Inversion of Nighttime PM2.5 Mass Concentration in Beijing Based on the VIIRS Day-Night Band
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Instrumentation
2.2. Data
2.2.1. PM2.5 Mass Concentration Data
2.2.2. VIIRS DNB Nighttime Light Data
2.2.3. Meteorological Data
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Theoretical Basic
2.3.2. Models
3. Results and Discussion
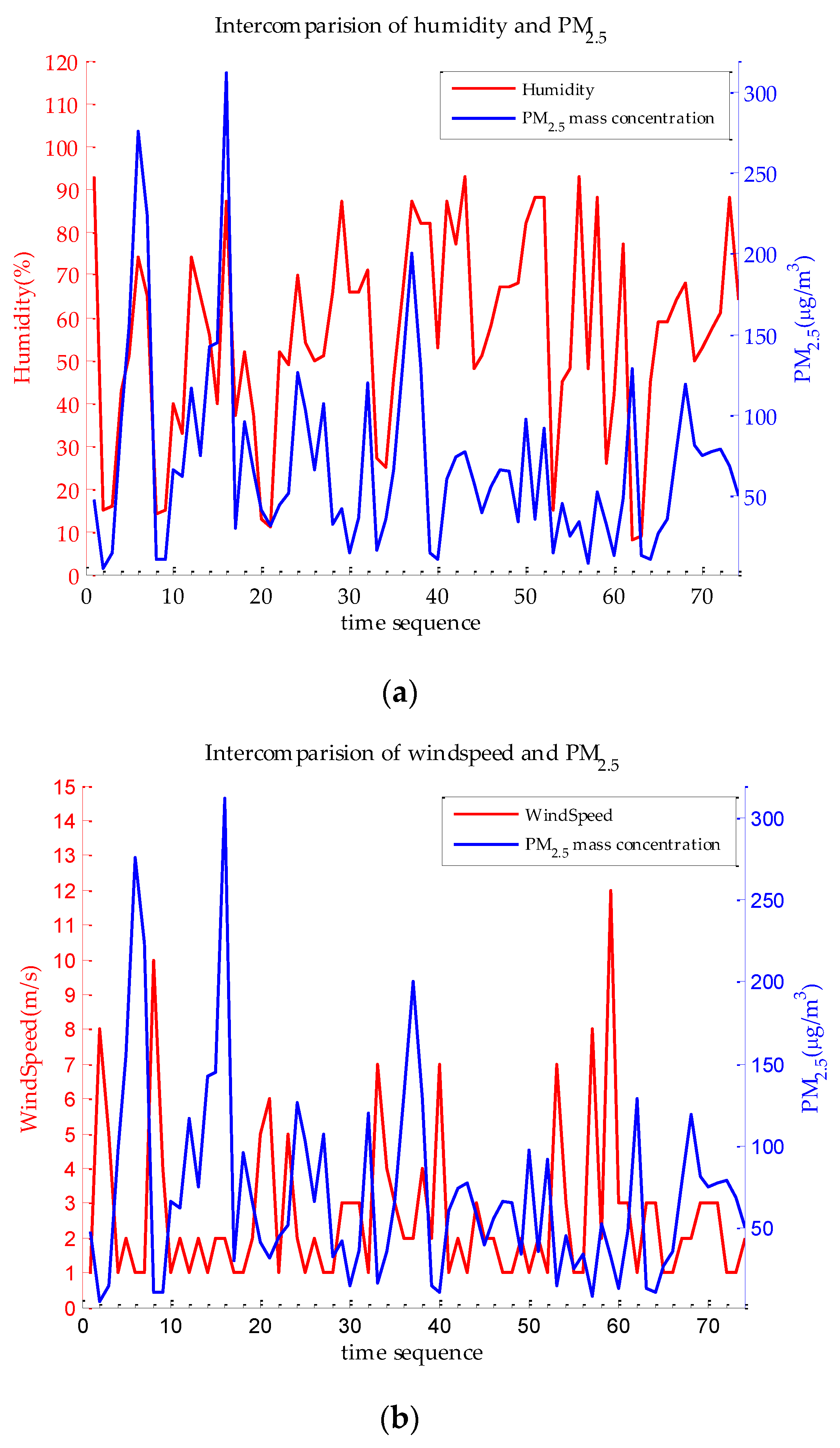
3.1. Analysis of Meteorological Element
3.2. Model Verification
3.3. Relative Humidity Impact Analysis
3.4. Influence of PM2.5 Concentration on the Application Scope of BP Neural Network Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Guideline on Speciated Particulate Monitoring; Report Prepared for U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA; Desert Research Institute: Reno, NV, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.M.; Ma, Y.L.; He, K.B. A brief introduction to PM2.5 and related research. World Environ. 2000, 2000, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gomišček, B.; Hauck, H.; Stopper, S.; Preining, O. Spatial and temporal variations of PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and particle number concentration during the AUPHEP—Project. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3917–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A novel calibration approach of MODIS AOD data to predict PM2.5 concentration. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 9769–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Park, R.J. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 using aerosol optical depth determined from satellite remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cheng, T.H.; Gu, X.F.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Xiang, K. Comparison of four ground-level PM2.5 estimation models using PARASOL aerosol optical depth data from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.D.; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lindsey, D.T.; Lee, T.F.; Hawkins, J.D. Suomi satellite brings to light a unique frontier of nighttime environmental sensing capabilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15706–15711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.E.; Miller, S.D.; Turk, F.J.; Schueler, C.; Julian, R.; Deyo, S.; Dills, P.; Wang, S. The NPOESS VIIRS day/night visible sensor. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Fujita, E.M.; Lu, Z.; Lawson, D.R.; Ashbaugh, L.L. Temporal and spatial variations of PM2.5 and PM10 aerosol in the Southern California air quality study. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 2061–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Xu, X.F.; Fujita, E.M.; Lu, Z.; Lawson, D.R.; Ashbaugh, L.L. Seasonal and diurnal variations of ambient PM2.5 concentration in urban and rural environment in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Review of PM2.5 and PM10 apportionment for fossil fuel combustion and other sources by the chemical mass balance receptor model. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 222–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Aegerter, C.; Xu, X.; Szykman, J.J. Potential application of VIIRS Day/Night Band for monitoring nighttime surface PM2.5 air quality from space. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Estimation of the PM2.5 pollution levels in Beijing based on nighttime light data from the defense meteorological satellite program-operational linescan system. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.; Sioutas, C.; Koutraki, P.; Reiss, R.; Lurmann, F.W.; Roberts, P.T. Evaluation of the TEOM® method for measurement of ambient particulate mass in urban areas. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1997, 47, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijing municipal environmental monitoring center. Available online: http://www.bjmemc.com.cn (accessed on 14 October 2016).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, C.; Wang, F. Assessment of Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership VIIRS emissive band calibration and inter-sensor comparisons. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CalSKY. Available online: http://www.calsky.com (accessed on 14 October 2016).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Keith, D.M.; Tuttle, B.T.; Baugh, K.E. Spectral identification of lighting type and character. Sensors 2010, 10, 3961–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Miller, S.D.; Turk, F.J. Strategy for studying nocturnal aerosol optical depth using artificial lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4599–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Mao, J.T.; Lau, A.K.; Yuan, Z.B.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, X.Y. Application of MODIS satellite product to the air pollution research in Beijing. Sci. China Ser. D 2005, 35, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- An, X.Q.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, Y.S. A modeling analysis of a heavy air pollution episode occurred in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Fang, M.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.; He, K.; Ye, B. The water-soluble ionic composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai and Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| No. | Site | District | Location | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Dingling | Changping | Suburb | 116.170 | 40.287 |
| B | Changping | Changping | Suburb | 116.230 | 40.195 |
| C | Huairou | Huairou | Suburb | 116.643 | 40.394 |
| D | Shunyi | Shunyi | Suburb | 116.720 | 40.144 |
| E | Wanliu | Haidian | Urban | 116.315 | 39.994 |
| F | OlympicCenter | Chaoyang | Urban | 116.407 | 40.003 |
| G | Xigong | Xicheng | Urban | 116.366 | 39.867 |
| H | Tiantan | Dongcheng | Urban | 116.434 | 39.874 |
| I | Dongsi | Dongcheng | Urban | 116.434 | 39.952 |
| J | Nongzhan | Chaoyang | Urban | 116.473 | 39.971 |
| K | Gucheng | Shijingshan | Urban | 116.223 | 39.928 |
| L | Guanyuan | Xicheng | Urban | 116.361 | 39.942 |
| MB | NMB | NME | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple regression model | 10.71 | 18% | 62% | 46.03 |
| BP neural network model | 0.17 | 0.29% | 16% | 14.02 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Shi, H.; Yu, H.; Yang, P. Inversion of Nighttime PM2.5 Mass Concentration in Beijing Based on the VIIRS Day-Night Band. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7100136
Zhao X, Shi H, Yu H, Yang P. Inversion of Nighttime PM2.5 Mass Concentration in Beijing Based on the VIIRS Day-Night Band. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(10):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7100136
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaoran, Hanqing Shi, Hong Yu, and Pinglv Yang. 2016. "Inversion of Nighttime PM2.5 Mass Concentration in Beijing Based on the VIIRS Day-Night Band" Atmosphere 7, no. 10: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7100136
APA StyleZhao, X., Shi, H., Yu, H., & Yang, P. (2016). Inversion of Nighttime PM2.5 Mass Concentration in Beijing Based on the VIIRS Day-Night Band. Atmosphere, 7(10), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7100136






