Chemical Force Microscopy Study on the Interactions of COOH Functional Groups with Kaolinite Surfaces: Implications for Enhanced Oil Recovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
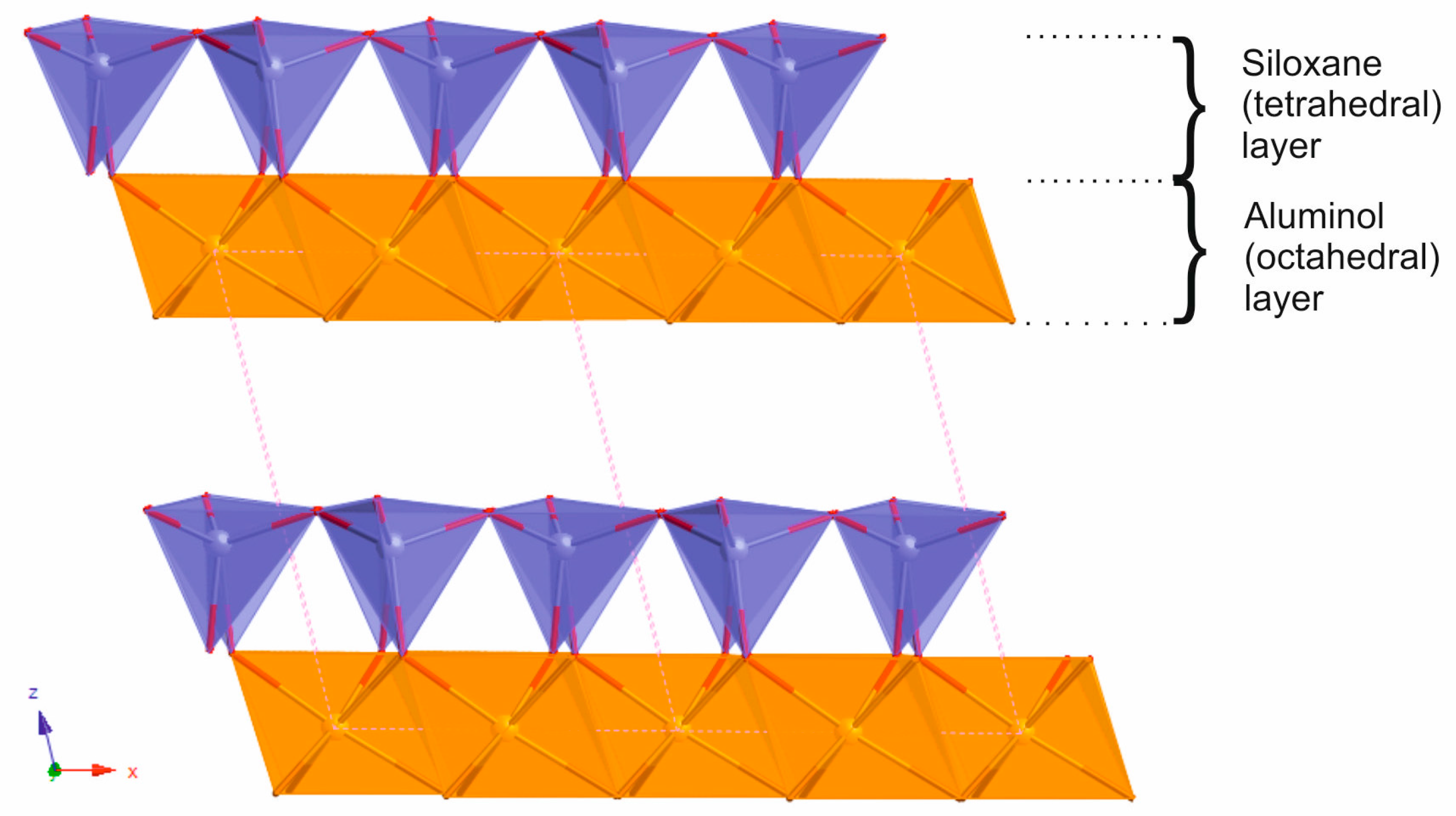
2.1. Oriented Kaolinite Sample Preparation
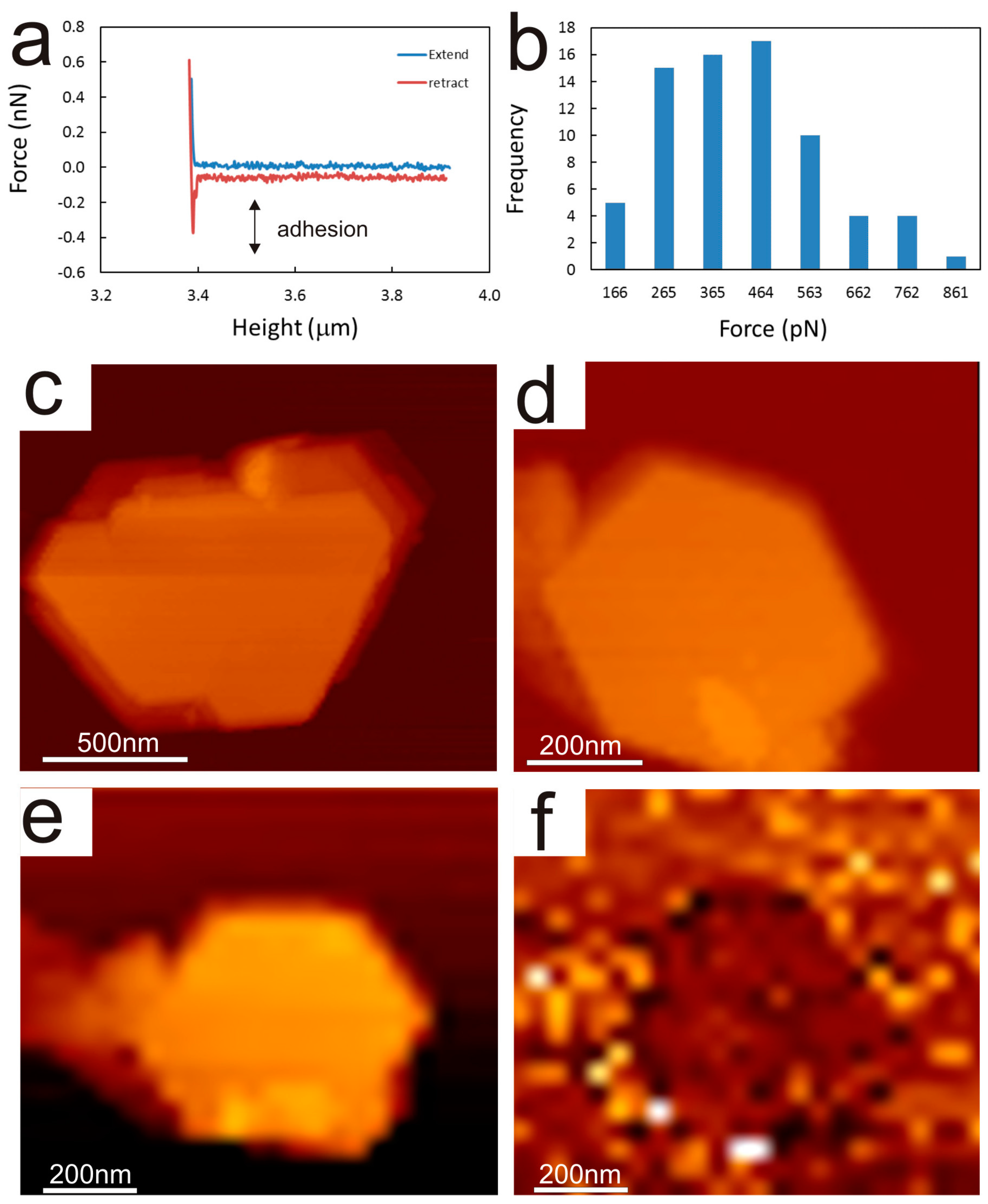
2.2. Chemical Force Microscopy
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Aqueous Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
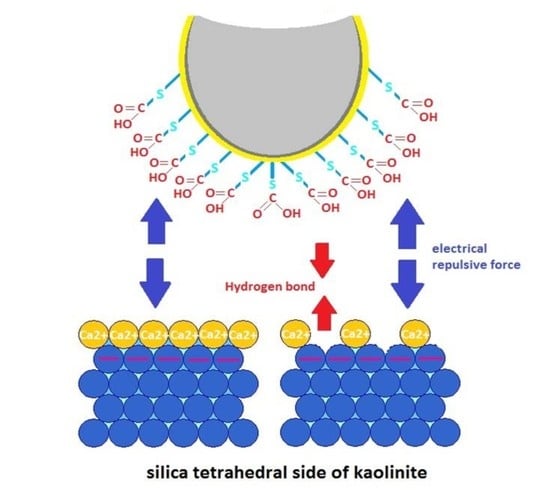
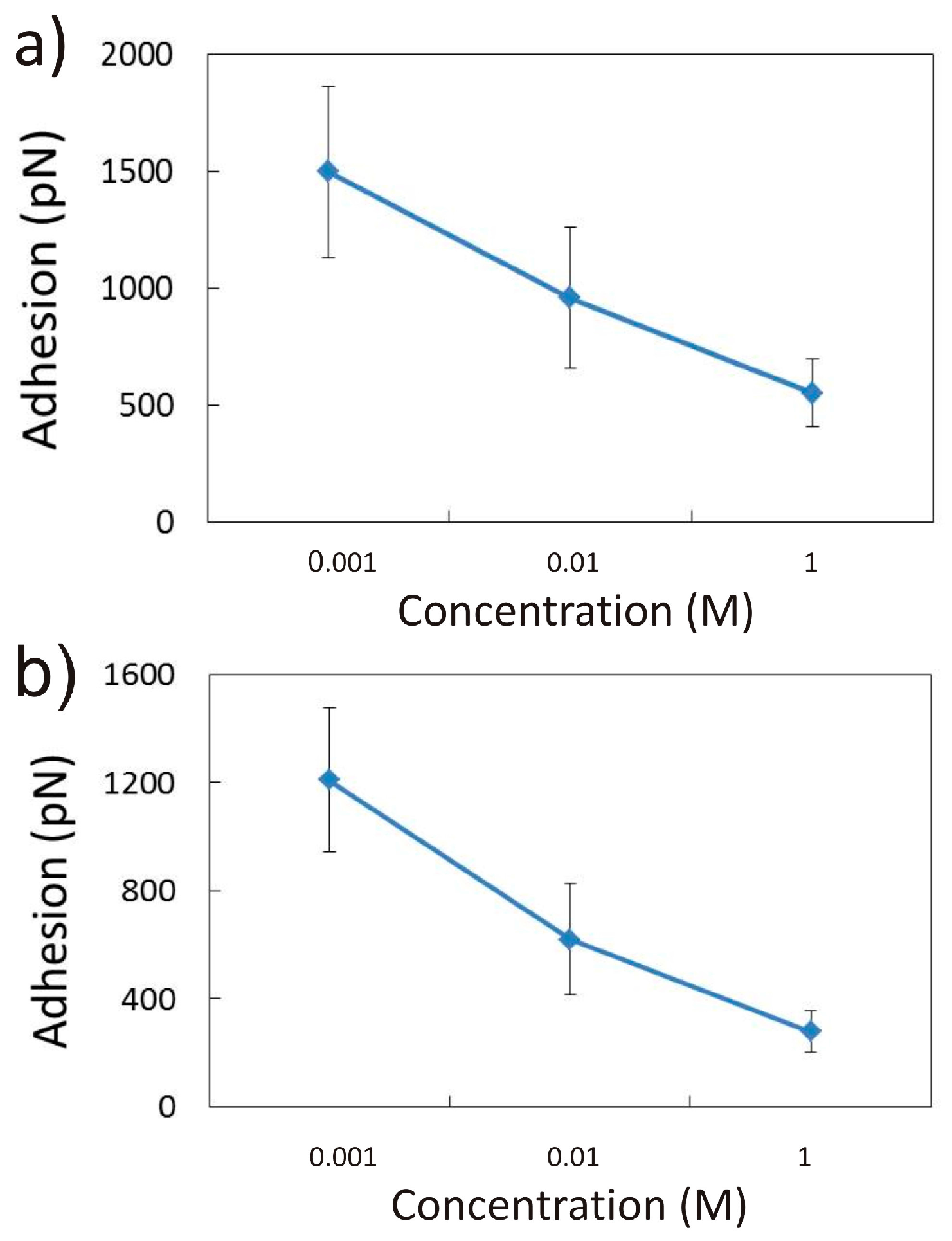
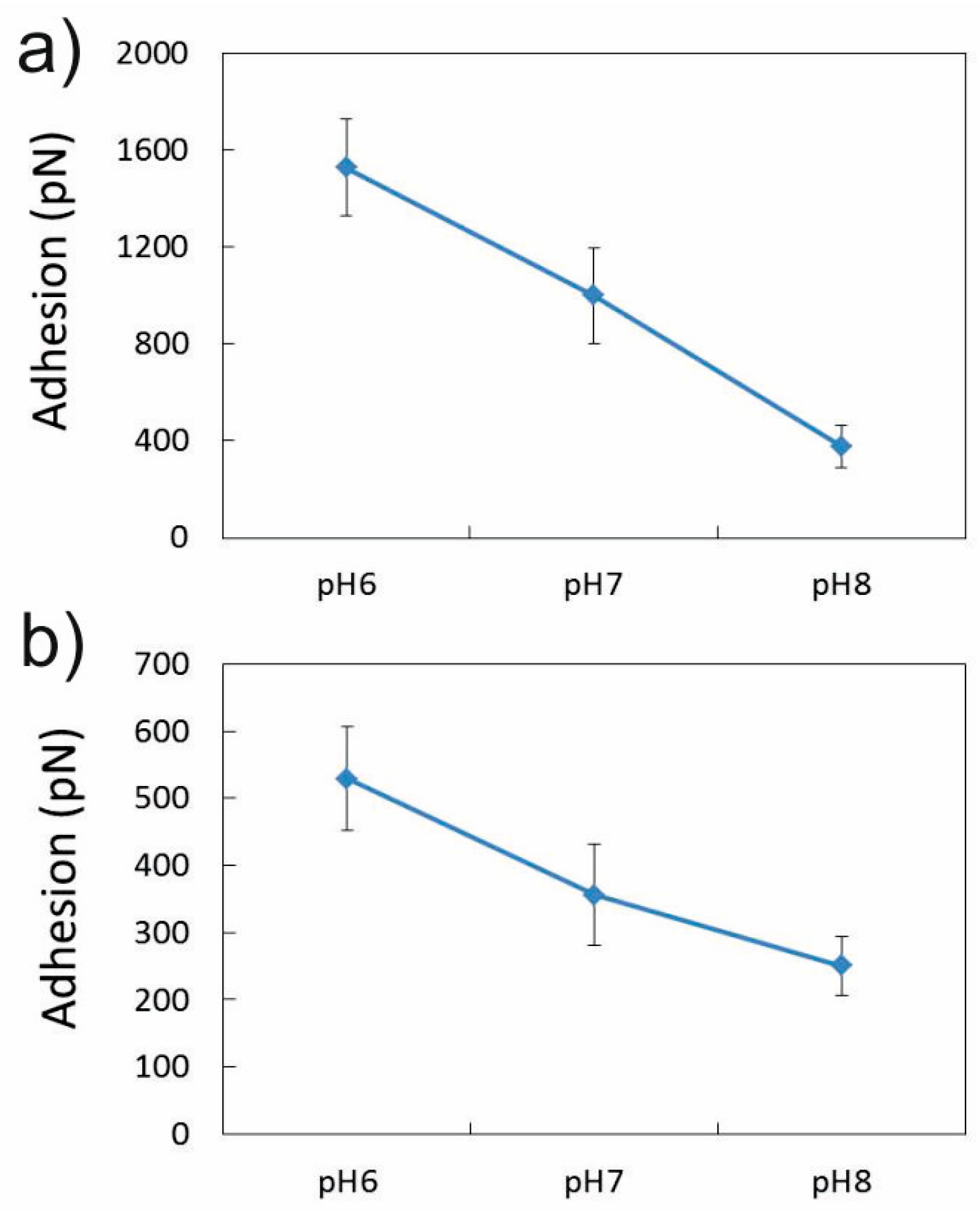
3.1. Adhesion of –COOH Groups to the Siloxane Face
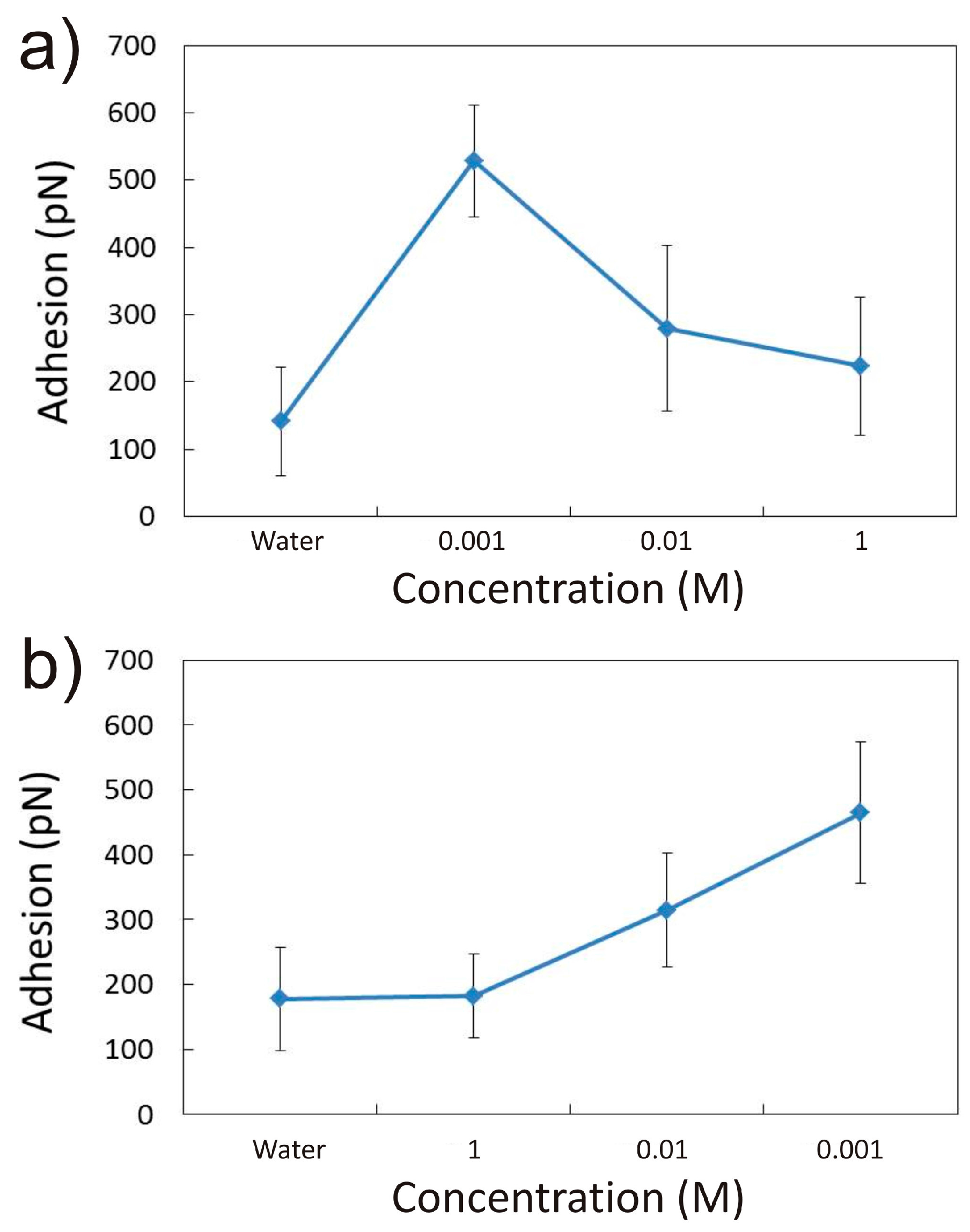
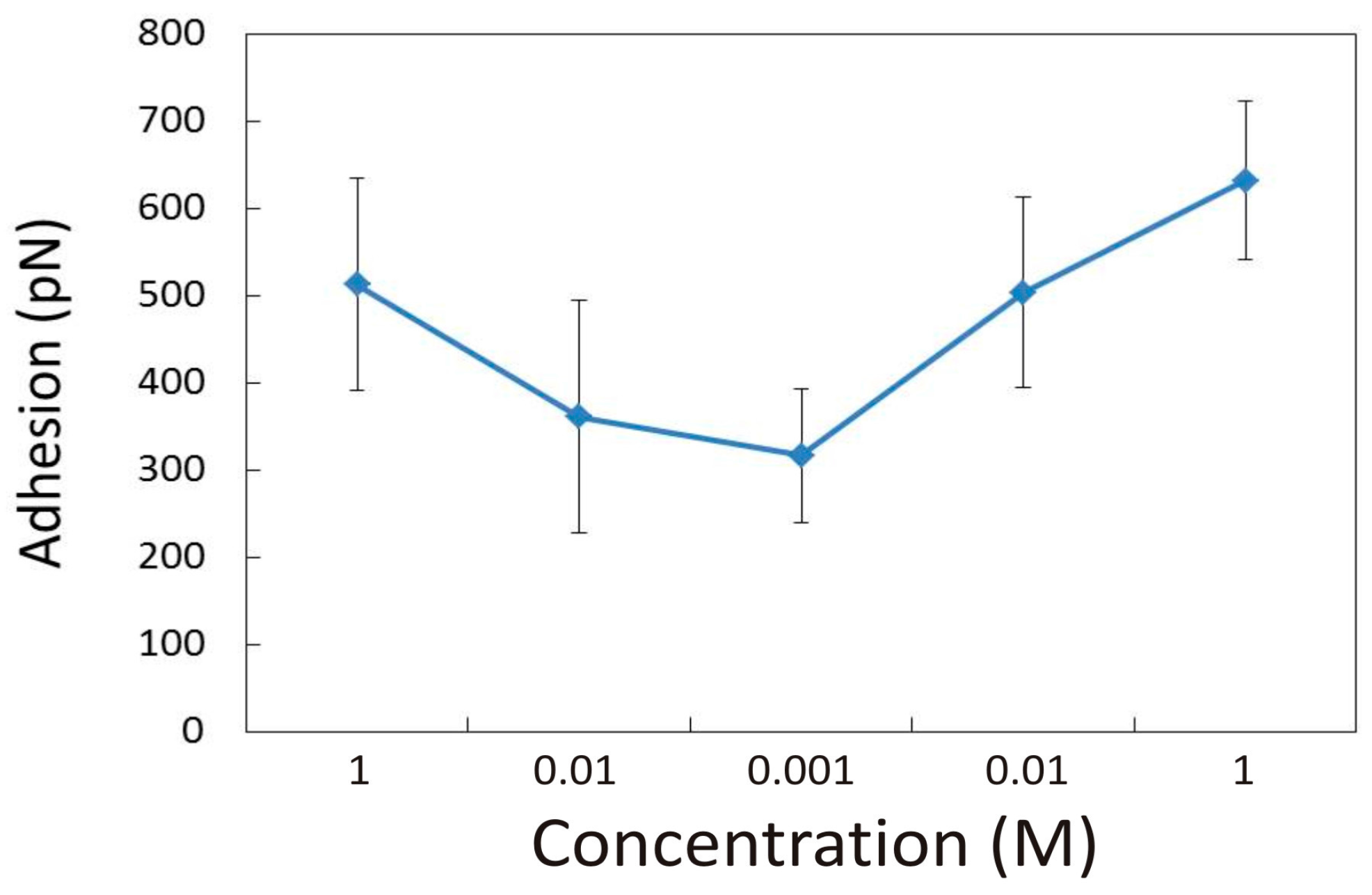
3.1.1. Effect of CaCl2 Concentration
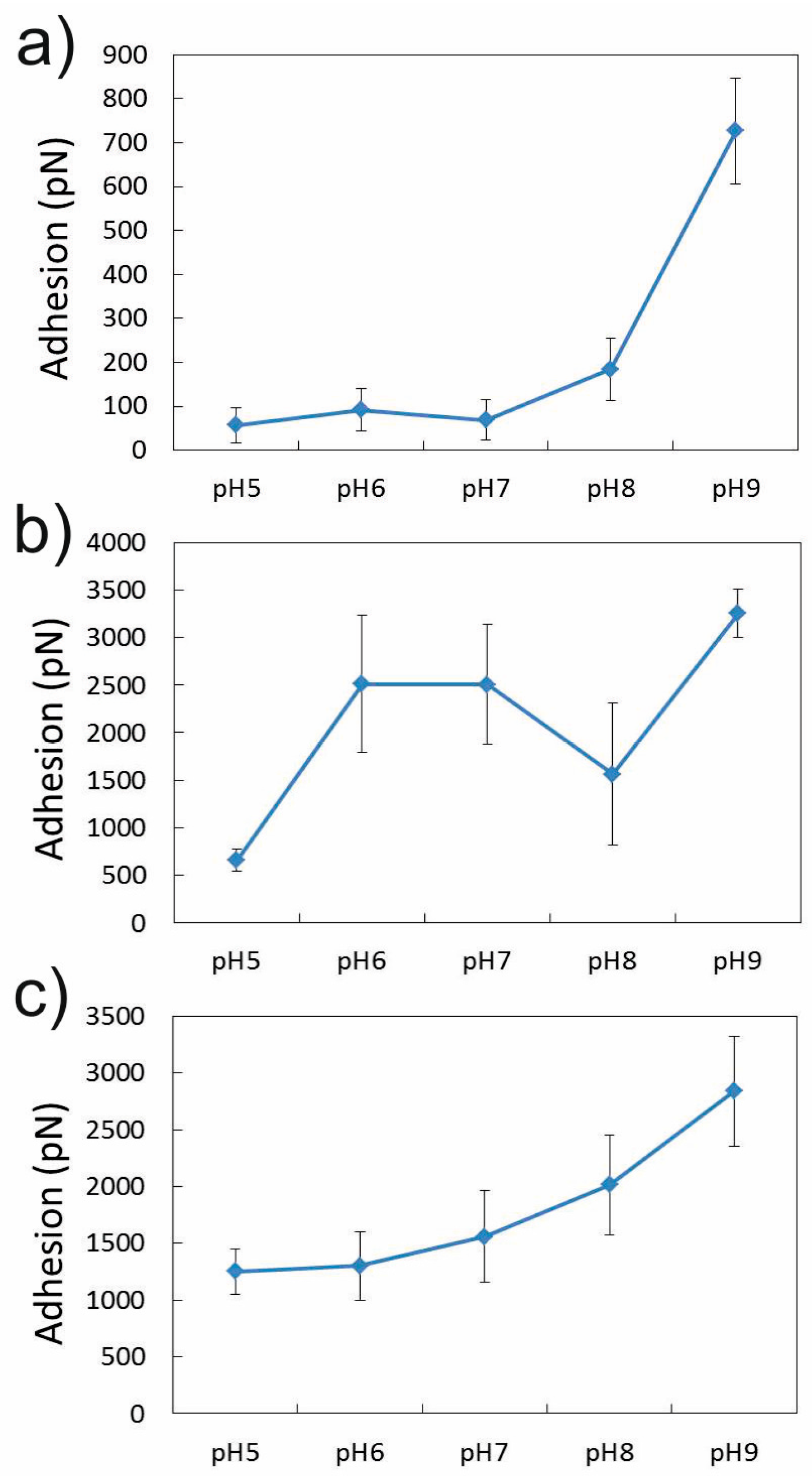
3.1.2. Effect of pH in the Presence of 0.001 M CaCl2
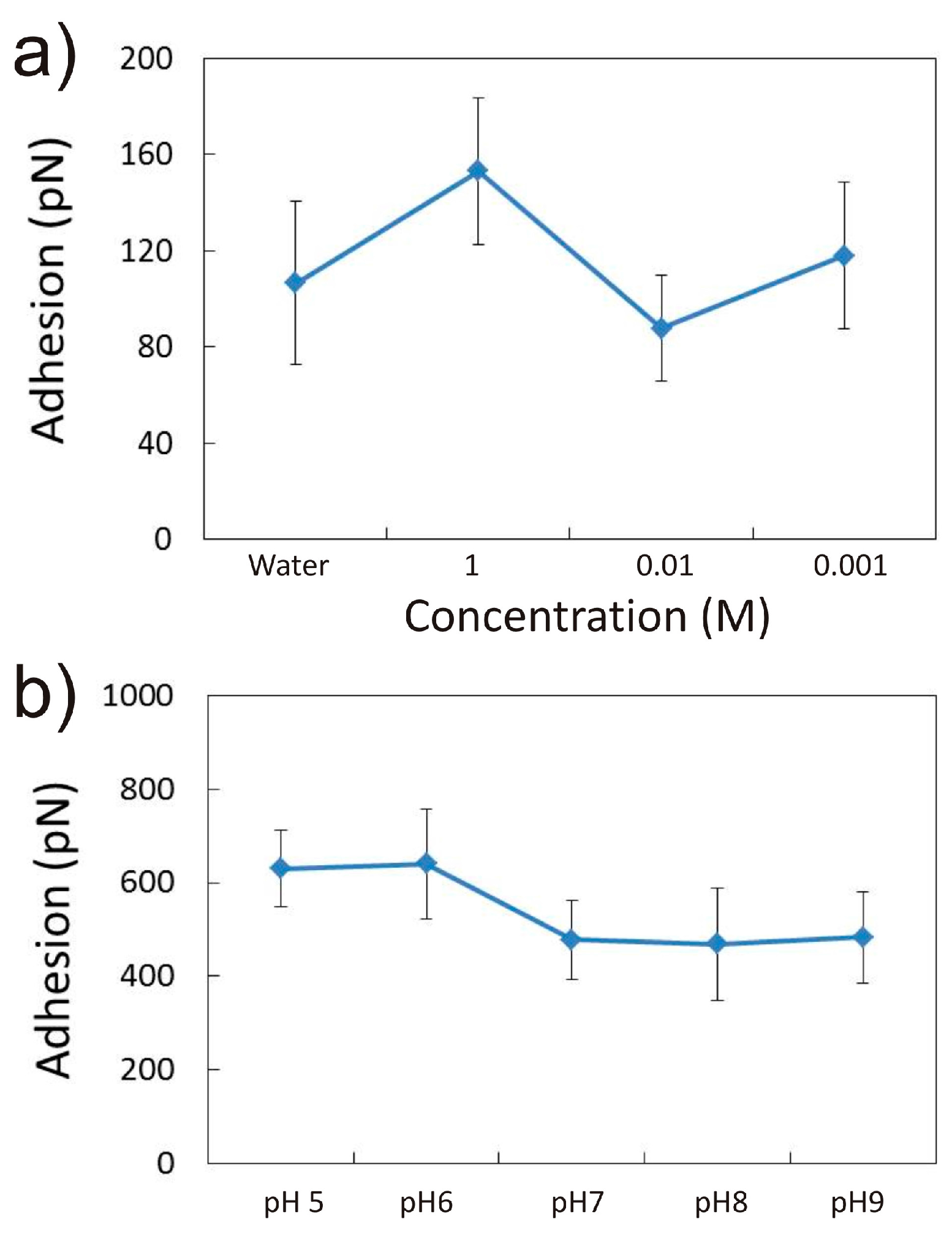
3.1.3. Effect of NaCl Concentration and pH
3.2. Adhesion of –COOH Groups to the Aluminol Face
3.2.1. Influence of CaCl2 Concentration
3.2.2. Influence of pH
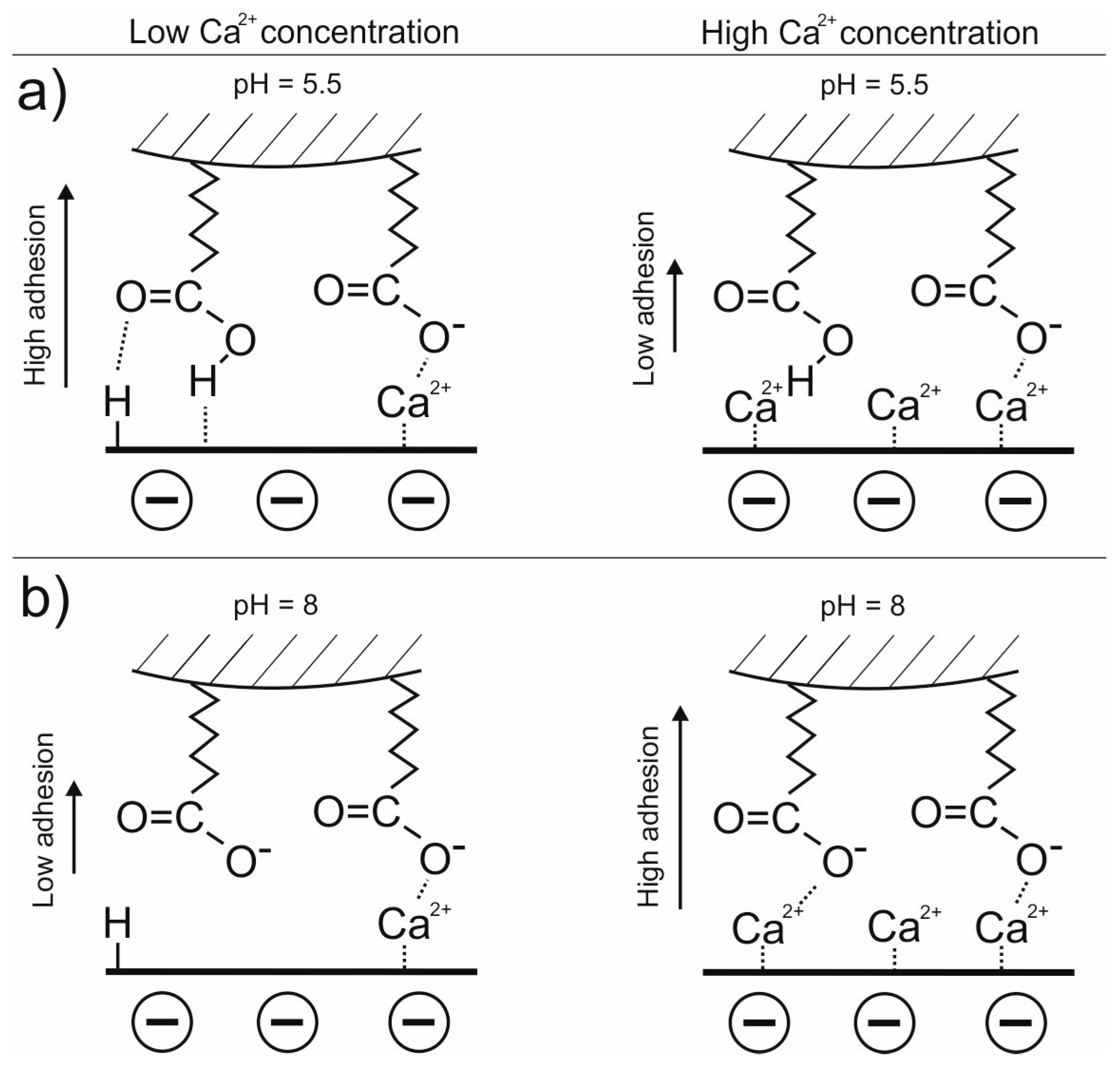
3.3. DLE vs. MIE Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Muggeridge, A.; Cockin, A.; Webb, K.; Frampton, H.; Collins, I.; Moulds, T.; Salino, P. Recovery Rates, Enhanced oil Recovery and Technological Limits. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2014, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.D.; Vinogradov, J.; Hamon, G.; Chamerois, M. Evidence, mechanisms and improved understanding of controlled salinity waterflooding part 1: Sandstones. Fuel 2016, 185, 772–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.J. Critical review of low-salinity waterflooding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 120, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.; Puntervold, T.; Austad, T. Water based eor from clastic oil reservoirs by wettability alteration: A review of chemical aspects. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lager, A.; Webb, K.J.; Collins, I.R.; Richmond, D.M. Losal Enhanced Oil Recovery: Evidence of Enhanced Oil Recovery at the Reservoir Scale; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Austad, T.; Rezaeidoust, A.; Puntervold, T. Chemical Mechanism of Low Salinity Water Flooding in Sandstone Reservoirs; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kareem, R.; Cubillas, P.; Gluyas, J.; Bowen, L.; Hillier, S.; Greenwell, H.C. Multi-technique approach to the petrophysical characterization of berea sandstone core plugs (cleveland quarries, USA). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 149, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilner, E.; Andersson, M.P.; Hassenkam, T.; Matthiesen, J.; Salino, P.A.; Stipp, S.L.S. The effect of ionic strength on oil adhesion in sandstone—The search for the low salinity mechanism. Sci Rep.-UK 2015, 5, 9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Gupta, V.; Du, H.; Wang, X.; Miller, J.D. Surface charge and wetting characteristics of layered silicate minerals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 179–182, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Miller, J.D. Surface force measurements at the basal planes of ordered kaolinite particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Zhao, C.L.; Klaassen, A.; van den Ende, D.; Mugele, F.; Siretanu, I. Characterization of the surface charge distribution on kaolinite particles using high resolution atomic force microscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 175, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miller, J.D.; Yin, X.; Gupta, V.; Wang, X. Influence of ionic strength on the surface charge and interaction of layered silicate particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 432, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jupille, J. Analysis of mineral surfaces by atomic force microscopy. In Spectroscopic Methods in Mineralogy and Materials Science; Henderson, G.S., Neuville, D.R., Downs, R.T., Eds.; The Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2014; p. 800. [Google Scholar]
- Hassenkam, T.; Skovbjerg, L.L.; Stipp, S.L.S. Probing the intrinsically oil-wet surfaces of pores in north sea chalk at subpore resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6071–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthiesen, J.; Hassenkam, T.; Bovet, N.; Dalby, K.N.; Stipp, S.L.S. Adsorbed organic material and its control on wettability. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassenkam, T.; Andersson, M.P.; Hilner, E.; Matthiesen, J.; Dobberschutz, S.; Dalby, K.N.; Bovet, N.; Stipp, S.L.S.; Salino, P.; Reddick, C.; et al. Could atomic-force microscopy force mapping be a fast alternative to core-plug tests for optimizing injection-water salinity for enhanced oil recovery in sandstone? SPE J. 2016, 21, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhrimenko, D.V.; Dalby, K.N.; Skovbjerg, L.L.; Bovet, N.; Christensen, J.H.; Stipp, S.L.S. The surface reactivity of chalk (biogenic calcite) with hydrophilic and hydrophobic functional groups. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 128, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiesen, J.; Bovet, N.; Hilner, E.; Andersson, M.P.; Schmidt, D.A.; Webb, K.J.; Dalby, K.N.; Hassenkam, T.; Crouch, J.; Collins, I.R.; et al. How naturally adsorbed material on minerals affects low salinity enhanced oil recovery. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 4849–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovbjerg, L.L.; Okhrimenko, D.V.; Khoo, J.; Dalby, K.N.; Hassenkam, T.; Makoyicky, E.; Stipp, S.L.S. Preferential adsorption of hydrocarbons to nanometer-sized clay on chalk particle surfaces. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 3642–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassenkam, T.; Mitchell, A.C.; Pedersen, C.S.; Skovbjerg, L.L.; Bovet, N.; Stipp, S.L.S. The low salinity effect observed on sandstone model surfaces. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2012, 403, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassenkam, T.; Pedersen, C.S.; Dalby, K.; Austad, T.; Stipp, S.L.S. Pore scale observation of low salinity effects on outcrop and oil reservoir sandstone. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2011, 390, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, H.; Xu, S.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, T.; Hu, G.; Wang, J. Effect of specific functional groups on oil adhesion from mica substrate: Implications for low salinity effect. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, K.M.S.; Pedersen, C.S.; Bovet, N.; Dalby, K.N.; Hassenkam, T.; Andersson, M.P.; Okhrimenko, D.; Stipp, S.L.S. Adhesion of alkane as a functional group on muscovite and quartz: Dependence on ph and contact time. Langmuir 2014, 30, 14476–14485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, B.; Ceccato, M.; Andersson, M.P.; Dobberschütz, S.; Rodriguez-Blanco, J.D.; Dalby, K.N.; Hassenkam, T.; Stipp, S.L.S. Salinity-dependent adhesion response properties of aluminosilicate (k-feldspar) surfaces. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 4670–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, K.M.S.; Bovet, N.; Hassenkam, T.; Dideriksen, K.; Pedersen, C.S.; Jensen, C.M.; Okhrimenko, D.V.; Stipp, S.L.S. Change in organic molecule adhesion on alpha-alumina (sapphire) with change in nacl and cacl2 solution salinity. Langmuir 2014, 30, 8741–8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagha, L.; Wang, S.; Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Masliyah, J. Probing adsorption of polyacrylamide-based polymers on anisotropic basal planes of kaolinite using quartz crystal microbalance. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3989–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezenov, D.V.; Noy, A.; Ashby, P. Chemical force microscopy: Probing chemical origin of interfacial forces and adhesion. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2005, 19, 313–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, J.L.; Bechhoefer, J. Calibration of atomic-force microscope tips. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 64, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.J.; Jaschke, M. Calculation of thermal noise in atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 1995, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lager, A.; Webb, K.J.; Black, C.J.J.; Singleton, M.; Sorbie, K.S. Low Salinity Oil Recovery—An Experimental Investigation1; Society of Petrophycists and Well Log Analyst: Houston, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sorbie, K.S.; Collins, I. A Proposed Pore-Scale Mechanism for How Low Salinity Waterflooding Works; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Olsson, M.H.M.; Hassenkam, T.; Stipp, S.L.S. A ph-resolved view of the low salinity effect in sandstone reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5346–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezenov, D.V.; Noy, A.; Rozsnyai, L.F.; Lieber, C.M. Force titrations and ionization state sensitive imaging of functional groups in aqueous solutions by chemical force microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 2006–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleven, R.; Alstad, J. Interaction of alkali, alkaline-earth and sulphate ions with clay minerals and sedimentary rocks. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1996, 15, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugele, F.; Bera, B.; Cavalli, A.; Siretanu, I.; Maestro, A.; Duits, M.; Cohen-Stuart, M.; van den Ende, D.; Stocker, I.; Collins, I. Ion adsorption-induced wetting transition in oil-water-mineral systems. Sci. Rep.-UK 2015, 5, 10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, L.; Ida, L. Adsorption of carboxylic acids on reservoir minerals from organic and aqueous phase. SPE Reservoir Eval. Eng. 1998, 1, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogden, A. Removal of crude oil from kaolinite by water flushing at varying salinity and ph. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2012, 402, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Siretanu, I.; Duits, M.H.G.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Mugele, F. Ion effects in the adsorption of carboxylate on oxide surfaces, studied with quartz crystal microbalance. Colloid Surf. A 2016, 494, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.L.; Ebeling, D.; Siretanu, I.; van den Ende, D.; Mugele, F. Extracting local surface charges and charge regulation behavior from atomic force microscopy measurements at heterogeneous solid-electrolyte interfaces. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16298–16311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Experiment | Water | NaCl (0.001 M) | NaCl (0.01 M) | NaCl (1 M) | CaCl2 (0.001 M) | CaCl2 (0.01 M) | CaCl2 (1 M) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kao-Si-1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5.5 | |||
| kao-Si-2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 5.5 | |||
| kao-Si-3 | 1 | 5 | 4/6 | 3/7 | 8 | |||
| kao-Si-4 | 1 | 2 | 5/6/7/8/9 | |||||
| kao-Si-5 | 1 | 2 | 5/6/7/8/9 | |||||
| kao-Si-6 | 1 | 2 | 5/6/7/8/9 | |||||
| kao-Si-7 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 5.5 | |||
| kao-Si-8 | 1 | 2 | 5/6/7/8/9 | |||||
| kao-Si-9 | 1/5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 5.5 |
| kao-Si-10 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5.5 | |||
| Kao-Al-1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5.5 | |||
| kao-Al-2 | 1 | 2 | 6/7/8 | |||||
| kao-Al-3 | 1 | 2 | 6/7/8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santha, N.; Cubillas, P.; Saw, A.; Brooksbank, H.; Greenwell, H.C. Chemical Force Microscopy Study on the Interactions of COOH Functional Groups with Kaolinite Surfaces: Implications for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Minerals 2017, 7, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7120250
Santha N, Cubillas P, Saw A, Brooksbank H, Greenwell HC. Chemical Force Microscopy Study on the Interactions of COOH Functional Groups with Kaolinite Surfaces: Implications for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Minerals. 2017; 7(12):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7120250
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantha, Nipada, Pablo Cubillas, Adrian Saw, Harry Brooksbank, and Hugh Christopher Greenwell. 2017. "Chemical Force Microscopy Study on the Interactions of COOH Functional Groups with Kaolinite Surfaces: Implications for Enhanced Oil Recovery" Minerals 7, no. 12: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7120250
APA StyleSantha, N., Cubillas, P., Saw, A., Brooksbank, H., & Greenwell, H. C. (2017). Chemical Force Microscopy Study on the Interactions of COOH Functional Groups with Kaolinite Surfaces: Implications for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Minerals, 7(12), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7120250