-
 National Multicenter Study on the Prevalence of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in the Post-COVID-19 Era in Argentina: The RECAPT-AR Study
National Multicenter Study on the Prevalence of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in the Post-COVID-19 Era in Argentina: The RECAPT-AR Study -
 Infected Fractures and Prosthetic Joints Have Very Similar Microbiology
Infected Fractures and Prosthetic Joints Have Very Similar Microbiology -
 Efflux Pump Inhibitors Enhance Activity of NBTIs Against Gram-Negative Bacteria
Efflux Pump Inhibitors Enhance Activity of NBTIs Against Gram-Negative Bacteria
Journal Description
Antibiotics
Antibiotics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of antibiotics, published monthly online by MDPI. The Croatian Pharmacological Society (CPS) is affiliated with Antibiotics and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Pharmacology and Pharmacy) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics )
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
4.3 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.6 (2023)
Latest Articles
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of ESBL-, AmpC-, and Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and High-Risk Escherichia coli CC131, with the First Report of ST1193 as a Causative Agent of Urinary Tract Infections in Human Patients in Algeria
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 485; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050485 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background: High-risk Escherichia coli clones, such as sequence type (ST)131 and ST1193, along with multidrug-resistant (MDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae, are globally recognized for their significant role in urinary tract infections (UTIs). This study aimed to provide an overview of the virulence factors, clonal
[...] Read more.
Background: High-risk Escherichia coli clones, such as sequence type (ST)131 and ST1193, along with multidrug-resistant (MDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae, are globally recognized for their significant role in urinary tract infections (UTIs). This study aimed to provide an overview of the virulence factors, clonal diversity, and antibiotic resistance profiles of extended-spectrum cephalosporin (ESC)-E. coli and K. pneumoniae causing UTIs in humans in the Tebessa region of Algeria. Methods: Forty E. coli and 17 K. pneumoniae isolates exhibiting ESC-resistance were recovered (July 2022–January 2024) from urine samples of patients at three healthcare facilities to be phenotypically and genotypically characterized. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) was performed on the ST1193 clone. Results: Among K. pneumoniae isolates, all except one harbored CTX-M-15, with a single isolate carrying blaCTX-M-194. Additionally, two K. pneumoniae isolates co-harboring blaCTX-M-15 and blaNDM exhibited phenotypic and genotypic hypervirulence traits. Fluoroquinolone resistance (FQR) was detected in 94.1% of K. pneumoniae isolates. The E. coli isolates carried diverse ESC-resistance genes, including CTX-M-15 (87.5%), CTX-M-27 (5%), CTX-M-1, CMY-59, and CMY-166 (2.5% each). Co-carriage of blaESC and blaOXA-48 was identified in three E. coli isolates, while 62.5% exhibited FQR. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that 52.5% of E. coli belonged to phylogroup B2, including the high-risk clonal complex (CC)131 CH40-30 (17 isolates) and ST1193 (one isolate). In silico analysis of the ST1193 genome determined O75:H5-B2 (CH14-64), and the carriage of IncI1-I(Alpha) and IncF [F-:A1:B10] plasmids. Notably, core genome single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis demonstrated high similarity between the Algerian ST1193 isolate and a previously annotated genome from a hospital in Northwest Spain. Conclusions: This study highlights the spread and genetic diversity of E. coli CC131 CH40-30 and hypervirulent K. pneumoniae clones in Algeria. It represents the first report of a CTX-M-15-carrying E. coli ST1193 in the region. The findings emphasize the urgent need for antibiotic optimization programs and enhanced surveillance to curb the dissemination of high-risk clones that pose an increasing public health threat in Algeria. A simplified method based on virulence traits for E. coli and K. pneumoniae is proposed here for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) monitoring.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genomic Analysis of Antimicrobial Drug-Resistant Bacteria)
Open AccessArticle
Heterogeneity of Biofilm Formation Among Staphylococcus aureus and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Species in Clinically Relevant Intravenous Fat Emulsions
by
Gustavo R. Alvira-Arill, Oscar R. Herrera, Jeremy S. Stultz and Brian M. Peters
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 484; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050484 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Compared to soybean oil intravenous fat emulsion (SO-IFE), use of mixed-oil IFE (MO-IFE) is associated with reduced rates of catheter-related bloodstream infections caused by coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species (CoNS) in pediatric patients receiving parenteral nutrition. Methods: Using an in vitro biofilm
[...] Read more.
Background: Compared to soybean oil intravenous fat emulsion (SO-IFE), use of mixed-oil IFE (MO-IFE) is associated with reduced rates of catheter-related bloodstream infections caused by coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species (CoNS) in pediatric patients receiving parenteral nutrition. Methods: Using an in vitro biofilm model, this study aimed to assess the impact of IFEs on biofilm formation among Staphylococcus species. S. aureus, S. capitis, S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, S. hominis, and S. lugdunensis were cultivated as biofilms in media supplemented with SO-IFE, MO-IFE, or fish oil IFE (IFE). Biomass was quantified by the crystal violet method, and follow-up planktonic growth assays assessed antimicrobial effects of IFEs. Results: Compared to SO-IFE, MO-IFE and FO-IFE significantly inhibited biofilm formation of S. aureus but did not impact planktonic growth. Contrary to clinical data, CoNS biofilm formation was not impacted by any of the IFEs tested. S. aureus biofilm inhibition in IFEs was further investigated by comparing differences following growth in SO-IFE supplemented with capric acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), or eicosapenaenoic acid (EPA) to concentrations matching those of MO-IFE. Capric acid supplementation was associated with significant reduction in biofilm formation compared to SO-IFE alone. However, this was attributed to a bactericidal effect based on follow-up planktonic growth assays. Conclusions: These results suggest that biofilm formation in S. aureus is variably impacted by fatty acid composition in clinically relevant IFEs, with capric acid exhibiting bactericidal activity against tested isolates.
Full article
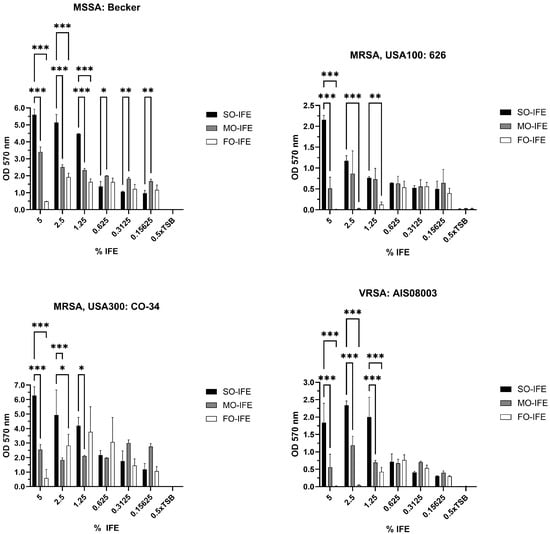
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Repurposing Mouthwashes: Antifungal and Antibiofilm Abilities of Commercially Available Mouthwashes Against Candida spp.
by
Marie Maziere, Paulo Rompante, José Carlos Andrade, Beatriz S. F. De Oliveira, Mariana C. Alves and Celia Fortuna Rodrigues
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 483; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050483 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The main objective was to evaluate and compare the antifungal efficacy against Candida spp. in commercially available mouthwashes distributed in the European market. Indeed, the solution to emerging infectious diseases may no longer lie in costly new drug development but rather
[...] Read more.
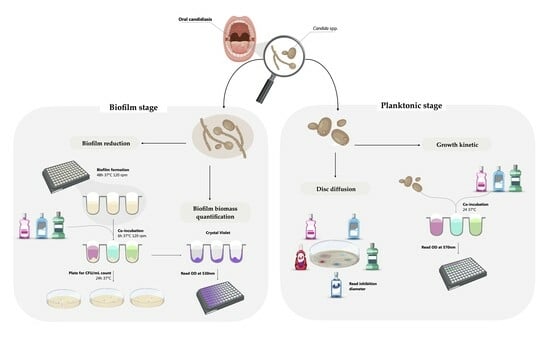
Background/Objectives: The main objective was to evaluate and compare the antifungal efficacy against Candida spp. in commercially available mouthwashes distributed in the European market. Indeed, the solution to emerging infectious diseases may no longer lie in costly new drug development but rather in unlocking the untapped potential of existing substances. Materials and Methods: Eighteen mouthwashes, chosen based on their composition, were tested in vitro against ten Candida strains, including clinical isolates of oral origin and reference strains, in both planktonic and biofilm forms. The antifungal susceptibility testing was conducted using the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) disc diffusion method and the evaluation of the kinetic growth in planktonic Candida. Biofilm reduction was determined by the evaluation of the minimal biofilm eradication concentration (MBEC). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was performed to evaluate potential morphological alterations of Candida biofilms. Results: Most mouthwashes effectively reduced biomass production and colony-forming unit (CFU) count. Parodontax Extra showed the highest efficacy. In the disc diffusion assay, Gum Paroex 0.12% exhibited the largest average inhibition zone diameter. Some unusual trends in the data may be explained by a higher reaction of fungal cells and the release of excess biomass during co-incubation in higher concentration of mouthwashes. SEM images revealed significant morphological alterations. Conclusion: Mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine digluconate, either alone or in combination with cetylpyridinium chloride and other active compounds, emerged as a common factor among the most efficacious formulations. In vivo studies will be essential to validate these findings, but mouthwashes may serve as a valuable adjuvant in the treatment of oral candidiasis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbial Biofilms: Identification, Resistance and Novel Drugs)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Dairy Products in Romania
by
Filippos Georgios Nikolaou, Liora Mihaela Colobatiu, Laurentiu Mihai Ciupescu, Alexandra Tabaran, Ariana Raluca Hategan, Romolica Mihaiu, Radu Tanasuica, Magdalena Maria Poenaru and Marian Mihaiu
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 482; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050482 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Listeria monocytogenes is a significant foodborne pathogen associated with dairy products, which can pose serious public health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. This study aimed to assess the prevalence, serotype distribution, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from dairy
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Listeria monocytogenes is a significant foodborne pathogen associated with dairy products, which can pose serious public health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. This study aimed to assess the prevalence, serotype distribution, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from dairy products collected in Romania over a three-year period (2021–2023). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive study addressing these issues within the country. Methods: A total of 10,306 dairy samples, including milk, cheeses, ice cream, yogurt, and other dairy-based products, were collected and analyzed using standard microbiological methods. Molecular serotyping was performed to identify the most common serogroups. The antimicrobial susceptibility of the isolates was also conducted. Results: The overall prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes was 0.41% (43/10,306). The most frequently detected serogroup was IVb (74.41%), followed by IIa (23.25%) and IIb (2.32%). Ice cream was the most affected product, followed by fresh telemea made from cow milk. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed higher resistance rates for oxacillin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (13.95% each), while all isolates were susceptible to ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, and moxifloxacin. Conclusions: The findings emphasize the need for continuous monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes in dairy products, particularly ice cream and fresh cheeses, due to their high contamination rates. The study’s results are valuable for comparative analysis with findings from other countries, helping to establish a broader understanding of Listeria monocytogenes contamination trends and resistance profiles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Challenges in Food Safety: Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors, and Biofilm Formation in Food-Borne Pathogens)
►▼
Show Figures
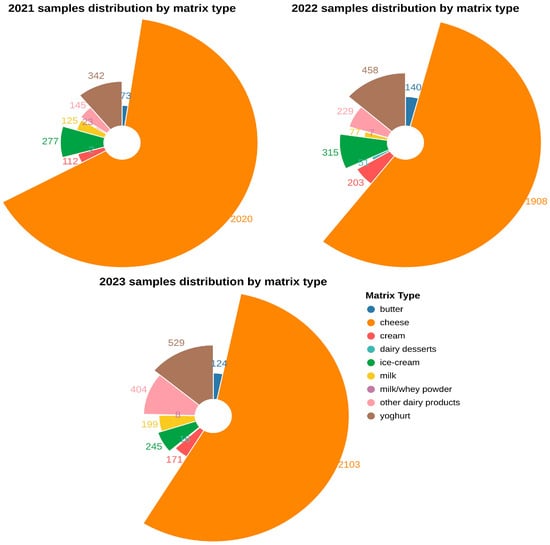
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pulsed Blue Light and Phage Therapy: A Novel Synergistic Bactericide
by
Amit Rimon, Jonathan Belin, Ortal Yerushalmy, Yonatan Eavri, Anatoly Shapochnikov, Shunit Coppenhagen-Glazer, Ronen Hazan and Lilach Gavish
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 481; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050481 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) strains are an increasing cause of morbidity and mortality. Pulsed blue light (PBL) enhances porphyrin-induced reactive oxygen species and has been clinically shown to be harmless to the skin at low doses. Bacteriophages, viruses that
[...] Read more.
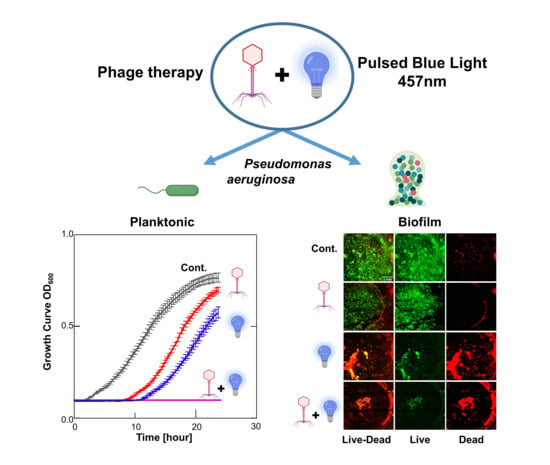
Background: Antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) strains are an increasing cause of morbidity and mortality. Pulsed blue light (PBL) enhances porphyrin-induced reactive oxygen species and has been clinically shown to be harmless to the skin at low doses. Bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, offer a promising non-antibiotic bactericidal approach. This study investigates the potential synergism between low-dose PBL and phage therapy against P. aeruginosa in planktonic cultures and preformed biofilms. Methods: We conducted a factorial dose–response in vitro study combining P. aeruginosa-specific phages with PBL (457 nm, 33 kHz) on both PA14 and multidrug-resistant PATZ2 strains. After excluding direct PBL effects on phage titer or activity, we assessed effectiveness on planktonic cultures using growth curve analysis, CFU, and PFU. Biofilm efficacy was evaluated using CFU post-sonication, crystal violet staining, and live/dead staining with confocal microscopy. Finally, we assessed reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a potential mechanism using the nitro blue tetrazolium reduction assay. ANOVA or Kruskal–Wallis tests with post hoc Tukey or Conover–Iman tests were used for comparisons (n = 5 biological replicates and technical triplicates). Results: The bacterial growth lag phase was significantly extended for phage alone or PBL alone, with a synergistic effect of up to 144% (p < 0.001 for all), achieving a 9 log CFU/mL reduction at 24 h (p < 0.001). In preformed biofilms, synergistic combinations significantly reduced biofilm biomass and bacterial viability (% Live, median (IQR): Control 80%; Phage 40%; PBL 25%; PBL&Phage 15%, p < 0.001). Mechanistically, PBL triggered transient ROS in planktonic cultures, amplified by phage co-treatment, while a biphasic ROS pattern in biofilms reflected time-dependent synergy. Conclusions: Phage therapy combined with PBL demonstrates a synergistic bactericidal effect against P. aeruginosa in both planktonic cultures and biofilms. Given the strong safety profile of PBL and phages, this approach may lead to a novel, antibiotic-complementary, safe treatment modality for patients suffering from difficult-to-treat antibiotic-resistant infections and biofilm-associated infections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antibiofilm Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Selective Chromogenic Medium for Detecting Meropenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Respiratory Samples
by
Carmen Cintora Mairal, Guillermo Martín-Gutiérrez, Ángel Rodríguez-Villodres, José Miguel Cisneros, José Antonio Lepe and José Manuel Ortiz de la Rosa
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 480; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050480 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Meropenem is widely used to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections; however, the pathogen’s increasing resistance compromises its efficacy. In this study, we aimed to develop a selective culture medium for detecting the presence of meropenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in respiratory specimens within 24
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Meropenem is widely used to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections; however, the pathogen’s increasing resistance compromises its efficacy. In this study, we aimed to develop a selective culture medium for detecting the presence of meropenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in respiratory specimens within 24 h. Methods: The medium’s performance was challenged using a collection of 130 clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains (of which 85 were meropenem-susceptible, 14 were meropenem-intermediate, and 21 were meropenem-resistant). Subsequently, clinical validation was carried out using 130 respiratory samples. Results: The selective medium demonstrated excellent sensitivity (average 98.7%) and specificity (average 90%) across bacterial concentrations ranging from 1 × 104 to 1 × 108 CFU/mL, and a high negative predictive value (average 99.2%) compared to the broth microdilution (BMD) method. Clinical validation with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and tracheobronchial aspirate (TBA) clinical specimens (N = 130) revealed a strong performance, with 92,3% categorical agreement. Conclusions: This method accelerates susceptibility testing, is user-friendly, and delivers reliable results, contributing to the optimization of empirical treatment for respiratory tract infections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Epidemiology and Mechanisms of Carbapenem Resistance in Clinical Gram-Negative Bacteria)
►▼
Show Figures
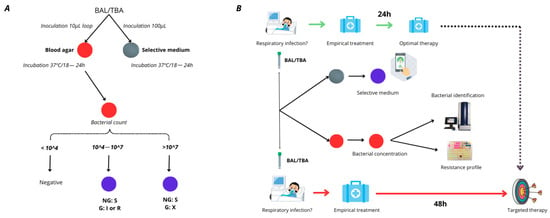
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Misconceptions and Behavioral Risks in Parental Antibiotic Use on Romanian Children: A Cross-Sectional Study on Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices
by
Alin Iuhas, Radu Galiș, Marius Rus, Andreea Balmoș, Cristian Marinău, Larisa Niulaș, Zsolt Futaki, Dorina Matioc and Cristian Sava
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 479; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050479 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global health threat, with antibiotic misuse in pediatric populations being a significant contributing factor. In Romania, antibiotic consumption and resistance rates are among the highest in Europe. Objective: To assess Romanian parents’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding
[...] Read more.
Background: Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global health threat, with antibiotic misuse in pediatric populations being a significant contributing factor. In Romania, antibiotic consumption and resistance rates are among the highest in Europe. Objective: To assess Romanian parents’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding antibiotic use in children, and to identify key misconceptions and behavioral risks contributing to inappropriate antibiotic use. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 400 parents of hospitalized children in a pediatric department in Romania. Participants completed a 15 item structured questionnaire. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, and binary logistic regression to examine associations and control for potential confounding effects between education level, residential environment, and parental misconceptions regarding antibiotic use. Results: Among the 400 surveyed caregivers, 86% (n = 344) held at least one misconception regarding antibiotic use. Additionally, 42.5% (n = 170) of participants reported that they had never heard of the concept of antibiotic resistance. Misconceptions were significantly more prevalent among individuals with lower levels of education and those residing in rural areas (p < 0.001). While 89.8% (n = 359) stated that they had never administered antibiotics to their children without a physician’s recommendation, a separate subset of 28% (n = 112) acknowledged that they had asked a doctor to prescribe antibiotics for their child. Moreover, 23.3% (n = 93) reported seeking a second medical opinion when antibiotics were not initially prescribed. Conclusions: Despite high adherence to medical advice, widespread misconceptions persist. These findings highlight the need for targeted, population-specific educational interventions to promote rational antibiotic use and address AMR in high-burden settings like Romania.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antibiotic Use in the Communities—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
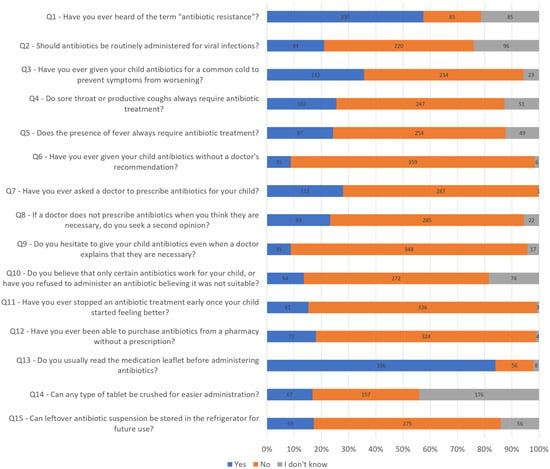
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae and Riemerella anatipestifer Isolates from Clinical Cases of Waterfowl in Hungary Between 2022 and 2023
by
Ádám Kerek, Ábel Szabó and Ákos Jerzsele
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 478; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050478 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background:Riemerella anatipestifer and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae remain clinically significant pathogens in the waterfowl industry, causing substantial economic losses and posing potential zoonotic risks. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) continues to spread in the poultry sector, making regular surveillance of bacterial isolates essential. Methods: In
[...] Read more.
Background:Riemerella anatipestifer and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae remain clinically significant pathogens in the waterfowl industry, causing substantial economic losses and posing potential zoonotic risks. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) continues to spread in the poultry sector, making regular surveillance of bacterial isolates essential. Methods: In this study, eight R. anatipestifer and eighteen E. rhusiopathiae strains were isolated from clinical cases in Hungarian waterfowl between 2022 and 2023. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values were determined for antibiotics of veterinary and public health significance. Results: For R. anatipestifer, high resistance rates were observed for spectinomycin, lincomycin, and tiamulin, while beta-lactam antibiotics (amoxicillin, ceftriaxone, and imipenem) demonstrated strong efficacy. Among the E. rhusiopathiae isolates, resistance to amoxicillin (89%) and enrofloxacin (61%) was notable, whereas ceftriaxone and doxycycline exhibited moderate antibacterial effects. Conclusions: Our findings underscore the importance of targeted antimicrobial use in the waterfowl industry. Beta-lactam antibiotics remain effective, whereas rising resistance to fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides raise serious concerns. Routine AMR surveillance and the adoption of alternative strategies are crucial for controlling infections and maintaining flock health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Virulence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Production in Veterinary, Zoonotic and Food-Related Pathogens)
►▼
Show Figures
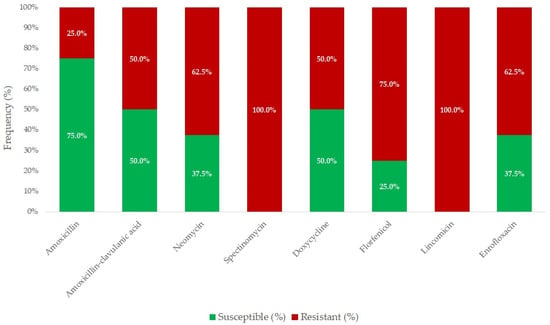
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dissemination of Tylosin Residues in the Poultry Environment: Evaluating Litter and Droppings as Sources of Risk
by
María Belén Vargas, Ignacia Soto, Francisco Mena, Paula Cortés, Ekaterina Pokrant, Lina Trincado, Matías Maturana, Andrés Flores, Aldo Maddaleno, Lisette Lapierre and Javiera Cornejo
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 477; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050477 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Tylosin, a veterinary antimicrobial belonging to the macrolide family, is commonly used in the poultry industry. Residues generated from its use can be present in the litter and droppings of treated birds. Due to the diverse uses of poultry byproducts, such as
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Tylosin, a veterinary antimicrobial belonging to the macrolide family, is commonly used in the poultry industry. Residues generated from its use can be present in the litter and droppings of treated birds. Due to the diverse uses of poultry byproducts, such as fertilizing agricultural soils or incorporation into the diets of other animal species, there is a risk to public health, as the presence of antimicrobial residues favors the development of antimicrobial resistance, which is a global problem. Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the dissemination of tylosin residues from the litter and droppings of treated birds and untreated birds in a controlled broiler environment. Methods: Bird droppings and litter samples were collected and analyzed using HPLC-MS/MS to detect and quantify tylosin residues. Results: The residue concentrations detected in the dropping matrix only exceeded the Limits of Quantification (LOQ = 4 µg kg−1) in the treated group. The litter matrix had statistically significant differences between the study groups. The persistence of tylosin residues in the litter of birds at day 42 was 290.16 µg kg−1 in the treated group (A) and 9.35 µg kg−1 in the adjacent untreated group (B.1). Conclusions: The results indicate that exposure distance influences tylosin residue dissemination.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibiotics Use and Antimicrobial Stewardship)
►▼
Show Figures
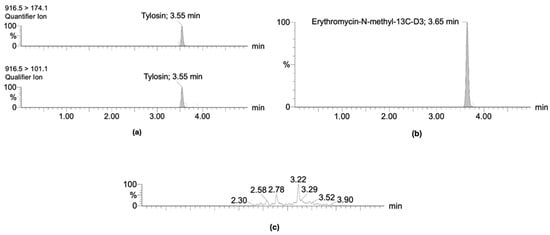
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Clinical Effectiveness of Penicillin-Free Therapies in First-Line and Rescue Treatments for Helicobacter pylori: A Systematic Review
by
Kenza El Boury, Hind Boudarf, Imane Adoud, Soukaina Ouannass, Oussama Abi, Hanane Delsa, Fatima Azzahra Lahlou, Samy Iskandar, Meryem El Jemli, Idrissa Diawara, Mohamed Amine Senhaji, Lhousaine Balouch, Zakaria Belrhiti and Mohamed Kettani Halabi
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 476; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050476 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and Aims: Amoxicillin is one of the most effective antibiotics for treating Helicobacter pylori infections and is widely used in first-line treatment regimens. However, patients with penicillin allergies cannot receive penicillin-based therapies, which significantly limits effective eradication options. This allergy often compels clinicians
[...] Read more.
Background and Aims: Amoxicillin is one of the most effective antibiotics for treating Helicobacter pylori infections and is widely used in first-line treatment regimens. However, patients with penicillin allergies cannot receive penicillin-based therapies, which significantly limits effective eradication options. This allergy often compels clinicians to choose alternative regimens that may be less effective, thereby increasing the risk of treatment failure. Consequently, therapeutic options for these patients are more restricted, and clinicians must carefully select the most appropriate regimen, taking into account both efficacy and the potential for antimicrobial resistance. This review aims to systematically evaluate the efficacy of penicillin-free treatment regimens for the eradication of H. pylori in patients with penicillin allergies. Specifically, it seeks to identify, analyze, and synthesize current clinical evidence to determine the most effective alternative therapies, thereby supporting evidence-based clinical decision-making. Methods: A literature search was conducted using the PubMed and Scopus databases. We began by reviewing the titles and abstracts of all identified studies to determine eligibility. Next, we assessed the full text of potentially eligible articles according to inclusion and exclusion criteria to establish the eligibility of each study. Results: This review included 26 studies comprising 2713 participants, evaluating penicillin-free therapies for H. pylori eradication in penicillin-allergic patients. Key findings demonstrated high eradication rates with bismuth-based quadruple therapies (88–97%), doxycycline-based regimens (86%), and quinolone-based therapies (75–100%), with Sitafloxacin exceeding 90% efficacy. Minocycline-based regimens also showed promising outcomes, with eradication rates between 80% and 85%. Although the PPI–clarithromycin–metronidazole combination was moderately effective, it was less favored as a first-line option. Overall, bismuth-based and quinolone-based therapies emerged as the most effective alternatives. Conclusions: In patients allergic to penicillin, bismuth quadruple therapy has demonstrated an excellent rate of eradication. Quinolone-based regimens are emerging as a promising alternative in first-line treatment or in cases of treatment failure. Vonoprazan-based therapy is an effective regimen. Combined with clarithromycin and metronidazole, vonoprazan enhances eradication rates and demonstrates effectiveness, including in clarithromycin-resistant strains.
Full article
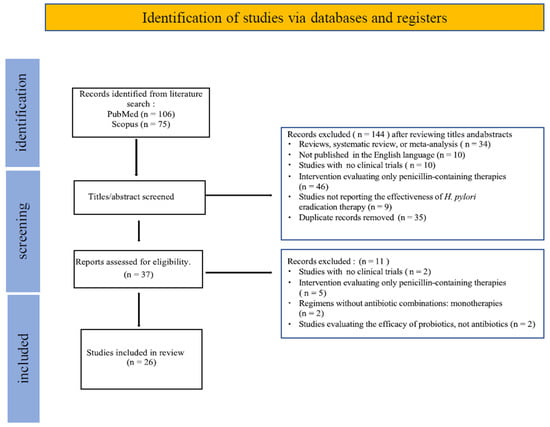
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High Prevalence of Cefiderocol Resistance Among New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae High-Risk Clones in Hungary
by
Lilla Buzgó, Zsanett Kiss, Dániel Göbhardter, Virág Lesinszki, Erika Ungvári, Zoltán Rádai, Levente Laczkó, Ivelina Damjanova, Gábor Kardos and Ákos Tóth
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 475; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050475 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The global spread of carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae (CPKP) strains represent a severe public health threat due to very limited choice of antibacterial therapy. Cefiderocol, a novel siderophore-cephalosporin, may represent a new therapeutic option but resistance is increasingly being described. Our aim was
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The global spread of carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae (CPKP) strains represent a severe public health threat due to very limited choice of antibacterial therapy. Cefiderocol, a novel siderophore-cephalosporin, may represent a new therapeutic option but resistance is increasingly being described. Our aim was to investigate in vitro cefiderocol susceptibility among CPKP strains in Hungary and assess correlations between resistance, carbapenemase types, and clonal lineages. Methods: The study was performed on 420 CPKP strains from 34 Hungarian healthcare institutes (HCIs) submitted to the National Reference Laboratory of Antimicrobial Resistance (March 2021 to April 2023). The disk diffusion method (Liofilchem, Via Scozia, Italy) was used for in vitro cefiderocol susceptibility testing (according to EUCAST guidelines). For molecular epidemiologic investigation, we used whole genome sequencing (Illumina MiSeq, 150 bp paired-end) and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Carbapenemase gene type was determined by multiplex PCR. Statistical analysis was performed in R (v.4.2.0). Results: Dominant high-risk clones (ST147, ST395, ST258) exhibited regional distribution, with ST147/NDM-1 strains showing the highest cefiderocol resistance (75%). Overall resistance was 65%. Carbapenemase gene types occurred as follows: 35 blaVIM, 53 blaKPC, 57 blaOXA-48-like, 153 blaNDM, and 122 blaOXA-48-like+blaNDM. Cefiderocol resistance rates by carbapenemase type were 20%, 44%, 70%, and 75% in the case of blaVIM, blaOXA-48-like, blaKPC, blaNDM, and blaOXA-48-like+blaNDM. Conclusions: The results show a high prevalence of cefiderocol resistance in CPKP in Hungary, with different rates of resistance in different carbapenemase gene-carrying high-risk clones, highlighting the growing challenge in treating these infections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibiotic Therapy in Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
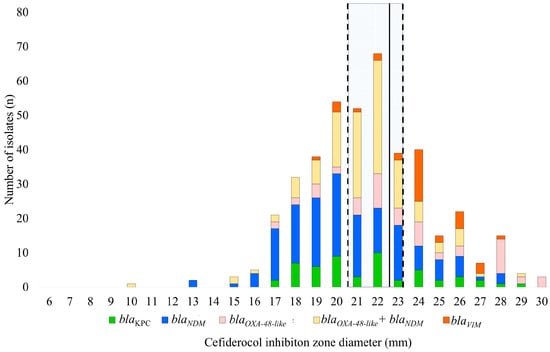
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Rapid Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Voriconazole Based on High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: A Single-Center Pilot Study in Outpatients
by
Satoru Morikawa, Yusuke Yagi, Moemi Okazaki, Narika Yanagisawa, Tomoaki Ishida, Kohei Jobu, Takumi Maruyama, Takahiro Kato, Miyuki Matsushita, Yu Arakawa, Yuka Yamagishi and Yukihiro Hamada
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 474; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050474 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Voriconazole (VRCZ) use requires accurate monitoring to avoid suboptimal drug levels and adverse effects. In addition, the appearance of resistant fungal strains is a problem that needs attention. Blood concentration measurement is the monitoring technique of choice; however, it is slow, limiting
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Voriconazole (VRCZ) use requires accurate monitoring to avoid suboptimal drug levels and adverse effects. In addition, the appearance of resistant fungal strains is a problem that needs attention. Blood concentration measurement is the monitoring technique of choice; however, it is slow, limiting its clinical application. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical utility of rapid therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) for VRCZ using high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection (HPLC-UV) compared to conventional outsourced liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) testing in outpatient care. Methods: VRCZ blood concentrations were measured using HPLC-UV and LC-MS/MS. Reporting times, accuracy, and clinical outcomes were assessed for outpatients receiving VRCZ treatment. Safety was monitored for renal, hepatic, and visual toxicities. Results: HPLC-UV significantly reduced reporting times (0.433 h vs. 74.3 h, p < 0.001), and Deming’s regression analyses showed a strong correlation with LC-MS/MS results (Pearson’s r = 0.988). Bland–Altman analysis showed an average difference of 0.025 μg/mL between HPLC-UV and LC-MS/MS. Prospective monitoring of three outpatients revealed no adverse events, enabling safe and effective VRCZ dosing. Conclusions: Rapid VRCZ TDM using HPLC-UV is a cost-effective and feasible approach for outpatient care, significantly improving reporting times and patient safety. Further studies and cross-facility collaboration are needed to expand its application.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and/or TDM of Antimicrobial Agents)
►▼
Show Figures
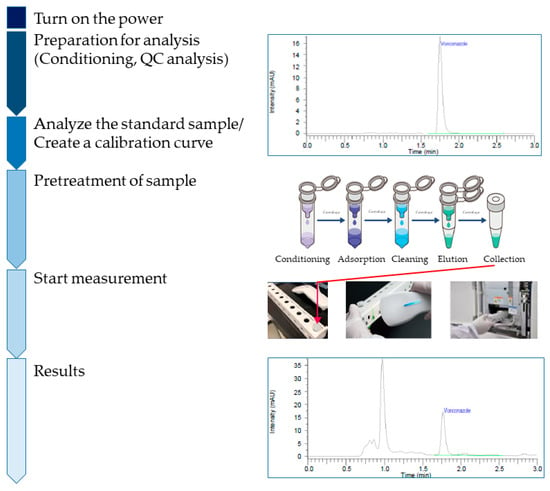
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Rame Hau et al. The Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with the Presence of Antibiotic Residues in Milk from Peri-Urban Dairy Cattle Farms in Kathmandu, Nepal. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 98
by
Erda E. Rame Hau, Minu Sharma, Bal K. Sharma Khanal, Peter D. Sly, Deirdre Mikkelsen, Nicholas Clark and Ricardo J. Soares Magalhães
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 473; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050473 - 7 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
There were errors in the original publication [...]
Full article
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Terbinafine Resistance in Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton indotineae: A Literature Review
by
Aditya K. Gupta, Susmita, Hien C. Nguyen, Amanda Liddy, Vasiliki Economopoulos and Tong Wang
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 472; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050472 - 7 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Terbinafine has been the gold standard for the management of superficial fungal infections. The etiological agent generally is Trichophyton rubrum (T. rubrum); however, there has been increased reporting of a new terbinafine-resistant strain of the T. mentagrophytes complex (T.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Terbinafine has been the gold standard for the management of superficial fungal infections. The etiological agent generally is Trichophyton rubrum (T. rubrum); however, there has been increased reporting of a new terbinafine-resistant strain of the T. mentagrophytes complex (T. mentagrophytes ITS genotype VIII otherwise known as T. indotineae). Here, we review the epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of T. rubrum and T. indotineae infections. Methods: We conducted a systematic literature search using PubMed, Embase (Ovid), and Web of Science, resulting in 83 qualified studies with data summarized for clinical features, antifungal susceptibility, and terbinafine resistance mechanisms and mutations. Results: Dermatophytosis is most commonly caused by T. rubrum; however, in certain parts of the world, especially in the Indian subcontinent, T. indotineae infections have been reported more frequently. The majority of T. rubrum isolates remain susceptible to terbinafine (over 60% of isolates show MIC50 and MIC90 < 0.5 µg/mL). In contrast, for T. indotineae, 30% of isolates exhibit MIC50 ≥ 0.5 µg/mL and 80% exhibit MIC90 ≥ 0.5 µg/mL. Frequently detected squalene epoxidase (SQLE) mutations in T. rubrum are Phe397Leu/Ile (41.6%) and Leu393Phe (20.8%); in T. indotineae, these include Phe397Leu (33.0%) and Ala448Thr (24.5%). Other potential terbinafine resistance mechanisms in T. rubrum and T. indotineae are discussed. Conclusions: T. rubrum generally remain susceptible in vitro to terbinafine in contrast to T. indotineae. The essential components of an effective antifungal stewardship emphasize accurate clinical and laboratory diagnosis, susceptibility testing, and appropriate antifungal therapy selection with a multidisciplinary approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Worldwide Problem of Antifungal Resistance: From Basic to Clinic)
►▼
Show Figures
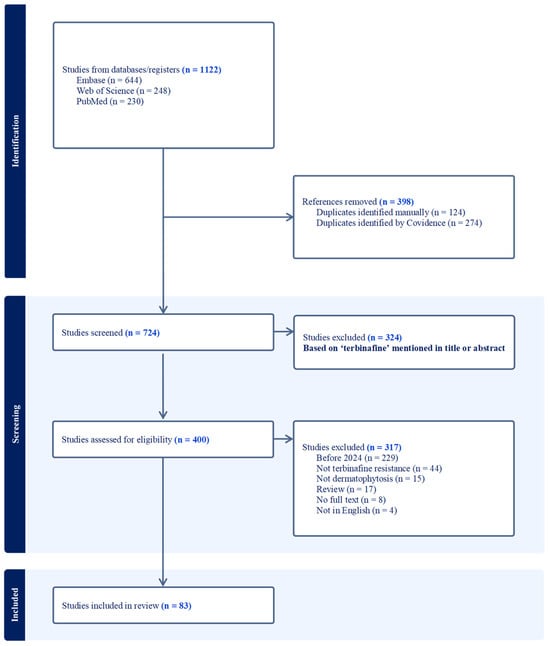
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
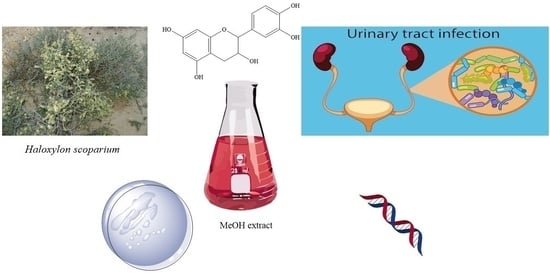
Use of Haloxylon scoparium Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria from Urinary Tract Infections
by
Fouad Bahri, Abdelhadi Boussena, Antoni Szumny, Youcef Bahri, El-Mokhtar Bahri, Adam Figiel and Piotr Juszczyk
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 471; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050471 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
Background: The emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria in the urinary tract and the decrease in the efficacy of antibiotics prompted us to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the methanolic extract of the aerial parts of Haloxylon scoparium against six isolated (MDR) bacteria. Methods: Phenolic
[...] Read more.
Background: The emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria in the urinary tract and the decrease in the efficacy of antibiotics prompted us to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the methanolic extract of the aerial parts of Haloxylon scoparium against six isolated (MDR) bacteria. Methods: Phenolic compound profiling of the extract of interest was performed by HPLC-DAD. Acute oral toxicity was tested in vivo. The antibiotic susceptibility of the isolates was assessed against 23 antibiotics using the disk diffusion method. The identification of the isolates was performed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The antibacterial activity of the extract was assessed using agar well diffusion, minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs), and minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBCs) methods. Results: Phenolic compound profiling of the extract revealed that epicatechin (85%) was the major compound. The extract also showed no symptoms of toxicity, adverse effects, or mortality in mice at the recommended dose. Overall, the extract at 200 µg/mL was effective against all isolates. The zones of inhibition ranged from 9.25 to 19.5 mm. Gram-positive S. aureus bacteria recorded the highest inhibitory effect with 19.5 mm against the five Gram-negative bacteria (9.25–17.25 mm). The MIC of the extracts against clinical isolates ranged from 50 to 100 µg/mL. The extract was bactericidal against S. aureus, E. coli, E. ludwigii, and K. pneumoniae with an MBC of 100, 100, 200, and 200 µg/mL, respectively. Conclusions: The results conclude that the extract could be an effective source of antimicrobial agents for the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by MDR bacteria.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial Activity of Plants Against Emerging or Drug-Resistant Human Pathogens)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Staphylococcus aureus: A Review of the Pathogenesis and Virulence Mechanisms
by
Rahima Touaitia, Assia Mairi, Nasir Adam Ibrahim, Nosiba S. Basher, Takfarinas Idres and Abdelaziz Touati
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 470; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050470 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a formidable human pathogen responsible for infections ranging from superficial skin lesions to life-threatening systemic diseases. This review synthesizes current knowledge on its pathogenesis, emphasizing colonization dynamics, virulence mechanisms, biofilm formation, and antibiotic resistance. By analyzing studies from PubMed, Scopus,
[...] Read more.
Staphylococcus aureus is a formidable human pathogen responsible for infections ranging from superficial skin lesions to life-threatening systemic diseases. This review synthesizes current knowledge on its pathogenesis, emphasizing colonization dynamics, virulence mechanisms, biofilm formation, and antibiotic resistance. By analyzing studies from PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, we highlight the pathogen’s adaptability, driven by surface adhesins (e.g., ClfB, SasG), secreted toxins (e.g., PVL, TSST-1), and metabolic flexibility in iron acquisition and amino acid utilization. Nasal, skin, and oropharyngeal colonization are reservoirs for invasive infections, with biofilm persistence and horizontal gene transfer exacerbating antimicrobial resistance, particularly in methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). The review underscores the clinical challenges of multidrug-resistant strains, including vancomycin resistance and decolonization strategies’ failure to target single anatomical sites. Key discussions address host–microbiome interactions, immune evasion tactics, and the limitations of current therapies. Future directions advocate for novel anti-virulence therapies, multi-epitope vaccines, and AI-driven diagnostics to combat evolving resistance. Strengthening global surveillance and interdisciplinary collaboration is critical to mitigating the public health burden of S. aureus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Staphylococcus— Molecular Pathogenesis, Virulence Regulation and Antibiotics Resistance)
►▼
Show Figures
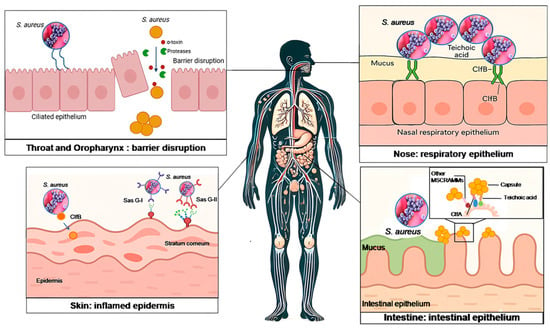
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Diversity and Safety Assessment of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from European Hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) Caught in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean
by
Lara Díaz-Formoso, Diogo Contente, Javier Feito, Belén Orgaz, Pablo E. Hernández, Juan Borrero, Estefanía Muñoz-Atienza and Luis M. Cintas
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 469; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050469 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The overuse and misuse of antibiotics has contributed significatively to the growing problem of the emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance genes among bacteria, posing a serious global challenge to the treatment of bacterial infectious diseases. For these reasons, there is a
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The overuse and misuse of antibiotics has contributed significatively to the growing problem of the emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance genes among bacteria, posing a serious global challenge to the treatment of bacterial infectious diseases. For these reasons, there is a current and growing interest in the development of effective alternative or complementary strategies to antibiotic therapy for the prevention of fish diseases, which are mainly based on the use of probiotics—in particular, those belonging to the Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) group. In this context, the aim of the present study was to characterise, evaluate the genetic diversity and assess the safety of candidate probiotic LAB strains for aquaculture isolated from faeces and intestines of European hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) caught in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean (Ireland). Methods: The direct antimicrobial activity of the LAB isolates was tested by the Stab-On-Agar method against key ichthyopathogens. Subsequently, their taxonomic classification and genetic diversity were determined by 16SrDNA sequencing and Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus-PCR (ERIC-PCR), respectively. To ensure the in vitro safety of the LAB isolates, their biofilm-forming ability was assessed by a microtiter plate assay; their sensitivity to major antibiotics used in aquaculture, human and veterinary medicine by a broth microdilution method and their haemolytic and gelatinase activity by microbiological assays. Results: All LAB isolates were biofilm producers and susceptible to chloramphenicol, oxytetracycline, flumequine and amoxicillin. A total of 30 isolates (85.7%) were resistant to at least one of the tested antibiotics. None of the 35 LAB isolates showed haemolytic or proteolytic activity. Conclusions: Among the isolated strains, five LAB strains exhibiting the highest antimicrobial activity against aquaculture-relevant ichthyopathogens, taxonomically identified as Streptococcus salivarius, Enterococcus avium and Latilactobacillus sakei, were selected for further characterisation as potential probiotic candidates to promote sustainable aquaculture. To our knowledge, this is the first study to report that hake intestines and faeces represent viable ecological niches for the isolation of LAB strains with antimicrobial activity.
Full article
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Distribution of Fimbrial Genes and Their Association with Virulence and Levofloxacin Resistance/Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Production in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
by
Masao Mitsui, Takanori Sekito, Mai Maruhashi, Yuki Maruyama, Takehiro Iwata, Yusuke Tominaga, Satoshi Katayama, Shingo Nishimura, Kensuke Bekku, Motoo Araki, Hidetada Hirakawa and Takuya Sadahira
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 468; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050468 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Urinary tract infection (UTI) is predominantly caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). Previous studies have reported that the fimbriae of UPEC are involved in virulence and antimicrobial resistance. We aimed to analyze the fimbrial gene profiles of UPEC and investigate the specificity
[...] Read more.
Background: Urinary tract infection (UTI) is predominantly caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). Previous studies have reported that the fimbriae of UPEC are involved in virulence and antimicrobial resistance. We aimed to analyze the fimbrial gene profiles of UPEC and investigate the specificity of these expressions in symptomatic UTI, urinary device use, and levofloxacin (LVFX) resistance/extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) production. Methods: A total of 120 UPEC strains were isolated by urine culture between 2019 and 2023 at our institution. They were subjected to an antimicrobial susceptibility test and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to identify 14 fimbrial genes and their association with clinical outcomes or antimicrobial resistance. Results: The prevalence of the papG2 gene was significantly higher in the symptomatic UTI group by multivariate analyses (OR 5.850, 95% CI 1.390–24.70, p = 0.016). The prevalence of the c2395 gene tended to be lower in the symptomatic UTI group with urinary devices (all p < 0.05). In LVFX-resistant UPEC strains from both the asymptomatic bacteriuria (ABU) and the symptomatic UTI group, the expression of the papEF, papG3, c2395, and yadN genes tended to be lower (all p < 0.05). Conclusion: The fimbrial genes of UPEC are associated with virulence and LVFX resistance, suggesting that even UPEC with fewer motility factors may be more likely to ascend the urinary tract in the presence of the urinary devices. These findings may enhance not only the understanding of the virulence of UPEC but also the management of UTI.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Mechanisms in Gram-Negative Bacteria: An Alliance for Success)
Open AccessReview
Antibiotic De-Escalation in the Intensive Care Unit: Rationale and Potential Strategies
by
Sarah Singer Matuszak, Lauren Kolodziej, Scott Micek and Marin Kollef
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 467; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050467 - 3 May 2025
Abstract
Antibiotic de-escalation (ADE) is important to help optimize antibiotic use and balance the positive and negative effects of antimicrobial therapy. ADE should be performed promptly, and infections should be treated with the shortest course of antimicrobials as clinically feasible to avoid unnecessary use
[...] Read more.
Antibiotic de-escalation (ADE) is important to help optimize antibiotic use and balance the positive and negative effects of antimicrobial therapy. ADE should be performed promptly, and infections should be treated with the shortest course of antimicrobials as clinically feasible to avoid unnecessary use of broad-spectrum antimicrobials. Several tools have been developed to increase efficient ADE, including rapid diagnostic tests (ex. multiplex PCR), MRSA nasal PCR/culture, and biomarkers. Multiplex PCR and MRSA nasal PCR/culture have been associated with reductions in inappropriate antibiotic use. Procalcitonin, a biomarker, has been associated with shorter antimicrobial durations in some studies; however, widespread use may be limited by lack of specificity for bacterial infections, cost, and lack of set cut-off points. Additional biomarkers such as IL-6, HMGB1, presepsin, sTREM-1, CD64, PSP, proadrenomedullin, and pentraxin-3 are currently being studied. As technology improves, additional tools may be leveraged to better optimize ADE even better, such as antimicrobial spectrum scoring tools and artificial intelligence (AI). Spectrum scores, which quantify antibiotic activity using specific numeric values, could be incorporated into electronic health records to identify patients on unnecessarily broad antibiotics. AI modeling has the potential to predict personal antibiograms or provide the probability that an empiric regimen may cover a particular infection, among other potential applications. This review will discuss the literature associated with ADE in the ICU, selected tools to help guide ADE, and perspectives on how to implement ADE into clinical practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue A Themed Issue in Honor of Professor Helen Giamarellou—Outstanding Contributions in the Fields of Antimicrobial Resistance and Difficult-to-Treat Resistance Pathogens)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stability of Nine Time-Dependent Antibiotics for Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy (OPAT) Use
by
Elise d’Huart, Ibtissem Boutouha, Clara Berardi, Jean Vigneron, Béatrice Demore and Alexandre Charmillon
Antibiotics 2025, 14(5), 466; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050466 - 3 May 2025
Abstract
Background: The use of an elastomeric diffuser is favored to administer outpatient antibiotic therapy. A study published in 2022 highlighted the instability of several antibiotics in elastomeric devices at 37 °C. The objective was to evaluate the stability of nine time-dependent antibiotics that
[...] Read more.
Background: The use of an elastomeric diffuser is favored to administer outpatient antibiotic therapy. A study published in 2022 highlighted the instability of several antibiotics in elastomeric devices at 37 °C. The objective was to evaluate the stability of nine time-dependent antibiotics that are unstable at 37 °C at lower concentrations and a reduced storage temperature of 32 °C. Methods: Chemical stability was assessed by pH measurement and high-performance liquid chromatography. Physical stability was evaluated by visual and subvisual inspection. The solutions were considered stable if the remaining drug percentage was ≥90%, the maximum variation in pH was less than 1, the particle count was within acceptable limits and the visual aspect remained unchanged after storage. Results: Solutions showing stability for 24 h are composed of 12.5 mg/mL cefiderocol in NS (normal saline) and 50–133 mg/mL piperacillin in NS-D5W (5% dextrose). Additionally, 12.5 mg/mL amoxicillin in NS; 12.5 mg/mL cefepime in NS-D5W; 12.5 mg/mL cefiderocol in D5W; 25 mg/mL cefiderocol in NS-D5W; 12.5 mg/mL cefotaxime in NS-D5W; 12.5 mg/mL cefoxitin in NS-D5W; 12.5 mg/mL ceftazidime in NS-D5W; 25 mg/mL ceftazidime in NS; 25 mg/mL cloxacillin in NS-D5W; and 25–50 mg/mL oxacillin in NS were shown to be stable for 12 h. Notably, 25 mg/mL amoxicillin in NS, 50 mg/mL cloxacillin in NS and 25 mg/mL oxacillin in D5W were shown to be stable for 8 h. Conclusions: These 12–24 h stability data indicate that these antibiotics can be administered by continuous infusion using only one–two elastomeric devices per day, facilitating outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy (OPAT).
Full article

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Antibiotics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antibiotics, Biomedicines, JCM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics
Challenges and Future Prospects of Antibacterial Therapy
Topic Editors: Kwang-sun Kim, Zehra EdisDeadline: 30 June 2025
Topic in
Antibiotics, Antioxidants, JoF, Microbiology Research, Microorganisms
Redox in Microorganisms, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Michal Letek, Volker BehrendsDeadline: 31 July 2025
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Veterinary Sciences, Antibiotics, Zoonotic Diseases
Animal Diseases in Agricultural Production Systems: Their Veterinary, Zoonotic, and One Health Importance, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Ewa Tomaszewska, Beata Łebkowska-Wieruszewska, Tomasz Szponder, Joanna Wessely-SzponderDeadline: 30 September 2025
Topic in
Antibiotics, JPM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Medicines
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modelling in Drug Discovery and Development
Topic Editors: Inaki F. Troconiz, Victor Mangas Sanjuán, Maria Garcia-Cremades MiraDeadline: 31 October 2025

Conferences
26–29 August 2025
The 5th International Symposium on Frontiers in Molecular Science
Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms of Biological Function and Drug Discovery based on Protein Structure/Function Analysis
Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms of Biological Function and Drug Discovery based on Protein Structure/Function Analysis

21–23 May 2025
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Antibiotics: Challenges and Strategies for the Antibiotic Resistance Crisis

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
New Approaches in Antimicrobial Drug Discovery and Design
Guest Editor: Robert PenchovskyDeadline: 10 May 2025
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
Clostridioides difficile Infection, 3rd Edition
Guest Editor: Guido GranataDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antimicrobials in Critically Ill Patients
Guest Editor: Young Ran LeeDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
What’s New: Natural and Synthetic Antibacterials and/or Agents with Multiple Activities? (3rd Edition)
Guest Editor: Maria SinicropiDeadline: 15 May 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Antimicrobial Prescribing and Antimicrobial Use in Healthcare Settings
Collection Editors: Masayuki Maeda, Yuichi Muraki
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Staphylococcus— Molecular Pathogenesis, Virulence Regulation and Antibiotics Resistance
Collection Editor: Ewa Szczuka
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Editorial Board Members' Collection Series: Structural Aspects of AMPs and Antimicrobials
Collection Editors: J. Michael Conlon, Marc Maresca, Bong-Jin Lee, Aurélie Tasiemski
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Synthetic and Natural Products-Based Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic Agents
Collection Editor: Antonio Eduardo Miller Crotti






