Spatiotemporal Distribution of Eutrophication in Lake Tai as Affected by Wind
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
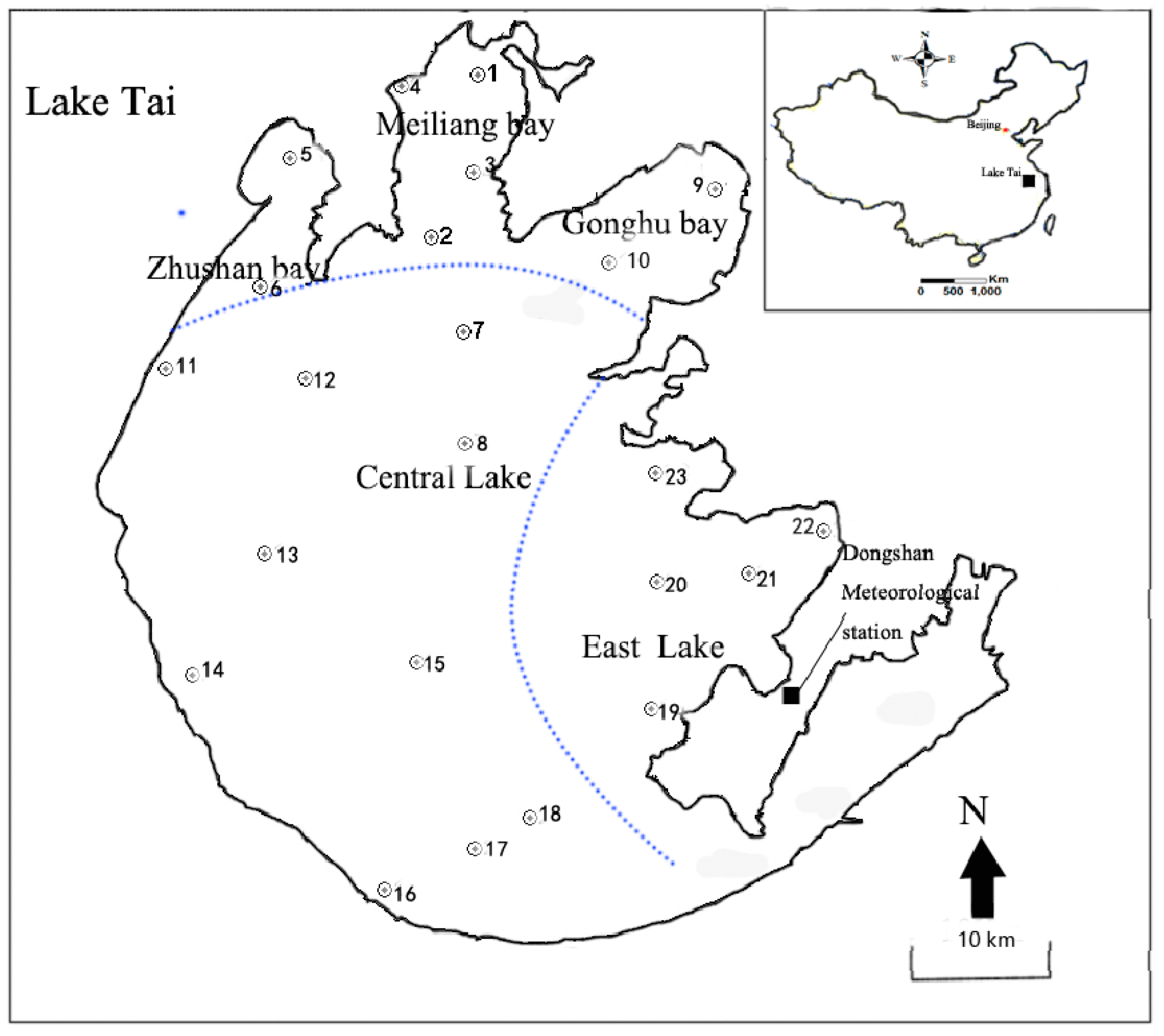
2.1. Lake Tai
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Analysis Methods
3. Results
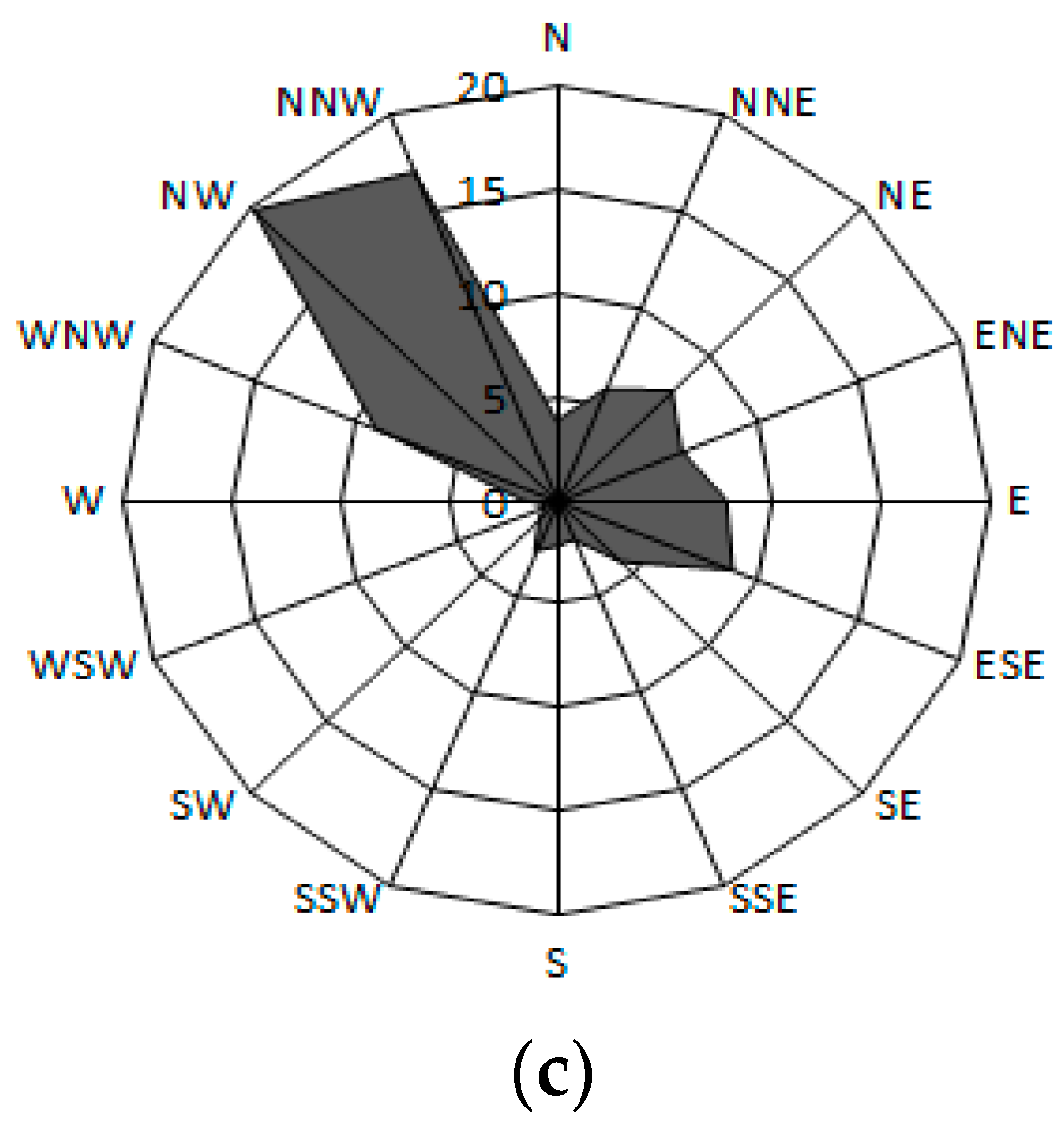
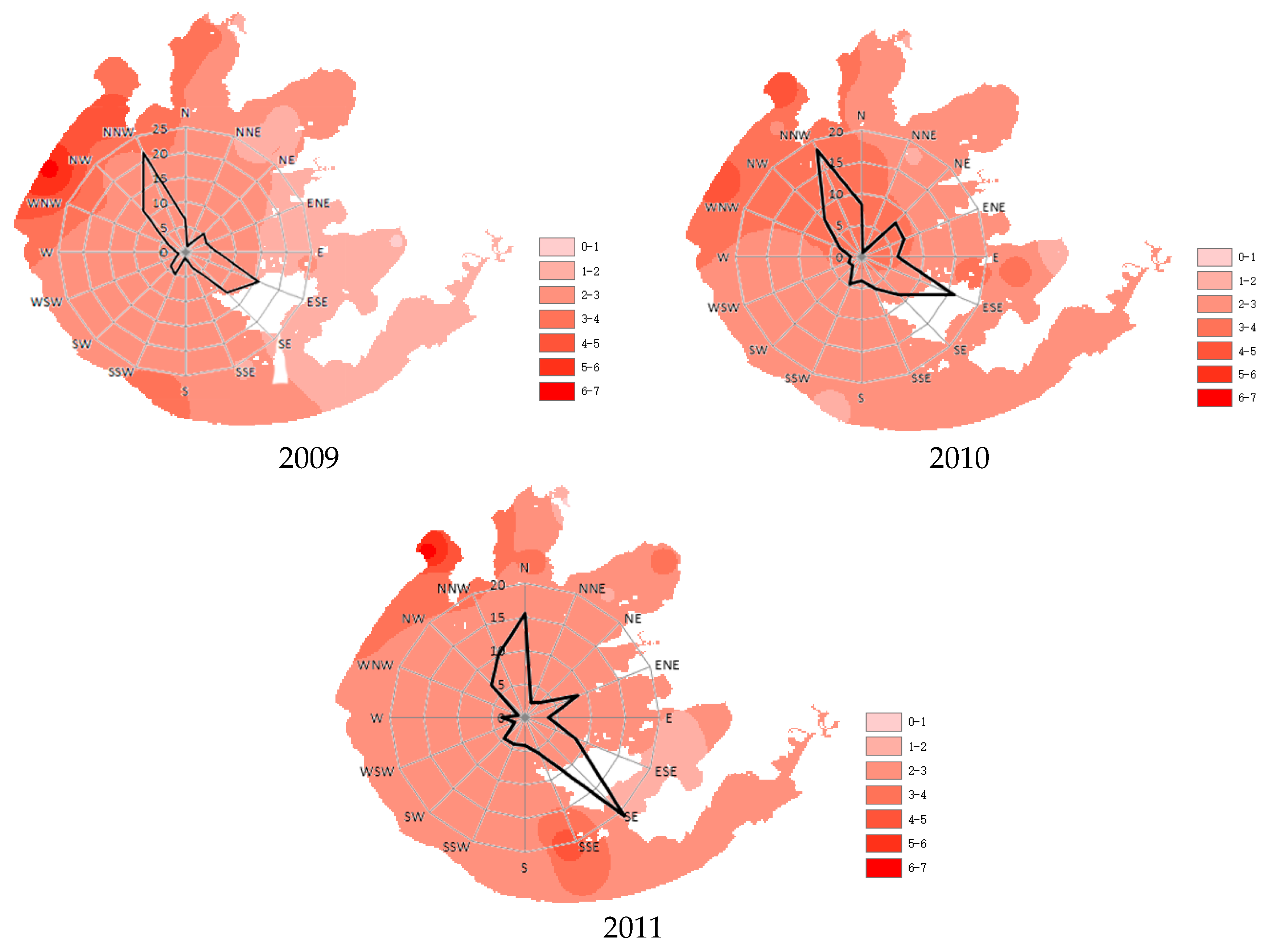
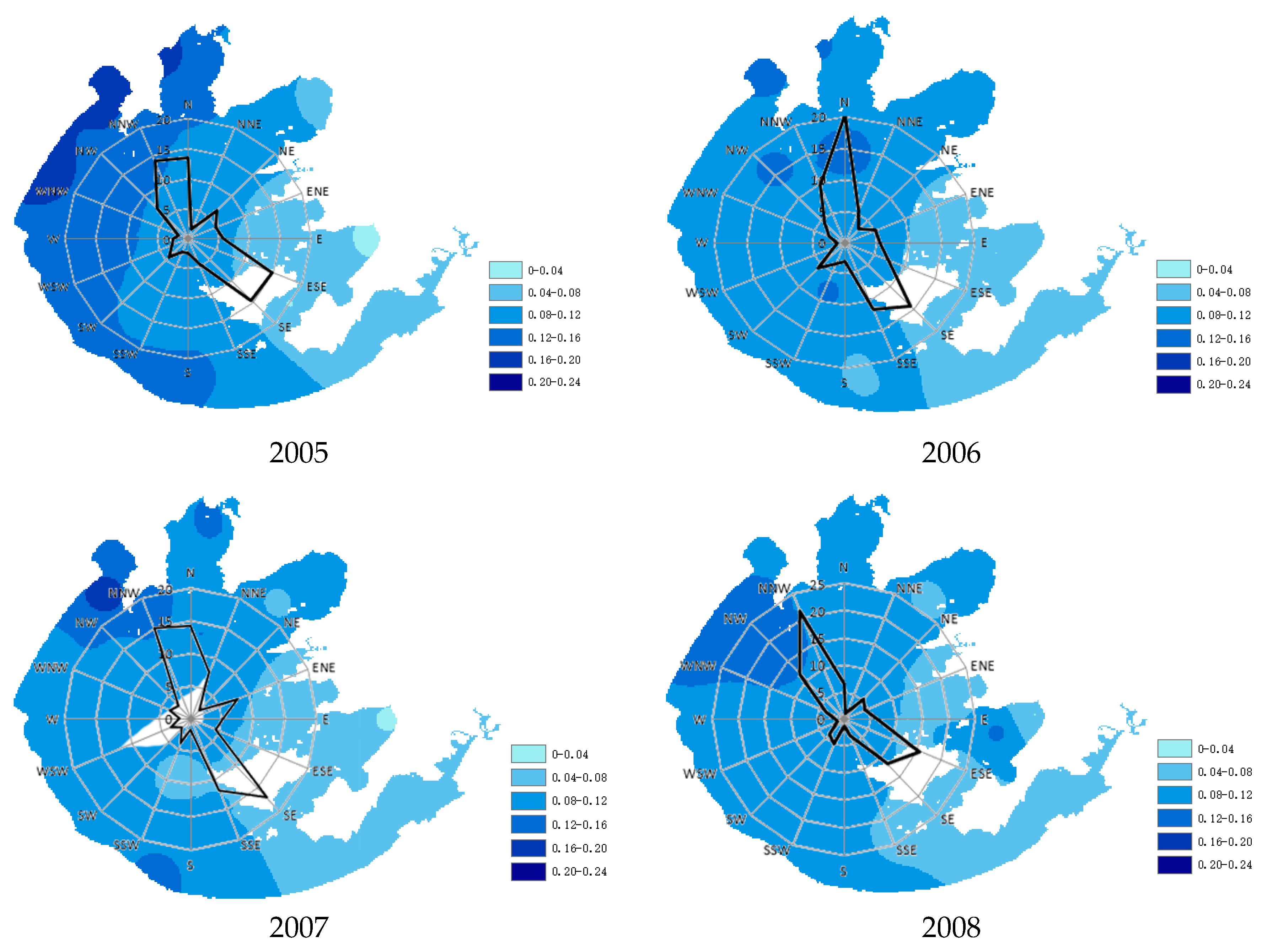
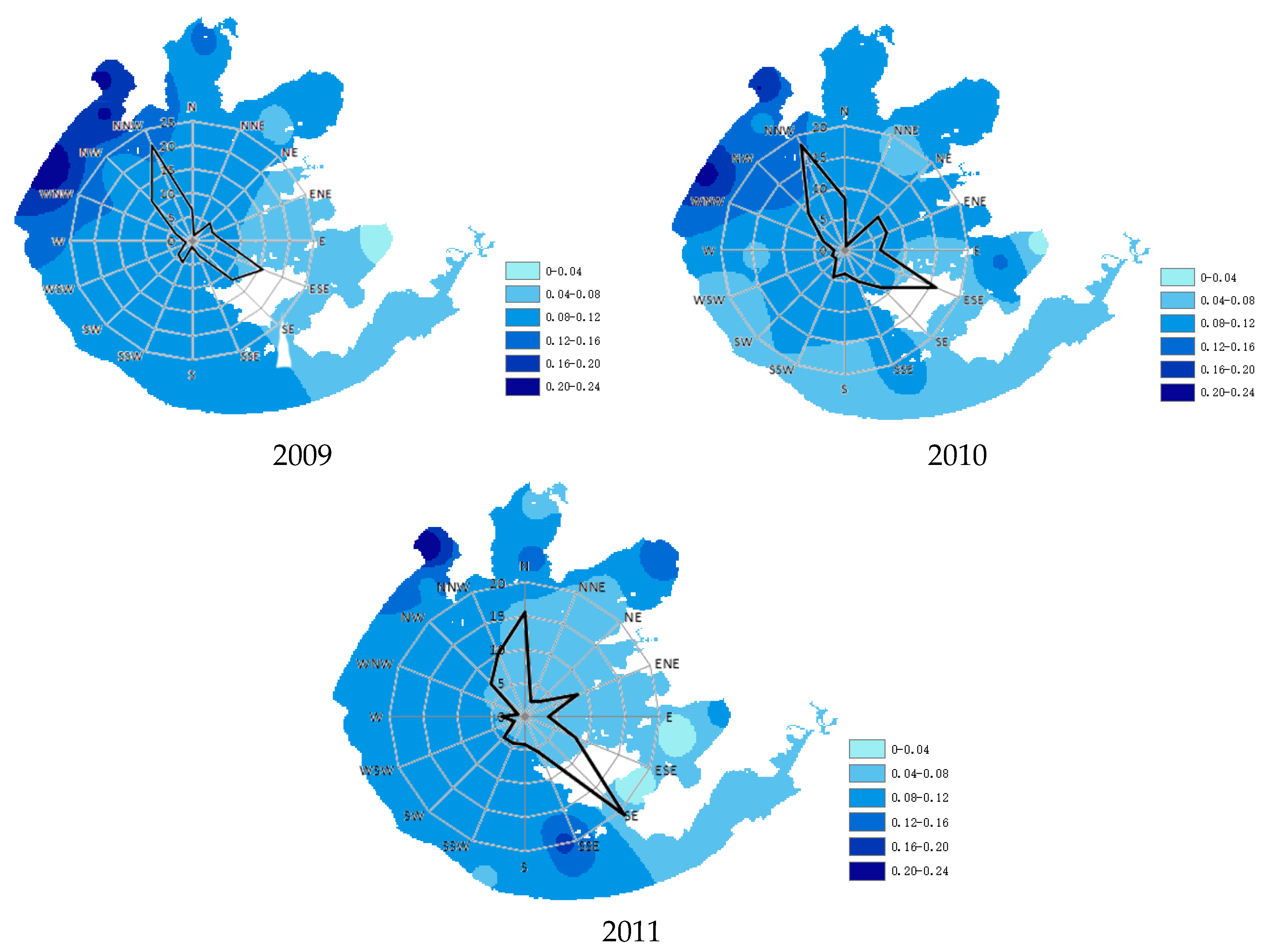
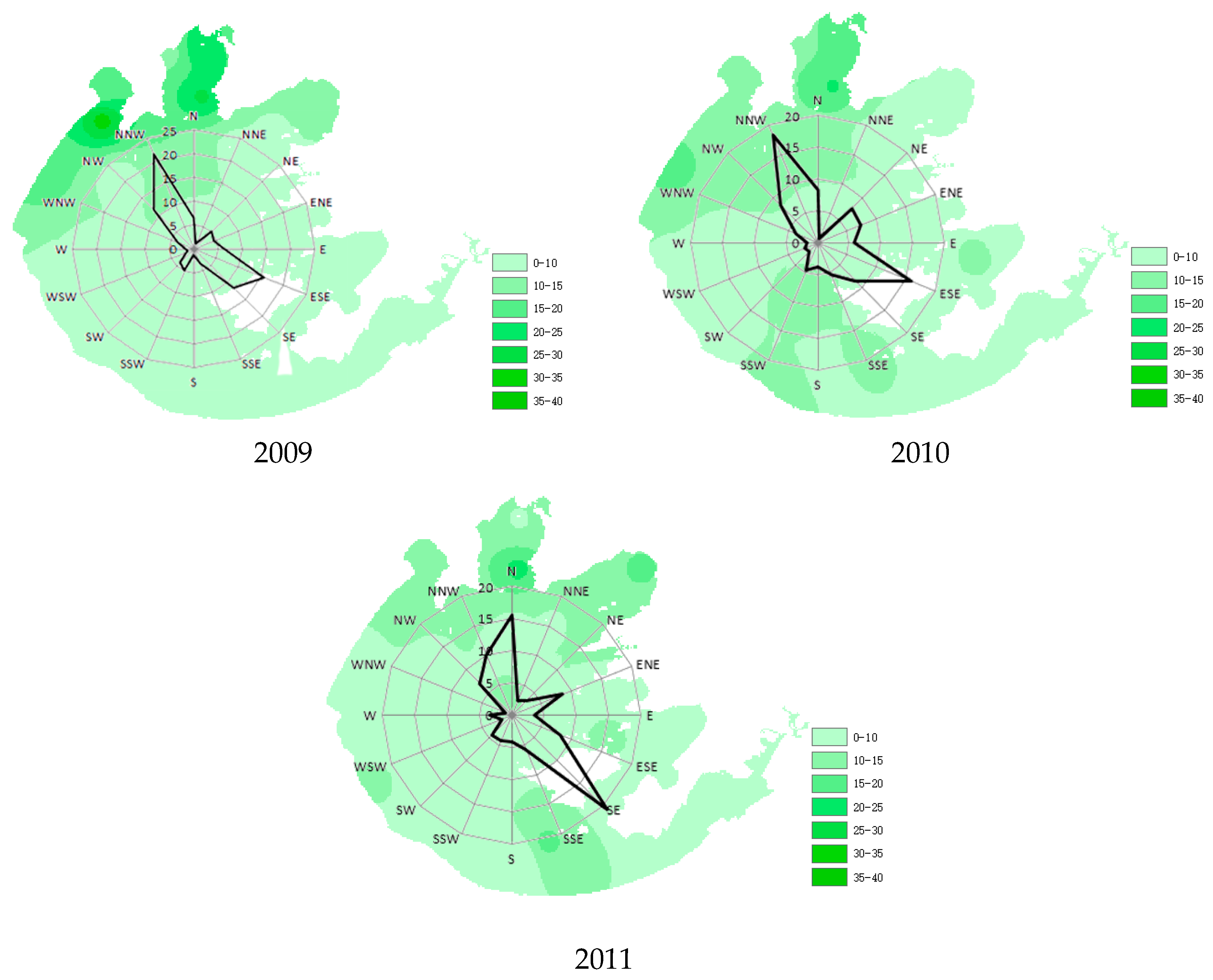
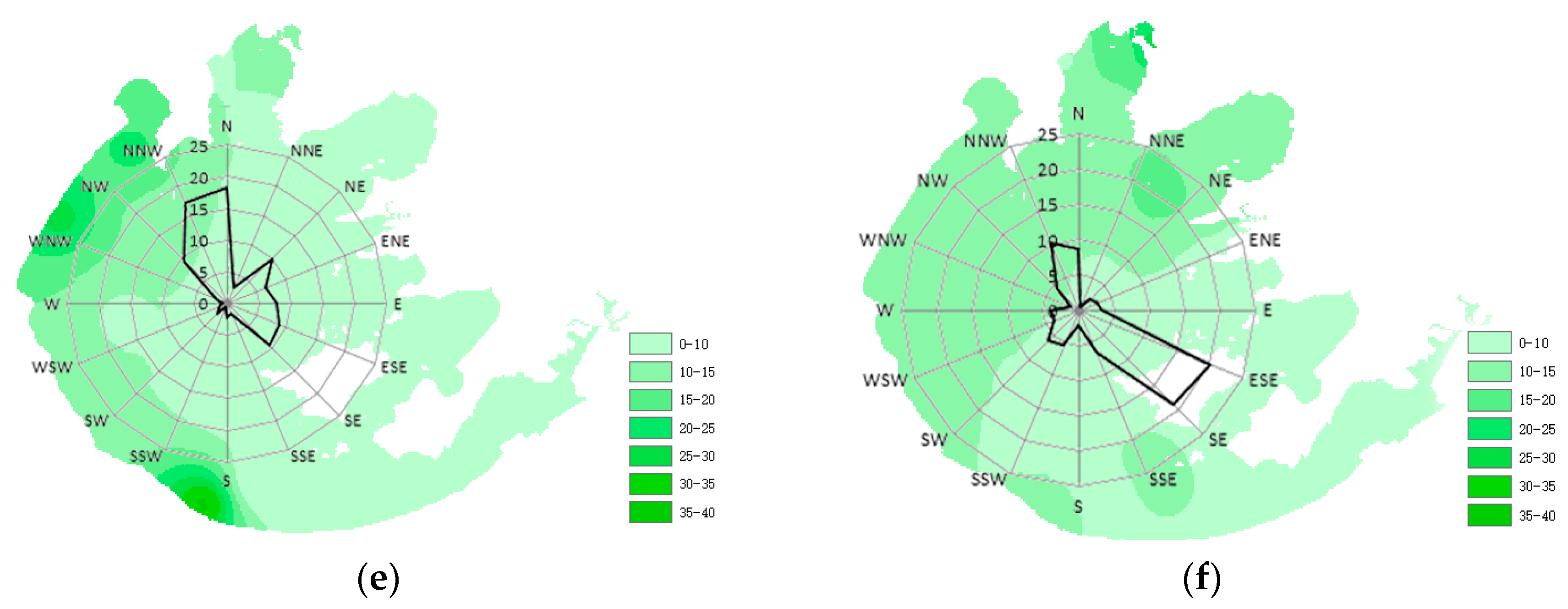
3.1. Wind Direction and Speed
3.2. Effects of Wind Direction on Water Quality
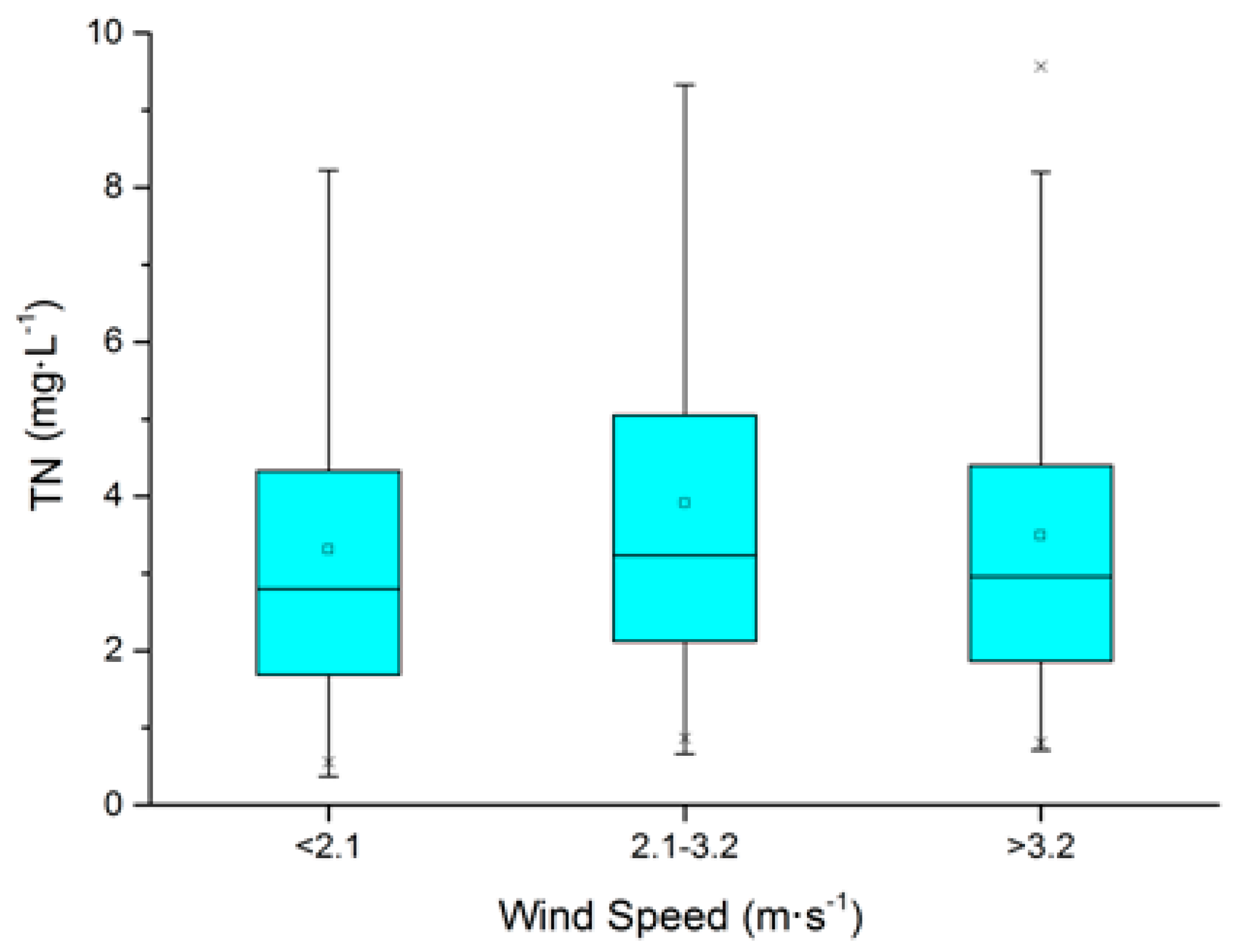
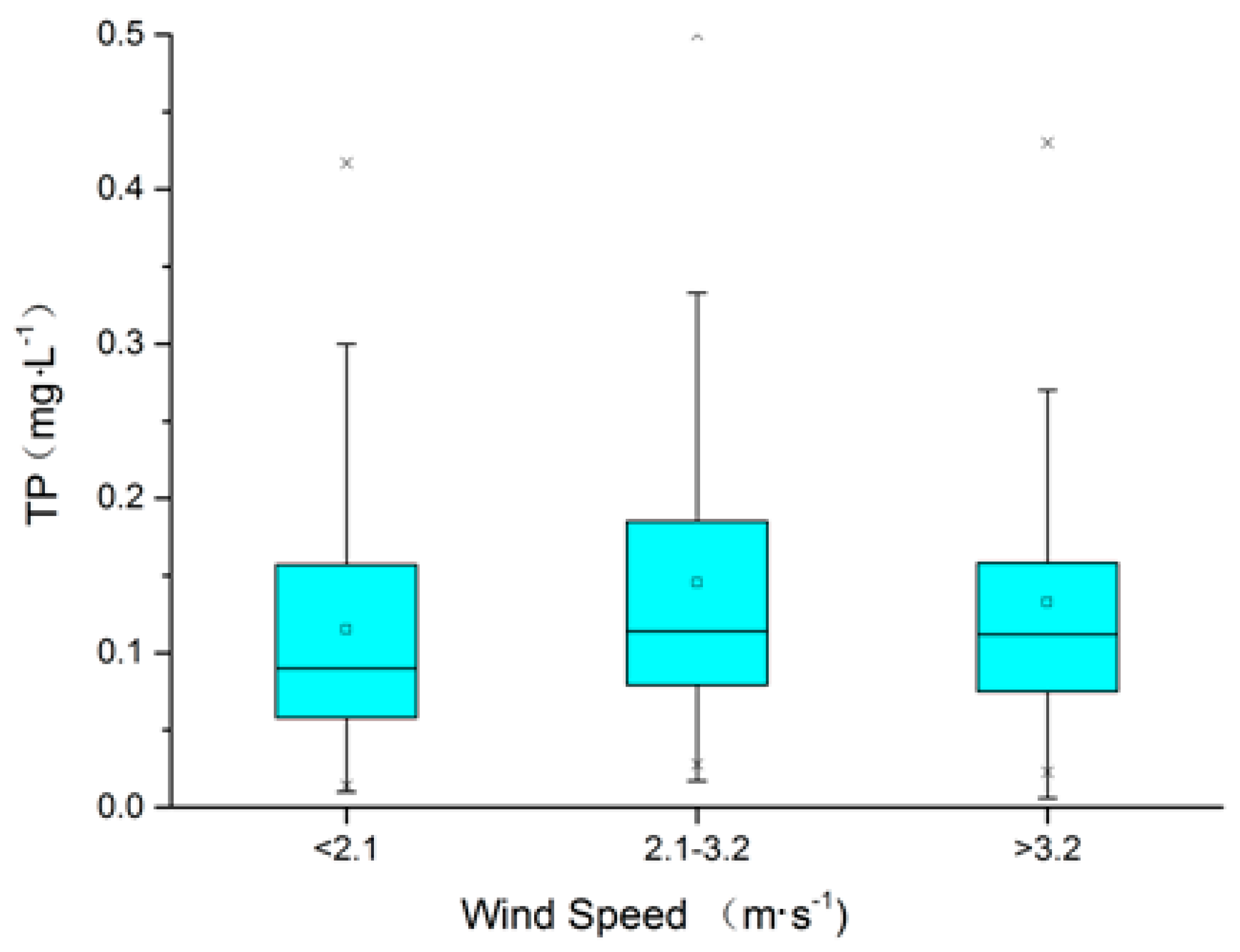
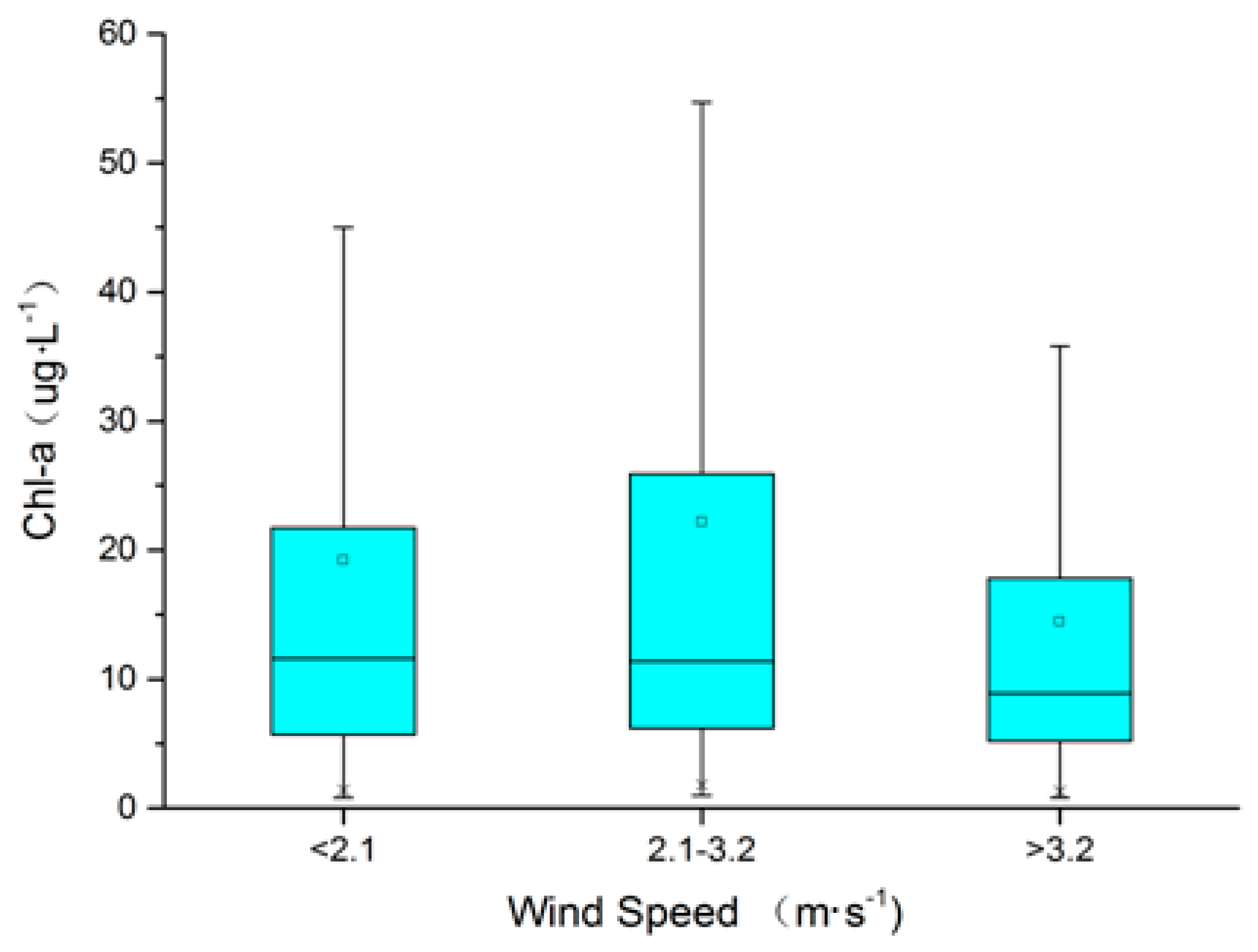
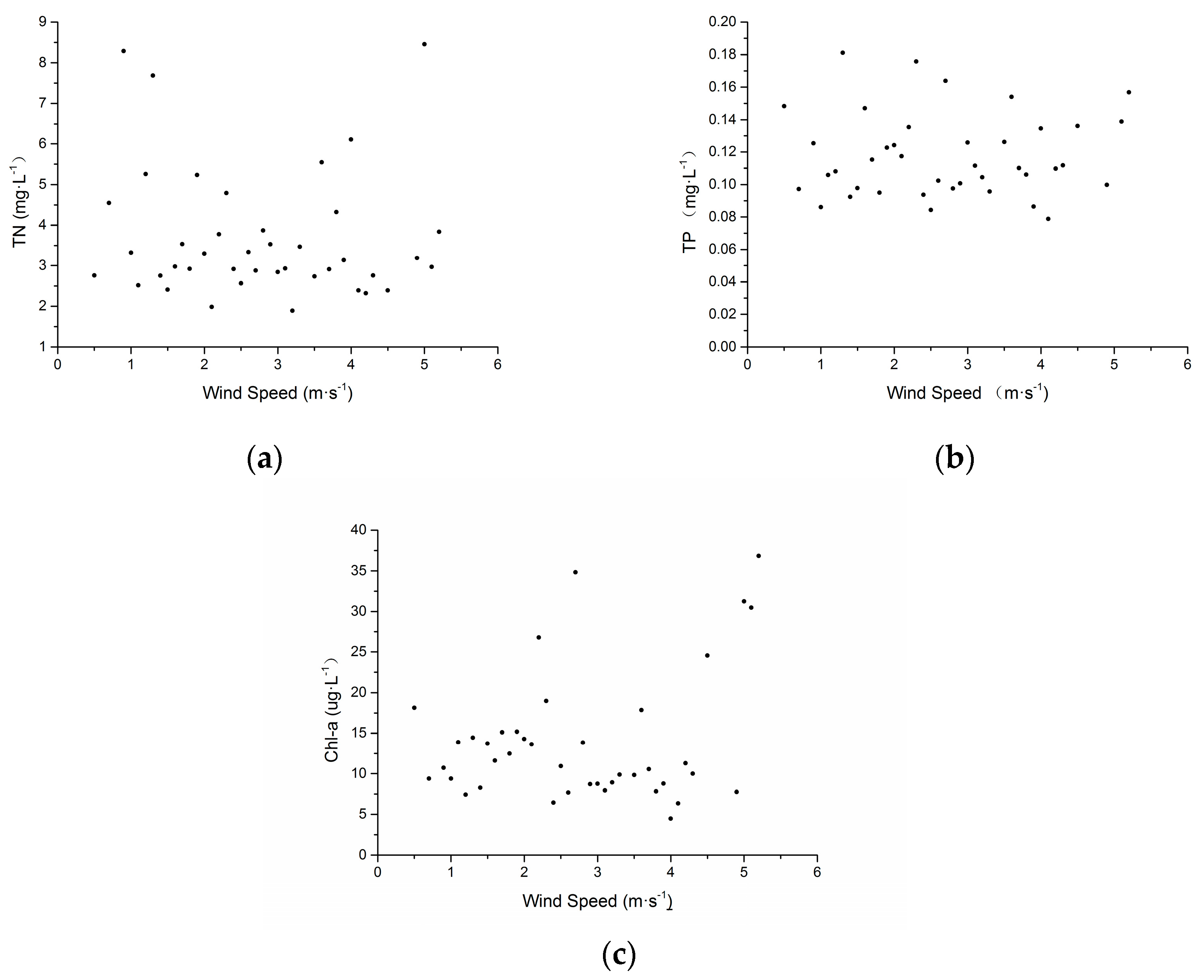
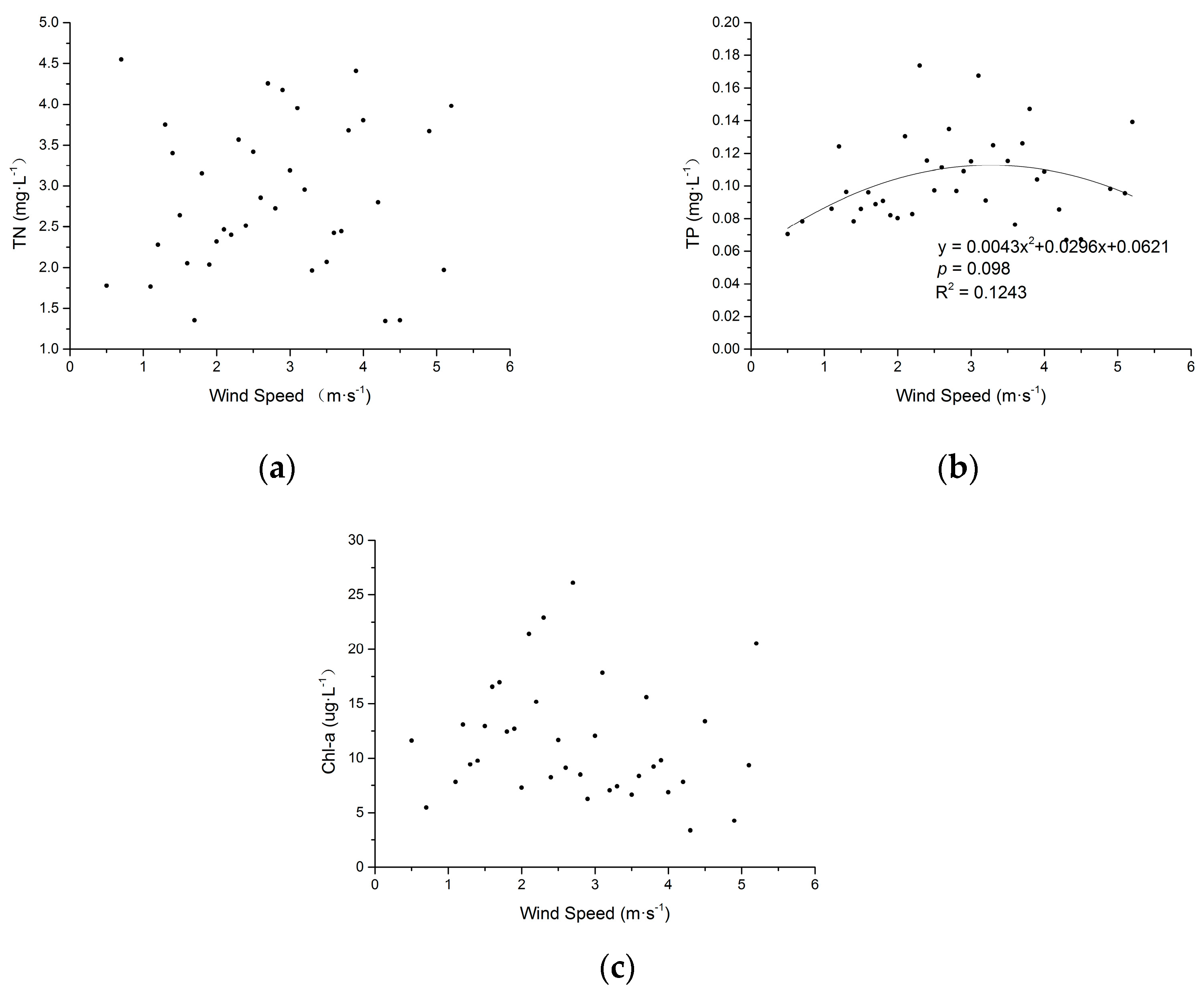
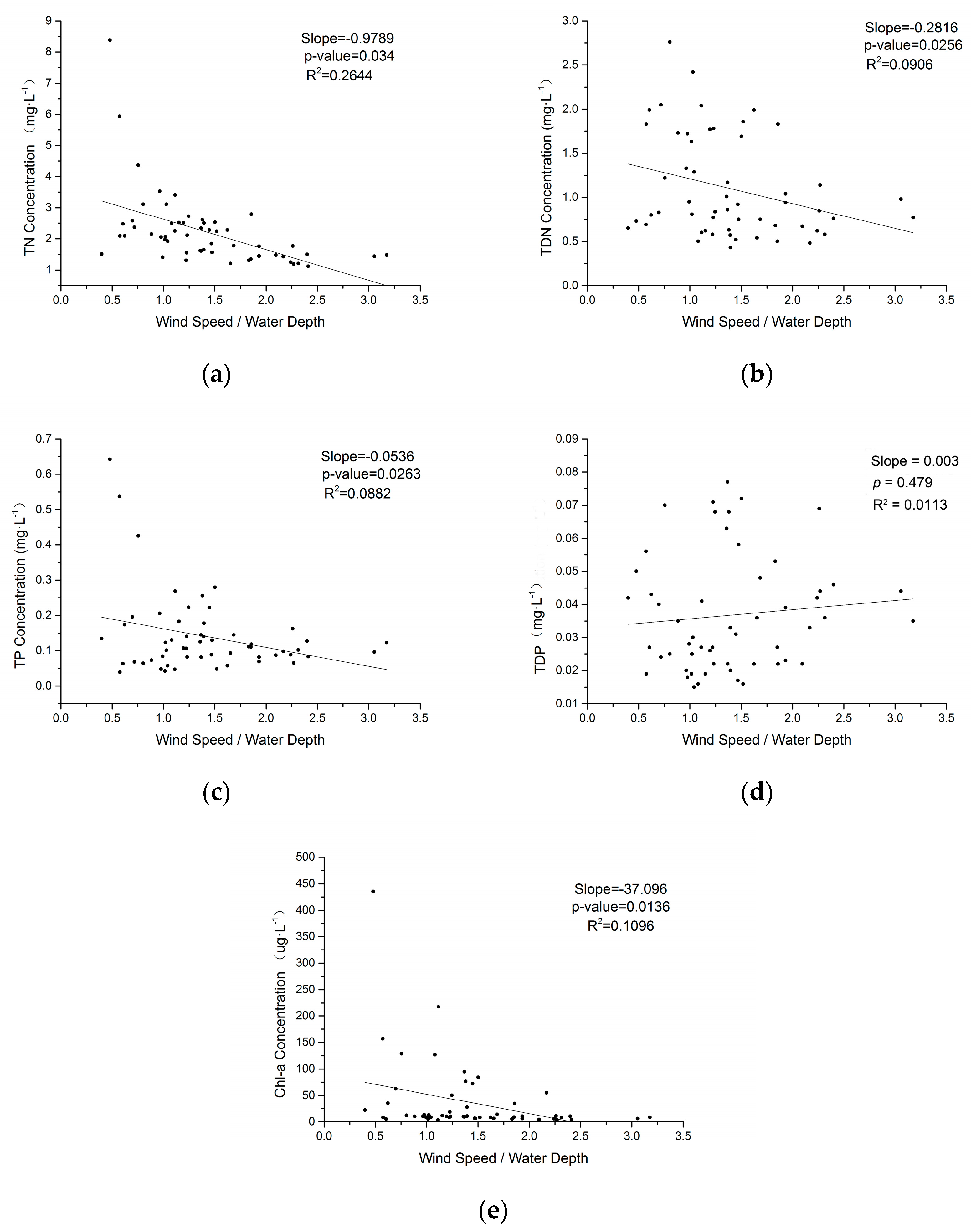
3.3. Effects of Wind Speed on Water Quality
3.4. Effects of Wind-Induced Shear Stress on Water Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekol, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Adachi, Y.; Suzuki, M. Floating and sedimentation of a single Microcystis floc collected from surface bloom. Water Res. 1993, 27, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterialblooms in a hypereutrophic lake (Taihu Lake, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2007, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijssel, J.C.; Hecky, R.E.; Kishe-Machumu, M.A.; Meijer, S.; Pols, J.; Van Tienderen, K.; Ververs, J.; Wanink, J.H.; Witte, F. Climatic variability in combination with eutrophication drives adaptive responses in the gills of Lake Victoria cichlids. Oecologia 2016, 182, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Jacobsen, B.; Hansen, R.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Mazzeo, N.; Branco, C.W.C. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulation—The successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Duan, H.T.; Shi, X.L.; Yu, Y.; Kong, F.X. Contributions of meteorology to the phenology of cyanobacterial blooms: Implications for future climate change. Water Res. 2012, 46, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, Q.; Xi, B.; Wang, X.; Jia, K.; Huo, S.; Su, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. Effects of lake-basin morphological and hydrological characteristics on the eutrophication of shallow lakes in east China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, I.D.; Lopez, R.; Pozo, I.; Green, A.J. Nutrient and sediment dynamics in a Mediterranean shallow lake in southwest Spain. Limnetica 2012, 31, 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Havens, K.E.; Fukushima, T.; Xie, P.; Iwakuma, T.; James, R.T.; Takamura, N.; Hanazato, T.; Yamamoto, T. Nutrient dynamics and eutrophication of shallow lakes Kasumigaura (Japan), Donghu (PR China), and Okeechobee (USA). Environ. Pollut. 2001, 111, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.E.L.; Couceiro, F.; Fones, G.R.; Helsby, R.; Amos, C.L.; Black, K.; Parker, E.R.; Greenwood, N.; Statham, P.J.; Kelly-Gerreyn, B.A. In situ flume measurements of resuspension in the North Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, C.; Anim, D.O.; Yu, Z.; Acharya, K. Improved Yangtze River diversions: Are they helping to solve algal bloom problems in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, J.; Reitzel, K.; de Barbanere, H.; Gogoll, A.; Rydin, E. Release of organic P forms from lake sediments. Water Res. 2011, 45, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.H.; Li, W.; Liu, G.H.; Yuan, L.Y. The effect of different submerged macrophyte species and biomass on sediment resuspension in a shallow freshwater lake. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 88, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Zhong, J.; Fan, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S. Effects of hydrodynamics process on phosphorus fluxes from sediment in large, shallow Taihu Lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.P.; Mitchell, S.F. An empirical model for sediment resuspension in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 1996, 317, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.G.; Bombardelli, F.A.; Schladow, S.G. Sediment resuspension in a shallow lake. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçyigit, M.B.; Falconer, R.A. Three-dimensional numerical modelling of wind-driven circulation in a homogeneous lake. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johengen, T.H.; Biddanda, B.A.; Cotner, J.B. Stimulation of Lake Michigan plankton metabolism by sediment resuspension and river runoff. J. Great Lakes Res. 2008, 34, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, B.V.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chubarenko, I.P.; Hutter, K. Wind-driven current simulations around the Island Mainau (Lake Constance). Ecol. Model. 2001, 138, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Schwab, D.J. Relationships between wind-driven and hydraulic flow in Lake St. Clair and the St. Clair Babin Delta. J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.V. Relation of plankton to hydrographic conditions in Sweetwater Lake. J. Am. Waterworks Assoc. 1949, 41, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Verduin, J. A comparison of phytoplankton data obtained from a mobile sampling method with those obtained from a single station. Am. J. Bot. 1951, 38, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, I.T. Effect of wind on the distribution of phytoplankton cells in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Walsby, A.E. Water blooms. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1975, 50, 437–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookes, J.D.; Regel, R.H.; Ganf, G.G. Changes in the photochemistry of Microcystis aeruginosa in response to light and mixing. New Phytol. 2003, 158, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ostos, E.; Cruz-Pizarro, L.; Basanta, A.; George, D.G. The influence of wind-induced mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant and sinking phytoplankton species. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.F.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Luo, L.C.; Ding, Y.Q.; Bian, G.Y. Dynamics of cyanobacterial bloom formation during short-term hydrodynamic fluctuation in a large shallow, eutrophic and wind-exposed, LakeTaihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8546–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.J.; Hu, W.P.; Zhu, Z.C. Ecological impacts of water transfers on Lake Taihu from the Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 26, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.B.; Guo, C.S.; Wang, D.M.; Du, P.; Luo, Y.; Wan, J.; Meng, W. Distribution, sources and composition of antibiotics in sediment, overlying water and pore water from Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L. Doing battle with the green monster of Lake Taihu. Science 2007, 317, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, R. China aims to turn tide against toxic lake pollution. Science 2011, 333, 1210–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Xi, B.; Jia, K.; Huo, S.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Xu, B. Evaluation of a modified Monod model for predicting algal dynamics in Lake Tai. Water 2015, 7, 3626–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Luo, L. Effects of typhoon Morakot on a large shallow lake system, Lake Taihu, China. Ecohydrology 2012, 5, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, R.W.; Hoyer, M.V.; Canfield, D.E. The potential for wave disturbance in shallow Florida lakes. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2000, 16, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bao, L.; Zeng, E.Y. Recent advances in the field measurement of the diffusion flux of hydrophobic organic chemicals at the sediment-water interface. Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 56, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Vandervieren, E. An adjusted boxplot for skewed distributions. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 5186–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cózar, A.; Gálvez, J.A.; Hull, V.; García, C.M.; Loiselle, S.A. Sediment resuspension by wind in a shallow lake of Esteros del Iberá (Argentina): A model based on turbidmetry. Ecol. Model. 2005, 186, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xi, B.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; He, L.; Liu, H. Experiment study of the effects of hydrodynamic disturbance on the interaction between the cyanobacterial growth and the nutrients. J. Hydrodyn. 2016, 28, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.Q.; Hu, W.P.; Gao, G.; Luo, L.C.; Zhang, J.S. Dynamic mechanism and conceptual model of inner source release of sediments suspension from Taihu Lake. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1822–1831. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.F.; Qin, B.Q.; Brookes, J.D.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhu, M.Y.; Yan, W.M.; Wang, Z. The influence of changes in wind patterns on the areal extension of surface cyanobacterial blooms in a large shallow lake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, X.B.; Jia, Y.F.; Shields, F.D., Jr.; Wang, S.S.; Cooper, C.M. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of cohesive sediment transport and wind wave impact in a shallow oxbow lake. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.C.; Gao, G.; Gu, B.H. Estimation of internal nutrient release in large shallow Lake Taihu. Sci. China 2006, 49, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyr, H.; MaCabe, S.K.; Nürnberg, G.K. Phosphorus sorption experiments and potential for internal phosphorus loading in littoral areas of a stratified lake. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.S. Ecology of Phytoplankton; Cambridge University Press: Cambridege, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, J.; Weissing, F.J. Light-limited growth and competition for light in well-mixed aquatic environments: An elementary model. Ecology 1994, 75, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.B.; Hamilton, D.P. Simulation of vertical position of buoyancy regulating Microcystis aeruginosa in a shallow eutrophic lake. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 62, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.G.; Edwards, R.W. The effect of wind on the distribution of chlorophyll a and crustacean zooplankton in a shallow eutrophic reservoir. J. Appl. Ecol. 1976, 13, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Sample Size ➀ | Min ➁ | Max ➁ | Median ➁ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Production | ||||
| Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) (µg·L−1) ➂ | 1153 | 0.8 | 189.7 | 19 |
| Chemical Parameters | ||||
| Total nitrogen (TN) (mg·L−1) ➂ | 1153 | 0.4 | 20.8 | 3.6 |
| Total phosphorus (TP) (mg·L−1) ➂ | 1153 | 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.13 |
| Climate | ||||
| Daily average wind speed (m·s−1) ➃ | 7182 | 0.3 | 11.3 | 3.09 |
| Water Quality | Abbreviation | Meiliang and Zhushan Bay | Central Lake | East Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll-a (μg·L−1) | Chl-a | 27.3 | 12.81 | 6.10 |
| Total nitrogen (mg·L−1) | TN | 4.55 | 2.85 | 1.81 |
| Total phosphorus (mg·L−1) | TP | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Pang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Eutrophication in Lake Tai as Affected by Wind. Water 2017, 9, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030200
Zhang W, Xu Q, Wang X, Hu X, Wang C, Pang Y, Hu Y, Zhao Y, Zhao X. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Eutrophication in Lake Tai as Affected by Wind. Water. 2017; 9(3):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030200
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenhui, Qiujin Xu, Xixi Wang, Xiaozhen Hu, Cheng Wang, Yan Pang, Yanbin Hu, Yang Zhao, and Xiao Zhao. 2017. "Spatiotemporal Distribution of Eutrophication in Lake Tai as Affected by Wind" Water 9, no. 3: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030200
APA StyleZhang, W., Xu, Q., Wang, X., Hu, X., Wang, C., Pang, Y., Hu, Y., Zhao, Y., & Zhao, X. (2017). Spatiotemporal Distribution of Eutrophication in Lake Tai as Affected by Wind. Water, 9(3), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030200







