Big Data Driven Smart Logistics and Sustainable Supply Chain
A special issue of Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This special issue belongs to the section "Sustainable Management".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (10 April 2023) | Viewed by 2923
Special Issue Editors
2. School of Economics and Management, Chang’an University, Xi’an 710064, China
Interests: big data decision-making; smart transportation management; hazardous materials; transportation management
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Big data provides unprecedented opportunities for the development of logistics and sustainable supply chains. Taking full advantage of big data, we can make more informed decision and management choices, e.g., improving energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, enhancing supply chain value, and more. Logistics and sustainable supply chains have been at the forefront of utilizing and implementing big data. Machine intelligence and blockchain technologies have already been applied in this area.
A quick Web of Science search on logistics and sustainable supply chain clearly demonstrates a rapid and steady growth in the area, as demonstrated in Figure 1:
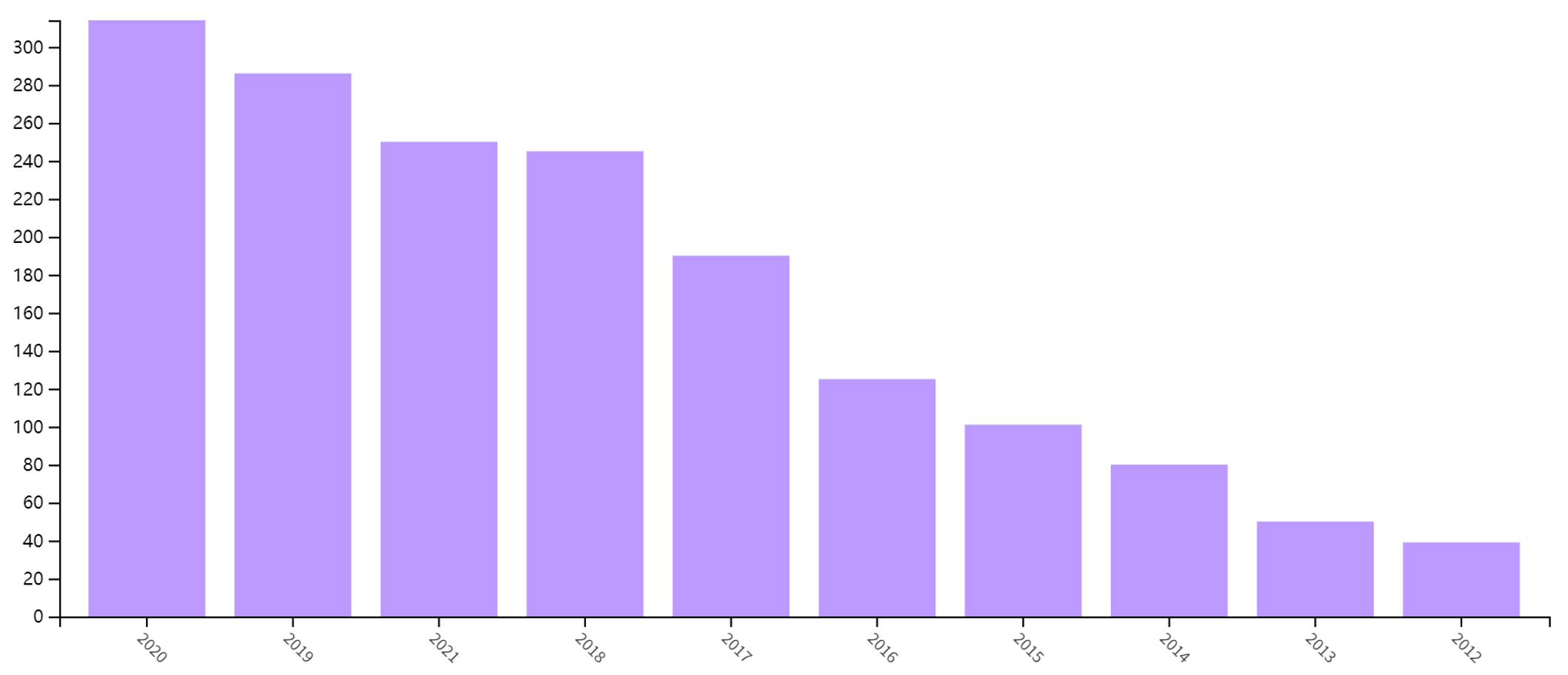
Figure 1. The number of publications related to logistics and sustainable supply chain.
There have been a significant number of publications in the area, however there is a lack of focused material that brings together recent advancements in logistics and sustainable supply chains in the era of big data.
The aim of this Special Issue is to explore state-of-the-art operational research and management science developments, to embrace big data applications to tackle established and emerging challenges in the smart logistics and sustainable supply chain field, and to further promote the efficiency and sustainability of logistics and supply chain systems. In this context, systematic reviews, case studies, mathematical and simulation models that emphasize the management, assessment and optimization of Big Data Driven Smart Logistics and Sustainable Supply Chain are invited for submission.
Prof. Dr. Xiang Li
Prof. Dr. Yanfei Lan
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- big data
- smart logistics
- sustainable supply chain management
- traffic transportation management
- risk management in sustainable supply chains
- innovation in sustainable supply chains
- energy efficiency
- emission reduction
- smart business models






