Stakeholder Engagement and Knowledge Co-Creation in Water Planning: Can Public Participation Increase Cost-Effectiveness?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Public Participation and the Water Framework Directive
Danish Evaluations on Water Planning and Public Participation
3. Case Study—Danish Water Councils
3.1. The Use of Water Councils to Actively Involve the Public
3.2. Framework for the Water Council Work
4. Materials and Methods
Cost-Effectiveness: The 16 Measures and Their Costs
- The initial investment (e.g., buying land, excavations, etc.)
- Compensation given to farmers for the areas affected
- Running costs related to the maintenance of the streams, etc.
- Administrative costs
5. Results
5.1. Water Council Output Evaluation
5.2. Measures Chosen: Outputs and Investments
5.3. Cost-Effectiveness of Measures Chosen
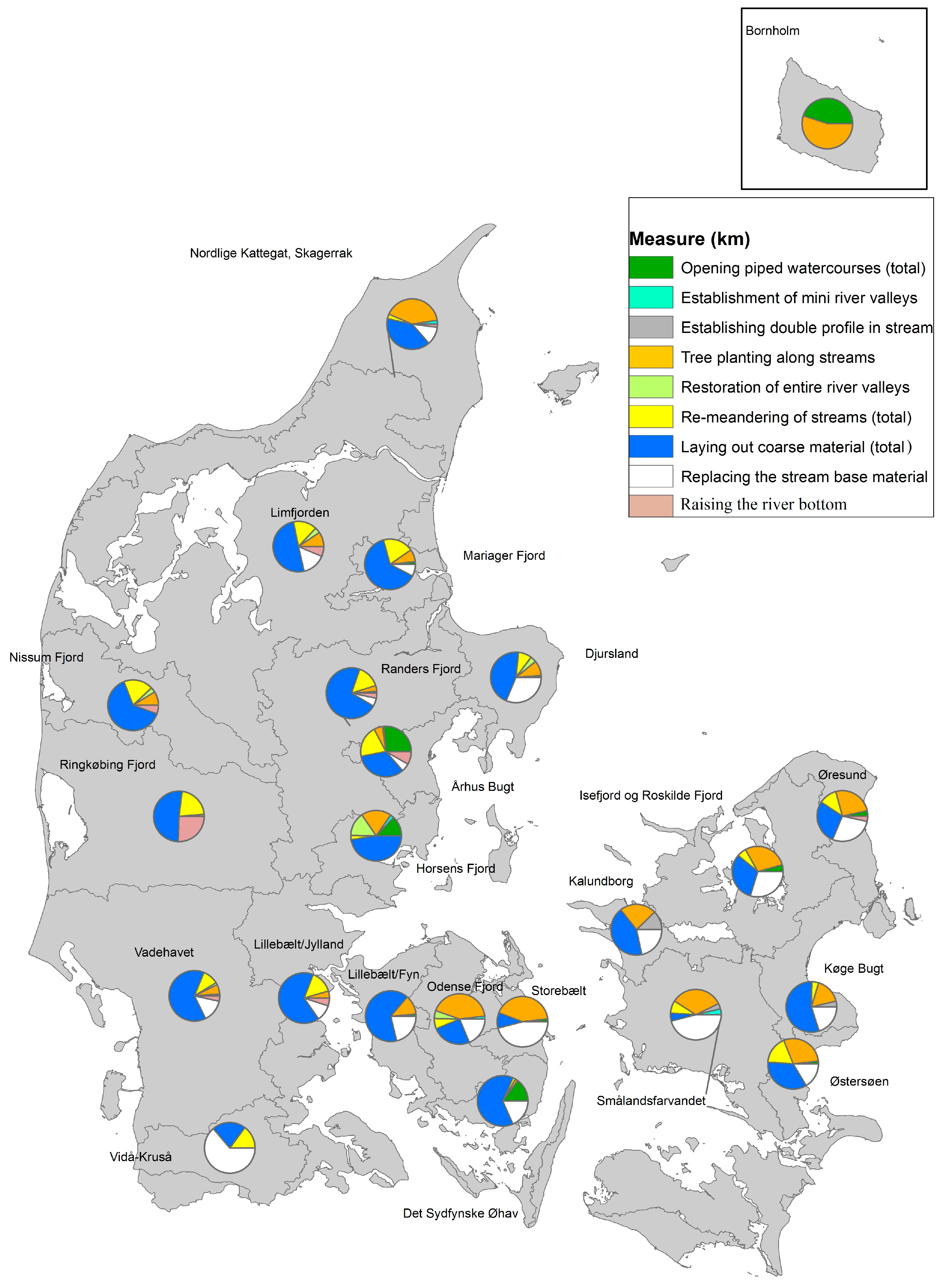
5.4. Geographical Differences in the Chosen Measures—“Be the River as it Rolls Along”
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Organization | Type of Organizations | Scale of Work |
|---|---|---|
| Landøkonomisk Selskab | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Nordsjællands Landboforening | Agricultural association | Local |
| Fredensborg Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Gribskov Vandløbslaug | Drainage interests | Local |
| Esrum Å-laug | Angler association | Local |
| Farum Naturparks Venner | Nature conservation | Local |
| Kastrup-Tiset Landvindingslag | Drainage interests | Local |
| Varde Å Sammenslutningen | Angler association | Local |
| Fugleværnsfonden | Ornithologist association | National |
| Dansk Landbrug Sydhavsøerne | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Havelse Ålaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Holbæk Ålav | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Vandløbslaug for Værebro Å | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Vandløbslav for Roskilde Kommune | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Værløse Naturgruppe | Nature conservation | Local |
| DI Hovedstaden | Industry | National |
| Landbrug og Fødevarer | Agricultural association | National |
| Bæredygtigt Landbrug | Agricultural association | National |
| Dansk Skovforening | Forestry association | National |
| Odderbæk Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Økologisk Landsforening | Organic agricultural association | National |
| Vestjysk Landboforening | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Dansk Amatørfiskerforening | Angler association | National |
| Herning Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Friluftsrådet | Recreational (Danish outdoor council) | National |
| Danske Kloakmestre | Sewerage association | National |
| Dansk Akvakultur | Danish aquaculture farming business | National |
| Danske Vandløb | Drainage and agricultural interests | National |
| Foreningen til bevarelse af Tange Sø | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Vandløbslauget for Alling Å | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Vandløbslauget GST | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Randers Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Tønder roklub | Recreational (rowing club) | Local |
| DOF | Ornithologist association | National |
| FVD | Water supply association | National |
| Syd-Østsjællands Landboforening | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Gefion | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Amagerlandets Producentforening | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Bestyrelsen for Vallensbæk Moses Pumpelag | Drainage association | Local |
| Køge Sports- og Stevns Lystfiskerforeninger | Angler association | Local |
| Tryggevælde- og Stevns Ådals Bevarelse | Nature conservation | Local |
| I/S Vandsamarbejdet Greve | Water supply association | Local |
| LandboNord | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Familielandbruget Midtjylland | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Haslevgaard ålaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Nordøstvendsyssels ålaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Dansk land og strandjagt | Hunting association | National |
| Liver å Lystfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Dansk kano og kajakforbund | Recreational (Danish Canoe and Kayak Federation) | National |
| Sjællandske Familiebrug | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Odsherred Landboforening | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Andaks og Istebjerggrøftens ålaug/Tranemose Ålaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Halleby å sammenslutningen | Angler association | Local |
| Oplandsrådet for Norsminde Fjord | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Djursland Landboforening | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Korup Ålaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Vandløbslauget Stensmark Bæk og Saltbæk | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Østjydsk Familielandbrug | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Vandløbslaug ved Ryom Å | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Sportsfiskerforeningen for Grenaa og Omegn | Angler association | Local |
| Landsforeningen Levende Hav | Nature conservation (fishery) | Regional |
| Syddjurs vandråd | Water supply association | Local |
| Bornholmslandbrug | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Vandpleje Bornholm | Angler association | Regional |
| Bornholms Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Dansk Landbrug Midt-Østjylland | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Langaa Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Foreningen til nedlæggelsen af Tange Sø | Nature conservation | Local |
| Vandrådet i Favrskov Kommune | Water supply association | Local |
| Uldum Kær Naturlaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Centrovice | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Nyborg Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Fyns Familielandbrug | Agricultural association | Local |
| Langeland Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Kerteminde Forsyning A/S | Water supply association | Local |
| Gråsten Nor I/S | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Kerteminde vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Svendborg vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Odense Bys Museer | Recreation (museum association) | Local |
| IDA-Fyn-BYG | Industry | Regional |
| Assens Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Faaborg-Midtfyn Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Nordfyns Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Odense Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Patriotisk Selskab | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Ærø Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| DANVA | Water supply and wastewater association | National |
| Dansk Miljøteknologi | Industry | National |
| Familielandbruget Vestjylland | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Herning Ikast Landboforening, | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Holstebro Struer Landboforening | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Agri Nord | Agricultural association | Regional |
| DN | Nature Conservation | National |
| Lemvigegnens Landboforening | Agricultural association | Regional |
| Løgstør Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Skalsådalens Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Aalestrup Lystfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Aulum sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | Local |
| Talerøret for Skive-Karup Å | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Centralforeningen for Limfjorden | Fishery association | Regional |
| Fjordvenner .dk | Nature conservation | Regional |
| Bibæk Vandløbslaug | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Sønderjyske Vandløb | Drainage and agricultural interests | Regional |
| Danmarks Jægerforbund | Hunter association | National |
| Ferskvandsfiskeriforeningen for Danmark | Fishery association | National |
| Ravsted og omegns vandløbslaug (tsunamigruppen) | Drainage and agricultural interests | Local |
| Sportsfiskerforeningen Vidå | Angler association | Local |
| Danmarks Sportsfiskerforening | Angler association | National |
Appendix B
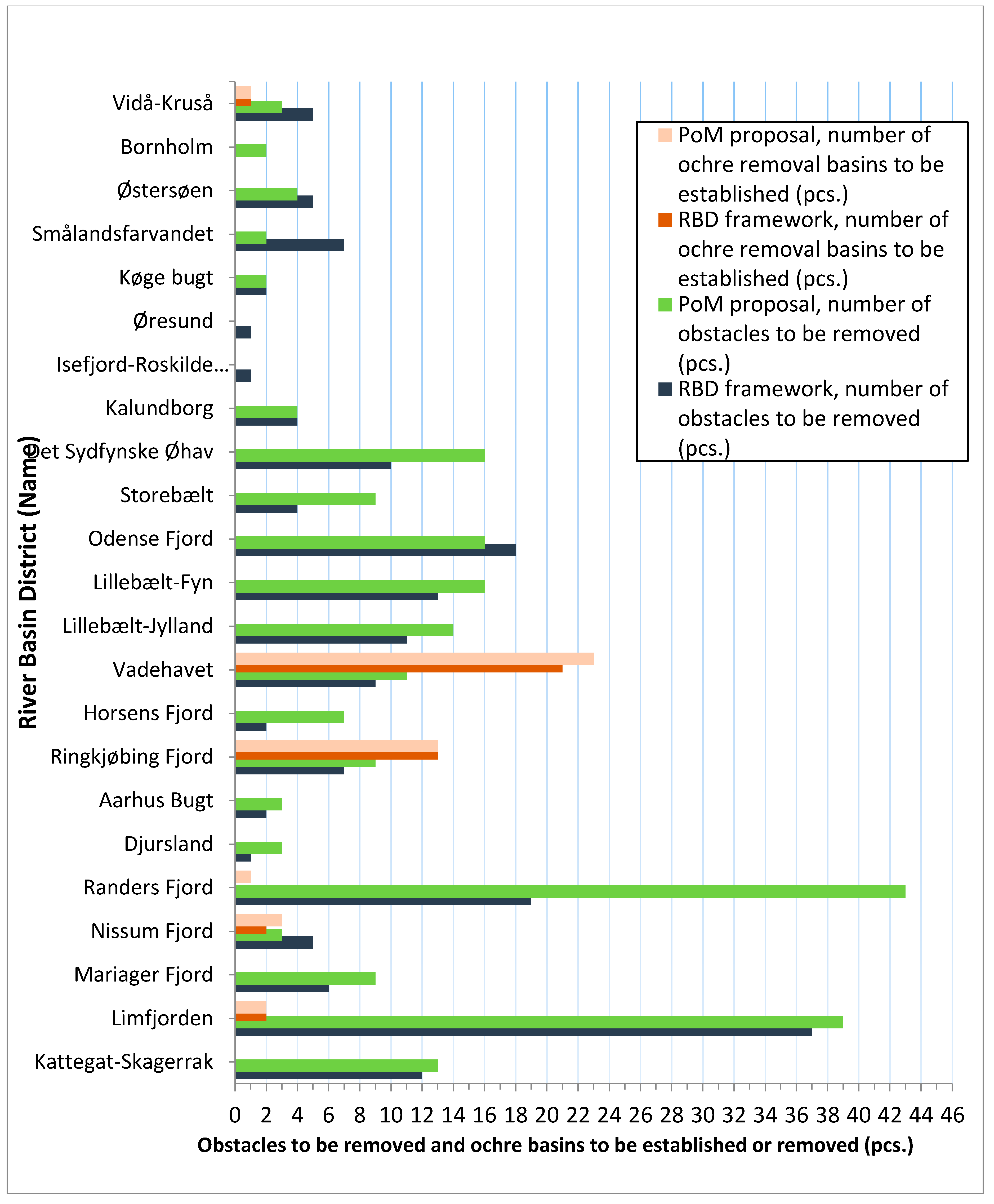
Appendix C
| Restoration Measures | Water Council Proposed Measures (km/pcs. a). | % of Total km Based Measures Used | Water Council Proposed Measures and Their Investment Costs (Excl. Adm. and Maintenance Expenses) (Mill. €/km. or pcs.) | % of Total Investment Costs km Based Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smaller restoration measures | ||||
| Laying out coarse material | 728 | 40 | 20.1 | 29 |
| Laying out coarse material + tree planting | 108 | 6 | 3.9 | 6 |
| Raising the river bottom | 77 | 4 | 4.9 | 7 |
| Tree planting along streams | 320 | 18 | 2.8 | 4 |
| Total smaller restoration measures | 1233 | 68 | 31.7 | 46 |
| Major restorations | ||||
| Restoration of entire river valleys | 24 | 1 | 5.7 | 8 |
| Re-meandering of streams | 194 | 11 | 16.1 | 23 |
| Re-meandering of streams b | 2 | 0 | 0.6 | 1 |
| Replacing the stream base material | 312 | 17 | 4.9 | 7 |
| Opening piped watercourse sections c | 17 | 1 | 2.1 | 3 |
| Opening piped watercourse sections d | 9 | 0 | 1.1 | 2 |
| Opening piped watercourse sections e | 1 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 |
| Establishment of mini river valleys | 16 | 1 | 4.8 | 7 |
| Establishing double profile in stream | 11 | 1 | 2.3 | 3 |
| Total major restorations | 586 | 32 | 37.9 | 54 |
| Total km based measures | 1820 | 100 | 69.6 | 100 |
| Other measures | ||||
| Removal of obstacles (Ob) | 222 | - | 12 | - |
| Sand traps (ST) | 266 | - | 1.7 | - |
| Ochre-removal basins (ORB) | 42 | - | 11.9 | - |
| Total other measures | 228Ob, 266ST, 43ORB | - | 25.6 | - |
| Total all measures | 1820km, 228Ob, 266ST, 43 ORB | - | 95.2 | - |
References
- Stoate, C.; Boatman, N.D.; Borralho, R.; Rio Carvalho, C.; de Snoo, G.; Eden, P. Ecological impacts of arable intensification in Europe. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 63, 337–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhuis, P.H.; Leuven, R.S.E.W. River restoration and flood protection: Controversy or synergism? Hydrobiologia 2001, 444, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.J. The human role in changing river channels. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, P.; Werner, B.; Christiansen, T.; Collins, R.; Belchior, C.; Jacobsen, B.; Solheim, A.L.; Austnes, K.; Kodeš, V.; Semaradova, S.; et al. European Waters—Assessment of Status and Pressures; EEA Report No. 8/2012; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. River Basin Management Plans; Report from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council on the Implementation of the Water Framework Directive; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Nature Agency. Basisanalyse for Vandområdeplanerne 2015–2021; Overfladevandet og Grundvandets Karakteristika; Påvirkning og Arealanvendelse; Tilstand og Vurdering; (Characteristics of Surface Water and Groundwater for the 2. Generation (2015–2021) of River Basin Management Plans); Environmental Ministry Danish Nature Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Economics and the Environment: The Implementation Challenge of the Water Framework Directive; A guidance document (WATECO) 7; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Berbel, J.; Martin-Ortega, J.; Mesa, P. A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Water-Saving Measures for the Water Framework Directive: The Case of the Guadalquivir River Basin in Southern Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Environment of Denmark. Retningslinjer for Udarbejdelse af Vandområdeplaner 2015–2021. Intern Arbejdsinstruks, SVANA, 2016. Available online: http://svana.dk/media/203204/retningslinjer-vp2-22_12_2014.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Dalgaard, T.; Hansen, B.; Hasler, B.; Hertel, O.; Hutchings, N.J.; Jacobsen, B.H.; Jensen, L.S.; Kronvang, B.; Olesen, J.E.; Schjørring, J.K.; et al. Policies for agricultural nitrogen management—Trends, challenges and prospects for improved efficiency in Denmark. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsøe, M.H.; Graversgaard, M.; Noe, N. The challenge of legitimizing spatially differentiated regulation: Experiences from the implementation of the Danish Buffer zone act. Land Use Policy 2017, 62, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.; Jacobsen, B.H. Combining Active Farmer Involvement with detailed Farm Data in Denmark: A Promising Method for Achieving Water Framework Directive targets? Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2625–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.; Jacobsen, B.H. Participation in the implementation of the Water Framework Directive in Denmark: The prospects for active involvement. Water Policy 2011, 13, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission on Nature and Agriculture. Richer Nature, New Environmental Regulation and New Growth Opportunities for Agriculture. Executive Summary. The Danish Commission on Nature and Agriculture, 2013. Available online: www.naturoglandbrug.dk (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Graversgaard, M.; Gertz, F.; Wiborg, I.A.; Kjeldsen, C.; Dalgaard, T. Vandråd—et nybrud i dansk vandforvaltning. (Water councils—A new starting point in Danish water management). Vand Jord. 2015, 22, 1. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, B.H.; Tegner, H.; Baaner, L. Implementing the Water Framework Directive in Denmark—Lessons on agricultural measures from a legal and regulatory perspective. Land Use Policy. submitted.
- European Union. Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC); Guidance Document No. 8; Public Participation in Relation to the Water Framework Directive; Produced by Working Group 2.9; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Boeuf, B.; Fritsch, O. Studying the implementation of the Water Framework Directive in Europe: A meta-analysis of 89 journal articles. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallis, G.; Butler, D. The EU water framework directive: Measures and implications. Water Policy 2001, 3, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaika, M. The Water Framework Directive: A New Directive for a Changing Social, Political and Economic European Framework. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2003, 11, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, E. The European Water Framework Directive and water management research. Phys. Chem. Earth 2003, 28, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Borja, A.; Carstens, J.; Carvalho, L.; Elliott, M.; Feld, C.K.; Heiskanen, A.S.; Johnson, R.; Moe, J.; Pont, D.; et al. The European Water Framework Directive at the age of 10: A critical review of the achievements with recommendations for the future. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Page, B.; Kaika, M. The EU Water Framework Directive: Part 2. Policy innovation and the shifting choreography of governance. Eur. Environ. 2003, 13, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, T. The governance of land use in river basins: Prospects for overcoming problems of institutional interplay with the EU Water Framework Directive. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastens, B.; Newig, J. Will participation foster the successful implementation of the water framework directive? The case of agricultural groundwater protection in northwest Germany. Local Environ. Int. J. Justice Sustain. 2008, 13, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rault, P.A.K.; Jeffrey, P.J. Deconstructing public participation in the Water Framework Directive: Implementation and compliance with the letter or with the spirit of the law? Water Environ. J. 2008, 22, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, L. Facing the water framework directive challenges: A baseline of stakeholder participation in the European Union. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijerink, S.; Wiering, M. River Basin Management in Europe: The ‘Up- and Downloading’ of a New Policy Discourse. In The Disoriented State: Shifts in Governmentality, Territoriality and Governance; Arts, B., van Houtum, H.J., Eds.; Springer Science: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 181–200. [Google Scholar]
- Steyaert, P.; Ollivier, G. The European Water Framework Directive: How ecological assumptions frame technical and social change. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 25. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol12/iss1/art25/ (accessed on 3 March 2017). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, A.; Lacroix, K.E.M. Public Participation in Water Planning in the Ebro River Basin (Spain) and Tucson Basin (U.S., Arizona): Impact on Water Policy and Adaptive Capacity Building. Water 2016, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochskämper, E.; Challies, E.; Newig, J.; Jager, N.W. Participation for effective environmental governance? Evidence from Water Framework Directive implementation in Germany, Spain and the United Kingdom. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.; Fritsch, O.; Cook, H.; Schmid, M. Evaluating participation in WFD river basin management in England and Wales: Processes, communities, outputs and outcomes. Land Use Policy 2014, 38, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.E.; Booher, D.E. Consensus building and complex adaptive systems. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1999, 65, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, S.D. , Measuring the Effects of Stakeholder Participation on the Quality of Local Plans Based on the Principles of Collaborative Ecosystem Management. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2003, 22, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, D. Adaptive Capacity and Community-Based Natural Resource Management. Environ. Manag. 2005, 35, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newig, J.; Pahl-Wostl, C.; Sigel, K. The Role of Public Participation in Managing Uncertainty in the Implementation of the Water Framework Directive. Eur. Environ. 2005, 15, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.; Howe, J. Stakeholder participation and the water framework directive: The case of the Ribble Pilot. Local Environ. Int. J. Justice Sustain. 2006, 11, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, A.C.; Andersson, L.; Olsson, J.A.; Johansson, M. Defining goals in participatory water management: Merging local visions and expert judgements. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2011, 54, 909–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, O.; Newig, J. Participatory governance and sustainability: Findings of a meta-analysis of stakeholder involvement in environmental decision making. In Reflexive Governance for Global Public Goods; Brousseau, E., Dedeurwaerdere, T., Siebenhüner, B., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 181–204. [Google Scholar]
- Drazkiewicz, A.; Challies, E.; Newig, J. Public participation and local environmental planning: Testing factors influencing decision quality and implementation in four case studies from Germany. Land Use Policy 2015, 46, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koontz, T.M.; Newig, J. Cross-level information and influence in mandated participatory planning: Alternative pathways to sustainable water management in Germany’s implementation of the EU Water Framework Directive. Land Use Policy 2014, 38, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Abbot, C. The Usual Suspects? Public Participation under the Aarhus Convention. Mod. Law Rev. 2003, 66, 80–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koontz, T.; Thomas, C. What Do We Know and Need to Know about the Environmental Outcomes of Collaborative Management? Public Adm. Rev. 2006, 66, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstock, K.L.; Richard, C. Evaluating stakeholder involvement in river basin planning: A Scottish case study. Water Policy 2007, 9, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, W. Aspirations and Realities under the Water Framework Directive: Proceduralisation, participation and Practicalities. J. Environ. Law 2009, 21, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, G.; Blöschl, G.; Loucks, D.P. Evaluating participation in water resource management: A review. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.Y.; Jordan, A.; Searle, K.R.; Butler, A.; Chapman, D.S.; Simmons, P.; Watt, A.D. Does stakeholder involvement really benefit biodiversity conservation? Biol. Conserv. 2013, 158, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newig, J.; Koontz, T.M. Mulit-level governance, policy implementation and participation: The EU’s mandated participatory planning approach to implementing environmental policy. J. Eur. Public Policy 2014, 21, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefferink, D.; Wiering, M.; Uitenboogaart, Y. The EU Water Framework Directive: A multi-dimensional analysis of implementation and domestic impact. Land Use Policy 2011, 28, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourblanc, M.; Crabbé, A.; Liefferink, D.; Wiering, M. The marathon of the hare and the tortoise: Implementing the EU Water Framework Directive. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2013, 56, 1449–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.Ø.; Frederiksen, P.; Saarikoski, H.; Rytkönen, A.; Pedersen, A.B. How different institutional arrangements promote integrated river basin management. Evidence from the Baltic Sea Region. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, N.W.; Challies, E.; Kochskämper, E.; Newig, J.; Benson, D.; Blackstock, K.; Collins, K.; Ernst, A.; Evers, M.; Feichtinger, J.; et al. Transforming European Water Governance? Participation and River Basin Management under the EU Water Framework Directive in 13 Member States. Water 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.; Klauer, B.; Manstetten, R. The environment as a challange for governmental responsibility—The case of the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitenboogaart, Y.J.; Kempen, J.J.H.; van Rijswick, H.F.M.W.; van Wiering, M.A. The Implementation of the WFD in the Netherlands. The Meuse River Basin District and the Dommel Catchment. In Dealing with Complexity and Policy Discretion. A Comparison of the Implementation Process of the European Water Framework Directive in Five Member states; SDU Uitgevers: Den Haag, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 57–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gertz, F.; Knudsen, L.; Wiborg, I. Problematisk dansk implementering. (Problematic Danish implementation). Vand Jord. 2012, 3, 100–103. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Danish Nature Agency. Vandplaner Med fem Vandveje. [Homepage of Naturstyrelsen, 2013. Available online: http://naturstyrelsen.dk/nyheder/2013/maj/vandplanermedfemvandveje/ (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Folketinget. FT nr. 1606, Lov om Vandplanlægning. LOV nr 1606 af 26/12/2013. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/forms/r0710.aspx?id=161126 (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Danish Nature Agency. Vejledning om Arbejdet Med Forslag Til Indsatsprogram for Vandløbsindsatsen. 2014, p. 5. Available online: http://svana.dk/media/nst/8439930/vejledning.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Boeuf, B.; Fritsch, O.; Martin-Ortega, J. Undermining European Environmental Policy Goals? The EU Water Framework Directive and the Politics of Exemptions. Water 2016, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.; O’Brien, S. Progress on stakeholder participation in the implementation of the Water Framework Directive in the Republic of Ireland. Biol. Environ. Proc. R. Irish Acad. 2009, 109b, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.; Ottow, B.; Francois, G.; von Korff, Y. Beyond dry feet? Experiences from a participatory water-management planning case in The Netherlands. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundmark, C.; Jonsson, G. Prospects for learning in river management: Exploring the initial implementation of the Water Framework Directive in a Swedish river basin. Environ. Educ. Res. 2014, 20, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzén, F.; Hammer, M.; Balfors, B. Institutional development for stakeholder participation in local water management—An analysis of two Swedish catchments. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, E.; Kranz, N.; Hansen, W. Public Participation in River Basin Management in Germany. From Borders to Natural Boundaries. In HarmoniCOP/WP 4; Ecologic—Institute for International and European Environmental Policy: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Graversgaard, M.; Thorsøe, M.H.; Kjeldsen, C.; Dalgaard, T. Evaluating public participation in Denmark’s water councils: How policy design and boundary judgements affect water governance! Outlook Agric. 2016, 45, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Nature Agency. Fordeling af Vandløbsindsatsen Samt Økonomisk Ramme, 2015–2021. 2014. Available online: http://naturstyrelsen.dk/media/nst/8433205/kort.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Sabatier, P.A.; Focht, W.; Lubell, M.; Trachtenberg, Z.; Vedlitz, A.; Matlock, M. Collaborative approaches to watershed management. In Swimming Upstream: Collaborative Approaches to Watershed Management; Sabatier, P.A., Focht, W., Lubell, M., Trachtenberg, Z., Vedlitz, A., Matlock, M., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Innes, J.E.; Booher, D.E. Planning with Complexity—An Introduction to Collaborative Rationality for Public Policy; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, E.A.; Jepsen, N.; Nielsen, J.; Koed, A. Virkemidler til Forbedring af de Fysiske Forhold i Vandløb; DCE—Nationalt Center for Miljø og Energi—Videnskabelig Rapport fra DCE—Nationalt Center for Miljø og Energi; Aarhus Universitet: Aarhus, Denmark, 2013; Volume 86, Available online: http://dce2.au.dk/pub/SR86.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- European Union. European Union. Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). In Economics and Environment and the Implementation Challenge of the WFD European Commission; Guidance Document No. 1; European Union: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Balana, B.B.; Vinten, A.; Slee, B. A review on cost-effectiveness analysis of agri-environmental measures related to the EU WFD: Key issues, methods, and applications. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatrup-Pedersen, A.; Riis, T. Impacts of different weed cutting practices on macrophyte species diversity and composition in a Danish stream. River Res. Appl. 2004, 20, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Holm, P.E.; Jensen, P.N.; Larsen, T.; Ovesen, N.B.; Pedersen, M.L.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Styczen, M. Faglig Udredning om Grødeskæring i Vandløb; DCE—Nationalt Center for Miljø og Energi, 106 s.—Videnskabelig Rapport fra DCE—Nationalt Center for Miljø og Energi; Aarhus Universitet: Aarhus, Denmark; Available online: http://dce2.au.dk/pub/SR188.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Jacobsen, B.H. Beregning af vandløbsvirkemidlers omkostningseffektivitet (Calculation of the cost-efficiency of measures used when managing streams). In Note for the Danish Nature Agency; Memo. 2014/8.; Department of Food and Resource Economics, University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, B.H. In Search of Cost-Effective Measures; IFRO Report, No. 191; Institute of Food and Resource Economics, Copenhagen University: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Nature Agency. Vandrådspakken Notat om Virkemiddelkatalog for Vandløb. 2014. Available online: http://naturstyrelsen.dk/media/nst/8437103/virkemiddelkatalog.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Jacobsen, B.H. Analyse af Landbrugets Omkostninger ved Implementering af Vandplanerne fra 2011 (Analysis of the Agricultural Costs When Implementing the RBMP from 2011); Memo. 2012/6; Department of Food and Resource Economics, University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fabricius, K.; Danish Nature Agency, Randbøl, Denmark. Personal communication, 19 January 2016.
- Gadgil, M.; Olsson, P.; Berkes, F.; Folke, C. Exploring the role of local ecological knowledge in ecosystem management: Three case studies. In Navigating Social-Ecological System: Building Resilience for Complexity and Changes; Berkes, F., Colding, J., Folke, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 189–209. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, T.; Newig, J. Multilevel Water Governance and Problems of Scale: Setting the Stage for a Broader Debate. Environ. Manag. 2010, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Lieshout, M.; Dewulf, A.; Aarts, N.; Termeer, C. The Power to Frame the Scale? Analysing Scalar Politics over, in and of a Deliberative Governance Process. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2014, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Catchment Based Approach: Improving the Quality of Our Water Environment. 2013. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/catchment-based-approach-improving-the-quality-of-our-water-environment (accessed on 3 March 2017).
- Evaluation of the Catchment Based Approach—Pilot Stage; Final Evaluation Report; Cascade Consulting: Manchester, UK, 2013.
- Rees, Y.; Kingsley-Rowe, D.; Cryle, P.; Conlan, K. Evaluation of the Catchment Based Approach: Phase 2; Final Report: WT1559; DEFRA: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Graversgaard, M. Evaluering af Vandrådsarbejdet; Udarbejdet for Naturstyrelsen, Morten Graversgaard: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, M. Stakeholder participation for environmental management: A literature review. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 2417–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

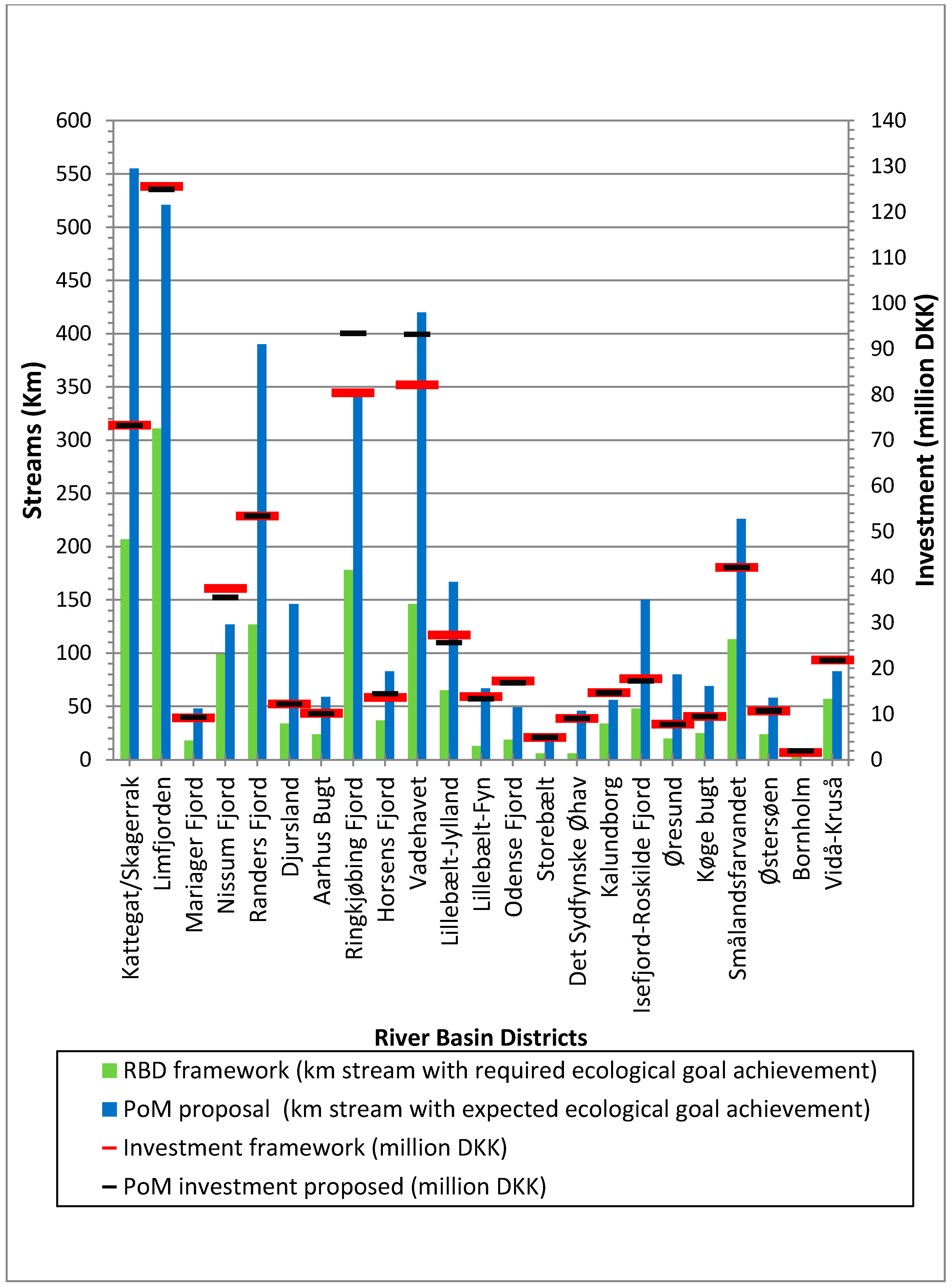

| Restoration Measures | Cost (excl. Administrative and Maintenance Expenses) (€ per km) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 stream (Width < 2 m) | Type 2 Stream (Width 2–10 m) | Type 3 Stream (Width > 10 m) | ||
| Smaller Restorations | Laying out coarse material (+tree planting) | 14,000 (24,000) | 42,000 (53,000) | 84,000 (97,000) |
| Raising the river bottom bed | 47,000 | 80,000 | 97,000 | |
| Tree planting along streams | 9000 | 9000 | 9000 | |
| Re-meandering of streams | 63,000 | 93,000 | 318,000 | |
| Major Restorations | Re-meandering of streams b | 218,000 | 260,000 | 742,000 |
| Replacing the stream base material | 11,000 | 19,000 | 60,000 | |
| Establishment of mini river valleys | 250,000 | 384,000 | - | |
| Restoration of entire river valleys | 143,000 | 257,000 | 328,000 | |
| Establishing double profile in stream | 160,000 | 218,000 | - | |
| Opening piped watercourse sections c | 126,000 (63,000–190,000) 1 | 947,000 (63,000–1,420,000) 1 | 947,000 (473,000–1,420,000) 1 | |
| Opening piped watercourse sections d | 126,000 (63,000–190,000) 1 | 947,000 (63,000–1,420,000) 1 | 947,000 (473,000–1,420,000) 1 | |
| Opening piped watercourse sections e | 371,000 (185,000–556,000) 1 | 1,331,000 (185,000–1,996,000) 1 | 1,331,000 (665,000–1,996,000) 1 | |
| Removal of obstacles | 38,000 (13,000–80,000) 1 | 147,000 (27,000–201,000) 1 | 704,000 (352,000–1,055,000) 1 | |
| Other Measures | Establishment of sand traps | 3000 | 11,000 | - |
| Establishment of ochre-removal basins | 164,000 | 390,000 | 390,000 | |
| Outputs | Minimum Requirements Prepared by the Nature Agency | Initial Water Council Proposals for PoMs | Final Water Council Proposals for PoMs (RBMPs 2015–2021) | Water Council Index (PoM 2015/RBD 2014) ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investments (Million €) | 93 | 96 | 93 | 100 |
| Obstacles (No.) | 181 | 222 | 228 | 125 |
| Ochre-Removal Basins (No.) | 39 | 42 | 43 | 110 |
| Length Streams (km) | 1615 | 3664 | 3800 * | 235 |
| Measures (Stream Width 2 m a) | Investment (Excl. Adm. and Maintenance Costs) (€/km/Year) b | Annual Costs (Excl. Adm. Costs). (€/km/Year) c | Adm. Costs (€/km) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low costs | Tree planting | 8700 | 270 | 0 |
| Replacing the stream base material | 10,700 | 670 | *** | |
| Laying out coarse material | 13,800 | 800 | 4000–11,300 | |
| Medium costs | Raising the river bottom | 47,200 | 2330 | 0 |
| Removal of obstacles | 38,200 | 2000 | 5700–7000 | |
| Establishment of sand traps | 3000 | 2700 | 2100–2900 | |
| High costs | Re-meandering of streams | 62,800 | 4300 | 6700–11,000 |
| Opening piped watercourse sections | 125,800 | 8700 | 14,700–248,000 | |
| Establishment of mini river valleys | 249,000 | 11,300 | 0 | |
| Ochre-removal basins | 163,500 | 12,000 | *** | |
| Restoration of entire river valleys | 142,700 | 9700 | *** |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graversgaard, M.; Jacobsen, B.H.; Kjeldsen, C.; Dalgaard, T. Stakeholder Engagement and Knowledge Co-Creation in Water Planning: Can Public Participation Increase Cost-Effectiveness? Water 2017, 9, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030191
Graversgaard M, Jacobsen BH, Kjeldsen C, Dalgaard T. Stakeholder Engagement and Knowledge Co-Creation in Water Planning: Can Public Participation Increase Cost-Effectiveness? Water. 2017; 9(3):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030191
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraversgaard, Morten, Brian H. Jacobsen, Chris Kjeldsen, and Tommy Dalgaard. 2017. "Stakeholder Engagement and Knowledge Co-Creation in Water Planning: Can Public Participation Increase Cost-Effectiveness?" Water 9, no. 3: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030191
APA StyleGraversgaard, M., Jacobsen, B. H., Kjeldsen, C., & Dalgaard, T. (2017). Stakeholder Engagement and Knowledge Co-Creation in Water Planning: Can Public Participation Increase Cost-Effectiveness? Water, 9(3), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030191








