The Lysozyme Inhibitor Thionine Acetate Is Also an Inhibitor of the Soluble Lytic Transglycosylase Slt35 from Escherichia coli
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Enzyme Activity Assay
2.1.1. Effect of the Buffer
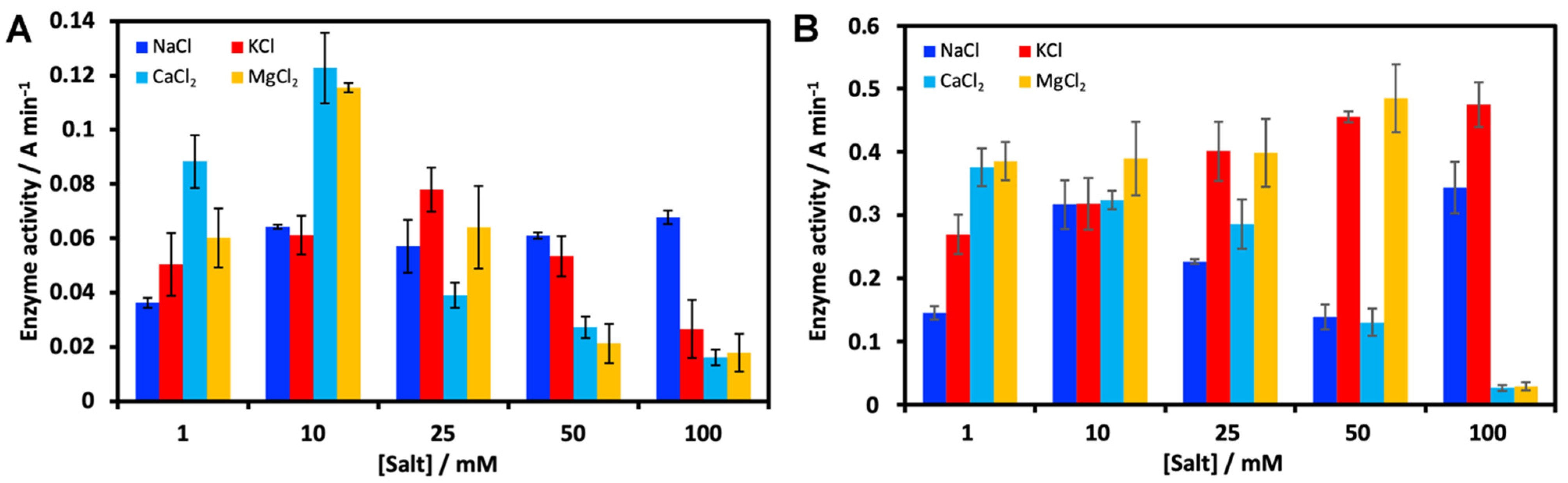
2.1.2. Effect of Salts
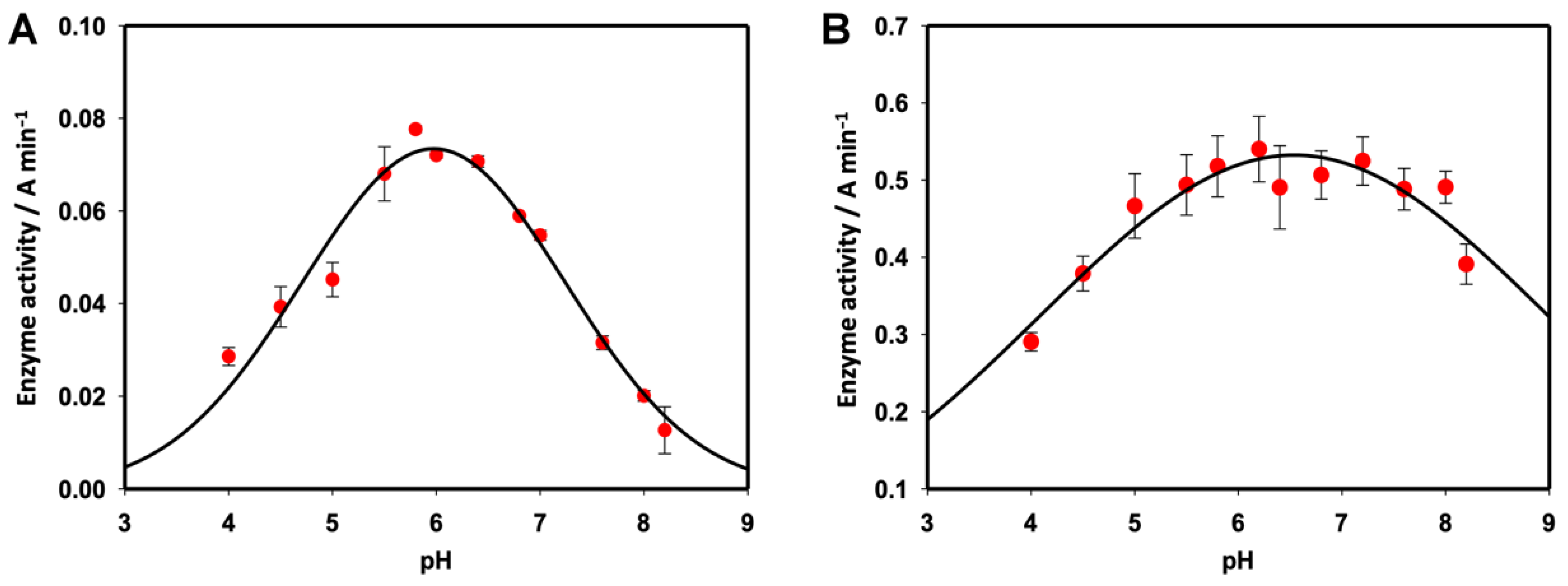
2.1.3. Effect of pH
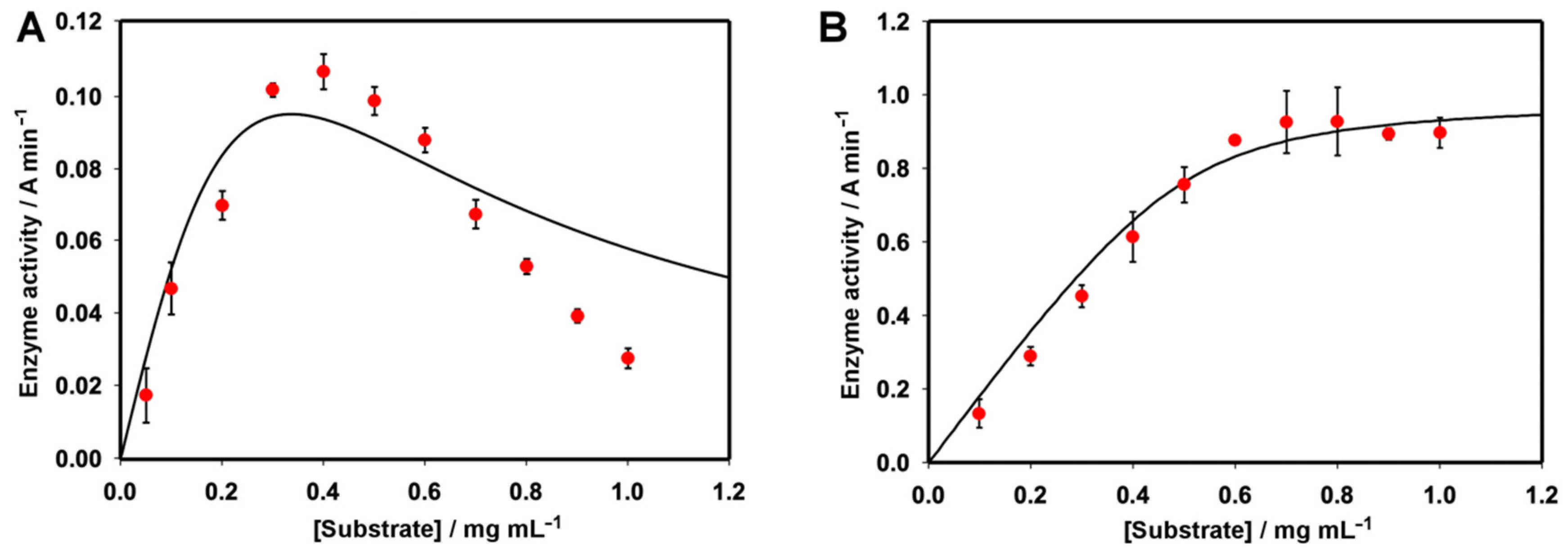
2.1.4. Effect of the Substrate
2.1.5. Effect of Temperature
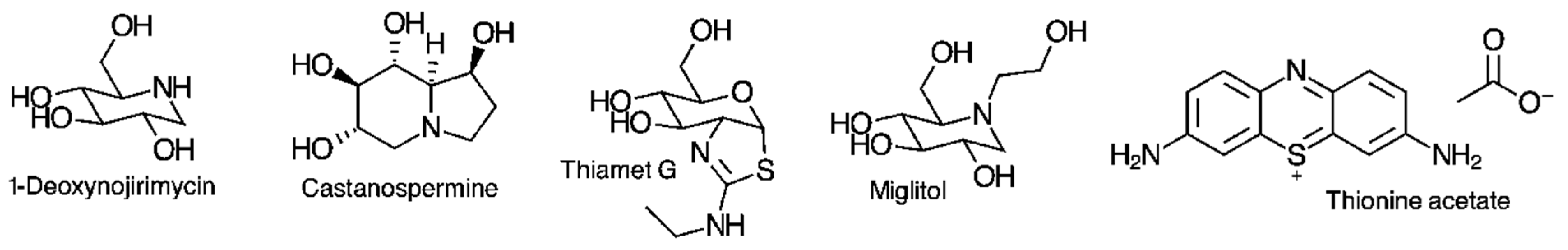
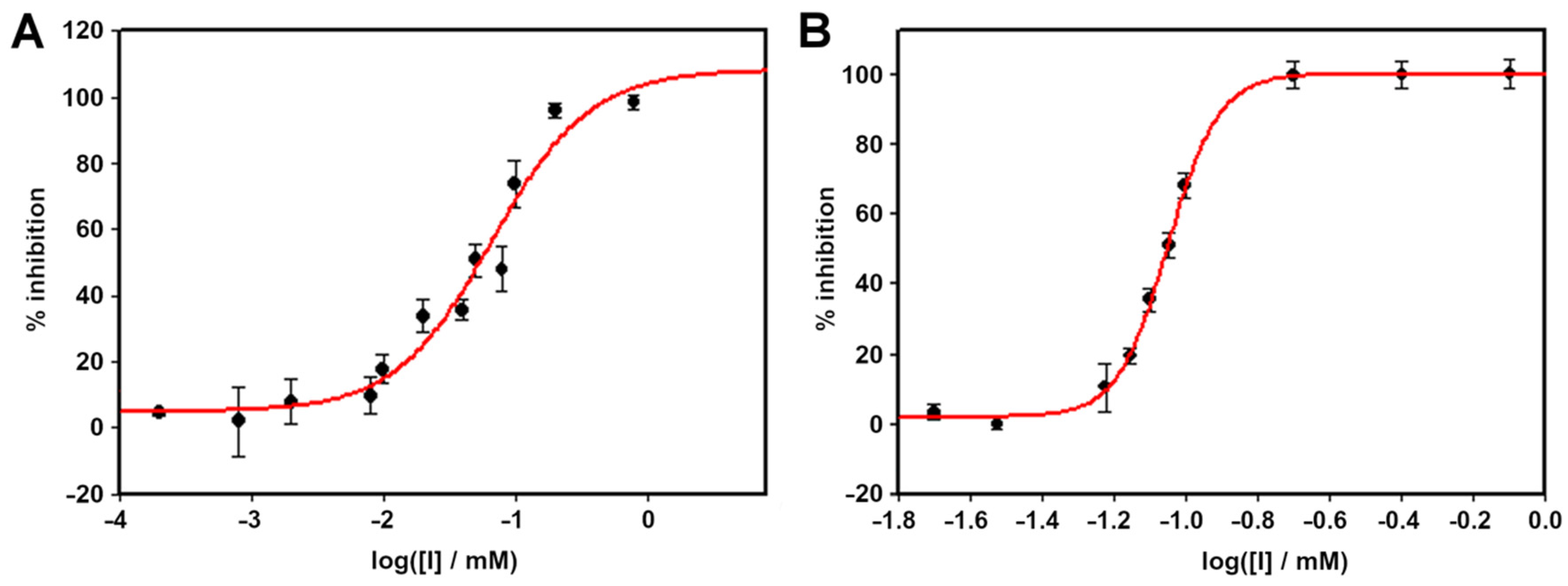
2.2. Enzyme Inhibition Studies
2.3. Binding Studies
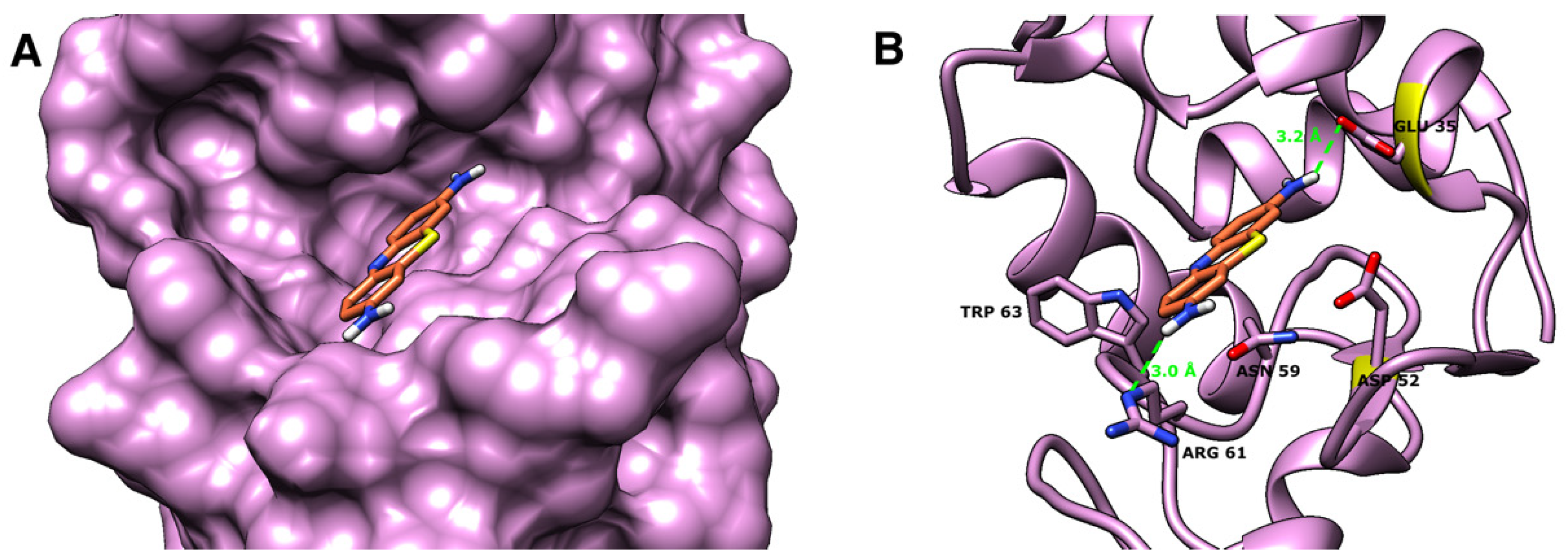
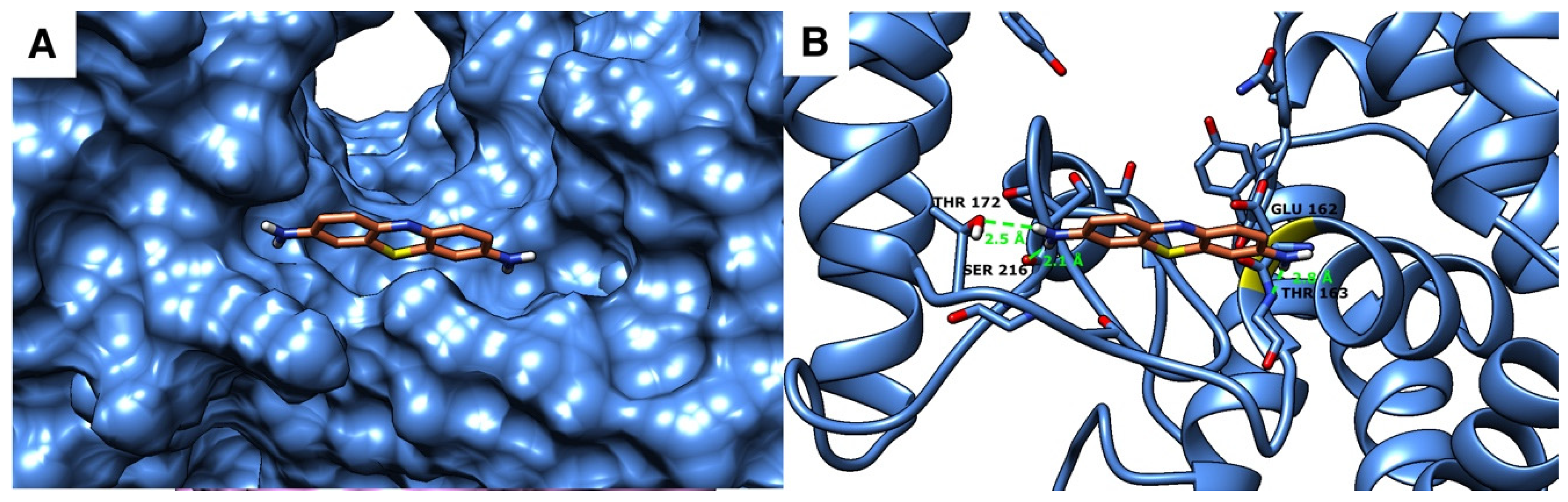
2.4. Molecular Docking Studies
2.5. Antibacterial Testing
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents and Enzymes
3.2. Protein Production and Purification
3.3. Enzyme Activity
3.4. Enzyme Inhibition
3.5. Saturation Transfer Difference NMR
3.6. Determination of Kd
3.7. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Vollmer, W.; Blanot, D.; de Pedro, M.A. Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barreteau, H.; Kovač, A.; Boniface, A.; Sova, M.; Gobec, S.; Blanot, D. Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 168–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodell, E.W. Recycling of murein by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 163, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Harish, K.; Dhakan, D.B.; Sharma, V.K. Prediction of peptidoglycan hydrolases- a new class of antibacterial proteins. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Höltje, J.V. From growth to autolysis: The murein hydrolases in Escherichia coli. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 164, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heijenoort, J. Peptidoglycan hydrolases of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 636–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheurwater, E.; Reid, C.W.; Clarke, A.J. Lytic transglycosylases: Bacterial space-making autolysins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dik, D.A.; Marous, D.R.; Fisher, J.F.; Mobashery, S. Lytic transglycosylases: Concinnity in concision of the bacterial cell wall. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 52, 503–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höltje, J.V.; Mirelman, D.; Sharon, N.; Schwarz, U. Novel type of murein transglycosylase in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1975, 124, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, C.; Frère, J.-M.; Normark, S. Cytosolic Intermediates for Cell Wall Biosynthesis and Degradation Control Inducible β-Lactam Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Cell 1997, 88, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adin, D.M.; Engle, J.T.; Goldman, W.E.; McFall-Ngai, M.J.; Stabb, E. V Mutations in ampG and lytic transglycosylase genes affect the net release of peptidoglycan monomers from Vibrio fischeri. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boudreau, M.A.; Fisher, J.F.; Mobashery, S. Messenger functions of the bacterial cell wall-derived muropeptides. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2974–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorbara, M.T.; Philpott, D.J. Peptidoglycan: A critical activator of the mammalian immune system during infection and homeostasis. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 243, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.J.; Dupont, C. O-acetylated peptidoglycan: Its occurrence, pathobiological significance, and biosynthesis. Can. J. Microbiol. 1992, 38, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, J.M.; Strating, H.; Weadge, J.T.; Clarke, A.J. Peptidoglycan O Acetylation and Autolysin Profile of Enterococcus faecalis in the Viable but Nonculturable State. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monchois, V.; Abergel, C.; Sturgis, J.; Jeudy, S.; Claverie, J.M. Escherichia coli ykfE ORFan gene encodes a potent inhibitor of C-type lysozyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18437–18441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, C.A.; Scheurwater, E.M.; Clarke, A.J. The vertebrate lysozyme inhibitor Ivy functions to inhibit the activity of lytic transglycosylase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14843–14847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Templin, M.F.; Edwards, D.H.; Höltje, J. V A murein hydrolase is the specific target of bulgecin in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 20039–20043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, A.; Kintaka, K.; Nakao, M.; Shinagawa, S. Bulgecin A, a bacterial metabolite which in concert with beta-lactam antibiotics causes bulge formation. J. Antibiot. 1982, 35, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonis, M.; Williams, A.; Guadagnini, S.; Werts, C.; Boneca, I.G. The Effect of Bulgecin A on Peptidoglycan Metabolism and Physiology of Helicobacter pylori. Microb. Drug Resist. 2012, 18, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skalweit, M.J.; Li, M. Bulgecin A as a β-lactam enhancer for carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates containing various resistance mechanisms. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 3013–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loveridge, E.J.; Jones, C.; Bull, M.J.; Moody, S.C.; Kahl, M.W.; Khan, Z.; Neilson, L.; Tomeva, M.; Adams, S.E.; Wood, A.C.; et al. Reclassification of the specialized metabolite producer Pseudomonas mesoacidophila ATCC 31433 as a member of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, A.H.; Wheeler, R.; Thiriau, C.; Haouz, A.; Taha, M.; Boneca, I.G. Bulgecin A: The Key to a Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor That Targets Lytic Transglycosylases. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomoshige, S.; Dik, D.A.; Akabane-Nakata, M.; Madukoma, C.S.; Fisher, J.F.; Shrout, J.D.; Mobashery, S. Total Syntheses of Bulgecins A, B, and C and Their Bactericidal Potentiation of the β-Lactam Antibiotics. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dik, D.A.; Madukoma, C.S.; Tomoshige, S.; Kim, C.; Lastochkin, E.; Boggess, W.C.; Fisher, J.F.; Shrout, J.D.; Mobashery, S. Slt, MltD, and MltG of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as Targets of Bulgecin A in Potentiation of β-Lactam Antibiotics. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, A.; Martin, R.; Mena-Barragán, T.; Verdaguer, X.; García Fernández, J.M.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; Riera, A. Stereoselective synthesis of 2-acetamido-1,2-dideoxyallonojirimycin (DAJNAc), a new potent hexosaminidase inhibitor. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3638–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scofield, A.M.; Witham, P.; Nash, R.J.; Kite, G.C.; Fellows, L.E. Castanospermine and other polyhydroxy alkaloids as inhibitors of insect glycosidases. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1995, 112, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xia, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Shen, X.; Yang, Q. Exploring NAG-thiazoline and its derivatives as inhibitors of chitinolytic β-acetylglucosaminidases. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borges de Melo, E.; da Silveira Gomes, A.; Carvalho, I. α- and β-Glucosidase inhibitors: Chemical structure and biological activity. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 10277–10302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaraj, K.; Anandakumar, S.; Ilanchelian, M. Probing the binding interaction of thionine with lysozyme: A spectroscopic and molecular docking investigation. Dye. Pigment. 2015, 112, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasonská, B.; Čadková, M.; Kovářová, A.; Bílková, Z.; Korecká, L.; Horák, D. Thionine-Modified Poly(glycidyl methacrylate) Nanospheres as Labels of Antibodies for Biosensing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24926–24931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.B.; Pang, G.C.; Liang, X.Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.M. Study on a hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on horseradish peroxidase/GNPs-thionine/chitosan. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 62, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, M.; Phoenix, D.A.; Laycock, S.L.; Wareing, D.R.; Wright, P.A. Photobactericidal activity of phenothiazinium dyes against methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 160, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hash, J.H. Measurement of bacteriolytic enzymes. J. Bacteriol. 1967, 93, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Asselt, E.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. Binding of calcium in the EF-hand of Escherichia coli lytic transglycosylase Slt35 is important for stability. FEBS Lett. 1999, 458, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, R.C.; Neuberger, A.; Wilson, B.M. The dependence of lysozyme activity on pH and ionic strength. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Enzymol. 1969, 178, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vocadlo, D.J.; Davies, G.J.; Laine, R.; Withers, S.G. Catalysis by hen egg-white lysozyme proceeds via a covalent intermediate. Nature 2001, 412, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartik, K.; Redfield, C.; Dobson, C.M. Measurement of the individual pKa values of acidic residues of hen and turkey lysozymes by two-dimensional 1H NMR. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, T.K.; Turner, G.J. Structural basis of perturbed pKa values of catalytic groups in enzyme active sites. IUBMB Life 2002, 53, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Larter, R. Role of substrate inhibition kinetics in enzymatic chemical oscillations. Biophys. J. 1994, 67, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, J.F. Kinetics of the reversible inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions by tight-binding inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Enzymol. 1969, 185, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, W.M.; Eyring, H. Hydrostatic Pressure and Ionic Strength Effects on the Kinetics of Lysozyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 2417–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumagai, I.; Sunada, F.; Takeda, S.; Miura, K. Redesign of the substrate-binding site of hen egg white lysozyme based on the molecular evolution of C-type lysozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 4608–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Blázquez, B.; Hesek, D.; Lee, M.; Llarrull, L.I.; Boggess, B.; Oliver, A.G.; Fisher, J.F.; Mobashery, S. Inhibitors for Bacterial Cell-Wall Recycling. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Hesek, D.; Llarrull, L.I.; Lastochkin, E.; Pi, H.; Boggess, B.; Mobashery, S. Reactions of All Escherichia coli Lytic Transglycosylases with Bacterial Cell Wall. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3311–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIntosh-Smith, S.; Price, J.; Sessions, R.B.; Ibarra, A.A. High performance in silico virtual drug screening on many-core processors. Int. J. High Perform. Comput. Appl. 2014, 29, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Dauter, M.; Alkire, R.; Joachimiak, A.; Dauter, Z. Triclinic lysozyme at 0.65 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2007, 63, 1254–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Asselt, E.J.; Dijkstra, A.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Takacs, B.; Keck, W.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli lytic transglycosylase Slt35 reveals a lysozyme-like catalytic domain with an EF-hand. Structure 1999, 7, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Asselt, E.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystallographic Studies of the Interactions of Escherichia coli Lytic Transglycosylase Slt35 with Peptidoglycan. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraft, A.R.; Prabhu, J.; Ursinus, A.; Höltje, J.-V. Interference with Murein Turnover Has No Effect on Growth but Reduces β-Lactamase Induction in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 7192–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korsak, D.; Liebscher, S.; Waldemar, V. Susceptibility to Antibiotics and β-Lactamase Induction in Murein Hydrolase Mutants of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simm, A.M.; Loveridge, E.J.; Crosby, J.; Avison, M.B.; Walsh, T.R.; Bennett, P.M. Bulgecin A: A novel inhibitor of binuclear metallo-β-lactamases. Biochem. J. 2005, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Mass of Thionine Acetate/μg | Inhibition Zone Diameter/mm |
|---|---|
| 0 | 25 ± 1 |
| 125 | 25 ± 2 |
| 250 | 28 ± 1 |
| 500 | 30 ± 1 |
| 1000 | 31 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mezoughi, A.B.; Costanzo, C.M.; Parker, G.M.; Behiry, E.M.; Scott, A.; Wood, A.C.; Adams, S.E.; Sessions, R.B.; Loveridge, E.J. The Lysozyme Inhibitor Thionine Acetate Is Also an Inhibitor of the Soluble Lytic Transglycosylase Slt35 from Escherichia coli. Molecules 2021, 26, 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144189
Mezoughi AB, Costanzo CM, Parker GM, Behiry EM, Scott A, Wood AC, Adams SE, Sessions RB, Loveridge EJ. The Lysozyme Inhibitor Thionine Acetate Is Also an Inhibitor of the Soluble Lytic Transglycosylase Slt35 from Escherichia coli. Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144189
Chicago/Turabian StyleMezoughi, Aysha B., Chiara M. Costanzo, Gregor M. Parker, Enas M. Behiry, Alan Scott, Andrew C. Wood, Sarah E. Adams, Richard B. Sessions, and E. Joel Loveridge. 2021. "The Lysozyme Inhibitor Thionine Acetate Is Also an Inhibitor of the Soluble Lytic Transglycosylase Slt35 from Escherichia coli" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144189
APA StyleMezoughi, A. B., Costanzo, C. M., Parker, G. M., Behiry, E. M., Scott, A., Wood, A. C., Adams, S. E., Sessions, R. B., & Loveridge, E. J. (2021). The Lysozyme Inhibitor Thionine Acetate Is Also an Inhibitor of the Soluble Lytic Transglycosylase Slt35 from Escherichia coli. Molecules, 26(14), 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144189







