The Fractional Preferential Attachment Scale-Free Network Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Motivation
2. The Fractional Preferential Attachment Scale-Free Network Model
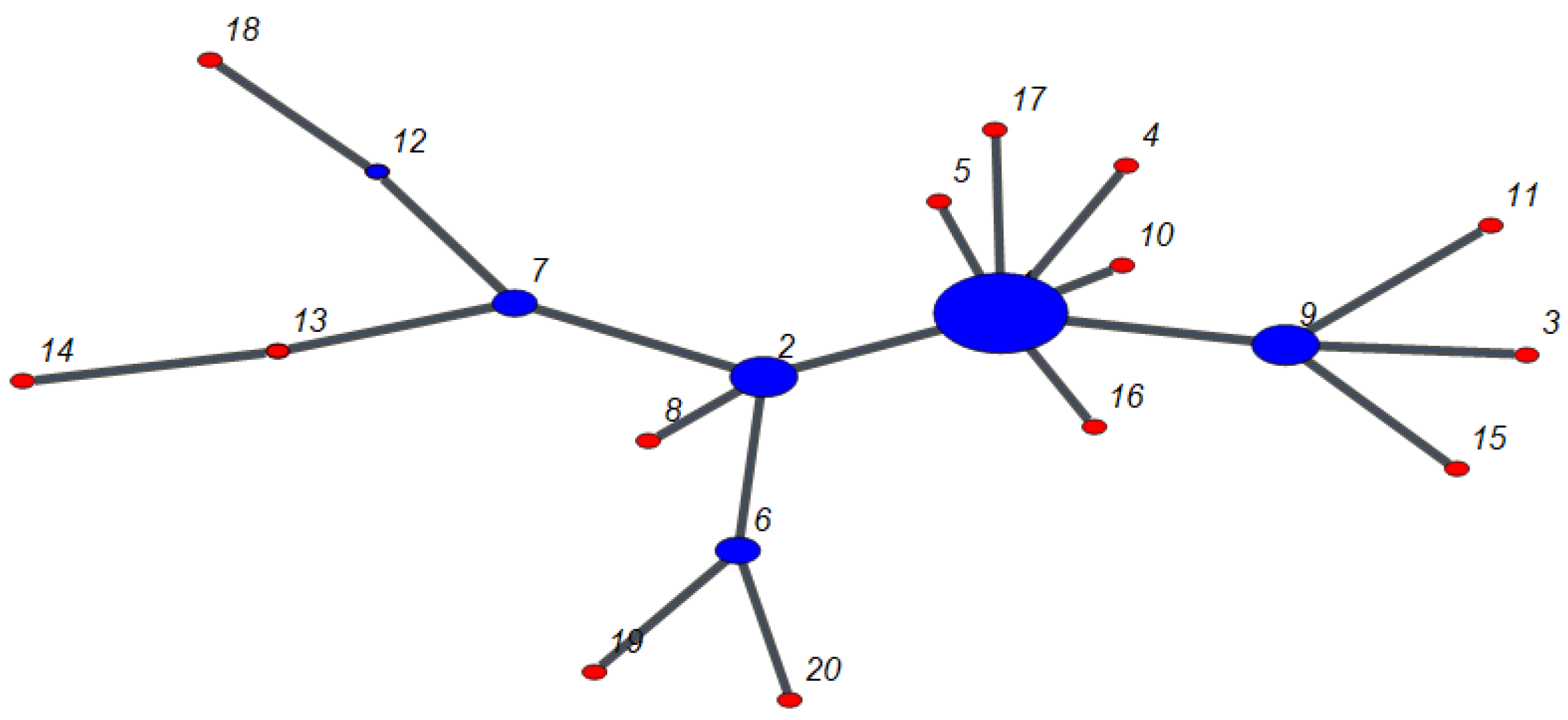
2.1. The Model
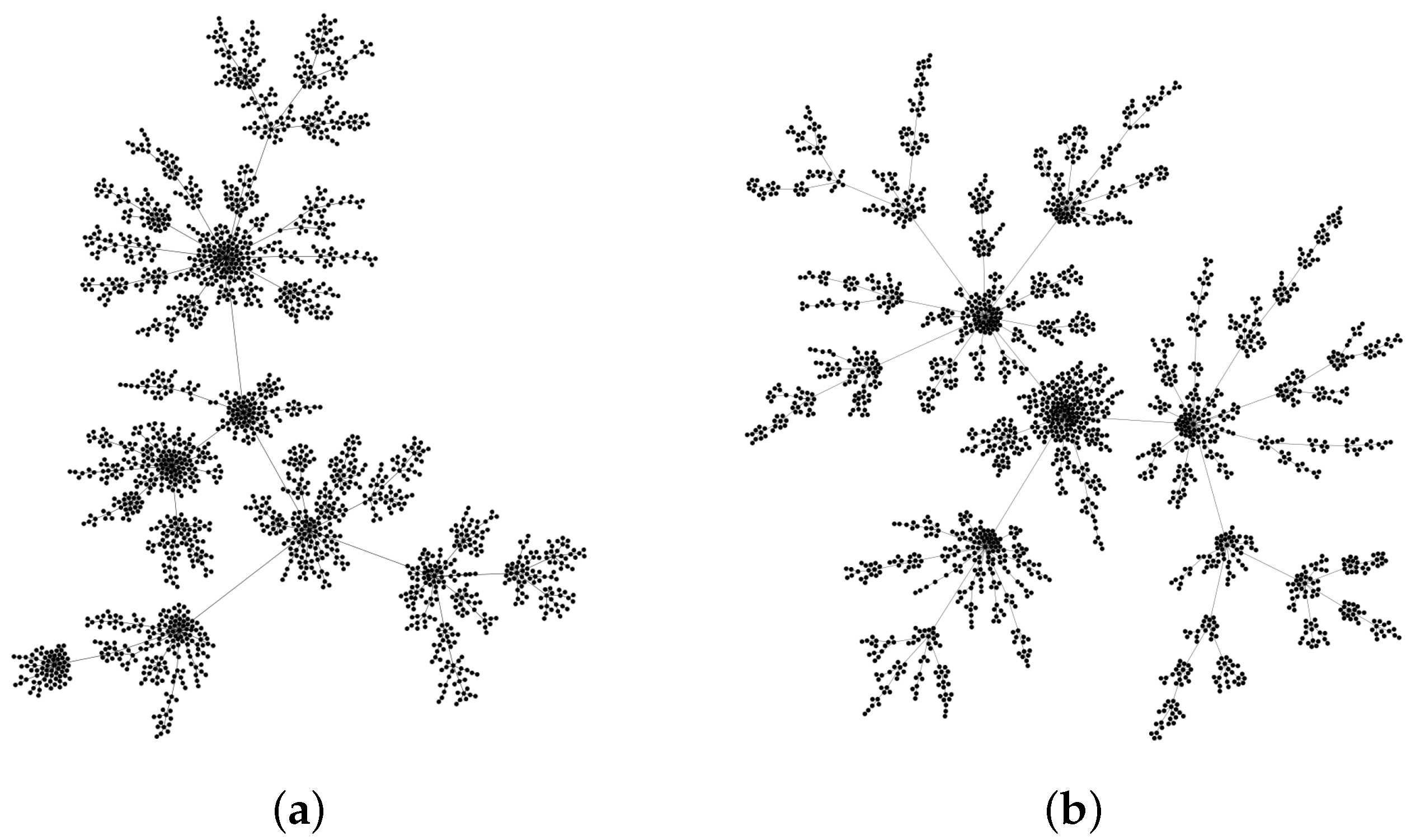
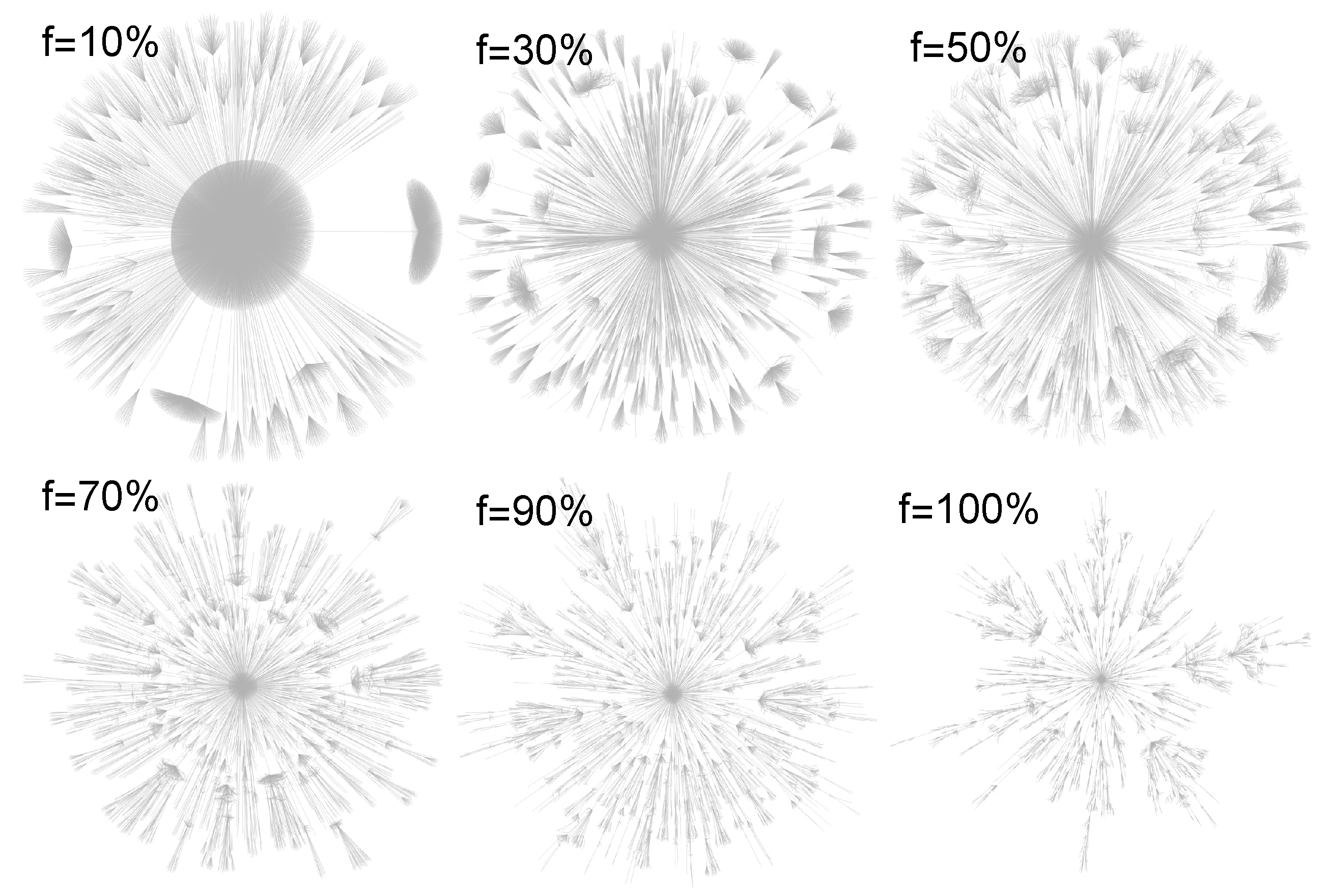
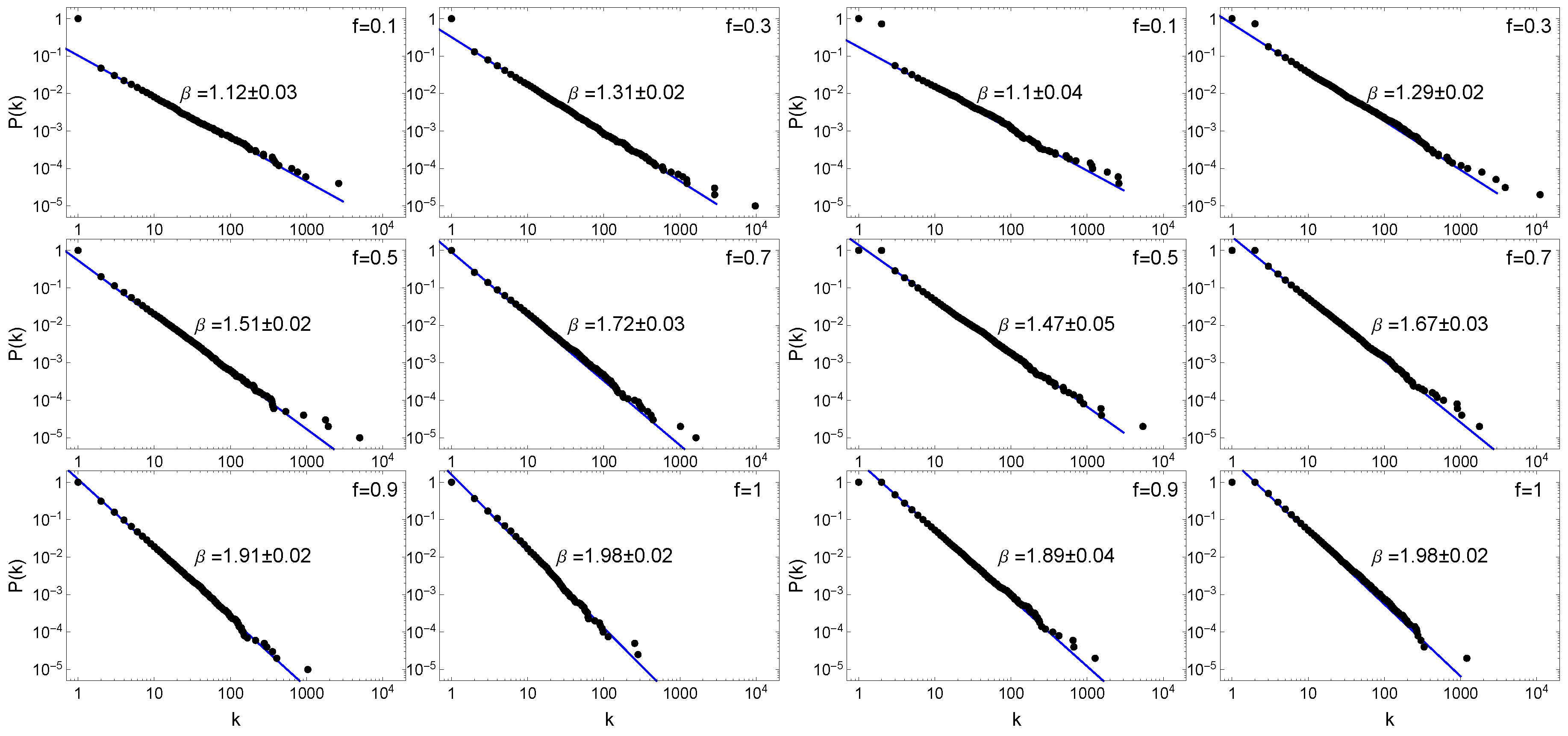
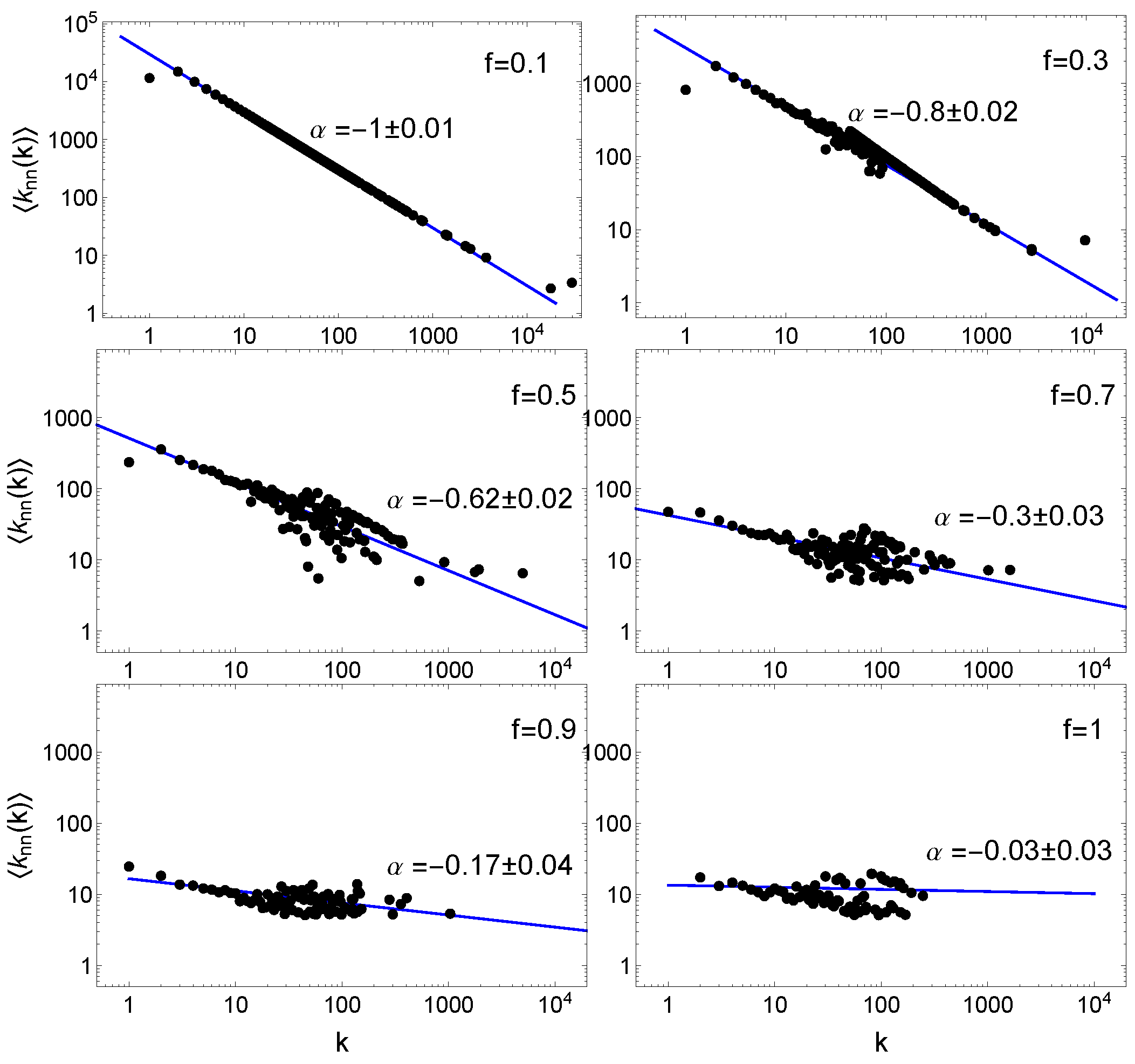
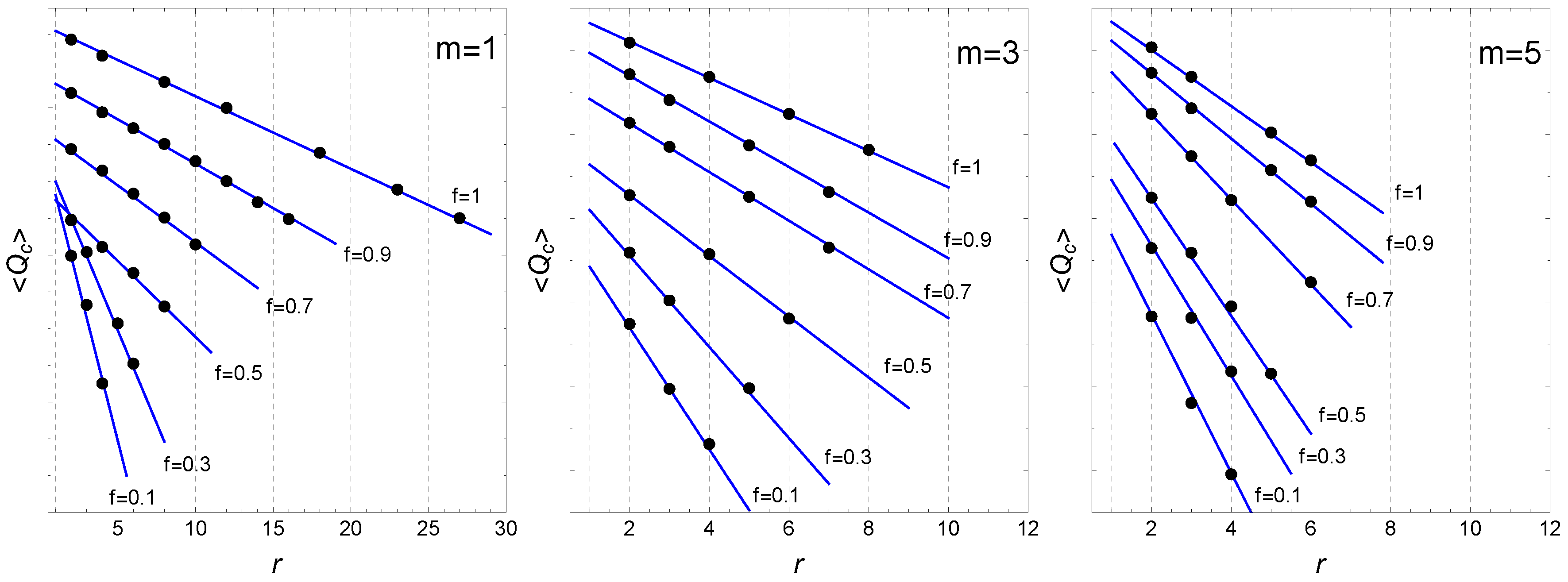
2.2. the Network Topology
2.3. the Fractal Analysis
3. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faloutsos, M.; Faloutsos, P.; Faloutsos, C. On power-law relationships of the Internet topology. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2008, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegura, E.W.; Calvert, K.L.; Donahoo, M.J. A quantitative comparison of graph-based models for Internettopology. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 1997, 5, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vazquez, A.; Vespignani, A. Dynamical and correlation properties of the Internet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 258701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albert, R.; Jeong, H.; Barabasi, A.L. Diameter of the world-wide web. Nature 1999, 401, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, D. Souped-up search engines. Nature 2000, 405, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broder, A.; Kumar, R.; Maghoul, F.; Raghavan, P.; Rajagopalan, S.; Stata, R.; Tomkins, A.; Wiener, J. Graph structure in the web. Comput. Netw. 2000, 33, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Martinez, N.D. Simple rules yield complex food webs. Nature 2000, 404, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljeros, F.; Edling, C.R.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Stanley, H.E.; Aberg, Y. The web of human sexual contacts. Nature 2001, 411, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronen, S.; Gonçalves, B.; Hua, K.Z.; Vespignanib, A.; Pinkere, S.; Hidalgoa, C.A. Links that speak: The global language network and its association with global fame. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5616–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, R.; Barabasi, A.L. Topology of evolving net- works: Local events and universality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, M.E.J. The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Jeong, H.; Neda, Z.; Ravasz, E.; Schubert, A.; Vicsek, T. Evolution of the social network of scientific collaborations. Physical A 2002, 311, 590–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drożdż, S.; Kulig, A.; Kwapień, J.; Niewiarowski, A.; Stanuszek, M. Hierarchical organization of H. Eugene Stanley scientific collaboration community in weighted network representation. J. Inf. 2017, 11, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.; Tombor, B.; Albert, R.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabasi, A.L. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 2000, 407, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.; Mason, S.; Barabasi, A.L.; Oltvai, Z.N. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 2001, 411, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rak, R.; Kwapień, J.; Oświȩcimka, P.; Ziȩba, P.; Drożdż, S. Universal features of mountain ridge networks on Earth. J. Complex Netw. 2020, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdös, P.; Rényi, A. On the evolution of random graphs. Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci. 1960, 5, 17–61. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, K.I.; OH, E.; Jeong, H.; Kahng, B.; Kim, D. Classification of scale-free networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12583–12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.F.; Chen, G. Complex networks: Small-world, scale-free and beyond. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2003, 3, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, M.E.J. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, D.J. The ‘new’ science of networks. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2004, 30, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemarchand, G.A. The long-term dynamics of co-authorship scientific networks: Iberoamerican countries (1973–2010). Res. Policy 2012, 41, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, C.S.; Leydesdorff, L. Network structure, self-organization and the growth of international collaboration inscience. Res. Policy 2005, 34, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gay, B.; Dousset, B. Innovation and network structural dynamics: Study of the alliance network of a major sector of the biotechnology industry. Res. Policy 2005, 34, 1457–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereich, S.; Morters, P. Random networks with sublinearpreferential attachment: Degree evolutions. Electron. Probab. 2009, 14, 1222–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorogovtsev, S.N.; Mendes, J.F.F.; Samukhin, A.N. Structure of Growing Networks with Preferential Linking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 85, 4633–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaral, L.A.N.; Scala, A.; Barthélémy, M.; Stanley, H.E. Classes of small-world networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11149–11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redner, S. How popular is your paper? An empirical study of the citation distribution. Eur. Phys. J. B 1998, 4, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancho, R.F.I.; Solé, R.V. The small world of human language. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2001, 268, 2261–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwapień, J.; Gworek, S.; Drożdż, S.; Gorski, A.Z. Structure and evolution of the foreign exchange networks. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2009, 40, 175–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kwapień, J.; Drożdż, S. Physical approach to complex systems. Phys. Rep. 2012, 515, 115–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S. Collective dynamics of ’small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Havlin, S. Scale-Free Networks are Ultrasmall. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 058701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vazquez, A.; Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Large-scale topological and dynamical properties of Internet. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 066130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, P.-J.; Jeong, H. Statistical properties of sampled networks. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 016102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barabási, A.L. Network Science. Degree Correlation. Available online: http://barabasi.com/ (accessed on 18 September 2014).
- Song, C.; Havlin, S.; Makse, H.A. Self-similarity of complex networks. Nature 2005, 433, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, C.; Havlin, S.; Makse, H.A. Origins of fractality in the growth of complex networks. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Scale-Free Network | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|
| World Wide Web link networks | 2.1–2.7 | [4] |
| Internet connections at the router level | 2.4–2.5 | [1] |
| Actor cooccurrence in films | 2.3 | [26,28] |
| Scientific collaboration networks | 2.5–3 | [11,13] |
| Mountain ridge networks | 2.6–2.7 | [16] |
| Scientific paper citation networks | 3 | [29] |
| Word-cooccurrence networks | 2.8 | [30] |
| Protein interaction networks | 2.4 | [15] |
| Biochemical cellular pathway | 2–2.4 | [14] |
| Currency comovement networks | 2.4–2.7 | [31,32] |
| f | D | L | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m = 1 | |||||||
| 0.1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 3.3 | 29,819 | ||
| 0.3 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 4.4 | 9726 | ||
| 0.5 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 5.4 | 4981 | ||
| 0.7 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 7.2 | 1621 | ||
| 0.9 | 0 | 2 | 16 | 9.5 | 1038 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 2 | 33 | 11.6 | 825 | ||
| m = 2 | |||||||
| 0.1 | 0.48 | 3.3 | 4 | 2.5 | 39,849 | ||
| 0.3 | 0.11 | 3.9 | 6 | 3.1 | 15,050 | ||
| 0.5 | 0.03 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 7395 | ||
| 0.7 | 0 | 4.1 | 8 | 4.8 | 3771 | ||
| 0.9 | 0 | 4.1 | 9 | 5.2 | 1873 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 4.2 | 10 | 5.5 | 1207 | ||
| m = 3 | |||||||
| 0.1 | 0.61 | 5.6 | 4 | 2.19 | 58,123 | ||
| 0.3 | 0.13 | 5.9 | 5 | 3.2 | 26,823 | ||
| 0.5 | 0.04 | 6 | 6 | 3.6 | 16,125 | ||
| 0.7 | 0.01 | 6 | 7 | 4.1 | 7020 | ||
| 0.9 | 0.003 | 6 | 7 | 4.5 | 3589 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 4.7 | 2852 | ||
| m = 5 | |||||||
| 0.1 | 0.58 | 9.1 | 4 | 2.05 | 75,652 | ||
| 0.3 | 0.17 | 9.6 | 4 | 2.81 | 42,873 | ||
| 0.5 | 0.06 | 9.9 | 5 | 3.19 | 33,129 | ||
| 0.7 | 0.013 | 9.9 | 6 | 3.6 | 10,435 | ||
| 0.9 | 0 | 10.1 | 6 | 3.78 | 6141 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 10.2 | 6 | 3.99 | 3948 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rak, R.; Rak, E. The Fractional Preferential Attachment Scale-Free Network Model. Entropy 2020, 22, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22050509
Rak R, Rak E. The Fractional Preferential Attachment Scale-Free Network Model. Entropy. 2020; 22(5):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22050509
Chicago/Turabian StyleRak, Rafał, and Ewa Rak. 2020. "The Fractional Preferential Attachment Scale-Free Network Model" Entropy 22, no. 5: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22050509
APA StyleRak, R., & Rak, E. (2020). The Fractional Preferential Attachment Scale-Free Network Model. Entropy, 22(5), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22050509






