Nature-Inspired Biomolecular Corona Based on Poly(caffeic acid) as a Low Potential and Time-Stable Glucose Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
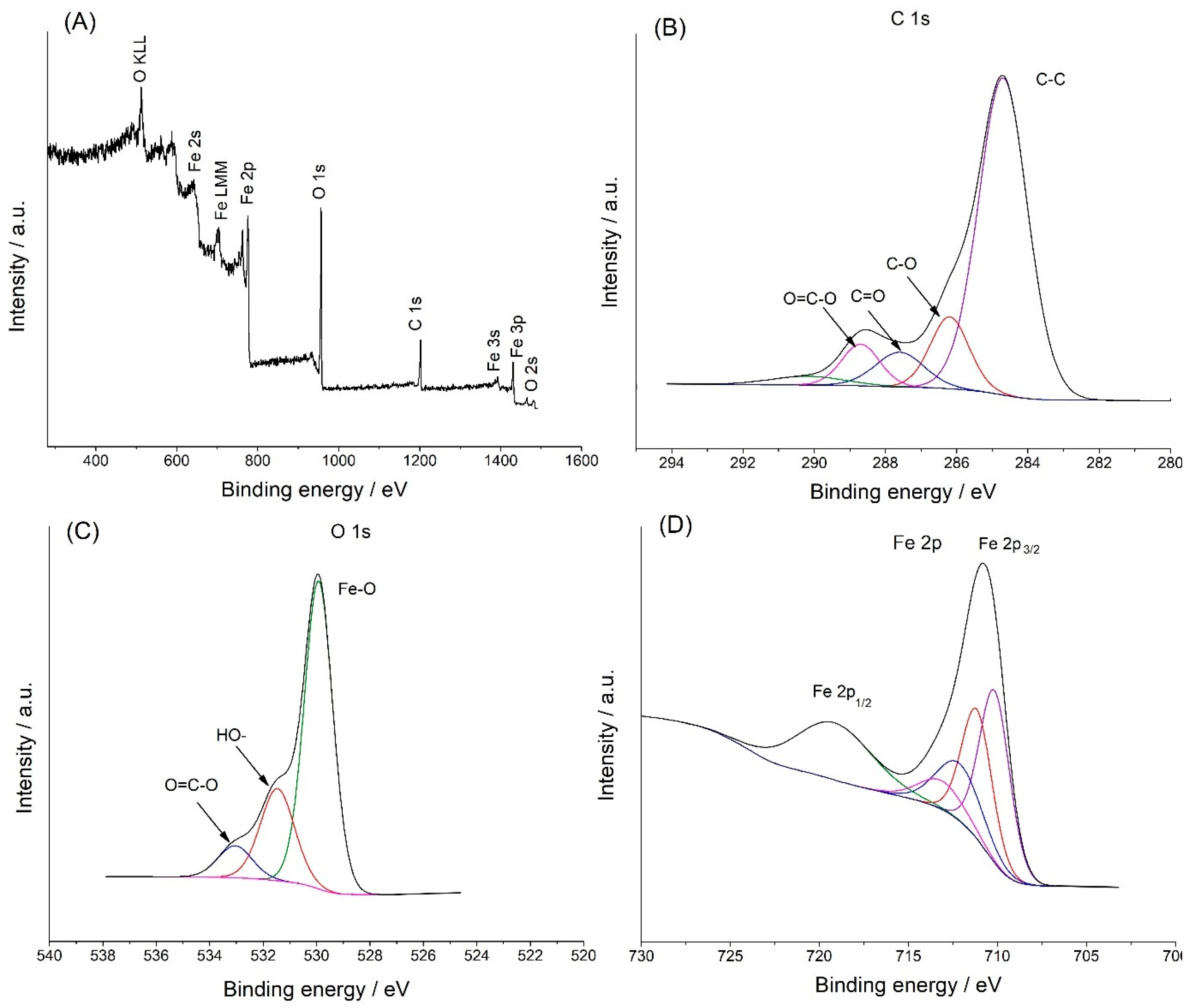
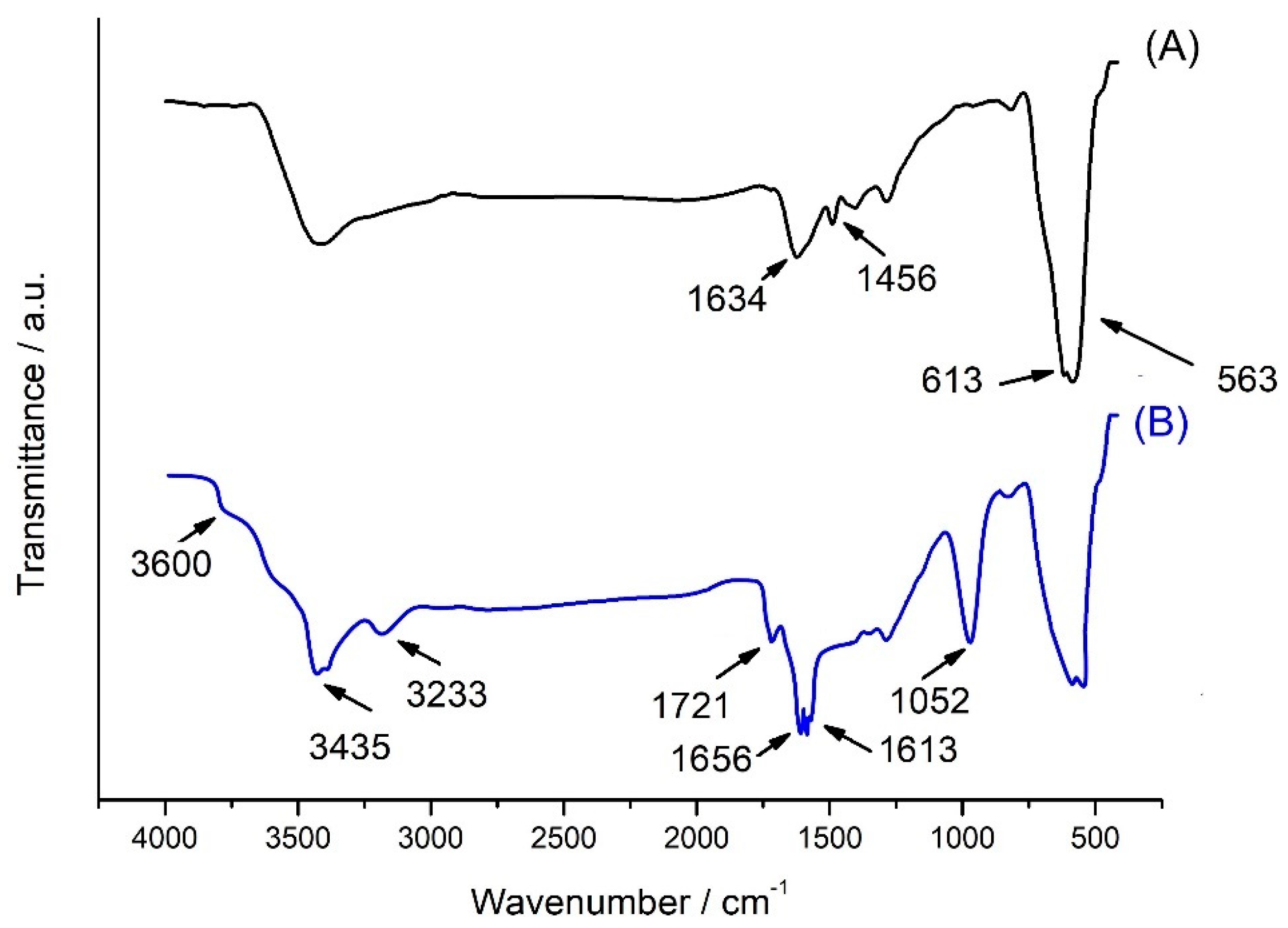
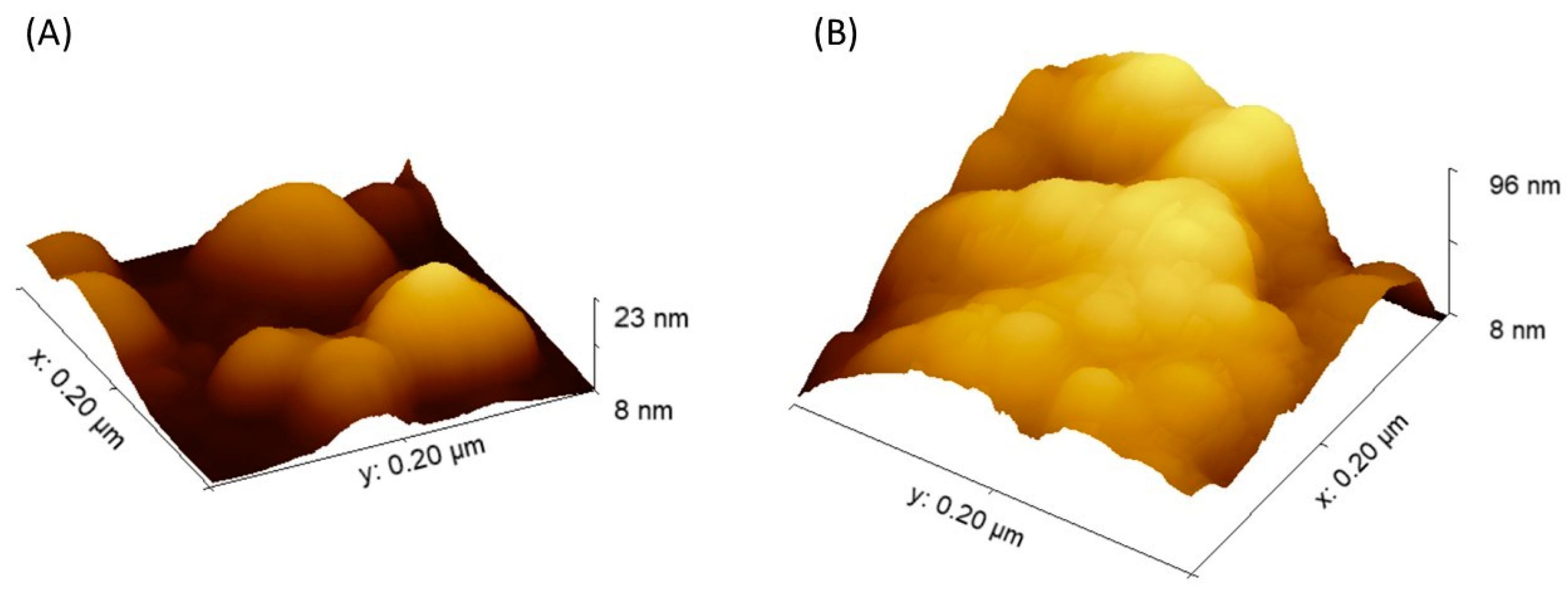
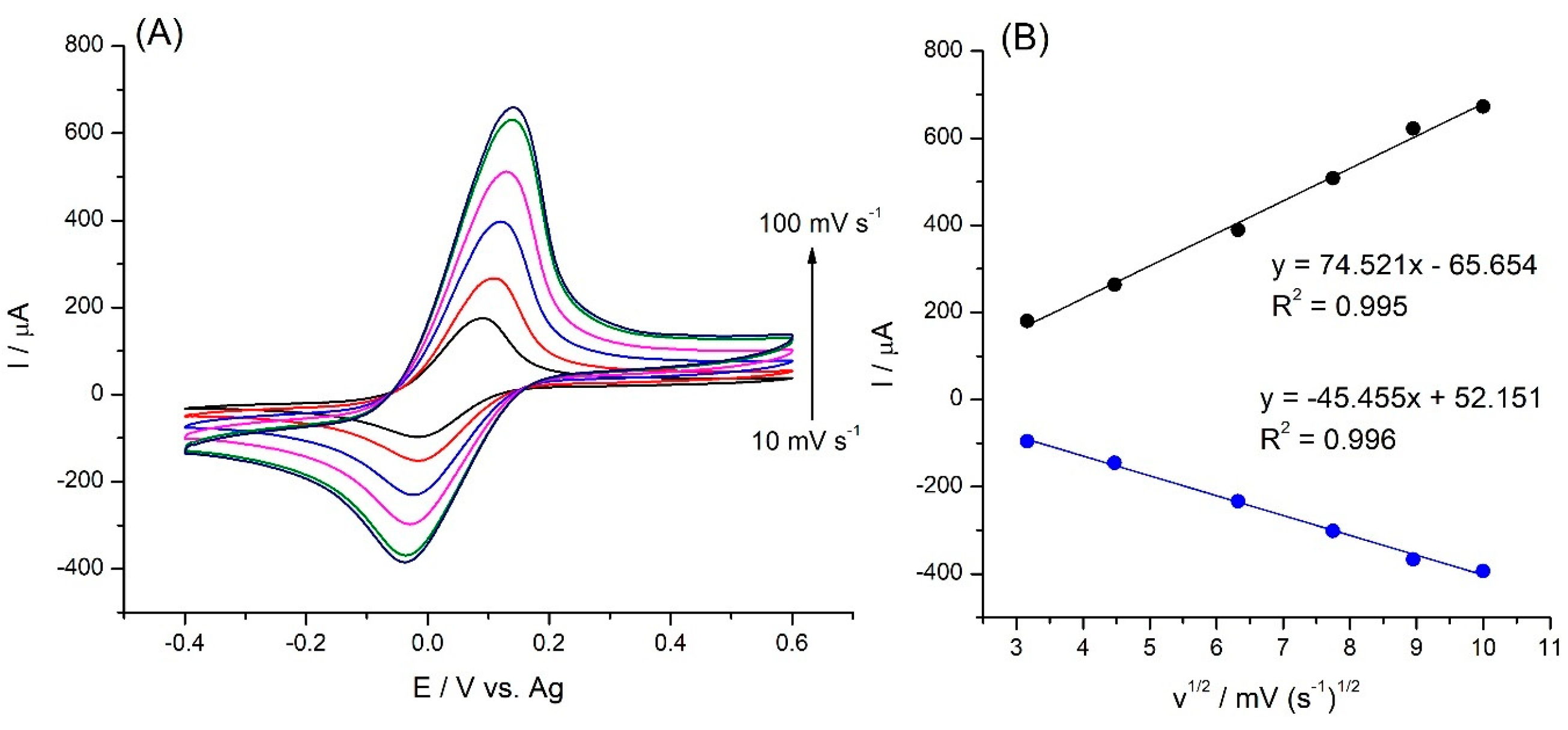
2. Results and Discuss
2.1. Morphological Characterization
2.2. Immobilization of Glucose Oxidase (GOx)
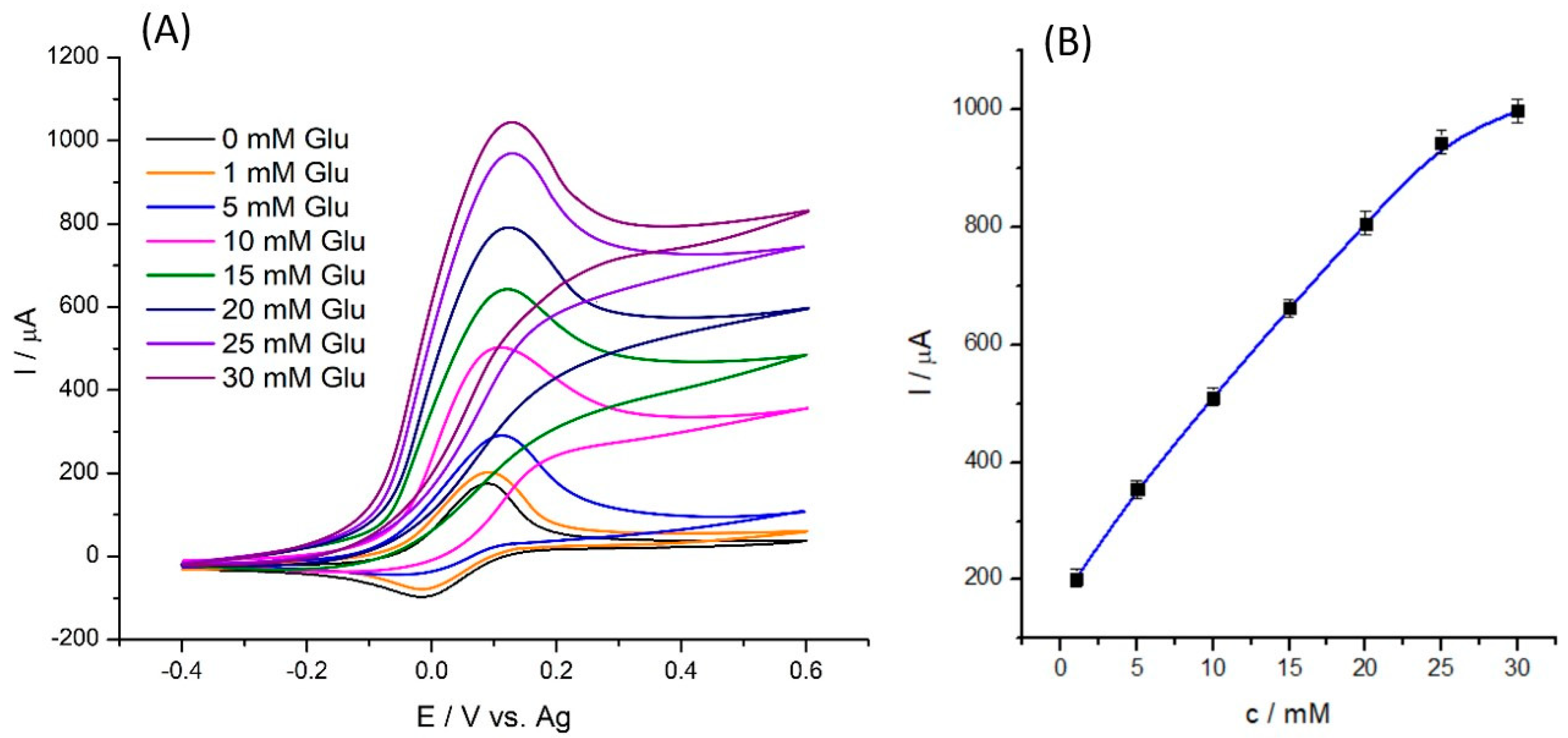
2.3. Electrochemical Tests of SPE/Fe3O4@PCA-GOx Electrode
2.4. Interferents Tests
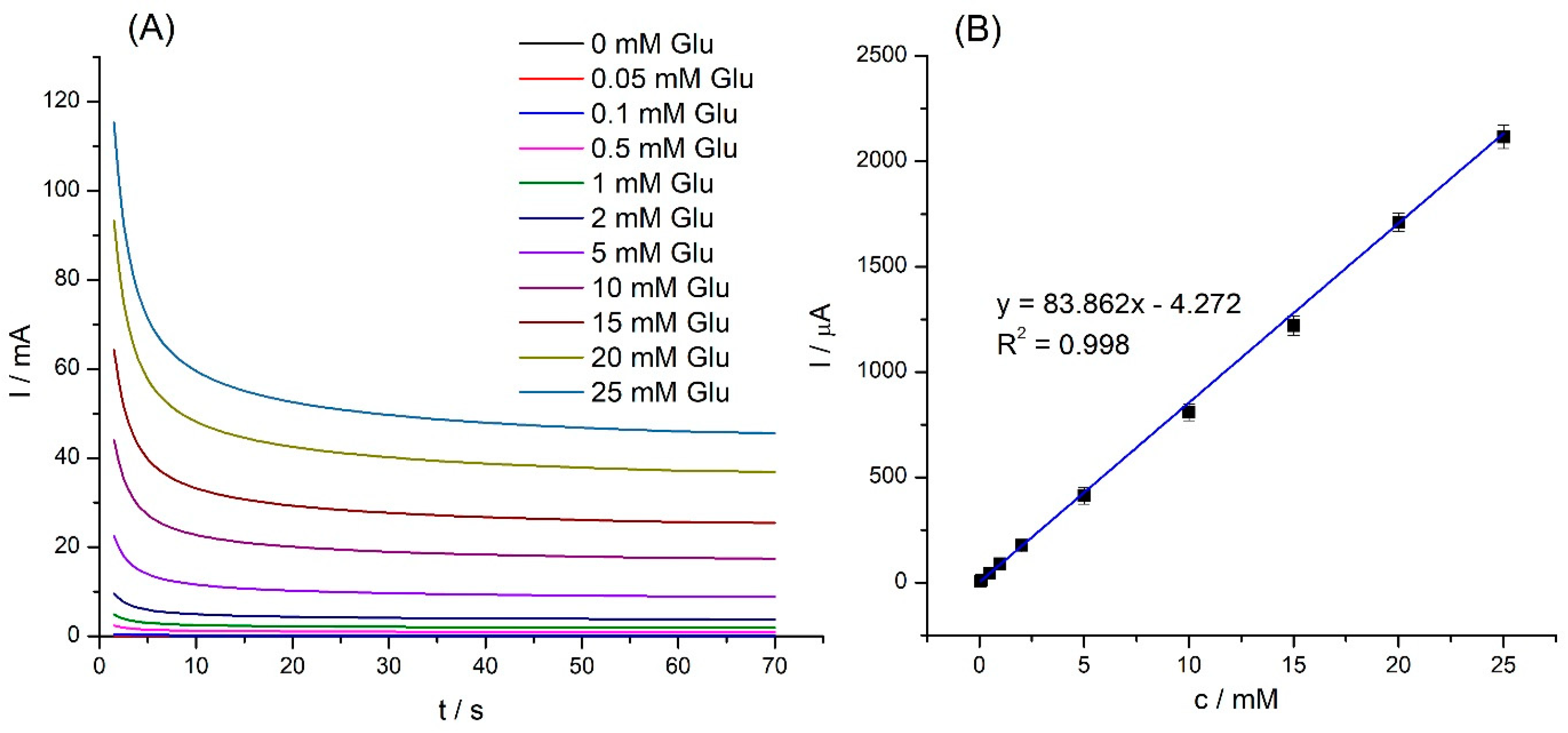
2.5. Optimization Tests
2.6. Real Sample Analysis
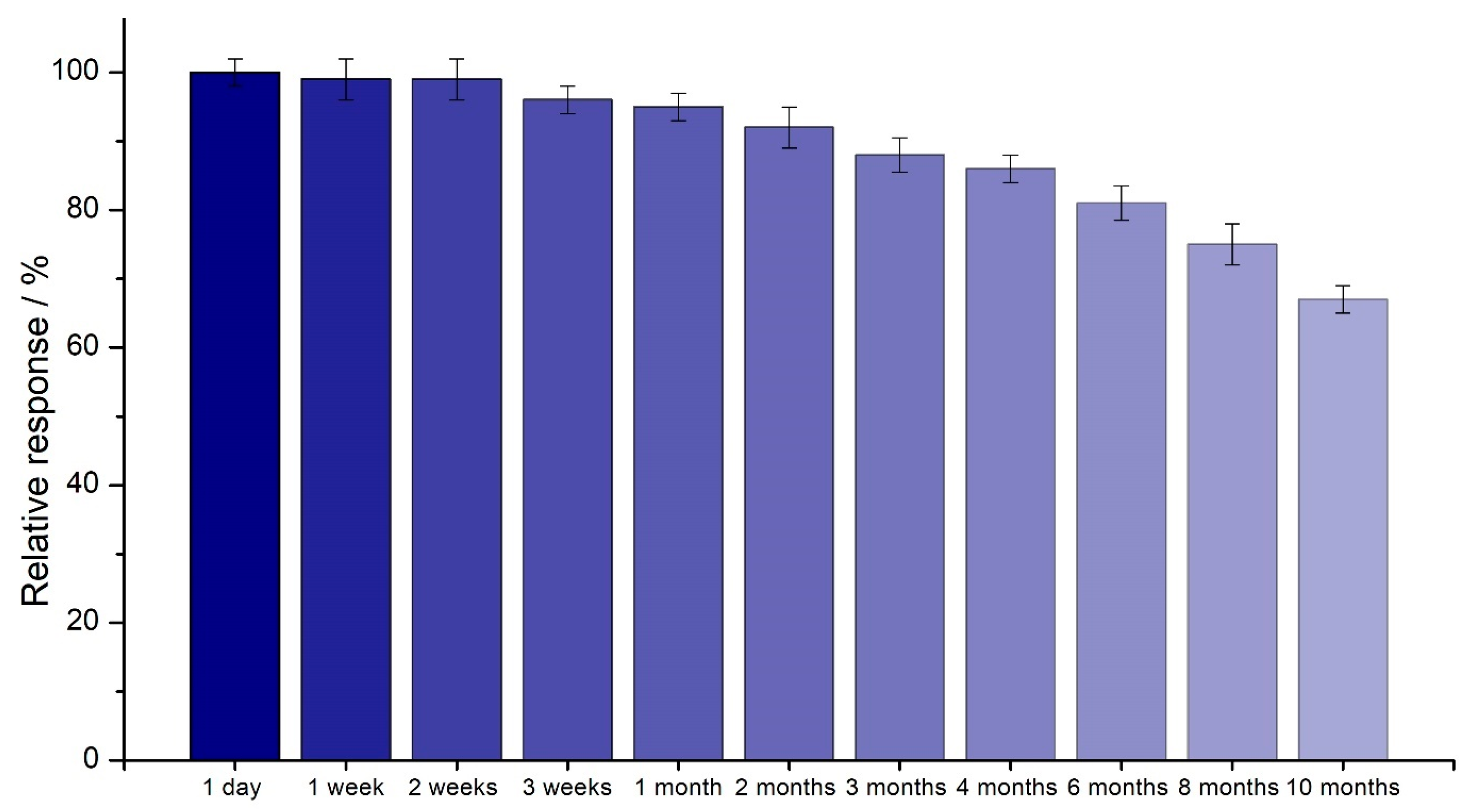
2.7. Time Stability and Reproducibility of the SPE/Fe3O4@PCA-GOx Biosensor
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4@PCA-GOx Biomolecular Corona
3.3. Fabrication of SPE/Fe3O4@PCA-GOx Electrode
3.4. Physicochemical Analysis
3.5. Electrochemical Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cheng, Y.; Gong, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Nie, G.; Xie, X.; Chen, M.; et al. A Touch-Actuated Glucose Sensor Fully Integrated with Microneedle Array and Reverse Iontophoresis for Diabetes Monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 203, 114026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharroubi, A.T. Diabetes Mellitus: The Epidemic of the Century. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyakin, A.A. Glucose Biosensors for Clinical and Personal Use. Electrochem. Commun. 2021, 125, 106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzak, A.; Kuznowicz, M.; Rębiś, T.; Jesionowski, T. Portable Glucose Biosensor Based on Polynorepinephrine@magnetite Nanomaterial Integrated with a Smartphone Analyzer for Point-of-Care Application. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 145, 108071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jędrzak, A.; Kuznowicz, M.; Jesionowski, T. Mobile-assisted diagnostic biosensor for point-of-care glucose detection in real human samples with rapid response and long-live stability. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2023, 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.D.; Setford, S.J. Enzymatic Biosensors. Mol Biotechnol. 2006, 32, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznowicz, M.; Rębiś, T.; Jędrzak, A.; Nowaczyk, G.; Szybowicz, M.; Jesionowski, T. Glucose Determination Using Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Sensor Based on Electroactive Poly(Caffeic Acid)@MWCNT Decorated with CuO Nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.J.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y.J.; Liu, X.X. Glucose Biosensor Based on Immobilization of Glucose Oxidase on Porous Screen Printed Electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, H.R.; Golabi, S.M. Caffeic Acid Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Reduced Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NADH). J. Solid State Electrochem. 2000, 4, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kesavan, S.; Kumar, D.R.; Dhakal, G.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, Y.R.; Shim, J.-J. Poly (Caffeic Acid) Redox Couple Decorated on Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide for Electrocatalytic Sensing Free Chlorine in Drinking Water. Nanomaterials 2022, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Shen, S.; Yuan, M.; Liu, W.; Tu, Q.; Yu, R.; Wang, J. Au Nanoparticles/Poly(Caffeic Acid) Composite Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Voltammetric Determination of Acetaminophen. Talanta 2016, 159, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.T.; Ward, K.R.; Tschulik, K.; Chapman, G.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical Detection of Glutathione Using a Poly(Caffeic Acid) Nanocarbon Composite Modified Electrode. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.B.; Ren, W.; Luo, H.Q. Simultaneous Voltammetric Measurement of Ascorbic Acid and Dopamine on Poly(Caffeic Acid)-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2008, 12, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rębiś, T.; Kuznowicz, M.; Jędrzak, A.; Milczarek, G.; Jesionowski, T. Design and Fabrication of Low Potential NADH-Sensor Based on Poly(Caffeic Acid)@multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 386, 138384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbach, M.; Freckmann, G.; Hinzmann, R.; Kulzer, B.; Ziegler, R.; Heinemann, L.; Schnell, O. Interferences and Limitations in Blood Glucose Self-Testing: An Overview of the Current Knowledge. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, B.H. Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Monitoring: Sources of Errors in Measurement. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, H.; Luo, J.; Wei, Y. “Click” Magnetic Nanoparticle-Supported Palladium Catalyst: A Phosphine-Free, Highly Efficient and Magnetically Recoverable Catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura Coupling Reactions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohzadi, H.; Soleiman-Beigi, M. XPS and Structural Studies of Fe3O4-PTMS-NAS@Cu as a Novel Magnetic Natural Asphalt Base Network and Recoverable Nanocatalyst for the Synthesis of Biaryl Compounds. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, P.; Hussain, S.; Jia, L.; Lin, D.; Yin, X.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, L. FeS2/Carbon Hybrids on Carbon Cloth: A Highly Efficient and Stable Counter Electrode for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.A.J.; Andrade, P.L.; Silva, M.P.C.; Bustamante, A.D.; de Los Santos Valladares, L.; Albino Aguiar, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Coated with Fucan Polysaccharides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 343, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yan, B.; Xing, T.; Chen, G. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Caffeic Acid/Fe@cotton Fabric and Its Oil-Water Separation Performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.W.; Heckert, G.; Neves, L.F.; Tan, Y.; Kao, D.Y.; Harrison, R.G.; Resasco, D.E.; Schmidtke, D.W. Adsorption of Glucose Oxidase onto Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Its Application in Layer-by-Layer Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7917–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznowicz, M.; Jędrzak, A.; Rębiś, T.; Jesionowski, T. Biomimetic Magnetite/Polydopamine/β-Cyclodextrins Nanocomposite for Long-Term Glucose Measurements. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 174, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzak, A.; Rębiś, T.; Kuznowicz, M.; Jesionowski, T. Bio-Inspired Magnetite/Lignin/Polydopamine-Glucose Oxidase Biosensing Nanoplatform. From Synthesis, via Sensing Assays to Comparison with Others Glucose Testing Techniques. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Ma, X.; Miao, K.; Ma, P.; Wang, Q. Enzymatic Biosensor Based on Dendritic Gold Nanostructure and Enzyme Precipitation Coating for Glucose Sensing and Detection. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 162, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, B.; Amarnath, C.A.; Sawant, S.N. Pectin Coated Polyaniline Nanoparticles for an Amperometric Glucose Biosensor. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40917–40923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzak, A.; Rębiś, T.; Klapiszewski, Ł.; Zdarta, J.; Milczarek, G.; Jesionowski, T. Carbon Paste Electrode Based on Functional GOx/Silica-Lignin System to Prepare an Amperometric Glucose Biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Cheng, H.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, H. Development of Glucose Biosensors Based on Nanostructured Graphene-Conducting Polyaniline Composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Jaime, A.F.; Quílez-Bermejo, J.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Metal Free Electrochemical Glucose Biosensor Based on N-Doped Porous Carbon Material. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 367, 137434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Hao, W.; Wu, Q.; Peng, J.; Tu, J.; Cao, Y. 3D Hollow-out TiO2 Nanowire Cluster/GOx as an Ultrasensitive Photoelectrochemical Glucose Biosensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Luo, Y.; Xiong, H.; Yao, S.; Zhu, M.; Song, H. A Novel Amperometric Glucose Biosensor Based on Fe3O4-Chitosan-β-Cyclodextrin/MWCNTs Nanobiocomposite. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tu, J.; Zhen, C. Photoelectrochemical Glucose Biosensor Based on the Heterogeneous Facets of Nanocrystalline TiO2/Au/Glucose Oxidase Films. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 2723–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, Z.D.; Song, Y.Y. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanospheres Derived from Cocoon Silk as Metal-Free Electrocatalyst for Glucose Sensing. Talanta 2015, 144, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Agrawal, A.; Pandey, G.; Kumar, S.; Awasthi, K.; Awasthi, A. Carbon Nano-Onion-Decorated ZnO Composite-Based Enzyme-Less Electrochemical Biosensing Approach for Glucose. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 37748–37756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Hou, H. Preparation of Ni(OH)2 Nanoplatelet/Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Hybrids for Highly Sensitive Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensors. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19345–19352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, F.; Gu, Z. Vertically Aligned Pt Nanowire Array/Au Nanoparticle Hybrid Structure as Highly Sensitive Amperometric Biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Guo, X.D. A Gold Nanoparticles Deposited Polymer Microneedle Enzymatic Biosensor for Glucose Sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 358, 136917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçoğlu, İ.O.; Erden, P.E.; Kenar, A.; Kılıç, E. Application of Central Composite Design for the Optimization of Electrode Surface Composition for Glucose Biosensor Fabrication. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Proposed Glucose Biosensor Enables the Detection of Glucose in All Glucose Concentrations That Occur in Human Blood, in Accordance with the WHO Guidelines. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/indicator-metadata-registry/imr-details/238040 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Harris, J.M.; Reyes, C.; Lopez, G.P. Common Causes of Glucose Oxidase Instability in in Vivo Biosensing: A Brief Review. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.; Popov, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Development and Practical Application of Glucose Biosensor Based on Dendritic Gold Nanostructures Modified by Conducting Polymers. Biosensors 2022, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasuksom, K.; Sirivat, A. Chronoampermetric Detection of Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on Doped Polyindole/MWCNT Composites Modified onto Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode as Portable Sensing Device for Diabetes. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 28505–28518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Yang, X.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, H.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J. Development of GO/Co/Chitosan-Based Nano-Biosensor for Real-Time Detection of D-Glucose. Biosensors 2022, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christwardana, M.; Frattini, D. Electrochemical Study of Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Biocatalyst: Thermal Degradation after Long-Term Storage. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to Biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Time/h | Fe3O4 NPs/mg g−1 | Fe3O4@PCA/mg g−1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.3 |
| 2 | 3.2 ± 0.4 | 10.2 ± 0.2 |
| 5 | 6.2 ± 0.3 | 18.3 ± 0.4 |
| 10 | 10.2 ± 0.3 | 24.2 ± 0.2 |
| 24 | 17.3 ± 0.2 | 38.1 ± 0.3 |
| 48 | 15.5 ± 0.4 | 30.2 ± 0.5 |
| Electrode | Sensitivity (μA mM−1 cm−2) | Limit of Detection (μM) | Linear Range (mM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@PNE-GOx | 97.30 | 6.10 | 0.2–24.0 | [4] |
| GOx-SiO2/Lig/Fc/CPE | 11.0 | 145.0 | 0.5–9.0 | [27] |
| GOxEPC-DenAu/CC | 72.45 | 6.70 | 0.02–31.7 | [25] |
| RA–PANI/CS–GOx | 22.10 | 2.77 | 0.01–1.09 | [28] |
| PANI-TT-GOx | 23.57 | 1.0 | 0.005–5.0 | [29] |
| TiO2NWc/GOx | 58.90 | 8.7 | 0.0–2.0 | [30] |
| Fe3O4−CS−CD/MWCNTs/GOx | 23.59 | 19.3 | 0.04–1.04 | [31] |
| TiO2/Au/GOx | 16.86 | 0.83 | 0.01–3.0 | [32] |
| CNS-Nafion-GOx | 7.31 | 39.1 | 0.08–2.04 | [33] |
| Fe3O4@PCA-GOx | 1198.0 | 5.23 | 0.05–25.0 | This work |
| Sample | Glucose Concentration/mM | SPE/Fe3O4@PCA-GOx | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Find/mM | Recovery/% | ||
| human serum | 2.8 | 2.74 ± 0.05 | 97.9 ± 1.79 |
| 6.9 | 6.84 ± 0.05 | 99.1 ± 0.72 | |
| 9.2 | 9.09 ± 0.10 | 98.8 ± 1.08 | |
| human blood | 3.2 | 3.14 ± 0.04 | 98.2 ± 1.25 |
| 6.3 | 6.21 ± 0.06 | 98.6 ± 0.95 | |
| 14.7 | 14.43 ± 0.05 | 98.2 ± 0.34 | |
| Biosensor System | Maintained Storage Stability (%) | Storage Time (Days) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPE/Fe3O4@PNE-GOx | 75.1 | 140 | [4] |
| Ppy/GOx/GR | 29.7 | 35 | [41] |
| CHI-GOx/APTES/dPIn | 76.7 | 28 | [42] |
| Go/Co/chitosan-GOx | 70.0 | 14 | [43] |
| GC/MWCNT/Fe3O4/PDA/β-CD-GOx | 63.0 | 210 | [23] |
| CNT/PEI/GOx | 66.7 | 120 | [44] |
| SPE/Fe3O4@PCA-GOx | 67.5 | 300 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuznowicz, M.; Jędrzak, A.; Jesionowski, T. Nature-Inspired Biomolecular Corona Based on Poly(caffeic acid) as a Low Potential and Time-Stable Glucose Biosensor. Molecules 2023, 28, 7281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217281
Kuznowicz M, Jędrzak A, Jesionowski T. Nature-Inspired Biomolecular Corona Based on Poly(caffeic acid) as a Low Potential and Time-Stable Glucose Biosensor. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217281
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuznowicz, Maria, Artur Jędrzak, and Teofil Jesionowski. 2023. "Nature-Inspired Biomolecular Corona Based on Poly(caffeic acid) as a Low Potential and Time-Stable Glucose Biosensor" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217281
APA StyleKuznowicz, M., Jędrzak, A., & Jesionowski, T. (2023). Nature-Inspired Biomolecular Corona Based on Poly(caffeic acid) as a Low Potential and Time-Stable Glucose Biosensor. Molecules, 28(21), 7281. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217281








