1. Introduction
Radio frequency resources are rapidly becoming scarcer because of the dramatic increased use of wireless and mobile communication devices. The industry may regard this spectral resource scarcity as a result of too much wireless traffic. However, it has been shown that the spectrum depletion is due to inefficient static spectrum allocation by regulators rather than because of heavy transmission. Many researchers and practitioners believe that this paradox can be resolved by cognitive radio reassigning statically assigned but rarely used frequency resources to secondary (or unlicensed) users [
1,
2]. This would give unlicensed users the opportunity to access the lightly used spectrum along with the time or frequency domain.
A cognitive radio scheme can also be applied to wireless sensor networks (WSNs) since one of the main goals of WSNs is timely data transmission using resource-constrained sensors. Cognitive radio can assist in realizing timely transmission in WSNs, especially when the spectrum efficiency is very poor.
For example, in healthcare or telemedicine, sensors are used to monitor a patient’s vital signs and transmit the data in a timely manner. In this case, many sensors may transmit their monitored results concurrently, since different vital signs need to be transmitted immediately. Furthermore, several patients may be cared for within a limited physical space (e.g., a ward). To complicate the scenario, we assume a situation in which wireless devices, such as wireless patient-monitoring systems, operate in an unlicensed industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) band.
We have established three criteria, outlined below, for the deployment of cognitive radio in WSNs.
1.1. Maximum Spectral Efficiency and Fair Spectrum Allocation with Priority
When unused spectrum resources are limited, the resources should be allocated with the goal of maximizing the spectral efficiency and fairness. Furthermore, a sensor containing more urgent data should have a higher transmission priority than that of other sensors. This can be achieved by maximizing the proportional fairness with demand weights [
3], maximizing the weighted log-sum utility function in terms of the spectrum resources. Maximization of this sum leads to the principle called weighted proportional fairness. The main feature of proportional fairness is that it results in allocation that is less fair in terms of demand but is more effective in terms of the total throughput (or total utilization) achieved by all sensors.
1.2. Minimum Spectrum Handover
The other primary objective of WSNs is long-term functionality. However, dynamic spectrum allocation causes additional energy consumption at sensors because frequency resynchronization (i.e., spectrum handover) occurs too often. It has been shown that all the processes of decoding, channel estimation, and frequency and timing synchronization require a certain amount of power in a software-radio system [
4]. We also simulated ZigBee standard radio using OMNET++ 3.3 [
5] and measured the amount of energy consumed when spectrum handover occurs in frequency domain. The simulation showed that a single spectrum handover requires 110.75% of the energy consumption compared with receiving energy and 96.06% compared with transmission. This means that more spectrum handovers lead to more power consumption. Hence, unnecessary spectrum handover should be eliminated or at least minimized.
1.3. Spectrum Allocation by A Central Authority
Wireless networks have two spectrum allocation schemes: centralized and distributed. These two schemes are compared in [
6,
7]. In a centralized scheme, a centralized authority (such as a base station or dedicated coordinator or TV band white space (TVWS) base station [
8,
9,
10,
11]) detects and identifies unused spectrums and allocates them to unlicensed users following a predefined policy. All of these processes may be performed separately by different entities, i.e., a detector, identifier, and allocator. There is an overhead in message exchange since all of the results of the spectrum allocation should be delivered to all of the sensors for every transmission request. Furthermore, the range of spectrum detection by the central authority is limited.
In a distributed scheme, each unlicensed user (i.e., sensor in WSNs) should have the ability to detect unused spectrum. In addition, they may exchange their spectrum information and vindicated spectrum resources to improve the overall network performance. This implies that every sensor should have full implementation of cognitive radio. However, it is impossible to let every sensor possess all cognitive radio functions. Consider a small WSN in which the sensors are distributed somewhat densely, such as a patient-monitoring system in an intensive care unit; in such a case, the centralized method is preferred over the distributed one.
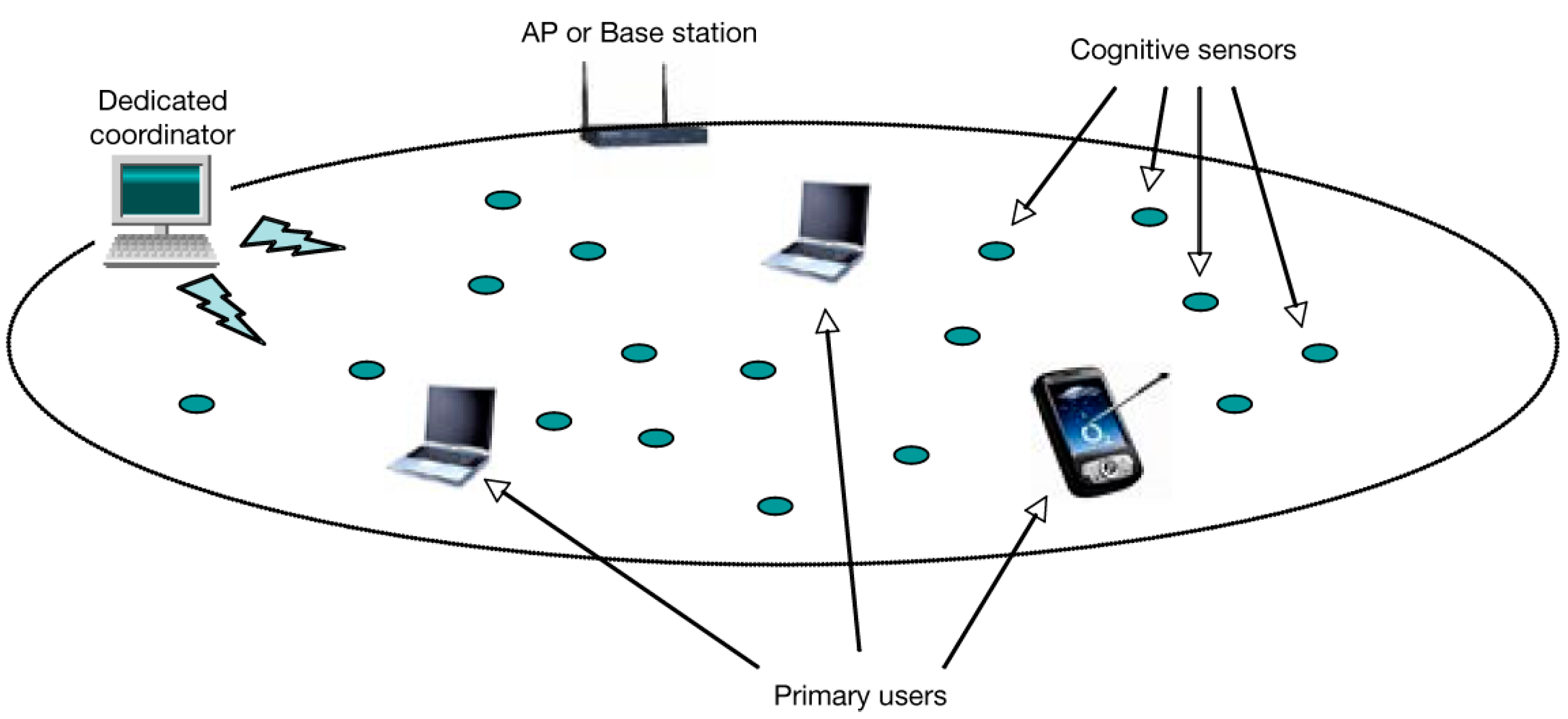
In this paper, we consider a centralized scheme with densely distributed sensors located within a cell or segment boundary, as shown in
Figure 1. It is assumed that transmitting sensors request spectrum from the central authority (or dedicated coordinator). Then, the central authority allocates spectrum to each sensor according to the following principals: (1) maximum utilization of idle spectrums, (2) proportionally fair allocation, and (3) transmission priority among sensors, while (4) avoiding unnecessary spectrum handovers.
We model the problem of spectrum allocation as a multi-objective (or bi-objective) optimization problem. Following scalarization of the multi-objective utility functions, we convert the multi-objective functions into a single-objective function using modified game theory (MGT) [
12].
We use a cooperative approach to identify the approximate solution of the problem modelled using MGT. Note that the proposed algorithm has complexity O(N2M), where N and M are the numbers of sensors and unused spectrum resources, respectively. In numerical experiments, we show that the proposed algorithm yields fair spectrum allocation reflecting the priority of each sensor and avoiding unnecessary spectrum handover.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we present related work.
Section 3 outlines the system model and problem formulations. In
Section 4, we scalarize the multi-objective problem using MGT. In
Section 5, we propose a cooperative algorithm to identify an approximate solution.
Section 6 describes the results of numerical experiments. Finally, we conclude the paper in
Section 7.
2. Related Work
There are many remarkable studies related to centralized cognitive radio system using TVWS. A few of them are [
8,
9].
In [
8], the authors studied the performance degradation that occurs when independently-operated unlicensed users share TVWS channels, and showed that there are key parameters, such as number of secondary networks (SNs), number of unlicensed users in each SN, and interference range of each SN, that affect the performance of TVWS.
In [
9], the authors addressed issues related to transmission power control and distributed detection of idle spectrums in TVWS.
Moreover, many research studies have addressed the cognitive radio WSNs.
In [
13], the authors proposed a resource-allocation algorithm for cognitive radio sensor networks assuming energy-harvesting-enabled spectrum sensors. They formulated the problem into a mixed integer nonlinear program and proposed a cross-entropy-based algorithm to achieve maximum channel availability. They also considered a power control algorithm for data sensors.
In [
14], the authors deployed the concept of in-band wireless energy transmissions (named green power beacon) to cognitive radio sensors. They proposed an algorithm for controlling the interference among the wireless energy transmissions and data transmissions.
Various multi-objective optimization problems and techniques were addressed in [
15]. The authors noted that single-objective optimization approaches may be unfair and unreasonable in real WSN applications.
Energy efficient opportunistic channel access in cognitive radio sensor networks was considered in [
16]. The authors also considered switching to a licensed channel and channel access sequence for energy saving. Additionally, they also discussed separate power control schemes for intra-cluster and inter-cluster data transmission.
For the issue of proportional fair resource allocation, in a study by Han et al. [
17], a centralized scheme was discussed for achieving fair subcarrier allocation for a multiuser orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) system using the Nash bargaining solution (NBS). The authors explained the proportional fairness using the NBS concept. There are also many studies on the proportional fair resource allocation in wireless sensor networks, such as [
18].
Recently, a few studies (such as [
19,
20]) have mentioned the effectiveness of cooperative approaches (especially, cooperative spectrum sensing).
3. System Model
Considering a spectrum sharing using TVWS system, we make the following assumptions:
For simplicity, the spectrum resources are defined as multiple spectrum units.
The frequency bands accessed by each sensor do not need to be contiguous by assuming OFDMA [
21,
22,
23].
All idle spectrum units are detected and maintained by a TVWS base station or whitespace database (WSDB) [
10] or coexistence enabler [
11].
More than two sensors can share a spectrum unit if they do not interfere with one another.
The spectrum is allocated periodically. That is, the TVWS base station detects unused spectrum units and allocates them to sensors that request transmissions at the start of every predefined epoch.
Spectrum handover may occur at a receiver as well as at a transmitter. Here, we focus on minimizing spectrum handover only at the transmitter side.
According to the definition in [
17], the resource allocation scheme
P is proportionally fair if and only if, for any other feasible allocation scheme
M, we have
where
U is the user set, and
is the average resource of user
i with allocation scheme
M. Equation (1) implies that any change in allocation must have a negative average change for the system. A proportionally fair allocation scheme is equivalent to a scheme that maximizes the sum of the natural logarithmic average user resource, which can be written formally as
Then, we formulate the problem in the form of multi-objective nonlinear programming:
Parameters
V: set of transmitting sensors.
S: set of unused spectrum units.
Lis (binary): indicates that spectrum unit s has been synchronized with sensor i at its previous transmission epoch.
wi: the weight that reflects the priority of sensor i. A sensor with higher priority will be allocated more spectrum units. The priority is translated as the demand of each sensor for spectrum resources.
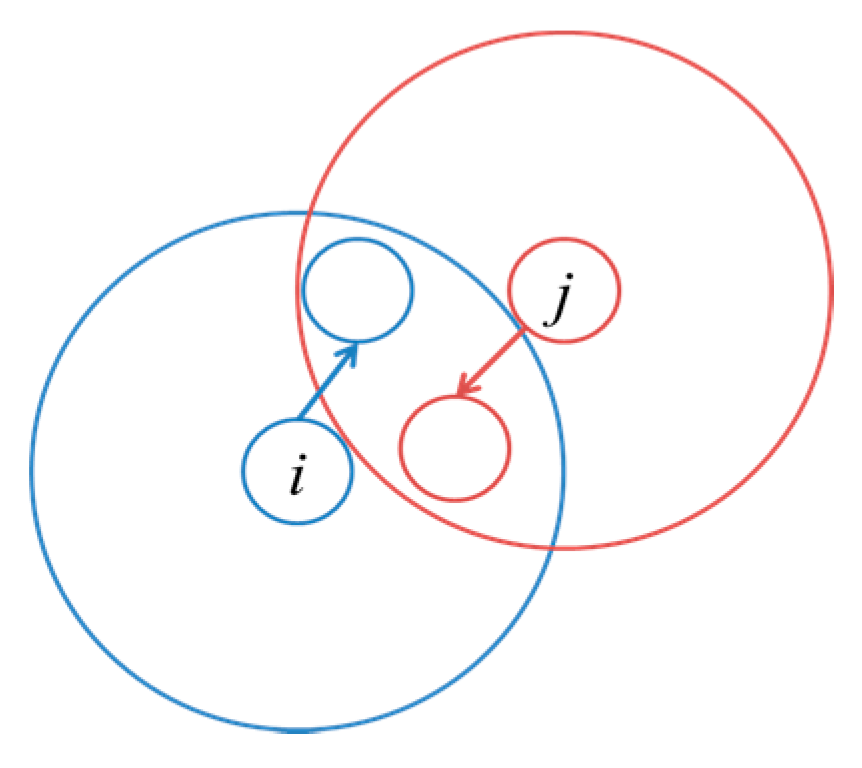
Rij (binary): indicates that the transmission of sensor
i can interfere with sensor
j (see
Figure 2). Therefore, sensors
i and
j cannot use the same spectrum unit. We let
Rij = 0 if
i =
j or sensor
i and
j are transmitting to the same destination.
xis (binary): indicates that sensor i is synchronized with spectrum unit s during the current transmission epoch.
Using Equation (3), we can achieve weighted fair spectrum allocation, as well as maximum spectrum utilization. Using Equation (4), we can avoid unnecessary spectrum handover. Equation (5) indicates that if Rij = 1; i.e., if the target of sensor i is within the transmission range of sensor j, they cannot share the same spectrum units.
4. Modified Game Theory Approach
In this section, we briefly review the basic concepts of MGT introduced in [
12]. Then, we propose an algorithm for spectrum allocation.
4.1. Basics for Modified Game Theory
In game theory, each player has an objective function such that he/she establishes a strategy for maximizing his/her utility at the expense of the utilities of other players. If we apply this theory to a multi-objective optimization problem, each player’s utility is defined as an objective function whose value is determined relative to the values of the other players’ objective functions. To achieve fair utility allocation to each player, a bargaining model or super-criterion is established, and the optimal solution in a Pareto sense is obtained by maximizing the objective function of the bargaining model or the super-criterion. Given each player’s objective function fi(X), the Pareto optimal solution is obtained by solving the following single objective optimization problem:
Subject to
where
r is the number of objectives,
c = [
c1,
c2, …,
cr]
T, and Equations (8) and (9) are the constraints of the original multi-objective problem. Then, the super-criterion, also known as the NBS [
24], is constructed as follows:
where
, and
Xi* is the optimal design vector obtained when only
fi is minimized. Then, each objective function
fi(
X) is normalized as
fni(
X) by following the normalization procedure that gives 0 and 1 as the minimum and maximum values, respectively:
This leads to the vector of normalized functions: fn = [fn1 fn2 … fnr]T.
Then, the super-criterion S in Equation (10) is maximized such that the optimal solution of S leads to the optimal solution of all of the objective functions (c*) in a Pareto sense and the final optimal solution (X* = Xc*). Hence, the problem given in Equation (6) and the maximization of S should be computed simultaneously with c and X being the decision variables, which is not feasible in reality.
Here, a modification of the original game (i.e., MGT) is proposed. MGT yields a solution that is sufficiently close to the optimal solution of the original game. The algorithm for MGT is as follows:
(a) Formulate the normalized super-criterion,
Sn, as
(b) Formulate a Pareto optimal objective function
FC in terms of the normalized objective functions using the goal programming method as
(c) The new optimization problem is posed as
Note that the constraints of the objective functions guarantee that Sn has a value between 0 and 1.
Consequently, MGT introduces a way to solve the NBS, for example, by expressing it as a normalized form using the goal programming technique as done here. We describe the deployment of MGT to the spectrum allocation in the next subsection.
4.2. MGT for the Problem of Spectrum Allocations in WSNs
The problem of spectrum allocations can be scalarized into a single objective optimization problem using MGT with the following steps.
(a) Convert the maximization problem into minimization problem as follows:
Uw is the value of Equation (18) with the optimal solution of the problem given by Equations (19) and (20). In a similar way, Hw is the value of Equation (19) with the optimal solution of the problem defined by Equations (18) and (20). That is, Uw is obtained by solving the optimization problem given by Equations (19) and (20), and Hw is yielded by solving the optimization problem given by Equations (18) and (20). Then, Uw and Hw act as upper bounds of the two objective functions.
(d) Formulate a Pareto optimal objective function
FC in terms of the normalized objective functions using the goal programming method as follows:
where
q ≥ 2.
(e) The multi-objective problem is converted into a single objective one (i.e., scalarized) as
5. Cooperative Approach
In
Section 4, we scalarize the multi-objective (i.e., bi-objective) optimization problem as a single-objective one. However, the scalarized problem is still non-convex and intractable. Therefore, we use a cooperative approach to find an approximate solution in reasonable time.
Before solving the problem, we define Uw, and Hw as the upper bounds of the solution. The optimal <H*, Uw> can be computed using the algorithm given in Algorithm 1 in reasonable time, whose complexity is O(N2M), where N and M are the numbers of transmitting sensors and unused spectrum units, respectively. As shown in the algorithm, the spectrums are synchronized according to Lis (that is defined allocation vector in previous transmission epoch) initially (Step 1). If Lis satisfies the constraint (that is, (xis + xjs) Rij > 1), then there will be no spectrum handover and H* will be optimal. Otherwise, they negotiate the ownership in order not to interfere each other and in the direction of improving Uw (Step 2). That is, start with best solution and then let spectrum handover occur only when the constraint is not satisfied. The solution must be optimal. It is true that there may be other sets of xis satisfying (xis + xjs) Rij > 1, but there are no other sets that yield better H* than the algorithm does.
Since Uw serves as the upper bound of U in the algorithm, it is essential to improve Uw to obtain a better U without compromising H*.
However, finding optimal F(X) and <U*, Hw> is intractable. Thus, we envisage a cooperative approach to determine the approximate minimum F(X) and <U*, Hw> in reasonable time.
| Algorithm 1. The algorithm for determining optimal UW and H*. |
| Step 1. Initialization | for each i V and s S
set xis = Lis |
| Step 2. Call Negotiation | for each i, j V and s S {
if ((xis + xjs)Rij > 1)
call Negotiate(i, j, s)
} |
| Step 3. Define Uw and H* | Define Uw and H* using Equations (18) and (19). |
Subroutine Negotiate(i, j, s) {
xis = 1, xjs = 0
Compute U using Equation (18) and store it in temp1.
xis = 0, xjs = 1 Compute U using Equation (18) and store it in temp2.
if temp1 < temp2
xis = 1, xjs = 0
} |
Cooperative algorithms are devised separately according to whether sensors have the ability to control transmission power. Algorithm 2 shows the algorithm for sensors that cannot control transmission power.
In Step 1, all the functions are initialized with the worst values they can have. In Step 2, a winner is selected based on the computation results of the function in Equation (25)—assigning the spectrum unit to the winner improves the objective function the most.
| Algorithm 2. The cooperative game-based algorithm without transmission power control. |
| Step 1. Initialization | For the minimum F(X),
-ϕ(X) = F(X)
-U* = , H*=
For finding <U*, Hw>,
-ϕ(X) = .
For all,
-minϕ(X) = ∞
-Assign all idle spectrum units to sensors. |
| Step 2. Winner selection on each spectrum | for each s S {
for each i V {
for each j (≠ i) V
xjs = 0
xis = 1
Compute ϕ(X).
if (ϕ(X) < minϕ(X)) {
minϕ(X) = ϕ(X)
winner = i
}
xis = 0.
}
Assign spectrum unit s to winner.
} |
| Step 3. U* and Hw | For finding <U*, Hw>, U* = ϕ(X) and Hw = . |
Algorithm 3 shows the algorithm for sensors that have the ability to control transmission power.
In Step 2, each sensor selects its negotiation partner (that is, coalition member) with which it is to negotiate the spectrum ownership in Step 3. The negotiation partner is selected in the direction of achieving best values of the objective function in Equation (25).
The time complexities of both algorithms are O(N2M), where N and M are the numbers of transmitting sensors and unused spectrum units, respectively. However, using this algorithm, it is impossible to improve Hw without compromising U*. Therefore, we get Hw using the computation result of U*.
| Algorithm 3. The cooperative game-based algorithm with transmission power control. |
| Step 1. Initialization | For the minimum F(X),
-ϕ(X) = F(X)
-U* =, H* =
For finding <U*, Hw>,
-ϕ(X) = .
For all,
-Assign all idle spectrum units to sensors.
-negotiated[i] = 0 for all i V. |
| Step 2. Forming coalitions | Copy X to Y.
Sort i V in accordance with wi and arrange the index k = 1, …, |V| from the largest to smallest.
for k = 1, …, |V| {
if (!negotiated[k]) {
minϕ(Y) = ∞
for each j (≠ i) V {
if (!negotiated[j]) {
Negotiate(k, j, Y) and compute ϕ(Y).
if (ϕ(Y) < minϕ(Y)) {
minϕ(Y) = ϕ(Y)
coalition[k] = j
}
}
}
negotiated[k] = 1, negotiated[coalition[k]] = 1
}
} |
| Step 3. Negotiation in each coalition | for each i V
Negotiate(i, coalition[i], X)
if X satisfies Equation (20), go to Step 4; else go to Step 2. |
| Step 4. U* and Hw | For finding <U*, Hw>, U* = ϕ(X) and Hw = . |
Subroutine Negotiate(a, b, Z) {
for each s S {
if ((zas + zbs)Rij > 1)
zas = 1, zbs = 0
Compute ϕ(Z) and store it in ϕ1(Z).
zas = 0, zbs = 1
Compute ϕ(Z) and store it in ϕ2(Z).
if (ϕ1(Z) < ϕ2(Z))
zas = 1, zbs = 0
}
} |
In both algorithms, we do not initialize U* and H* using their optimal values when we compute the minimum F(X), as shown in Step 1. Instead, we use their lower bounds to avoid computing the best U* and H* in every coalition and negotiation step. Nonetheless, the algorithm yields satisfactory results (i.e., <U, H>).
Assuming that no sensor is able to control transmission power, each spectrum unit is occupied by only one sensor. Therefore, we let a winner sensor selected among the competitors occupy each spectrum unit while improving the objective: minimum F(X) or maximum proportional fairness.
If each sensor can control the transmission power, i.e., avoid interfering with other sensors that lie outside its target range, a coalition is formed (Step 2). Coalition formation depends on the weight assigned to each sensor: a sensor with the highest priority finds its coalition partner first. Then, each sensor tries to negotiate spectrum ownership with its partner to improve the main objective (Step 3). These processes continue while the constraint in Equation (28) is satisfied.
6. Numerical Experiments
It is important to compare the quality of the MGT solutions, i.e.,
U and
H, and
U*, determined in the cooperative algorithm, with the optimal solutions, i.e., the optimal
U* and
H*. We can determine the optimal
H* easily using Algorithm 1, but it is impossible to obtain the optimal
U* within a reasonable time. Here,
U and
U* are compared with a crude upper bound obtained by linear programming (LP) relaxation. To determine the upper bound, the nonlinear program used to find the optimal
U* needs to be linearized by piece-wise linearization. All the experiments are implemented using C language, and we use GNU Linear Programming Toolkit (GLPK) library [
25] (also written in C) to solve the approximated linear program.
For the experiment, we generate random topologies of 20 and 40 sensors and generate < source, destination > pairs randomly.
Table 1 shows the main parameters used in our experiments.
Table 2 shows the results as a tuple of
U and
H when 20 nodes are used. The column headed <-
U*, -
Hw> indicates the results obtained when we optimize only
U using the algorithms in Algorithms 2 and 3. The column <-
Uw, -
H*> indicates the results obtained when we optimize only
H using the algorithm in Algorithm 1. The column <-
U, -
H> shows the results of MGT using the algorithms in Algorithms 2 and 3. The results of LP relaxation are shown in the last column of
Table 2.
In the case without transmission power control, we observe that U obtained from MGT is even better than the value determined by optimizing only U, and we can obtain the optimal H. (-U means −1 × U, and the objective is to minimize U. Therefore -U becomes larger as the solution is closer to the optimal. Similarly, -H becomes larger as we get a better solution).
In the case with transmission power control, MGT is balanced between the two objectives. Furthermore, U and H are better than those in the case without transmission power control, since each spectrum unit can be shared by more than two sensors if they do not interfere with one another.
In both cases, we also observe that the improvement in one objective cannot be achieved without deterioration in the other objective, where each U is very close to the LP bound of U* with a factor of 2 or less.
According to the results listed in
Table 3 for a node size of 40, we see that the improvement obtained in one objective penalizes the other, and the result of MGT is a balance among the different objectives. In addition, the solutions of
U are very close to the LP bound of
U, with a factor of approximately 2 without transmission power control, whereas they are less than 1 with transmission power control.
We have shown that the spectrum bands are allocated fairly in accordance with the weights.
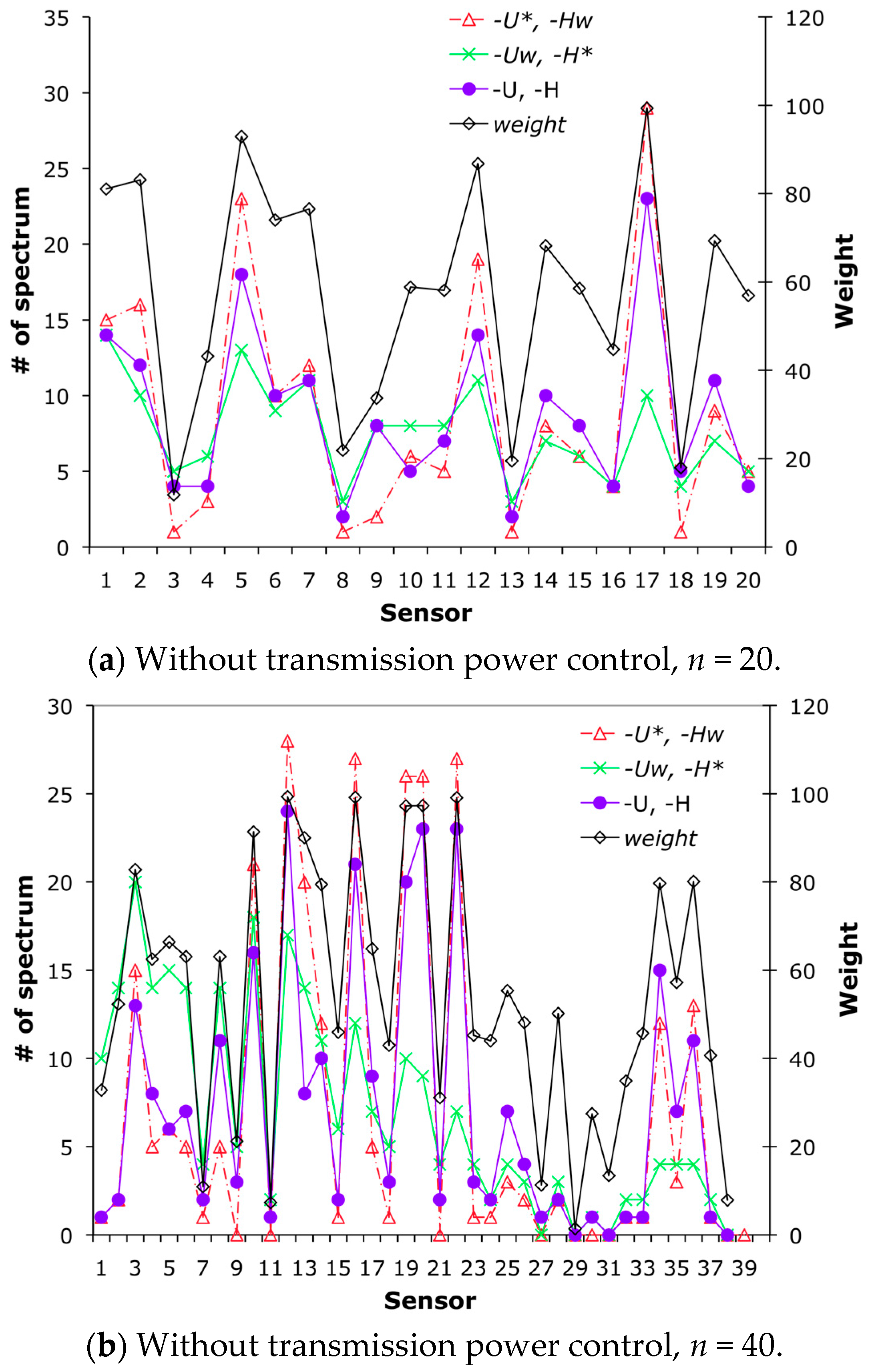
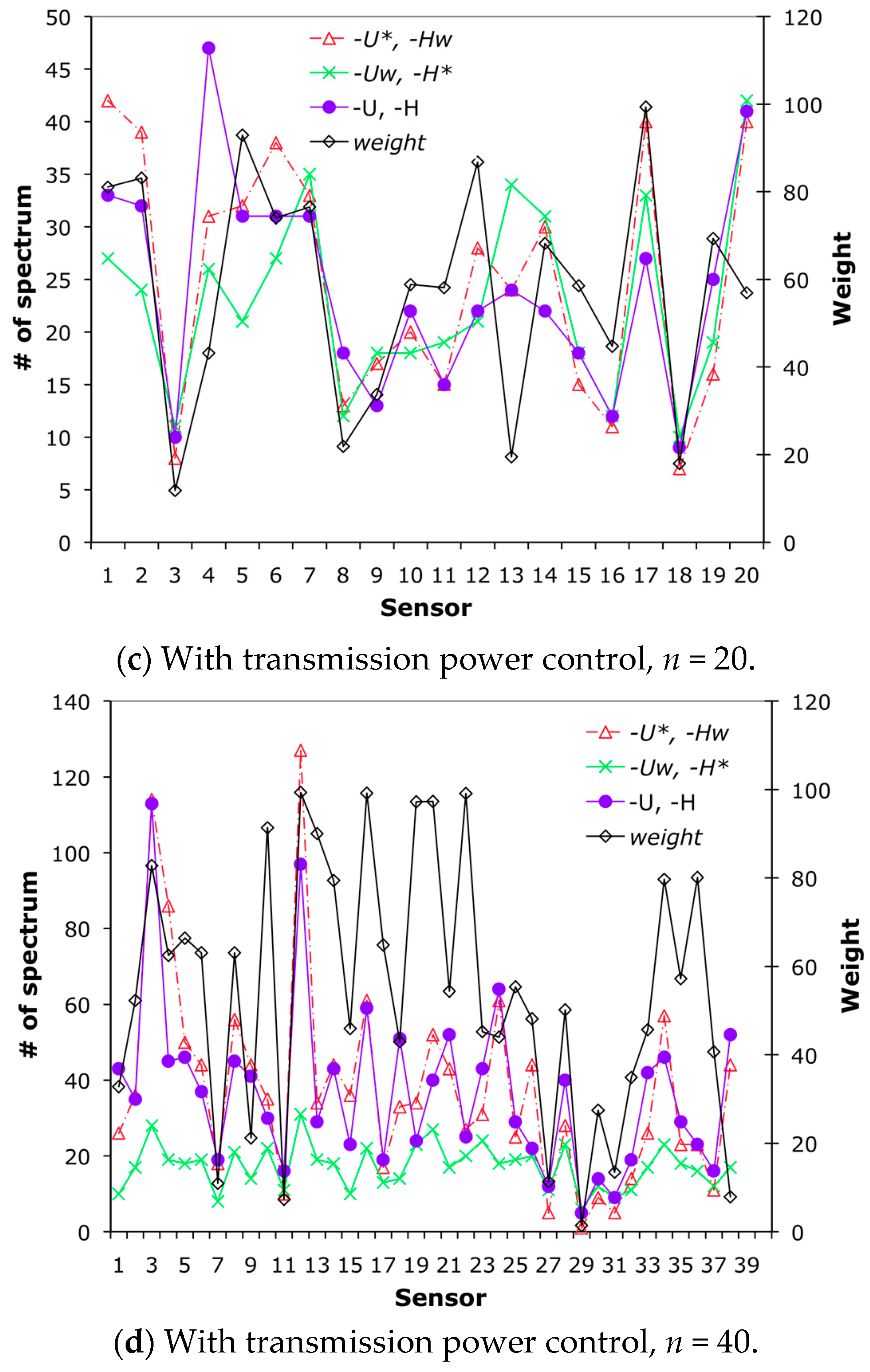
Figure 3 shows the number of assigned spectrum units for each sensor according to the three algorithms.
Figure 3a,b show the results obtained without transmission power control, in which every spectrum unit is occupied by one sensor only.
Figure 3c,d show the results obtained with transmission power control. As shown in
Figure 3a,b, MGT with the cooperative approach allocates the spectrum bands according to the weight of the sensor. However, as shown in
Figure 3c,d, the number of assigned spectrum units does not correspond to their respective weights in some cases (e.g., see sensor 13 in
Figure 3c). This is because this sensor interferes with fewer sensors than do other sensors, as shown in
Figure 3c. Therefore, such sensors have been allowed to occupy more spectrum units than other sensors, irrespective of their weights. Furthermore, it shows the solutions given by the cooperative algorithms (Algorithms 2 and 3), i.e., <-
U, -
H> in the graphs, lie between <-
U*, -
Hw> and <-
Uw, -
H*>, which implies the solutions of the multi-objective problem are between the solutions of the two single objective problems.
We have also measured the time elapsed in completing the allocation, and it was measured as being around 2 min with 20 nodes, and 7 min with 40 nodes.
In order to show how the spectrums are allocated fairly reflecting the priorities, we compute the fairness index [
26] given as
where
n is the number of sensors. The fairness index is a widely used metric to measure the level of fairness. The allocation becomes fairer as the index is close to 1.
For the purpose of comparison, we solve the optimization problem replacing Equation (3) with the following objective:
The optimization problem with Equation (30) becomes a max-weighted-sum utility problem: maximizing the total number of spectrums allocated to all sensors reflecting each sensor’s priority. Then the fairness index is computed with wi = 1 for all sensors.
In a similar way, we call the original optimization problem a max-weighted-log-sum utility problem.
We measured the fairness index with the network of 40 sensors, and
Table 4 shows the fairness index measured by solving each optimization problem.
As shown in
Table 4, better fairness is yielded by solving the max-weighted-log-sum utility problem. Furthermore, it is observed that better fairness is obtained with transmission power control.
7. Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper, we formulated the spectrum allocation problem of a resource-constrained WSN as a bi-objective optimization problem and devised a cooperative algorithm to determine approximate solutions. We considered the following goals: proportionally fair allocations, maximum spectral efficiency, allocation in proportion to the priority of each sensor, and avoidance of unnecessary spectrum handover. The first three goals are achieved by maximizing the proportional fairness associated with weight and priority. To maximize proportional fairness, two different algorithms were proposed according to the existing transmission power control at each sensor. We also proposed an algorithm to minimize the number of spectrum handoffs.
The numerical results of the cooperative algorithms are balanced between maximizing the proportional fairness and minimizing the number of spectrum handovers. We also compared the solutions of the algorithm with LP bounds and observed that the algorithm yields solutions quite close to the optimal.
We notice that it may be feasible to let the algorithm run in a distributive manner. Since a distributive algorithm runs on a resource-constrained sensor, it should be implemented as less computationally complex as possible with low message overhead. Although the complexity of the current algorithm is bounded polynomially, it becomes inefficient for a large sensor network, e.g., one with more than 1000 nodes. Therefore, it is necessary to devise a faster algorithm with negligible loss of accuracy; this is one of our future research objectives.