Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Conditions in Kenyan Rural Schools: Are Schools Meeting the Needs of Menstruating Girls?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
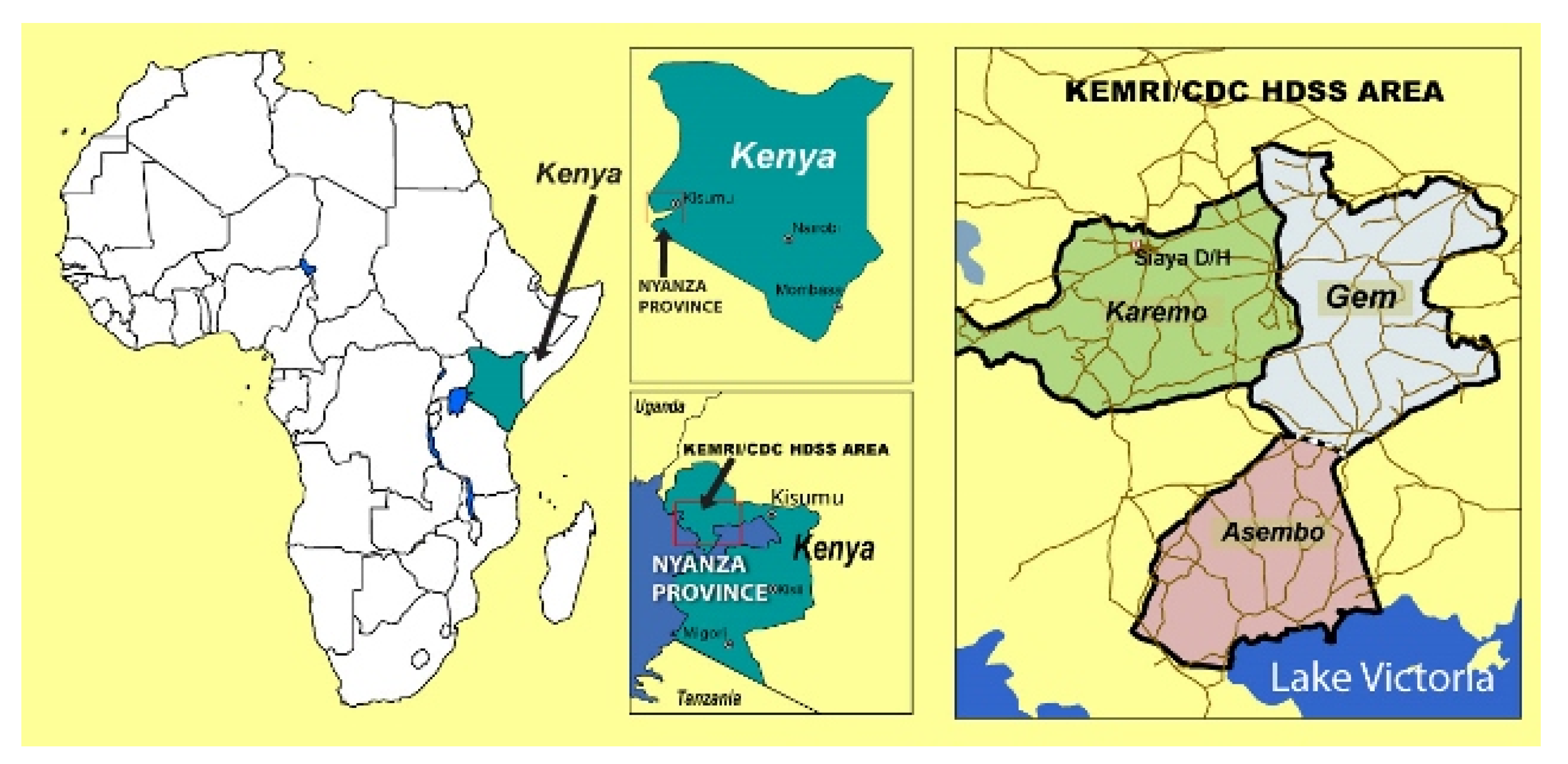
2.1. Study Site and Population
2.2. Study Design and School Sampling
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Definitions of Indicators
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics and School Population
3.2. WASH Facilities
3.3. WASH Facilities and MHM for Menstruating Girls
3.4. WASH Support from Non-governmental organizations (NGOs)
| Indicator | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| OBSERVED | ||
| Girls | ||
| Washing water provided for girls | 8 (13) | |
| Girl: latrine ratio ≤ 25:1 | 25 (40) | |
| Private place for girls to change | 20 (32) | |
| Separate latrine block for girls | 52 (84) | |
| Girls and Boys | ||
| Standard pupil: latrine ratio for boys and girls | 16 (25) | |
| Latrine cleaning supplies | 8 (13) | |
| Handwashing water available | 41 (66) | |
| Handwashing facility at school | 47 (75) | |
| Soap at handwashing station | 1 (2) | |
| REPORTED | ||
| Girls | ||
| Washing water provided for girls | ||
| Always | 30 (49) | |
| Sometimes | 7 (11) | |
| Never | 25 (40) | |
| Sanitary pads provided at school | ||
| Always | 6 (10) | |
| Sometimes | 17 (27) | |
| Never | 39 (63) | |
| Boys and Girls | ||
| Water availability at school | ||
| Always | 40 (64) | |
| Sometimes | 8 (13) | |
| Never | 14 (23) | |
| Soap provided at school | ||
| Always | 6 (10) | |
| Sometimes | 4 (6) | |
| Never | 52 (84) | |
| Schools Reported Receiving Water or Handwashing Intervention from NGO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | Yes | No | ||
| N (%) | N (%) | P | RR (CI) | |
| OBSERVED LATRINES | n=550 | n=248 | ||
| Good latrine structure, lock on door and clean | 101 (18) | 31 (13) | 0.05* | 1.5 (1.0, 2.1) |
| OBSERVED SCHOOLS | n=43 | n=19 | ||
| Handwashing water available for pupils | 36 (84) | 6 (32) | <0.001* | 2.7 (1.4, 5.2) |
| Handwashing facility at school | 37 (86) | 10 (53) | 0.01* | 1.6 (1.1, 2.5) |
| REPORTED SCHOOLS | n=43 | n=19 | ||
| Handwashing water available today | 34 (79) | 10 (53) | 0.07 | 1.5 (1.0, 2.4) |
| Water for handwashing is “always” available | 32 (74) | 8 (42) | 0.03* | 1.8 (1.0, 3.1) |
| Washing water provided for girls | 27 (63) | 3 (16) | 0.001* | 4.0 (1.4, 11.6) |
| Schools Reported Receiving Latrines from NGO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | Yes | No | ||
| N (%) | N (%) | P | RR (CI) | |
| OBSERVED LATRINES | n=440 | n=358 | ||
| Good latrine structure, no lock on door | 319 (73) | 244 (68) | 0.21 | 1 (1.0, 1.2) |
| Good latrine structure, lock on door | 94 (21) | 87 (24) | 0.37 | 0.9 (0.7, 1.1) |
| Good latrine structure, lock on door and clean | 69 (16) | 57 (16) | 1.00 | 1 (0.7, 1.3) |
| Ventilated Improved Pit latrines (VIP)† | 122 (28) | 25 (7) | <0.001* | 4.1 (2.7, 6.1) |
| OBSERVED SCHOOLS | n=32 | n=28 | ||
| Good pupil latrine ratio | 7 (22) | 9 (32) | 0.55 | 0.7 (0.3, 1.6) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosure
References
- United Nations. The Millennium Development Goals Report 2013; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, Y. Making education a priority in the post-2015 development agenda. In Report of the Global Thematic Consultation on Education in the Post-2015 Development Agenda; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. water, Sanitation and Hygiene Standards for Schools in Low-cost Settings; Adams, J., Bartram, J., Chartier, Y., Sims, J., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fewtrell, L.; Prüss-Üstün, A.; Bos, R.; Gore, F.; Bartram, J. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: Quantifying the Health Impact at National and Local Levels in Countries with Incomplete Water Supply and Sanitation Coverage; WHO Environmental Burden of Disease Series No. 15; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Garrett, V.; Ogutu, P.; Mabonga, P.; Ombeki, S.; Mwaki, A.; Aluoch, G.; Phelan, M.; Quick, R.E. Diarrhoea prevention in a high-risk rural Kenyan population through point-of-use chlorination, safe water storage, sanitation, and rainwater harvesting. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairncross, S.; Hunt, C.; Boisson, S.; Bostoen, K.; Curtis, V.; Fung, I.C.H.; Schmidt, W.P. Water, sanitation and hygiene for the prevention of diarrhoea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, M.; Desai, M.; Elimelech, M. Assessment of latrine use and quality and association with risk of trachoma in rural Tanzania. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 104, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, I.C.H.; Cairncross, S. Ascariasis and handwashing. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Harris, J.R.; Juliao, P.; Nygren, B.; Were, V.; Kola, S.; Sadumah, I.; Faith, S.H.; Otieno, R.; Obure, A.; et al. Impact of a hygiene curriculum and the installation of simple handwashing and drinking water stations in rural Kenyan primary schools on student health and hygiene practices. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, D.A.P.; Guyatt, H.L. Schools for health: Focus on health, education and the school-age child. Parasitol. Today 1996, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, C.E.; Freeman, M.C.; Ravani, M.; Migele, J.; Mwaki, A.; Ayalo, M.; Ombeki, S.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Quick, R. The impact of a school-based safe water and hygiene programme on knowledge and practices of students and their parents: Nyanza Province, western Kenya, 2006. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Blanton, E.; Ombeki, S.; Oluoch, G.; Mwaki, A.; Wannemuehler, K.; Quick, R. Evaluation of the role of school children in the promotion of point-of-use water treatment and handwashing in schools and households—Nyanza Province, western Kenya, 2007. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, K.E.; Okello, G.; Turner, E.L.; Njagi, K.; McHaro, C.; Kengo, J.; Allen, E.; Dubeck, M.M.; Jukes, M.C.H.; Brooker, S.J. Impact of intermittent screening and treatment for malaria among school children in Kenya: A cluster randomised trial. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.; Ma, H.; Ou, J.; Billhimer, W.; Long, T.; Mintz, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Luby, S. A cluster-randomized controlled trial evaluating the effect of a handwashing-promotion program in Chinese primary schools. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Talaat, M.; Afifi, S.; Dueger, E.; El-Ashry, N.; Marfin, A.; Kandeel, A.; Mohareb, E.; El-Sayed, N. Effects of hand hygiene campaigns on incidence of laboratory-confirmed influenza and absenteeism in schoolchildren, Cairo, Egypt. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 619–625. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, M.C.; Greene, L.E.; Dreibelbis, R.; Saboori, S.; Muga, R.; Brumback, B.; Rheingans, R. Assessing the impact of a school-based water treatment, hygiene and sanitation programme on pupil absence in Nyanza Province, Kenya: A cluster-randomized trial. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2012, 17, 380–391. [Google Scholar]
- Dreibelbis, R.; Greene, L.E.; Freeman, M.C.; Saboori, S.; Chase, R.P.; Rheingans, R. Water, sanitation, and primary school attendance: A multi-level assessment of determinants of household-reported absence in Kenya. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2013, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garn, J.V.; Greene, L.E.; Dreibelbis, R.; Saboori, S.; Rheingans, R.D.; Freeman, M.C. A cluster-randomized trial assessing the impact of school water, sanitation and hygiene improvements on pupil enrollment and gender parity in enrollment. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2013, 3, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M. Structural factors influencing menstruating school girls’ health and well-being in Tanzania. Comp. J. Comp. Int. Educ. 2012, 43, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, L.; Nyothach, E.; Alexander, K.; Odhiambo, F.O.; Eleveld, A.; Vulule, J.; Rheingans, R.; Laserson, K.F.; Mohammed, A.; Phillips-Howard, P.A. We keep it secret so no one should know—A qualitative study to explore young schoolgirls attitudes and experiences with menstruation in rural western Kenya. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79132. [Google Scholar]
- McMahon, S.; Winch, P.; Caruso, B.; Obure, A.; Oguti, E.; Ochari, I.; Rheingans, R. The girl with her period is the one to hang her head Reflections on menstrual management among schoolgirls in rural Kenya. Int. Health Hum. Rights 2011, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, T.; Fernandes, M. Menstrual hygiene in South Asia: A neglected issue for WASH (water, sanitation and hygiene) programmes. Gend. Dev. 2010, 18, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.; Lloyd, C.; Mensch, B. Menstruation and school absenteeism: Evidence from rural Malawi. Comp. Educ. Rev. 2013, 57, 260–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, E.; Shordt, K.; Krukkert, I. School Sanitation and Hygiene Eduation: Results from the Assessment of a Six-country Pilot Project; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA; IRC: Delft, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- House, S.; Mahon, T.; Cavill, S. Menstrual Hygiene Matters: A Resource for Improving Menstrual Hygiene around the World. Available online: http://www.wateraid. org/what-we-do/our-approach/research-and-publications/view-publication?id=02309d73–8e41–4d04-b2ef-6641f6616a4f&sc_lang=en (accessed on 3 January 2014).
- Jasper, C.; Le, T.-T.; Bartram, J. Water and sanitation in schools: A systematic review of the health and educational outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2772–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, J.; Okal, J.; Kabiru, C.W.; Zulu, E.M. Emotional and psychosocial aspects of menstrual poverty in resource-poor settings: A qualitative study of the experiences of adolescent girls in an informal settlement in Nairobi. Health Care Women Int. 2013, 34, 891–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpter, C.; Torondel, B. A systematic review of the health and social effects of menstrual hygiene management. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.; Kjellén, M.; Pensulo, C. Girls’ and women’s unmet needs for menstrual hygiene management (MHM): The interactions between MHM and sanitation systems in low-income countries. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M. Ideologies of sexuality, menstruation and risk: Girls’ experiences of puberty and schooling in northern Tanzania. Cult. Health Sex. 2009, 11, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips-Howard, P.A. Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Liverpool, UK. Unpublished work. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Odhiambo, F.O.; Laserson, K.F.; Sewe, M.; Hamel, M.J.; Feikin, D.R.; Adazu, K.; Ogwang, S.; Obor, D.; Amek, N.; Bayoh, N.; et al. Profile: The KEMRI/CDC health and demographic surveillance system—Western Kenya. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omwami, E.M.; Omwami, R.K. Public investment and the goal of providing universal access to primary education by 2015 in Kenya. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2009, 30, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, J.; Kaburu, A.; Limboro, C.; Kimutai, A. Are our children learning? Annual Learning Assessment Report; Uwezo Kenya: Nairobi, Kenya, 2012. Available online: http://www.pokot.org/ wp-content/uploads/2012/05/Uwezo-20111.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2013).
- Alexander, K.T.; Dreibelbis, R.; Freeman, M.C.; Ojeny, B.; Rheingans, R. Improving service delivery of water, sanitation, and hygiene in primary schools: A cluster-randomized trial in western Kenya. J. Water Health 2013, 11, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, S.; Mwaki, A.; Porter, S.E.; Okech, B.; Freeman, M.C.; Rheingans, R.D. Sustaining school hand washing and water treatment programmes: Lessons learned and to be learned. Waterlines 2011, 30, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Kenya. National School Health Policy; Government of Kenya: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009.
- Sommer, M. Putting menstrual hygiene management on to the school water and sanitation agenda. Waterlines 2010, 29, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.; Vasquez, E.; Worthington, N.; Sahin, M. WASH in schools empowers girls’ education. In Proceedings of the Menstrual Hygiene Management in Schools Virtual of the Conference 2012, New York, NY, USA, 27 September 2012.
- Luby, S.P.; Kadir, M.A.; Yushuf Sharker, M.A.; Yeasmin, F.; Unicomb, L.; Sirajul Islam, M. A community-randomised controlled trial promoting waterless hand sanitizer and handwashing with soap, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2010, 15, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.; Cobb, E.; Donachie, P.; Judah, G.; Curtis, V.; Schmidt, W.-P. The effect of handwashing with water or soap on bacterial contamination of hands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, K.; Mwaki, A.; Caruso, B.; Ochari, I.; Freeman, M.; Saboori, S.; Dreibelbis, R.; Rheingans, R. An Evaluation of the Financial Mangement of SWASH+ Programs in SWASH+ Primary Schools; IRC: Delft, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 14. Available online: http://www.ircwash.org/resources/evaluation-financial-management-wash-programs-swash-plus-primary-schools-swash-plus (accessed on 4 February 2014).
- Birdthistle, I.; Dickson, K.; Freeman, M.; Javidi, L. What Impact does the Provision of Separate Toilets for Girls at Schools have on their Primary and Secondary School Enrolment, Attendance and Completion? A Systematic Review of the Evidence; EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, Institute of Education, University of London: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- UNICEF. Raising even more Clean Hands: Advancing Health, Learning and Equity through WASH in Schools; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Snel, M. The Worth of School Sanitation and Hygiene Education; IRC International Water and Sanitation Centre: Delft, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- IRC; UNICEF. Towards Effective Programming for WASH in Schools: A Manual for Scaling up Programmes for Water, Sanitation and Hygiene in Schools; IRC Internation Water and Sanitation Centre: Delft, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Adukia, A. Sanitation and Education; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. Available online: http://scholar.harvard.edu/files/adukia/files/adukia_sanitation_and_education.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexander, K.T.; Oduor, C.; Nyothach, E.; Laserson, K.F.; Amek, N.; Eleveld, A.; Mason, L.; Rheingans, R.; Beynon, C.; Mohammed, A.; et al. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Conditions in Kenyan Rural Schools: Are Schools Meeting the Needs of Menstruating Girls? Water 2014, 6, 1453-1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6051453
Alexander KT, Oduor C, Nyothach E, Laserson KF, Amek N, Eleveld A, Mason L, Rheingans R, Beynon C, Mohammed A, et al. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Conditions in Kenyan Rural Schools: Are Schools Meeting the Needs of Menstruating Girls? Water. 2014; 6(5):1453-1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6051453
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexander, Kelly T., Clifford Oduor, Elizabeth Nyothach, Kayla F. Laserson, Nyaguara Amek, Alie Eleveld, Linda Mason, Richard Rheingans, Caryl Beynon, Aisha Mohammed, and et al. 2014. "Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Conditions in Kenyan Rural Schools: Are Schools Meeting the Needs of Menstruating Girls?" Water 6, no. 5: 1453-1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6051453
APA StyleAlexander, K. T., Oduor, C., Nyothach, E., Laserson, K. F., Amek, N., Eleveld, A., Mason, L., Rheingans, R., Beynon, C., Mohammed, A., Ombok, M., Obor, D., Odhiambo, F., Quick, R., & Phillips-Howard, P. A. (2014). Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Conditions in Kenyan Rural Schools: Are Schools Meeting the Needs of Menstruating Girls? Water, 6(5), 1453-1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6051453




