Exploring Simplicity Bias in 1D Dynamical Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Problem Set-Up
2.1. Background Theory and Pertinent Results
2.1.1. AIT and Kolmogorov Complexity
2.1.2. The Coding Theorem and Algorithmic Probability
2.1.3. The Simplicity Bias Bound
2.1.4. Estimating Pattern Complexity
2.2. Digitised Map Trajectories
3. Results
3.1. Logistic Map
3.1.1. Parameter Intervals
3.1.2. Connection of Simplicity and Probability
3.1.3. Simplicity Bias Appears When Bias Appears
3.1.4. Distribution of Complexities
3.1.5. Complex and Pseudo-Random Outputs
3.1.6. Pre-Chaotic Regime
3.2. Gauss Map (“Mouse Map”)
3.3. Sine Map
3.4. Bernoulli Map
3.5. Tent Map
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Impact of the Number of Iterations
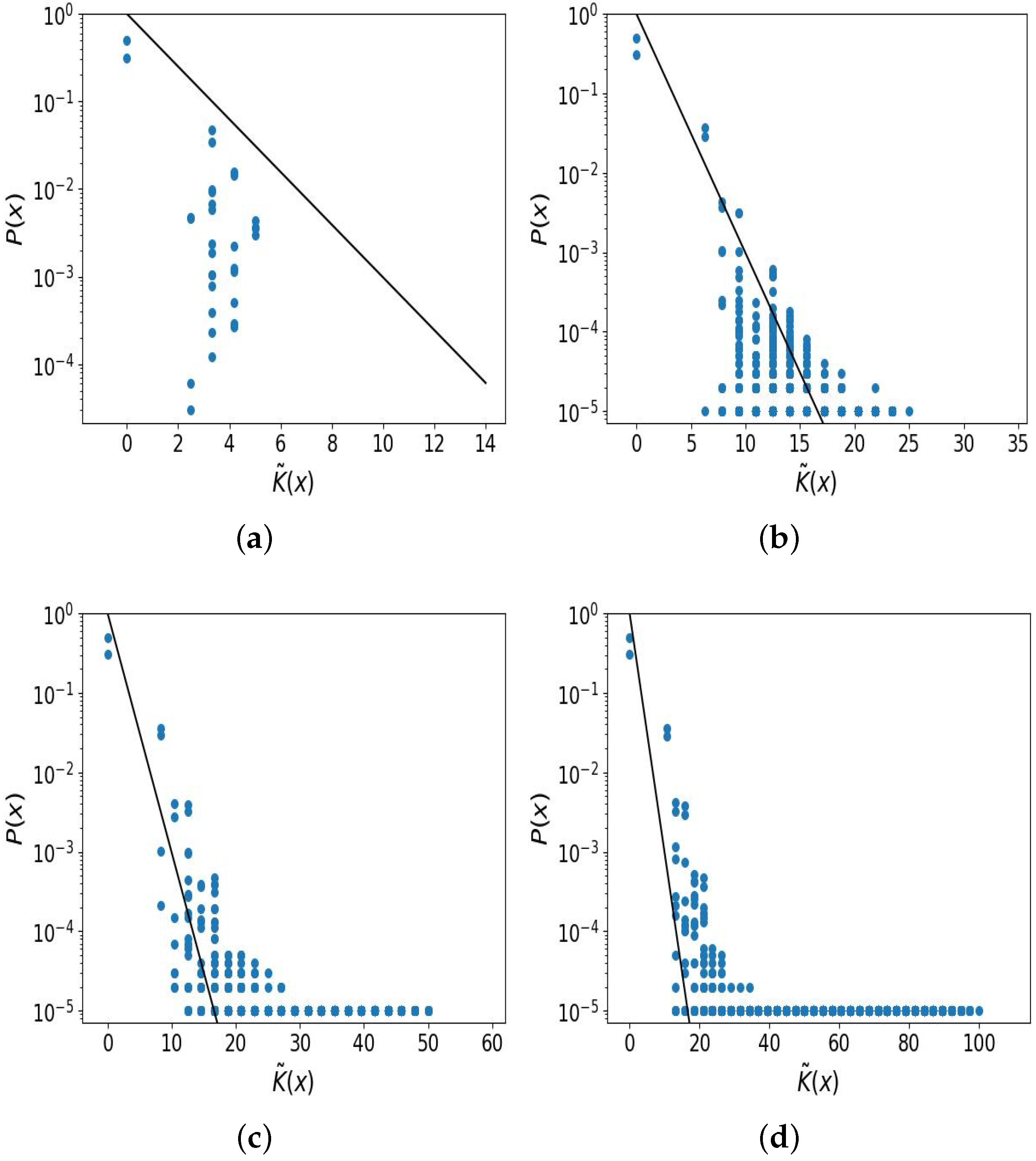
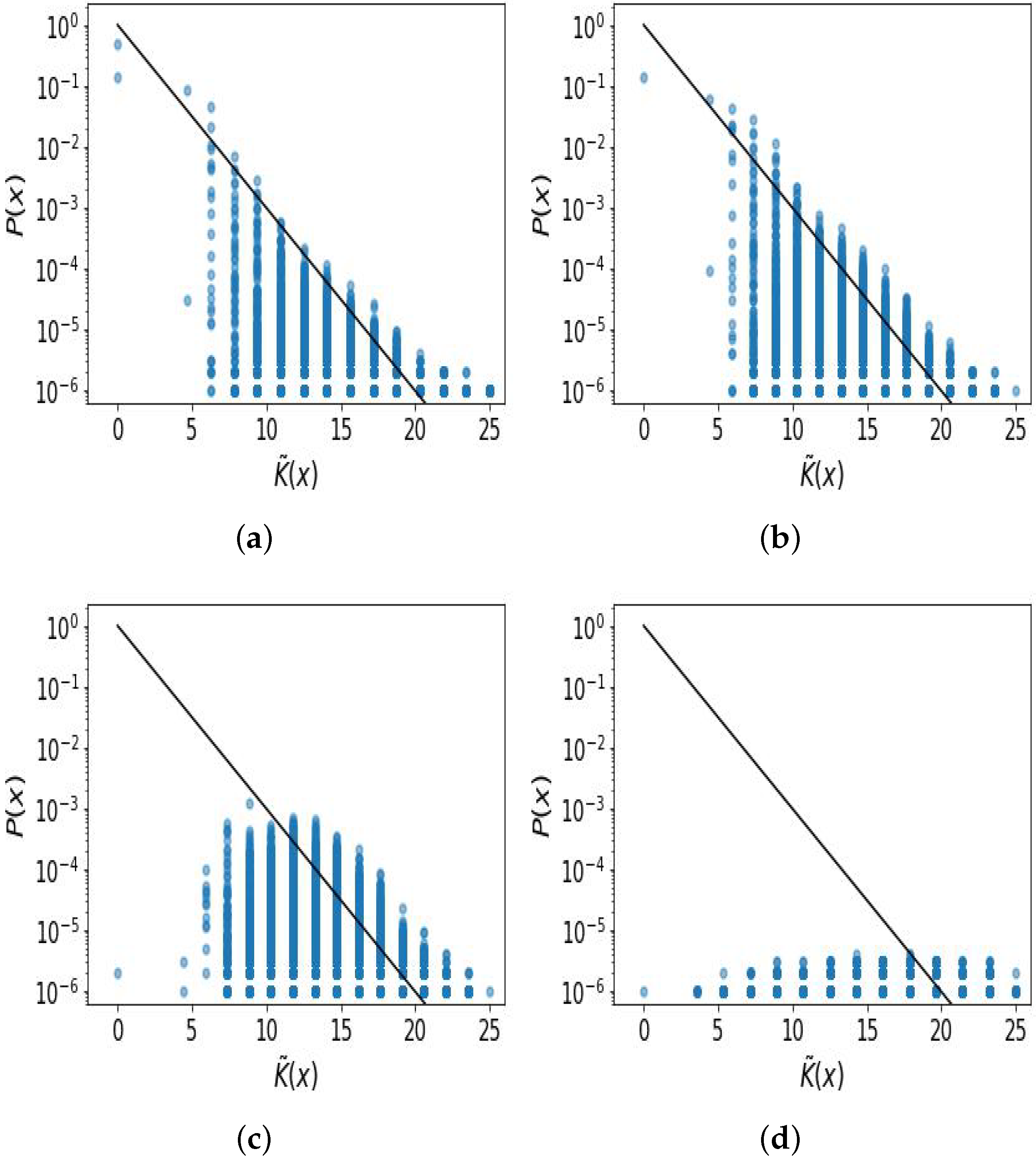
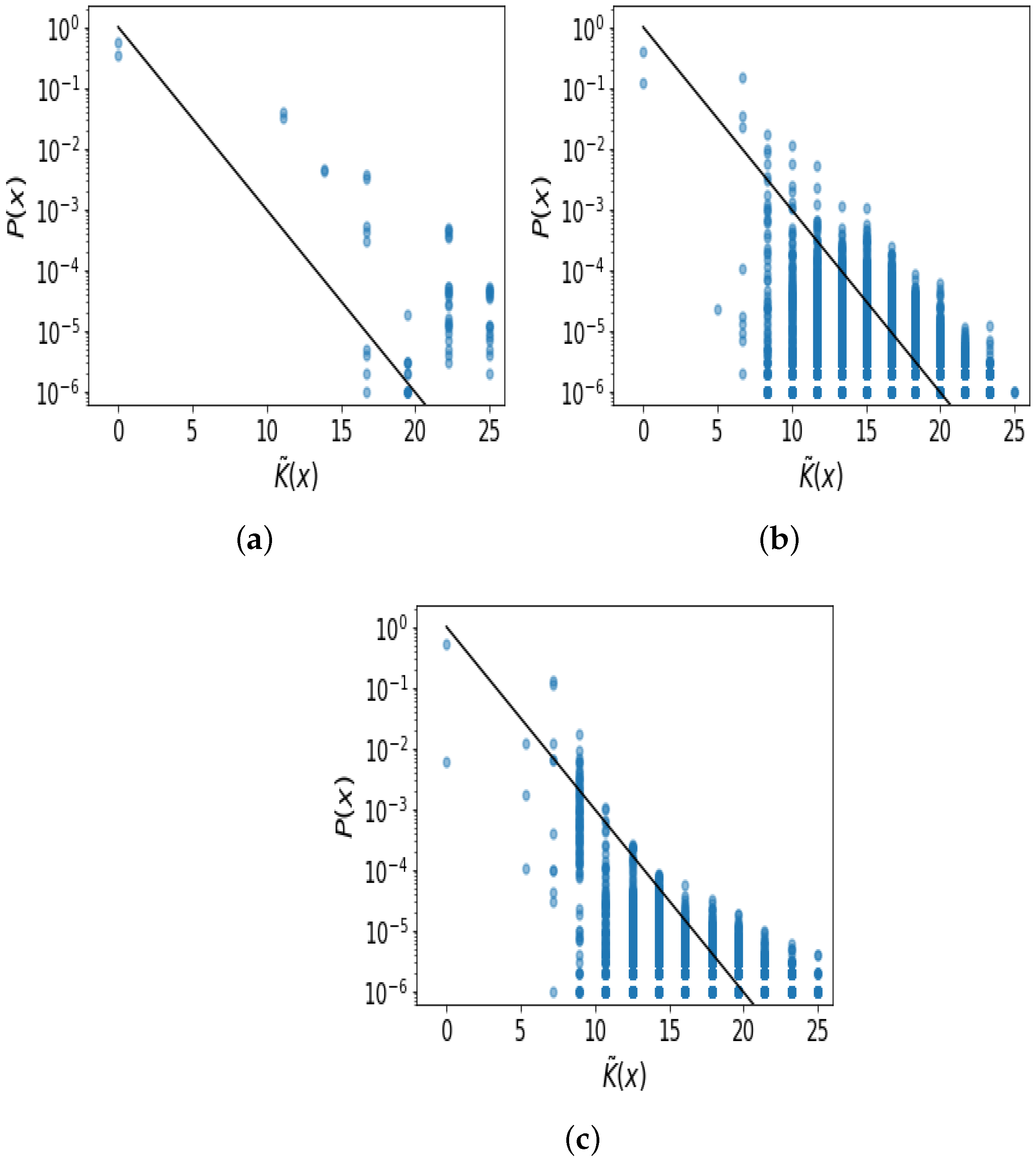
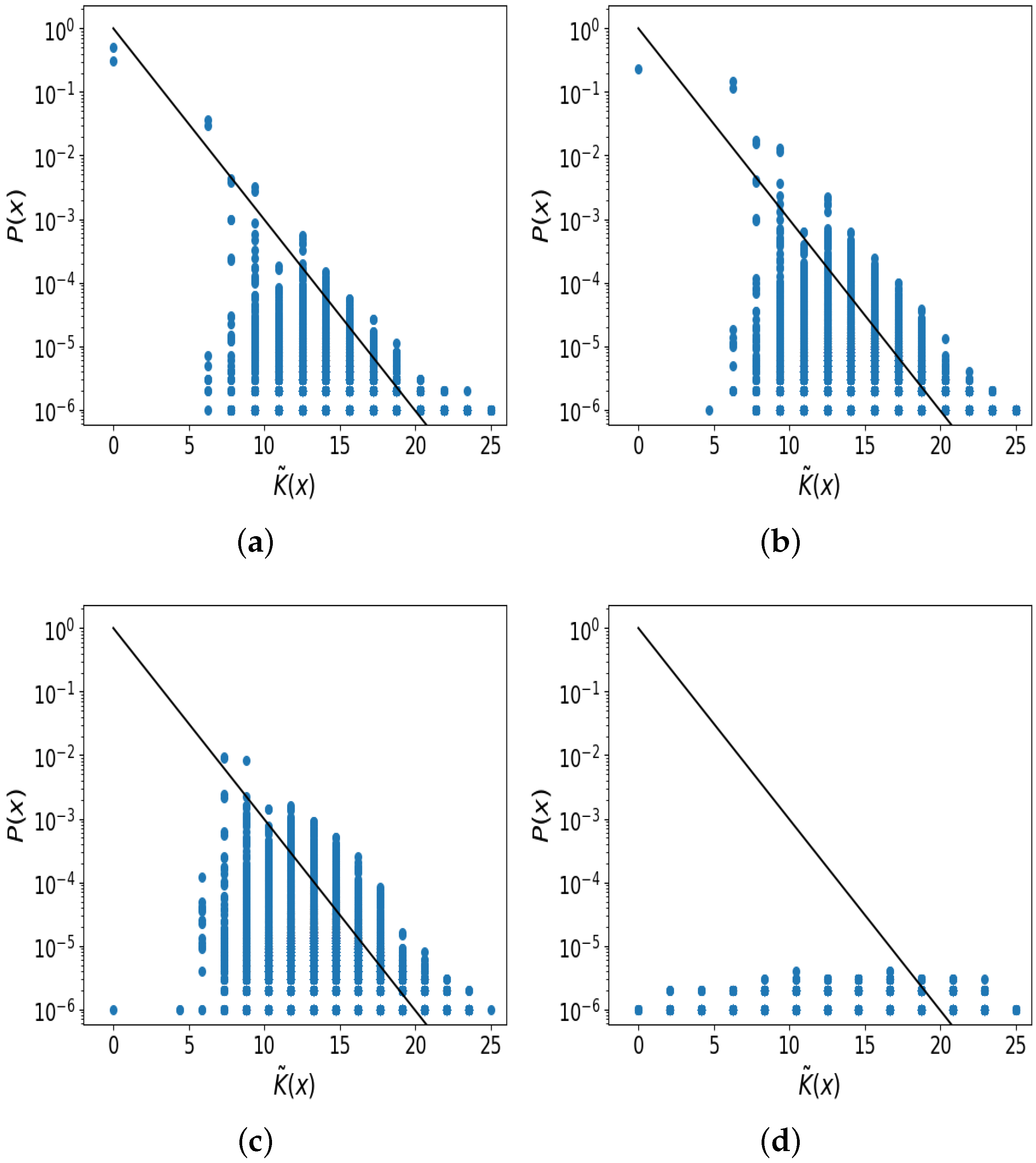
Appendix B. Alternate Figures Highlighting Density of Points
References
- Dingle, K.; Camargo, C.Q.; Louis, A.A. Input–output maps are strongly biased towards simple outputs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, K.; Pérez, G.V.; Louis, A.A. Generic predictions of output probability based on complexities of inputs and outputs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomonoff, R.J. A preliminary report on a general theory of inductive inference (revision of report v-131). Contract AF 1960, 49, 376. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Three approaches to the quantitative definition of information. Probl. Inf. Transm. 1965, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitin, G.J. A theory of program size formally identical to information theory. J. ACM 1975, 22, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, K.; Batlle, P.; Owhadi, H. Multiclass classification utilising an estimated algorithmic probability prior. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2023, 448, 133713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, K.; Kamal, R.; Hamzi, B. A note on a priori forecasting and simplicity bias in time series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 609, 128339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.G.; Dingle, K.; Greenbury, S.F.; Camargo, C.Q.; Doye, J.P.K.; Ahnert, S.E.; Louis, A.A. Symmetry and simplicity spontaneously emerge from the algorithmic nature of evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113883119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempel, A.; Ziv, J. On the complexity of finite sequences. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 22, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, J.; Lempel, A. A universal algorithm for sequential data compression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1977, 23, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaye, J.P.; Zenil, H. Numerical evaluation of algorithmic complexity for short strings: A glance into the innermost structure of algorithmic randomness. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 219, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Toscano, F.; Zenil, H.; Delahaye, J.-P.; Gauvrit, N. Calculating Kolmogorov complexity from the output frequency distributions of small Turing machines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, R.M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature 1976, 261, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselblatt, B.; Katok, A. A First Course in Dynamics: With a Panorama of Recent Developments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hilborn, R.C. Chaos and Nonlinear Dynamics: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers; Oxford University Press on Demand: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Vitanyi, P.M.B. An Introduction to Kolmogorov Complexity and Its Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Calude, C.S. Information and Randomness: An Algorithmic Perspective; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gács, P. Lecture Notes on Descriptional Complexity and Randomness; Boston University, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, Computer Science Department: Boston, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, A.; Uspensky, V.; Vereshchagin, N. Kolmogorov Complexity and Algorithmic Randomness; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2022; Volume 220. [Google Scholar]
- Turing, A.M. On computable numbers, with an application to the entscheidungsproblem. J. Math. 1936, 58, 345–363. [Google Scholar]
- Grunwald, P.; Vitányi, P. Shannon information and Kolmogorov complexity. arXiv 2004, arXiv:cs/0410002. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.H. The thermodynamics of computation—A review. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1982, 21, 905–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolchinsky, A.; Wolpert, D.H. Thermodynamic costs of turing machines. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 033312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, W.H. Algorithmic randomness and physical entropy. Phys. Rev. A 1989, 40, 4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolchinsky, A. Generalized zurek’s bound on the cost of an individual classical or quantum computation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.06838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.P. Law without law: From observer states to physics via algorithmic information theory. Quantum 2020, 4, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avinery, R.; Kornreich, M.; Beck, R. Universal and accessible entropy estimation using a compression algorithm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 178102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiniani, S.; Chaikin, P.M.; Levine, D. Quantifying hidden order out of equilibrium. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 011031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferragina, P.; Giancarlo, R.; Greco, V.; Manzini, G.; Valiente, G. Compression-based classification of biological sequences and structures via the universal similarity metric: Experimental assessment. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.; Zenil, H.; Davies, P.C.W.; Walker, S.I. Formal definitions of unbounded evolution and innovation reveal universal mechanisms for open-ended evolution in dynamical systems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, S.D. Algorithmic Information Theory for Physicists and Natural Scientists; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vitányi, P.M. Similarity and denoising. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 371, 20120091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilibrasi, R.; Vitányi, P.M.B. Clustering by compression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2005, 51, 1523–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A. Laws of information conservation (nongrowth) and aspects of the foundation of probability theory. Probl. Peredachi Informatsii 1974, 10, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, M. A natural bias for simplicity. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, K.; Novev, J.K.; Ahnert, S.E.; Louis, A.A. Predicting phenotype transition probabilities via conditional algorithmic probability approximations. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaskandarani, M.; Dingle, K. Low complexity, low probability patterns and consequences for algorithmic probability applications. Complexity 2023, 2023, 9696075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, D. Marcus, B. An Introduction to Symbolic Dynamics and Coding; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kanso, A.; Smaoui, N. Logistic chaotic maps for binary numbers generations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 40, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A. Chaos and Chance: An Introduction to Stochastic Apects of Dynamics; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar, F.; Schuster, H.G. Easily calculable measure for the complexity of spatiotemporal patterns. Phys. Rev. A 1987, 36, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingard, C.; Rees, H.; Valle-Pérez, G.; Louis, A.A. Do deep neural networks have an inbuilt occam’s razor? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.06670. [Google Scholar]
- Feigenbaum, M.J. The universal metric properties of nonlinear transformations. J. Stat. Phys. 1979, 21, 669–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenbaum, M.J. Universal behavior in nonlinear systems. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1983, 7, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binous, H. Bifurcation Diagram for the Gauss Map from the Wolfram Demonstrations Project. 2011. Available online: https://demonstrations.wolfram.com/BifurcationDiagramForTheGaussMap/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Patidar, V. Co-existence of regular and chaotic motions in the gaussian map. Electron. J. Theor. Phys. 2006, 3, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Suryadi, M.T.; Satria, Y.; Prawadika, L.N. An improvement on the chaotic behavior of the gauss map for cryptography purposes using the circle map combination. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1490, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S. Mitchell Feigenbaum (1944–2019), 4.66920160910299067185320382…. 2023. Available online: https://writings.stephenwolfram.com/2019/07/mitchell-feigenbaum-1944-2019-4-66920160910299067185320382/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Griffin, J. The Sine Map. 2013. Available online: https://people.maths.bris.ac.uk/~macpd/ads/sine.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Dong, C.; Rajagopal, K.; He, S.; Jafari, S.; Sun, K. Chaotification of sine-series maps based on the internal perturbation model. Results Phys. 2021, 31, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, D.J. Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C. Unpredictability and undecidability in dynamical systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.D.; Onorati, E.; Cubitt, T.S. Uncomputably complex renormalisation group flows. Nat. Commun. 2022, 1364, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S. Undecidability and intractability in theoretical physics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 54, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, S. A New Kind of Science; Wolfram Media: Champaign, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Svozil, K. Randomness & Undecidability in Physics; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, S. Uncomputability and physical law. In The Incomputable: Journeys beyond the Turing Barrier; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, A.; Merali, Z.; Sloan, D. Undecidability, Uncomputability, and Unpredictability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop, R.H. On the learnability of the uncomputable. In ICML; Citeseer: Forest Grove, OR, USA, 1996; pp. 302–309. [Google Scholar]
- Valle-Perez, G.; Camargo, C.Q.; Louis, A.A. Deep learning generalizes because the parameter-function map is biased towards simple functions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.08522. [Google Scholar]
- Mingard, C.; Skalse, J.; Valle-Pérez, G.; Martínez-Rubio, D.; Mikulik, V.; Louis, A.A. Neural networks are a priori biased towards boolean functions with low entropy. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11522. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattamishra, S.; Patel, A.; Kanade, V.; Blunsom, P. Simplicity bias in transformers and their ability to learn sparse boolean functions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.12316. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Salman, H. A fine-grained spectral perspective on neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.10599. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, S. Measures of complexity: A nonexhaustive list. IEEE Control. Syst. Mag. 2001, 21, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, M. Complexity: A Guided Tour; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bialek, W.; Nemenman, I.; Tishby, N. Complexity through nonextensivity. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2001, 302, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek, W.; Nemenman, I.; Tishby, N. Predictability, complexity, and learning. Neural Comput. 2001, 13, 2409–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, J.B.; Ahnert, S.E.; Fink, T.M.A. When are cellular automata random? EPL Europhys. Lett. 2008, 84, 50005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arnold, L.; Jones, C.K.; Mischaikow, K.; Raugel, G.; Arnold, L. Random Dynamical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, T.S.; Engel, M.; Lamb, J.S.W.; Rasmussen, M. Hopf bifurcation with additive noise. Nonlinearity 2018, 31, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, K.; Lamb, J.S.W.; Lázaro-Camí, J.-A. Knudsen’s law and random billiards in irrational triangles. Nonlinearity 2012, 26, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hamzi, B.; Dingle, K. Simplicity bias, algorithmic probability, and the random logistic map. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2024, 463, 134160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.S. Algorithmic complexity of points in dynamical systems. Ergod. Theory Dyn. Syst. 1993, 13, 807–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudno, A.A. The complexity of the trajectories of a dynamical system. Russ. Math. Surv. 1978, 33, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’yugin, V.V. Ergodic theorems for algorithmically random points. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.13465. [Google Scholar]
- Zenil, H.; Kiani, N.A.; Marabita, F.; Deng, Y.; Elias, S.; Schmidt, A.; Ball, G.; Tegnér, J. An algorithmic information calculus for causal discovery and reprogramming systems. Iscience 2019, 19, 1160–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry-Jack, M.; O’keefe, S. Fourier transform bounded kolmogorov complexity. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2023, 453, 133824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dingle, K.; Alaskandarani, M.; Hamzi, B.; Louis, A.A. Exploring Simplicity Bias in 1D Dynamical Systems. Entropy 2024, 26, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050426
Dingle K, Alaskandarani M, Hamzi B, Louis AA. Exploring Simplicity Bias in 1D Dynamical Systems. Entropy. 2024; 26(5):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050426
Chicago/Turabian StyleDingle, Kamal, Mohammad Alaskandarani, Boumediene Hamzi, and Ard A. Louis. 2024. "Exploring Simplicity Bias in 1D Dynamical Systems" Entropy 26, no. 5: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050426
APA StyleDingle, K., Alaskandarani, M., Hamzi, B., & Louis, A. A. (2024). Exploring Simplicity Bias in 1D Dynamical Systems. Entropy, 26(5), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26050426





