Continuous-Time Quantum Walk in Glued Trees: Localized State-Mediated Almost Perfect Quantum-State Transfer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
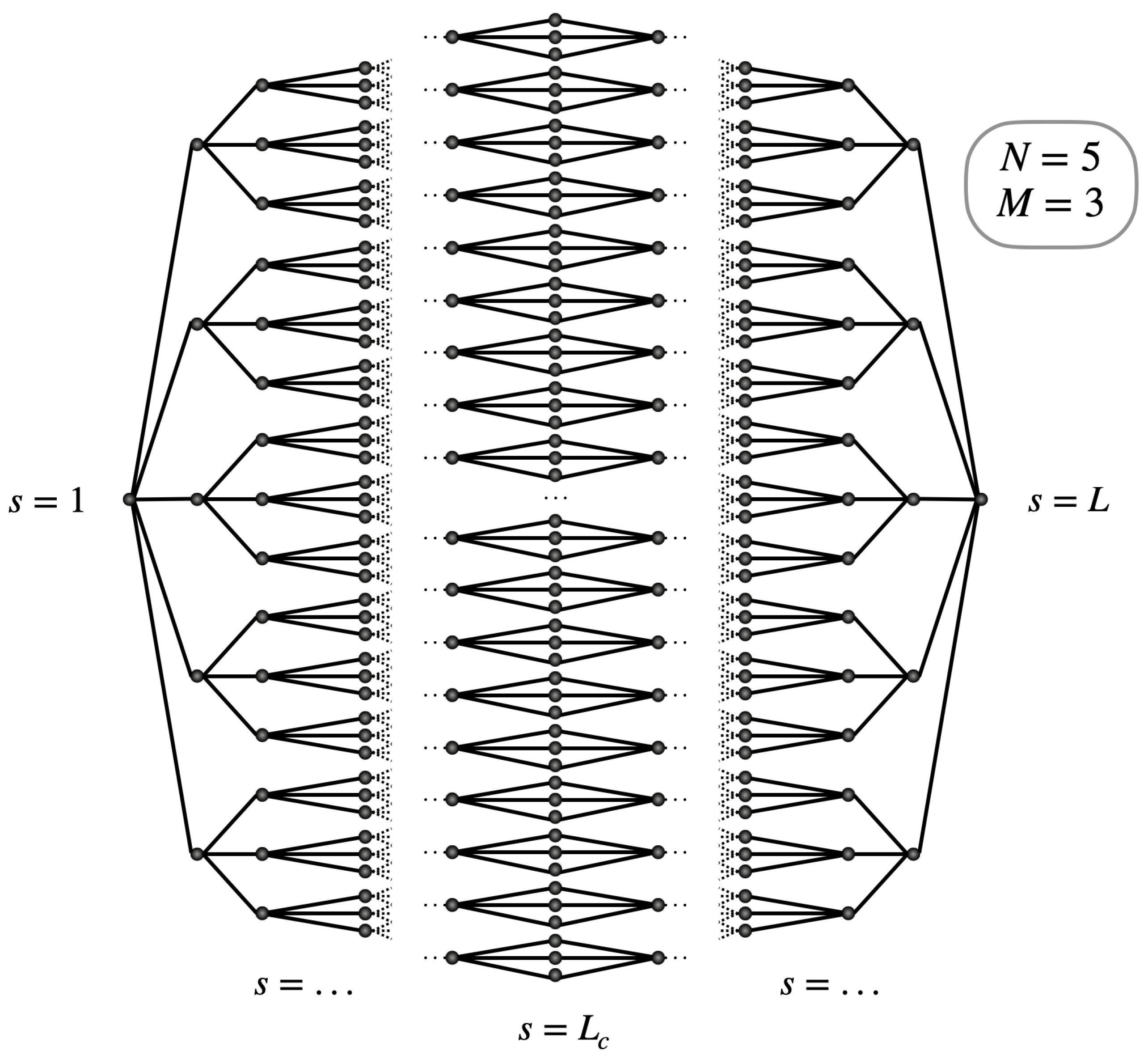
2.1. Glued Trees and CTQW
2.2. Column Subspace and Restricted Hamiltonian
2.3. Quantum Dynamics
3. Numerical Results
3.1. Spectral Properties of the Hamiltonian
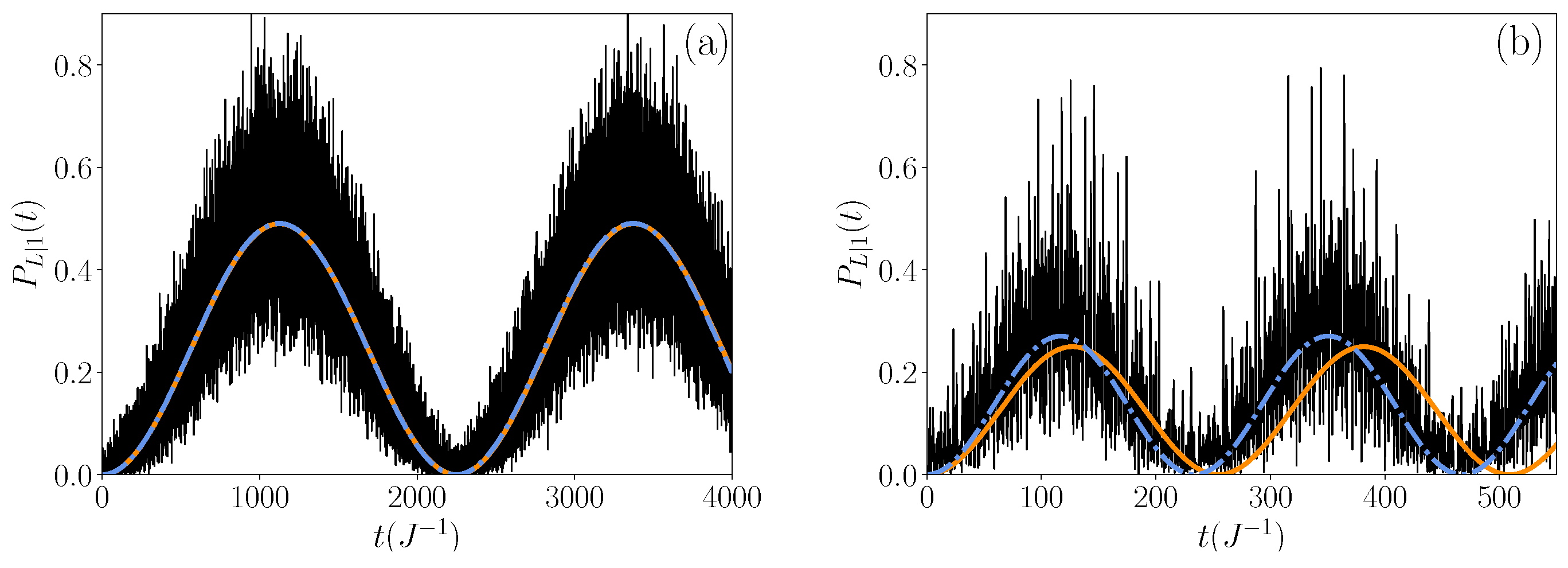
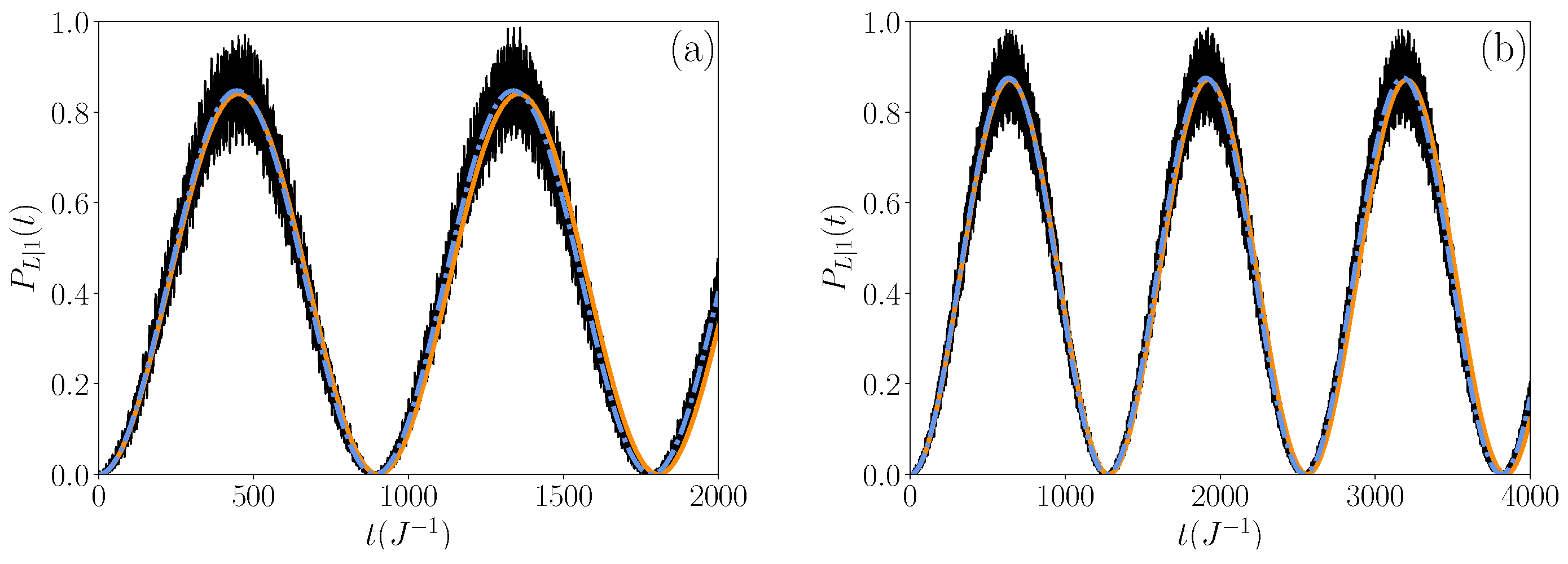
3.2. Time Evolution of the Transfer Probability
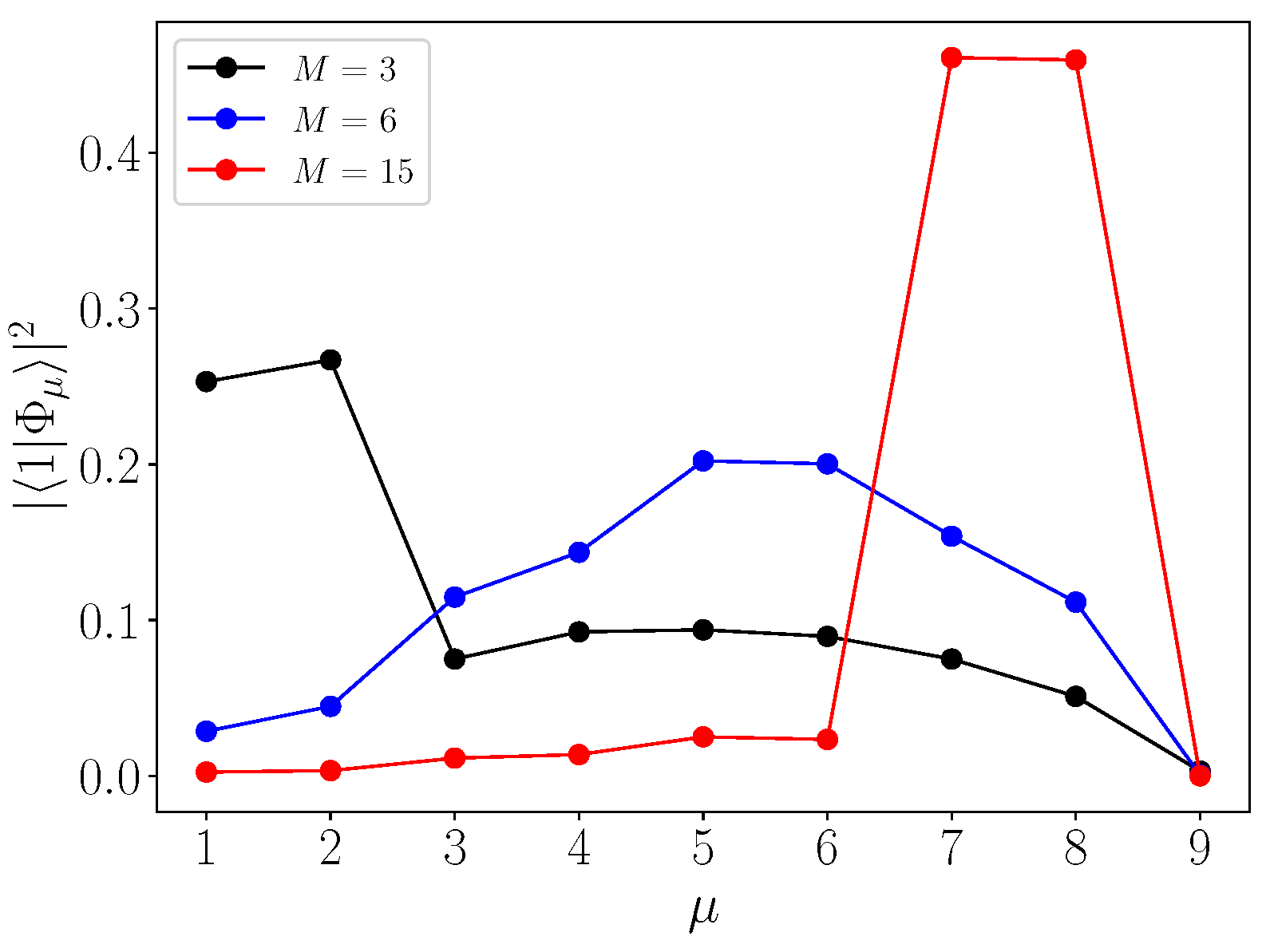
3.3. Spectral Decomposition of the Initial Walker’s State
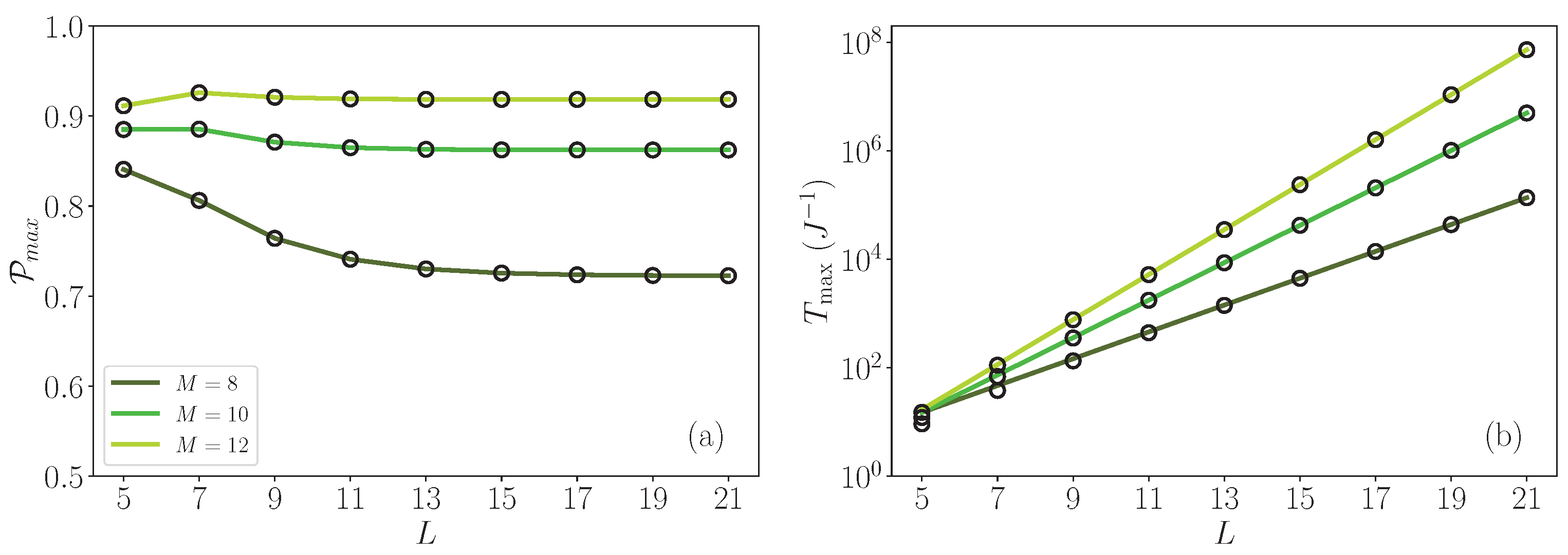
3.4. Characterization of the Smoothed Probability and Optimization of the Transfer
4. Interpretation and Discussion
4.1. Eigenstates and Mode Equations
4.2. Localization in the Limit
4.3. Localized State-Mediated Quantum Transfer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farhi, E.; Gutmann, S. Analog analogue of a digital quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 1998, 57, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santha, M. Quantum walk based search algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Theory and Applications of Models of Computation, Xi’an, China, 25–29 April 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Venegas-Andraca, S.E. Quantum walks: A comprehensive review. Quantum Inf. Process. 2012, 11, 1015–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, K.; Garhwal, S.; Kumar, A. Quantum walk and its application domains: A systematic review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 41, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W. Review on quantum walk algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1748, 032022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentle, J.E. Random Number Generation and Monte Carlo Methods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt, C.D., Jr.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneil, D.G.; Krueger, R.M. A Unified View of Graph Searching. Siam J. Discret. Math. 2008, 22, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, S.; Page, L. The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual Web search engine. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 1998, 30, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgeot, B.; Giraud, O.; Shepelyansky, D.L. Spectral properties of the Google matrix of the World Wide Web and other directed networks. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 056109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apers, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Novo, L.; Roland, J. Quadratic speedup for spatial search by continuous-time quantum walk. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 160502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, E.; Goldstone, J.; Gutmann, S. A Quantum Algorithm for the Hamiltonian NAND Tree. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M.; Farhi, E.; Gutmann, S. An Example of the Difference Between Quantum and Classical Random Walks. Quantum Inf. Process 2002, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M.; Cleve, R.; Deotto, E.; Farhi, E.; Gutmann, S.; Spielman, D.A. Exponential algorithmic speedup by quantum walk. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fifth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC03), ACM, SIGACT, New York, NY, USA, 9–11 June 2003; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Shenvi, N.; Kempe, J.; Whaley, K.B. Quantum random-walk search algorithm. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 67, 052307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M.; Goldstone, J. Spatial search by quantum walk. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 022314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouthier, V. Exciton-mediated quantum search on a star graph. Quantum Inf. Process 2015, 14, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Novo, L.; Roland, J. Finding a marked node on any graph via continuous-time quantum walks. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 102, 022227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, L.K. Quantum Mechanics Helps in Searching for a Needle in a Haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambainis, A. Quantum Walk Algorithm for Element Distinctness. SIAM J. Comput. 2007, 37, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrman, H.; Spalek, R. Quantum verification of matrix products. In Proceedings of the Seventeenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithm, SIAM Activity Group on Discrete Mathematics, Miami, FL, USA, 22–24 January 2006; p. 880. [Google Scholar]
- Magniez, F.; Santha, M.; Szegedy, M. Quantum Algorithms for the Triangle Problem. SIAM J. Comput. 2007, 37, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulken, O.; Bierbaun, V.; Blumen, A. Coherent exciton transport in dendrimers and continuous-time quantum walks. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouthier, V. Exciton localization-delocalization transition in an extended dendrimer. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 234111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouthier, V. Disorder-enhanced exciton delocalization in an extended dendrimer. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 022818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.L.; Andrade, R.F.S.; Souza, A.M.C. Localization properties of a tight-binding electronic model on the Apollonian network. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 214202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darazs, Z.; Anishchenko, A.; Kiss, T.; Blumen, A.; Mulken, O. Transport properties of continuous-time quantum walks on Sierpinski fractals. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 032113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agliari, E.; Blumen, A.; Mulken, O. Quantum-walk approach to searching on fractal structures. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 012305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, S. Continuous-time quantum walks on star graphs. Ann. Phys. 2009, 324, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziletti, A.; Borgonovi, F.; Celardo, G.L.; Izrailev, F.M.; Kaplan, L.; Zelevinsky, V.G. Coherent transport in multibranch quantum circuits. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 052201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P. Coherent exciton transport and trapping on long-range interacting cycles. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 011117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anishchenko, A.; Blumen, A.; Mulken, O. Enhancing the spreading of quantum walks on star graphs by additional bonds. Quantum Inf. Process 2012, 11, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouthier, V. The excitonic qubit on a star graph: Dephasing-limited coherent motion. Quantum Inf. Process 2015, 14, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalouz, S.; Pouthier, V.; Falvo, C. The excitonic qubit coupled with a phonon bath on a star graph: Anomalous decoherence and coherence revivals. Quantum Inf. Process 2017, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalouz, S.; Pouthier, V. Continuous-time quantum walk on an extended star graph: Trapping and superradiance transition. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 022304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.J.; Santandrea, M.; Huang, Z.; Corrielli, G.; Crespi, A.; Yung, M.H.; Osellame, R.; Peruzzo, A. Experimental perfect state transfer of an entangled photonic qubit. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Han, J.; Chen, T.; Xu, Y.; Cai, W.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Xue, Z.Y.; Yin, Z.q.; et al. Perfect quantum state transfer in a superconducting qubit chain with parametrically tunable couplings. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2018, 10, 054009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christandl, M.; Datta, N.; Ekert, A.; Landahl, A.J. Perfect state transfer in quantum spin networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 187902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A. Perfect, efficient, state transfer and its application as a constructive tool. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 2010, 8, 641–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Tang, H.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.M.; Gao, J.; Chang, Y.J.; Wang, T.Y.; Dou, J.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Quantum fast hitting on glued trees mapped on a photonic chip. Optica 2020, 7, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.L.; Ruan, Y. State transfer on two-fold Cayley trees via quantum walks. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 020304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, C.H.; DiVincenzo, D.P. Quantum information and computation. Nature 2000, 404, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgarth, D. Quantum state transfer and time-dependent disorder in quantum chains. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2007, 151, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mulken, O.; Blumen, A. Continuous-time quantum walks: Models for coherent transport on complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2011, 502, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M.; Gosset, D.; Webb, Z. Universal Computation by Multiparticle Quantum Walk. Science 2013, 339, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M. Universal Computation by Quantum Walk. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 180501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.G.; Tarrataca, L.; Nahilmov, N. Laplacian versus adjacency matrix in quantum walk search. Quantum Inf. Process. 2016, 15, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjonqueres, M.C.; Spanjaard, D. Concepts in Surface Physics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Malinin, S.V.; Tretiak, S.; Chernyak, V.Y. Effective tight-binding models for excitons in branched conjugated molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 064109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Wang, J. Single-point position and transition defects in continuous time quantum walks. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaac, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Continuous-time quantum walks with defects and disorder. Phys. Rev. 2013, 88, 042334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatelli, F.; Benedetti, C.; Paris, M.G. Scattering as a quantum metrology problem: A quantum walk approach. Entropy 2020, 22, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouthier, V. Vibron-phonon coupling strength in a finite-size lattice of H-bonded peptide units. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 031913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbukh, I.S.; Perelman, N.F. Fractional revivals: Universality in the long-term evolution of quantum wave packets beyond the correspondence principle dynamics. Phys. Lett. A 1989, 139, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, R.; Kostelecky, V.A.; Tudose, B. Wave-packet revivals for quantum systems with nondegenerate energies. Phys. Lett. A 1996, 222, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berry, M.V. Quantum fractals in boxes. J. Phys. A 1996, 29, 6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, E.J.; Katsanos, D.E.; Evangelou, S.N. Fractal noise in quantum ballistic and diffusive lattice systems. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 195107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Song, Z.; Sun, C.P. Fractional revivals of the quantum state in a tight-binding chain. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 75, 012113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




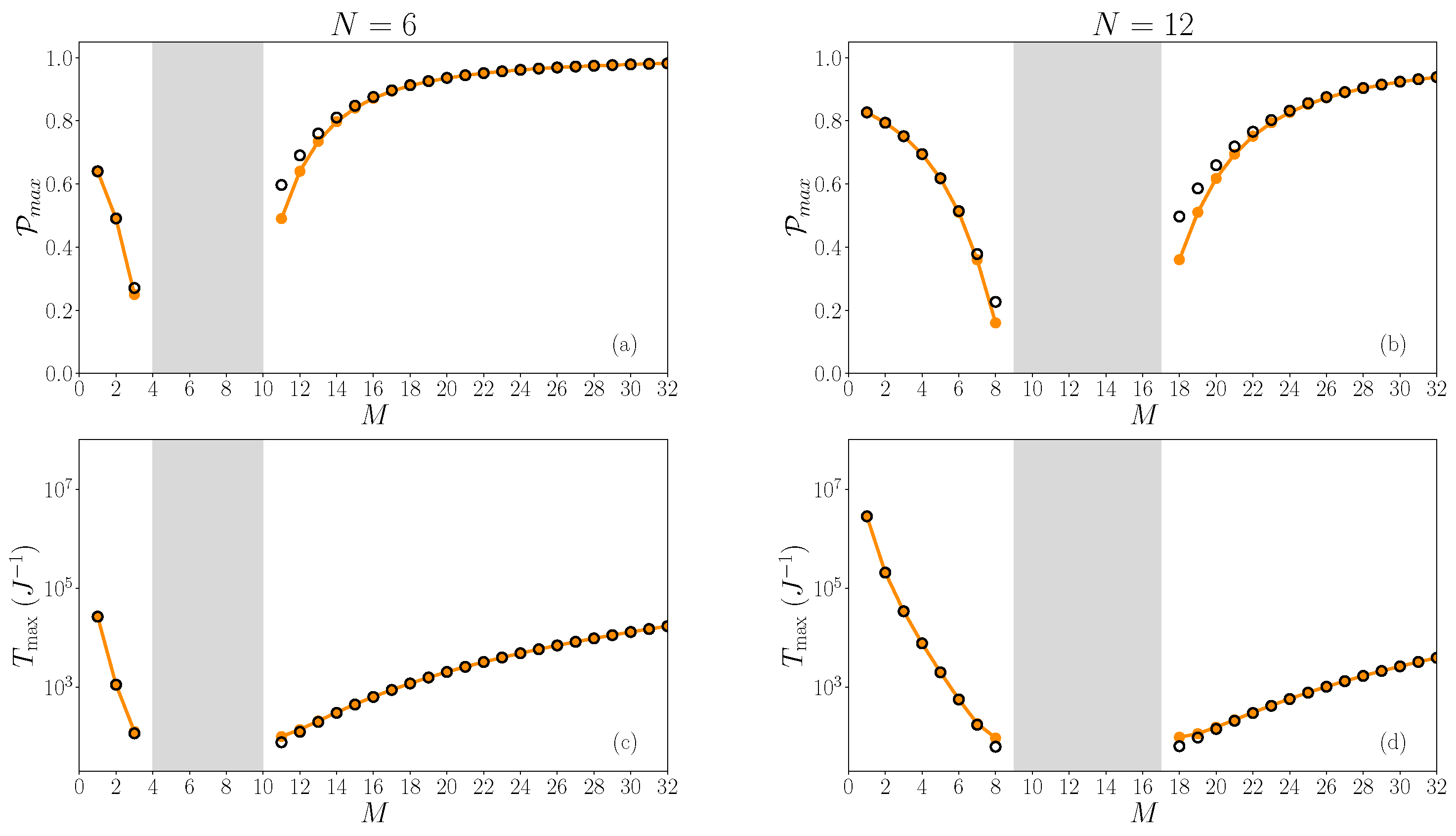
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pouthier, V.; Pepe, L.; Yalouz, S. Continuous-Time Quantum Walk in Glued Trees: Localized State-Mediated Almost Perfect Quantum-State Transfer. Entropy 2024, 26, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060490
Pouthier V, Pepe L, Yalouz S. Continuous-Time Quantum Walk in Glued Trees: Localized State-Mediated Almost Perfect Quantum-State Transfer. Entropy. 2024; 26(6):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060490
Chicago/Turabian StylePouthier, Vincent, Lucie Pepe, and Saad Yalouz. 2024. "Continuous-Time Quantum Walk in Glued Trees: Localized State-Mediated Almost Perfect Quantum-State Transfer" Entropy 26, no. 6: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060490
APA StylePouthier, V., Pepe, L., & Yalouz, S. (2024). Continuous-Time Quantum Walk in Glued Trees: Localized State-Mediated Almost Perfect Quantum-State Transfer. Entropy, 26(6), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060490





