A Comparison of Selective Pressures in Plant X-Linked and Autosomal Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Transcriptomic Data
2.3. Orthology Inference and Identification of X-Linked and Autosomal Genes
2.4. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
2.5. Analyses of Selection on Coding Sequences Using dN/dS Methods
2.6. DNA Polymorphism Analyses
2.7. Sex-Biased Gene Expression
2.8. Analyses of Codon Bias
3. Results
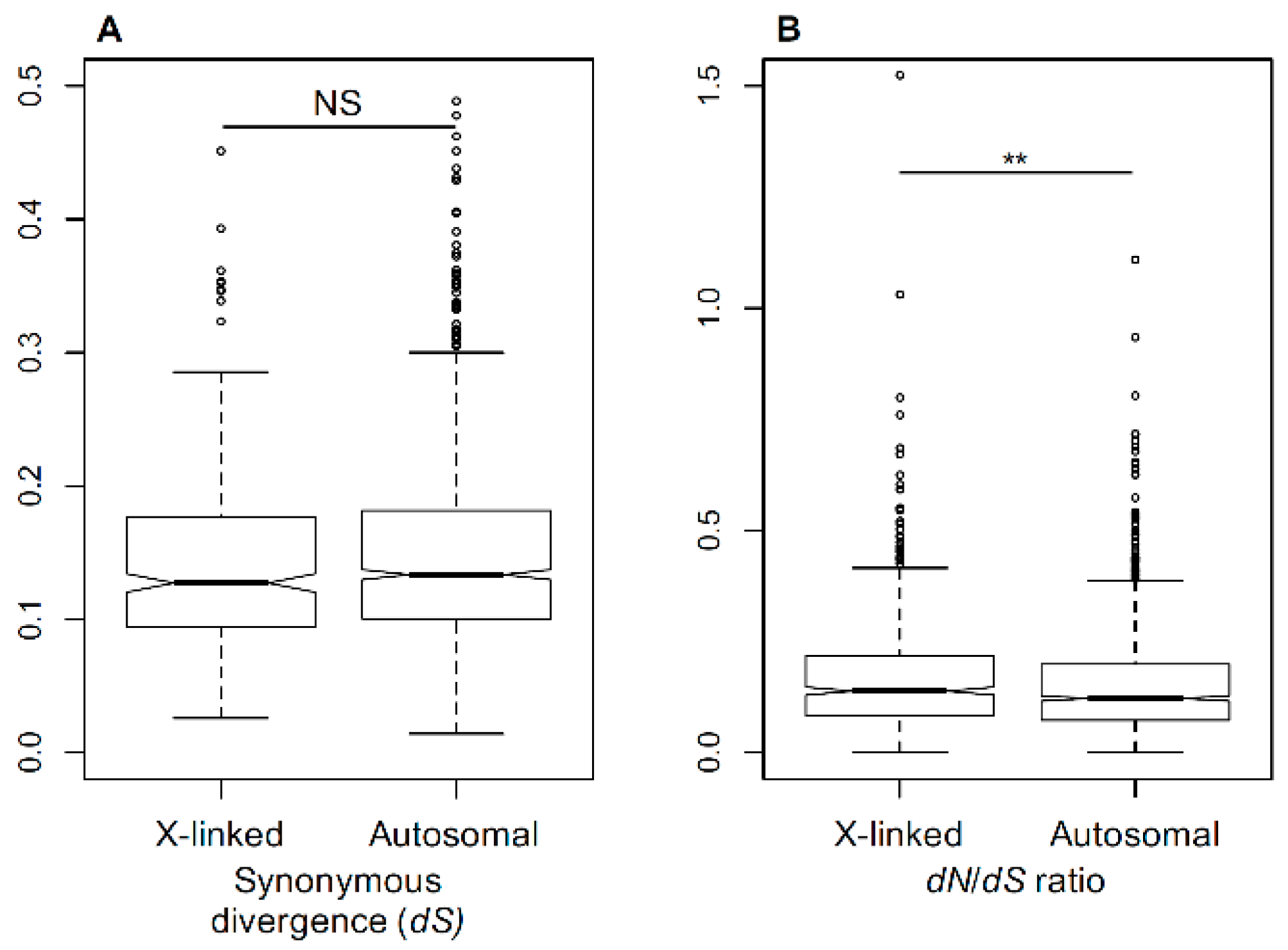
3.1. Substitution Rates in X-Linked and Autosomal Genes
3.2. Faster-X Evolution Following Transition to Dioecy
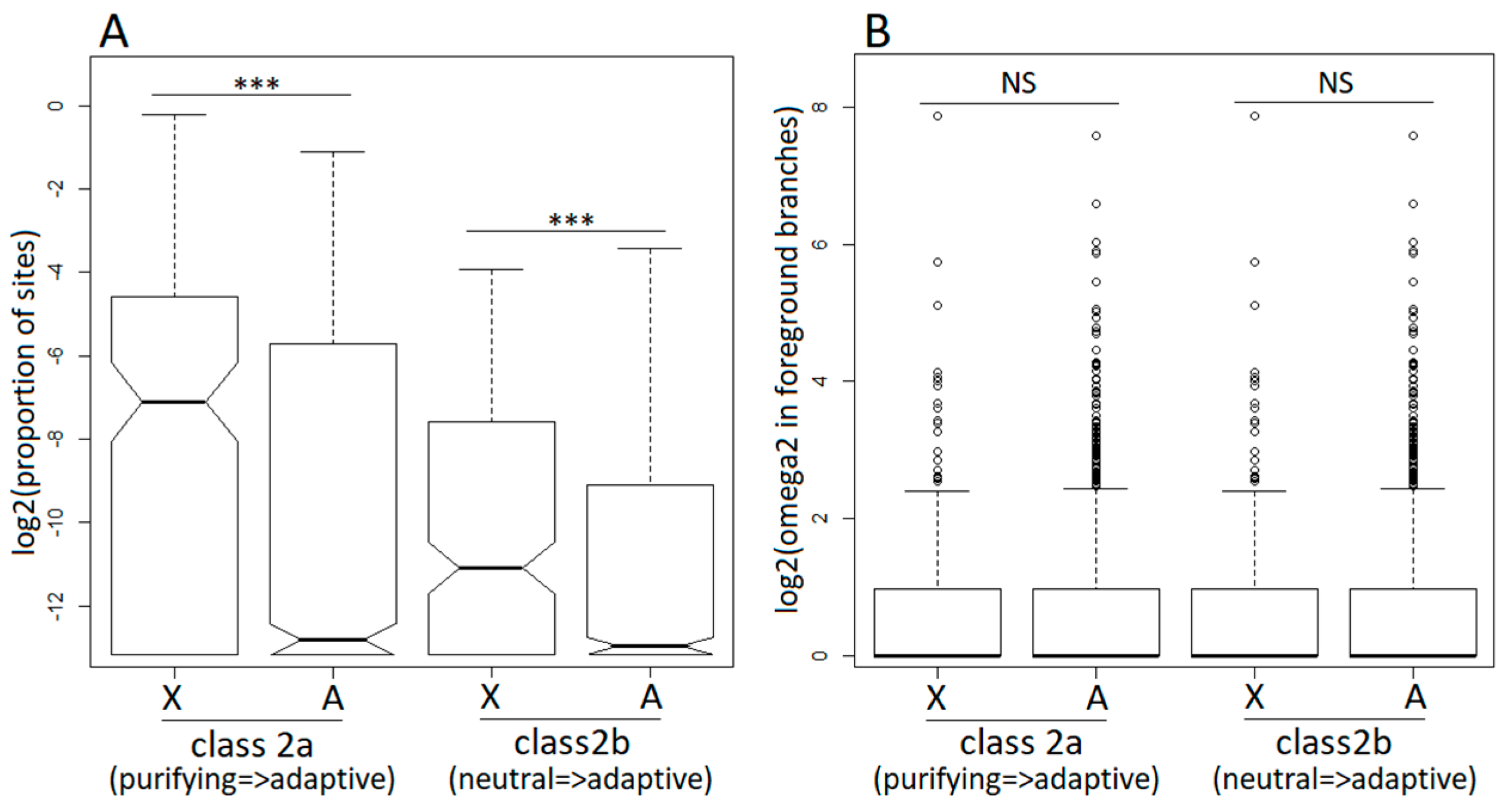
3.3. Positive Selection in X-Linked and Autosomal Genes
3.4. Purifying Selection in X-Linked and Autosomal Genes
3.5. Selection on Codon Usage Bias
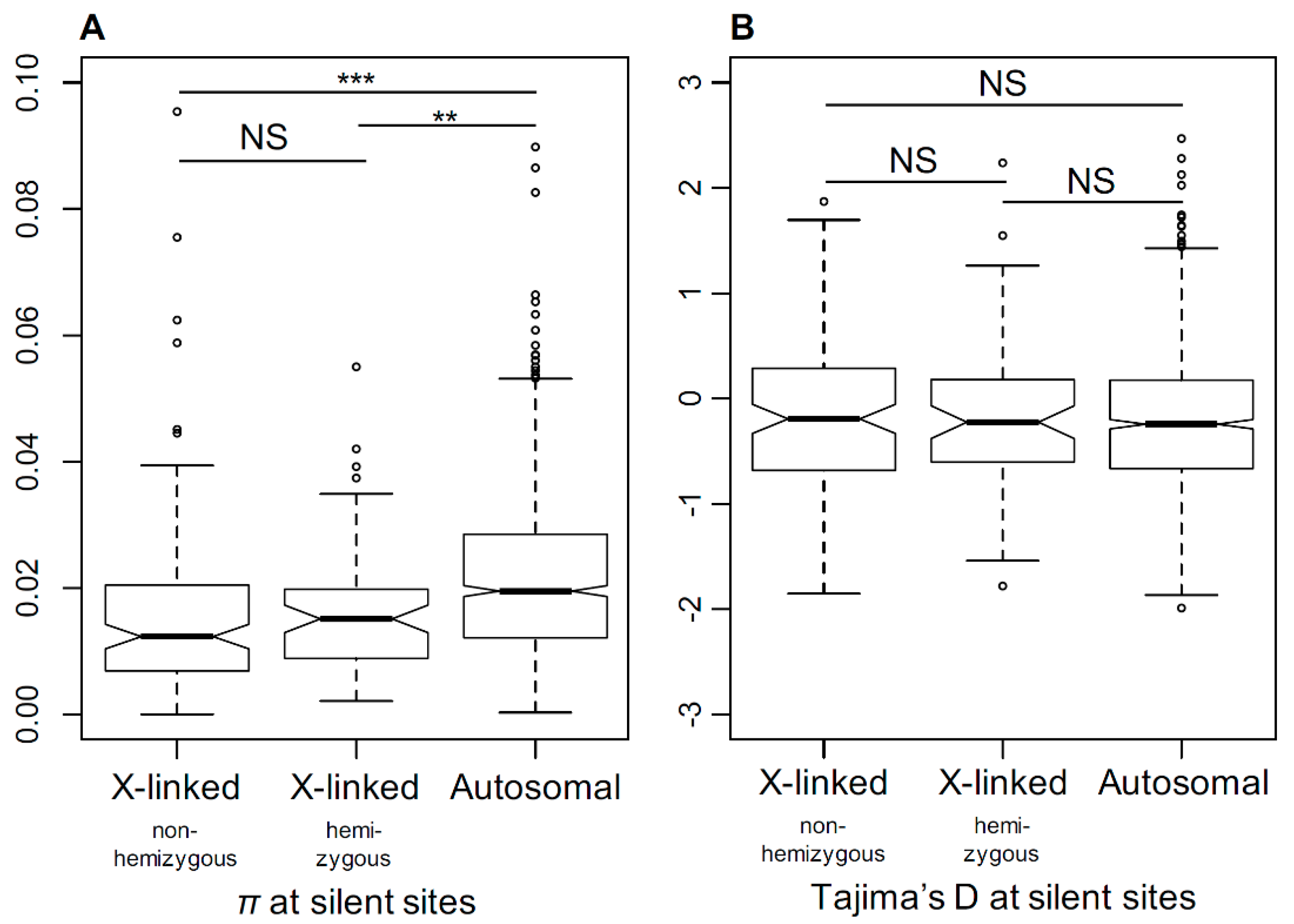
3.6. Genetic Diversity in X-Linked and Autosomal Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. Faster-X Evolution in Silene
4.2. Genetic Diversity
4.3. Codon Bias
4.4. Factors Affecting the Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachtrog, D. Y chromosome evolution: Emerging insights into processes of Y-chromosome degeneration. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicoso, B.; Charlesworth, B. Evolution on the X chromosome: Unusual patterns and processes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemp, N.; Tavares, R.; Muyle, A.; Charlesworth, D.; Marais, G.A.; Widmer, A. Evolution of sex-biased gene expression in a dioecious plant. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgill, D.; Zhang, Y.; Parisi, M.; Oliver, B. Demasculinization of X chromosomes in the Drosophila genus. Nature 2007, 450, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtrog, D.; Toda, N.R.; Lockton, S. Dosage compensation and demasculinization of X chromosomes in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.E.; Moghadam, H.K.; Mank, J.E. Trade-off between selection for dosage compensation and masculinization on the avian Z chromosome. Genetics 2012, 192, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, B.; Coyne, J.A.; Barton, N.H. The relative rates of evolution of sex-chromosomes and autosomes. Am. Nat. 1987, 130, 113–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.P.; Connallon, T. The faster-X effect: Integrating theory and data. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, B.; Campos, J.L.; Jackson, B.C. Faster-X evolution: Theory and evidence from Drosophila. Molec. Ecol. 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtrog, D.; Mank, J.E.; Peichel, C.L.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Otto, S.P.; Ashman, T.L.; Hahn, M.W.; Kitano, J.; Mayrose, I.; Ming, R.; et al. Sex determination: Why so many ways of doing it? PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crow, J.F.; Kimura, M. An introduction to Population Genetics Theory; Alpha Editions: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1970; pp. 173–253. ISBN 0-8087-5968. [Google Scholar]
- Vicoso, B.; Charlesworth, B. Effective population size and the faster-X effect: An extended model. Evol. 2009, 63, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connallon, T. Adaptive protein evolution of X-linked and autosomal genes in Drosophila: Implications for faster-X hypotheses. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 2566–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackton, T.B.; Corbett-Detig, R.B.; Nagaraju, J.; Vaishna, L.; Arunkumar, K.P.; Hartl, D.L. Positive selection drives faster-Z evolution in silkmoths. Evolution 2014, 68, 2331–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeramah, K.R.; Gutenkunst, R.N.; Woerner, A.E.; Watkins, J.C.; Hammer, M.F. Evidence for increased levels of positive and negative selection on the X chromosome versus autosomes in humans. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2267–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvilsom, C.; Qian, Y.; Bataillon, T.; Li, Y.; Mailund, T.; Salle, B.; Carlsen, F.; Li, R.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, T.; et al. Extensive X-linked adaptive evolution in central chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carneiro, M.; Albert, F.W.; Melo-Ferreira, J.; Galtier, N.; Gayral, P.; Blanco-Aguiar, J.A.; Villafuerte, R.; Nachman, M.W.; Ferrand, N. Evidence for widespread positive and purifying selection across the European rabbit (Oryctolagus. cuniculus) genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselle, M.; Faivre, N.; Ballenghien, M.; Galtier, N.; Nabholz, B. Hemizygosity enhances purifying selection: Lack of fast-Z evolution in two satyrine butterflies. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3108–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westergaard, M. The mechanism of sex determination in dioecious flowering plants. Adv. Genet. 1958, 9, 217–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, D. Plant sex chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2016, 67, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopulos, A.S.; Chester, M.; Ridout, K.; Filatov, D.A. Rapid Y-degeneration and dosage compensation in plant sex chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13021–13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, J.; Hollister, J.D.; Wang, W.; Barrett, S.C.; Wright, S.I. Genetic degeneration of old and young Y-chromosomes in the flowering plant Rumex hastatulus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7713–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Na, J.K.; Yu, Q.; Gschwend, A.R.; Han, J.; Zeng, F.; Aryal, R.; VanBuren, R.; Murray, J.E.; Zhang, W.; et al. Sequencing papaya X and Yh chromosomes reveals molecular basis of incipient sex chromosome evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13710–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brothers, A.N.; Delph, L.F. Haldane’s rule is extended to plants with sex chromosomes. Evolution 2010, 64, 3643–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.S.; Filatov, D.A. The large-X effect in plants: Increased species divergence and reduced gene flow on the Silene X-chromosome. Molec. Ecol. 2016, 25, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, G.; Antonovics, J.; Biere, A.; Charlesworth, D.; Delph, L.F.; Filatov, D.; Giraud, T.; Hood, M.E.; Marais, G.A.; McCauley, D.; et al. Silene as a model system in ecology and evolution. Heredity 2009, 103, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasovec, M.; Chester, M.; Ridout, K.; Filatov, D.A. The mutation rate and the age of the sex chromosomes in Silene latifolia. Curr. Biol. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Bergero, R.; Qiu, S.; Forrest, A.; Borthwick, H.; Charlesworth, D. Expansion of the pseudo-autosomal region and ongoing recombination suppression in the Silene latifolia sex chromosomes. Genetics 2013, 194, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Bergero, R.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Campos, J.L.; Cezard, T.; Gharbi, K.; Charlesworth, D. RAD mapping reveals an evolving, polymorphic and fuzzy boundary of a plant pseudoautosomal region. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibalina, M.V.; Filatov, D.A. Plant Y-chromosome degeneration is retarded by haploid purifying selection. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desfeux, C.; Maurice, S.; Henry, J.P.; Lejeune, B.; Gouyon, P.H. Evolution of reproductive systems in the genus Silene. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1996, 263, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 30 March 2017).
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Transdecoder development team. Transdecoder (find coding regions with transcripts). Available online: https://transdecoder.github.io/ (accessed on 28 May 2017).
- Yang, Y.; Smith, S.A. Orthology inference in nonmodel organisms using transcriptomes and low-coverage genomes: Improving accuracy and matrix occupancy for phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevado, B.; Atchison, G.W.; Hughes, C.E.; Filatov, D.A. Widespread adaptive evolution during repeated evolutionary radiations in new world lupins. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, A.J.; Van Dongen, S.; Ouzounis, C.A. An efficient algorithm for large-scale detection of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. Mafft multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loytynoja, A. Phylogeny-aware alignment with PRANK. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1079, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosiol, C.; Holmes, I.; Goldman, N. An empirical codon model for protein sequence evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimodaira, H.; Hasegawa, M. Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimodaira, H.; Hasegawa, M. CONSEL: For assessing the confidence of phylogenetic tree selection. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 1246–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate - a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B Met. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.H.; Nielsen, R.; Goldman, N.; Pedersen, A.M.K. Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 2000, 155, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Nielsen, R.; Yang, Z.H. Evaluation of an improved branch-site likelihood method for detecting positive selection at the molecular level. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Genome Project Data Processing, S. The sequence alignment/map format and samtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The genome analysis toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevado, B. Vcf2fas: Converts vcf file(s) to fasta format. Available online: https://github.com/brunonevado/vcf2fas (accessed on 25 December 2017).
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Ferretti, L.; Raineri, E.; Jené, J.; Marmorini, G.; Burgos, W.; Vera, G. Mstatspop: Statistical analysis using multiple populations for genomic data. Available online: https://bioinformatics.cragenomica.es/numgenomics/people/sebas/software/software.html (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, F. The “effective number of codons” used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer-RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 146, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, J.; Sharp, P.M. Correspondence analysis of codon usage. Available online: http://codonw.sourceforge.net (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- Qiu, S.; Bergero, R.; Zeng, K.; Charlesworth, D. Patterns of codon usage bias in Silene latifolia. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Kumar, S.; Nei, M. A new method of inference of ancestral nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Genetics 1995, 141, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kryazhimskiy, S.; Plotkin, J.B. The population genetics of dN/dS. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, V.; Campos, J.L.; Charlesworth, B. The effects of sex-biased gene expression and X-linkage on rates of adaptive protein sequence evolution in Drosophila. Biol. Lett. 2015, 11, 20150117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.S.; Yang, Z.; Goldman, N.; Nielsen, R. Accuracy and power of statistical methods for detecting adaptive evolution in protein coding sequences and for identifying positively selected sites. Genetics 2004, 168, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.D.; Larracuente, A.M.; Clark, A.G. Contrasting the efficacy of selection on the X and autosomes in Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, B. The role of background selection in shaping patterns of molecular evolution and variation: Evidence from variability on the Drosophila X chromosome. Genetics 2012, 191, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andolfatto, P. Contrasting patterns of X-linked and autosomal nucleotide variation in Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.D.; Macpherson, J.M.; Jensen, J.D.; Petrov, D.A. Similar levels of X-linked and autosomal nucleotide variation in African and non-African populations of Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doust, J.L.; Obrien, G.; Doust, L.L. Effect of density on secondary sex characteristics and sex-ratio in Silene alba (Caryophyllaceae). Am. J. Bot. 1987, 74, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.E.; Shahmahoney, N.; Lombard, L.A. Evolutionary dynamics of sex-ratio and gender dimorphism in Silene latifolia: II. Sex-ratio and flowering status in a potentially male-biased population. J. Her. 1995, 86, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.R. Genetics of sex ratio variation among natural populations of a dioecious plant. Evolution 1999, 53, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, D.L. Optimal sex ratio in Silene alba. Heredity 1967, 22, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J. Mol. Evol. 1986, 24, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akashi, H. Codon bias evolution in Drosophila. Population genetics of mutation-selection drift. Gene 1997, 205, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.R.; Moriyama, E.N. Evolution of codon usage bias in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 1997, 94, 7784–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVean, G.A.; Vieira, J. The evolution of codon preferences in Drosophila: A maximum-likelihood approach to parameter estimation and hypothesis testing. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 49, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; John, A.; Baeza-Centurion, P.; Li, B.; Akashi, H. Codon usage selection can bias estimation of the fraction of adaptive amino acid fixations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatov, D.A. Evolutionary history of Silene latifolia sex chromosomes revealed by genetic mapping of four genes. Genetics 2005, 170, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, S.J.; Filatov, D.A. A cytogenetic view of sex chromosome evolution in plants. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, E.C.; Armstrong, S.J.; Filatov, D.A. Evolution of neo-sex chromosomes in Silene diclinis. Genetics 2009, 182, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergero, R.; Qiu, S.; Charlesworth, D. Gene loss from a plant sex chromosome system. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergero, R.; Forrest, A.; Kamau, E.; Charlesworth, D. Evolutionary strata on the X chromosomes of the dioecious plant Silene latifolia: Evidence from new sex-linked genes. Genetics 2007, 175, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anisimova, M.; Bielawski, J.P.; Yang, Z.H. Accuracy and power of the likelihood ratio test in detecting adaptive molecular evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pie, M.R. The influence of phylogenetic uncertainty on the detection of positive Darwinian selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautenberg, A.; Hathaway, L.; Oxelman, B.; Prentice, H.C. Geographic and phylogenetic patterns in Silene section Melandrium (Caryophyllaceae) as inferred from chloroplast and nuclear DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 57, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slancarova, V.; Zdanska, J.; Janousek, B.; Talianova, M.; Zschach, C.; Zluvova, J.; Siroky, J.; Kovacova, V.; Blavet, H.; Danihelka, J.; et al. Evolution of sex determination systems with heterogametic males and females in Silene. Evolution 2013, 67, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| df | LRT at 5% Significance | LRT at 1% Significance | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | in | X-Linked (PAR Excluded) | Autosomal | X-Linked (PAR Excluded) | Autosomal | ||||||||
| Type | LRT | All | Hemizygous | F-Biased | All | All | Hemizygous | F-Biased | All | ||||
| Genes: | 204 | 41 | 84 | 925 | 204 | 41 | 84 | 925 | |||||
| 2 rate/1 rate | branch | 2 | 18(8.8%) | 5(12.2%) | 7(8.3%) | 73(7.9%) | 11(5.4%) | 1(2.4%) | 4(4.8%) | 55(5.9%) | |||
| M2a/M1a | site | 2 | 12(5.9%) | 3(7.3%) | 5(5.95%) | 84(9.1%) | 5(2.5%) | 1(2.4%) | 2(2.4%) | 49(5.3%) | |||
| M8/M7 | site | 2 | 24(11.8%) | 5(12.2%) | 8(9.5%) | 145(15.7%) | 7(3.4%) | 2(4.9%) | 4(4.8%) | 82(8.9%) | |||
| new model A | br.-site | 1 | 6(2.9%) | 1(2.4%) | 3(3.6%) | 55(5.9%) | 2(0.98%) | 1(2.4%) | 0 | 27(2.9%) | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krasovec, M.; Nevado, B.; Filatov, D.A. A Comparison of Selective Pressures in Plant X-Linked and Autosomal Genes. Genes 2018, 9, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9050234
Krasovec M, Nevado B, Filatov DA. A Comparison of Selective Pressures in Plant X-Linked and Autosomal Genes. Genes. 2018; 9(5):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9050234
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrasovec, Marc, Bruno Nevado, and Dmitry A. Filatov. 2018. "A Comparison of Selective Pressures in Plant X-Linked and Autosomal Genes" Genes 9, no. 5: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9050234
APA StyleKrasovec, M., Nevado, B., & Filatov, D. A. (2018). A Comparison of Selective Pressures in Plant X-Linked and Autosomal Genes. Genes, 9(5), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9050234





