Detection of VOCs and Biogenic Amines Through Luminescent Zn–Salen Complex-Tethered Pyrenyl Arms
Abstract
1. Introduction
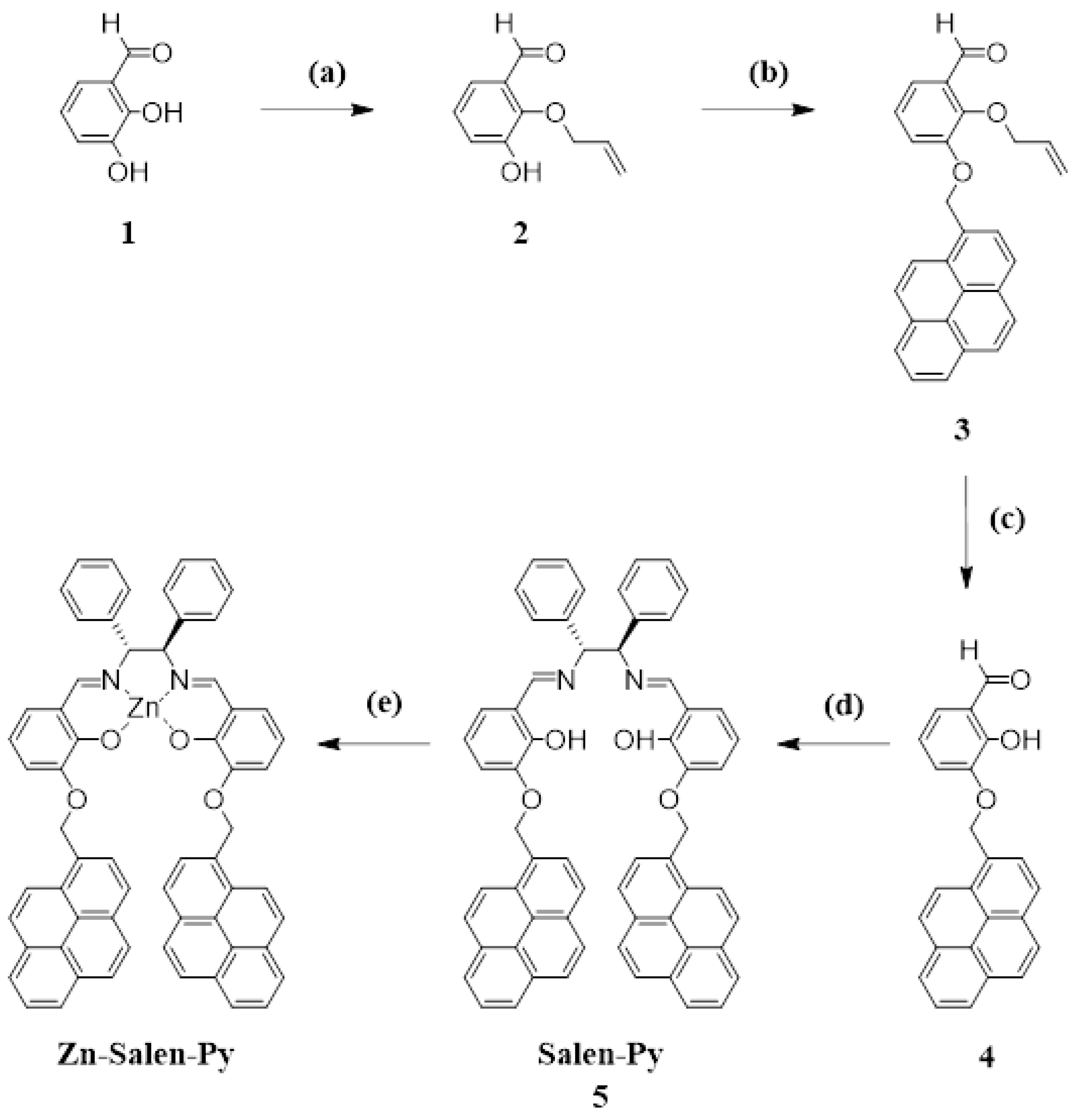
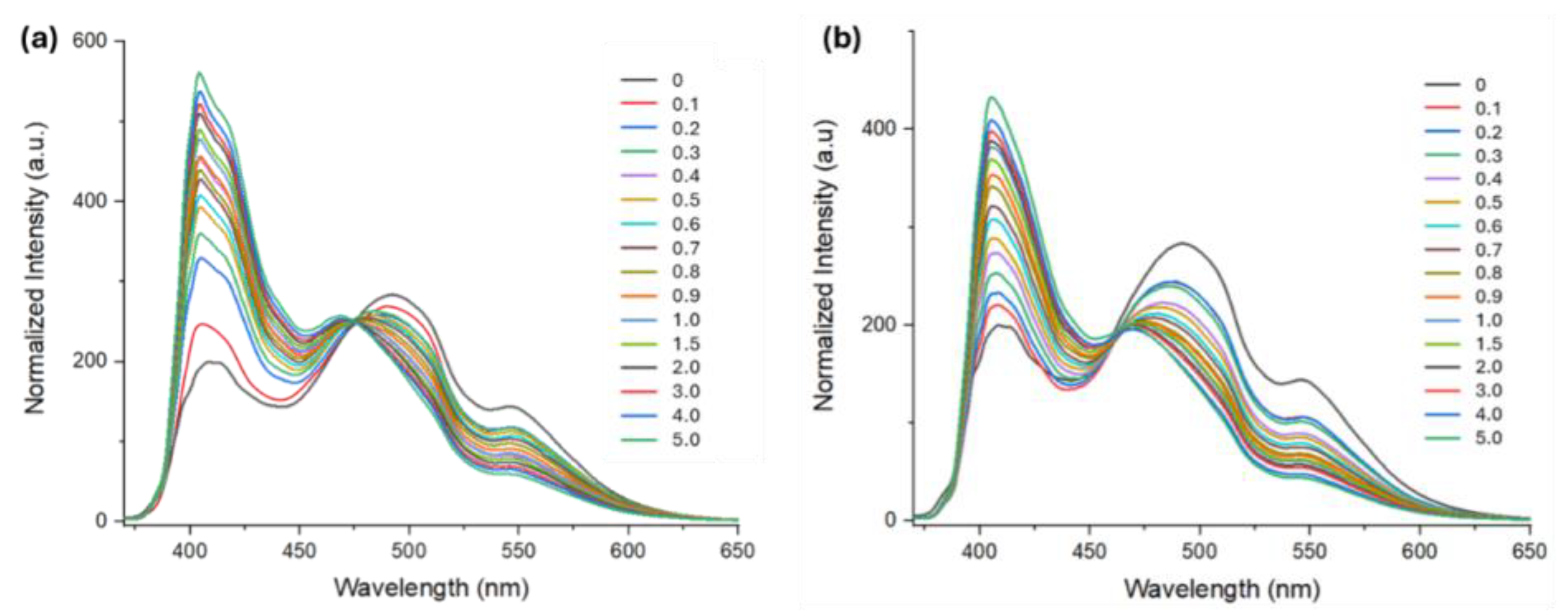
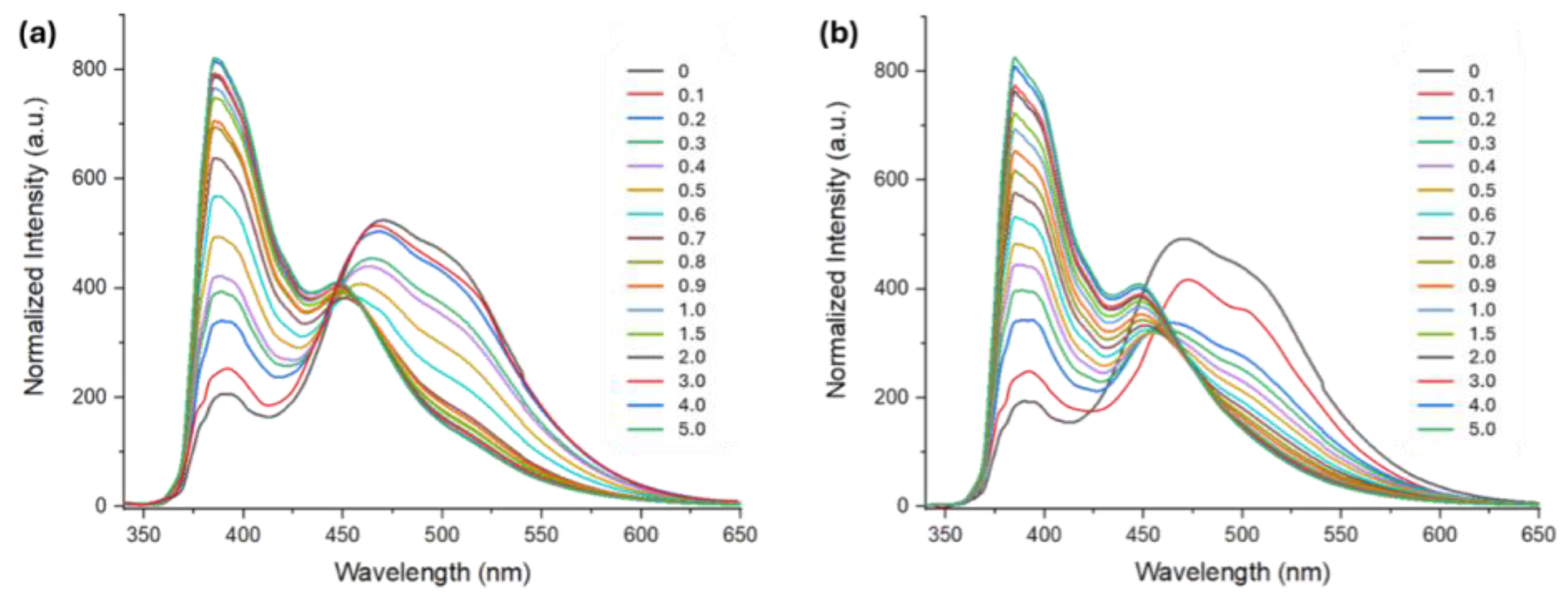
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sellegri, K.; Hanke, M.; Umann, B.; Arnold, F.; Kulmala, M. Measurements of Organic Gases During Aerosol Formation Events in the Boreal Forest Atmosphere During QUEST. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-K. Amines as Occupational Hazards for Visual Disturbance. Ind. Health 2016, 54, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poste, A.E.; Grung, M.; Wright, R.F. Amines and Amine-Related Compounds in Surface Waters: A Review of Sources, Concentrations and Aquatic Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Wexler, A.S.; Clegg, S.L. Atmospheric Amines—Part I. A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 524–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangotra, A.; Singh, S.K. Volatile Organic Compounds: A Threat to the Environment and Health Hazards to Living Organisms—A Review. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 382, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha Turna, N.; Chung, R.; McIntyre, L. A Review of Biogenic Amines in Fermented Foods: Occurrence and Health Effects. Heliyon 2024, 10, 24501–24512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeun, D.; Davaatseren, M.; Chung, M.-S. Biogenic Amines in Foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaguey-Hernández, Y.; Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Ojeda-Ramirez, D.; Añorve-Morga, J.; González-Olivares, L.G.; Castañeda-Ovando, A. Biogenic Amines Levels in Food Processing: Efforts for Their Control in Foodstuffs. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110341–110354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.R. Significance of Biogenic Amines to Food Safety and Human Health. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainetdinov, R.R.; Hoener, M.C.; Berry, M.D.; Witkin, J.M. Trace Amines and Their Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 549–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hembury, G.A.; Borovkov, V.V.; Inoue, Y. Chirality-Sensing Supramolecular Systems. Chem. Rev. 2007, 108, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes Müller, D.; Quadro Oreste, E.; Grazielle Heinemann, M.; Dias, D.; Kessler, F. Biogenic Amine Sensors and its Building Materials: A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 175, 111221–111241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, A.; Hwang, H.-J.; Mah, J.-H. Validation of an HPLC Analytical Method for Determination of Biogenic Amines in Agricultural Products and Monitoring of Biogenic Amines in Korean Fermented Agricultural Products. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tırıs, G.; Sare Yanıkoğlu, R.; Ceylan, B.; Egeli, D.; Kepekci Tekkeli, E.; Önal, A. A Review of the Currently Developed Analytical Methods for the Determination of Biogenic Amines in Food Products. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Q.; Li, G.; An, T. A New Method of Simultaneous Determination of Atmospheric Amines in Gaseous and Particulate Phases by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 114, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, L.R.; Manchanda, A.K.; Singh, G.; Verma, R.S. Cyclic Voltammetry of Aromatic Amines in Aqueous and non-Aqueous Media. Electrochim. Acta 1982, 27, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yue, C.; Ke, Y.; Qu, H.; Zeng, L. Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Biogenic Amines, Nitrite and Sulfite in Food: Progress, Challenges and Perspective. Adv. Agrochem. 2023, 2, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, T.; Cao, H.; Zhang, J.; James, T.D.; Sun, X. Fluorometric Detection of Volatile Amines Using an Indanonalkene Platform. Org. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Garai, B.; Prakasam, T.; Benyettou, F.; Varghese, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Gándara, F.; Pasricha, R.; Baias, M.; Jagannathan, R.; et al. Fluorescence Turn on Amine Detection in a Cationic Covalent Organic Framework. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-X.; Yan, Z.-J.; Liu, W.-X.; Chen, X.-M.; Ding, M.-H.; Tang, L.-L.; Zeng, F. Rapid and Visual Detection of Volatile Amines Based on Their Gas–Solid Reaction with Tetrachloro-p-Benzoquinone. Molecules 2024, 29, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, N.; Zedler, L.; Mayerhöfer, T.G.; Mohr, G.J. Functional Liquid Crystal Films Selectively Recognize Amine Vapours and Simultaneously Change Their Colour. Chem. Commun. 2006, 14, 1512–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpel, J.E.; Wouters, C.; Herzer, N.; Ziegler, J.; Broer, D.J.; Bastiaansen, C.W.M.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. An Optical Sensor for Volatile Amines Based on an Inkjet-Printed, Hydrogen-Bonded, Cholesteric Liquid Crystalline Film. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelen, Y.; Puglisi, R.; Debije, M.G.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Photonic Liquid Crystal Polymer Absorbent for Immobilization and Detection of Gaseous Nerve Agent Simulants. ACS Appl. Opt. Mater. 2022, 1, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ran, X.; Tang, H.; Cao, D. Recent Advances on Reaction-Based Amine Fluorescent Probes. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 194, 109634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Carpentier, R.; Lepeintre, M.; Testa, C.; Pappalardo, A.; Bartik, K.; Jabin, I. Development of a Cone Homooxacalix[3]arene-Based Fluorescent Chemosensor for the Selective Detection of Biogenic Ammonium Ions in Protic Solvents. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 10903–10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Hou, X.; Yang, H.; Zou, Y.; Ju, P. A Novel Bicoumarin-Based Multifunctional Fluorescent Probe for Naked-Eye Sensing of Amines/Ammonia. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Youa, J.; Ju, P. A Novel Biomass-Based Reusable AIE Material: AIE Properties and Potential Applications in Amine/Ammonia Vapor Sensing and Information Storage. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8404–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Haynes, C.J.E. Supramolecular Coordination Complexes as Optical Biosensors. ChemPlusChem 2021, 86, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, R.; Sun, Q.; Lai, W.; Su, Q.; Huang, W.; Liu, X. Recent Progress in Metal–Organic Complexes for Optoelectronic Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3259–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.W.; Hext, N.M. Supramolecular Optical Chemosensors for Organic Analytes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.; El-Zohry, A.M.; Shekhah, O.; Yin, J.; Jia, J.; Aggarwal, H.; Emwas, A.H.; Mohammed, O.F.; Eddaoudi, M. Unprecedented Ultralow Detection Limit of Amines using a Thiadiazole-Functionalized Zr(IV)-Based Metal−Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7245–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leelasree, T.; Dixit, M.; Aggarwal, H. Cobalt-Based Metal—Organic Frameworks and its Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Discriminative Sensing of Amines and On-Site Detection of Ammonia. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDenburgh, K.L.; Liu, Y.; Sadhukhan, T.; Benson, C.R.; Cox, N.M.; Erbas-Cakmak, S.; Qiao, B.; Gao, X.; Pink, M.; Raghavachari, K.; et al. Multi-State Amine Sensing by Electron Transfers in a BODIPY Probe. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, C.; Nunes, M.; Pereira, C.; Fernandes, D.M.; Peixoto, A.F.; Rocha, M. Metallo(Salen) Complexes as Versatile Building Blocks for the Fabrication of Molecular Materials and Devices with Tuned Properties. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 394, 104–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, R.; Pappalardo, A.; Gulino, A.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Supramolecular Recognition of a CWA Simulant by Metal–Salen Complexes: The First Multi-Topic Approach. Chem. Comm. 2018, 54, 11156–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attinà, A.; Oliveri, I.P.; Di Bella, S. Detection of Volatile Primary Aliphatic Amines: Highly Selective and Sensitive Vapoluminescent Sensing of n-Butylamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 419, 136414–136425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, M.; Oliveri, I.P.; Munzi, G.; Lo Presti, F.; Di Bella, S. Stimuli-Responsive Properties of a Zinc(II) Salen-Type Schiff-Base Complex and Vapochromic Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 3850–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballistreri, F.P.; Pappalardo, A.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. Heteroditopic Chiral Uranyl–Salen Receptor for Molecular Recognition of Amino Acid Ammonium Salts. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 20, 3806–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, C.; Brancatelli, G.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Geremia, S.; Pappalardo, A.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Sciotto, D. Novel Chiral (Salen)Mn(III) Complexes Containing a Calix[4]arene Unit in 1,3-Alternate Conformation as Catalysts for Enantioselective Epoxidation Reactions of (Z)-Aryl Alkenes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, R.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Sfrazzetto, G.T. Chiral Zn–Salen Complexes: A New Class of Fluorescent Receptors for Enantiodiscrimination of Chiral Amines. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, G.; Oliveri, I.P.; Punzo, F.; Thompson, A.L.; Di Bella, S.; Failla, S. Structure and Aggregation Properties of a Schiff-Base Zinc(II) Complex Derived from cis-1,2-Diaminocyclohexane. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 13040–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consiglio, G.; Failla, S.; Fortuna, C.G.; D’Urso, L.; Forte, G. Aggregation of a Zn(II)-Salen Complex: Theoretical Study of Structure and Spectra. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2015, 1067, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumur, F.; Contal, E.; Wantz, G.; Gigmes, D. Photoluminescence of Zinc Complexes: Easily Tunable Optical Properties by Variation of the Bridge Between the Imido Groups of Schiff Base Ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 25, 4186–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnik, F.M. Photophysics of Preassociated Pyrenes in Aqueous Polymer Solutions and in Other Organized Media. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 587–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, G.K.; Kim, S.H.; Sorin, E.J.; Narayanaswami, V. The Extent of Pyrene Excimer Fluorescence Emission Is a Reflector of Distance and Flexibility: Analysis of the Segment Linking the LDL Receptor-Binding and Tetramerization Domains of Apolipoprotein E3. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 6207–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Mishra, G.; Pathak, A.K.; Pandey, S.; Awasthi, C.; Pandey, M.D.; Behera, K. Pyrene-Appended Luminescent Probes for Selective Detection of Toxic Heavy Metals and Live Cell Applications. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202303914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, T. Variation of the Emission Efficiency and Wavelength from Fluorescent Zinc Salen Complexes upon Systematic Structural Modifications. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 30642–30654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, E.J.; Won, H.N.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, K.-H.; Yoon, J. Unique Blue Shift Due to the Formation of Static Pyrene Excimer: Highly Selective Fluorescent Chemosensor for Cu2+. Tetr. Lett. 2006, 47, 4577–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Adam, C.; Cockroft, S.L. Quantifying Solvophobic Effects in Nonpolar Cohesive Interactions. JACS 2015, 137, 10084–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilming, F.M.; Becker, J.; Schreiner, P.R. Quantifying Solvophobic Effects in Organic Solvents Using a Hydrocarbon Molecular Balance. JOC 2021, 87, 1874–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzewitsch, A.N.; Liu, H.; Lin, B.; Li, P.; Pellechia, P.J.; Shimizu, K.D. Empirical Model of Solvophobic Interactions in Organic Solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 63, e202314962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroselli, M.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Zhao, M.-K.; Rebek, J., Jr.; Yu, Y. C-H···X-C Bonds in Alkyl Halides Drive Reverse Selectivities in Confined Spaces. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, R.; Cavallaro, A.; Pappalardo, A.; Petroselli, M.; Santonocito, R.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G. A New BODIPY-Based Receptor for the Fluorescent Sensing of Catecholamines. Molecules 2024, 29, 3714–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroselli, M.; Saccone, M.; Cametti, M. Aryl Boronic Acids in Columnar Stacked Co-crystalline Materials: Key-Factors Governing the Assembly with Quinones. ChemPhysChem 2023, 24, e202200883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
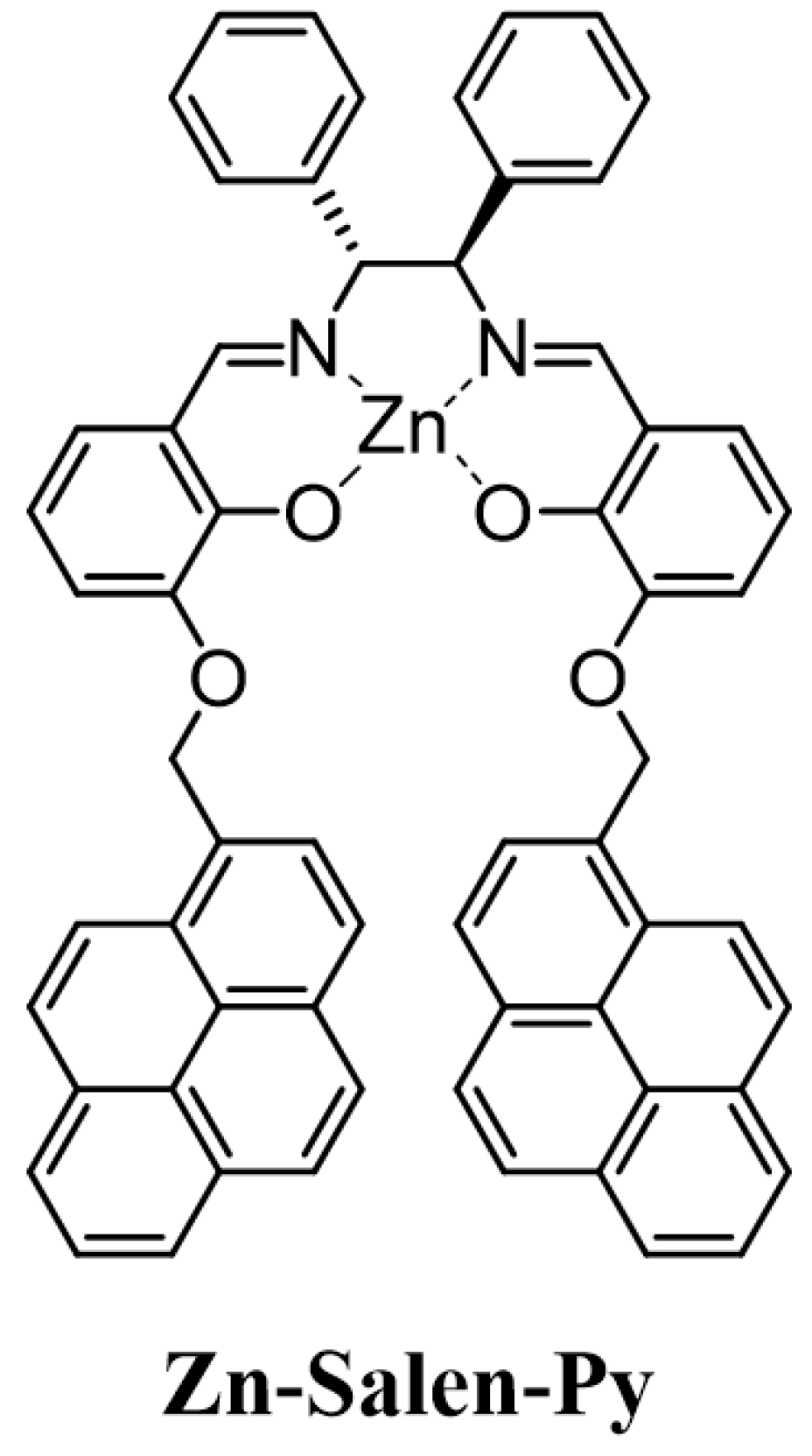
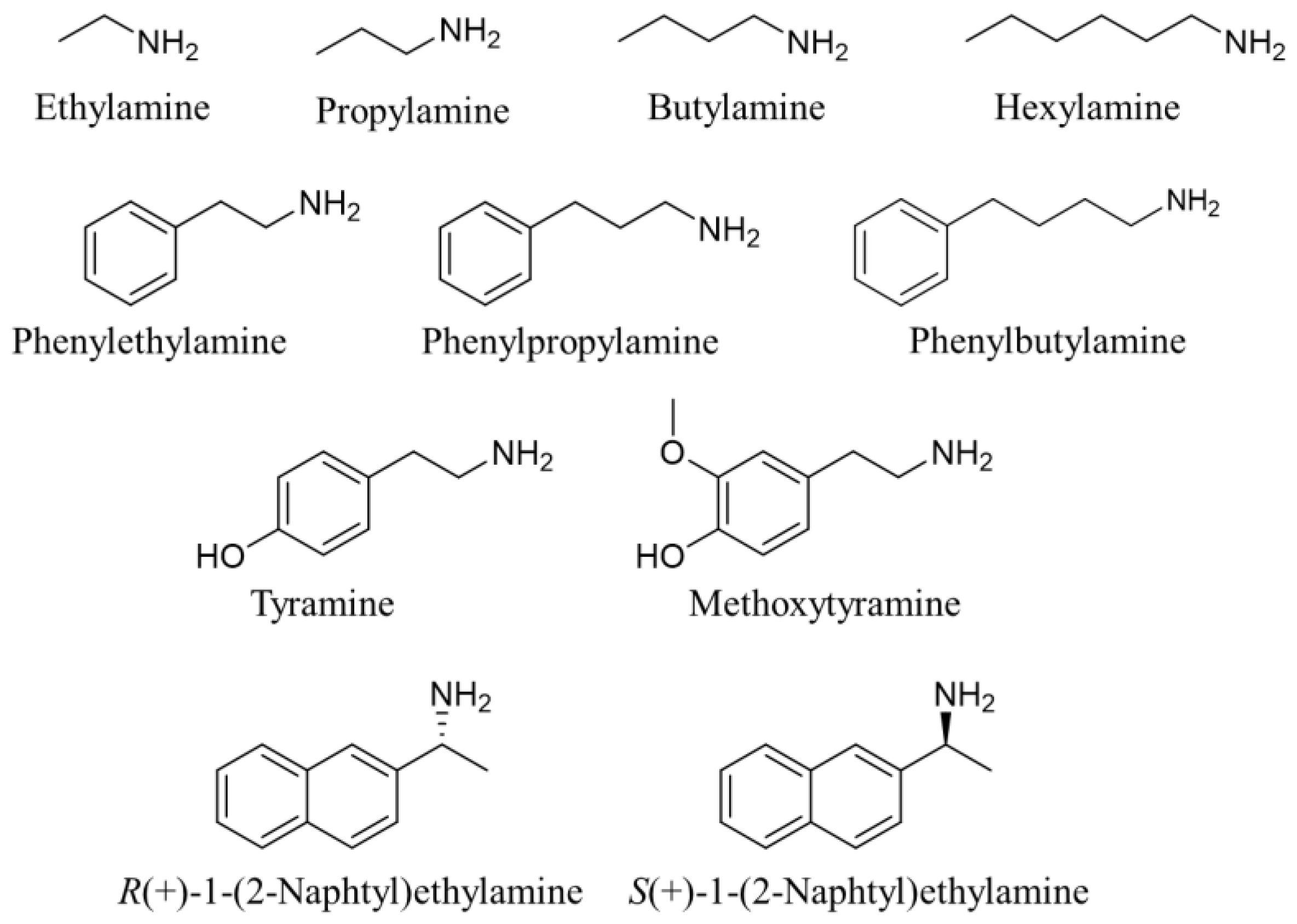
| Entry | Guest | Binding Constant (logK) a | LOD (µM) b |
| 1 c | Ethylamine | 5.34 ± 0.01 | 0.22 |
| 2 c | Propylamine | 6.03 ± 0.01 | 0.21 |
| 3 c | Butylamine | 6.21 ± 0.01 | 0.23 |
| 4 c | Hexylamine | 6.45 ± 0.02 | 0.15 |
| 5 c | Phenylethylamine | 6.39 ± 0.02 | 0.35 |
| 6 c | Phenylpropylamine | 6.45 ± 0.01 | 0.27 |
| 7 c | Phenylbutylamine | 6.49 ± 0.01 | 0.22 |
| 8 c | Tyramine | 5.90 ± 0.01 | 0.13 |
| 9 c | Methoxytyramine | 5.69 ± 0.01 | 0.17 |
| 10 d | R(+)-1-(2-Naphtyl)ethylamine | 7.59 ± 0.07 | 0.12 |
| 11 d | S(−)-1-(2-Naphtyl)ethylamine. | 5.61 ± 0.02 | 0.28 |
| Entry | Guest | Complexation Energy (Ecomplex) |
| 1 | Ethylamine | 19.2 |
| 2 | Hexylamine | 17.9 a |
| 3 | Phenylethylamine | 16.2 |
| 4 | Phenylbutylamine | 15.8 a |
| 5 | R(+)-1-(2-Naphtyl)ethylamine | 14.9 |
| 6 | S(−)-1-(2-Naphtyl)ethylamine. | 10.9 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puglisi, R.; Testa, C.; Scuderi, S.; Greco, V.; Trusso Sfrazzetto, G.; Petroselli, M.; Pappalardo, A. Detection of VOCs and Biogenic Amines Through Luminescent Zn–Salen Complex-Tethered Pyrenyl Arms. Molecules 2024, 29, 5796. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235796
Puglisi R, Testa C, Scuderi S, Greco V, Trusso Sfrazzetto G, Petroselli M, Pappalardo A. Detection of VOCs and Biogenic Amines Through Luminescent Zn–Salen Complex-Tethered Pyrenyl Arms. Molecules. 2024; 29(23):5796. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235796
Chicago/Turabian StylePuglisi, Roberta, Caterina Testa, Sara Scuderi, Valentina Greco, Giuseppe Trusso Sfrazzetto, Manuel Petroselli, and Andrea Pappalardo. 2024. "Detection of VOCs and Biogenic Amines Through Luminescent Zn–Salen Complex-Tethered Pyrenyl Arms" Molecules 29, no. 23: 5796. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235796
APA StylePuglisi, R., Testa, C., Scuderi, S., Greco, V., Trusso Sfrazzetto, G., Petroselli, M., & Pappalardo, A. (2024). Detection of VOCs and Biogenic Amines Through Luminescent Zn–Salen Complex-Tethered Pyrenyl Arms. Molecules, 29(23), 5796. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235796










