Moist Orographic Convection: Physical Mechanisms and Links to Surface-Exchange Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Moist Static Instability
2.2. Mountain Airflow Dynamics
2.2.1. Mechanically Forced Flows
2.2.2. Thermally Forced Flows
2.2.3. Parameters Controlling the Dominant Forcing
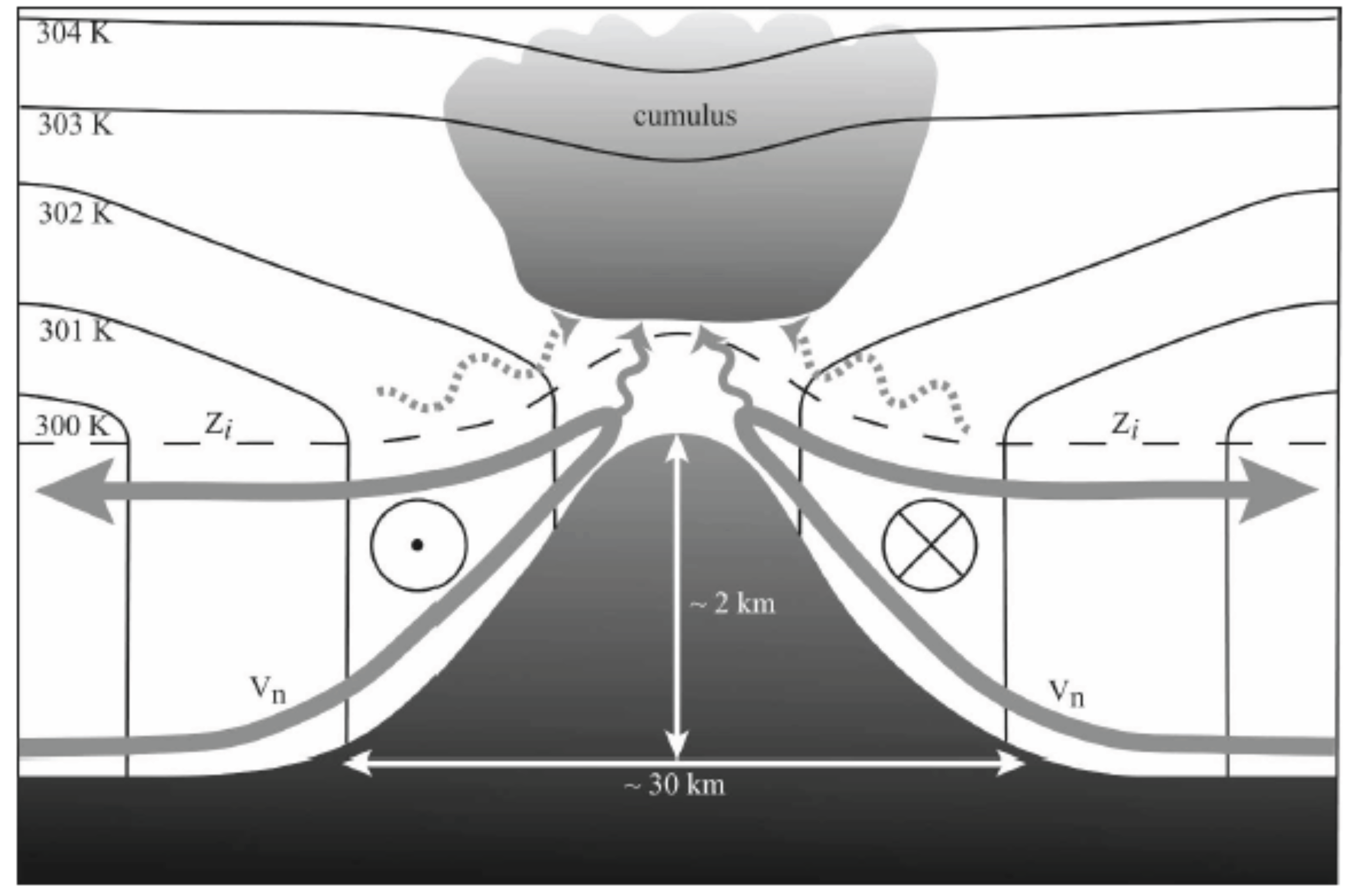
2.2.4. Interactions between Mechanical and Thermal Responses
3. Preconditioning
- CIN must locally equal zero, or sufficient forced lifting must be provided to overcome it,
- CAPE must be sufficient for ascending cloudy thermals to overcome adverse processes that mitigate cloud development.
3.1. Mechanically Forced Convection
3.2. Thermally Forced Convection
3.3. Orographic Impacts on Supercell Storm Environments
4. Trigger Mechanisms
4.1. Mechanical
4.1.1. Direct Orographic Ascent
4.1.2. Upstream Blocking
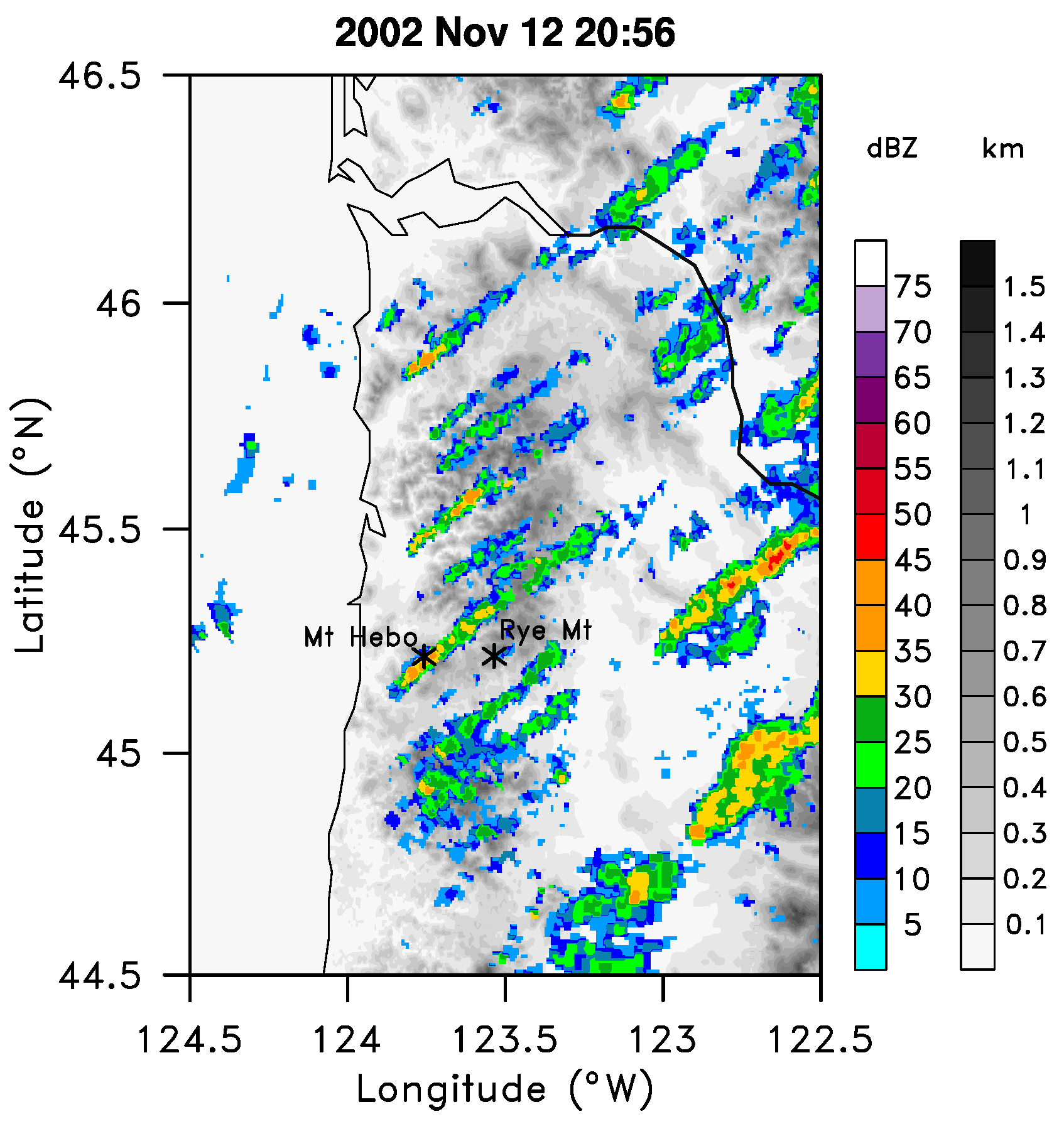
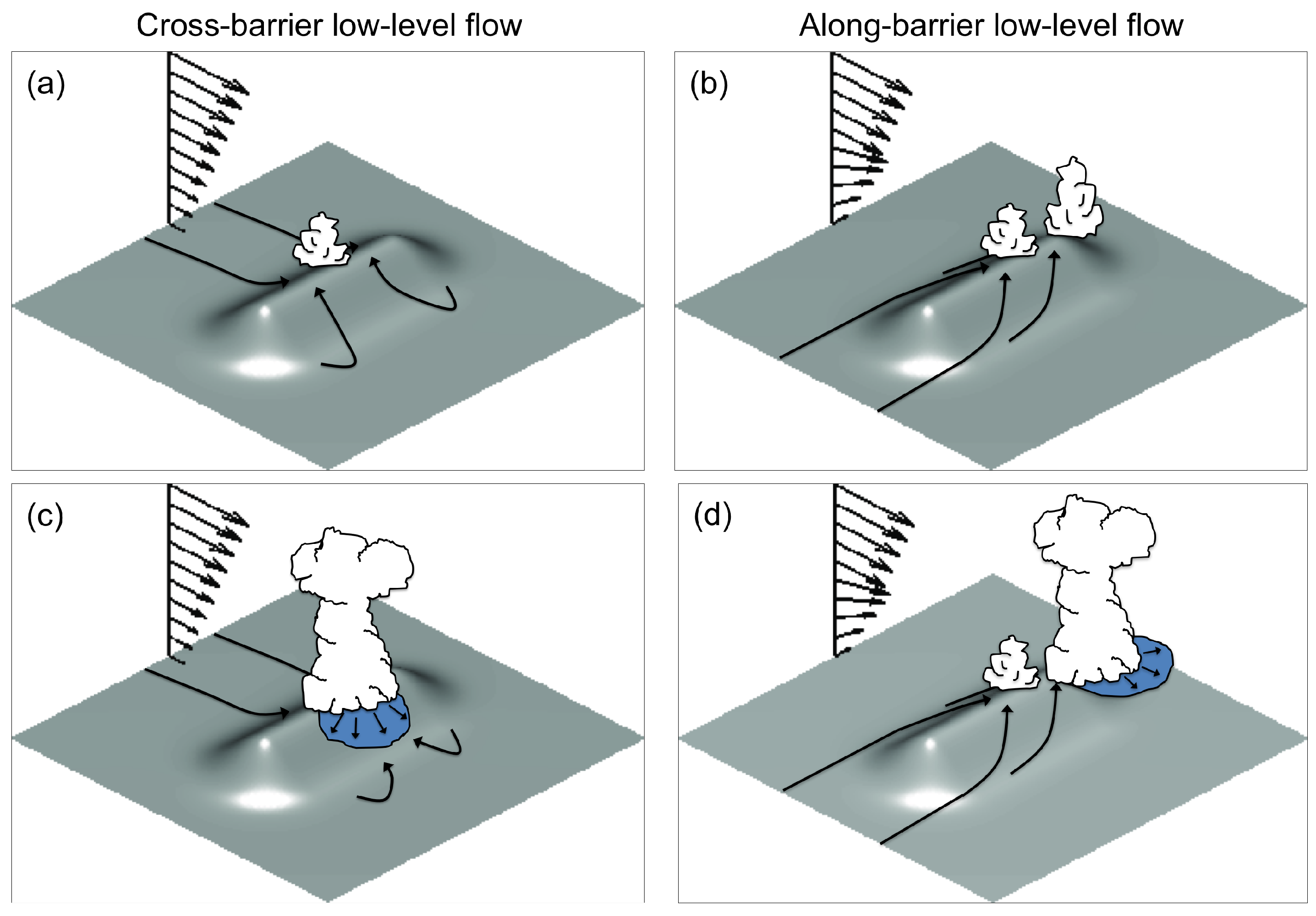
4.1.3. Lee-Side Convergence
4.1.4. Mountain Waves
4.2. Thermal
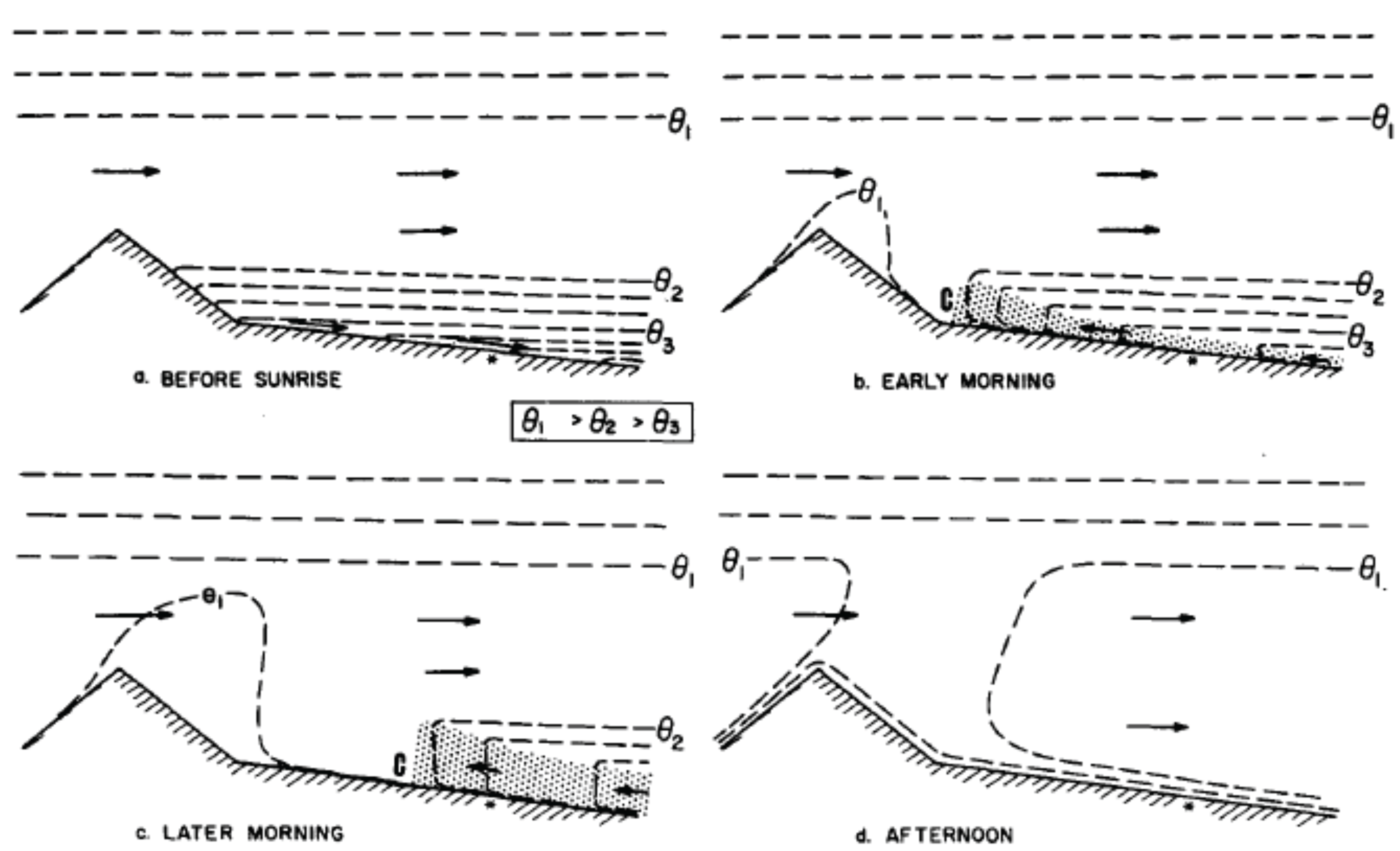
4.2.1. Daytime Flows
4.2.2. Nighttime Flows
4.2.3. Combined Mechanical and Thermal Forcing
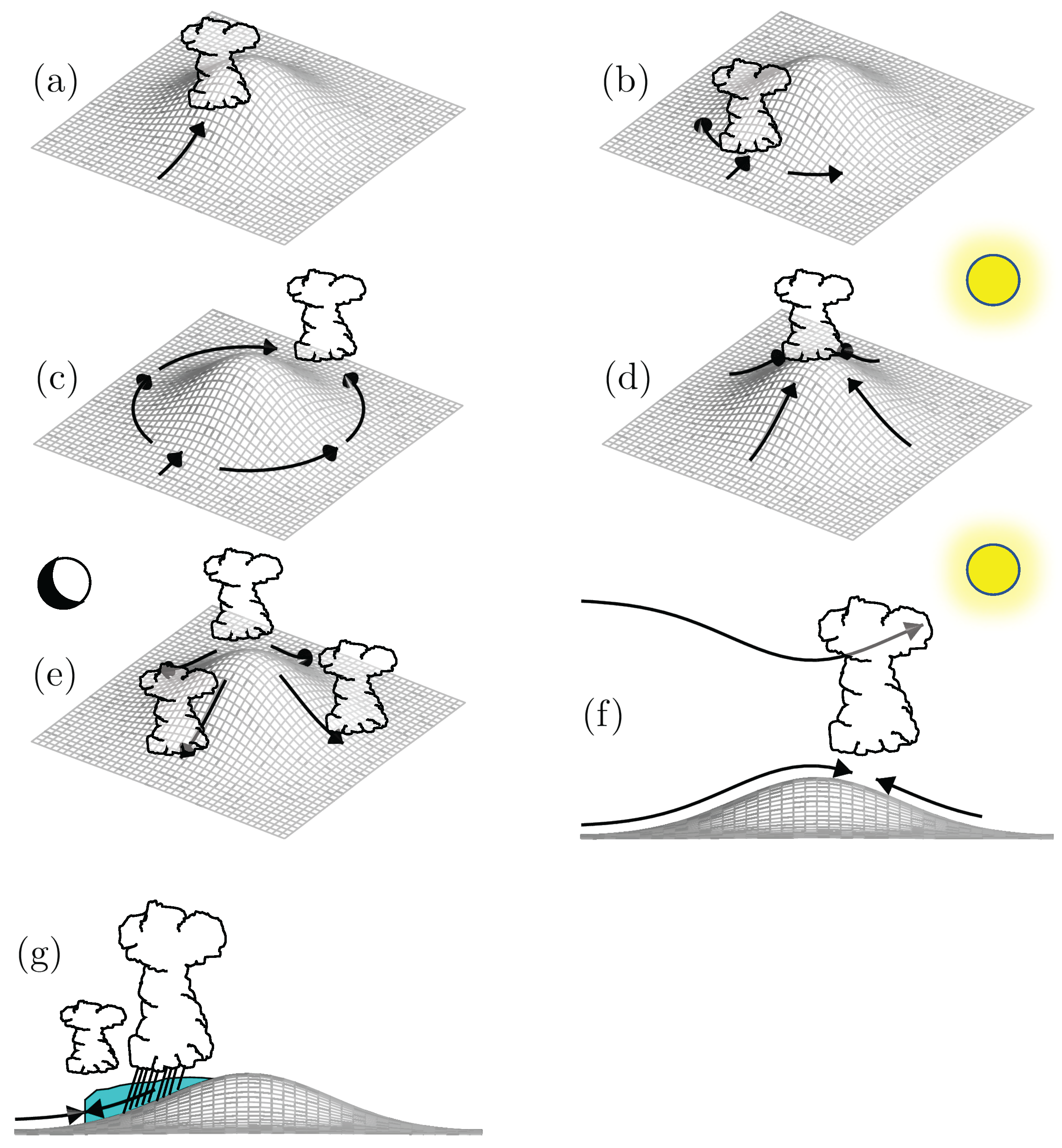
4.2.4. Diabatic Feedbacks
5. Summary and Outlook
5.1. Outstanding Challenges
5.2. Building a Better Understanding
5.2.1. Observations
5.2.2. Numerical Simulations and Theory
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frei, C.; Schär, C. A precipitation climatology of the Alps from high-resolution rain-gauge observations. Int. J. Climatol. 1998, 18, 873–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B.; Barstad, I.; Bonneau, L. Orographic precipitation and Oregon’s climate transition. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B.; Schafer, P.; Kirshbaum, D.J.; Regina, E. Orographic precipitation in the tropics: Experiments in Dominica. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1698–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durran, D.R.; Klemp, J.B. On the effects of moisture on the Brunt-Väisälä frequency. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 39, 2152–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Durran, D.R. Factors governing cellular convection in orographic precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 682–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A. Cloud Dynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; 573p. [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron, T. On the low level redistribution of atmospheric water caused by orography. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cloud Physics, Tokyo and Sapporo-shi, Japan, 24 May–1 June 1965; pp. 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, M.J.; Roach, W.T. Orographic rainfall in warm sectors of depressions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1977, 103, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demko, J.C.; Geerts, B. A numerical study of the evolving convective boundary layer and orographic circulation around the Santa Catalina Mountains in Arizona. Part II: Interaction with deep convection. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B. The influence of mountains on the atmosphere. Adv. Geophys. 1979, 21, 87–230. [Google Scholar]
- Banta, R.M. The role of mountain flows in making clouds. In Atmospheric Processes over Complex Terrain; Meteorological Monographs; American Meteor Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 23, pp. 229–283. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, G.H. Orographic precipitation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2005, 33, 645–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L. Mesoscale Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; 630p. [Google Scholar]
- Houze, R.A. Orographic effects on precipitating clouds. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colle, B.A.; Smith, R.B.; Wesley, D.A. Theory, observations, and predictions of orographic precipitation. In Mountain Weather Research and Forecasting: Recent Progress and Current Challenges; Chow, F.K., De Wekker, S.F., Snyder, B.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 291–344. [Google Scholar]
- Saucier, W.J. Principles of Meteorological Analysis; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1955; 438p. [Google Scholar]
- Bryan, G.H.; Fritsch, J.M. Moist absolute instability: The sixth static stability state. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 1207–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B. Hydrostatic flow over mountains. Adv. Geophys. 1989, 31, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pierrehumbert, R.T.; Wyman, B. Upstream effects of mesoscale mountains. J. Atmos. Sci. 1985, 977–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ólafsson, H.; Bougeault, P. The effect of rotation and surface friction on orographic drag. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Wang, C.C. Boundary layer updrafts driven by airflow over heated terrain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 1425–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, P.A.; Durran, D.R. Estimating topographic blocking using a Froude number when the static stability Is nonuniform. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.J. Calculation of airflow over an arbitrary ridge including diabatic heating and cooling. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisner, J.M.; Smolarkiewicz, P.K. Thermally forced low Froude number flow past three-dimensional obstacles. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J. On upstream blocking over heated mountain ridges. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.; Schär, C. Diabatic modification of airflow over a mesoscale orographic ridge: A model study of the coupled response. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 112, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzi, A.; Tartaglione, N.; Malguzzi, P. Numerical simulations of the 1994 Piedmont flood: Role of orography and moist processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardi, D.; Whiteman, C.D. Diurnal mountain wind systems. In Mountain Weather Research and Forecasting: Recent Progress and Current Challenges; Chow, F.K., De Wekker, S.F., Snyder, B.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 35–119. [Google Scholar]
- Demko, J.C.; Geerts, B. Boundary layer energy transport and cumulus development over a heated mountain: An observational study. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, N.A.; Tucker, D.F. Flow over heated terrain. Part I: Linear theory and idealized numerical simulations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J. On thermally forced circulations over heated terrain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 1690–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, E.P.; Renno, N.O.; Dias, M.A.F.S. Convective circulations induced by surface heterogeneities. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.S.; Parker, D.J. A modeling study and scaling analysis of orographic effects on boundary layer shallow convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Kirshbaum, D.J. Thermally forced convection over a mountainous tropical island. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 2484–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, H.W.; Mobbs, S.D.; Vosper, S.B.; Brown, A.R. The effect of surface heating on hill-induced flow separation. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2008, 129, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, M.; van Baelen, J.; Richard, E. Influence of the wind profile on the initiation of convection in mountainous terrain. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nugent, A.D.; Smith, R.B.; Minder, J.R. Wind speed control of tropical convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 2695–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, S.P.; Hafner, J. The thermal wake of Kauai island: Satellite observations and numerical simulations. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 4568–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Fairman, J.G., Jr. Cloud trails past the Lesser Antilles. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 1425–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.L. Effects of terrain heights and sizes on island-scale circulations and rainfall for the island of Hawaii during HaRP. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 120–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M. Daytime boundary-layer evolution over mountainous terrain. Part I: Observations of the dry circulations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1984, 112, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, P.; Richardson, Y. Mesoscale Meteorology in Midlatitudes; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; 430p. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.K. Near-term effects of the lower atmosphere in simulated northwest flow snowfall forced over the southern Appalachians. Weather Forecast. 2012, 27, 1198–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeaupin, C.; Ducrocq, V.; Giordani, H. Sensitivity of torrential rain events to the sea surface temperature based on high-resolution numerical forecasts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Durran, D.R. Observations and modeling of banded orographic convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 1463–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffourg, F.; Ducrocq, V. Origin of the moisture feeding the heavy precipitating systems over southeastern France. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. 2011, 11, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, S.; Kalthoff, N.; Kottmeier, C. Atmospheric conditions associated with heavy precipitation events in comparison to seasonal means in the western Mediterranean region. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B. A differential model of thermal advection. Mon. Weather Rev. 1982, 110, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenburgh, W.J. One hundred inches in one hundred hours: Evolution of a Wasatch Mountain winter storm cycle. Weather Forecast. 2003, 18, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalthoff, N.; Kohler, M.; Barthlott, C.; Adler, B.; Mobbs, S.D.; Corsmeier, U.; Traumner, K.; Foken, T.; Eigenmann, R.; Krauss, L.; et al. The dependence of convection-related parameters on surface and boundary-layer conditions over complex terrain. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; Kalthoff, N.; Kohler, M.; Handwerker, J.; Wieser, A.; Corsmeier, U.; Kottmeier, C.; Lambert, D.; Bock, O. The variability of water vapour and pre-convective conditions over the mountainous island of Corsica. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, A.; Pal, S.; Aoshima, F.; Bender, M.; Blyth, A.; Corsmeier, U.; Cuesta, J.; Dick, G.; Dorninger, M.; Flamant, C.; et al. Observation of convection initiation processes with a suite of state-of-the-art research instruments during COPS IOP 8b. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adler, B.; Kalthoff, N. Multi-scale transport processes observed in the boundary layer over a mountainous island. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2014, 153, 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baelen, J.; Reverdy, M.; Trido, F.; Labbouz, L.; Dick, G.; Bender, M.; Hagen, M. On the relationship between water vapour field evolution and the life cycle of precipitation systems. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Carreras, L.; Parker, D.J.; Marsham, J.H. What is the mechanism for the modification of convective cloud distributions by land surface-induced flows? J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenegger, C.; Brockhaus, P.; Bretherton, C.S.; Schär, C. The soil moisture-precipitation feedback in simulations with explicit and parameterized convection. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 5003–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Geerts, B. The influence of soil moisture on the planetary boundary layer and on cumulus convection over an isolated mountain. Part I: Observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 1061–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.; Barthlott, C.; Krauss, L.; Kalthoff, N. Soil moisture variability and its influence on convective precipitation over complex terrain. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, C.; Kalthoff, N. A numerical sensitivity study on the impact of soil moisture on convection-related parameters and convective precipitation over complex terrain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 2971–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamovic, A.; Schlemmer, L.; Schär, C. Collective impacts of orography and soil moisture on the soil moisture-precipitation feedback. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A.; Schmid, W.; Fovell, R.G.; Schiesser, H.H. Hailstorms in Switzerland: Left movers, right movers, and false hooks. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 3345–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, P.; Dotzek, N. A numerical study of the effects of orography on supercells. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soderholm, B.; Ronalds, B.; Kirshbaum, D.J. The evolution of convective storms initiated by an isolated mountain ridge. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 1430–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffkneckt, P.; Serafin, S.; Grubisic, V. A long-lived supercell over mountainous terrain. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 2973–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A., Jr.; James, C.N.; Medina, S. Radar observations of precipitation and airflow on the Mediterranean side of the Alps: Autumn 1998 and 1999. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 2537–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Smith, R.B. Orographic precipitation in the tropics: Large-eddy simulations and theory. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 2559–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.; Smith, R.B.; Nugent, A.D. The dynamics of ascent-forced orographic convection in the tropics: results from Dominica. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 4067–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, C.S.; Schroeder, T.A. Trade wind rainfall atop Mount Waialeale, Kauai. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascencio, N.; Stein, J.; Chong, M.; Gheusi, F. Analysis and simulation of local and regional conditions for the rainfall over the Lago Maggiore Target Area during MAP IOP 2b. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 129, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrocq, V.; Nuissier, O.; Ricard, D.; Lebeaupin, C.; Thouvenin, T. A numerical study of three catastrophic precipitating events over western Mediterranean region (southern France). Part II: Mesoscale triggering and stationarity factors. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhner, L.; Nerding, K.N.; Corsmeier, U. Diagnostic study of a HyMeX heavy precipitation event over Spain by investigation of moisture trajectories. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, O.; Schär, C. Embedded cellular convection in moist flow past topography. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 2810–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, D.J.; Kirshbaum, D.J.; Gray, S.L. Under what conditions does embedded convection enhance orographic precipitation? Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 138, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Grant, A.L.M. Invigoration of cumulus cloud fields by mesoscale ascent. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 138, 2136–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniscloux, F.; Creutin, J.D.; Anquetin, S. Geostatistical analysis of orographic rainbands. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1835–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.I.; Gray, S.L.; Kirshbaum, D.J.; Roberts, N.M.; Schultz, D.M.; Fairman, J.G., Jr. The utility of convection-permitting ensembles for the prediction of stationary convective bands. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 1093–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosma, S.; Richard, E.; Miniscloux, F. The role of small-scale orographic features in the spatial distribution of precipitation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 128, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Bryan, G.H.; Rotunno, R.; Durran, D.R. The triggering of orographic rainbands by small-scale topography. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 1530–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Rotunno, R.; Bryan, G.H. The spacing of orographic rainbands triggered by small-scale topography. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 4222–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, O.; Schär, C. Dynamics of orographically triggered banded convection in sheared moist orographic flows. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 3542–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, R.L.; Durran, D.R. Interaction of low-level flow with the western Ghat mountains and offshore convection in the summer monsoon. Mon. Weather Rev. 1984, 112, 652–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, O.; Smull, B.F. Observations and impacts of upstream blocking during a widespread orographic precipitation event. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 129, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.; Houze, R.A. Air motions and precipitation growth in Alpine storms. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 129, 345–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davolio, S.; Volonté, A.; Manzato, A.; Pucillo, A.; Sicogna, A.; Ferrario, M.E. Mechanisms producing different precipitation patterns over north-eastern Italy: Insights from HyMeX-SOP1 and previous events. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, C. Topographically forced convergence in western Washington state. Mon. Weather Rev. 1981, 109, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.I.; Gray, S.L.; Kirshbaum, D.J.; Roberts, N.M.; Schultz, D.M.; Fairman, J.G., Jr. Synoptic versus orographic control on stationary convective banding. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, C.; Adler, B.; Kalthoff, N.; Handwerker, J.; Kohler, M.; Wieser, A. The role of Corsica in initiating nocturnal offshore convection. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffkneckt, P.; Richard, E.; Lambert, D. A highly localized high-precipitation event over Corsica. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durran, D.R. Mountain waves and downslope winds. In Atmospheric Processes over Complex Terrain; Meteorological Monographs; American Meteor Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 23, pp. 59–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tripoli, G.J.; Cotton, W.R. Numerical study of an observed orogenic mesoscale convective system. Part I: Simulated genesis and comparison with observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 273–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B.; Gleason, A.C.; Gluhosky, P.A.; Grubiŝić, V. The wake of St. Vincent. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, S.; Barros, A.P. A numerical study to investigate the relationship between moisture convergence patterns and orography in central Mexico. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1264–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frame, J.; Markowski, P. The interaction of simulated squall lines with idealized mountain ridges. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 1919–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.T.; Orville, H.D. A radar climatology of summertime convective clouds in the Black Hills. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1973, 12, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Schaaf, C.B. Thunderstorm genesis zones in the Colorado Rocky Mountains as determined by traceback of geosynchronous satellite images. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckwerth, T.M.; Wilson, J.W.; Hagen, M.; Emerson, T.J.; Pinto, J.O.; Rife, D.L.; Grebe, L. Radar climatology of the COPS region. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braham, R.R., Jr.; Draginis, M. Roots of orographic cumuli. J. Meteorol. 1960, 17, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.J.; Wilkening, M.H. Mountain-induced convection under fair weather conditions. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.J.; Wilkening, M.H. Flow and mixing in New Mexico cumuli. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 39, 2211–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orville, H.D. A photogrammetric study of the initiation of cumulus clouds over mountainous terrain. J. Atmos. Sci. 1965, 22, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Chen, T.; Somerville, R.C.J. Numerical solution of the Navier-Stokes equations with topography. J. Comput. Phys. 1975, 17, 276–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, C.; Corsmeier, U.; Meissner, C.; Braun, F.; Kottmeier, C. The influence of mesoscale circulation systems on triggering convective cells over complex terrain. Atmos. Res. 2006, 81, 150–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demko, J.C.; Geerts, B. A numerical study of the evolving convective boundary layer and orographic circulation around the Santa Catalina Mountains in Arizona. Part I: Circulation without deep convection. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 1902–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnder, J.A.; Hu, J.; Radzan, A. Evolution of the vertical thermodynamic profile during the transition from shallow to deep convection during CuPIDO 2006. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottmeier, C.; Kalthoff, N.; Barthlott, C.; Corsmeier, U.; van Baelen, J.; Behrendt, A.; Behrendt, R.; Blyth, A.; Coulter, R.; Crewell, S.; et al. Mechanisms initiating deep convection over complex terrain during COPS. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 931–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, L.J.; Blyth, A.M.; Burton, R.R.; Gadian, A.M.; Weckwerth, T.M.; Behrendt, A.; Girolamo, P.D.; Dorninger, M.; Lock, S.J.; Smith, V.H.; et al. Initiation of convection over the Black Forest mountains during COPS IOP15a. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Flamant, C.; Champollion, C.; Hagen, M.; Schmidt, K.; Kiemle, C.; Corsmeier, U.; Barthlott, C.; Di Girolamo, P. Forecasting summer convection over the Black Forest: A case study from the Convective and Orographically-induced Precipitation Study (COPS) experiment. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.B.; Nugent, A.; Minder, J.; Kirshbaum, D.J.; Warren, R.; Lareau, N.; Palany, P.; James, A.; French, J. Orographic precipitation in the tropics: The Dominica Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalthoff, N.; Adler, B.; Barthlott, C.; Corsmeier, U.; Mobbs, S.D.; Crewell, S.; Traumner, K.; Kottmeier, C.; Wieser, A.; Smith, V.; et al. The impact of convergence zones on the initiation of deep convection: A case study from COPS. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, J.E., Jr. On the relationship of convective cooling to nocturnal thunderstorms at Phoenix. Mon. Weather Rev. 1977, 105, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A., Jr.; Geotis, S.G.; Marks, F.D., Jr.; West, A.K. Winter monsoon convection in the vicinity of north Borneo. Part I: Structure and time variation of the clouds and precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1981, 109, 1595–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapes, B.E.; Warner, T.T.; Xu, M. Diurnal patterns of rainfall in northwestern South America: Part III. Diurnal gravity waves and nocturnal convection offshore. MWR 2003, 131, 830–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Kimura, F. Diurnal cycle of convective instability around the central mountains in Japan during the warm season. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.H. Why precipitation is mostly concentrated over islands in the Maritime Continent. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 65, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romatschke, U.; Houze, R.A., Jr. Characteristics of precipitating convective systems in the South Asian monsoon. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romatschke, U.; Houze, R.A., Jr. Characteristics of precipitating convective systems in the premonsoon season of South Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wapler, K.; Lane, T.P. A case of offshore convective initiation by interacting land breezes near Darwin, Australia. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2012, 115, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Carbone, R.E. Offshore propagation of coastal precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 4553–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassim, M.E.; Lane, T.P.; Grabowski, W.W. The diurnal cycle of rainfall over New Guinea in convection-permitting WRF simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Smith, R.B. The detection and significance of diurnal pressure and potential vorticity anomalies east of the Rockies. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 2734–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazón, J.; Pino, D. Nocturnal offshore precipitation near the Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2012, 120, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.K.; Jou, B.J.D. Radar observations of the diurnally forced offshore convective lines along the southeastern coast of Taiwan. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1613–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J. Cloud-resolving simulations of deep convection over a heated mountain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, J.; Barthott, C.; Kalthoff, N. Impact of upstream flow conditions on the initiation of moist convection over the island of Corsica. Atmos. Res. 2014, 145–146, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.M.; Lin, Y.L. Effects of orography on the generation and propagation of mesoscale convective systems in a two-dimensional conditionally unstable flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 3817–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Lin, Y.L. Effects of moist Froude number and CAPE on a conditionally unstable flow over a mesoscale mountain ridge. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglietta, M.M.; Rotunno, R. Numerical simulations of conditionally unstable flows over a ridge. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1865–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglietta, M.M.; Rotunno, R. Numerical simulations of sheared conditionally unstable flows over a mountain ridge. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 1647–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotunno, R.; Klemp, J.B.; Weisman, M.L. A theory for strong, long-lived squall lines. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, T.A. Meteorological analysis of an Oahu flood. Mon. Weather Rev. 1977, 105, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraceña, F.R.; Maddox, R.A.; Hoxit, L.R.; Chappell, C.F. Mesoanalysis of the Big Thompson storm. Mon. Weather Rev. 1979, 107, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, R.S. A review of the theoretical basis for bulk mass flux convective parameterization. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3529–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yano, J.I.; Plant, R.S. Convective quasi-equilibrium. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Fritsch, J.M. The role of the convective “trigger function” in numerical forecasts of mesoscale convective systems. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1992, 49, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, P.; Semane, N.; Lopez, P.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Beljaars, A.; Bormann, N. Representing Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Convection in Large-Scale Models. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 734–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.I.; Geleyn, J.F.; Köhler, M.; Mironov, D.; Quaas, J.; Soares, P.M.M.; Phillips, V.T.J.; Plant, R.S.; Deluca, A.; Marquet, P.; et al. Basic Concepts for Convection Parameterization in Weather Forecast and Climate Models: COST Action ES0905 Final Report. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 88–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Kalthoff, N.; Adler, B.; Pardyiak, E.; Paci, A. High-resolution observation of transport and exchange processes in mountainous terrain. Atmosphere submitted for publication. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khodayar, S.; Raff, F.; Kalthoff, N.; Bock, O. Diagnostic study of a high-precipitation event in the western Mediterranean: Adequacy of current operational networks. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawiarski, C.; Träumner, K.; Knigge, C.; Calhoun, R. Scopes and challenges of dual-doppler Lidar wind measurements—An error analysis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2013, 30, 2044–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, S.; Kalthoff, N.; Wickert, J.; Kottmeier, C.; Dorninger, M. High-resolution representation of the mechanisms responsible for the initiation of isolated thunderstorms over flat and complex terrains: Analysis of CSIP and COPS cases. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2013, 119, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwala, C.; Keis, F.; Kunstmann, H. Real-time data acquisition of commercial microwave link networks for hydrometeorological applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M.; Kunstmann, H.; Zougmore, F.; Cazenave, F.; Leijnse, H.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Chwala, C.; Keis, F.; Doumounia, A.; Boubacar, B.; et al. Improving rainfall measurement in gauge poor regions thanks to mobile telecommunication networks. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, ES49–ES51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühl, J.; Seifert, P.; Wandinger, U.; Baars, H.; Thomas Kanitz, J.S.; Myagkov, A.; Engelmann, R.; Skupin, A.; Heese, B.; Klepel, A.; et al. LACROS: The Leipzig Aerosol and Cloud Remote Observations System. In Proceedings of the Spie Remote Sensing, Dresden, Germany, 23–26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Löhnert, U.; Schween, J.H.; Acquistapace, C.; Ebell, K.; Maahn, M.; Barrera-Verdejo, M.; Hirsikko, A.; Bohn, B.; Knaps, A.; O’Connor, E.; et al. JOYCE: Jülich Observatory for Cloud Evolution. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalthoff, N.; Adler, B.; Wieser, A.; Kohler, M.; Träumner, K.; Handwerker, J.; Corsmeier, U.; Khodayar, S.; Lambert, D.; Kopmann, A.; et al. KITcube: A mobile observation platform for convection studies deployed during HyMeX. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitalla, T.; Bauer, H.S.; Wulfmeyer, V.; Zängl, G. Systematic errors of QPF in low-mountain regions as revealed by MM5 simulations. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panosetti, D.; Böing, S.; Schlemmer, L.; Schmidli, J. Idealized large-eddy and convection-resolving simulations of moist convection over mountainous terrain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 4021–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. The predictability of a flow which possesses many scales of motion. Tellus 1969, 21, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Snyder, C.; Rotunno, R. Effects of moist convection on mesoscale predictability. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirshbaum, D.J.; Adler, B.; Kalthoff, N.; Barthlott, C.; Serafin, S. Moist Orographic Convection: Physical Mechanisms and Links to Surface-Exchange Processes. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030080
Kirshbaum DJ, Adler B, Kalthoff N, Barthlott C, Serafin S. Moist Orographic Convection: Physical Mechanisms and Links to Surface-Exchange Processes. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(3):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030080
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirshbaum, Daniel J., Bianca Adler, Norbert Kalthoff, Christian Barthlott, and Stefano Serafin. 2018. "Moist Orographic Convection: Physical Mechanisms and Links to Surface-Exchange Processes" Atmosphere 9, no. 3: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030080
APA StyleKirshbaum, D. J., Adler, B., Kalthoff, N., Barthlott, C., & Serafin, S. (2018). Moist Orographic Convection: Physical Mechanisms and Links to Surface-Exchange Processes. Atmosphere, 9(3), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030080





