CO2 Capture: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Scalable Materials and Sustainable Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. How Is Collaboration Between Countries on Technologies for CO2 Capture?
3.2. In Which Journals Are These Technologies for CO2 Capture Being Published?
3.3. Most Relevant Keywords in CO2 Capture
3.4. Most Cited Articles on CO2 Capture
3.5. Literature Review: Emerging Technologies in CO2 Capture
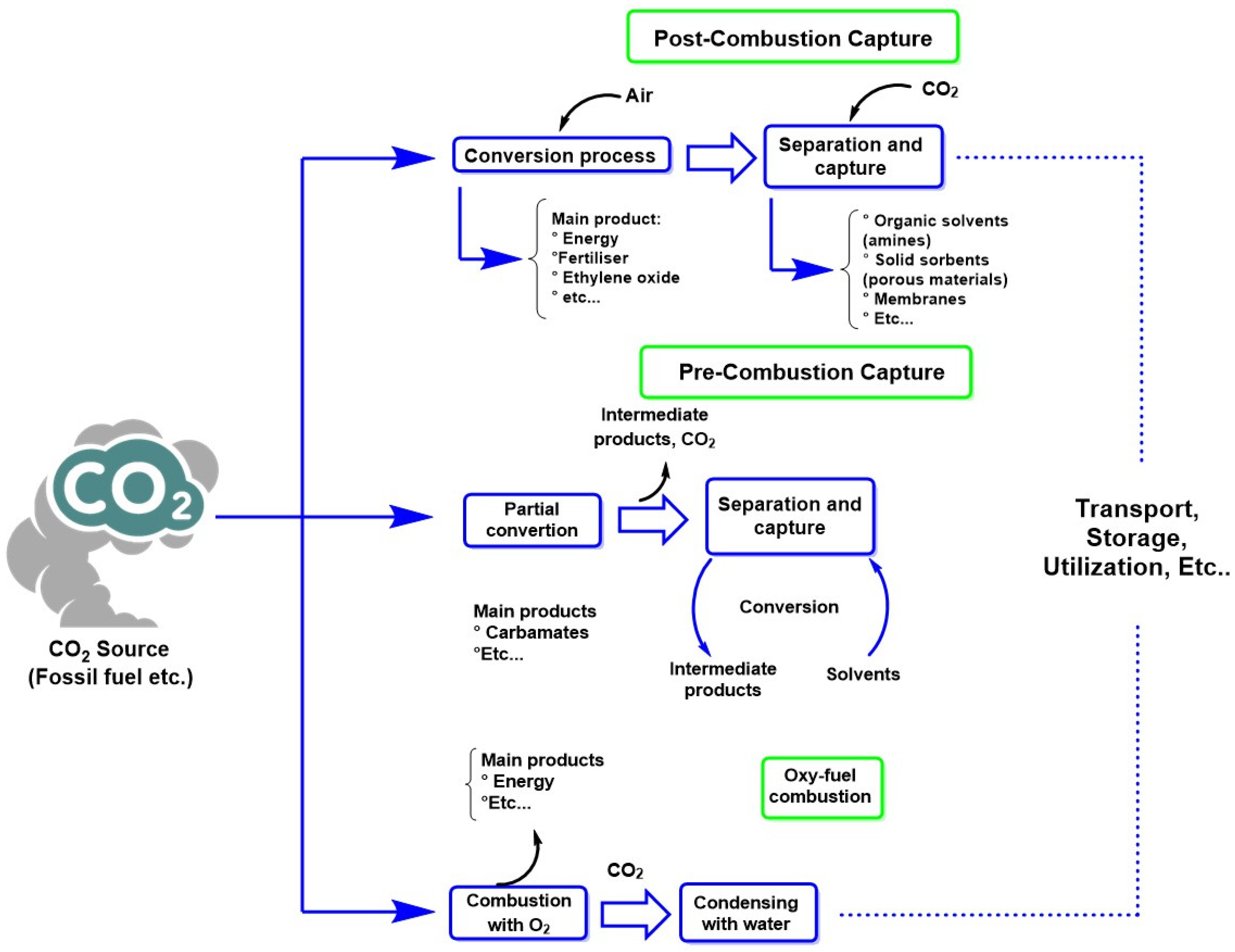
3.5.1. CO2 Capture Methods
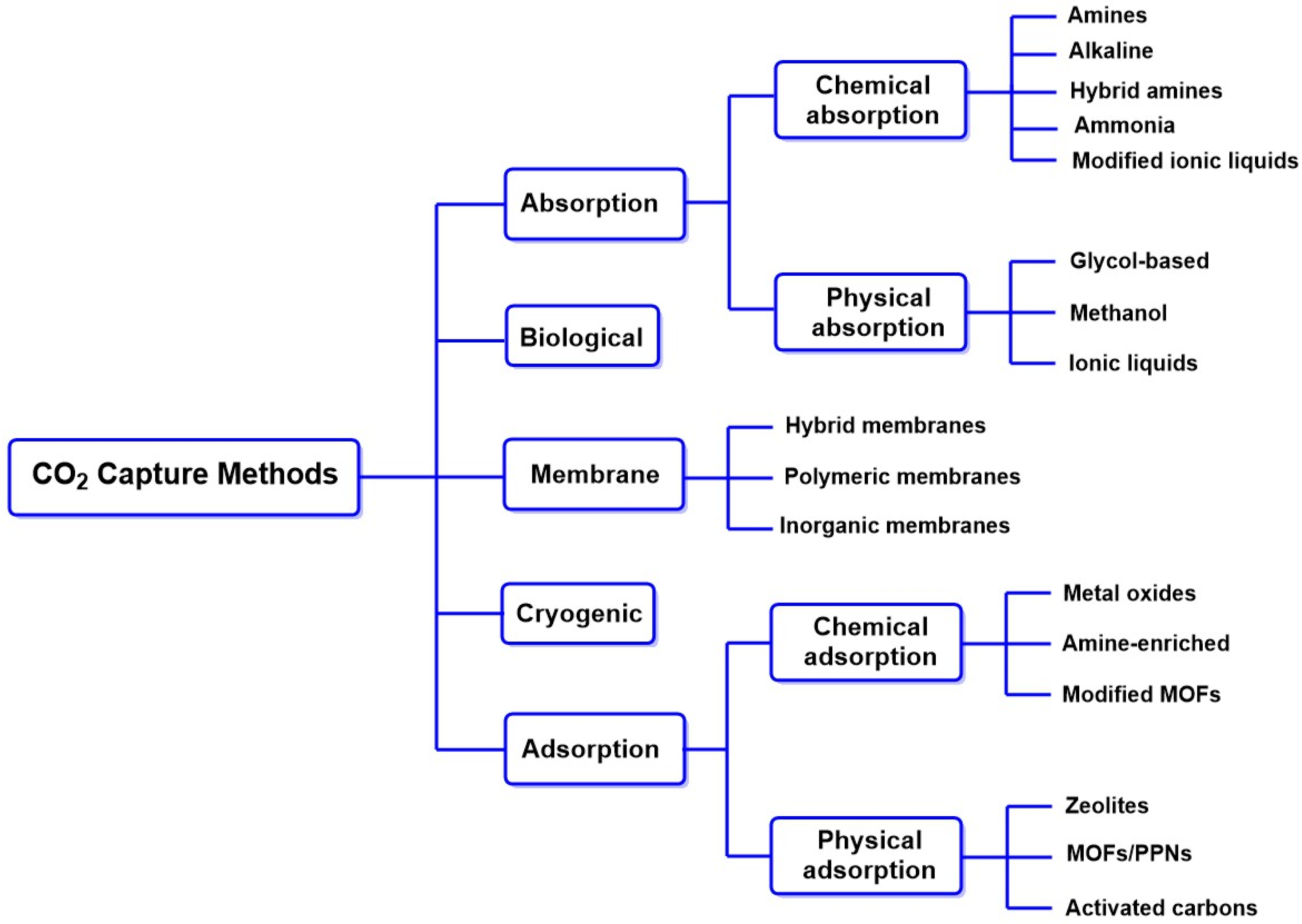
Traditional Methods of CO2 Absorption/Adsorption
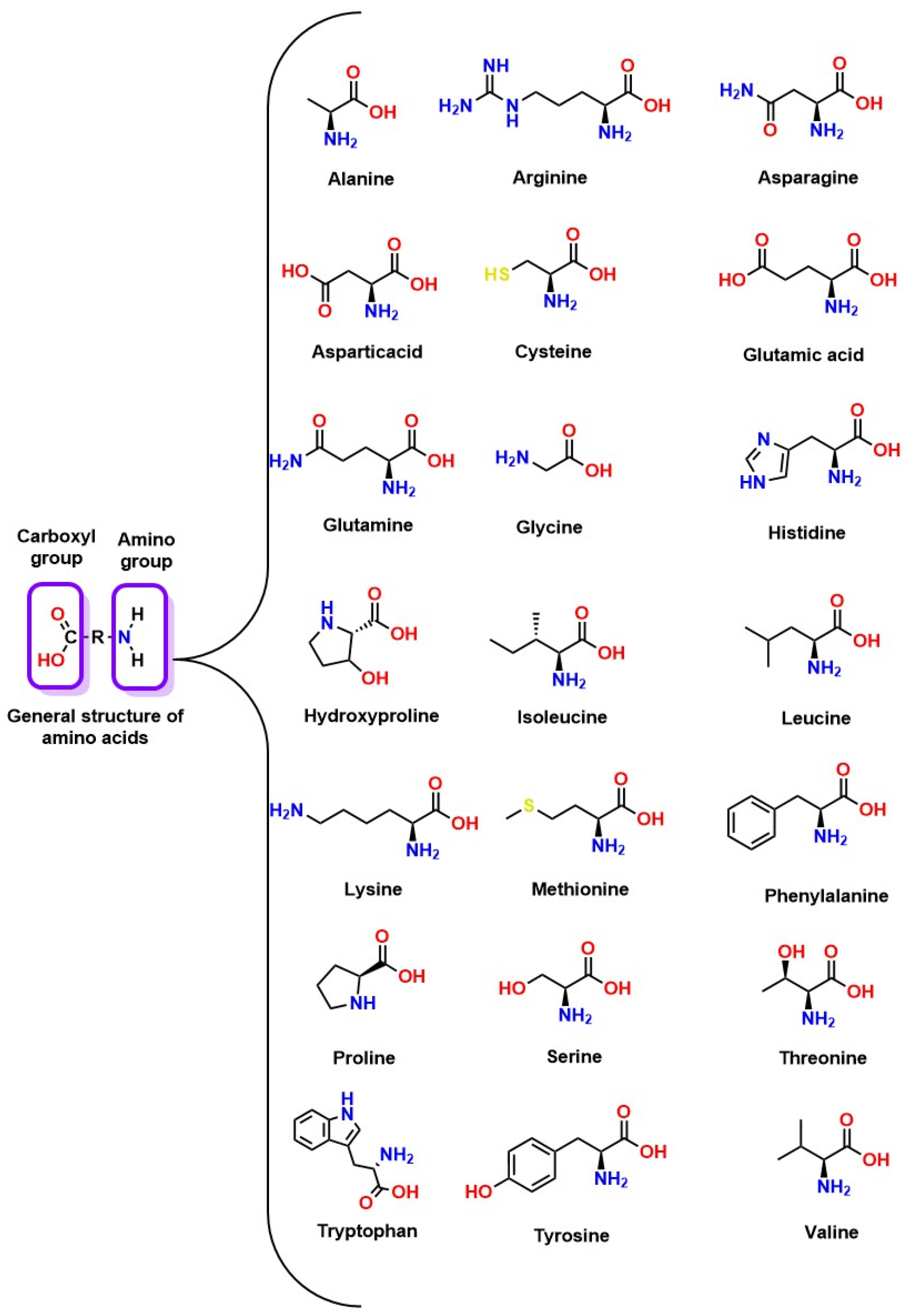
CO2 Absorption Through Amino Acids
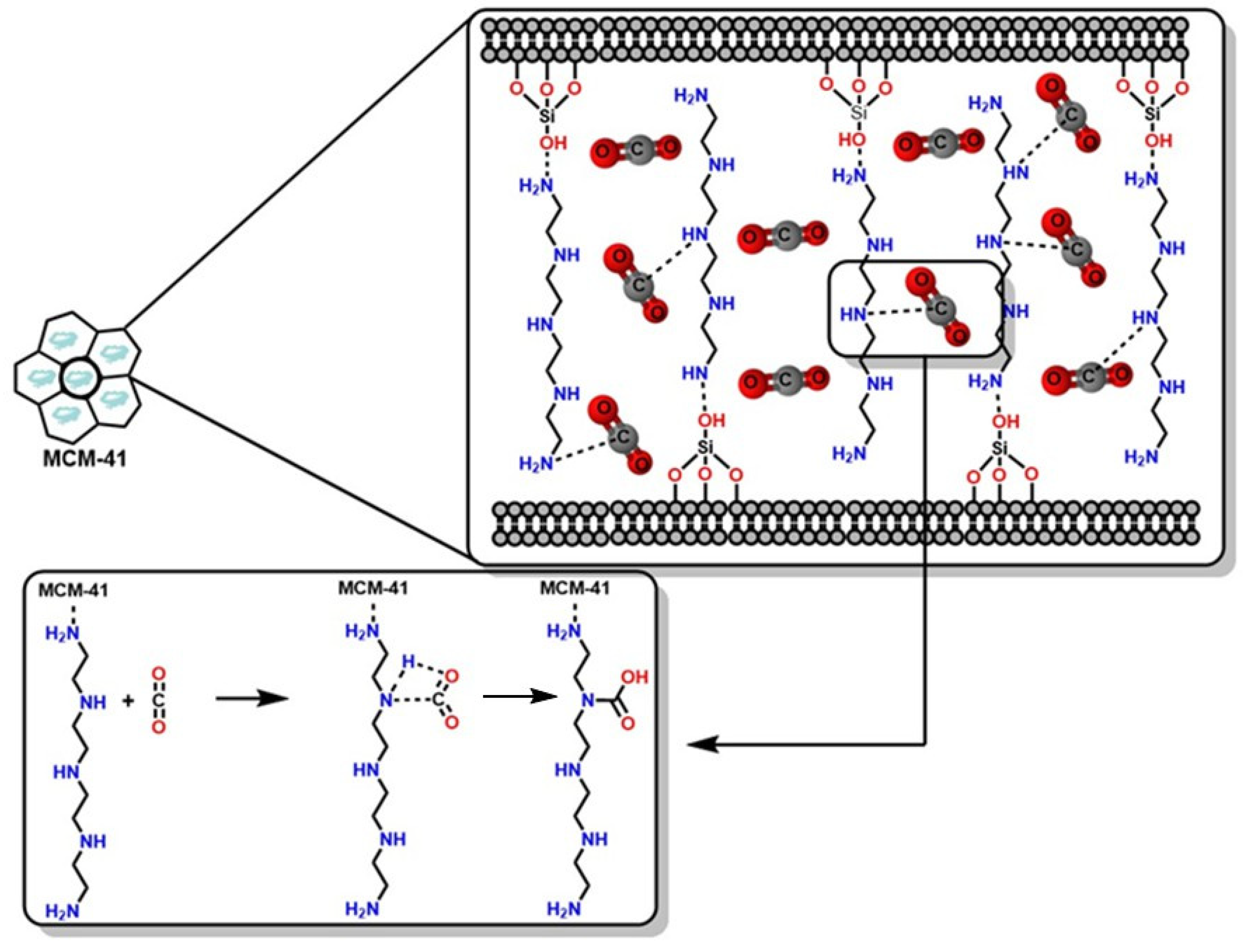
3.5.2. CO2 Adsorption Through Porous Materials
CO2 Absorption Through Functionalized Porous Materials
| Porous Material | Absorption Capacity (mg/g) | Synthesis | Mechanical Strength (MPa) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEI–MSP-0.32 | 144 ± 2.0 | One pot | 0.50 | [122] |
| PEI–MCM-41 | 76.0 | One pot | 5.50 | [124] |
| PEI–SBA | 118 ± 4.0 | One pot | 0.60 | [122] |
| PD–PEI | 53.7 | 3D printing | 0.15 | [125] |
| PEI–MCM-P | 103.8 | One pot | 0.46 | [126] |
| PD–TEPA | 98.1 | 3D printing | 0.33 | [125] |
| 5A–R4 | 60 | 3D printing | 0.35 | [127] |
| 13X–R4 | 61 | 3D printing | 0.69 | [127] |
| 70T–MM-550 | 151.1 ± 2.8 | Sol gel | 4.66 | [112] |
Adsorption of CO2 Through Polymeric Materials
Adsorption of CO2 Through Macrocyclic Polymeric Materials
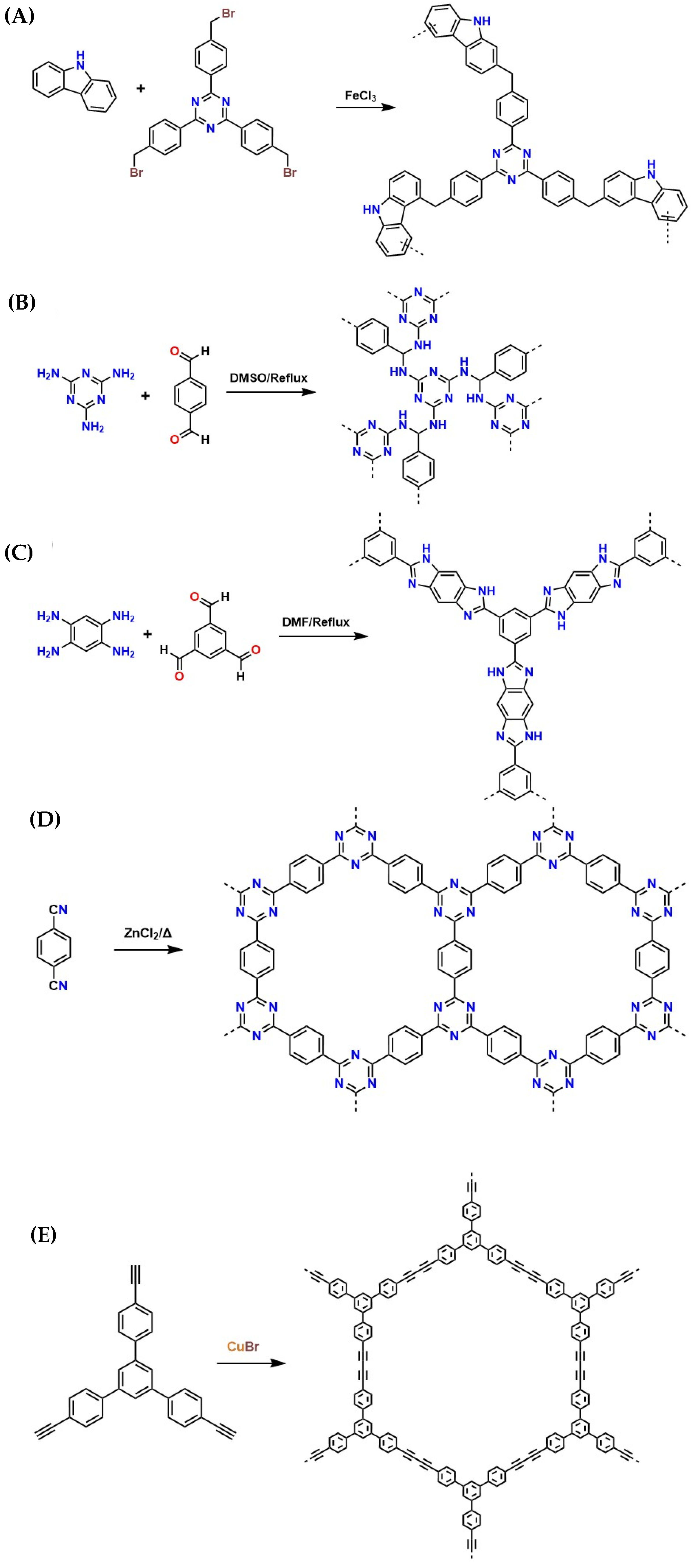
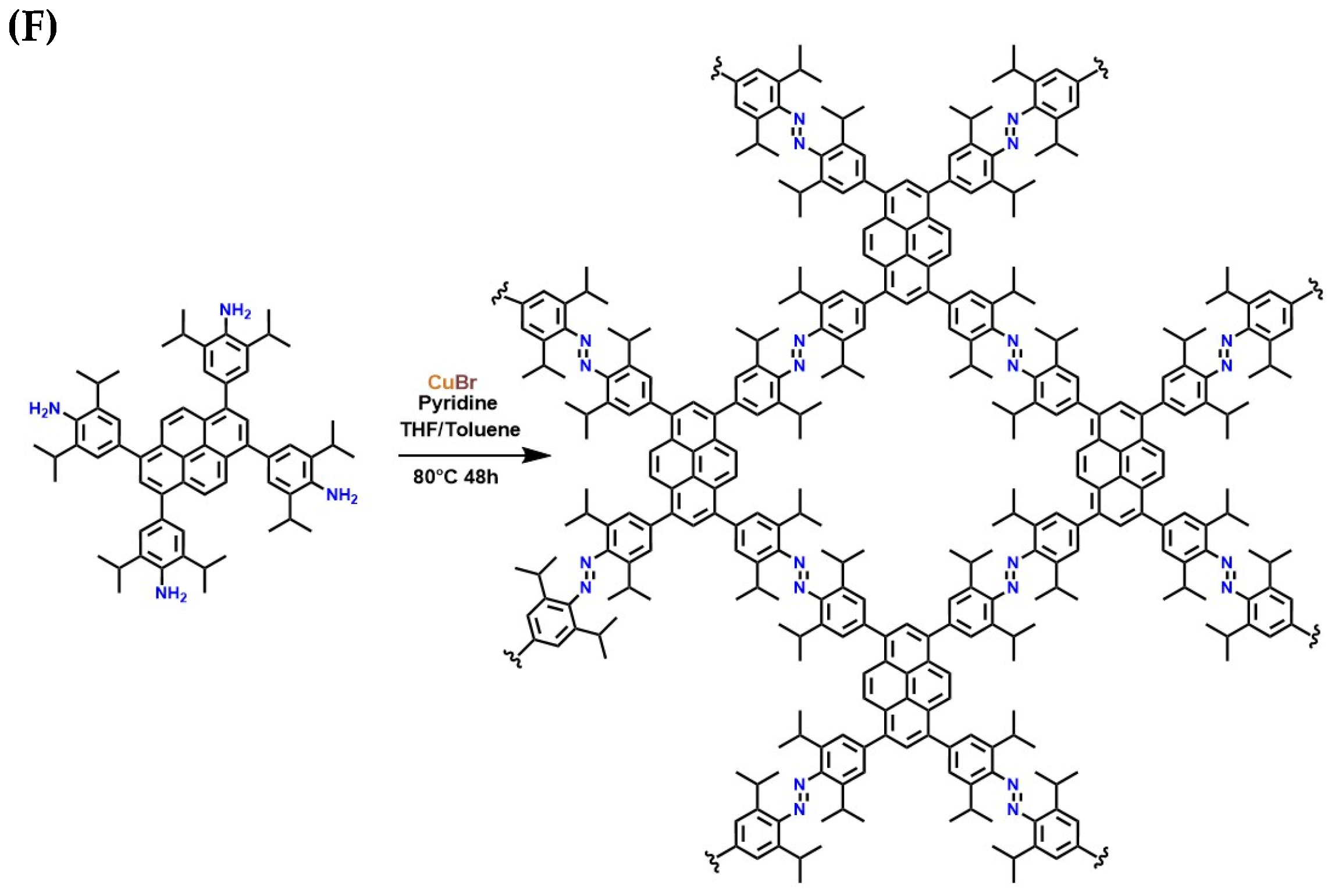
CO2 Adsorption Through MOF’s
3.5.3. Emerging Technologies for CO2 Capture
| Type of Technology | Material | Type of Amine/Polymer | Percentage of Amines/Polymer | Adsorption (mg-CO2/g-Material) | Advantages/Opportunities | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular sieve | MCM-41–PEI | PEI 1 | 75 | 215 | This mesoporous molecular sieve exhibits a synergistic effect on CO2 adsorption with PEI at 75 °C. This material increases the porosity and the diffusion of the gas through it. In addition, it improves its mechanical properties, which allows its recyclability. | Industrial scalability faces significant challenges, including high production costs due to complex synthesis processes and raw material prices. | [25] |
| Molecular sieve | PEI–MCM-41 | DEA 2/Silica | 25 | 2.41 | PEI–MCM-41 exhibits a high pore volume, allowing for a higher loading level of DEA compared to zeolite 13X. The CO2 capacity and adsorption rate of the DEA-impregnated PEI–MCM-41 reached maximum values at loading levels slightly above pore saturation. | The main disadvantages of these materials are high operating costs and incomplete desorption, which restrict their adsorption capacity. Although they have good humidity tolerance, their performance can be affected by variations in the composition of the gas stream. | [196] |
| Mesoporous silica | SBA-15 (SBA(P)) | TEPA 3 | 40 | 173 | This material is adequate for CO2 capture and has several advantages. First, it saves energy and time since the material must not be removed. The second advantage is that this material retains a slightly higher capacity for CO2 adsorption than the unmodified SBA-15 sample. Third, the existence of P123 in SBA-15 increases the reactivity against CO2 due to the presence of TEPA | Although it has a moderate adsorption capacity and good thermal stability, its main disadvantages are the material’s recyclability and high costs, which make it unsuitable for industrial scalability. | [197] |
| Molecular sieve | SBA-15 (SP) | TEPA/DEA/Sílice | 30 | 144 | Including amino groups in TEPA significantly improves the adsorption of CO2 on this amine-modified material. The presence of these groups is crucial since their absence would allow two amino groups to react with a single CO2 molecule, generating carbamate-type zwitterions. By contrast, adding hydroxyl groups using DEA prevents the formation of zwitterions by allowing only one amino group to react with each CO2 molecule. | Although this material has a moderate and long-lasting adsorption capacity, there are limitations to its recyclability and the high costs of the materials for its synthesis. In addition, its poor thermal behavior limits its application in high-temperature sectors. | [198] |
| Porous material | TEPAN/E-100AN | 4 MEA | 30 | 296 | This material allows moderate diffusion of the impregnated amines and moderate desorption, which is helpful for its recyclability under adsorption/desorption conditions. Furthermore, the initial adsorption and desorption rates shift earlier, and the ability to break the CO2 equilibrium decreases slightly when the temperature increases, indicating good desorption. Third, this material’s cyclic reproducibility are superior to those of the other materials tested, such as zeolite 13X. | One of the main disadvantages is the high synthesis costs, which can limit its industrial scalability. Another limitation is the initial desorption temperature at 75 °C, which could also be prohibitive for its application in many sectors. | [199] |
| Hyperbranched amino silica (HAS) | SBA-15 | - | - | 140 | The pore characteristics of the original SBA-15 support were physical boundaries that limited the number of amines incorporated into the adsorbent and the mass transfer to those amines. This is interesting for the study and design of polymers with specific pores. | In addition to the high production costs, this material requires functionalization to improve its CO2 capture capacity. Functionalization increases costs, which could be prohibitive for its scalability. | [200] |
The Promise of DAC in Harmful CO2 Emissions
3.5.4. Challenges to Overcome
3.5.5. Final Thoughts on the Future of Carbon Capture Technologies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramonet, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Ciais, P.; Levin, I.; Sha, M.K.; Steinbacher, M.; Sweeney, C. CO₂ in the Atmosphere: Growth and Trends Since 1850; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pressburger, L.; Dorheim, K.; Keenan, T.F.; McJeon, H.; Smith, S.J.; Bond-Lamberty, B. Quantifying Airborne Fraction Trends and the Destination of Anthropogenic CO2 by Tracking Carbon Flows in a Simple Climate Model. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 54005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. World CO2 Emissions: Simple Analysis and Its Relationship with Global Temperature Change. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 25, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Joint Research Centre. GHG Emissions of All World: 2021 Report; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Global Warming of 1.5 °C: IPCC Special Report on Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels in Context of Strengthening Response to Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-00-915794-0. [Google Scholar]
- Peres, C.B.; Resende, P.M.R.; Nunes, L.J.R.; de Morais, L.C. Advances in Carbon Capture and Use (CCU) Technologies: A Comprehensive Review and CO2 Mitigation Potential Analysis. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Application of Red Mud in Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 202, 114683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.; Roussanaly, S. CCUS Scenarios for the Cement Industry: Is CO2 Utilization Feasible? J. CO2 Util. 2022, 61, 102015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvy, R.; De Weireld, G. CO2 Utilization Technologies in Europe: A Short Review. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 2000627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.F.; First, E.L.; Boukouvala, F.; Floudas, C.A. A Multi-Scale Framework for CO2 Capture, Utilization, and Sequestration: CCUS and CCU. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2015, 81, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekemezie, I.O.; Digitemie, W.N. Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU): A Review of Emerging Applications and Challenges. Eng. Sci. Technol. J. 2024, 5, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, S.; Shreyash, N.; Singh, S.; Memon, A.R.; Sonker, M.; Tiwary, S.K.; Biswas, S. Opportunities, Challenges and the Way Ahead for Carbon Capture, Utilization and Sequestration (CCUS) by the Hydrocarbon Industry: Towards a Sustainable Future. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 15595–15616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslemani, H.; Liang, X.; Kaesehage, K.; Wilson, J. Business Models for Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Technologies in the Steel Sector: A Qualitative Multi-Method Study. Processes 2020, 8, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.; Rodosta, T.; Mahajan, K.; Damiani, D. An Overview of the Department of Energy’s CarbonSAFE Initiative: Moving CCUS toward Commercialization. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Aki, S. Hydrogel Particles for CO2 Capture. Polym. J. 2024, 56, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Du, Z.; Zou, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, C. Moisture-Responsive Hydrogel Impregnated in Porous Polymer Foam as CO2 Adsorbent in High-Humidity Flue Gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 7623–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pejcic, B.; Heath, C.; Wood, C.D. Carbon Capture with Polyethylenimine Hydrogel Beads (PEI HBs). J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 21468–21474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wood, C.D. A Highly Tunable Approach to Enhance CO2 Capture with Liquid Alkali/Amines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10874–10882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.; Adam, E.; Sabri, Y.; Myers, M.B.; Pejcic, B.; Wood, C.D. Amine-Infused Hydrogels with Nonaqueous Solvents: Facile Platforms to Control CO2 Capture Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 14758–14767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wood, C.D. Enhancing the CO2 Capture Efficiency of Amines by Microgel Particles. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2020, 103, 103172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Myers, M.B.; Versteeg, F.G.; Adam, E.; White, C.; Crooke, E.; Wood, C.D. Next Generation Amino Acid Technology for CO2 Capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 1692–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, A.; Ramazani, A.; Aghahosseini, H.; Aroua, M.K. The Application of Polymer Containing Materials in CO2 Capturing via Absorption and Adsorption Methods. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 48, 101526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatryfon, X.L.; Heliopoulos, N.S.; Molchan, I.S.; Zubeir, L.F.; Bezemer, N.D.; Arfanis, M.K.; Kontos, A.G.; Likodimos, V.; Iliev, B.; Romanos, G.E.; et al. CO2 Capture Efficiency, Corrosion Properties, and Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Amine Solutions Involving Newly Synthesized Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 12083–12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Chang, Z.; Luo, S. Progress toward Hydrogels in Removing Heavy Metals from Water: Problems and Solutions—A Review. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, C.; Andresen, J.M.; Miller, B.G.; Scaroni, A.W. Novel Polyethylenimine-Modified Mesoporous Molecular Sieve of MCM-41 Type as High-Capacity Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballew, B.S. Elsevier’s Scopus® Database. J. Electron. Resour. Med. Libr. 2009, 6, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A Tale of Two Databases: The Use of Web of Science and Scopus in Academic Papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.A.; Rodriguez-Sánchez, R.; Fdez-Valdivia, J. Ranking of the Subject Areas of Scopus. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Murdock, C.R.; Didas, S.A.; Jones, C.W. Direct Capture of CO2 from Ambient Air. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11840–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H. Recent Advances in Aerogels for Environmental Remediation Applications: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.; Linga, P.; Kumar, R.; Englezos, P. A Review of the Hydrate Based Gas Separation (HBGS) Process for Carbon Dioxide Pre-Combustion Capture. Energy 2015, 85, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.M.; Strazisar, B.R.; Granite, E.J.; Hoffman, J.S.; Pennline, H.W. Separation and Capture of CO2 from Large Stationary Sources and Sequestration in Geological Formations—Coalbeds and Deep Saline Aquifers. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2003, 53, 645–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Malfait, W.J.; Guerrero-Alburquerque, N.; Koebel, M.M.; Nyström, G. Biopolymer Aerogels and Foams: Chemistry, Properties, and Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7580–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Ho, W.S.W. Polymeric Membranes for CO2 Separation and Capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 628, 119244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Theato, P. CO2-Responsive Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; To, J.W.F.; Psarras, P.C.; Yan, H.; Atkinson, T.; Holmes, R.T.; Nordlund, D.; Bao, Z.; Wilcox, J. Tunable Polyaniline-Based Porous Carbon with Ultrahigh Surface Area for CO2 Capture at Elevated Pressure. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; He, C.; Sui, H.; He, L.; Li, X. Recent Advances of CO2-Responsive Materials in Separations. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 30, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Yang, Z.; Pan, F.; Zhou, Z.; Jing, G. Immobilization of Carbonic Anhydrase on Carboxyl-Functionalized Ferroferric Oxide for CO2 Capture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, M.; Lv, J.; Chen, K. Trends in Global Research in Forest Carbon Sequestration: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presty, R.; Massol, O.; Jagu, E.; da Costa, P. Mapping the Landscape of Carbon Dioxide Removal Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 103004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.N.; Zaidi, A.A.; Dutta, K.; Wahab, Y.A.; Jaafar, J.; Nusrat, R.; Ullah, I.; Kim, B. Past, Present and Future of Materials’ Applications for CO2 Capture: A Bibliometric Analysis. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4252–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Ghosh, P.K. The Economics of Forest Carbon Sequestration: A Bibliometric Analysis. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 2989–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkeng, A.D.N.; Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Du, W.; Qian, F. Transformation Technologies for CO2 Utilisation: Current Status, Challenges and Future Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, S.; Rodrigues de Souza, A.P.; Lobo Baeta, B.E. Technologies for Carbon Dioxide Capture: A Review Applied to Energy Sectors. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, F.; Aroua, M.K. Recent Trends in the Development of Adsorption Technologies for Carbon Dioxide Capture: A Brief Literature and Patent Reviews (2014–2018). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; Olabi, A.G.; Sayed, E.T.; Elsaid, K.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Progress in Carbon Capture Technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardisty, P.E.; Sivapalan, M.; Brooks, P. The Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Carbon Capture and Storage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 1460–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xing, L.; Opoku, K.N.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Ni, R.; Gao, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, F.; Yuan, A.; et al. Wastes against Wastes Treatment: Industrial Silica Fume Derived Porous Solid Amine Adsorbent for Efficient and Reversible Ultralow-Pressure CO2 Adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 352, 128257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, B.S.; Aksoylu, A.E. CO2 Adsorption on Chemically Modified Activated Carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyari, A.; Mofarahi, M.; Lee, C.-H. CO2 Adsorption by Conventional and Nanosized Zeolites. In Advances in Carbon Capture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 193–228. ISBN 978-0-12-819657-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sumida, K.; Rogow, D.L.; Mason, J.A.; McDonald, T.M.; Bloch, E.D.; Herm, Z.R.; Bae, T.-H.; Long, J.R. Carbon Dioxide Capture in Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 724–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meconi, G.M.; Tomovska, R.; Zangi, R. Adsorption of CO2 Gas on Graphene–Polymer Composites. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 32, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Nanomaterials for Adsorption and Conversion of CO2 under Gentle Conditions. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardsen, I.M.; Knuutila, H.K. A Review of Potential Amine Solvents for CO2 Absorption Process: Absorption Capacity, Cyclic Capacity and pKa. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2017, 61, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonenfant, D.; Mimeault, M.; Hausler, R. Determination of the Structural Features of Distinct Amines Important for the Absorption of CO2 and Regeneration in Aqueous Solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y. Phase Change Solvents for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture: Principle, Advances, and Challenges. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez-Martos, J.L.; Morrison, J.; Jauffret, G.; Elsarrag, E.; AlHorr, Y.; Imbabi, M.S.; Glasser, F.P. Environmental Assessment of Aqueous Alkaline Absorption of Carbon Dioxide and Its Use to Produce a Construction Material. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 107, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, A.; Gardoni, G.; Sponchioni, M.; Moscatelli, D. Valorisation of Glycerol and CO2 to Produce Biodegradable Polymer Nanoparticles with a High Percentage of Bio-Based Components. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 40, 101192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, K.; Taglieri, L.; Papa, A.A.; Di Lauro, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Gallifuoco, A. Non-Energy Valorization of Residual Biomasses via HTC: CO2 Capture onto Activated Hydrochars. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, C. Carbon Capture From Flue Gas and the Atmosphere: A Perspective. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 560849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakzad, P.; Mofarahi, M.; Ansarpour, M.; Afkhamipour, M.; Lee, C.-H. CO2 Absorption by Common Solvents. In Advances in Carbon Capture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 51–87. ISBN 978-0-12-819657-1. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-W.; Choi, B.-S.; Lee, J.-W. Chemical Absorption of Carbon Dioxide with Triethanolamine in Non-Aqueous Solutions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 23, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narku-Tetteh, J.; Muchan, P.; Idem, R. Effect of Alkanol Chain Length of Primary Alkanolamines and Alkyl Chain Length of Secondary and Tertiary Alkanolamines on Their CO2 Capture Activities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchan, P.; Saiwan, C.; Narku-Tetteh, J.; Idem, R.; Supap, T.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P. Screening Tests of Aqueous Alkanolamine Solutions Based on Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Structure for Blended Aqueous Amine Solution Selection in Post Combustion CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 170, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.A.; Dugas, R.; Van Wagener, D.H.; Nguyen, T.; Rochelle, G.T. Carbon Dioxide Capture with Concentrated, Aqueous Piperazine. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2010, 4, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Tan, C.-S. A Review of CO2 Capture by Absorption and Adsorption. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 745–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleman, H.; Maulud, A.S.; Man, Z. Review and Selection Criteria of Classical Thermodynamic Models for Acid Gas Absorption in Aqueous Alkanolamines. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2015, 31, 599–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Rongwong, W.; Liu, H.; Fu, K.; Gao, H.; Cao, F.; Zhang, R.; Sema, T.; Henni, A.; Sumon, K.; et al. Recent Progress and New Developments in Post-Combustion Carbon-Capture Technology with Amine Based Solvents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 40, 26–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.A.; Bogaerts, A.; De Kimpe, N.; Jacobs, P.A.; Marin, G.B.; Rabaey, K.; Saeys, M.; Verhelst, S. The Chemical Route to a Carbon Dioxide Neutral World. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, G.; Shen, Y. Absorption of Carbon Dioxide Using Ethanolamine-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10403–10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnes, J.M.; Ayash, A.A.; Dowson, G.R.M. CO2 Absorption Using Diethanolamine-Water Solutions in a Rotating Spiral Contactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Nguyen, T.; Voice, A.K.; Rochelle, G.T. Aqueous Ethylenediamine for CO2 Capture. ChemSusChem 2010, 3, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochelle, G.T. Air Pollution Impacts of Amine Scrubbing for CO2 Capture. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2024, 11, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhown, A.S.; Freeman, B.C. Analysis and Status of Post-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture Technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8624–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrag, D.P. Preparing to Capture Carbon. Science 2007, 315, 812–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadipelli, S.; Lu, Y.; Skipper, N.T.; Yildirim, T.; Guo, Z. Design of Hyperporous Graphene Networks and Their Application in Solid-Amine Based Carbon Capture Systems. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17833–17840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltsev, S.; Morris, J.; Kheshgi, H.; Herzog, H. Hard-to-Abate Sectors: The Role of Industrial Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in Emission Mitigation. Appl. Energy 2021, 300, 117322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
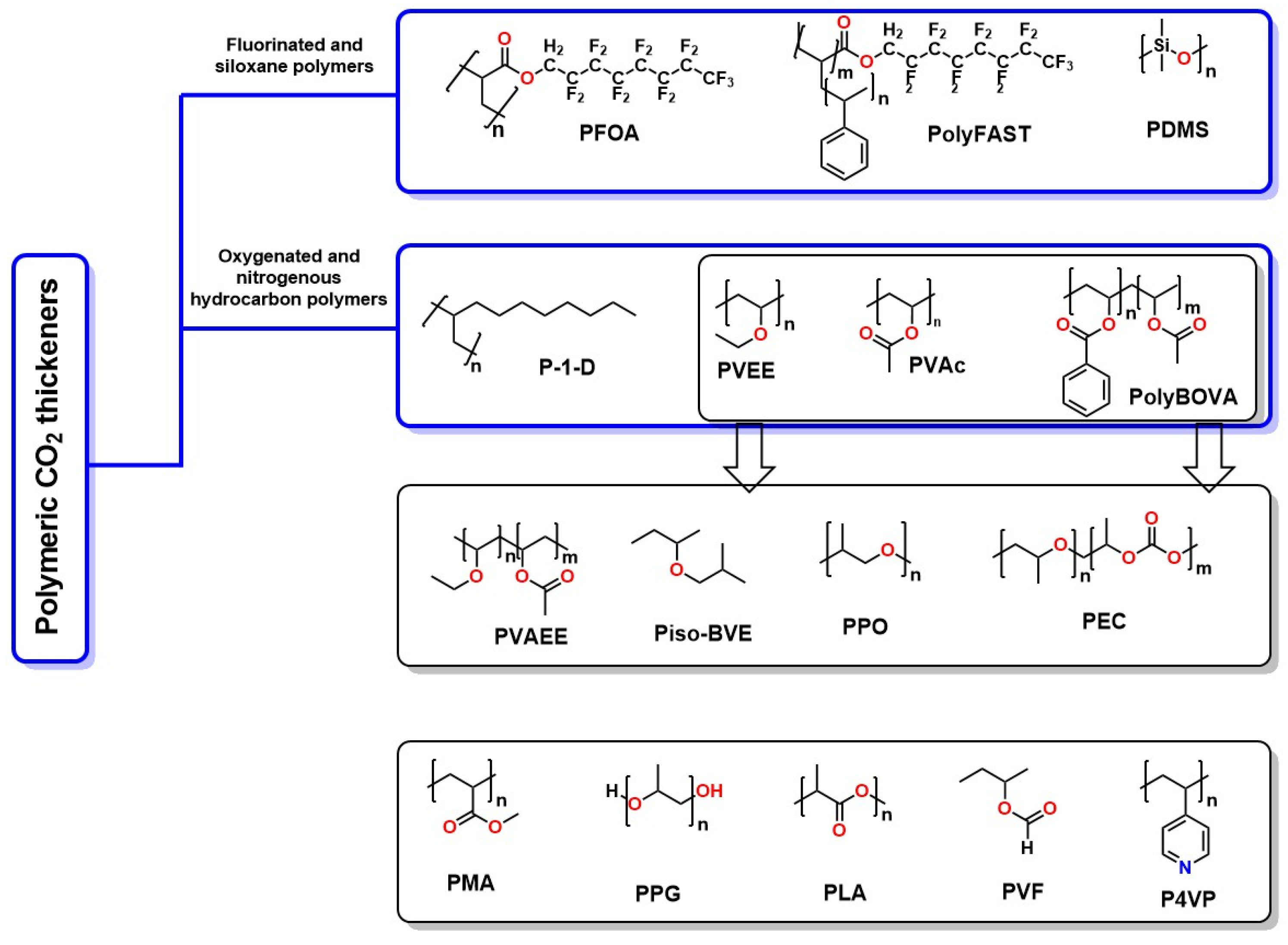
- Ricky, E.X.; Mwakipunda, G.C.; Nyakilla, E.E.; Kasimu, N.A.; Wang, C.; Xu, X. A Comprehensive Review on CO2 Thickeners for CO2 Mobility Control in Enhanced Oil Recovery: Recent Advances and Future Outlook. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 126, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSimone, J.M.; Guan, Z.; Elsbernd, C.S. Synthesis of Fluoropolymers in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. Science 1992, 257, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Siefert, N.S.; Morreale, B.D. Molecular Simulations of CO2, H2, H2O, and H2S Gas Absorption into Hydrophobic Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) Solvent: Solubility and Surface Tension. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 19253–19265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.; Firoozabadi, A. Effective Viscosification of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide by Oligomers of 1-Decene. iScience 2022, 25, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enick, R.; Beckman, E.; Hamilton, A. Inexpensive CO2 Thickening Agents for Improved Mobility Control of CO2 Floods; University of Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2005; p. 968338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Ni, R.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Deng, X. Research Progress on Supercritical CO2 Thickeners. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 5107–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Shi, J.; Cao, X.; Yuan, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Thickening Mechanism of Supercritical CO2 Thickener. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 706, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hinai, N.M.; Saeedi, A.; Wood, C.D.; Myers, M.; Valdez, R.; Sooud, A.K.; Sari, A. Experimental Evaluations of Polymeric Solubility and Thickeners for Supercritical CO2 at High Temperatures for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Gui, W.; Zhang, H.; Lv, W.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, M. Molecular Dynamics Study on the Dissolution Behaviors of Poly(Vinyl Acetate)-polyether Block Copolymers in Supercritical CO2. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, J. Research on Polyether-Based Hydrocarbon Thickener for CO2. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2021, 532, 112932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang Sefidi, V.; Luis, P. Advanced Amino Acid-Based Technologies for CO2 Capture: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20181–20194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistla, Y.S.; Khanna, A. CO2 Absorption Studies in Amino Acid-Anion Based Ionic Liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamborg, E.S.; Niederer, J.P.M.; Versteeg, G.F. Dissociation Constants and Thermodynamic Properties of Amino Acids Used in CO2 Absorption from (293 to 353) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, Y.; Jeong, S.K.; Park, K.T.; Nam, S.C. Absorption of CO2 into Aqueous Potassium Salt Solutions of L -Alanine and L -Proline. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 3910–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, A.M.; Shaikh, M.S. Aqueous Amino Acid Salts and Their Blends as Efficient Absorbents for CO2 Capture. In Energy Efficient Solvents for CO2 Capture by Gas-Liquid Absorption; Budzianowski, W.M., Ed.; Green Energy and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 117–151. ISBN 978-3-319-47261-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.; Li, Q.; Akhmedov, N.G.; Li, B.A.; Xing, M.; Wang, J.; Morsi, B.I.; Li, B. Innovative Cycling Reaction Mechanisms of CO2 Absorption in Amino Acid Salt Solvents. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 10, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Thee, H.; Tan, C.Y.; Chen, J.; Fei, W.; Kentish, S.; Stevens, G.W.; Da Silva, G. Amino Acids as Carbon Capture Solvents: Chemical Kinetics and Mechanism of the Glycine + CO2 Reaction. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 3898–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, R.; Mazinani, S.; Di Felice, R. State-of-the-Art of CO2 Capture with Amino Acid Salt Solutions. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftja, A.F.; Hartono, A.; Svendsen, H.F. Selection of Amine Amino Acids Salt Systems for CO2 Capture. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronu, U.E.; Hartono, A.; Svendsen, H.F. Kinetics of Carbon Dioxide Absorption into Aqueous Amine Amino Acid Salt: 3-(Methylamino)Propylamine/Sarcosine Solution. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 6109–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huck, J.M.; Lin, L.-C.; Berger, A.H.; Shahrak, M.N.; Martin, R.L.; Bhown, A.S.; Haranczyk, M.; Reuter, K.; Smit, B. Evaluating Different Classes of Porous Materials for Carbon Capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 4132–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao. On the Controllable Soft-Templating Approach to Mesoporous Silicates. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2821–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miricioiu, M.G.; Niculescu, V.-C. Fly Ash, from Recycling to Potential Raw Material for Mesoporous Silica Synthesis. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, M.; Hatami, M. Application of Three Dimensional Porous Aerogels as Adsorbent for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water/Wastewater: A Review Study. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, J.F.D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Ooi, R.E.H.; Foo, D.C.Y.; Tan, R.R. A Review of Optimization and Decision-Making Models for the Planning of CO2 Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Systems. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2018, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, J.; Iapichella, J.; Lefèvre, B.; Biolley, C.; Bellat, J.-P.; Fajula, F.; Galarneau, A. MCM-41 Silica Monoliths with Independent Control of Meso- and Macroporosity. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Nagai, D.; Monma, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ochiai, B. A Novel Construction of a Reversible Fixation−Release System of Carbon Dioxide by Amidines and Their Polymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2007–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglio, V.; Zaccone, C.; Vittoni, C.; Braschi, I.; Buscaroli, E.; Golemme, G.; Marchese, L.; Bisio, C. Silica Monolith for the Removal of Pollutants from Gas and Aqueous Phases. Molecules 2021, 26, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.S.; Borhan, A.; Ayoub, M.; Abd Ghani, N. Development and Progress of Functionalized Silica-Based Adsorbents for CO2 Capture. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, S.; Ghoshal, A.K. Amine Tethered Pore-Expanded MCM-41: A Promising Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yu, S.; Ma, K.; Liang, B.; Tang, S.; Liu, C.; Yue, H. Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Monolithic Adsorbents for Post-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascal-Hernandez, D.C.; Mendez-Lopez, M.; Insuasty, D.; García-Freites, S.; Sanjuan, M.; Márquez, E. Molecular Recognition between Carbon Dioxide and Biodegradable Hydrogel Models: A Density Functional Theory (DFT) Investigation. Gels 2024, 10, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panek, R.; Wdowin, M.; Franus, W.; Czarna, D.; Stevens, L.A.; Deng, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, H.; Snape, C.E. Fly Ash-Derived MCM-41 as a Low-Cost Silica Support for Polyethyleneimine in Post-Combustion CO2 Capture. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 22, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ding, L.; Kanamori, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Yang, H. Functionalization of Hierarchically Porous Silica Monoliths with Polyethyleneimine (PEI) for CO2 Adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 245, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegelman, R.L.; Kim, E.J.; Long, J.R. Porous Materials for Carbon Dioxide Separations. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, C.S.; Chuang, S.S.C. Spectroscopic Investigation into Oxidative Degradation of Silica-Supported Amine Sorbents for CO2 Capture. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Liu, M.; Sang, Y.; Huang, J. One-Pot Synthesis of Melamine-Based Porous Polyamides for CO2 Capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 285, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, S.; Jeon, S.; Deng, S.; Zhao, L.; Lee, K.B. Valorization of Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Plastic into N-Doped Microporous Carbon for CO2 Capture through a One-Pot Synthesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calleja, G.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz-Pérez, E.S. Development of High Efficiency Adsorbents for CO2 Capture Based on a Double-Functionalization Method of Grafting and Impregnation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Hwang, G.; Kim, H.; Haznedaroglu, B.Z.; Lee, B. Amine-Impregnated Millimeter-Sized Spherical Silica Foams with Hierarchical Mesoporous–Macroporous Structure for CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinthong, W.; Huang, C.-H.; Tan, C.-S. One-Pot Synthesis and Pelletizing of Polyethylenimine-Containing Mesoporous Silica Powders for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6481–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakpal, T.; Kumar, A.; Kamble, S.; Kumar, R. Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Amine Functionalized Silica Gel. Indian J. Chem. 2012, 51, 1214. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Seong, J.-K.; Jung, Y.-H.; Choi, S.-H.; Park, S.-D.; Yoon, Y.I.; Baek, I.-H. Amine Modified and Pelletized Mesoporous Materials: Synthesis, Textural–Mechanical Characterization and Application in Adsorptive Separation of Carbondioxide. Powder Technol. 2012, 219, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, H.; Eastman, S.; Al-Mamoori, A.; Hajari, A.; Rownaghi, A.A.; Rezaei, F. Formulation of Aminosilica Adsorbents into 3D-Printed Monoliths and Evaluation of Their CO2 Capture Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7489–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinthong, W.; Huang, C.-H.; Tan, C.-S. Polyallylamine and NaOH as a Novel Binder to Pelletize Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silicas for CO2 Capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, H.; Eastman, S.; Hajari, A.; Rownaghi, A.A.; Knox, J.C.; Rezaei, F. 3D-Printed Zeolite Monoliths for CO2 Removal from Enclosed Environments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27753–27761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, D.M.; Smit, B.; Long, J.R. Carbon Dioxide Capture: Prospects for New Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6058–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enjamuri, N.; Sarkar, S.; Reddy, B.M.; Mondal, J. Design and Catalytic Application of Functional Porous Organic Polymers: Opportunities and Challenges. Chem. Rec. 2019, 19, 1782–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Lyu, J.; A, S.; Xu, Q.; Newland, B.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Tai, H.; Wang, W. Complex Polymer Architectures through Free-Radical Polymerization of Multivinyl Monomers. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLachlan, M.J. Conjugated Shape-Persistent Macrocycles via Schiff-Base Condensation: New Motifs for Supramolecular Chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, P.; Modak, A.; Bhaumik, A. Porous Organic Polymers for CO2 Storage and Conversion Reactions. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Yang, W.; Feng, S.; Liu, H. Hybrid Porous Polymers Constructed from Octavinylsilsesquioxane and Benzene via Friedel–Crafts Reaction: Tunable Porosity, Gas Sorption, and Postfunctionalization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.; Branger, C.; Beurroies, I.; Denoyel, R.; Margaillan, A. Catechol Immobilized on Crosslinked Polystyrene Resins by Grafting or Copolymerization: Incidence on Metal Ions Adsorption. React. Funct. Polym. 2012, 72, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, B.; Yokota, K.; Fujii, A.; Nagai, D.; Endo, T. Reversible Trap−Release of CO2 by Polymers Bearing DBU and DBN Moieties. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusho, Y.; Endo, T. Capture and Release of CO2 by Polyamidine. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 3404–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayemiwo, K.A.; Chiarasumran, N.; Nabavi, S.A.; Loponov, K.N.; Manović, V.; Benyahia, B.; Vladisavljević, G.T. Eco-Friendly Fabrication of a Highly Selective Amide-Based Polymer for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 18160–18167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Zhao, A.; Shimizu, G.K.H.; Sarkar, P.; Gupta, R. Post-Combustion CO2 Capture Using Solid Sorbents: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 1438–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Kakimoto, K.; Ochiai, B.; Nagai, D. Synthesis and Chemical Recycling of a Polycarbonate Obtained by Anionic Ring-Opening Polymerization of a Bifunctional Cyclic Carbonate. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8177–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, J.Y.; Roth, P.J.; Evans, R.A.; Davis, T.P.; Lowe, A.B. Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain Transfer Synthesis of Amidine-based, CO2-responsive Homo and AB Diblock (Co)Polymers Comprised of Histamine and Their Gas-triggered Self-assembly in Water. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Smart Polymer Responsive to CO2. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9348–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Lee, H. A Pyrene Derived CO2-Responsive Polymeric Probe for the Turn-On Fluorescent Detection of Nerve Agent Mimics with Tunable Sensitivity. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 6888–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Feng, Y.; He, S.; Qu, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. CO2 Responsive Smart SingleWalled Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Kaleeswaran, D.; Nandi, S.; Vaidhyanathan, R.; Murugavel, R. Bulky Isopropyl Group Loaded Tetraaryl Pyrene Based Azo-Linked Covalent Organic Polymer for Nitroaromatics Sensing and CO2 Adsorption. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3572–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, A.; Pramanik, M.; Inagaki, S.; Bhaumik, A. A Triazine Functionalized Porous Organic Polymer: Excellent CO2 Storage Material and Support for Designing Pd Nanocatalyst for C–C Cross-Coupling Reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, A.; Nandi, M.; Mondal, J.; Bhaumik, A. Porphyrin Based Porous Organic Polymers: Novel Synthetic Strategy and Exceptionally High CO2 Adsorption Capacity. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kim, J.; Ahn, W.-S. Efficient Carbon Dioxide Capture over a Nitrogen-Rich Carbon Having a Hierarchical Micro-Mesopore Structure. Fuel 2012, 95, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, P.; Antonietti, M.; Thomas, A. Porous, Covalent Triazine-Based Frameworks Prepared by Ionothermal Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3450–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabensteiner, M.; Kinger, G.; Koller, M.; Gronald, G.; Hochenauer, C. Pilot Plant Study of Ethylenediamine as a Solvent for Post Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture and Comparison to Monoethanolamine. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. Liquid-Solid Phase-Change Absorption of Acidic Gas by Polyamine in Nonaqueous Organic Solvent. Fuel 2017, 209, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wan, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Conjugated Microporous Polymer Nanosheets for Overall Water Splitting Using Visible Light. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Jin, S.; Xu, H.; Nagai, A.; Jiang, D. Conjugated Microporous Polymers: Design, Synthesis and Application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.G.; Fossa, A.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Omotuyi, O.; Hylton-Edwards, H.; Dos Santos, E.M.; Gallo, A.; Liaw, C.; Toguedani, B. Advancing Sustainability through Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Technologies: The Hydrogel Case Study. J. Sustain. Dev. Law. Policy 2023, 14, 218–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, G. The Microstructure and Stability of Collagen Hydrogel Cross-Linked by Glutaraldehyde. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 130, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Shahani, S.; Sun, D.D.N.; Sharma, B.; Elisseeff, J.H.; Leong, K.W. Biodegradable and Photocrosslinkable Polyphosphoester Hydrogel. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Pei, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q. Construction of Ordered Structure in Polysaccharide Hydrogel: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Hina, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rajpar, A.H.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Alghamdi, N.A.; Wageh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Fundamental Concepts of Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Their Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
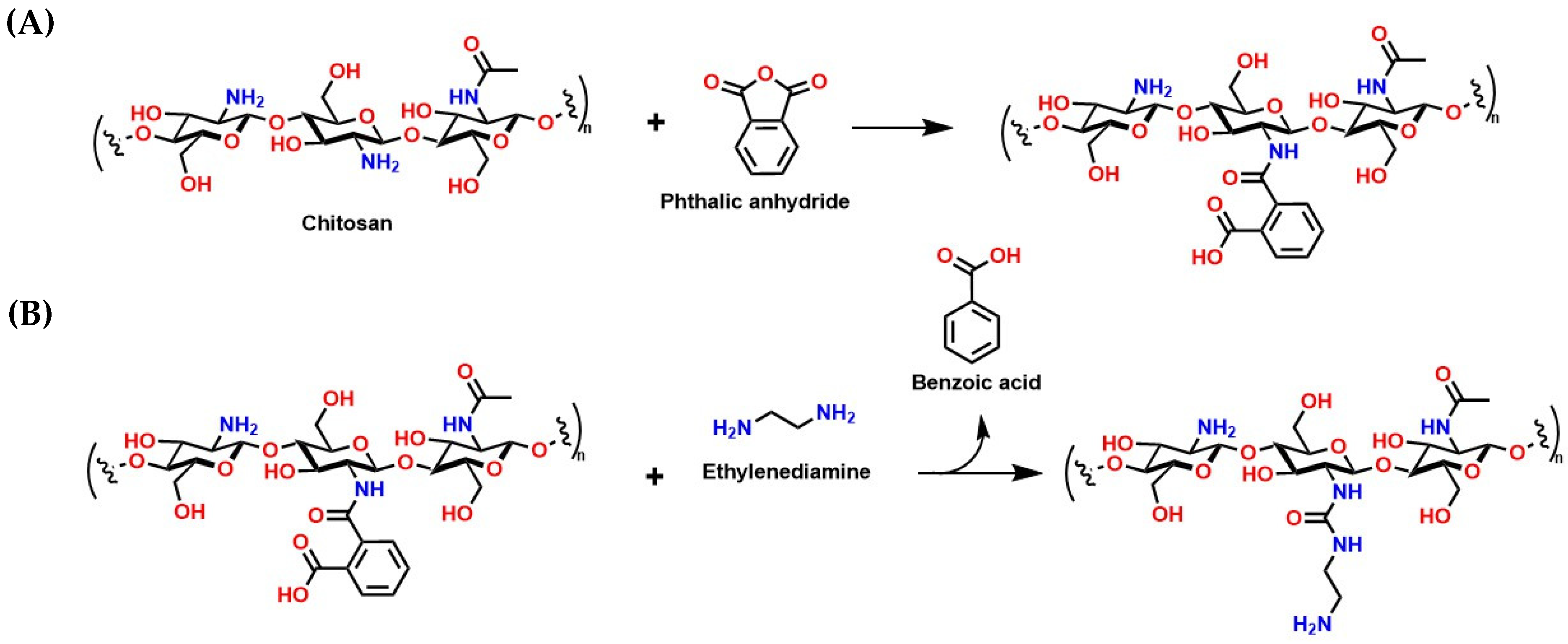
- Kumar, S.; Silva, J.D.A.E.; Wani, M.Y.; Dias, C.M.F.; Sobral, A.J.F.N. Studies of Carbon Dioxide Capture on Porous Chitosan Derivative. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronu, U.E.; Svendsen, H.F.; Hoff, K.A. Investigation of Amine Amino Acid Salts for Carbon Dioxide Absorption. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2010, 4, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Smith, K.H.; Wu, Y.; Mumford, K.A.; Kentish, S.E.; Stevens, G.W. Carbon Dioxide Capture by Solvent Absorption Using Amino Acids: A Review. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Pourebrahimi, S.; Malloum, A.; Pirooz, M.; Osagie, C.; Ghosh, S.; Zafar, M.N.; Dehghani, M.H. Hydrogel-Based Materials as Antibacterial Agents and Super Adsorbents for the Remediation of Emerging Pollutants: A Comprehensive Review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.M.; Braz, E.M.A.; Bezerra, R.D.S.; Morais, A.I.S.; Vieira, A.C.C.; Costa, M.P.; Rizzo, M.S.; Chaves, L.L.; Barreto, H.M.; Osajima, J.A.; et al. Study of the Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activity of Chitosan and Its Derivatives Chemically Modified with Phthalic Anhydride and Ethylenediamine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
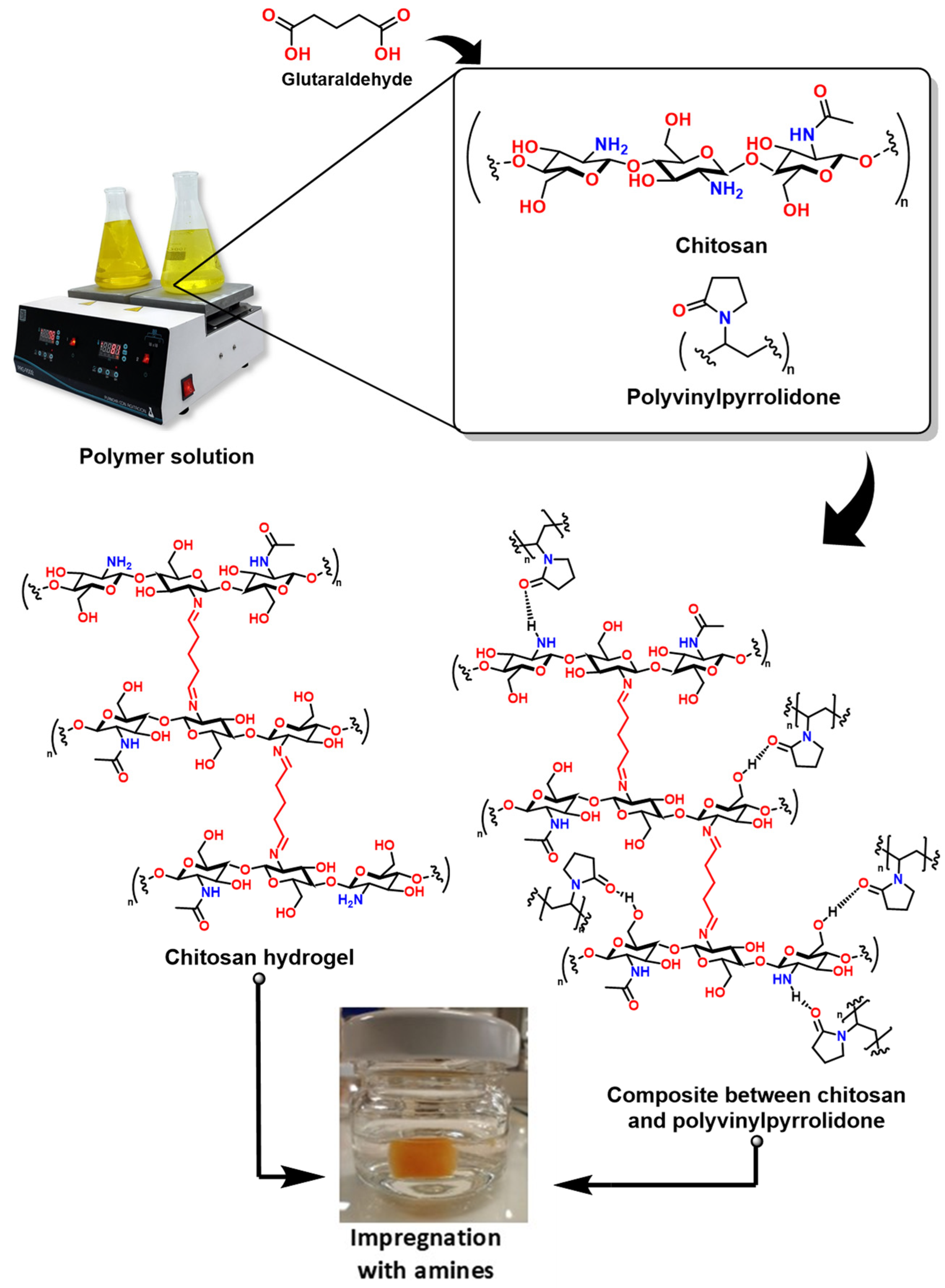
- Cigala, R.M.; De Luca, G.; Ielo, I.; Crea, F. Biopolymeric Nanocomposites for CO2 Capture. Polymers 2024, 16, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foong, S.Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Yiin, C.L.; Lock, S.S.M.; Loy, A.C.M.; Lim, J.Y.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Wan Mahari, W.A.; Liew, R.K.; Peng, W.; et al. Sustainable CO2 Capture via Adsorption by Chitosan-Based Functional Biomaterial: A Review on Recent Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 181, 113342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignard, B.; Gennen, S.; Jérôme, C.; Kleij, A.W.; Detrembleur, C. Advances in the Use of CO2 as a Renewable Feedstock for the Synthesis of Polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4466–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz, R.; Calleja, G. New Developments on Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Amine-Impregnated Silicas. Adsorption 2016, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, Z.; Edossa, G.D.; Bedasa, T.B.; Inki, L.G. Fabrication of pH-Responsive Chitosan/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Hydrogels for Controlled Release of Metronidazole and Antibacterial Properties. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.U.; Zhou, H. Recent Advances in Carbon Dioxide Capture with Metal-organic Frameworks. Greenh. Gases 2012, 2, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, A.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Metal−Organic Frameworks with Exceptionally High Capacity for Storage of Carbon Dioxide at Room Temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17998–17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, D.; Furukawa, H.; Wang, B.; Glover, T.G.; Yaghi, O.M. Highly Efficient Separation of Carbon Dioxide by a Metal-Organic Framework Replete with Open Metal Sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20637–20640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Simmons, J.M.; Srinivas, G.; Zhou, W.; Yildirim, T. Adsorption Sites and Binding Nature of CO2 in Prototypical Metal−Organic Frameworks: A Combined Neutron Diffraction and First-Principles Study. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1946–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markewitz, P.; Kuckshinrichs, W.; Leitner, W.; Linssen, J.; Zapp, P.; Bongartz, R.; Schreiber, A.; Müller, T.E. Worldwide Innovations in the Development of Carbon Capture Technologies and the Utilization of CO2. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisser, D. A Guide to Life-Cycle Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions from Electric Supply Technologies. Energy 2007, 32, 1543–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwich, E.G.; Aaberg, M.; Singh, B.; Strømman, A.H. Life-Cycle Assessment of Carbon Dioxide Capture for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 16, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziejarski, B.; Krzyżyńska, R.; Andersson, K. Current Status of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Technologies in the Global Economy: A Survey of Technical Assessment. Fuel 2023, 342, 127776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires Da Mata Costa, L.; Micheline Vaz De Miranda, D.; Couto De Oliveira, A.C.; Falcon, L.; Stella Silva Pimenta, M.; Guilherme Bessa, I.; Juarez Wouters, S.; Andrade, M.H.S.; Pinto, J.C. Capture and Reuse of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) for a Plastics Circular Economy: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuéllar-Franca, R.M.; Azapagic, A. Carbon Capture, Storage and Utilisation Technologies: A Critical Analysis and Comparison of Their Life Cycle Environmental Impacts. J. CO2 Util. 2015, 9, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Deng, Y.; Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Fan, X. Post-Combustion Carbon Capture. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Miccio, F.; Ammendola, P. Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide for Post-Combustion Capture: A Review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 12845–12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Okolie, J.A.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Niu, C.; Dalai, A.K. Review of Post-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture Technologies Using Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, D.; Gazzani, M.; Manzolini, G.; Dijk, E.V.; Carbo, M. Pre-Combustion CO2 Capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 40, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.A.M.; Chuah, C.Y.; Yang, E.; Poon, W.C. Advances in H2-Selective Metallic Membranes for Pre-Combustion CO2 Capture: A Critical Review. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirinik, M.; Ahmed, S.; Rahmanian, N. Comparative Techno-Economic Analysis of Carbon Capture Processes: Pre-Combustion, Post-Combustion, and Oxy-Fuel Combustion Operations. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziółkowski, P.; Głuch, S.; Ziółkowski, P.J.; Badur, J. Compact High Efficiency and Zero-Emission Gas-Fired Power Plant with Oxy-Combustion and Carbon Capture. Energies 2022, 15, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, S. The Energy Demand and Environmental Impacts of Oxy-Fuel Combustion vs. Post-Combustion Capture in China. Energy Strategy Rev. 2021, 38, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
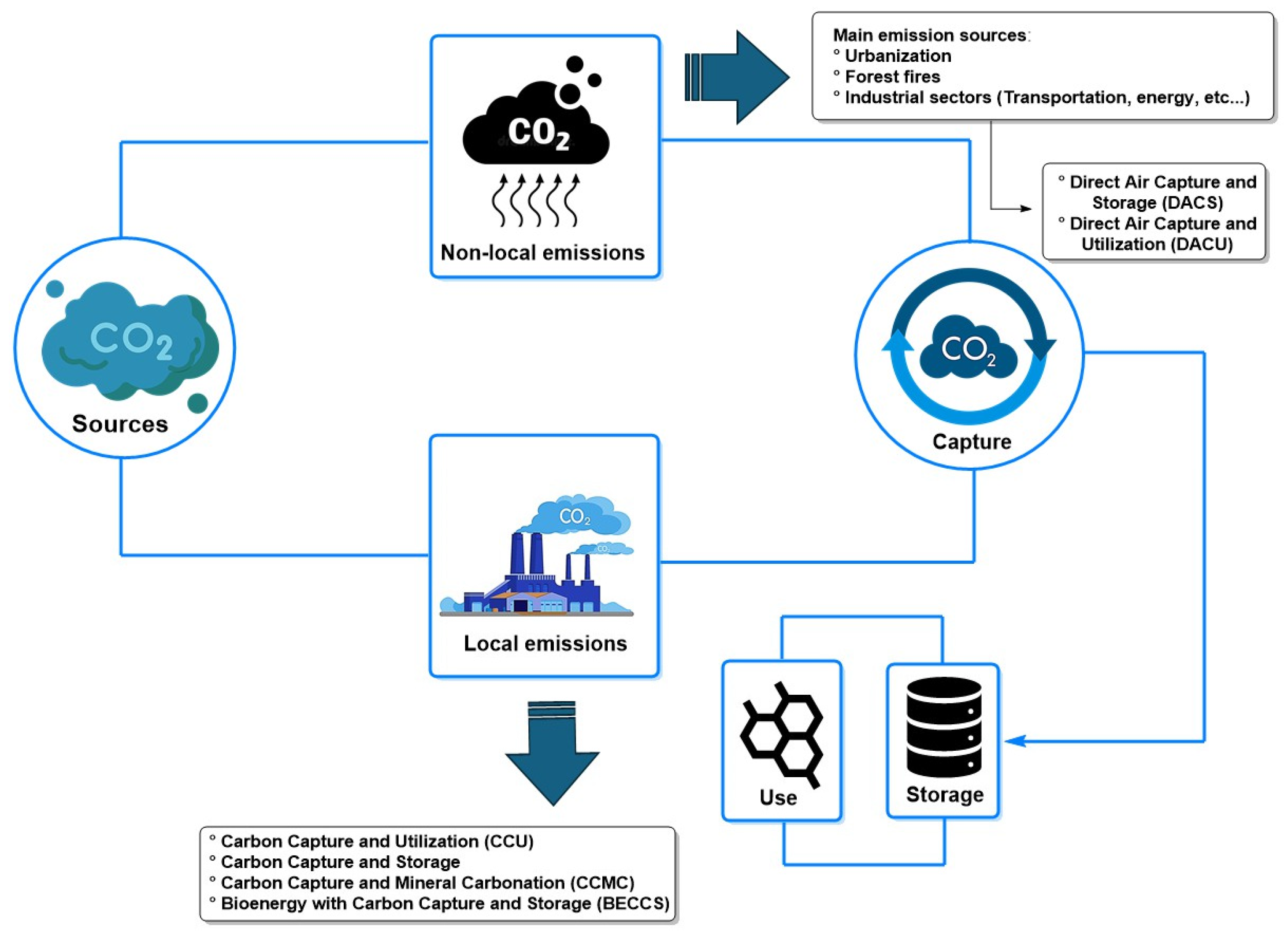
- Liu, E.; Lu, X.; Wang, D. A Systematic Review of Carbon Capture, Utilizationand Storage: Status, Progress and Challenges. Energies 2023, 16, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.; Fajardy, M.; Mac Dowell, N. Bio-Energy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS): Opportunities for Performance Improvement. Fuel 2018, 213, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, M.G.; Ritchie, J.; Shapland, J.; Pielke, R. IPCC Baseline Scenarios Have Over-Projected CO2 Emissions and Economic Growth. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamoori, A.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Rownaghi, A.A.; Rezaei, F. Carbon Capture and Utilization Update. Energy Technol. 2017, 5, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, Z. Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS). Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, R.G.; Huang, Z.; Guarnieri, M.T.; Ferrell, J.R.; Tao, L.; Schaidle, J.A. Transforming the Carbon Economy: Challenges and Opportunities in the Convergence of Low-Cost Electricity and Reductive CO2 Utilization. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 472–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, N.; Gomes, K.V.; McCormick, C.; Blumanthal, K.; Pisciotta, M.; Wilcox, J. A Review of Direct Air Capture (DAC): Scaling up Commercial Technologies and Innovating for the Future. Prog. Energy 2021, 3, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. Direct Air Capture: A Key Technology for Net Zero; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2022; ISBN 978-92-64-58587-4. [Google Scholar]
- Erans, M.; Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Hanak, D.P.; Clulow, Z.; Reiner, D.M.; Mutch, G.A. Direct Air Capture: Process Technology, Techno-Economic and Socio-Political Challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 1360–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allangawi, A.; Alzaimoor, E.F.H.; Shanaah, H.H.; Mohammed, H.A.; Saqer, H.; El-Fattah, A.A.; Kamel, A.H. Carbon Capture Materials in Post-Combustion: Adsorption and Absorption-Based Processes. C 2023, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, R.S.; Harlick, P.J.E.; Sayari, A. Applications of Pore-Expanded Mesoporous Silica. 2. Development of a High-Capacity, Water-Tolerant Adsorbent for CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 8007–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.B.; Chun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhu, J.H. CO2 Capture by As-Prepared SBA-15 with an Occluded Organic Template. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.B.; Sun, L.B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, J.H. Promoting the CO2 Adsorption in the Amine-Containing SBA-15 by Hydroxyl Group. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 114, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Filburn, T.P.; Gray, M.; Park, J.-W.; Song, H.-J. Screening Test of Solid Amine Sorbents for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 7419–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drese, J.H.; Choi, S.; Lively, R.P.; Koros, W.J.; Fauth, D.J.; Gray, M.L.; Jones, C.W. Synthesis–Structure–Property Relationships for Hyperbranched Aminosilica CO2 Adsorbents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3821–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, R. The Paris Agreement and the New Logic of International Climate Politics. Int. Aff. 2016, 92, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodiq, A.; Abdullatif, Y.; Aissa, B.; Ostovar, A.; Nassar, N.; El-Naas, M.; Amhamed, A. A Review on Progress Made in Direct Air Capture of CO2. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 102991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, R.A.; Kuuskraa, V.A.; Rossman, C.G.; Corser, M.M. Reconsidering CCS in the US Fossil-fuel Fired Electricity Industry under Section 45Q Tax Credits. Greenh. Gases 2019, 9, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Teng, F.; McLellan, B.C. A Critical Review on Deployment Planning and Risk Analysis of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) toward Carbon Neutrality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, D.; Zakharova, M. Polymeric and Crystalline Materials for Effective and Sustainable CO2 Capture. AppliedChem 2024, 4, 236–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H. Amine-Based Capture of CO2 for Utilization and Storage. Polym. J. 2021, 53, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kong, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Carbon Dioxide Capture and Methane Storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminu, M.D.; Nabavi, S.A.; Rochelle, C.A.; Manovic, V. A Review of Developments in Carbon Dioxide Storage. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 1389–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huisingh, D. Carbon Dioxide Storage Schemes: Technology, Assessment and Deployment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, A.H.; Amin, M.T.; Khan, F.; El-Halwagi, M.M. Analysis of CO2 Pipeline Regulations from a Safety Perspective for Offshore Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS). J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 439, 140734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Santivarangkna, C.; Rajput, M.S.; Benjakul, S. Trends in Shrimp Processing Waste Utilization: An Industrial Prospective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Seo, Y.; Wood, C.D. Application of Amine Infused Hydrogels (AIHs) for Selective Capture of CO2 from H2/CO2 and N2/CO2 Gas Mixture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 288, 119799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gür, T.M. Carbon Dioxide Emissions, Capture, Storage and Utilization: Review of Materials, Processes and Technologies. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 89, 100965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, R.; Wen, S.; Ning, P.; Helal, M.H.; Salem, M.A.; Xu, B.B.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Huang, M.; Guo, Z.; et al. Progress and Current Challenges for CO2 Capture Materials from Ambient Air. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 2721–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

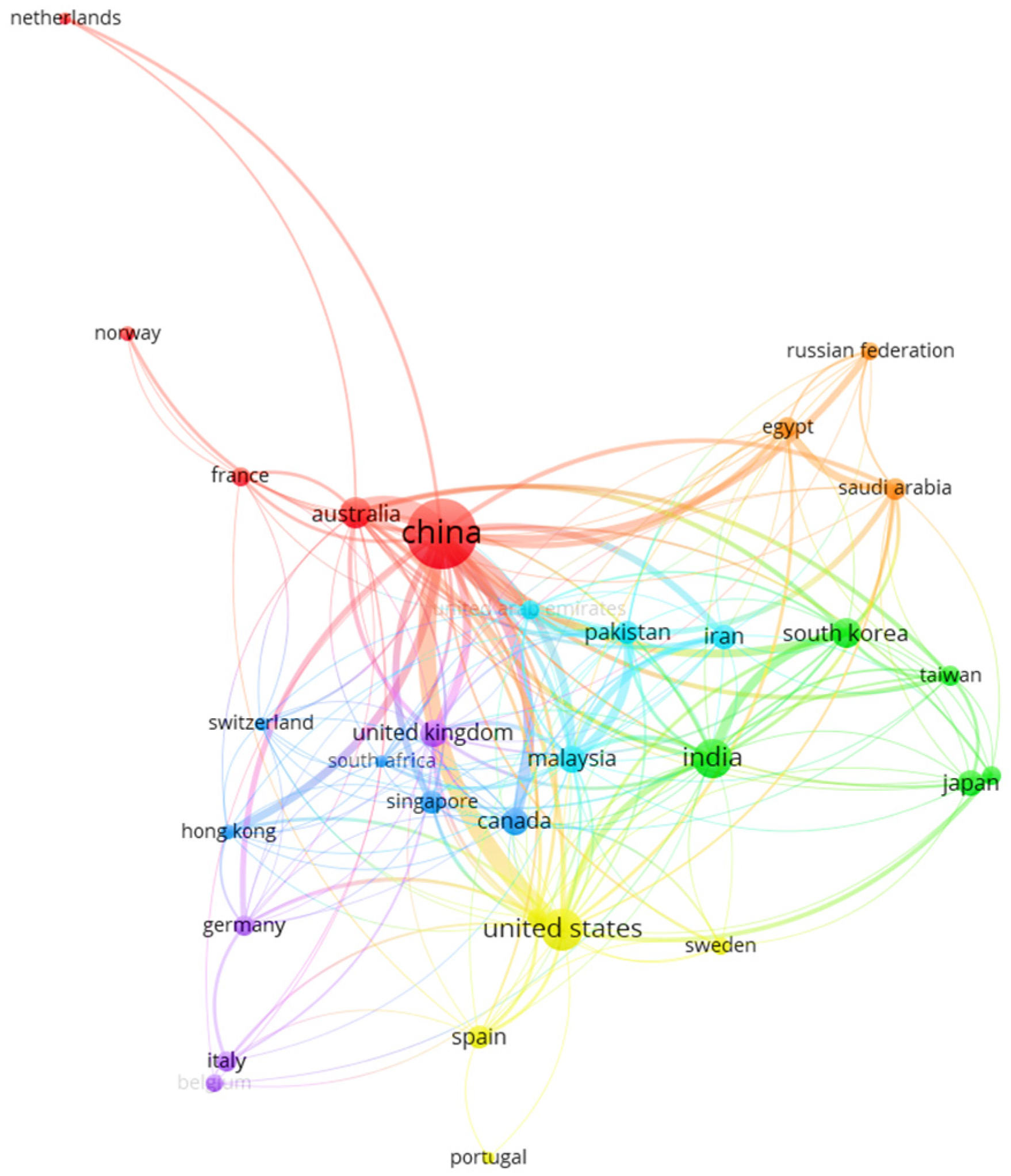

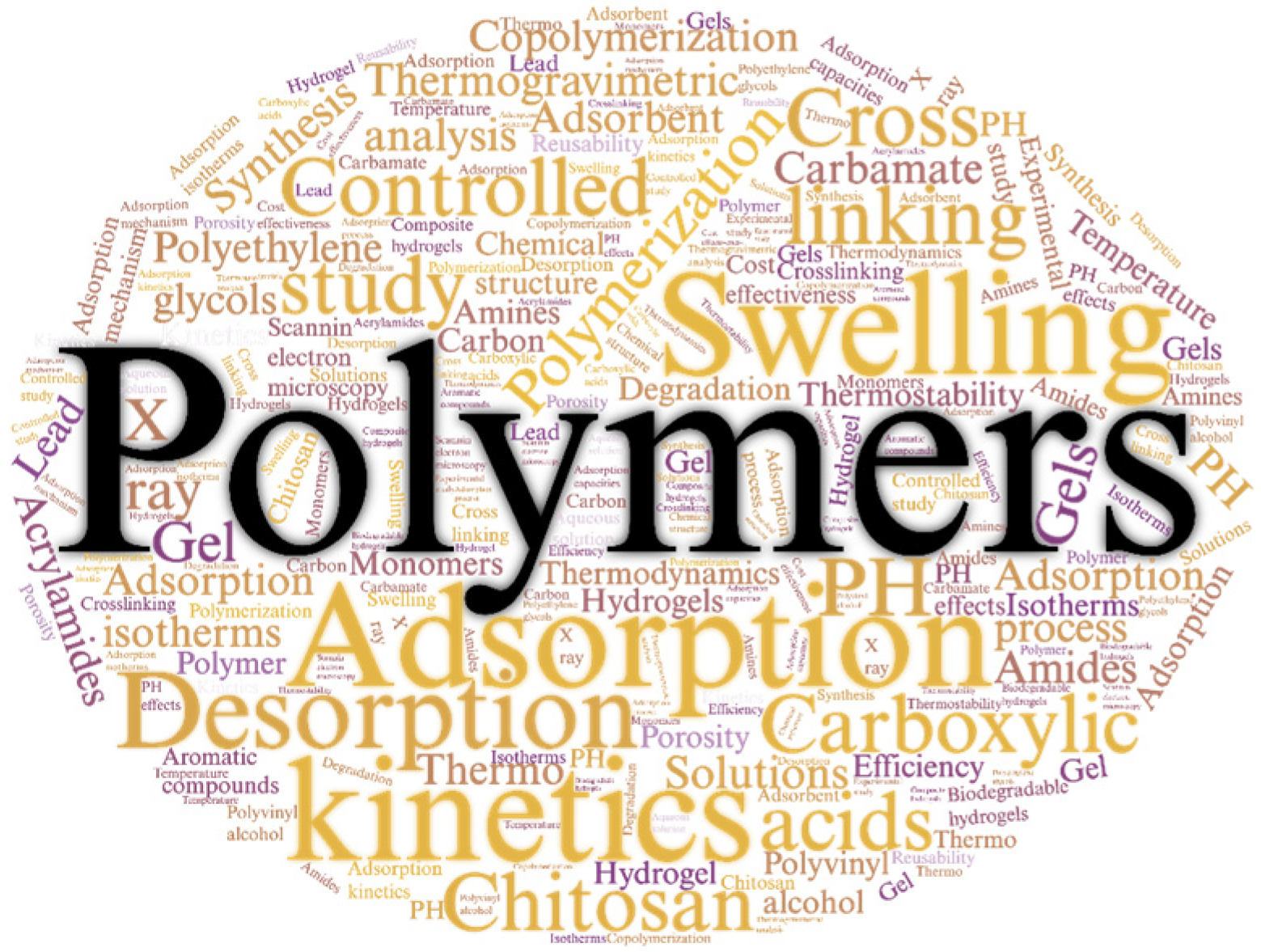
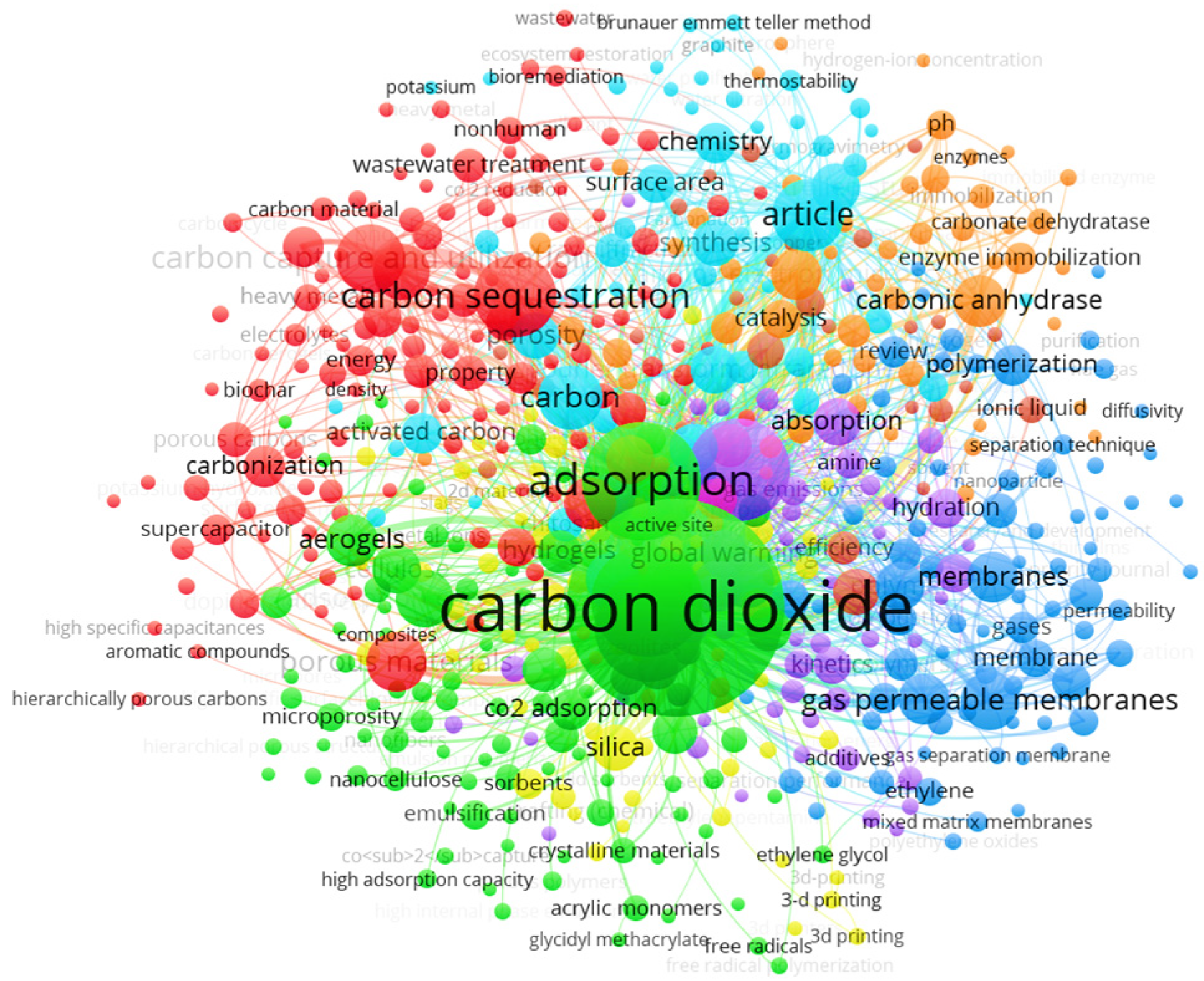
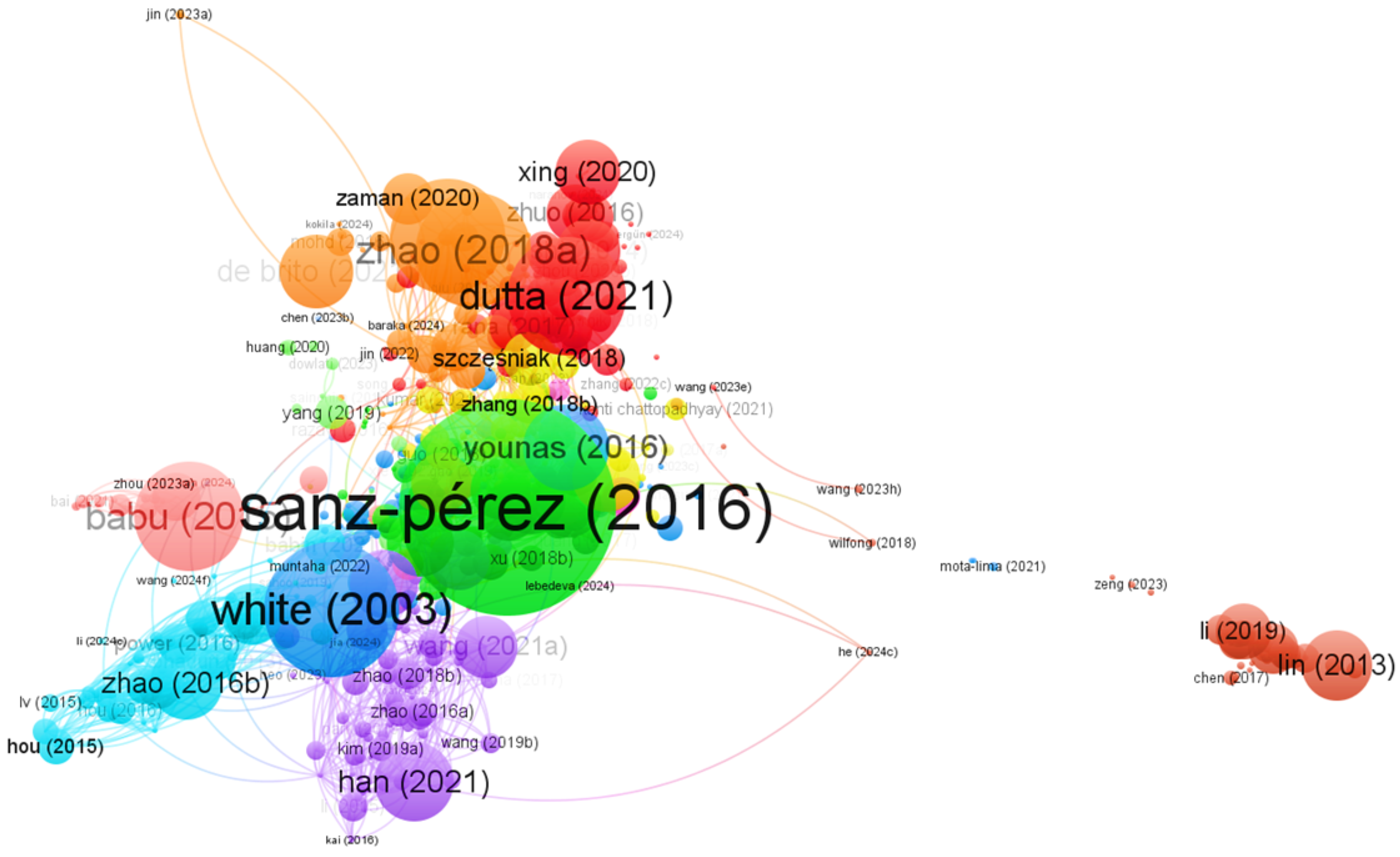



| Country | Published Documents | Citations |
|---|---|---|
| China | 323 | 7404 |
| United States | 89 | 5056 |
| India | 79 | 2407 |
| Australia | 42 | 1564 |
| South Korea | 40 | 707 |
| Malaysia | 32 | 913 |
| Canada | 30 | 1596 |
| United Kingdom | 29 | 929 |
| Iran | 23 | 392 |
| Portugal | 5 | 908 |
| Journal | Number of Documents | Cite | Journal Impact Factor (Year 2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Separation and Purification Technology | 48 | 373 | 8.1 |
| Chemical Engineering Journal | 35 | 1318 | 13.3 |
| Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research | 18 | 483 | 3.8 |
| Journal of Membrane Science | 15 | 1030 | 8.4 |
| Journal of CO2 Utilization | 14 | 454 | 7.2 |
| Energy & Fuels | 13 | 503 | 5.2 |
| ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces | 12 | 390 | 8.3 |
| Chemosphere | 10 | 123 | 8.1 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 9 | 402 | 9.7 |
| Carbon Capture Science & Technology | 5 | 70 | 10.4 |
| Most Relevant Articles in the Field of CO2 Capture | Journal | Cite | Impact Factor (Year 2023) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Capture of CO2 from Ambient Air | Chemical Reviews | 1580 | 51.4 | [32] |
| Separation and Capture of CO2 from Large Stationary Sources and Sequestration in Geological Formations—Coalbeds and Deep Saline Aquifers | Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association | 714 | 2.8 | [35] |
| Recent Advances in Aerogels for Environmental Remediation Applications: A review | Chemical Engineering Journal | 551 | 13.3 | [33] |
| Biopolymer Aerogels and Foams: Chemistry, Properties, and Applications | Journal of the German Chemical Society | 538 | 16.1 | [36] |
| A review of the Hydrate-Based gas Separation (HBGS) Process for Carbon Dioxide Pre-combustion Capture | Energy | 510 | 9.0 | [34] |
| Polymeric Membranes for CO2 Separation and Capture | Journal of Membrane Science | 298 | 8.4 | [37] |
| CO2-Responsive Polymers | Macromolecular Rapid Communications | 244 | 5.734 | [38] |
| Tunable Polyaniline-Based Porous Carbon with Ultrahigh Surface Area for CO2 Capture at Elevated Pressure | Advanced Energy Materials | 133 | 24.4 | [39] |
| Recent Advances in CO2-responsive Materials in Separations | Journal of CO2 Utilization | 72 | 7.2 | [40] |
| Immobilization of Carbonic Anhydrase on Carboxyl-functionalized Ferroferric Oxide for CO2 Capture | International Journal of Biological Macromolecules | 26 | 7.7 | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrascal-Hernández, D.C.; Grande-Tovar, C.D.; Mendez-Lopez, M.; Insuasty, D.; García-Freites, S.; Sanjuan, M.; Márquez, E. CO2 Capture: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Scalable Materials and Sustainable Solutions. Molecules 2025, 30, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030563
Carrascal-Hernández DC, Grande-Tovar CD, Mendez-Lopez M, Insuasty D, García-Freites S, Sanjuan M, Márquez E. CO2 Capture: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Scalable Materials and Sustainable Solutions. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030563
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrascal-Hernández, Domingo Cesar, Carlos David Grande-Tovar, Maximiliano Mendez-Lopez, Daniel Insuasty, Samira García-Freites, Marco Sanjuan, and Edgar Márquez. 2025. "CO2 Capture: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Scalable Materials and Sustainable Solutions" Molecules 30, no. 3: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030563
APA StyleCarrascal-Hernández, D. C., Grande-Tovar, C. D., Mendez-Lopez, M., Insuasty, D., García-Freites, S., Sanjuan, M., & Márquez, E. (2025). CO2 Capture: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Scalable Materials and Sustainable Solutions. Molecules, 30(3), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030563










