Emergence of Inequality in Income and Wealth Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
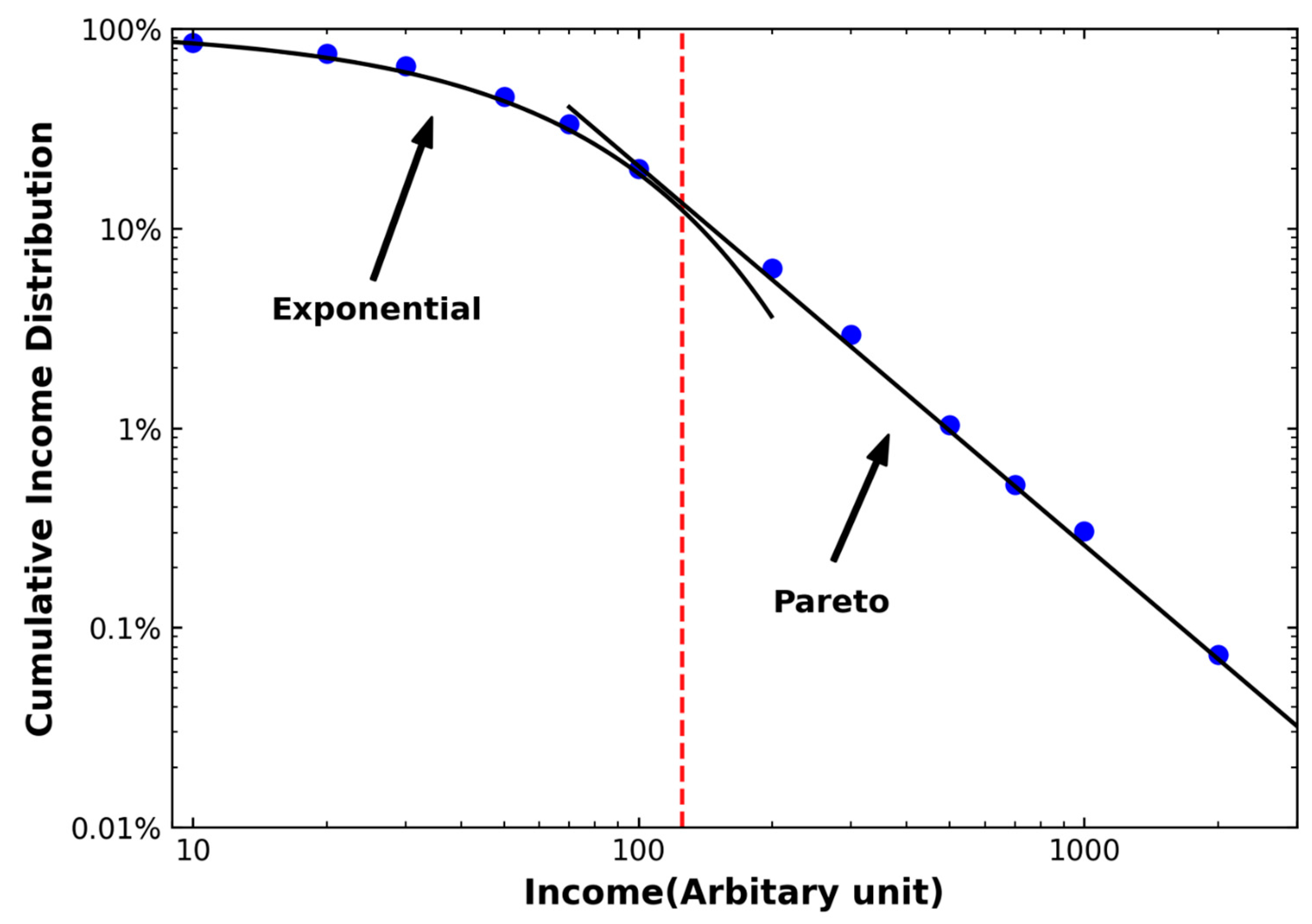
2. Wealth and Income Distribution
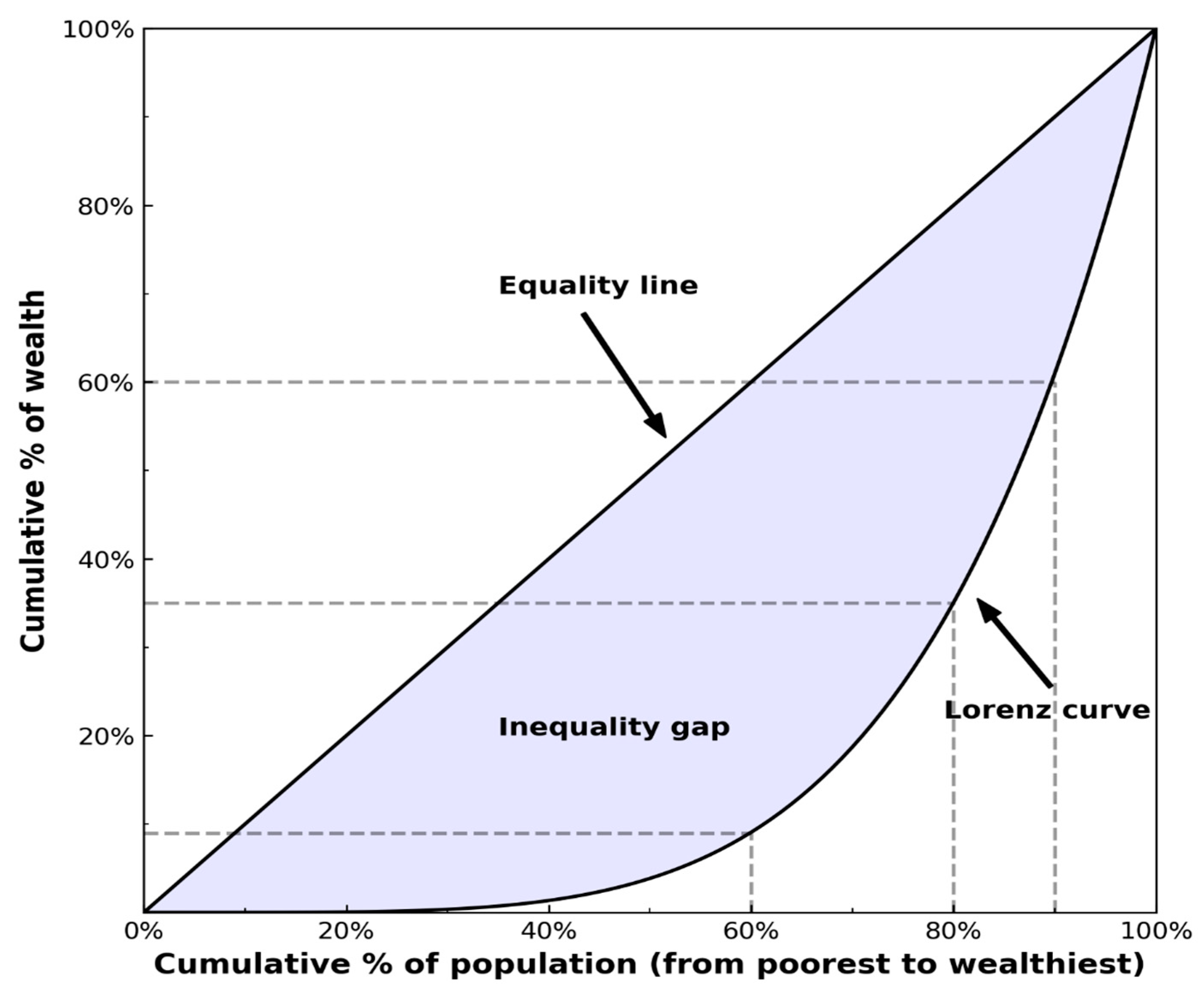
3. Measures of Wealth Inequality
4. Models of Income and Wealth Distribution
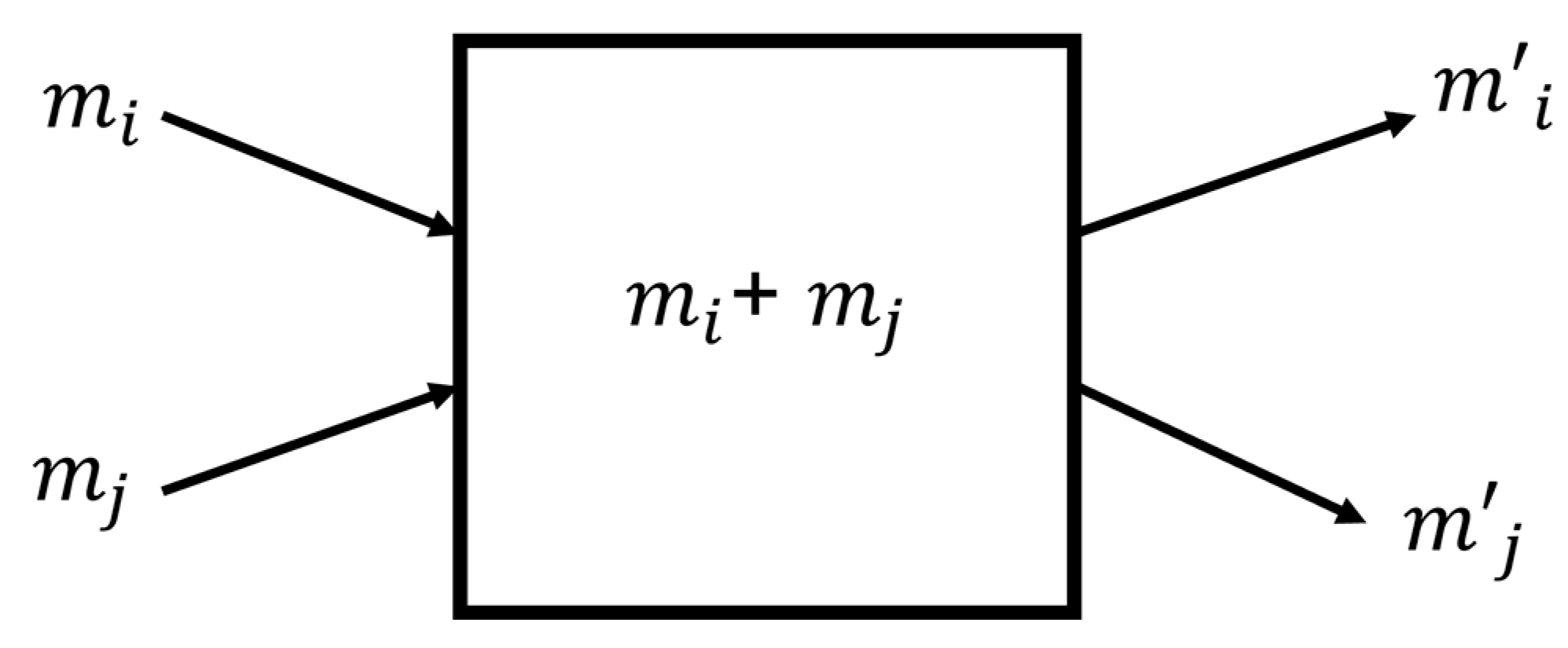
4.1. Stochastic Multiplicative Process
4.2. Boltzmann Distribution of Wealth
4.3. Kinetic Exchange Models of Wealth
4.4. Money Exchange Models with Saving
4.5. Money Exchange Models with Tax
4.6. Non-Conservative Kinetic Exchange Models of Wealth
4.7. Kinetic Exchange Models with Wealth Condensation
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pareto, V. Cours d’economie politique. J. Pol. Econ. 1898, 6, 437–580. [Google Scholar]
- Gibrat, R. Les Inégalités Economiques; Sirely: Paris, France, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B. The Pareto-Levy law and distribution of income. Int. Econ. Rev. 1960, 1, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piketty, T.; Saez, E. Inequality in the long run. Science 2014, 344, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, J. The Surplus Theory of Social Stratification and the Size Distribution of Personal Wealth. Soc. Forces 1986, 65, 293–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, J. Deriving the size distribution of personal wealth from “the rich get richer, the poor get poorer. J. Math. Sociol. 1993, 18, 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lux, T. Emergent statistical wealth distributions in simple monetary exchange models: A critical review. In Econophysics of Wealth Distributions; Chatterjee, A., Yarlagadda, S., Chakrabarti, B.K., Eds.; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.; Chakrabarti, B.K. Econophysics: An emerging discipline. Econ. Pol. Wkly. 2012, 47, 44–65. [Google Scholar]
- Souma, W. Universal structure of the personal income distribution. Fractals 2000, 6, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, H.; Nagahara, Y.; Okazaki, M.P.; Souma, W.; Takayasu, H.; Takayasu, M. Pareto’s law for income of individuals and debt of bankrupt companies. Fractals 2000, 8, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragulescu, A.; Yakovenko, V.M. Exponential and power-law probability distributions of wealth and income in the United Kingdom and the United States. Phys. A 2001, 299, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovenko, V.M.; Rosser, J.B. Statistical mechanics of money, wealth, and income. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 1703–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Yakovenko, V.M.; Di Matteo, T. A study of the personal income distribution in Australia. Phys. A 2006, 370, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegati, M.; Keen, S.; Lux, T.; Ormerod, P. Worrying Trends in Econophysics. Phys. A 2006, 370, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, K.; Birdi, A.; Eliassi-Rad, T.; Farrell, H.; Garcia, D.; Lewsandowsky, S.; Palacios, P.; Ross, D.; Sornette, D.; Thebault, K. Stability od democracies: A complex systems perspective. Eur. J. Phys. 2019, 40, 014002. [Google Scholar]
- Angle, J. The inequality process and the distribution of income blacks and whites. J. Math. Sociol. 1992, 17, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, J. The statistical signature of pervasive competition on wage and salary incomes. J. Math. Sociol. 2002, 26, 217–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, J. The inequality process as a wealth maximizing process. Phys. A 2006, 367, 388–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ispolatov, S.; Krapivsky, P.L.; Redner, S. Wealth distributions in asset exchange models. Eur. Phys. J. B 1998, 2, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchaud, J.-P.; Mezard, M. Wealth condensation in a simple model of economy. Phys. A 2000, 282, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragulescu, A.; Yakovenko, V.M. Statistical mechanics of money. Eur. Phys. J. B 2000, 17, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, A.; Chakrabarti, B.K. Statistical mechanics of money: How saving propensity affects its distribution. Eur. Phys. J. B 2000, 17, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, B.K.; Chakraborti, A.; Chakravarty, S.R.; Chatterjee, A. Econophysics of Income and Wealth Distributions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mantegna, R.N.; Stanley, H.E. An Introduction to Econophysics: Correlations and Complexity in Finance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchaud, J.-P.; Potters, M. Theory of Financial Risk and Derivatives Pricing: From Statistical Physics to Risk Management; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Abergel, F.; Aoyama, H.; Chakrabarti, B.K.; Chakraborti, A.; Ghosh, A. Econophysics and Data Driven Modelling of Market Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca, M.; Heisalu, E.; Chakraborti, A. Basic kinetic wealth-exchange models: Common features and open problems. Eur. Phys. J. B 2010, 73, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca, M.; Chakraborti, A. Kinetic exchange models: From molecular physics to social physics. Am. J. Phys. 2013, 81, 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi, U.; Scalas, E.; Viarengo, P. Statistical equilibrium in simple exchange games II: The redistribution game. Eur. Phys. J. B 2007, 60, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, J.L. Response to “Worrying Trends in Econphysics”. Phys. A 2006, 371, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinsalu, E.; Patriarca, M. Kinetic models of immediate exchange. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebault, K.; Bradley, S.; Reutlinger, A. Modelling inequality. Br. J. Philos. Sci. 2018, 69, 691–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydiner, E.; Cherstvy, A.G.; Metzler, R. Wealth distribution, Pareto law, and stretched exponential decay of money: Computer simulations analysis of agent-based models. Phys. A 2018, 490, 278–288. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, P. How fast is the top tail of the wealth distribution. Rev. Income Wealth 2018, 64, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghosia, B. Kinetics of wealth and the Pareto law. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 042804. [Google Scholar]
- Banzhaf, W. The effect of taxes on wealth inequality in artificial chemistry models of economic activity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255719. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.; Chakrabarti, B.K.; Manna, S.S. Pareto law in a kinetic model of market with random saving propensity. Phys. A 2004, 335, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Chakrabarti, B.K.; Manna, S.S. Money in gas-like markets: Gibbs and Pareto laws. Phys. Scr. 2003, T106, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Reptowicz, P.; Hutzler, S.; Richmond, P. Dynamics of money and income distributions. Phys. A 2005, 356, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriarca, M.; Chkraborti, A.; Kaski, K. Statistical model with a standard gamma distribution. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 016104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Chakrabarti, B.K. Kinetic exchange models for income and wealth distributions. Eur. Phys. J. B 2007, 60, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Lin, C. A simple and efficient kinetic model for wealth distribution with saving propensity effect: Based on lattice gas automaton. Phys. A 2021, 561, 125283. [Google Scholar]
- Fernades, L.; Tempere, J. Effect of segregation on inequality in kinetic models of wealth exchange. Eur. Phys. J. B 2020, 93, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, P. 80/20 Sales and Marketing; Entrepreneur Press: Irvine, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.E.J. Power laws, Pareto distribution and Zipf’s law. Contemp. Phys. 2005, 46, 323–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwell, M. Outliers: The Story of Success; Back Bay Books: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nirei, M.; Souma, W. A two fragment model of income distribution dynamics. Rev. Income Wealth 2007, 53, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Souma, W.; Aoyama, H.; Kaizoji, T.; Aoki, M. Growth and fluctuations of personal income. Phys. A 2003, 321, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Solomon, S. New evidence for the power-law distribution of wealth. Phys. A 1997, 24, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegna, R.N.; Stanley, H.E. The scaling behavior of an economic index. Nature 1995, 376, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, N.J.; Riberiro, M.B. Evidence for the Gompertz curve in the income distribution of Brazil 1978–2005. Eur. Phys. J. B 2009, 67, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Montroll, E.W.; Shlesinger, M.F. Maximum entropy formalism, fractals, scaling phenomena, and 1/f noise: A tail of tials. J. Stat. Phys. 1983, 32, 209–230. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.; Yarlagadda, S.; Chkrabarti, B.K. Econophysics of Wealth Distribution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, F.; Gallegati, M. Power law tails in the Italian personal income distribution. Phys. A 2005, 350, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, X.; Lizbetinov, L. Evidence of Chinese income dynamics and its effects on income scaling law. Phys. A 2017, 487, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, C.; Mendes, A.L.; Machado, J.A. A review of power laws in real life phenomena. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 3558–3578. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiber, C.; Kotz, S. Statistical Size Distributions in Economics and Actuarial Sciences; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Regions at a Glance; KDI Economic Information Center: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gosh, A.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Chakrabarti, B.K. Inequality in societies, academic institutions, and science journals: Gini and k-indices. Phys. A 2014, 410, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, J.G. Homogenous middles vs. heterogenous tails, and the end of the inverted-U: The shape of the rich is what it’s all about. Develop. Chang. 2011, 42, 87–153. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinso, A. On the measurement of inequality. J. Econ. Theory 1970, 2, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, R.; Rocha, H. Inequality measures for wealth distribution: Population vs. individuals’ perspective. Phys. A 2018, 492, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar]
- KDI. Economic Concepts: Income Distribution Policy; KDI Economic Information Center: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaki, N.; Wright, R. A search-theoretic approach to monetary economics. Am. Econ. Rev. 1993, 83, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Molico, M. The distribution of money and prices in search equilibrium. Int. Econ. Rev. 2006, 47, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, N.; Ding, N.; Wang, Y. How required reserve ratio affects distribution and velocity of money. Phys. A 2005, 357, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriarca, M.; Chakraborti, A.; Kaski, K. Gibbs versus non-Gibbs distributions in money dynamics. Phys. A 2004, 340, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriarca, M.; Chakraborti, A.; Kaski, K.; Germano, G. Kinetic theory models for the distribution of wealth: Power law from overap of exponentials. In Econophysics of Wealth Distributions; Chatterjee, A., Yarlagadda, S., Chakrabarti, B.K., Eds.; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca, M.; Chakraborti, A.; Germano, G. Influence of saving propensity on the power-law tail of the wealth distribution. Phys. A 2006, 369, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piketty, T. Capital in the 21st Century; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmo, A. Optimal taxation: An introduction to the literature. J. Pub. Econ. 1976, 6, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, P.M.C. Rich or poor: Who should pay higher tax rates? Europhys. Lett. 2017, 119, 40007. [Google Scholar]
- Sahasranaman, A.; Jensen, H.J. Dynamics of transformation from segregation to mixed wealth cities. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166960. [Google Scholar]
- Heady, C. Optimal taxation as a guide to tax policy: A survey. Fiscal Stud. 1993, 14, 15–41. [Google Scholar]
- Guala, S. Taxes in a wealth distribution model by inelastically scattering of particles. Interdiscip. Descr. Complex Syst. 2009, 7, 76798. [Google Scholar]
- Bisi, M.; Spiga, G.; Toscani, G. Kinetic Models of Conservative Economies with Wealth Redistribution. Commun. Sci. Math. 2009, 7, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- During, B.; Matthes, D.; Toscani, G. Kinetic equations modelling wealth redistribution: A comparison of approaches. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 056103. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, B.; Chakrabarti, B.K. Variation of Gini and Kolkata indices with saving propensity in the kinetic exchange model of wealth distribution: An analytical study. Phys. A 2022, 594, 127051. [Google Scholar]
- Ciesla, M.; Snarska, M. A simple mechanism causing wealth condensation. Entropy 2020, 22, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, D.S.; Quimbay, C.J. Non-conservative kinetic model of wealth exchange with saving of production. Eur. Phys. J. B 2020, 93, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, J.T.; Bettencourt, L.M.A. Statistical dynamics of wealth inequality in stochastic models of growth. Phys. A 2022, 607, 128180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nener, J.; Laguna, M.F. Wealth exchange models and machine learning: Finding optimal risk strategies in multiagent economic systems. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 104, 014305. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, W.; Lubbers, N.; Liu, K.K.L.; Khouw, T.; Gould, H. Mean-field theory of an asset exchange model with economic growth and wealth distribution. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 104, 014151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.L.; Lubbers, N.; Klein, W.; Tobochnik, J.; Boghosian, B.M.; Gould, H. Simulation of a generalized asset exchange model with economic growth and wealth condensation. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 104, 014150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nener, J.; Laguna, M.F. Optimal risk in wealth exchange models: Agent dynamics from a microscopic perspective. Phys. A 2021, 566, 125625. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Liu, Z. Emergence of income inequality: Origin, distribution and possible policies. Phys. A 2020, 537, 122767. [Google Scholar]
- Slanina, F. Inelastically scattering particles and wealth distribution in an open economy. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 046102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.-Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, D.-S.; Kim, D.H. Wealth dynamics in world trade. Comp. Phys. Commun. 2011, 182, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qunag, L.A.; Jung, N.; Cho, E.S.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.W. Agent-based models in social physics. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2018, 72, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobi, A.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, J.W. Structure of trade flow networks for world commodities. Phys. A 2020, 556, 124761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, S.; Pareschi, L.; Toscani, G. On a kinetic model for a simple market economy. J. Stat. Phys. 2005, 120, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisi, M. Kinetic model for international trade allowing transfer of individuals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2022, 380, 20210156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, U.; Mohanty, P.K. Modeling wealth distribution in growing markets. Eur. Phys. J. B 2008, 65, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, Z.; Johnston, D.; Jurkiewicz, J.; Kaminski, M.; Nowak, M.A.; Papp, G.; Zhahed, I. Wealth Condensation in Pareto macroeconomics. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 026102. [Google Scholar]
- Pianegonda, S.; Iglesias, J.R.; Abramson, G.; Vega, J.L. Wealth redistribution with conservative exchanges. Phys. A 2003, 322, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.-W. Comment on “Wealth Condensation in Pareto macroeconomies”. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 048101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinomiya, T. Bouchaud-Mezard model on a random network. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 036111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moukarzel, C.F. Multiplicative asset exchange with arbitrary return distributions. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2011, 11, P08023. [Google Scholar]
- Moukarzel, C.F.; Goncalves, S.; Iglesias, J.R.; Rodriguez-Achach, M.; Huerta-Quintanilla, R. Wealth condensation in a multiplicative random asset exchange model. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2007, 143, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.A.; Gade, P.M. Emergence of power-law in a market with mixed models. Phys. A 2007, 384, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Pan, Q.; Qian, Q.; He, M.; Sun, Q. A multi-agent dynamic model based on different kinds of bequests. Phys. A 2013, 392, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatella-Flores, N.; Rodriguez-Achach, M.; Coronel-Brizio, H.F.; Hernandez-Montoya, A.R. Wealth distribution of simple exchange models coupled with extremal dynamics. Phys. A 2015, 417, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Bose-Einstein condensation mechanism in economic system. EPL 2015, 110, 58002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorro, C. A simple probabilistic approach of the Yard-Sale model. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2016, 112, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boghosian, B.M.; Devitt-Lee, A.; Johnson, M.; Li, J.; Marcq, J.A.; Wang, H. Oligarchy as a phase transition: The effect of wealth-attained advantage in a Fokker-Planck description of asset exchange. Phys. A 2017, 476, 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- Polk, S.L.; Boghosian, B.M. The nonstationary of wealth distribution tails near wealth condensation criticality. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2021, 81, 1306051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, C.; Park, J.; Mafwele, B.J.; Le, Q.A.; Park, H.J.; Lee, J.W. Emergence of Inequality in Income and Wealth Dynamics. Entropy 2023, 25, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25081129
Cho C, Park J, Mafwele BJ, Le QA, Park HJ, Lee JW. Emergence of Inequality in Income and Wealth Dynamics. Entropy. 2023; 25(8):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25081129
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Changhee, Jihun Park, Biseko Juma Mafwele, Quang Anh Le, Hye Jin Park, and Jae Woo Lee. 2023. "Emergence of Inequality in Income and Wealth Dynamics" Entropy 25, no. 8: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25081129
APA StyleCho, C., Park, J., Mafwele, B. J., Le, Q. A., Park, H. J., & Lee, J. W. (2023). Emergence of Inequality in Income and Wealth Dynamics. Entropy, 25(8), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25081129





