Abstract
This paper presents measurements and analyses of the concentrations of black carbon (BC), particle number concentration (PNC), and PM2.5 (≤2.5 μm) while commuting by ferries in Istanbul. In this context, exposures to the mentioned pollutants were estimated for car ferry, fast ferry, and at the piers, and for two travel routes, for a total of 89 trips. BC, PNC, and PM2.5 measurements were simultaneously performed in a ferry and at the piers, and the correlation between pollutant concentrations, meteorological parameters, and environmental factors were analyzed. The mean concentrations for all pollutants in car ferry were lower than the average concentrations in fast ferry. The concentration ratios of fast ferry to car ferry for BC, PNC, and PM2.5 were 6.4, 1.2, and 1.3, respectively. High variability in the concentrations was observed at the piers and in ferry during berthing. The highest mean concentrations (±standard deviation) of BC (14.3 ± 10.1 µg m−3) and PNC (42,005 ± 30,899 pt cm−3) were measured at Yalova pier. The highest mean concentration (±standard deviation) of PM2.5 (26.1 ± 11.5) was measured at Bostancı pier. It was observed that the main external sources of BC, PNC, and PM2.5 at the piers were road transport, residential heating, and shipping activity. There were no significant correlations between BC, PNC, and PM2.5 in fast ferry, while BC was positively correlated with PNC (r = 0.61, p < 0.01) and PM2.5 (r = 0.76, p < 0.01) in car ferry. At the piers, significant relations between pollutants and meteorological variables were observed. It was noticed that there was no significant difference between summer and winter in ferry and at the pier concentrations of BC, PNC, and PM2.5 except for Yenikapı pier and Bakırköy pier. The highest total exposure to PNC and PM2.5 was in car ferry mode, while the highest total exposure to BC was in fast ferry mode.
1. Introduction
Sea transport is an alternative public transport type in metropolitan cities. Passenger ferries in populous urban port cities are simply another commuting choice, alongside cars, trains, and buses. Passenger ferries provide a faster option to navigate in metropolitan cities. Travelling with fast ferry reduces the commuting time and provides a comfortable trip [1]. Passenger vessels maintain stability over time due to their regular services [2]. Although passenger vessels are not as common as road vehicles and rail systems, the commuter exposure in marine transport is an important issue for passengers due to the high exhaust emission of vessels. The commuters are exposed to air pollutants sourced from passenger vessels during disembarking and boarding. Vessel traffic and passenger shipping are sources of air pollution at the piers [2], shipping-related air pollutants are responsible for cardiopulmonary and lung cancer deaths, with most deaths occurring close to coastlines [3]. There is no sufficient data nor detailed information available on commuter exposure in ferry and at the piers. Most of marine air quality studies are about the determination of emissions from ships. Only a few studies were conducted in ferry. Lau and Chan [4] investigated the volatile organic compound VOC levels in ferry, road transport, and railway, and they revealed that the exposure levels in ferry were the lowest. Chan et al. [5] collected PM10 samples in ferry in Hong Kong, they found PM10 levels in ferries were higher than the air-conditioned roadway transport.
Particles with an aerodynamic diameter smaller than 0.1 µm are defined as ultrafine particles (UFP) [6]. UFP contribute to 90% of particle number concentration (PNC) in urban areas and the major source of UFP is combustion engines [7,8]. Due to the small size of the UFP, it easily causes adverse effects on respiratory and cardiovascular systems [9]. Black carbon (BC), a component of fine particle (PM2.5) [10], causes respiratory diseases including lung cancer [11], and is also considered as the second most major pollutant affecting climate change after CO2 [12]. Compared to PM2.5 (aerodynamic diameter smaller than 2.5 µm), BC has a greater impact on cardiovascular and respiratory morbidity and mortality [13]. The short-term and long-term effects of BC and PM2.5 concentrations with intermediate cardiovascular endpoints were reported [14]. The short-term effects of BC and PM2.5 were heart rhythm abnormalities and increased respiratory symptoms [15,16], while the long-term effects of BC and PM2.5 reported increased coronary artery calcification [17].
The ship emissions at piers/harbors cause the largest PM emissions at low engine loads during stops [18]. The impact on the PM10 concentration from in-port ships was estimated to be +28.9 µg/m3 and this mainly concerned the impact on particles in the size fraction smaller than 1 µm (40%) [19]. Recently, there have been many studies on personal exposure to PM2.5, UFP, and BC [20,21,22,23,24]; however, most of these studies were performed for road transport (buses and personal cars), rail system, and subway. The studies on the measurement of pollutant exposures in marine mass transport is very limited. These limited studies showed that passengers are exposed to air pollutants during the day when they are traveling in vessels and waiting at the piers [5,25,26].
Istanbul city is located in the northwestern Turkey (latitude 41°00′ N, longitude 28°97′ E) with a population of 14.4 million [27], and the Bosphorus that separates the Asian and European continents is located in the middle of the city. Approximately 70% of Istanbul city is surrounded by Marmara Sea, Black Sea, and Istanbul strait. Small passenger vessels are widely used in Istanbul. The Istanbul strait (Bosphorus) separates the city into two parts, and marine transports are mostly preferred between the two sides of the strait to avoid road traffic in rush-hours. The percentage of sea transportation in Istanbul is 3.2% among the urban public transport modes and the total number of people carried on a day is 341,854 [28]. Different types of passenger vessels (slow ferry, fast ferry, car ferry, and water taxi) are used for marine domestic commuting in Istanbul. Fast ferry and car ferry are preferred on the routes that require long travelling time, because they offer more comfort and shorter commuting time in comparison to road transport. Several studies were carried out to determine the concentration of PM10, PM2.5, and particle number in road transport vehicles [29,30] and in the subway [31,32] in Istanbul. This is the first comprehensive study conducted on personal exposure in marine transport where also the relationships between air pollutants and environmental factors are presented. The aim of this study is to determine the in-vessel and outdoor concentrations of BC, PNC, and PM2.5 in fast ferry, car ferry, and at the piers and to investigate the relationship between the pollutants and meteorological parameters.
2. Methodology
2.1. Features of Ferry Modes and Piers
The measurement operation in this study was conducted in Bakırköy-Bostancı fast ferry line and Yenikapı-Yalova car ferry line (Figure 1). Bakırköy-Bostancı line is common for domestic trips with fast ferry, while Yenikapı-Yalova line provides transport from Istanbul to the south of the Marmara Sea with car ferry. Fast ferry has an enclosed space for passengers. Car ferry has two separate areas: Enclosed space to carry passengers and partly enclosed vehicle park area. The number of trips and route characteristics are given in Table 1 and the ferry characteristics are given in Table S1 (see supplementary S1). There is one stop—Kadıköy pier—on the fast ferry route. Kadıköy pier has very intense traffic for slow ferries, which are preferred for short trips. Bakırköy, Bostancı, Yenikapı, and Yalova are terminal piers, which are mostly used for departures of fast ferry and car ferry. The number of departures at the piers varies depending on the season and route and the probable external emission sources at the piers are also different depending on the season (Table S2, see Supplementary S1).
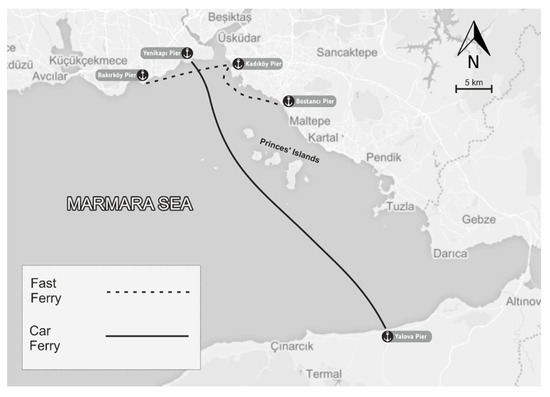
Figure 1.
Routes for fast ferry and car ferry.

Table 1.
The route characteristics.
2.2. Measurement and Instrumentation
The mass concentration of BC, PM2.5, and PNC within a range 10–1000 nm was measured simultaneously, from June 2016 to September 2017 in two different ferry lines (Bakırköy-Bostancı and Yenikapı-Yalova) and four piers (Bakırköy, Bostancı, Yenikapı, and Yalova piers). The measurement process was done as follows: First, the pollutants measurements were carried out for 15 min at the pier. Then, the in-ferry measurements were performed until the end of the ferry route. Lastly, measurements were taken for 15 min at the pier. Similarly, the measurements were performed on the return route. In the fast ferry and car ferry, the researchers were always sitting in the middle of the ferry. The trips were completed by three researchers. The inlets of the instruments were placed at breathing height. Fast ferry and car ferry were powered by diesel engines and they were mechanically ventilated. We had no control over ventilation in ferries. For safety reasons, the passengers in the fast ferry were not allowed to go out during travel, and the door was only opened at the piers. In contrast, the passengers were allowed to go to deck during travel in car ferry.
BC was monitored by using microAeth AE51, a portable aethalometer (AethLabs, USA). The microAeth was operated at a flow rate of 100 mL min−1, the data was recorded every 10 seconds and was outfitted with a 2.5-µm inlet. The filter strips in the AE51 were changed when attenuation value was in the range 75–80. MicroAeth, AE51 has noise (peak and negative values) because of instrument maintenance; measurement sensitivity, such as vibration; humidity; flow rate; and operating conditions. These deviations and negative values are needed for post-processing or smoothing. The optimized noise-reduction averaging (ONA) algorithm (aethlabs.com), which was developed by Hagler et al. [33], was first applied for smoothing the obtained BC data. After post processing, a correction was applied for filter loading [34,35]. Lastly, the data for all trips were checked and the measurements with error signals were excluded, whereof 15% of all data were removed from the analysis.
PNC was monitored with CPC Model 3007 portable condensation particle counter (TSI Inc., Shoreview, MN, USA). The measurement correction for preventing the underestimation of PNC was applied according to Westerdahl et al. (2005) [36] (see Supplementary S3). The pDR 1200 portable real-time aerosol monitor (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, USA) was used to measure PM2.5. The measurement accuracy of pDR 1200 was tested through the reference method. The details of the data processing for BC, correction method for PNC, and the accuracy measurement results for PM2.5 (Figure S4, see Supplementary S3) were given in the previous study conducted by Onat et al. [37]. The calibration of CPC and microAeth was done by the manufacturers.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis of the means of 89 trips for BC, PM2.5, and PNC in two different modes were performed. Pearson correlation coefficients (r) were created to interpret the relation between meteorological variables; trip-averaged concentrations of pollutants, and the pollutant concentrations at the pier. Meteorological data were supplied by the Turkish State Meteorological Service for the following parameters; temperature (°C), wind speed (m sn−1), pressure (mbar), and relative humidity (%), for 1 h time resolution. The monthly average of the meteorological parameters is shown in Table S8 (see Supplementary S1). SPSS Version 20 was used for the statistical analysis. A statistically significant correlation was accepted as p-value < 0.05 and a Student’s t-test was proceeded.
2.4. Exposure Estimation
The personal exposure to pollutants in ferry and at the piers were estimated by Equation 1 [23]. In this study, the ventilation rate for a ferry passenger was assumed as 12.7 L min−1 given by Zuurbier et al. [38] for a bus passenger. The average wait at the pier was assumed to be 5 minutes. The commuter’s exposure per mile and per kilometer was estimated in order to compare exposures from different travel modes according to Equation S1 (see Supplementary S2.)
Commute Exposure (μg) = Concentration (μg/m3) × Time (min) × Inhalation Rate (m3/min)
3. Results and Discussion
The personal exposure to BC, PM2.5, and PNC in ferry and at the piers were measured for 89 trips in two different commuting modes (fast ferry and car ferry) and two different routes, distributed between the winter (40%) and the summer (60%). Knowing that 15% of BC measurements were ignored as they were considered ineligible (e.g., data with error signals or negative values). The overall mean concentrations of BC, PM2.5, and PNC during the trips in ferries and at the piers are given in Table 2. The mean and median concentrations on monthly basis for fast ferry and car ferry are given in Tables S3 and S4, and for the pier they are given in Tables S5 and S6 (see supplementary S1).

Table 2.
Pollutants descriptive in ferry and at the pier.
The results and discussion are presented in four parts as 1) comparison of exposure concentrations and spatial variation in ferry and at the pier are discussed, 2) the relation between pollutants and meteorological parameters were statistically analyzed, 3) the seasonal variation of exposure concentration was discussed, and 4) commute exposure was estimated in ferry and at the pier.
3.1. Concentration in Ferry
Figure 2 shows the mean concentrations and the 10th, 25th, 75th, and the 90th percentiles for BC, PNC, and PM2.5 during the trips and at the piers. The mean concentrations of BC during the trips ranged from 0.3 to 22.9 µg m−3, with the highest values recorded in fast ferry. The trip mean concentrations for PNC ranged from 4807 to 65,311 pt cm−3, and for PM2.5 they ranged from 3.3 to 64.4 µg m−3. The overall mean concentration results showed that the pollutant concentrations in car ferry were lower than the concentrations in fast ferry (Table 2). Our PNC and PM2.5 mean concentration results were lower in comparison with the previous study conducted by Knibbs et al. [25]. They observed that PNC and PM2.5 mean concentrations in ferry were 55,400 pt cm−3 and 58.3 µg m−3, respectively. In Hong Kong, Chan et al. [5] found that the mean concentration of PM10 in ferry was 81 µg m−3 in winter, but they did not mention the ratio of PM2.5 to PM10. In another study conducted in Hong Kong, the mean PM2.5 concentration was found as 60 µg m−3 (three trips only), which is higher compared to road transport modes (bus, car, minibus) [39]. In comparison with the previous study in Istanbul conducted by Onat et al. [37], our PM2.5 results were lower compared to bus, but higher than compared to car (windows closed mode). WHO recommends the 24-h mean guideline value of PM2.5 as 25 µg/m3 for the indoor air of living spaces in residences. However, there is no recommended value of PM2.5 for indoor air of public transport [40].
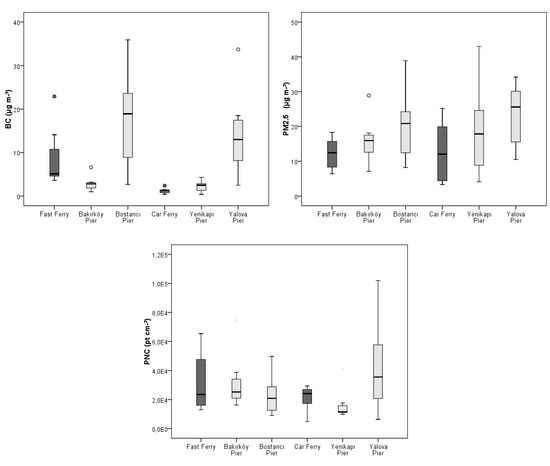
Figure 2.
Boxplot of mean BC, PM2.5, and PNC concentrations for in-ferry and at the pier. The boxes represent the interquartile range (25th to 75th percentile), whiskers represent 10th and 90th percentile, and the middle lines represent the mean values, the circles represent the outliers.
We observed that the mean concentrations of BC in fast ferry and car ferry were 7.7 and 1.2 µg/m3, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, the exposure concentration of BC in ferry was not investigated in the previous studies. We found only one study on BC exposure in canal boats in Bangkok conducted by Velasco et al. [26]. They found that the mean concentrations of BC ranged from 15 to 411 µg m−3 inside canal boats (the surroundings of the boats were open).
We observed that the ratio of fast ferry to car ferry for PNC and PM2.5 were 1.2 and 1.3, respectively. The greatest difference was found for BC with a ratio of 6.4 for fast ferry to car ferry. The in-ferry pollutant concentrations might be affected by the proximity to the city, the number of the stops along the route, and the pollutant concentrations at pier. Figure 3 shows time series of all measured variables measured during round-trips for fast ferry and car ferry. The round trips were split into sections as ‘in-ferry’ and ‘at pier’ for a more detailed analysis. We observed that there were large variations in the concentrations at the piers and in ferry during berthing. The marine vessels are an important source of air pollution at the piers [2], during acceleration-deceleration of ferry vessels, the engine exhaust emissions increase [41]. Kadıköy pier, which is a stop between terminal piers (Bakırköy and Bostancı piers), has the highest ferry activity (Table S2, Supplementary S1). When fast ferry approaches the pier for the passenger boarding-disembarking, the outdoor emissions move to the interior of the ferry with the doors being opened, which can increase the pollutant concentrations inside the ferry. The exhaust sourced from ferry diesel engine could easily go into ferry cabins [42]. It can be seen that the pollutant concentrations in ferry began to drop after the doors were closed. As shown in Figure 3a, BC and PNC values in car ferry reached the peak levels during the opening of the doors at Kadıköy pier. When the doors were closed during the trip, the pollutant values were low, when the doors were opened at Kadıköy pier, the pollutant concentrations increased up to five times. Kadıköy pier, which has dense ferry traffic and also has external emission sources such as road traffic and residential heating, may affect the air quality (Table S2, see supplementary S1). The external sources such as road traffic and outdoor concentration affect the particulate concentrations in vessels [5]. The exhaust emissions from the dense ferry activity around Kadıköy pier can affect the BC concentration levels in the fast ferries. The car ferries do not stop between terminal piers, and there are probably no external sources while travelling along this route. In car ferry, BC and PM2.5 concentrations were steady during travel (Figure 3b). When a car ferry approaches the Yalova terminal pier, PNC is slightly increased, mutatis mutandis, during the return trip. The Yalova-Topçular port is located about 5 km away from the Yalova pier, and shipping activities in the Marmara Sea can affect the PNC levels in the car ferries.
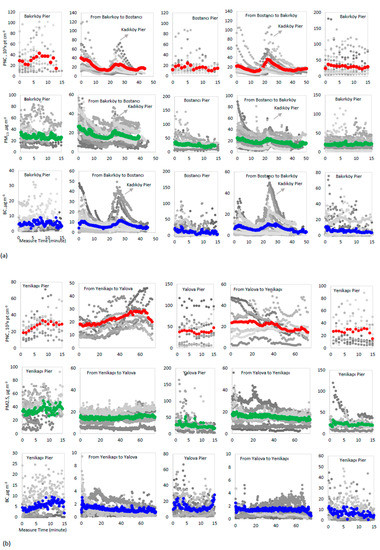
Figure 3.
Time series of the concentrations of black carbon (BC), PM2.5, and particle number concentration (PNC) during trips for (a) fast ferry and (b) car ferry. The mean concentrations of all trips are illustrated with a red line for PNC, a green line for PM2.5 and a blue line for BC. *The gray dots show all of the measurements. The graphs from left to right in Figure 3a show Bakırköy pier, in fast ferry from Bakırköy to Bostancı, Bostancı pier, in fast ferry from Bostancı to Bakırköy, and Bakırköy pier, respectively. The graphs from left to right in Figure 3b show Yenikapı pier, in car ferry from Yenikapı to Yalova, Yalova pier, in car ferry from Yalova to Yenikapı, and Yenikapı pier, respectively.
The exposure concentrations for all pollutants in the car ferries were lower than the corresponding concentrations observed at the piers (Table 2). The fast ferries travel along the coastline of the city, while the car ferries usually travel through the Marmara Sea, far from the city coast. The long travel time and operating of ventilation might cause the lower pollutant concentrations in car ferry. Particulate level is greatly affected by the ventilation system onboard the transport [5].
3.2. Concentration at the Pier
The mean concentrations of the pollutants exhibited large variations at the piers (Figure 2). The daily mean concentrations of BC, PM2.5, and PNC at the piers ranged 0.4–39.4 µg m−3, 4.1–88.6 µg/m3, and 5925–101,886 pt cm−3, respectively. Considering the mean of all measurements, PM2.5 concentrations at the piers were similar, ranging 23.4–26.1 µg m−3, but higher than the PM2.5 concentrations in the ferries. The highest mean concentrations of BC (14.3 ± 10.1 µg m−3) and PNC (42,005 ± 30,899 pt cm−3) were measured at Yalova pier (Table 2). Yalova pier is affected by the ship emissions from Yalova-Topçular port located about 5 km away (Figure S1, see Supplementary S1). The shipping emissions at ports and the size of the shipping vessels are crucial factors to air pollutant emissions [2,19,43]. Furthermore, during loading and unloading operations of car ferry, the emission concentration at the piers increases [44]. Road exhaust emissions have a major impact on the ultrafine fraction of PM [45,46], where UFP constitute more than 90% of the total number of particles in the regions affected by exhaust emissions [8].
Velasco et al. [26] found that the mean BC concentrations of BC at the piers and inside the canal boats were much higher than the urban background concentration of BC. In this study, we observed that the concentration of BC, PNC, and PM2.5 at the piers were similar to or higher than the road transport environment [42]. Our obtained BC results are lower than the concentrations measured at a canal pier in Bangkok, where BC was determined to range 74–136 µg m−3 by Velasco et al. [26].
The ferry activity at the piers is variable (Table S2, see Supplementary S1). The second highest mean concentration of BC (12.3 µg m−3) was measured at the Bostancı pier. Fast ferry traffic is very intense throughout the day in Bostancı pier, since different modes of marine transport are available such as slow ferry and water taxi. Therefore, more than one pier is used in Bostancı. The intense vessel traffic can affect the pollutant concentrations at the piers [2]. If more than two boats approach the pier at the same time, longer-term concentrations may occur during heavy passenger voyages [26] and the time schedules of ferry vessels may increase the level of emission during acceleration-deceleration [41]. The marine transport significantly contributes to air pollution, particularly in coastal areas [3]. Bakirköy is the pier where the ferry traffic is least pronounced, but there is a marina close to this pier (Figure S1, see Supplementary S1).
The location of the piers and their proximity to the external emission sources vary. Therefore, the preliminary evaluation of potential sources of BC, PNC and PM2.5 at the piers were investigated by means of polar plots. Polar plots show the pollutant concentrations by wind direction and wind speed as a continuous surface [47]. Polar plots are given in Figure S2 (see supplementary S1). Our findings are summarized below:
At Bakırköy pier, BC increases toward the NE-E sector, particularly by the influence of moderate and strong winds from NE, and to a minor extent from the E. These findings suggest that BC seems to be related to more residential and main road traffic emissions than to the marine vessel activities at the pier. PM2.5 increases towards the NW, which can be related to external sources such as main roads and urban settlements. PNC increases towards the SW quadrant, these moderate winds from the SW quadrant can be related to marine vessel motors. Yacht marine activities are the main source of PNC at pier.
At the Bostancı pier, BC and PNC increase by the influence of weak winds from South, and this finding indicates that it is caused by local source. PM2.5 increases towards the NNW, particularly by the influence of weak and moderate winds from NNW and moderate winds from NW, which indicate that external sources (such as road traffic) are the main sources of these particles. The main contributions of PM2.5 are the local sources such as road traffic and marine activities.
At Yalova pier, the main contributions to BC are local sources such as marine activities and road traffic, but BC also increases by the influence of strong winds from NNE. Vehicle traffic (loading and unloading operations) at the pier is an important emission source, and exhaust emissions dominate the air pollution concentrations at the pier. The main source of PM2.5 is local, but the concentrations of PM2.5 increase by the influence of moderate winds from N and E, and strong winds from N and NNE. PNC increases by the influence of moderate and strong winds from SEE and the east and east-north. Particularly, moderate winds from the East indicate that the shipping port activities and the road traffic are the main sources of PNC, while strong winds from NE indicate the ship emissions in the Marmara Sea constitute the main source of PNC. However, the emission sources at Yalova pier exhibit large temporal variations.
At Yenikapı pier, polar plots show that the main sources of BC, PM2.5, and PNC are the same. At weak winds, all pollutants increase towards the SW-SE quadrants. These findings suggest that marine activities are the main source of both BC, PNC, and PM2.5. PM2.5 and PNC increase towards the SW, E, and NE. Moderate winds from E and NE indicate that road traffic and residential burning also constitute important sources of particles.
Overall, the polar plot results show that the main external sources at the piers are vehicle exhaust, residential heating, and shipping activity, and they could affect the concentration of BC, PNC, and PM2.5 at the pier.
3.3. Seasonal Variations in Ferry and at the Piers
In this study, the differences between the concentrations in-ferry and at the piers for BC, PNC, and PM2.5 during summer and winter were investigated by using independent-samples t-test. Winter and summer periods were accepted as November–April and May–October, respectively. We observed that there were no significant differences between summer and winter for the pollutant concentrations in fast ferry and in car ferry (Table 3). However, for the Yenikapı pier the difference between summer and winter was statistically significant for all the pollutants, and for the Bakırköy pier the difference was significant for PM2.5. At Yenikapı pier and Bakırköy pier, the pollutant concentrations were in general higher in the winter than in summer. Table 4 shows that there were significant differences in BC, PM2.5, and PNC concentrations at Yenikapı pier and in PM2.5 concentration at Bakırköy pier (p < 0.05). The probable reasons for that might be the ferry activities, more idling of the engines during wintertime, the high vertical mixing height during summertime, and external emission sources at the piers. The polar plots Figure S2 (see Supplementary S1) show that the main sources of BC, PM2.5, and PNC are local (ferry and dock activities close to Yenikapı pier) and external sources (domestic heating and traffic) such as at Yenikapı pier. The number of ferry departures were approximately two times greater in summer than in winter at Yenikapı pier during the study campaign (Table S2, see Supplementary S1), but all pollutant concentrations during winter were higher than during summer at Yenikapı pier. It is probably due to the residential heating contribution and the meteorological conditions in winter such as lower mixing height [48] affecting the concentrations at pier. Unlike Yenikapı pier, there was no difference in the number of ferry departures between summer and winter at Bakırköy pier (Table S2, see Supplementary S1). The main source of PM2.5 at Bakırköy pier is urban settlements (Figure S1), while the main sources of BC and PNC are ferry facilities, marina facilities, and traffic. Domestic heating emissions might contribute to the PM2.5 concentrations in winter.

Table 3.
In-ferry t-test results for the differences between season (mean difference = summer – winter).

Table 4.
At pier t-test results for the differences between season (mean difference = summer – winter).
3.4. Correlations between Pollutants and Meteorology
Table 5 presents the Pearson correlation coefficients for the meteorological parameters (temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure) and PNC, BC, and PM2.5 concentrations for in-ferry and at the pier. There was no observation of any significant correlation between BC, PNC, and PM2.5 in fast ferry. In car ferry, BC was positively correlated with PNC (r = 0.61, p < 0.01) and PM2.5 (r = 0.76, p < 0.01), but there was no significant correlation between PNC and PM2.5. Similar to the results in this study, a previous study conducted by Knibbs et al. [25] did not find any significant correlation between PNC and PM2.5 (r = 0.14, p = 0.72) in ferry.

Table 5.
Pearson correlation coefficients between pollutants trip-averaged concentration and meteorological variables for (a) inside car ferry and passenger ferry, (b) at the pier. Bold numbers indicate significant correlation coefficients at p-values (**: p < 0.01; *: p < 0.05), Grey backgrounds show the correlation coefficients for fast ferry, Yalova pier and Bostancı pier. *** in-ferry values.
We observed significant correlations among the pollutants at Yenikapı pier. PM2.5 was significantly correlated with PNC and BC at Yenikapı and Bakırköy piers, while no correlation was found between these parameters at Yalova and Bostancı piers (Table 5). BC and PNC were highly correlated at Yenikapı pier (r = 0.86, p < 0.01) and moderately correlated at Bostancı pier (r = 0.57, p < 0.01). PNC and PM2.5 were also moderately correlated at Yenikapı pier (r = 0.50, p < 0.05) and Bakırköy pier (r = 0.38, p < 0.05). The reason for these correlations might be due to the similarity of the pollutant sources at the piers, unlike the Yalova pier. At Yenikapı pier, BC, PM2.5, and PNC were significantly correlated with each other, and the main sources of the pollutants were very similar (marine activities and road traffic).
We observed that only BC was correlated with meteorological parameters in ferry. In fast ferry, BC was positively and weakly correlated with temperature (r = 0.30, p < 0.05 for in-ferry temperature; r = 0.37, p < 0.01 for outdoor temperature). BC was negatively and moderately correlated with atmospheric pressure (r = −0.47, p < 0.01). In the previous study, BC was significantly negatively associated with atmospheric pressure in bus and light rail [37]. Furthermore, BC was negatively associated with humidity (r = −0.52, p < 0.05 for car ferry).
At the piers, we observed significant relations between pollutants and meteorological variables. BC was positively and moderately correlated with temperature (r = 0.40, p < 0.05 for Bostancı pier). PNC (r = −0.35) and PM2.5 (r = −0.36) were negatively and weakly associated (p < 0.05) with temperature at Bakırköy pier. Temperature has been reported to be both positively and negatively correlated with BC, PM2.5, and PNC concentrations [37,49,50,51,52]. In vehicle dominated areas, the correlation between PNC and temperature is more likely to be negative due to condensation of volatile compounds in emissions [8]. BC and PNC were negatively correlated with humidity at Yenikapı pier (r = −0.54 and r = −0.53, respectively, p < 0.05). PM2.5 was positively associated with humidity at Bostancı pier (r = 0.45, p < 0.01). BC was negatively and highly correlated with atmospheric pressure at Bostancı pier (r = −0.60, p < 0.01) and weakly correlated at Bakırköy pier (r = −0.35, p < 0.05). Wind speed was not significantly correlated with any of the pollutants, but there was a negative tendency for all pollutants in ferry and at the piers. Wind speed is a significant factor for dilution and transport of exhaust emissions [53]. Knibbs et al. [25] reported that there were no statistically significant correlations between wind speed and UFP or between wind speed and PM2.5 in ferry.
3.5. Correlation between Urban Air and Pier for PM2.5 Concentration
The urban air quality monitoring in Istanbul has been conducted by the Ministry of Environment and Urban Planning. The conventional air pollutants (nitrogen dioxide (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), PM10 and PM2.5) are monitored with real-time monitors located at different sites, there are 38 air quality monitoring stations (AQMS). For PM2.5, we analyzed the relation between the concentration at an AQMS and the concentration at the pier. The nearest AQMS (Figure S3, see Supplementary S1) to the pier were considered for the correlation analysis. The hourly PM2.5 data at the AQMS were paired with PM2.5 concentrations at the pier by calculating the time-weighted average of the matching time period. The correlation results are given in Figure 4. We observed that there were significant correlations between the concentrations at the AQMS and at the piers. Figure 4 shows that the correlation for PM2.5 between Çatladıkapı AQMS and Bakırköy pier was r = 0.62 (p < 0.01). The correlations for PM2.5 between Bostancı pier and the AQMS in Umraniye1 and Umraniye 2 were found as r = 0.569 (p < 0.01) and 0.619 (p < 0.01), respectively.
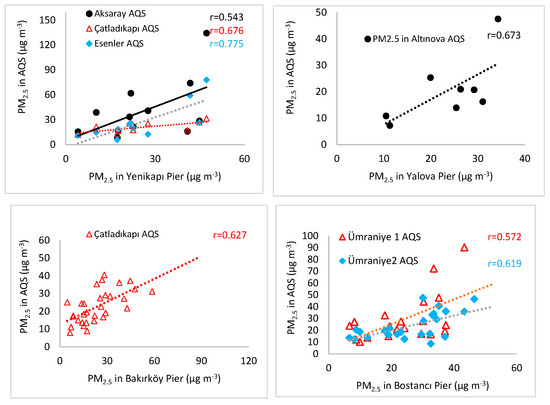
Figure 4.
Scatterplots and Pearson correlation coefficients between the mean concentration of PM2.5 in fixed air quality station (AQS) and the mean concentration of PM2.5 at the piers (Yenikapı, Yalova, Bakırköy, and Bostancı).
For PM2.5, we also observed significant correlations between AQMS and Yenikapı pier, and Yalova pier. The concentration of PM2.5 at Yenikapı pier showed significant correlations with PM2.5 concentrations at Esenler AQMS (r = 0.77, p < 0.01), at Çatladıkapı (r = 0.67, p < 0.05), and at Aksaray AQMS (r = 0.54, p < 0.06). A correlation of (r = 0.673, p < 0.06) between Yalova pier and Altınova AQMS was found. These findings showed that the urban background concentrations could affect the concentration of PM2.5 at the piers.
3.6. Estimation of Commuter Exposure
The means and standard deviations of commuter exposures to PNC, BC, and PM2.5 per mile for in-ferry and at the piers are given in Table 6. The mean concentrations of pollutants provided in Table 2 were used for the calculations. The exposure calculations with median values and exposure per kilometer values are given in Tables S7 and S8, respectively (see Supplementary S1). The highest average exposure per mile for BC was in fast ferry with 0.19 μg mile−1 (0.11 μg km−1). The highest average exposures per mile for PNC and PM2.5 were in car ferry with 6.2 × 108 particles mile−1 (3.88 × 108 particles km−1) and 0.43 μg mile−1 (0.27 μg km−1). When we considered the total exposure during travel in ferry and waiting time at the pier, we explored that the highest total exposure to PNC and PM2.5 were in car ferry mode, while the highest total exposure to BC was in fast ferry mode. In the previous study conducted by Onat et al. [37] in Istanbul, the commuter exposures to PNC, BC, and PM2.5 in road transport (bus, metrobus, car windows open) were estimated higher than the commuter exposure in car ferry and fast ferry. We observed that the commuter exposure to PM2.5 in car ferry and fast ferry were similar to the commuter exposure to this pollutant in the light rail, while the commuter exposures to PNC and BC in fast ferry were estimated higher than the commuter exposures to these pollutants in the light rail.

Table 6.
Exposure concentrations of PNC, BC, and PM2.5 for ferry and pier.
4. Conclusions
The aim of the present study was to investigate the exposure to pollutants for ferry passengers. PNC, BC, and PM2.5 were measured in ferry and at the piers, by using portable devices. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive study on commuter exposure in ferry travel mode. Mean commuter exposure to PNC, BC, and PM2.5 varied with ferry route and the highest pollutant concentrations were observed during berthing. The highest mean exposures per mile for BC and PM2.5 were estimated in fast ferries, while the highest mean exposure per mile for PNC was estimated in car ferries. The seasonal statistically analysis results indicated that there were no significant differences between summer and winter for the pollutant concentrations in fast ferry and in car ferry, while for the Yenikapı pier the difference between summer and winter was statistically significant for all the pollutants. The location of the piers and the main external pollutant sources are important factors in determining commuter exposure at the piers. We also would like to note that there is an existing need for future studies to further investigate the influence of vessel ventilation parameters, ferry technical features, operational efficiency, and fuel type on commuter exposure.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/10/8/439/s1, Figure S1: The location of the piers, Figure S2: Polar plots of analysed air pollutants, Figure S3: Air Quality monitoring stations and the piers, Figure S4: Comparison of Thermo pDR 1200 and Thermo Partisol FRM sampler PM2.5 measurements, Table S1: The ferry characteristics, Table S2: Ferry activity and external emission sources at the piers, Table S3: The mean concentrations in fast ferry and car ferry in the monthly basis, Table S4: The median concentrations in fast ferry and car ferry in the monthly basis, Table S5: The mean concentrations at the pier in the monthly basis, Table S6: The median concentrations at the pier in the monthly basis, Table S7: Exposure concentrations of PNC, BC and PM2.5 (median ± std) for ferry and pier, Table S8: Exposure per/kilometer for PNC, BC and PM2.5. Table S9: Monthly average of meteorological parameters.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.O.; Data curation, Ü.A.Ş., B.U., Ö.A. and F.Ö.; Investigation, B.O., Ü.A.Ş and B.U.; Methodology, B.O. and Ü.A.Ş.; Project administration, B.O. and Ü.A.Ş.; Resources, B.U.; Validation, Ü.A.Ş.; Visualization, C.A.; Writing—review & editing, B.O.
Funding
This research was funded by the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) grant number 115Y263. And this research was funded by the Research Fund of the University of Istanbul grant numbers 25562 and 25952.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Corbett, J.J.; Farrell, A. Mitigating air pollution impacts of passenger ferries. Trans. Res. Part. D Trans. Environ. 2002, 7, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichavska, M.; Tovar, B. Port-city exhaust emission model: An application to cruise and ferry operations in Las Palmas Port. Trans. Res. Part A 2015, 78, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J.; Winebrake, J.J.; Green, E.H.; Kasibhatla, P.; Eyring, V.; Lauer, A. Mortality from ship emissions: A global assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8512–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.L.; Chan, L.Y. Commuter exposure to aromatic VOCs in public transportation modes in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 308, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.Y.; Lau, W.L.; Lee, S.C.; Chan, C.Y. Commuter exposure to particulate matter in public transportation modes in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3363–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles; John Willey & Sons. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report: Working Together for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z.; Jayaratne, E.R.; Keogh, D.U.; Ling, X. Ambient nano and ultrafine particles from motor vehicle emissions: Characteristics, ambient processing and implications on human exposure. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8113–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Fiotakis, K.; Vlachogianni, T. Airborne particulate matter and human health: Toxicological assessment and importance of size and composition of particles for oxidative damage and carcinogenic mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2008, 26, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Report to Congress on Black Carbon; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Fann, N.; Lamson, A.D.; Anenberg, S.C.; Wesson, K.; Risley, D.; Hubbell, B.J. Estimating the national public health burden associated with exposure to ambient PM2.5 and ozone. Risk Anal. Int. J. 2012, 32, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Kinne, S.; Kondo, Y.; Quinn, P.K.; Sarofim, M.C.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; Van Bree, L.; Ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Cassee, F.R.; et al. Black carbon as an additional indicator of the adverse health effects of airborne particles compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirrane, E.F.; Luben, T.J.; Benson, A.; Owens, E.O.; Sacks, J.D.; Dutton, S.J.; Madden, M.; Nichols, J.L. A systematic review of cardiovascular responses associated with ambient black carbon and fine particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, K.E.; Petkau, J.; Vedal, S.; Brauer, M. A case-crossover analysis of particulate air pollution and cardiac arrhythmia in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, K.; Johansson, C.; Forsberg, B. Estimated short-term effects of coarse particles on daily mortality in Stockholm, Sweden. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 120, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.D.; Adar, S.D.; Barr, R.G.; Budoff, M.; Burke, G.L.; Curl, C.L.; Davinglus, M.L.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Gassett, A.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; et al. Association between air pollution and coronary artery calcification within six metropolitan areas in the USA (The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Air Pollution): A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2016, 388, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.A. Exhaust emissions from high speed passenger ferries. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4189–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, F.; Roche, C.; Cazier, F.; Beaugard, C.; Courcot, D. Influence of ship emissions on NOx, SO2, O3 and PM concentrations in a North-Sea harbor in France. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lei, X.N.; Xiu, G.L.; Gao, C.Y.; Gao, S.; Qian, N.S. Personal exposure to black carbon during commuting in peak and off-peak hours in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Reche, C.; Rivas, I.; Minguillón, M.C.; Martins, V.; Vargas, C.; Ealo, M.; Fonseca, A.S.; Amato, F.; Sosa, G.; et al. Urban air quality comparison for bus, tram, subway and pedestrian commutes in Barcelona. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, I.; Kumar, P.; Hagen-Zanker, A.; de Fatima Andrade, M.; Slovic, A.D.; Pritchard, J.P.; Geurs, K.T. Determinants of black carbon, particle mass and number concentrations in London transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, W.; Vijayan, A.; Schulte, N.; Herner, J.D. Commuter exposure to PM2.5, BC, and UFP in six common transport microenvironments in Sacramento, California. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Roth, M.; Velasco, E. Particle exposure and inhaled dose during commuting in Singapore. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibbs, L.D.; de Dear, R.J. Exposure to ultrafine particles and PM2.5 in four Sydney transport modes. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3224–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.; Ho, K.J.; Ziegler, A.D. Commuter exposure to black carbon, carbon monoxide, and noise in the mass transport khlong boats of Bangkok, Thailand. Trans. Res. Part D Trans. Environ. 2013, 21, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TUIK, Turkish Statistical Institute. Available online: http://tuik.gov.tr/Start.do (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- IATR, Istanbul Annual Transportation Report. Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality; 2017. Available online: https://tuhim.ibb.gov.tr/İstatiksel-bilgiler/İbb-ulaşim-raporu-2017/ (accessed on 14 June 2019).
- Onat, B.; Stakeeva, B. Assessment of fine particulate matters in the subway system of Istanbul. Indoor Built Environ. 2012, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, B.; Alver Şahin, Ü.; Sivri, N. The relationship between particle and culturable airborne bacteria concentrations in public transportation. Indoor Built Environ. 2017, 26, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, Ü.A.; Onat, B.; Stakeeva, B.; Ceran, T.; Karim, P. PM10 concentrations and the size distribution of Cu and Fe-containing particles in Istanbul’s subway system. Trans. Res. Part D Trans. Environ. 2012, 17, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, B.; Stakeeva, B. Personal exposure of commuters in public transport to PM2.5 and fine particle counts. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, G.S.; Yelverton, T.L.; Vedantham, R.; Hansen, A.D.; Turner, J.R. Post-processing method to reduce noise while preserving high time resolution in aethalometer real-time black carbon data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T. Controlled generation of black carbon particles from a diffusion flame and applications in evaluating black carbon measurement methods. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1874–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Westerdahl, D.; Wu, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, K.M. On-road emission factor distributions of individual diesel vehicles in and around Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdahl, D.; Fruin, S.A.; Sax, T.; Fine, P.M.; Sioutas, C. Mobile platform measurements of ultrafine particles and associated pollutant concentrations on freeways and residential streets in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3597–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, B.; Şahin, Ü.A.; Uzun, B.; Akın, Ö.; Özkaya, F.; Ayvaz, C. Determinants of exposure to ultrafine particulate matter, black carbon, and PM2.5 in common travel modes in Istanbul. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuurbier, M.; Hoek, G.; Van den Hazel, P.; Brunekreef, B. Minute ventilation of cyclists, car and bus passengers: An experimental study. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lau, C.F.; Tong, V.W.T.; Zhang, K.K.; Westerdahl, D.; Ng, S.; Ning, Z. Assessment of personal integrated exposure to fine particulate matter of urban residents in Hong Kong. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Air Quality Guidelines. Global Update 2005. Particulate Matter; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen, J.P.; Brink, A.; Kalli, J.; Pettersson, H.; Kukkonen, J.; Stipa, T. A modelling system for the exhaust emissions of marine traffic and its application in the Baltic Sea area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9209–9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CATF—Clean Air Task Force. A Multi-City Investigation of Exposure to Diesel Exhaust in Multiple Commuting Modes; CATF Special Report 2007-1; New York, Clean Air Task Force: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alver, F.; Saraç, B.A.; Şahin, Ü.A. Estimating of shipping emissions in the Samsun Port from 2010 to 2015. Atmos. Pol. Res. 2018, 9, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E.; Suner, M. The changing role of diesel oil-gasoil-LPG and hydrogen based fuels in human health risk: A numerical investigation in ferry ship operations. Inter. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boarnet, M.G.; Houston, D.; Edwards, R.; Princevac, M.; Ferguson, G.; Pan, H.; Bartolome, C. Fine particulate concentrations on sidewalks in five Southern California cities. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4025–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, G.; Fuoco, F.C.; Stabile, L. Influential parameters on particle exposure of pedestrians in urban microenvironments. Atmos Environ. 2011, 45, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair-an R package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nazelle, A.; Fruin, S.; Westerdahl, D.; Martinez, D.; Ripoll, A.; Kubesch, N.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. A travel mode comparison of commuters’ exposures to air pollutants in Barcelona. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Determinants of personal exposure to PM2.5, ultrafine particle counts, and CO in a transport microenvironment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4737–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumbach, R.J.; Rich, D.Q.; Gandhi, S.; Amorosa, L.; Schneider, S.; Zhang, J.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; Gong, J.; Lelyanov, O.; Kipen, H.M. Acute changes in heart rate variability in subjects with diabetes following a highway traffic exposure. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 52, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Dufresne, A.; Infante-Rivard, C.; Joseph, L. Determinants of ultrafine particle exposures in transportation environments: Findings of an 8-month survey conducted in Montreal, Canada. J. Exp. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Fennell, P.; Britter, R. Effect of wind direction and speed on the dispersion of nucleation and accumulation mode particles in an urban street canyon. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Vu, T.V.; Beddows, D.C.; Harrison, R.M. Source apportionment of wide range particle size spectra and black carbon collected at the airport of Venice (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2016, 139, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).