.2. Hydrolysis of PLA Films
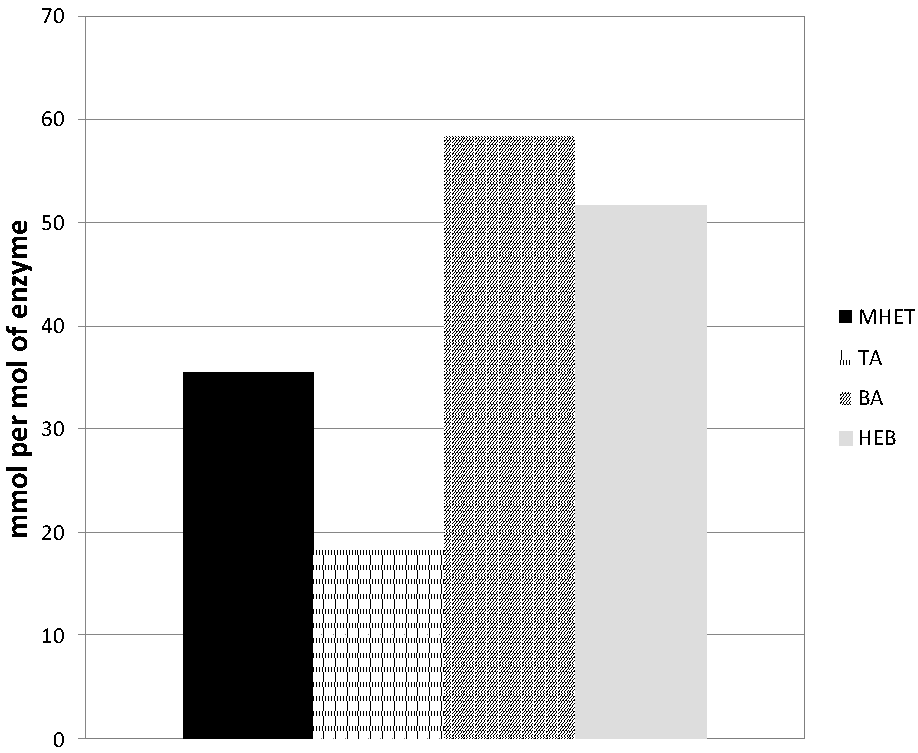
3.3. Hydrolysis of the PET Model Substrate bis(benzoyloxyethyl)terephthalate
3.4. Hydrolysis of PET Films
3.5. Hydrophilicity Measurement of Enzymatically Treated PLA and PET
| Initial | Control | Enzyme treated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 90.8° ± 3.3° | 74.8° ± 2.3° | 50.4° ± 9.9° |
| PLA | 75.5° ± 2.7° | 68.4° ± 2.3° | <20° |
Acknowledgements
References
- Guebitz, G.M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Enzymes go big: Surface hydrolysis and fictionalization of synthetic polymers. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Choct, M. Enzymes for the feed industry: Past, present and future. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2006, 62, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, O.; Borchert, T.V.; Fuglsang, C.C. Industrial enzyme applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, P. Application of enzymes in the pulp and paper industry applicaton. Biotechnol. Progr. 1999, 15, 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Hameed, A. Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, K.H. Detergent proteases. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Hakamada, Y.; Koike, K.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Moir, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Ito, S. Thermostable alkaline cellulase from an alkaliphilic isolate, bacillus Sp. KSM-S237. Extremophiles 1997, 1, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, G.W.; Gray, D. Towards novel processes for the fine-chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Koeller, K.M.; Wong, C.H. Enzymes for chemical synthesis. Nature 2001, 409, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Souter, P.F.; Perez-Prat, E.M.; Herrero Acero, E.; Pricelius, S.; Guebitz, G.M. Cleaning and/or Treatment Compositions. WO/2009/090576, 23 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen, A.; Schroeder Gald, S.O.; Fukuyama, S.; Matsui, T. Cutinase Variants. US6960459 B2, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, M.; Aichernig, N.; Guebitz, G.M.; Kokol, V. Enzymatic coating of lignocellulosic surfaces polyphenols. Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- Božič, M.; Gorgieva, S.; Kokol, V. Laccase-mediated functionalization of chitosan by caffeic and galic acids for modulating antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.; Matamá, T.; Kim, S.; Padrão, J.; Nugroho Prasetyo, E.; Kudanga, T.; Nyanhongo, G.S.; Guebitz, G.M.; Casal, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant linen via laccase-assisted grafting. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mai, C.; Milstein, O.; Hüttermann, A. Fungal laccase grafts acrylamide onto lignin in presence of peroxides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 51, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- Buchheit, O.; Eddoumy, F.; Sorrenti, E.; Di Martino, J.; Ruch, D. Modifications of the polylactic acid surface properties by DBD plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2011, 133, 030903–1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.A.; Choi, J.H.; Takizawa, S. Comparison of initial filtration resistance by pretreatment processes in the nanofiltration for drinking water treatment. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2007, 56, 352–362. [Google Scholar]
- Asatekin, A.; Kang, S.; Elimelech, M.; Mayes, A.M. Anti-fouling ultrafiltration membranes containing polyacrylonitrile-graft poly(ethyleneoxide) comb copolymer additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 298, 136–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Qiu, Y. Influence of the amount of absorbed moisture in nylon fibers on atmospheric pressure plasma processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 7453–7461. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Chu, P.K.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Fu, R.K.Y.; Ha, P.C.T.; Yan, Q. Plasma surface modification of poly vinyl chloride for improvement of antibacterial properties. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, M.; Fatarella, E.; Kovac, J.; Guebitz, G.M.; Kokol, V. Laccase induced grafting on plasma-pretreated polyprene. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2735–2741. [Google Scholar]
- Tressaud, A.; Durand, E.; Labrugère, C.; Kharitonov, A.P.; Kharitonova, L.N. Modification of surface properties of carbon-based and polymeric materials through fluorination routes: From fundamental research to industrial applications. J. Fluor. Chem. 2007, 128, 378–391. [Google Scholar]
- Guebitz, G.M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. New substrates for reliable enzymes: Enzymatic modification of polymers. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Nylon Chain Report 2010. YNFX Yarns and Fiber Exchange. Dated-23 Feb 2011.
- Vertommen, M.A.M.E.; Nierstrasz, V.A.; Veer, M.; Warmoeskerken, M.M.C.G. Enzymatic surface modification of poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Biotechnol. 2005, 120, 376–386. [Google Scholar]
- Oeser, T.; Wei, R.; Baumgarten, T.; Billig, S.; Foellner, C.; Zimmermann, W. High level expression of a hydrophobic poly(ethylene terephthalate) hydrolyzing carboxylesterase from thermobifida fusca KW3 in escherichia coli BL21(DE3). J. Biotechnol. 2010, 146, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero Acero, E.; Ribitsch, D.; Steinkellner, G.; Gruber, K.; Greimel, K.; Eiteljoerg, I.; Trotscha, E.; Wei, R.; Zimmermann, W.; Zinn, M.; et al. Enzymatic surface hydrolysis of PET: Effect of structural diversity on kinetic properties of cutinases from Thremobifida. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4632–4640. [Google Scholar]
- Donelli, I.; Freddi, G.; Nierstrasz, V.A.; Taddei, P. Surface structure and properties of poly-(ethylene terephthalate) hydrolyzed by alkali and cutinase. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Brueckner, T.; Eberl, A.; Heumann, S.; Rabe, M.; Guebitz, G.M. Enzymatic and chemical hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) fabrics. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 6435–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisch-Mark, M.; Herrmann, A.; Zimmermann, W. Increase of the hydrophilicity of polyethylene terephthalate fibers by hydrolases from thermomonospora fusca and fusarium solani f. sp pisi. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.; Silva, C.; O’Neill, A.; Micaelo, N.; Guebitz, G.; Soares, C.M.; Casal, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Tailoring cutinase activity towards polyethylene terephthalate and polyamide 6,6 fibers. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 128, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Eberl, A.; Heumann, S.; Brueckner, T.; Araújo, R.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Kaufmann, F. Enzymatic surface hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) and bis(benzoyloxyethyl) terephthalate by lipase and cutinase in the presence of surface active molecules. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 143, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, M.; Kellis, J.; Poulouse, A.J. Enzymatic modification of polyester. AATCC Rev. 2002, 2, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ribitsch, D.; Heumann, S.; Trotscha, E.; Herrero Acero, E.; Greimel, K.; Leber, R.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Deller, S.; Eiteljoerg, I.; Remler, P.; et al. Hydrolysis of polyethyleneterephthalate by para-nitrobenzylesterase from bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 951–960. [Google Scholar]
- Ronkvist, Å.M.; Xie, W.; Lu, W.; Gross, R.A. Cutinase-catalyzed hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5128–5138. [Google Scholar]
- Liebminger, S.; Eberl, A.; Sousa, F.; Heumann, S.; Fisher-Colbrie, G.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Guebitz, G.M. Hydrolysis of PET and bis-(benzoyloxyethyl) terephthalate with a new polyesterase from penicillium citrinum. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2007, 25, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, A.; Araújo, R.; Casal, M.; Guebitz, G.M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Effect of the agitation on the adsorption and hydrolytic efficiency of cutinases on polyethylene terephthalate fibres. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 7, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.W.; Do Chung, J. Synthesis and biodegradation behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate) oligomers. Polymer-Korea 2009, 33, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Nechwatal, A.; Blokesch, A.; Nicolai, M.; Krieg, A.; Kolbe, A.; Wolf, M.; Gerhardt, M. A contribution to the investigation of enzyme-catalysed hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) oligomers. Macromol.Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Heumann, S.; Eberl, A.; Pobeheim, H.; Liebminger, S.; Fischer-Colbrie, G.; Almansa, E.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Guebitz, G.M. New model substrates for enzymes hydrolysing polyethyleneterephthalate and polyamide fibers. J. Biochem. Bioph. Methods 2006, 69, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.E.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ribitsch, D.; Herrero Acero, E.; Greimel, K.; Eiteljoerg, I.; Trotscha, E.; Freddi, G.; Schwab, H.; Guebitz, G.M. Characterization of a new cutinase from Thermobifida Alba regarding PET-surface hydrolysis. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2012, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.-L.; Tang, S.-K.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhi, X.-Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.-H.; Li, W.-J. Thermobifida Halotolerans sp. nov., isolated from a salt mine sample, and emended description of the genus Thermobifida. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1821–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Thumarat, U.; Zhang, X.; Tang, M.; Kawai, F. Diversity of polyester-degrading bacteria in compost and molecular analysis of a thermoactive esterase from Thermobifida Alba AHK119. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 87, 771–779. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.C.; Chen, G.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, W.L.; Yang, C.H. Heterologous expression of thermostable acetylxylan esterase gene from thermobifida fusca and its synergistic action with xylanase for the production of xylooligosaccharide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 400, 718–723. [Google Scholar]
- Almansa, E.; Heumann, S.; Eberl, A.; Fischer-Colbrie, G.; Martinkova, L.; Marek, J.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Guebitz, G.M. Enzymatic surface hydrolysis of PET enhances bonding in PVC coating. Biocatal. Biotrans. 2008, 26, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
Appendix
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribitsch, D.; Herrero Acero, E.; Greimel, K.; Dellacher, A.; Zitzenbacher, S.; Marold, A.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Steinkellner, G.; Gruber, K.; Schwab, H.; et al. A New Esterase from Thermobifida halotolerans Hydrolyses Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polylactic Acid (PLA). Polymers 2012, 4, 617-629. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4010617
Ribitsch D, Herrero Acero E, Greimel K, Dellacher A, Zitzenbacher S, Marold A, Rodriguez RD, Steinkellner G, Gruber K, Schwab H, et al. A New Esterase from Thermobifida halotolerans Hydrolyses Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polylactic Acid (PLA). Polymers. 2012; 4(1):617-629. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4010617
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibitsch, Doris, Enrique Herrero Acero, Katrin Greimel, Anita Dellacher, Sabine Zitzenbacher, Annemarie Marold, Rosario Diaz Rodriguez, Georg Steinkellner, Karl Gruber, Helmut Schwab, and et al. 2012. "A New Esterase from Thermobifida halotolerans Hydrolyses Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polylactic Acid (PLA)" Polymers 4, no. 1: 617-629. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4010617
APA StyleRibitsch, D., Herrero Acero, E., Greimel, K., Dellacher, A., Zitzenbacher, S., Marold, A., Rodriguez, R. D., Steinkellner, G., Gruber, K., Schwab, H., & Guebitz, G. M. (2012). A New Esterase from Thermobifida halotolerans Hydrolyses Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polylactic Acid (PLA). Polymers, 4(1), 617-629. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4010617




