Spectroscopic Characterization and Nanosafety of Ag-Modified Antibacterial Leather and Leatherette
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Surface Modification of Leather and Leatherette
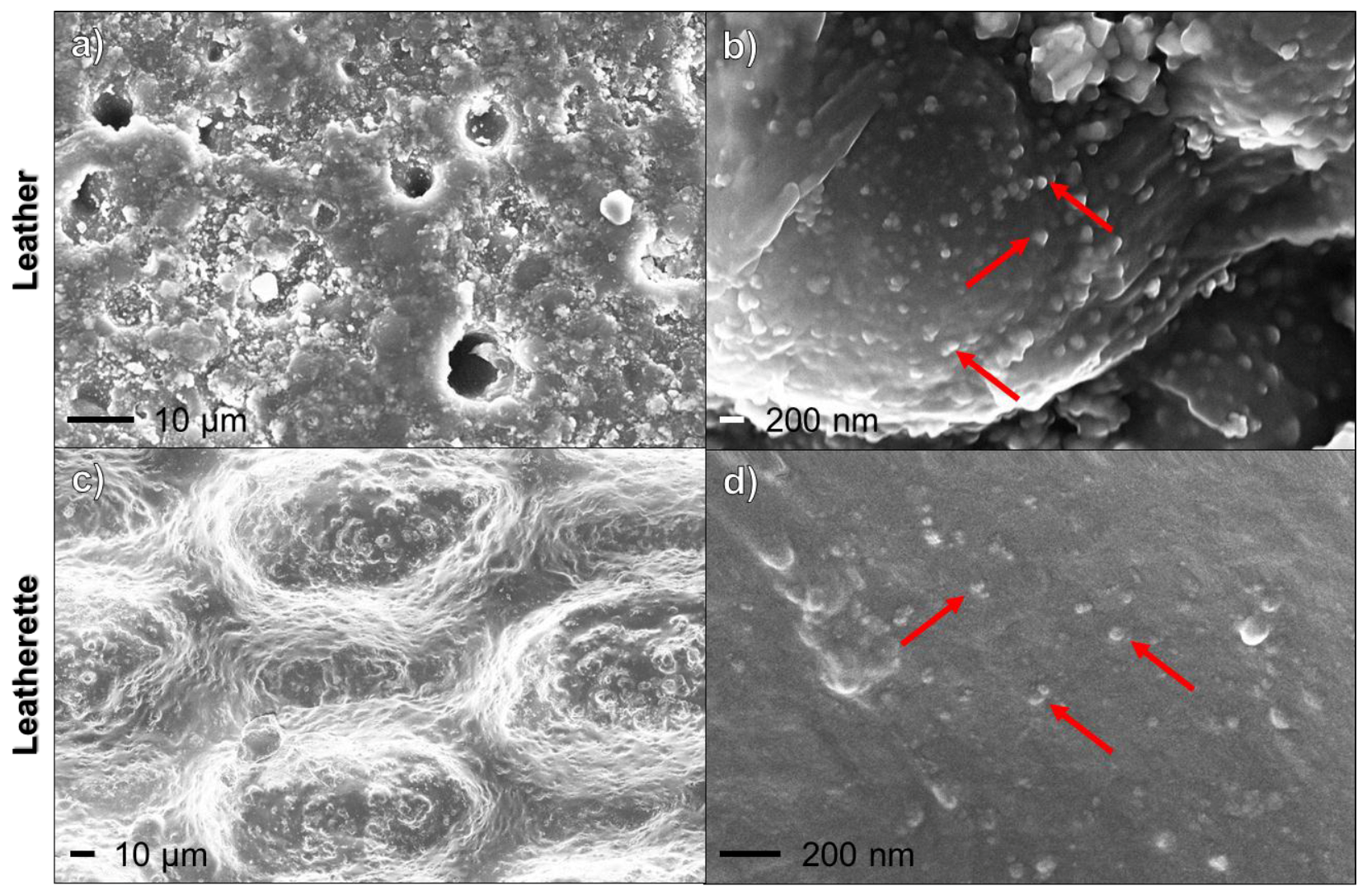
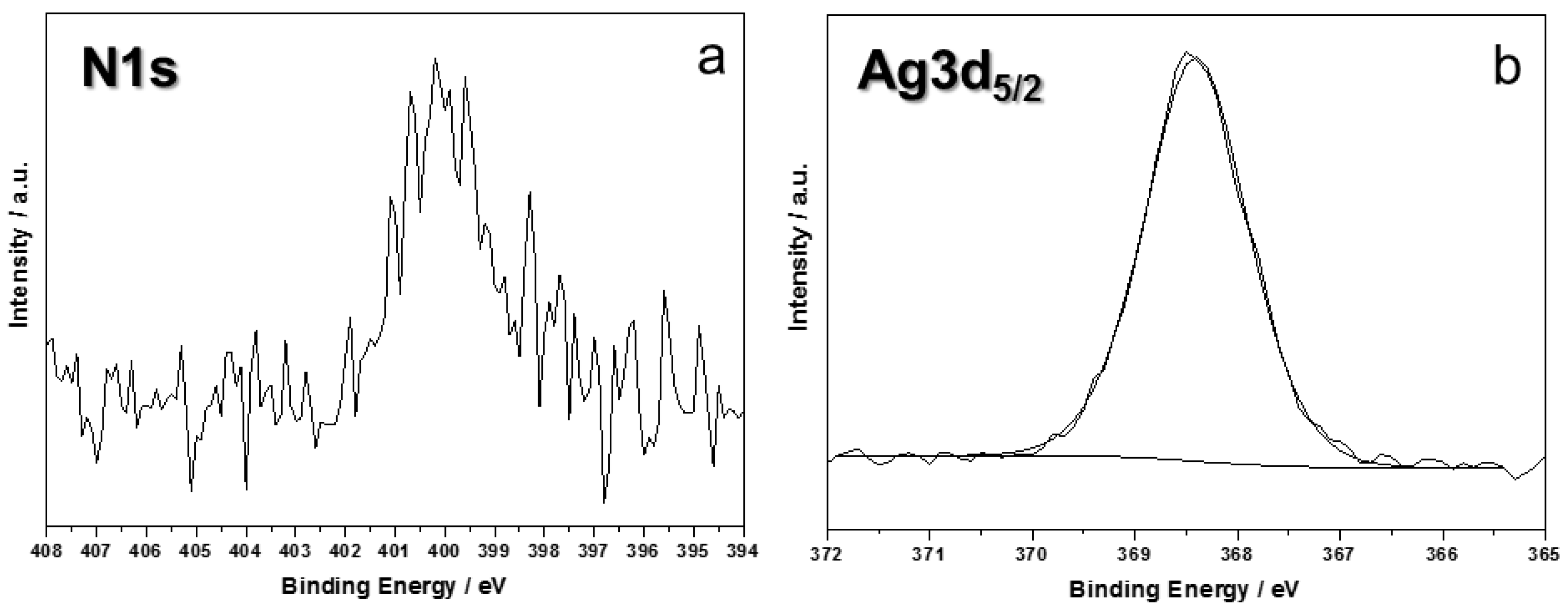
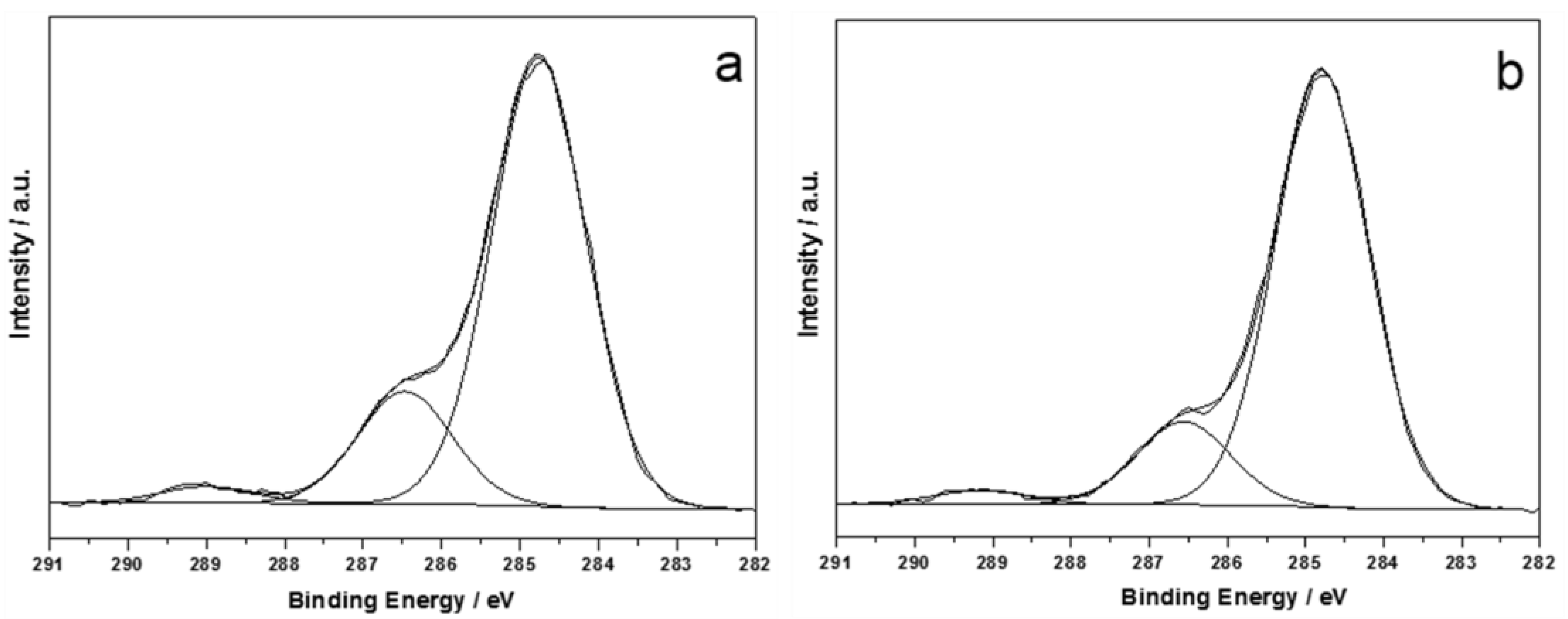
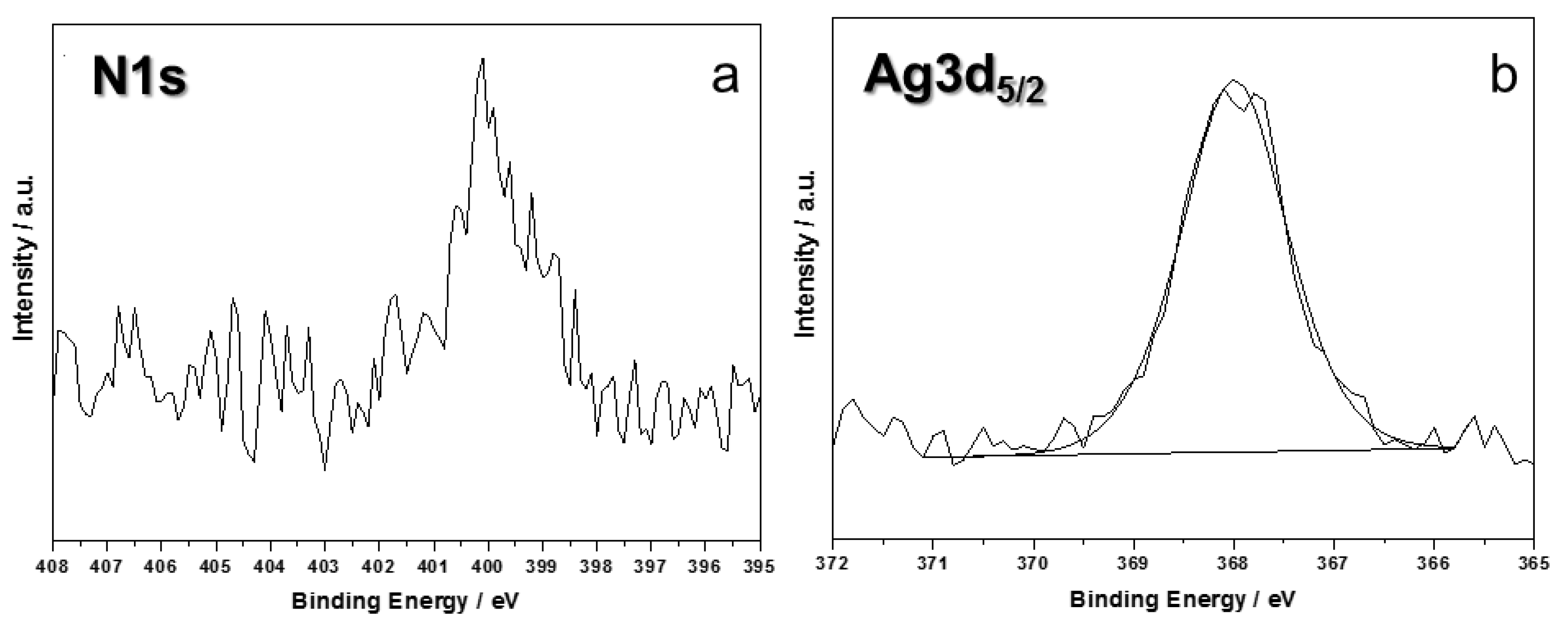
2.2. Surface Characterizations
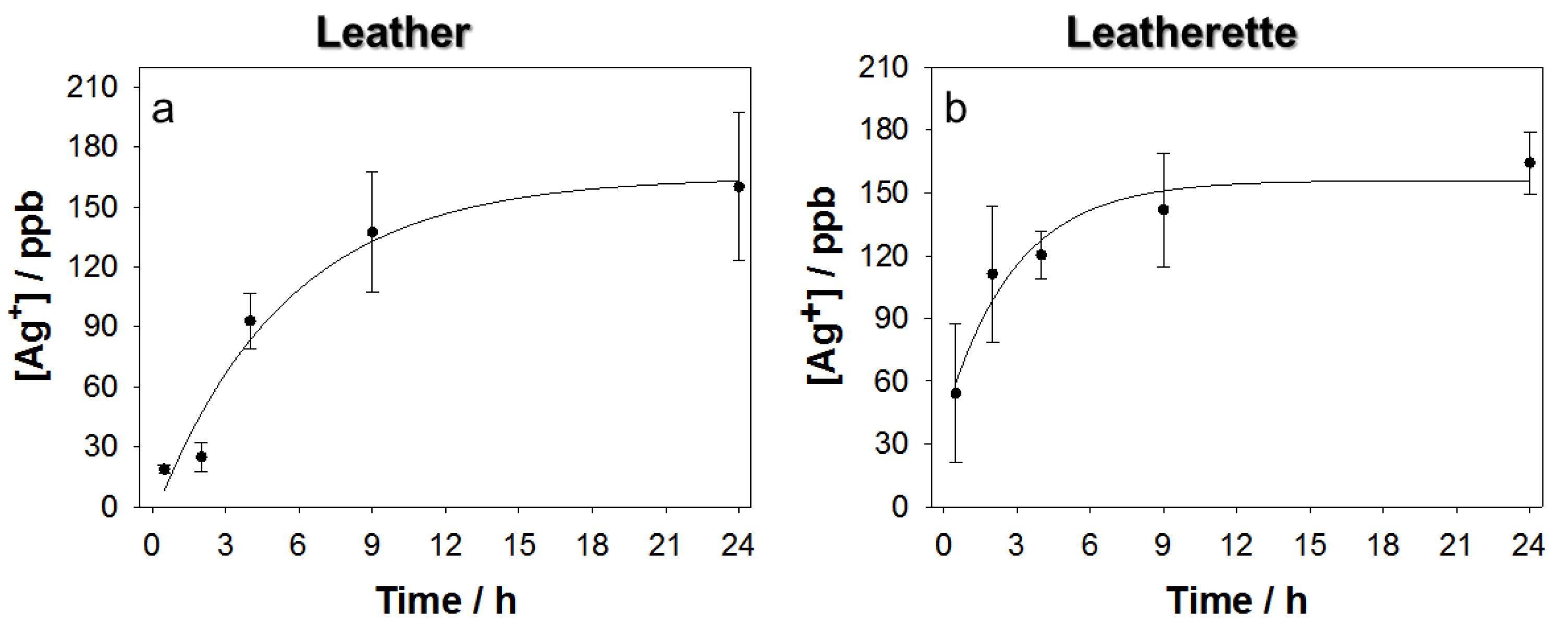
2.3. Evaluation of Ionic Release
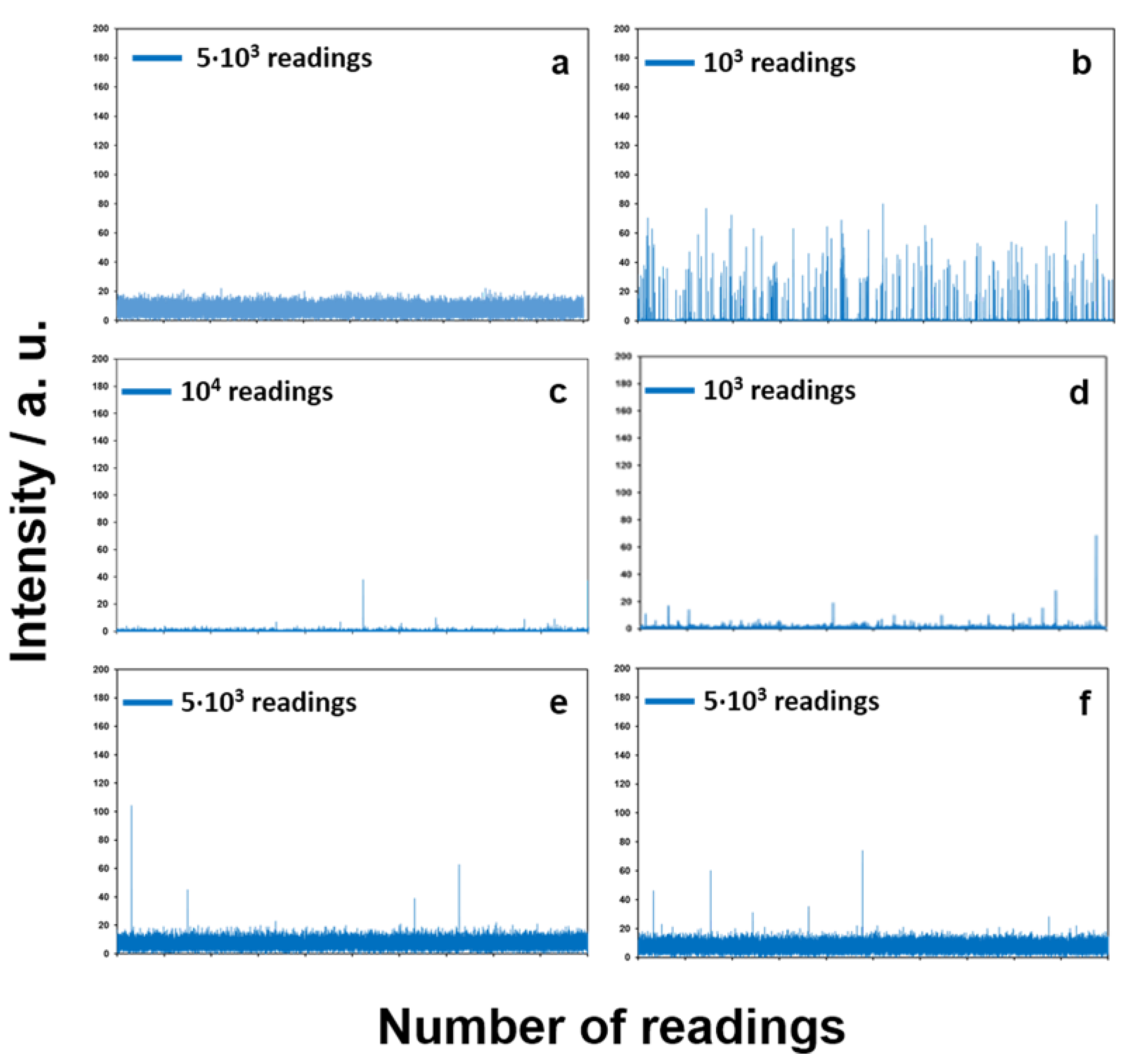
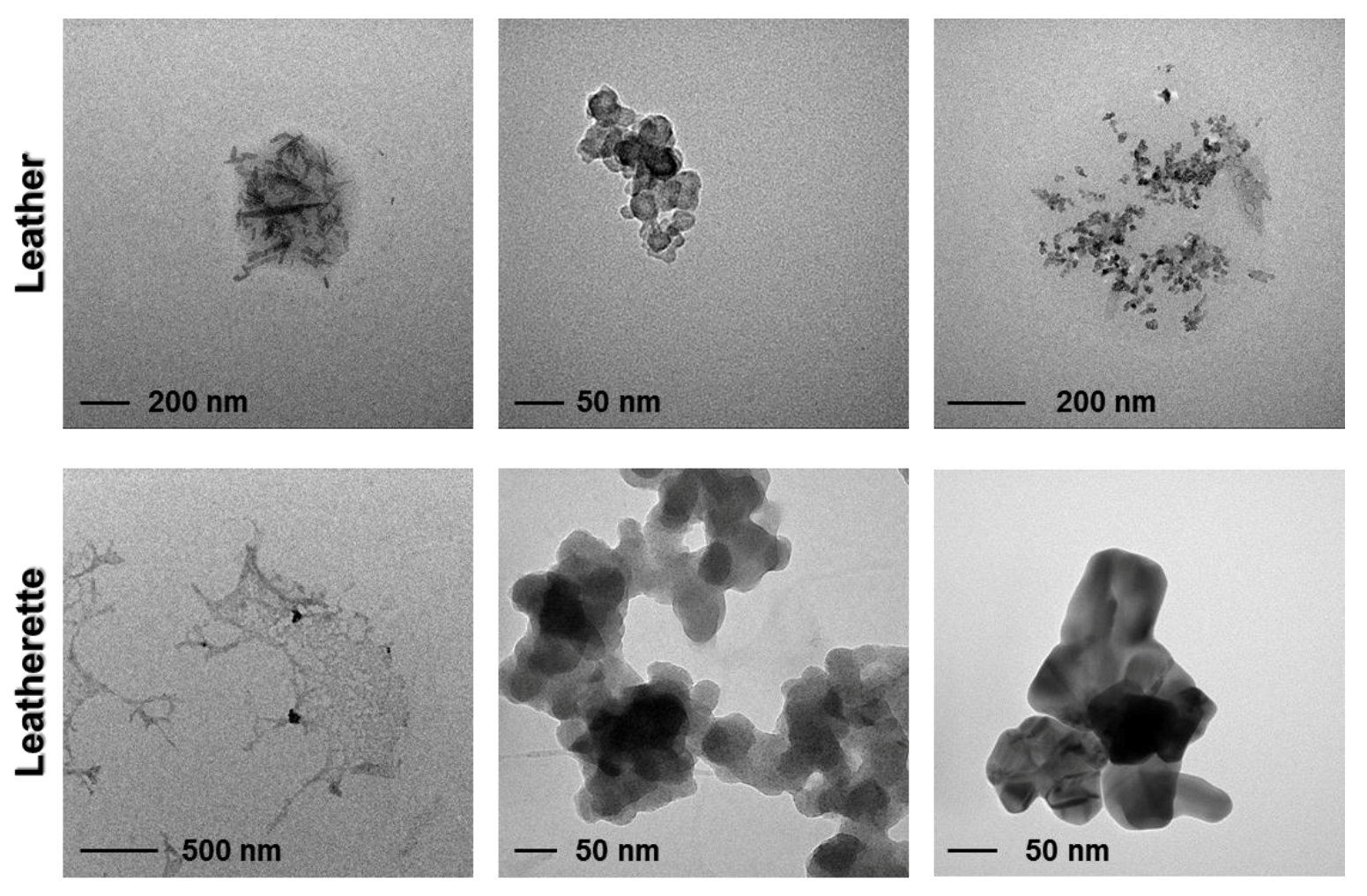
2.4. Assessment of Entire Nanoparticle Release
2.5. Biological Characterizations
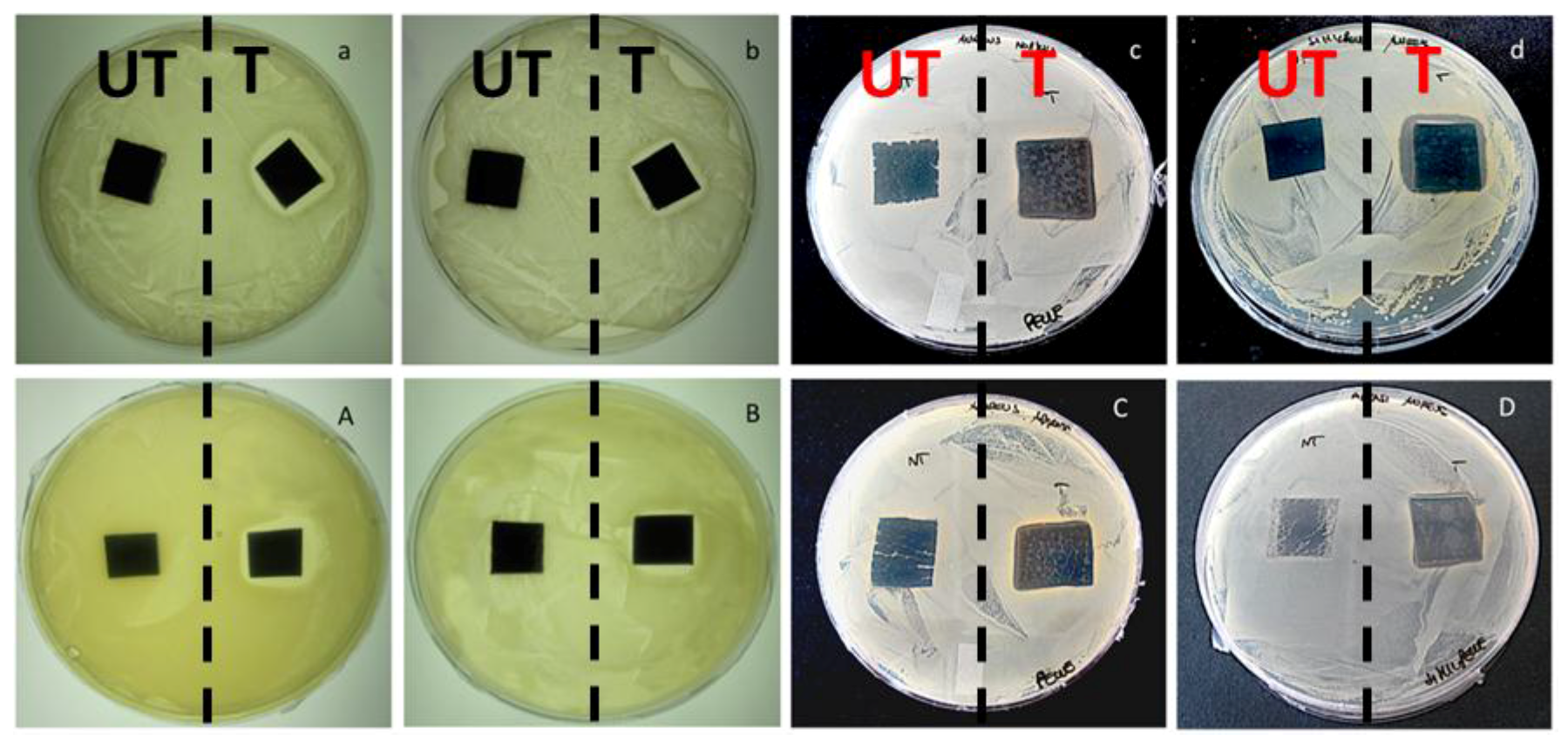
2.5.1. Antibacterial Tests
2.5.2. Biocompatibility of Leather and Leatherette
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Surface Modification of Leather and Leatherette
3.2. XPS Surface Characterization
3.3. Evaluation of Silver Ion Release
3.4. Assessment of Entire Nanoparticle Release
3.5. Biological Characterizations before and after Abrasion
3.5.1. Antibacterial Tests
3.5.2. MTT Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Yan, L.; Wang, R.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Q. Antimicrobial polyurethane synthetic leather coating with In-situ generated Nano-TiO2. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Gao, H.; Peng, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis of PEGylated chitosan copolymers as efficiently antimicrobial coatings for leather. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43465–43472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, N.; Rai, M. Nano-Antimicrobials: Progress and Prospects, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-3-642-24427-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardts, A.; Hammer, T.R.; Balluff, C.; Mucha, H.; Hoefer, D. A model of the transmission of micro-organisms in a public setting and its correlation to pathogen infection risks. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashgar, S.S.; El-Said, H.M. Pathogenic Bacteria Associated with Different Public Environmental Sites in Mecca City. Open J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lkhagvajav, N.; Koizhaiganova, M.; Yasa, I.; Çelik, E.; Sari, Ö.; Lkhagvajav, N.; Koizhaiganova, M.; Yasa, I.; Çelik, E.; Sari, Ö. Characterization and antimicrobial performance of nano silver coatings on leather materials. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, D.-L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, P.-X. Analyses of structures for a synthetic leather made of polyurethane and microfiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrini, P.; Peroni, G.; Corrieri, G.; Righi, G.P. Fibrous Materials Useful as Leather Substitutes and Consisting Essentially of Leather Fibers, Fibrils or Fibrides of Synthetic Polymers and Cellulose Fibers 1979. U.S. Patent 4,162,996, 31 July 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Pollini, M.; Paladini, F.; Licciulli, A.; Maffezzoli, A.; Sannino, A. Engineering Nanostructured Silver Coatings for Antimicrobial Applications. In Nano-Antimicrobials, 1st ed.; Cioffi, N., Rai, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 313–336. ISBN 978-3-642-24427-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Picca, R.A.; Cioffi, N. Recent advances in the synthesis and characterization of nano-antimicrobials. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid-ul-Islam; Shahid, M.; Mohammad, F. Green Chemistry Approaches to Develop Antimicrobial Textiles Based on Sustainable Biopolymers—A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 5245–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, M.; Paladini, F.; Licciulli, A.; Maffezzoli, A.; Sannino, A.; Nicolais, L. Antibacterial natural leather for application in the public transport system. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2013, 10, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, J.A.; French, G.L. Bacterial contamination on touch surfaces in the public transport system and in public areas of a hospital in London. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 803–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paladini, F.; Cooper, I.R.; Pollini, M. Development of antibacterial and antifungal silver-coated polyurethane foams as air filtration units for the prevention of respiratory diseases. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.H.; Sun, G. Photoactive antimicrobial agents/polyurethane finished leather. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S.; Seggiani, M.; Castiello, D. Leather manufacturing by using treated municipal wastewaters. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2015, 16, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Pollini, M.; Sannino, A.; Ambrosio, L. Metal-Based Antibacterial Substrates for Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larijani, B. Antimicrobial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Coated Leather on Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Med. Aromat. Plants 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, R.; Montazer, M.; Shahsavan, S. A new method to stabilize nanoparticles on textile surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 345, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre-López, I.; Payà-Nohales, F.; Cuesta-Garrote, N.; Arán-Ais, F.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.Á.; Orgilés-Barceló, C.; Bertazzo, M. Antimicrobial Effect of Coated Leather Based on Silver Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterisation and Microbiological Evaluation. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, P.; Cho, M.; Lee, S.-M.; Park, J.-H.; Bae, S.; Oh, B.-T. Antimicrobial fabrication of cotton fabric and leather using green-synthesized nanosilver. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, P.; Shim, J.; Bang, K.-S.; Oh, B.-T. Gold nanoparticles mediated coloring of fabrics and leather for antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 160, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, I.P.; Amaral, J.S.; Pinto, V.; Ferreira, M.J.; Barreiro, M.F. Development of chitosan-based antimicrobial leather coatings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, V.; Mohan, R.; Rangasamy, T.; Muralidharan, C. Antimicrobial activity of Myrobalan (Terminalia chebula Retz.) nuts: Application in raw skin preservation for leather making. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. (IJNPR) 2016, 7, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Pollini, M.; Sannino, A.; Maffezzoli, A.; Licciulli, A. Antibacterial Surface Treatments Based on Silver Clusters Deposition. WO Patent 2007074484 A2; International Application No. PCT/IT2005/000772, 5 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paladini, F.; De Simone, S.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Antibacterial and antifungal dressings obtained by photochemical deposition of silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Picca, R.A.; Ronco, R.; Bonerba, E.; Tantillo, G.; Pollini, M.; Sannino, A.; Valentini, A.; Cataldi, T.R.I.; Cioffi, N. Investigation of Industrial Polyurethane Foams Modified with Antimicrobial Copper Nanoparticles. Materials 2016, 9, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, N.; Colaianni, L.; Pilolli, R.; Calvano, C.; Palmisano, F.; Zambonin, P. Silver nanofractals: Electrochemical synthesis, XPS characterization and application in LDI-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picca, R.A.; Paladini, F.; Sportelli, M.C.; Pollini, M.; Giannossa, L.C.; Di Franco, C.; Panico, A.; Mangone, A.; Valentini, A.; Cioffi, N. Combined approach for the development of efficient and safe nanoantimicrobials: The case of nanosilver-modified polyurethane foams. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Picca, R.A.; Sportelli, M.C.; Cioffi, N.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Surface chemical and biological characterization of flax fabrics modified with silver nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaño, M.D.; Olesik, J.W.; Barber, A.G.; Challis, K.; Ranville, J.F. Single Particle ICP-MS: Advances toward routine analysis of nanomaterials. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5053–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborda, F.; Bolea, E.; Jiménez-Lamana, J. Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: A Powerful Tool for Nanoanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-H.; Kim, M.; Park, H.-S.; Shin, U.S.; Gong, M.-S.; Kim, H.-W. Size-dependent cellular toxicity of silver nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2012, 100A, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborda, F.; Jiménez-Lamana, J.; Bolea, E.; Castillo, J.R. Selective identification, characterization and determination of dissolved silver(I) and silver nanoparticles based on single particle detection by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolář, M.; Večeřová, R.; Pizúrová, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Nevěčná, T.; Zbořil, R. Silver Colloid Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Antibacterial Activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, S.D.; Gallo, A.L.; Paladini, F.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Development of silver nano-coatings on silk sutures as a novel approach against surgical infections. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.L.; Paladini, F.; Romano, A.; Verri, T.; Quattrini, A.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Efficacy of silver coated surgical sutures on bacterial contamination, cellular response and wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Pristine | Treated |
|---|---|---|
| Element | At% | At% |
| C | 69 ± 4.0 | 58 ± 3.0 |
| N | 0.5 ± 0.5 | 0.9 ± 0.5 |
| O | 21 ± 3.0 | 23.6 ± 0.6 |
| Si | 9 ± 1.0 | 17 ± 3.0 |
| Ag | / | 0.5 ± 0.2 |
| Br | 0.5 ± 0.5 | ≤0.5 |
| Sample | Pristine | Treated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Attribution | Relative % | Relative % |
| 284.8 ± 0.1 | C–C | 60 ± 2 | 57 ± 4 |
| 286.2 ± 0.2 | C–O, C–N | 29 ± 3 | 33 ± 1 |
| 287.4 ± 0.3 | C=O | 8.5 ± 0.9 | 5.7± 0.6 |
| 289.1 ± 0.3 | HN–COO | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 4.3 ± 0.7 |
| Sample | Pristine | Treated |
|---|---|---|
| Element | At% | At% |
| C | 68 ± 2 | 62.3 ± 0.9 |
| O | 21 ± 1 | 25.1 ± 0.5 |
| N | 0.8 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 |
| Si | 10.2 ± 0.5 | 10.7 ± 0.6 |
| Ag | / | 0.6 ± 0.2 |
| Sample | Pristine | Treated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Attribution | Relative % | Relative % |
| 284.8 ± 0.1 | C–C | 77 ± 2 | 81 ± 3 |
| 286.5 ± 0.2 | C–O, C–N | 20 ± 2 | 15 ± 2 |
| 289.1 ± 0.2 | HN–C=O | 3 ± 1 | 4 ± 2 |
| Dwell time (μs) | 50 |
| Settling time (μs) | 0 |
| Scan time (s) | 60 |
| Sample flow rate (mL/min) | 0.276 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sportelli, M.C.; Picca, R.A.; Paladini, F.; Mangone, A.; Giannossa, L.C.; Franco, C.D.; Gallo, A.L.; Valentini, A.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M.; et al. Spectroscopic Characterization and Nanosafety of Ag-Modified Antibacterial Leather and Leatherette. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7080203
Sportelli MC, Picca RA, Paladini F, Mangone A, Giannossa LC, Franco CD, Gallo AL, Valentini A, Sannino A, Pollini M, et al. Spectroscopic Characterization and Nanosafety of Ag-Modified Antibacterial Leather and Leatherette. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(8):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7080203
Chicago/Turabian StyleSportelli, Maria Chiara, Rosaria Anna Picca, Federica Paladini, Annarosa Mangone, Lorena Carla Giannossa, Cinzia Di Franco, Anna Lucia Gallo, Antonio Valentini, Alessandro Sannino, Mauro Pollini, and et al. 2017. "Spectroscopic Characterization and Nanosafety of Ag-Modified Antibacterial Leather and Leatherette" Nanomaterials 7, no. 8: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7080203
APA StyleSportelli, M. C., Picca, R. A., Paladini, F., Mangone, A., Giannossa, L. C., Franco, C. D., Gallo, A. L., Valentini, A., Sannino, A., Pollini, M., & Cioffi, N. (2017). Spectroscopic Characterization and Nanosafety of Ag-Modified Antibacterial Leather and Leatherette. Nanomaterials, 7(8), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7080203












