Physico-chemical Characteristics of Corrosion Scales from Different Pipes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Water Quality
2.3. Scale Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics
3.1.1. Apparent Description
3.1.2. Micromorphology
3.1.3. Surface Area and Porosity
3.2. Chemical Characteristics
3.2.1. Elemental Composition
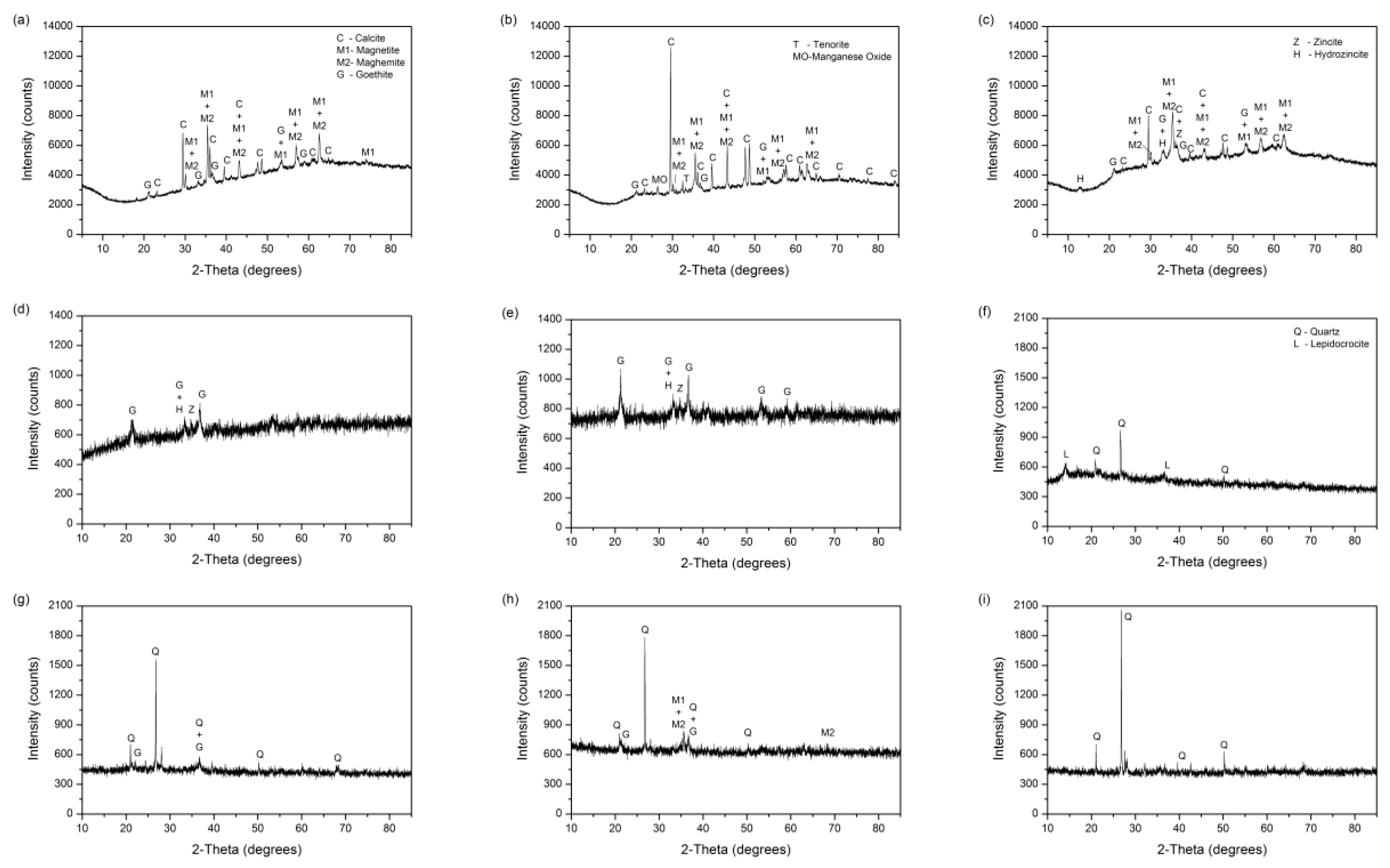
3.2.2. Crystalline Compounds
4. Discussion
4.1. Pipe Materials
4.2. Water Sources
4.3. Structures of Corrosion Scales
4.4. Hydraulic Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuovinen, O.H.; Button, K.S.; Vuorinen, A.; Carlson, L.; Mair, D.M.; Yut, L.A. Bacterial, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics of tubercles in distribution pipelines. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1980, 72, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.A.; Sorg, T.J.; Frietch, C. Accumulation of arsenic in drinking water distribution systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5365–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, P.; Snoeyink, V.L.; Bebee, J.; Jim, K.K.; Beckett, M.A.; Kriven, W.M.; Clement, J.A. Iron release from corroded iron pipes in drinking water distribution systems: Effect of dissolved oxygen. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, P.; Snoeyink, V.L.; Lytle, D.A.; Kriven, W.M. Iron corrosion scales: Model for scale growth, iron release, and colored water formation. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.A.; Dietz, J.D.; Mutoti, G.; Taylor, J.S.; Randall, A.A.; Cooper, C.D. Red water release in drinking water distribution systems. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2005, 97, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.A.; Dietz, J.D.; Mutoti, G.; Xiao, W.Z.; Taylor, J.S.; Desai, V. Optimizing source water blends for corrosion and residual control in distribution systems. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2006, 98, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerke, T.L.; Maynard, J.B.; Schock, M.R.; Lytle, D.L. Physiochemical characterization of five iron tubercles from a single drinking water distribution system: Possible new insights on their formation and growth. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2030–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schock, M.R.; Hyland, R.N.; Welch, M.M. Occurrence of contaminant accumulation in lead pipe scales from domestic drinking water distribution systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4285–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Herrera, J.E. Characteristics of lead corrosion scales formed during drinking water distribution and their potential influence on the release of lead and other contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6054–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Korshin, G.V.; Valentine, R.L.; Hill, A.S.; Friedman, M.J.; Reiber, S.H. Characterization of elemental and structural composition of corrosion scales and deposits formed in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4570–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Hill, A.S.; Friedman, M.J.; Valentine, R.L.; Larson, G.S.; Romero, A.M.Y.; Reiber, S.H.; Korshin, G.V. Occurrence of trace inorganic contaminants in drinking water distribution systems. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2012, 104, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, T.L.; Little, B.J.; Luxton, T.P.; Scheckel, K.G.; Maynard, J.B. Strontium concentrations in corrosion products from residential drinking water distribution systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5171–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Masters, S.; Edwards, M.A.; Falkinham, J.O.; Pruden, A. Effect of disinfectant, water age, and pipe materials on bacterial and eukaryotic community structure in drinking water biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Liu, Z.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Hai, Y. Characteristics of iron corrosion scales and water quality variations in drinking water distribution systems of different pipe materials. Water Res. 2016, 106, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueman, B.F.; Gagnon, G.A. Understanding the role of particulate iron in lead release to drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9053–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, T.E.; King, R.M. Corrosion by water at low flow velocity. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1954, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, T.E.; Skold, R.V. Corrosion and tuberculation of cast iron. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1957, 49, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Obrecht, M.F.; Pourbaix, M. Corrosion of metals in potable water systems. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1967, 59, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, P.; Snoeyink, V.L.; Bebee, J.; Kriven, W.M.; Clement, J.A. Physico-chemical characteristics of corrosion scales in old iron pipes. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.T.; Wu, G.X.; Guan, Y.T. Effect of bacterial communities on the formation of cast iron corrosion tubercles in reclaimed water. Water Res. 2015, 71, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Shi, B.Y.; Gu, J.N.; Wang, D.S.; Yang, M. Morphological and physicochemical characteristics of iron corrosion scales formed under different water source histories in a drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5423–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.J.; Hong, S.; Xiao, W.Z.; Taylor, J. Characteristics of iron corrosion scales established under blending of ground, surface, and saline waters and their impacts on iron release in the pipe distribution system. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 322–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.P.; Ellaway, M.; Adrien, R. Study of corrosion material accumulated on the inner wall of steel water pipe. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 2065–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontheimer, H.; Kolle, W.; Snoeyink, V.L. The siderite model of the formation of corrosion-resistant scales. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1981, 73, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, A.A.; Genin, J.M.R.; Bauer, P. Hyperfine interactions and structures of ferrous hydroxide and green rust II in sulfated aqueous media. Hyperfine Interact. 1988, 41, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drissi, H.; Refait, P.; Genin, J.M.R. The oxidation of Fe(OH)2 in the presence of carbonate ions: Structure of carbonate green rust one. Hyperfine Interact. 1994, 90, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Abdelmoula, M.; Genin, J.M.R. Mechanisms of formation and structure of green rust one in aqueous corrosion of iron in the presence of chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swietlik, J.; Raczyk-Stanislawiak, U.; Piszora, P.; Nawrocki, J. Corrosion in drinking water pipes: The importance of green rusts. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, T.E.; Skold, R.V. Laboratory studies relating mineral quality of water to corrosion of steel and cast iron. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1958, 14, 285–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Z.; Schonberger, K.D.; Peng, C.Y.; Ferguson, J.F.; Desormeaux, E.; Meyerhofer, P.; Luckenbach, H.; Korshin, G.V. Effects of blending of desalinated and conventionally treated surface water on iron corrosion and its release from corroding surfaces and pre-existing scales. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Liu, Z.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Wu, Y.Y. Effect mechanism of flow velocity on iron release from pipe surfaces in drinking water distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 37th IAHR World Congress, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–18 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Dzombak, D.A. Effects of simple organic acids on sorption of Cu2+ and Ca2+ on goethite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.P.; Koopal, L.K.; Hiemstra, T.; Meeussen, J.C.L.; Van Riemsdijk, W.H. Interactions of calcium and fulvic acid at the goethite-water interface. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boxall, J.B.; Dewis, N. Identification of discolouration risk through simplified modelling. In Proceedings of the World Water and Environmental Resources Congress, Anchorage, AK, USA, 15–19 May 2005; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Boxall, J.B.; Saul, A.J. Modeling discoloration in potable water distribution systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, J.B.; Prince, R.A. Modelling discolouration in a Melbourne (Australia) potable water distribution system. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2006, 55, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Boxall, J.B. Discolouration in potable water distribution systems: A review. Water Res. 2007, 41, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husband, S.; Boxall, J.B. Discolouration risk management for trunk mains. Water Distrib. Syst. Anal. 2010, 2010, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, R.L.; Smith, C.J.; Boxall, J.B.; Biggs, C.A. Pilot scale laboratory investigations into the impact of steady state conditioning flow on potable water discolouration. Water Distrib. Syst. Anal. 2010, 2010, 494–506. [Google Scholar]
- Fabbricino, M.; Korshin, G.V. Changes of the corrosion potential of iron in stagnation and flow conditions and their relationship with metal release. Water Res. 2014, 62, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Pipe ID | Sample ID | Pipe Material | Pipe Diameter (cm) | Pipe Age (Years) | Water Source | Service Position | Sampling Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1# | Unlined cast iron | 8.0 | 20 | Groundwater | Experimental water delivery system | / |
| 2# | Hybrid pipe | ||||||
| 3# | Galvanized iron | ||||||
| B | 4# | Galvanized iron | 3.5 | 20 | Groundwater | Service pipes | Screw section |
| 5# | Straight section | ||||||
| C | 6# | Unlined cast iron | 100 | 30 | Surface water | Trunk mains | Inner layer of corrosion tubercle |
| 7# | Middle layer of corrosion tubercle | ||||||
| 8# | Outer layer of corrosion tubercle | ||||||
| 9# | Flaky scale |
| Water Sources | pH | Hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | Turbidity (NTU) | SO42− (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | Al (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tsinghua University | Groundwater | 7.93 | 196.2 | 0.32 | 50.0 | 18.6 | <0.02 |
| Zhengzhou City | Yellow River | 7.98 | 235.8 | 0.19 | 85.6 | 54.2 | 0.07 |
| Danjiangkou Reservoir | 8.05 | 155.5 | 0.22 | 41.1 | 18.8 | 0.07 | |
| Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (×103 cm3/g) | Pore Size (Å) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET a | BJH b | BJH b | BET a | BJH b | ||
| Pipe B | 4# | 123.0 | 100.5 | 219.0 | 58.6 | 87.2 |
| 5# | 170.1 | 89.4 | 174.1 | 40.0 | 77.9 | |
| Pipe C | 6# | 50.5 | 59.7 | 87.8 | 54.0 | 58.8 |
| 7# | 81.7 | 87.3 | 104.6 | 41.4 | 47.6 | |
| 8# | 77.4 | 87.4 | 98.4 | 41.3 | 45.0 | |
| 9# | 31.8 | 36.7 | 58.0 | 73.3 | 62.6 | |
| Elemental Composition (mg/g) | Fe | Ca | Zn | S | Al | Si | Mg | Mn | Pb | K | P | Na | Ti | Cu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe A | 1# 2# 3# | 554.3 283.4 386.5 | 41.7 185.8 23.4 | 0.8 3.1 158.9 | 0.5 1.0 1.8 | 0.2 0.8 0.9 | 3.4 5.8 4.8 | 1.0 3.4 1.2 | 2.7 3.1 1.5 | 0.6 8.5 2.5 | 0.1 0.7 0.2 | / / / | / 0.2 0.1 | / 2.2 / | 1.0 0.5 0.4 |
| Pipe B | 4# 5# | 648.9 612.8 | 1.0 0.6 | 31.3 14.6 | 4.6 4.3 | 0.1 0.1 | 1.7 1.3 | 0.4 / | 0.3 0.2 | 0.3 0.2 | 0.1 0.1 | 0.8 0.3 | 0.2 0.2 | / / | / / |
| Pipe C | 6# 7# 8# 9# | 337.4 211.4 316.8 254.2 | 5.7 2.4 3.2 8.7 | 0.1 0.1 0.1 / | 68.7 11.2 5.7 15.7 | 3.9 6.4 6.3 2.8 | 1.2 1.6 0.8 1.6 | 1.9 2.5 2.3 1.7 | 2.1 0.2 0.6 1.5 | / / / / | 1.1 2.0 2.0 0.8 | 0.8 1.8 1.5 0.8 | 0.6 0.7 0.9 0.2 | 0.2 0.4 0.3 0.1 | / / / / |
| Chemical Composition (%) | Magnetite (Fe3O4) | Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) | Goethite (α-FeOOH) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe A | 1# 2# 3# | 17 46 32 | 29 22 26 | 54 32 42 |
| Pipe B | 4# 5# | 9 0 | 35 24 | 56 76 |
| Pipe C | 6# 7# 8# 9# | 35 28 27 20 | 26 29 27 38 | 39 43 46 42 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Physico-chemical Characteristics of Corrosion Scales from Different Pipes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Water 2018, 10, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070931
Li M, Liu Z, Chen Y. Physico-chemical Characteristics of Corrosion Scales from Different Pipes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Water. 2018; 10(7):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070931
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Manjie, Zhaowei Liu, and Yongcan Chen. 2018. "Physico-chemical Characteristics of Corrosion Scales from Different Pipes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems" Water 10, no. 7: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070931
APA StyleLi, M., Liu, Z., & Chen, Y. (2018). Physico-chemical Characteristics of Corrosion Scales from Different Pipes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Water, 10(7), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070931




