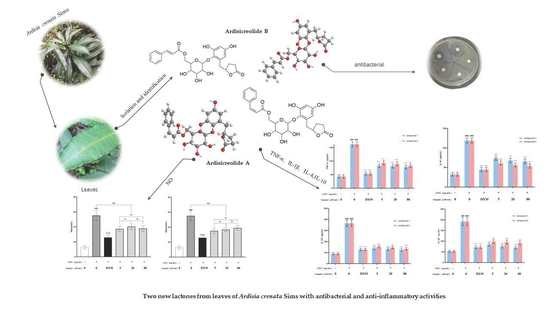
Two New Phenolic Glycosides with Lactone Structural Units from Leaves of Ardisia crenata Sims with Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure Elucidation
2.2. Effect of Compounds 1–6 on Antibacterial Activities
2.3. Effects of Compounds 1–2 on RAW264.7 Cells by CCK-8 Method
2.4. Effects of Compounds 1–2 on NO Production
2.5. Effects of Compounds 1–2 on Inflammatory Cytokines Production
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Characterization of Compounds 1–2
3.5. Antibacterial Activity Screening
3.6. Cell Culture
3.7. Primary Screening for Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
3.8. Determination of Inflammatory Cytokines
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kobayashi, H.; De Mejía, E. The genus Ardisia: A novel source of health-promoting compounds and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anh, N.H.; Ripperger, H.; Schmidt, J.; Porzel, A.; Van Sung, T.; Adam, G. Resorcinol derivatives from two Ardisia species. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaima, K.; Deguchi, J.; Matsuno, Y.; Kaneda, T.; Hirasawa, Y.; Morita, H. Vasorelaxant effect of FR900359 from Ardisia crenata on rat aortic artery. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 67, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.L.; Wang, N.L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Yao, X.S. Two new triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia crenata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 9, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.L.; Wang, N.L.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.S. Three new triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia crenata. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, S.-Y.; Xu, B.; Guo, W.; Liu, D.-L.; Cui, J.-R.; Yao, X.-S. Pro-apoptotic and microtubule-disassembly effects of ardisiacrispin (A + B), triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia crenata on human hepatoma Bel-7402 cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.-F.; Xu, J.-F.; Feng, Z.-M.; Zhang, P.-C. Cytotoxic triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Ardisia crenata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Kuang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P.; Koike, K. A simple and rapid method to identify and quantitatively analyze triterpenoid saponins in Ardisia crenata using ultrafast liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 102, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning-Ning, S.; Lei-Min, Y.; Zhang, M.-J.; Ren-Feng, A.; Wei, L.; Huang, X.-F. Triterpenoid saponins and phenylpropanoid glycoside from the roots of Ardisia crenata and their cytotoxic activities. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Yao, C.; FU, S.; Gong, Z.; Liu, T.; Yang, C.; Zha, J.; LI, Y. Study on HPLC Fingerprint of Miao Medicine Ardisia crenata. China Pharm. 2017, 28, 4285–4288. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, P.K.; Joshi, H. Coumarin: Chemical and pharmacological profile. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.-L.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Ravindar, L.; Rakesh, K. Antibacterial activities with the structure-activity relationship of coumarin derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 207, 112832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-H.; Yu, Z.-P.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Bao, J.; Zhu, K.-K.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, H. Triterpenoids and triterpenoid saponins from Dipsacus asper and their cytotoxic and antibacterial activities. Phytochemistry 2019, 162, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Khan, A.; Cai, S.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Kai, G.; Zhao, T.; Cheng, G.; Cao, J. Epigynumgenane-type pregnane glycosides from Epigynum cochinchinensis and their immunosuppressive activity. Phytochemistry 2019, 168, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yao, Y.-C.; Cai, S.-B.; Zhao, T.-R.; Yang, X.-Y.; Fan, J.; Li, X.-N.; Cao, J.-X.; Cheng, G.-G. Novel immunosuppressive pregnane glycosides from the leaves of Epigynum auritum. Fitoterapia 2017, 118, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.-G.; Kim, K.-W.; Li, J.; Lee, D.Y.; Yoon, D.; Jeong, J.T.; Kim, G.-S.; Oh, H.; An, R.-B.; Kim, Y.-C. Anti-inflammatory components isolated from Atractylodes macrocephala in LPS-induced RAW264. 7 macrophages and BV2 microglial cells. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paço, A.; Brás, T.; Santos, J.O.; Sampaio, P.; Gomes, A.C.; Duarte, M.F. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunoregulatory Action of Sesquiterpene Lactones. Molecules 2022, 27, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-C.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.-L.; Qiu, Y.-P.; Lou, D.-Y.; Zhou, L.-Q.; Yang, B.; He, Q.-J.; Weng, Q.-J. Sapidolide A alleviates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.L.; Christenson, J.K.; Wackett, L.P. Biosynthesis and chemical diversity of β-lactone natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Coelho, E.; Aguiar, T.Q.; Domingues, L. Microbial biosynthesis of lactones: Gaps and opportunities towards sustainable production. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.P.; Tan, C.H.; Wang, B.D.; Zhu, D.Y.; Kim, S.K. Chemical constituents from Myrsine africana L. Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Dong, H.; Yu, P.; Lu, L.; Du, W.; Cao, S. Total Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Velutone F. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1934578X221076653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Synthesis of New Lathyrane Diterpenoid Derivatives from Euphorbia lathyris and Evaluation of Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Rivera, S.; Gabayan, V.; Keller, C.; Taudorf, S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Ganz, T. IL-6 mediates hypoferremia of inflammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, C.; Xie, Q.-W. Nitric oxide synthases: Roles, tolls, and controls. Cell 1994, 78, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-C.; Ning, D.-S.; Fu, Y.-X.; Pan, Z.-H. Structure elucidation and anti-inflammatory mechanism of difengpienol C, a new neolignan isolated from Illicium difengpi. Fitoterapia 2021, 153, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, C.; Fan, C.; Xu, N.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, X.; Lu, Z.; Cao, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, L. Sheng-Mai Yin exerts anti-inflammatory effects on RAW 264.7 cells and zebrafish. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-W.; Shin, J.-S.; Chung, K.-S.; Lee, Y.-G.; Baek, N.-I.; Lee, K.-T. Anti-Inflammatory mechanisms of Koreanaside A, a lignan isolated from the flower of Forsythia koreana, against LPS-induced macrophage activation and DSS-induced colitis mice: The crucial role of AP-1, NF-κB, and JAK/STAT signaling. Cells 2019, 8, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; Dong, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of chemical components from Ginkgo biloba L. male flowers on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264. 7 macrophages. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Position | Ardisicreolide A | Ardisicreolide B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH | (J in Hz) | δC | δH | (J in Hz) | |
| 2 | 180.5 | - | - | 180.4 | - | - |
| 3 | 29.5 | 2.35 | m | 29.5 | 2.45 | dd (7.5, 8.9) |
| 4 | 28.3 | 1.90, 2.19 | m, m | 28.3 | 1.96, 2.23 | dtd (7.0, 8.9, 12.5), m |
| 5 | 82.8 | 4.76 | m | 82.8 | 4.84 | M |
| 6 | 36.5 | 2.85, 3.15 | dd (4.7, 14.1), dd (8.0, 14.1) | 36.6 | 2.87, 3.25 | dd (5.2, 14.0), dd (7.6, 14.0) |
| 1′ | 138.5 | - | - | 138.6 | - | - |
| 2′ | 151.5 | - | - | 151.6 | - | - |
| 3′ | 103.4 | 6.25 | d (2.9) | 103.4 | 6.23 | d (2.9) |
| 4′ | 155.9 | - | - | 155.9 | - | - |
| 5′ | 109.2 | 6.19 | d (2.9) | 109.2 | 6.18 | d (2.9) |
| 6′ | 133.0 | - | - | 132.9 | - | - |
| 1″ | 107.5 | 4.44 | d (7.6) | 107.6 | 4.57 | d (7.6) |
| 2″ | 75.4 | 3.28~3.46 | m (4H) | 75.4 | 3.37~3.62 | m (4H) |
| 3″ | 77.9 | 77.9 | ||||
| 4″ | 71.3 | 71.5 | ||||
| 5″ | 75.9 | 76.0 | ||||
| 6″ | 64.5 | 4.24, 4.50 | dd (6.5, 12.0), dd (2.0,12.0) | 64.7 | 4.34, 4.59 | dd (6.5, 12.0), dd (2.0,12.0) |
| 1‴ | 136.4 | - | - | 135.7 | - | - |
| 2‴ 6‴ | 130.7 | 7.49 | dd (1.9, 7.8, 2H) | 130.1 | 7.61 | dd (1.9, 7.8, 2H) |
| 3‴ 5‴ | 129.1 | 7.26 | m (3H) | 129.4 | 7.42 | m (3H) |
| 4‴ | 130.0 | 131.6 | ||||
| 7‴ | 144.8 | 7.06 | d (12.6) | 146.8 | 7.73 | d (16.0) |
| 8‴ | 120.3 | 5.98 | d (12.6) | 118.5 | 6.54 | d (16.0) |
| 9‴ | 167.6 | - | - | 168.3 | - | - |
| C(μg/mL) | Ardisicreolide B | Cef a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 50 | 100 | ||
| Escherichia coli | - | - | - | 16.63 ± 0.99 |
| P. aeruginosa | - | - | - | 19.30 ± 1.42 |
| Bacillus subtilis | 11.33 ± 1.01 | 13.2 ± 1.01 | 17.47 ± 1.53 | 29.37 ± 1.01 |
| Enterococcus Faecalis | - | - | - | 19.40 ± 1.01 |
| Proteus vulgaris | - | - | - | 18.47 ± 0.78 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | - | - | - | 28.40 ± 1.35 |
| Compound | Mean ± SD (μM/mL) |
|---|---|
| Ardisicreolide A | 24.46 ± 1.57 |
| Ardisicreolide B | 55.85 ± 4.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, X.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y. Two New Phenolic Glycosides with Lactone Structural Units from Leaves of Ardisia crenata Sims with Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Molecules 2022, 27, 4903. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154903
Tao H, Zhou Y, Yin X, Wei X, Zhou Y. Two New Phenolic Glycosides with Lactone Structural Units from Leaves of Ardisia crenata Sims with Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Molecules. 2022; 27(15):4903. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154903
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Huihui, Yongqiang Zhou, Xin Yin, Xin Wei, and Ying Zhou. 2022. "Two New Phenolic Glycosides with Lactone Structural Units from Leaves of Ardisia crenata Sims with Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities" Molecules 27, no. 15: 4903. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154903
APA StyleTao, H., Zhou, Y., Yin, X., Wei, X., & Zhou, Y. (2022). Two New Phenolic Glycosides with Lactone Structural Units from Leaves of Ardisia crenata Sims with Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Molecules, 27(15), 4903. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154903