Performance of a Novel Fertilizer-Drawn Forward Osmosis Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor (FDFO-MBR): Mitigating Salinity Build-Up by Integrating Microfiltration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
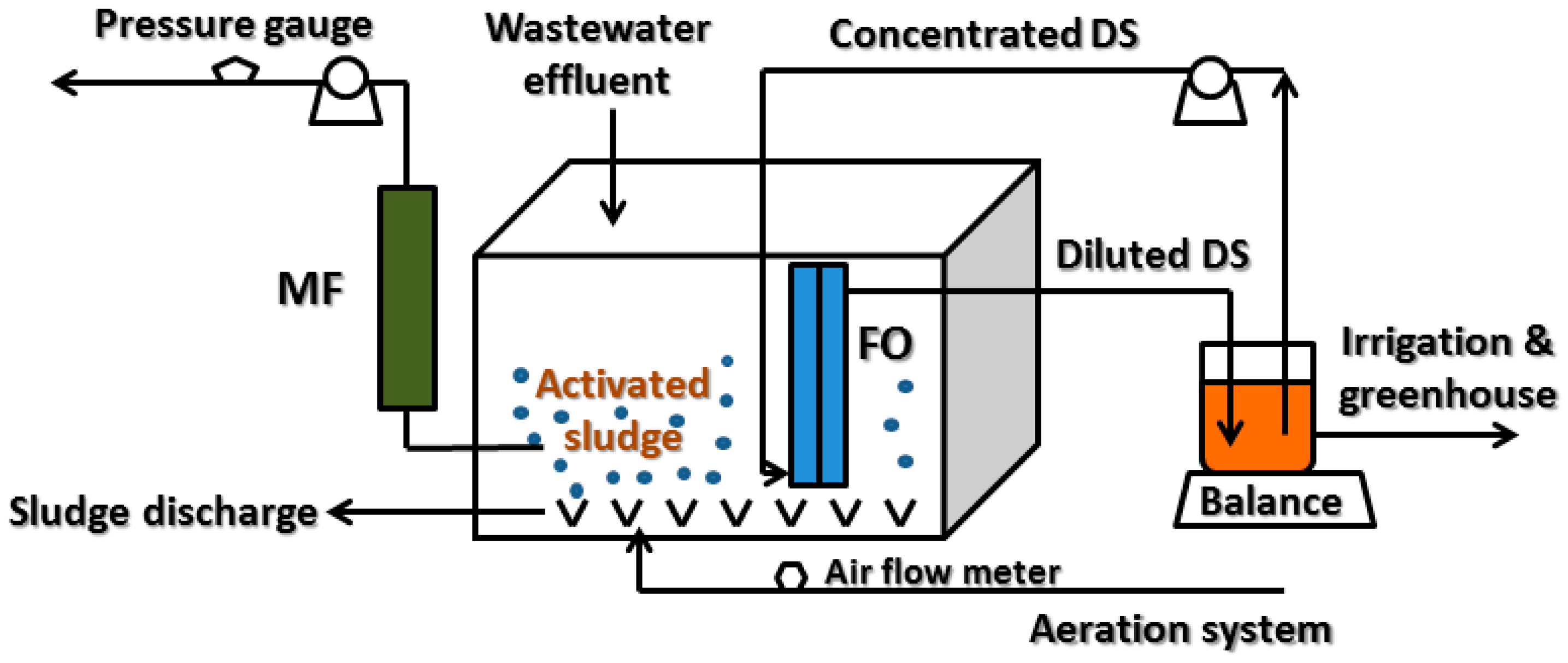
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
2.2. Chemicals and Operation Conditions
2.3. Analytical Methods
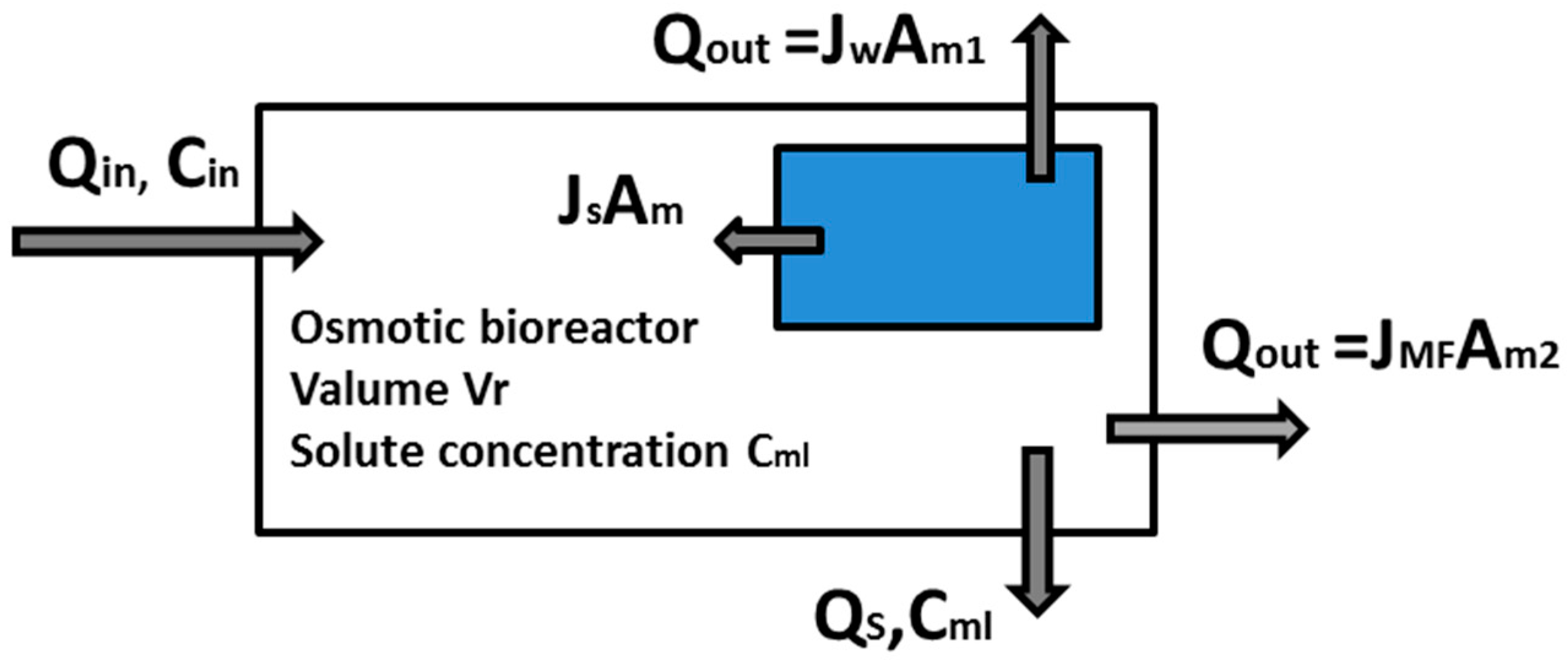
2.4. Mass Balance in the OMBR-MF System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Process Parameters
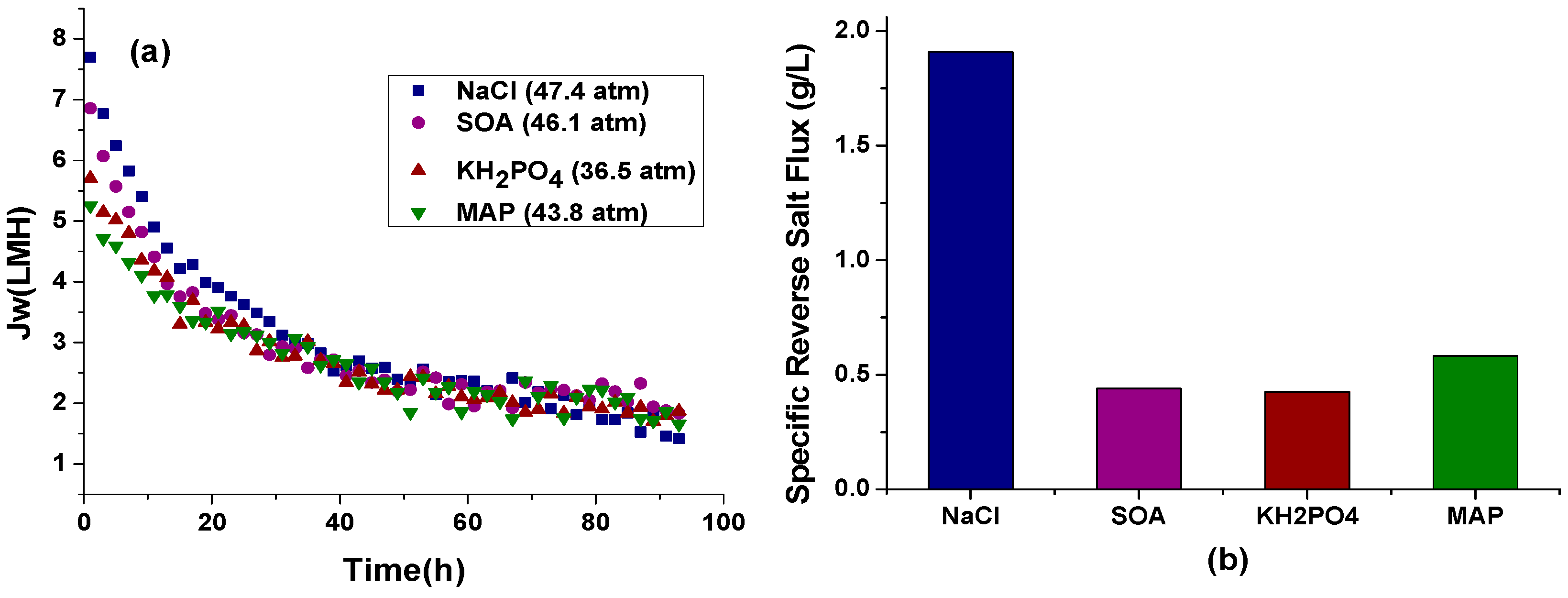
3.1.1. Effect of Different Types of Fertilizers
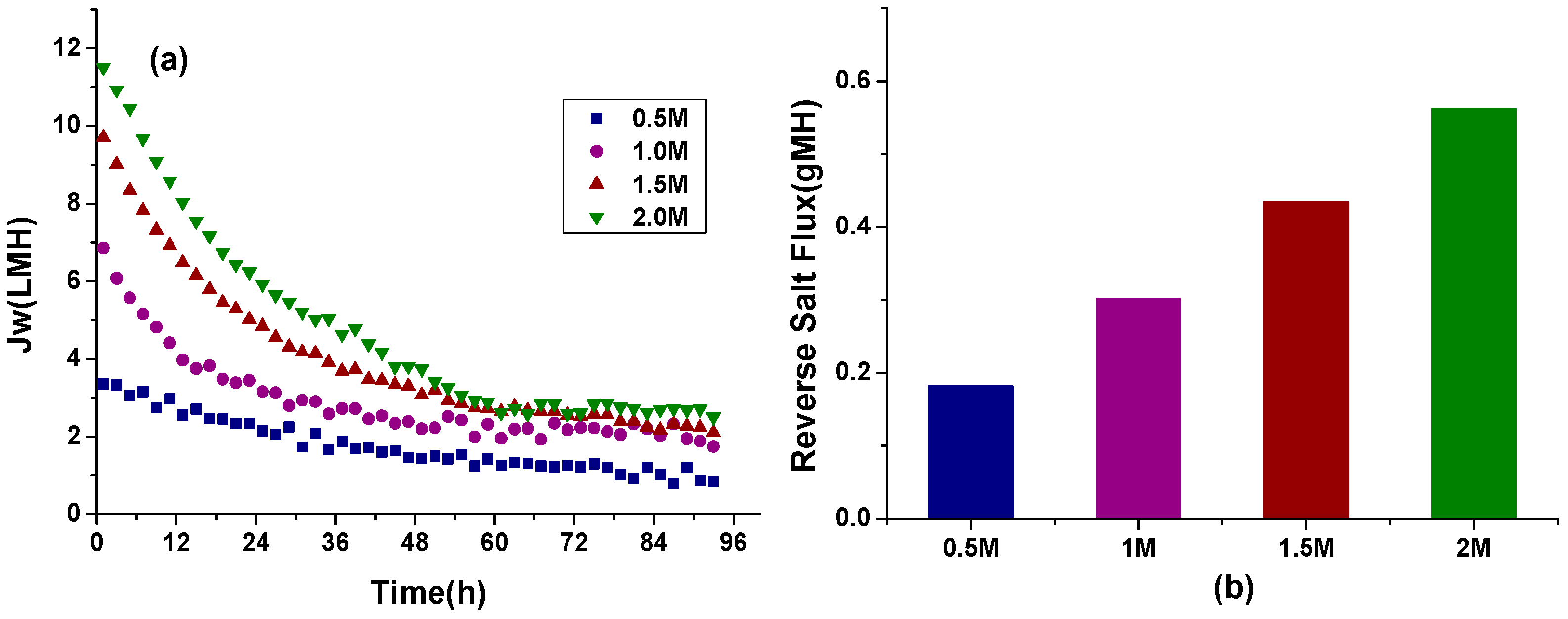
3.1.2. Effect of Different DS Concentration on Water Flux and RSF
3.1.3. Effect of Different DS Flow Rates on Water Flux and RSF
3.1.4. Effect of Different MF Permeate Fluxes on FO Water Flux and MF Outlet Pressure Change
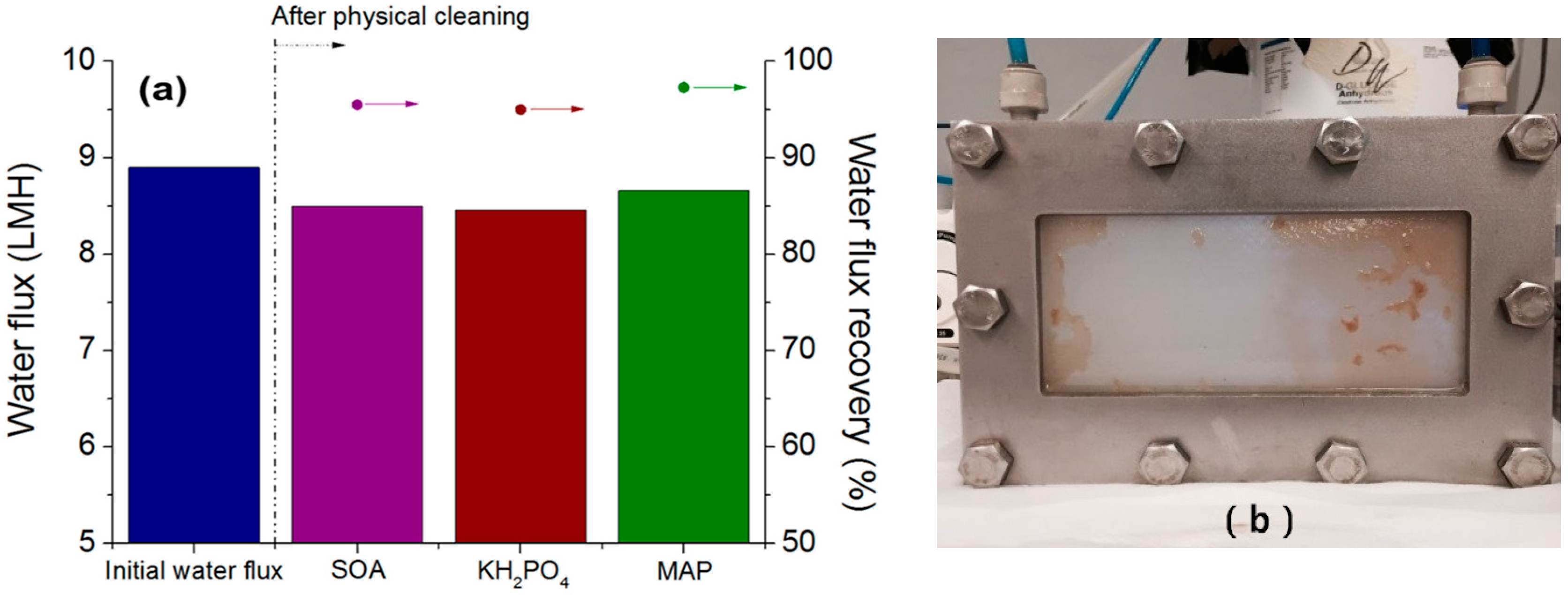
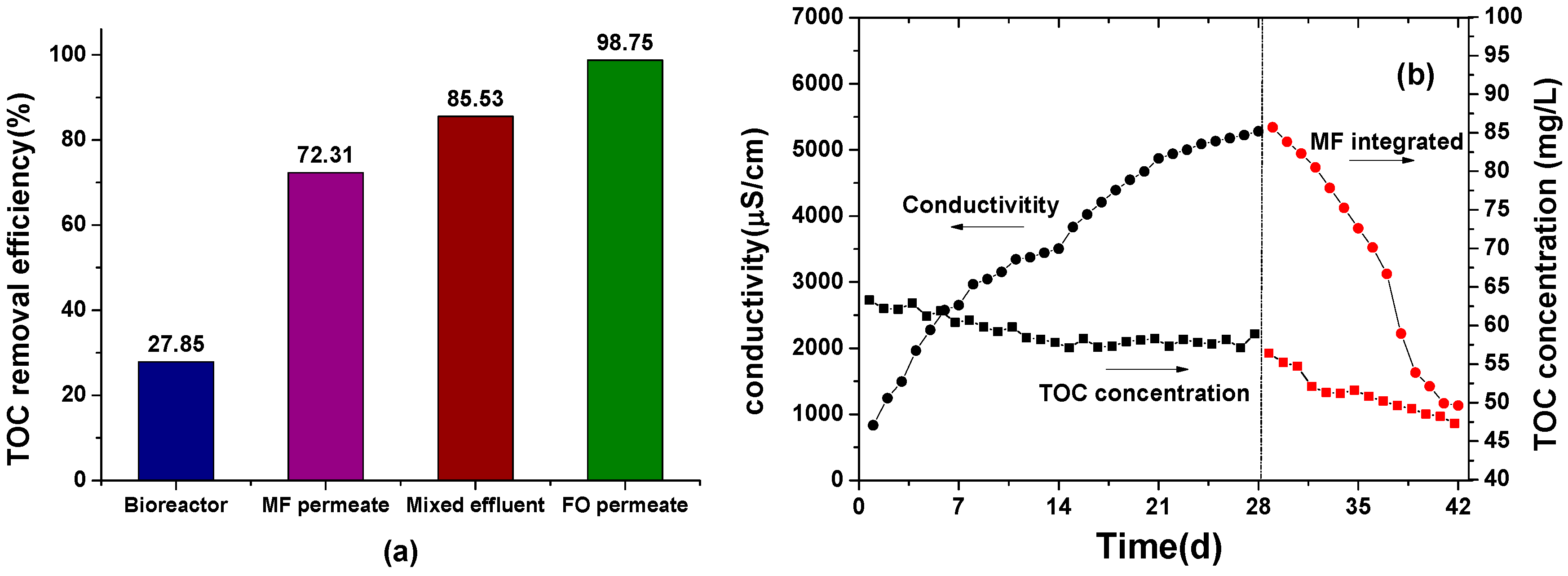
3.2. TOC Removal Efficiency and Mitigating Salt Accumulation by Incorporating MF
4. Conclusions
- This study demonstrated that the integration of the MF membrane could effectively control the salinity and enhance the stable FO flux and metabolic activity in the OMBR.
- The hydrodynamic conditions were found to have significant effect on the FO water flux and reverse salt flux.
- The optimum conditions for this hybrid system was found as follow: SOA as fertilizer DS, draw solution concentration of 1 M, FO draw solution flow rate of 200 mL/min and MF imposed flux of 10 LMH.
- In order to drive OMBR from laboratory research to real practical applications, the water flux of FO membrane must be improved and reverse salt flux must be decreased, which require breakthroughs in the development of FO membranes, draw solutions, operating conditions and other novel strategies.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trussell, R.R. Potential for Expanding the Nation’s Water Supply through Reuse of Municipal Wastewater; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Clay, J. World Agriculture and the Environment: A Commodity-by-Commodity Guide to Impacts and Practices; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, R.C.; Tsur, Y.; Roe, T.L.; Doukkali, R.; Dinar, A. Pricing irrigation water: A review of theory and practice. Water Policy 2002, 4, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, S. Mbr Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lay, W.C.L.; Liu, Y.; Fane, A.G. Impacts of salinity on the performance of high retention membrane bioreactors for water reclamation: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Cath, T.Y.; Marchand, E.A.; Childress, A.E. The forward osmosis membrane bioreactor: A low fouling alternative to MBR processes. Desalination 2009, 239, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, E.R.; Harmsen, D.; Korte, K.F.D.; Ruiken, C.J.; Qin, J.J.; Oo, H.; Wessels, L.P. Membrane fouling and process performance of forward osmosis membranes on activated sludge. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 319, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, W.J.; Zhang, J.; Lay, W.C.; Cao, B.; Fane, A.G.; Liu, Y. State of the art of osmotic membrane bioreactors for water reclamation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, R.W.; Regnery, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Cath, T.Y. Removal of trace organic chemicals and performance of a novel hybrid ultrafiltration-osmotic membrane bioreactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10859–10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; Von, G.U.; Wehrli, B. The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cath, T.; Childress, A.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, V.W.C.; Tang, C.Y. Osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Advances, challenges, and prospects for the future. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.; Sohn, J. A comprehensive review of hybrid forward osmosis systems: Performance, applications and future prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 497, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, A.; McDonald, J.; Khan, S.J.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Performance of a novel osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR) system: Flux stability and removal of trace organics. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, N.T.; Cath, T.Y. Solute coupled diffusion in osmotically driven membrane processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6769–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilli, A.; Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E. Selection of inorganic-based draw solutions for forward osmosis applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuntsho, S.; Hong, S.; Elimelech, M.; Shon, H.K. Forward osmosis desalination of brackish groundwater: Meeting water quality requirements for fertigation by integrating nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K.; Hong, S.; Lee, S.; Vigneswaran, S. A novel low energy fertilizer driven forward osmosis desalination for direct fertigation: Evaluating the performance of fertilizer draw solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K.; Majeed, T.; El Saliby, I.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Hong, S.; Lee, S. Blended fertilizers as draw solutions for fertilizer-drawn forward osmosis desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4567–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Chekli, L.; Shim, W.G.; Phuntsho, S.; Li, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.; Shon, H.K. Selection of suitable fertilizer draw solute for a novel fertilizer-drawn forward osmosis-anaerobic membrane bioreactor hybrid system. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.Y.; She, Q.; Lay, W.C.L.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Coupled effects of internal concentration polarization and fouling on flux behavior of forward osmosis membranes during humic acid filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 354, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, W.C.L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Mcdougald, D.; Tang, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Fane, A.G. Study of integration of forward osmosis and biological process: Membrane performance under elevated salt environment. Desalination 2011, 283, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Li, X.Y. Change in the fouling propensity of sludge in membrane bioreactors (MBR) in relation to the accumulation of biopolymer clusters. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4718–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, K.; Maruoka, S.; Katagami, R.; Bhatta, C.P.; Omori, D.; Matsuda, A. Effect of initial MLSS on operation of submerged membrane activated sludge process. Desalination 2011, 281, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, W.C.L.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Fane, A.G. Factors affecting flux performance of forward osmosis systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394–395, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janga, N.; Ren, X.; Kim, G.; Ahn, C.; Cho, J.; Kim, I.S. Characteristics of soluble microbial products and extracellular polymeric substances in the membrane bioreactor for water reuse. Desalination 2006, 202, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johir, M.A.; Vigneswaran, S.; Sathasivan, A.; Kandasamy, J.; Chang, C.Y. Effect of organic loading rate on organic matter and foulant characteristics in membrane bio-reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.; Lei, S.; Rong, W.; Tang, C.Y.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Characteristics and potential applications of a novel forward osmosis hollow fiber membrane. Desalination 2010, 261, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Tang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Lay, W.C.L.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Modeling salt accumulation in osmotic membrane bioreactors: Implications for FO membrane selection and system operation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chua, H.C.; Zhou, J.; Fane, A.G. Factors affecting the membrane performance in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of concentrative and dilutive internal concentration polarization on flux behavior in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Shon, H.K.; Hong, S. Organic fouling mechanisms in forward osmosis membrane process under elevated feed and draw solution temperatures. Desalination 2015, 355, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, R.W.; Wait, A.S.; Fernandes da Silva, A.; Herron, J.; Schutter, M.D.; Lampi, K.; Cath, T.Y. Long-term pilot scale investigation of novel hybrid ultrafiltration-osmotic membrane bioreactors. Desalination 2015, 363, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; He, Z. Enhancing wastewater reuse by forward osmosis with self-diluted commercial fertilizers as draw solutes. Water Res. 2016, 99, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goosen, M.F.A.; Sablani, S.S.; Al-Hinai, H.; Al-Obeidani, S.; Al-Belushi, R.; Jackson, D. Fouling of reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration membranes: A critical review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2261–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A.G. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Integration of micro-filtration into osmotic membrane bioreactors to prevent salinity build-up. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.S.; Dudley, L.Y. Biofouling in membrane systems—A review. Desalination 1998, 118, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Moghadam, M.K.; Madaeni, S.S. Hydrodynamic factors affecting flux and fouling during reverse osmosis of seawater. Desalination 2003, 151, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.T.; Mccutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis: Role of membrane orientation. Desalination 2006, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, B.R.; Rastogi, N.K.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S. Effect of process parameters on transmembrane flux during direct osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratna, D.; Jegatheesan, V. Implications of short and long term critical flux experiments for laboratory-scale MBR operations. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5361–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Ting, Y.P. Direct phosphorus recovery from municipal wastewater via osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR) for wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yao, C.; Bo, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Impacts of sludge retention time on sludge characteristics and membrane fouling in a submerged osmotic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coday, B.D.; Yaffe, B.G.; Xu, P.; Cath, T.Y. Rejection of trace organic compounds by forward osmosis membranes: A literature review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3612–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Cho, J.; Seo, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Ahn, K.H. Modeling of submerged membrane bioreactor process for wastewater treatment. Desalination 2002, 146, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, S.; Oda, Y.; Sasakawa, M.; Itonaga, T. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) performance for reducing energy demand. Thembrsite Com. 2012. Available online: http://www.thembrsite.com/about/ (accessed on 25 August 2016).
- Pophali, G.R.; Kaul, S.N.; Mathur, S. Influence of hydraulic shock loads and TDS on the performance of large-scale CETPs treating textile effluents in India. Water Res. 2003, 37, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogalakshmi, K.N.; Joseph, K. Effect of transient sodium chloride shock loads on the performance of submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7054–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rene, E.R.; Kim, S.J.; Park, H.S. Effect of COD/N ratio and salinity on the performance of sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Components | Unit | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose | mg/L | 80.50 |
| NH4Cl | mg/L | 14.70 |
| KH2PO4 | mg/L | 10.50 |
| Starch | mg/L | 85.30 |
| Peptone | mg/L | 18.00 |
| Milk powder | mg/L | 108.40 |
| Yeast | mg/L | 50.00 |
| Total Organic Carbon | mg/L | 92.31 |
| Total Nitrogen | mg/L | 42.32 |
| Total Phosphorus | mg/L | 10.48 |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Pathak, N.; Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Kim, Y.; Li, D.; Shon, H.K. Performance of a Novel Fertilizer-Drawn Forward Osmosis Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor (FDFO-MBR): Mitigating Salinity Build-Up by Integrating Microfiltration. Water 2017, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010021
Wang J, Pathak N, Chekli L, Phuntsho S, Kim Y, Li D, Shon HK. Performance of a Novel Fertilizer-Drawn Forward Osmosis Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor (FDFO-MBR): Mitigating Salinity Build-Up by Integrating Microfiltration. Water. 2017; 9(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jin, Nirenkumar Pathak, Laura Chekli, Sherub Phuntsho, Youngjin Kim, Dengxin Li, and Ho Kyong Shon. 2017. "Performance of a Novel Fertilizer-Drawn Forward Osmosis Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor (FDFO-MBR): Mitigating Salinity Build-Up by Integrating Microfiltration" Water 9, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010021
APA StyleWang, J., Pathak, N., Chekli, L., Phuntsho, S., Kim, Y., Li, D., & Shon, H. K. (2017). Performance of a Novel Fertilizer-Drawn Forward Osmosis Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor (FDFO-MBR): Mitigating Salinity Build-Up by Integrating Microfiltration. Water, 9(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010021








